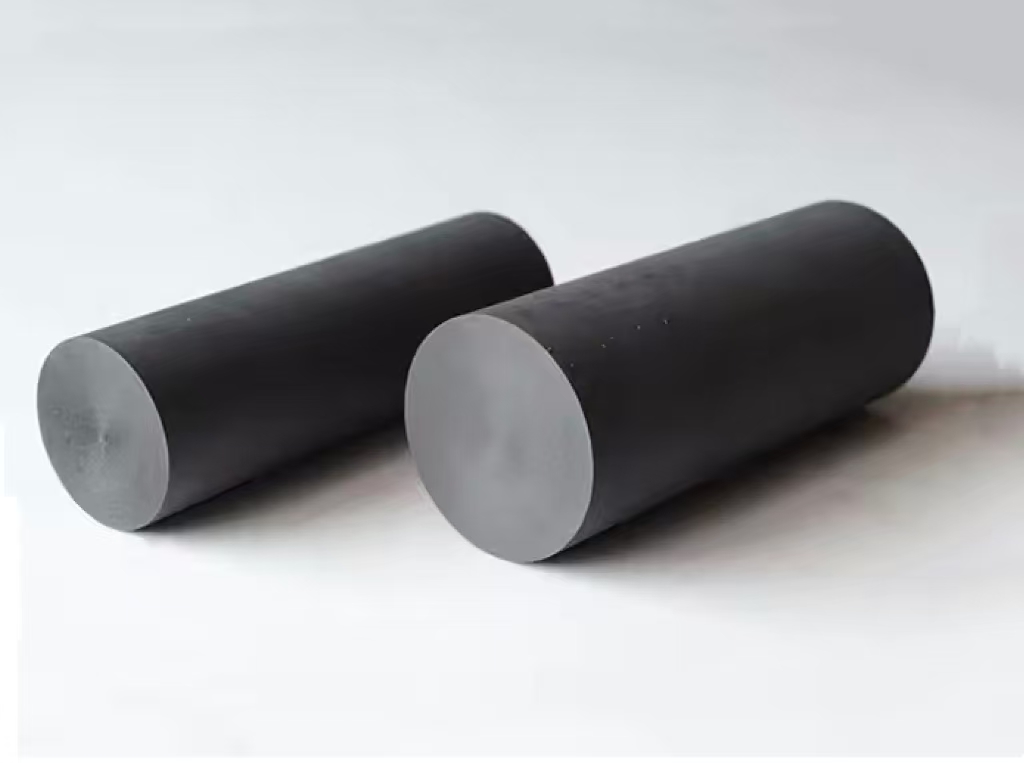
How to Source Graphite Bar Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for graphite bar
In the dynamic landscape of global commerce, sourcing high-quality graphite bars poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly rely on graphite for its exceptional thermal and electrical properties, understanding the nuances of procurement becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of graphite bars available, their diverse applications—from electrochemical processes to high-temperature environments—and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
B2B buyers will find actionable insights on how to evaluate suppliers based on quality, pricing, and reliability, ensuring that their procurement decisions align with their operational needs. Additionally, we will explore cost factors and market trends that impact pricing across different regions, particularly in emerging markets such as Vietnam and Brazil. By equipping international buyers with the necessary knowledge and tools, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating the global market for graphite bars doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With the right information at your fingertips, you can confidently source the materials that will drive your business forward.
Understanding graphite bar Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Purity Graphite Bar | Purity > 99.9%, superior conductivity | Electronics, semiconductors | Pros: Excellent performance; Cons: Higher cost due to purity. |
| Electrode Graphite Bar | Designed for electrochemical processes, corrosion resistant | Electrolysis, electroplating | Pros: Efficient in current conduction; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Heating Graphite Bar | High resistivity, generates heat when energized | Industrial heating furnaces, laboratory equipment | Pros: Effective for rapid heating; Cons: Requires careful handling due to high temperatures. |
| Refractory Graphite Bar | High-temperature resistance, low thermal expansion | Metallurgy, ceramics | Pros: Durable in extreme conditions; Cons: May be less flexible in applications. |
| Custom Graphite Bar | Tailored specifications based on application needs | Various industries requiring bespoke solutions | Pros: Meets specific requirements; Cons: Longer lead times for production. |
What are the Characteristics of High Purity Graphite Bars?
High purity graphite bars are characterized by their exceptional purity levels, typically exceeding 99.9%. This purity enhances their electrical conductivity and chemical stability, making them ideal for applications in electronics and semiconductors where performance is critical. Buyers should consider the higher cost associated with these bars, but the investment often yields better efficiency and product reliability, particularly in high-performance environments.
How Do Electrode Graphite Bars Stand Out?
Electrode graphite bars are specifically engineered for use in electrochemical applications, such as electrolysis and electroplating. Their corrosion-resistant properties and excellent electrical conductivity make them indispensable in these processes. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their electrochemical systems to ensure compatibility, as these bars are tailored for particular applications, limiting their versatility in other areas.
What Makes Heating Graphite Bars Suitable for Industrial Use?
Heating graphite bars are distinguished by their high resistivity, which allows them to generate substantial heat when energized. This feature is particularly advantageous in industrial heating furnaces and laboratory equipment, where rapid heating is essential. While they offer efficiency in heating applications, buyers must handle these bars with care due to the extreme temperatures they can reach, necessitating robust safety protocols.
Why Choose Refractory Graphite Bars?
Refractory graphite bars are designed to withstand high temperatures and exhibit low thermal expansion, making them suitable for use in metallurgy and ceramics. Their durability under extreme conditions is a significant advantage, but buyers should note that this durability may come at the cost of flexibility in application. Understanding the specific thermal and mechanical requirements of their processes is vital for buyers considering these bars.
How Can Custom Graphite Bars Meet Unique Industry Needs?
Custom graphite bars are manufactured according to specific requirements, allowing businesses to address unique challenges in various industries. Whether it’s for specialized applications or bespoke dimensions, these bars can be tailored to meet precise specifications. However, buyers should be prepared for potentially longer lead times and additional costs associated with custom production, which can impact project timelines and budgets.
Key Industrial Applications of graphite bar
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of graphite bar | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallurgical Industry | Electrodes for metal smelting processes | Enhances current conduction, improving efficiency and quality | High purity and conductivity specifications, availability of bulk supply |
| Electrical Engineering | Components in high-temperature applications | Provides reliable performance under extreme conditions | Temperature ratings, chemical stability, and custom dimensions |
| Chemical Processing | Electrodes for electrolysis and electroplating | Increases process efficiency and reduces downtime | Corrosion resistance and compatibility with chemicals used |
| Aerospace & Defense | Components in nuclear reactors | Ensures safety and reliability in critical applications | Certification standards, high purity requirements, and custom shapes |
| Manufacturing & Machining | EDM electrodes for precision machining | Achieves high precision and reduces waste in production | Consistency in dimensions and electrical properties |
How is Graphite Bar Utilized in the Metallurgical Industry?
In the metallurgical sector, graphite bars serve as electrodes in processes such as electrolytic aluminum and copper smelting. Their excellent electrical conductivity enables efficient current transmission, which is crucial for promoting the reduction reaction of metal ions. This not only enhances production efficiency but also improves the quality of the final product. International buyers should prioritize high-purity graphite bars to ensure optimal performance, while also considering bulk supply capabilities to meet production demands.
What Role Does Graphite Bar Play in Electrical Engineering?
Graphite bars are integral in electrical engineering, particularly in high-temperature applications like heating elements and electrical contacts. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining electrical conductivity makes them ideal for use in environments where traditional materials might fail. Buyers must assess the thermal resistance and chemical stability of graphite bars, ensuring they meet specific application requirements, especially in regions with diverse climatic conditions.
How is Graphite Bar Applied in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, graphite bars are utilized as electrodes for electrolysis and electroplating. Their inherent resistance to corrosion allows them to perform effectively in harsh chemical environments, thereby enhancing overall process efficiency. For international buyers, it’s crucial to consider the compatibility of graphite bars with the specific chemicals used in their processes, as well as their durability to withstand prolonged exposure.

Illustrative image related to graphite bar
Why is Graphite Bar Important in Aerospace & Defense?
Graphite bars are critical components in nuclear reactors, where they function as moderators to slow down neutrons, ensuring safe and efficient reactions. Their high purity and stable properties are essential in these applications to guarantee reliability and safety. Buyers in the aerospace and defense sectors should focus on sourcing graphite bars that meet stringent certification standards and can be customized to fit specific design requirements.
How is Graphite Bar Used in Manufacturing & Machining?
In the manufacturing and machining sectors, graphite bars are employed as electrodes for Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM). This application leverages the precise electrical properties of graphite to produce intricate metal parts with minimal waste. Buyers should ensure that the graphite bars sourced are consistent in dimensions and electrical properties, as this directly impacts the precision and quality of the machining process.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘graphite bar’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Concerns in Graphite Bar Procurement
The Problem: When sourcing graphite bars for industrial applications, B2B buyers often face challenges related to quality consistency. Variations in purity, electrical conductivity, and thermal resistance can severely impact the performance of the final product. Buyers may receive batches that do not meet their specified standards, leading to production delays and increased costs. This situation is particularly problematic in industries such as electronics and metallurgy, where precise specifications are critical for operational success.
The Solution: To ensure quality, buyers should establish a rigorous supplier evaluation process that includes requesting certifications and testing reports for graphite bars. It’s crucial to work with manufacturers that provide transparent information about their production processes and raw material sources. Implementing a system of quality checks upon receipt of the products can help catch any discrepancies early. Additionally, consider forming long-term partnerships with trusted suppliers to ensure consistency over time. Collaborating with suppliers on custom specifications can also mitigate the risk of receiving substandard materials.
Scenario 2: Difficulties in Customization for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many industries require graphite bars to meet unique specifications tailored to specific applications, such as high-temperature environments or chemically aggressive settings. Buyers often struggle to find suppliers who can provide customized solutions without long lead times or exorbitant costs. This lack of availability can lead to operational inefficiencies and potential safety hazards, especially in critical applications like nuclear reactors or specialized electrochemical processes.
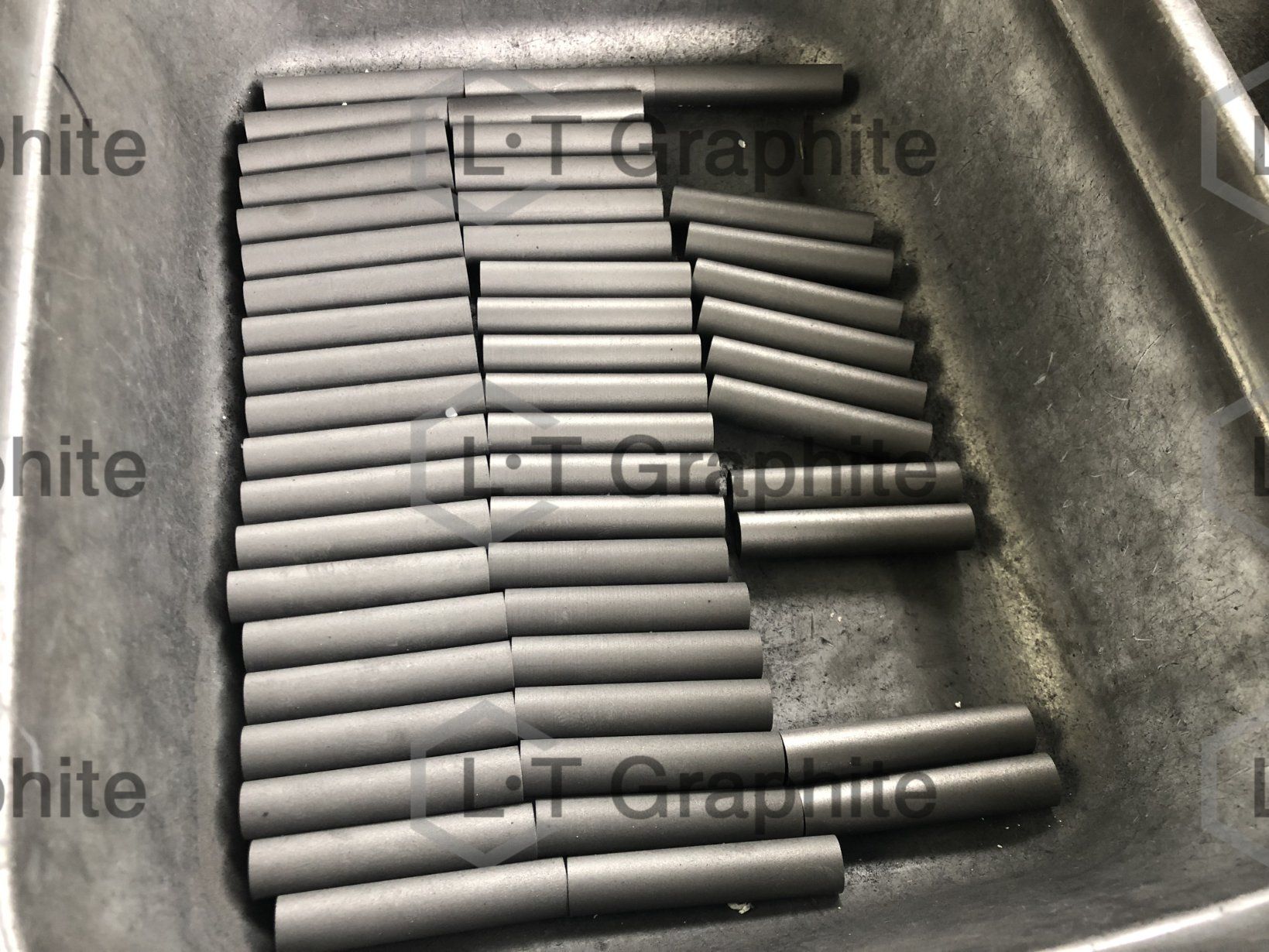

Illustrative image related to graphite bar
The Solution: To address customization challenges, B2B buyers should proactively communicate their specific requirements to suppliers early in the procurement process. Providing detailed specifications, including dimensions, thermal resistance, and chemical compatibility, will help suppliers understand the exact needs. Engaging in discussions about potential modifications or alternative materials can also yield viable solutions. Furthermore, consider working with manufacturers that specialize in bespoke graphite solutions, as they may have the capacity and expertise to meet your demands swiftly and efficiently.
Scenario 3: High Costs and Budget Constraints
The Problem: The price of graphite bars can vary significantly based on quality, source, and specific applications. B2B buyers often encounter budget constraints that limit their ability to procure high-quality materials. The temptation to opt for cheaper alternatives can lead to compromised product performance, affecting overall production quality and operational efficiency. This dilemma creates a challenging balance between maintaining quality and adhering to budgetary limits.
The Solution: To navigate cost issues effectively, buyers should conduct a thorough market analysis to understand the pricing landscape for graphite bars in their specific industry. This includes evaluating different suppliers and considering bulk purchasing to leverage volume discounts. Establishing a clear budget while prioritizing critical specifications can help in making informed decisions. Additionally, consider implementing a cost-benefit analysis to weigh the long-term gains of investing in high-quality graphite bars against the short-term savings of lower-cost alternatives. Engaging in open negotiations with suppliers about pricing and potential discounts for long-term contracts can also lead to more favorable terms.
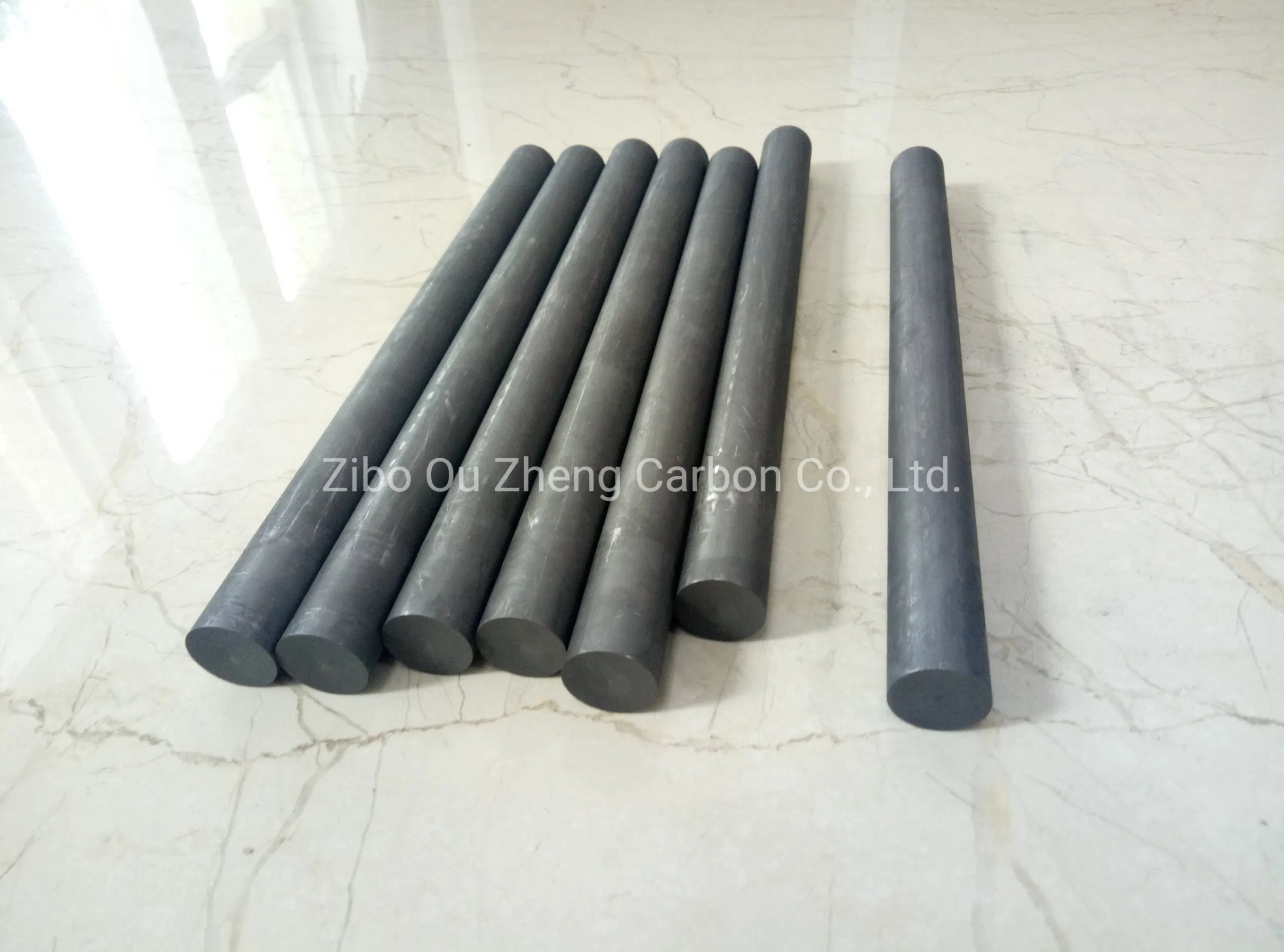

Illustrative image related to graphite bar
Strategic Material Selection Guide for graphite bar
What Are the Key Properties of Different Graphite Bar Materials?
When selecting graphite bars for industrial applications, understanding the properties of various materials is crucial. Here, we analyze four common types of graphite bars, focusing on their performance characteristics, pros and cons, and implications for international buyers.
High-Purity Graphite Bars
Key Properties: High-purity graphite bars typically boast a purity of over 99.9%, offering excellent electrical conductivity and thermal stability. They can withstand temperatures exceeding 2000°C and exhibit low thermal expansion, making them ideal for precision applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of high-purity graphite bars is their superior performance in demanding environments, such as electronics and semiconductors. However, they are often more expensive than other types due to the rigorous manufacturing processes required to achieve high purity levels.
Impact on Application: These bars are particularly suited for applications in electronics and aerospace, where reliability and performance are paramount. Their chemical stability also allows for use in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider compliance with international standards such as ASTM and JIS. Local sourcing may be limited, so understanding import regulations is essential.
Refractory Graphite Bars
Key Properties: Refractory graphite bars are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock, making them suitable for high-temperature applications in metallurgy and ceramics. They typically have a high tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability.
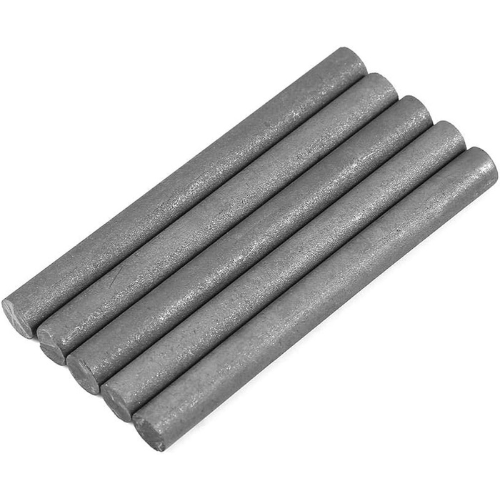

Illustrative image related to graphite bar
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of refractory graphite bars is their ability to maintain structural integrity under high heat. However, they can be more challenging to machine compared to other graphite materials, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: These bars are ideal for use in furnaces and kilns, where they provide insulation and support. Their resistance to thermal shock ensures longevity in harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected refractory graphite bars meet local and international standards for thermal performance. Understanding the local market for refractory materials is also critical, especially in regions with growing industrial sectors.
Electrode Graphite Bars
Key Properties: Electrode graphite bars are specifically designed for electrochemical applications, offering high electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. They can handle significant current loads and are often used in processes like electrolysis.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of these bars lies in their efficiency in electrochemical reactions, enhancing production rates. However, they may not perform well in high-temperature applications outside their intended use, limiting their versatility.
Illustrative image related to graphite bar
Impact on Application: These bars are commonly used in the production of aluminum and other metals, where they serve as electrodes. Their performance directly affects the efficiency and quality of the electrochemical processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: It is vital for buyers to verify that electrode graphite bars comply with industry standards relevant to their specific applications. This is particularly important in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Heating Graphite Bars
Key Properties: Heating graphite bars have a high resistivity, allowing them to generate substantial heat when energized. They are often used in industrial heating applications and can withstand high temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of heating graphite bars is their effectiveness in rapid heating applications. However, they may require specialized equipment for integration, which can increase overall costs.
Impact on Application: These bars are suitable for use in laboratory furnaces and industrial heating systems, where quick temperature changes are necessary. Their ability to maintain performance under high heat is crucial for efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the compatibility of heating graphite bars with their existing systems and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Understanding local market dynamics can also help in sourcing the right products.
Summary Table of Graphite Bar Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for graphite bar | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Graphite Bars | Electronics, semiconductors | Superior performance in demanding environments | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity | High |
| Refractory Graphite Bars | Furnaces, kilns | Excellent thermal shock resistance | More challenging to machine | Medium |
| Electrode Graphite Bars | Electrochemical processes (e.g., aluminum production) | High efficiency in electrochemical reactions | Limited versatility outside intended use | Medium |
| Heating Graphite Bars | Industrial heating systems, laboratory furnaces | Effective for rapid heating applications | Requires specialized integration equipment | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for graphite bars, ensuring that international B2B buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for graphite bar
The manufacturing process and quality assurance of graphite bars are critical aspects for international B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. Understanding these processes can help buyers evaluate potential suppliers effectively and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specific requirements.
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Graphite Bars?
The production of graphite bars typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial for ensuring the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications.
How Is Material Prepared for Graphite Bar Production?
The first step in manufacturing graphite bars involves selecting high-purity graphite raw materials. These materials are usually processed into graphite stock, which can be done through grinding and milling to achieve the desired grain size. Depending on the end application, additives may be included to enhance properties such as thermal and electrical conductivity.
The quality of the raw material is pivotal, as it directly affects the mechanical and thermal properties of the final product. B2B buyers should inquire about the sourcing of raw materials and any certifications that guarantee their quality, such as ISO standards.

Illustrative image related to graphite bar
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Graphite Bars?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming the graphite bars. Common techniques include:
-
Extrusion: This method involves forcing the graphite stock through a die to create the desired shape. It is suitable for producing continuous lengths of graphite bars with uniform dimensions.
-
Isostatic Pressing: A more advanced technique, isostatic pressing applies equal pressure from all sides, allowing for more intricate shapes and greater density. This method is often used for high-performance applications.
-
Molding: Custom molds can be used to create specific shapes and sizes, catering to unique industry requirements.
After forming, the graphite bars are typically subjected to a drying process to remove moisture, which can affect their integrity.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted for Graphite Bars?
The finishing stage of graphite bar production may involve machining and surface treatment. Machining processes, such as turning or milling, are used to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. Surface treatments, including coating or impregnation, can enhance properties such as wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Quality during the finishing stage is crucial as it directly influences the performance of the graphite bars in their intended applications. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust machining capabilities and quality control measures in place.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Relevant for Graphite Bar Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a vital component in the manufacturing of graphite bars, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations. Key quality assurance practices include adherence to international standards like ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for quality management systems.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For graphite bars, specific international standards may apply, including:
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for applications in oil and gas sectors, ensuring materials meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
B2B buyers should ask suppliers for documentation that demonstrates compliance with these standards, as they can provide assurance of quality and reliability.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are essential in the production of graphite bars. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various tests and measurements are conducted to monitor quality, including dimensional checks and material property assessments.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, a final inspection is performed to ensure the graphite bars meet all specifications and quality standards before they are shipped to customers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
To ensure quality, several testing methods may be employed during the manufacturing process, including:
-
Electrical Conductivity Tests: To verify the electrical properties of the graphite bars, ensuring they meet required specifications for conductivity.
-
Thermal Shock Resistance Tests: To assess how well the bars can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or deforming.
-
Mechanical Strength Tests: These tests measure tensile strength, compressive strength, and wear resistance, ensuring the graphite bars can perform under the stresses of their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. This can be achieved through:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the quality management processes in place.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide quality control reports and certifications that detail their compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance, providing unbiased evaluations of the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Assurance?
International buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality assurance. These may include:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements for graphite products. Understanding these regulations can help in selecting compliant suppliers.
-
Cultural Considerations: Communication barriers and cultural differences may impact how quality assurance practices are perceived and implemented. Establishing clear expectations and open lines of communication is crucial.
-
Logistics and Shipping: Quality assurance does not end at the manufacturing plant. Ensuring that products are protected during shipping and handling is vital to maintain quality upon arrival.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with graphite bars, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with suppliers. This knowledge not only helps in sourcing high-quality products but also ensures compliance with international standards, ultimately enhancing business operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘graphite bar’
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure graphite bars, ensuring that all critical factors are considered to make informed purchasing decisions. Graphite bars are essential components in various industries due to their unique properties, including high thermal conductivity, resistance to thermal shock, and chemical stability. Proper sourcing will facilitate seamless operations and enhance product quality.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements for your graphite bars is crucial before initiating the sourcing process. Consider factors such as size, shape (square, rectangular, or round), purity level, and intended application. Different industries may require unique properties, such as high-temperature resistance or electrical conductivity, so clarity here will streamline your sourcing efforts.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Begin your supplier search by identifying manufacturers and distributors with a proven track record in producing high-quality graphite bars. Look for companies that specialize in your specific needs and have experience servicing industries similar to yours. Utilize trade directories, industry forums, and recommendations to compile a list of potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing any agreements, verify that your chosen suppliers hold the necessary certifications and quality standards. This includes ISO certifications, which indicate adherence to international quality management standards, and any other relevant industry certifications. Ensuring suppliers meet these standards mitigates risks associated with product quality and compliance.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Acquiring samples is a vital step in assessing the quality of the graphite bars. Request samples that align with your technical specifications to evaluate their performance in real-world applications. Analyze the samples for consistency in dimensions, purity, and overall quality to ensure they meet your operational needs.
Step 5: Discuss Customization Options
Many suppliers offer customization to tailor graphite bars to specific applications. Engage with potential suppliers to discuss options for modifying dimensions, shapes, or even material compositions based on your unique requirements. Custom solutions can significantly enhance performance and efficiency in your operations.
Step 6: Inquire About Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have narrowed down your options, request detailed quotations from your shortlisted suppliers. Pay attention to unit prices, minimum order quantities, and any additional costs such as shipping or handling. Also, clarify payment terms and conditions to avoid unexpected expenses later in the process.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Effective communication is critical to a successful procurement process. Ensure that your suppliers provide clear contact points for support and inquiries. Establishing a reliable line of communication will facilitate timely updates on order status, delivery schedules, and any potential issues that may arise during the procurement process.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing graphite bars with confidence, ensuring that they select the right suppliers and products that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for graphite bar Sourcing
When sourcing graphite bars, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers. This knowledge empowers companies to make informed purchasing decisions, optimize budgets, and enhance supplier relationships.
What are the Key Cost Components in Graphite Bar Production?
The cost structure for graphite bars encompasses several critical components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver, material prices fluctuate based on graphite purity, sourcing location, and market demand. High-purity graphite is more expensive but offers superior conductivity and thermal stability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for processing and manufacturing graphite bars, impacting overall production costs. Labor costs vary significantly across regions, particularly between developed and emerging markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom molds and tooling for specific shapes or sizes can represent a substantial upfront investment. Customization often leads to higher costs but is necessary for specialized applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product consistency and adherence to specifications incurs additional costs. High-quality certifications (e.g., ISO) can enhance product value but may increase pricing.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs are significant, especially for international shipments. Incoterms influence these costs, determining who bears responsibility for shipping and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover operational risks and business sustainability. This margin can vary based on competition, market conditions, and supplier reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Graphite Bar Pricing?
Several factors significantly influence the pricing of graphite bars:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders generally attract lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their consumption patterns to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique specifications or customizations, such as size, shape, and purity level, can increase costs. Standard products often come at a lower price point.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certified products command premium prices. Buyers in sectors with stringent quality requirements must factor in these costs when evaluating suppliers.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and geographical location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record, while new entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) affects the total landed cost of goods. Understanding these terms is crucial for evaluating the overall price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Graphite Bar Sourcing Costs?
To enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing graphite bars, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to explore pricing flexibility. Leveraging long-term relationships can yield better terms and discounts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, evaluate the TCO, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan of the graphite bars. This holistic approach can reveal hidden costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of additional costs related to tariffs, taxes, and currency fluctuations. Building these factors into the budget is essential.
-
Supplier Diversity: Avoid dependency on a single supplier. Exploring multiple sources can enhance competitive pricing and mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
-
Regular Market Analysis: Keep abreast of market trends and pricing changes in the graphite sector. Understanding market dynamics can inform better timing for purchases.
Conclusion
While indicative prices for graphite bars can vary widely—ranging from $20 to $40 per unit depending on specifications and order volume—buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to ensure they are making cost-effective decisions. By understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and employing strategic sourcing techniques, B2B buyers can optimize their procurement processes for graphite bars.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing graphite bar With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Graphite Bar: A Comparative Analysis
In the landscape of industrial materials, selecting the right solution for high-performance applications is critical. Graphite bars are widely recognized for their excellent electrical conductivity, thermal resistance, and chemical stability. However, various alternatives can serve similar purposes depending on specific operational needs. This section evaluates graphite bars against two viable alternatives: copper bars and ceramic rods.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Graphite Bar | Copper Bar | Ceramic Rod |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal/electrical conductivity; excellent for high temps | Very high electrical conductivity; less thermal resistance than graphite | Good thermal and electrical insulation; high-temperature stability |
| Cost | Moderate ($26.88 each) | Higher cost due to material demand | Generally lower than graphite but varies with type |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to machine and shape | Requires more specialized handling due to ductility | Brittle nature makes machining challenging |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable | Moderate; corrosion may require treatment | Very low; resistant to chemical attack |
| Best Use Case | Electrochemical applications, high-temperature environments | Electrical applications, wiring, and grounding | High-temperature environments, insulating applications |
In-Depth Look at Alternatives
1. Copper Bar
Copper bars are renowned for their superior electrical conductivity, making them a preferred choice for electrical applications such as wiring and grounding. Their ductility allows for easy shaping and installation, which can be advantageous in many projects. However, copper does not perform as well under high-temperature conditions compared to graphite, as it can deform and lose conductivity. Additionally, the cost of copper has risen due to increased demand, which can impact budget considerations for B2B buyers.
2. Ceramic Rod
Ceramic rods present an alternative that excels in thermal resistance and electrical insulation. They are particularly useful in high-temperature applications, such as in furnaces and kilns, where materials must withstand extreme conditions. While they are generally more affordable than graphite bars, their brittleness poses challenges during machining and installation. Buyers must consider the potential for breakage and the need for careful handling, which could lead to increased labor costs.
Making the Right Choice: How to Select the Best Solution
When evaluating the right material for your application, consider the specific requirements of your operations. If electrical conductivity and high-temperature resistance are paramount, graphite bars may be the best fit. Conversely, if budget constraints or weight considerations are significant, copper bars or ceramic rods might provide viable alternatives. Always assess the long-term operational costs, including maintenance and replacement, alongside initial purchase price to ensure that your choice aligns with both performance and financial objectives.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for graphite bar
What are the Key Technical Properties of Graphite Bars for B2B Buyers?
Understanding the essential technical properties of graphite bars is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are the critical specifications that define the quality and functionality of graphite bars:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a graphite bar indicates its purity and composition, often expressed in percentage terms. High-purity graphite bars, typically above 99.9%, are preferred in industries like electronics and semiconductors due to their superior conductivity and chemical stability. Buyers should assess the material grade to ensure it meets their specific application requirements. -
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity is a key property of graphite bars, which determines their efficiency in conducting electricity. Measured in terms of resistivity (e.g., ohm-inches), higher conductivity implies lower resistivity. This property is vital for applications in electrochemical processes, where efficient current transmission is necessary for operational success. -
Thermal Resistance
The ability of a graphite bar to withstand high temperatures is another crucial factor. Many graphite bars can endure temperatures exceeding 2000°C, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as furnaces and reactors. Understanding thermal resistance helps buyers select the appropriate graphite bar for environments where heat exposure is a concern. -
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength, measured in psi (pounds per square inch), indicates the maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing. A tensile strength of around 4,200 psi for some graphite bars suggests a good balance between strength and flexibility, making them suitable for various mechanical applications. -
Dimensional Tolerance
Dimensional tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the size and shape of the graphite bar. Precise tolerances are critical for applications requiring exact fit and function, such as in machining and manufacturing processes. Buyers should specify their tolerance requirements to ensure compatibility with their production needs.
What are the Common Trade Terms Used in Graphite Bar Transactions?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers. Here are some common trade terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are used in another company’s end products. Buyers often seek graphite bars from OEMs to ensure compatibility and quality assurance in their applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers as it impacts inventory management and cost efficiency, particularly for bulk purchases of graphite bars. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products. Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and availability of graphite bars across different suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with these terms helps clarify shipping, insurance, and risk management, which is particularly important in international transactions involving graphite bars. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers to plan production schedules and manage supply chain logistics effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their negotiation strategies, ensure they are selecting the right graphite bars for their applications, and foster better supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the graphite bar Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Graphite Bar Sector?
The graphite bar market is witnessing robust growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for high-performance materials across industries such as electronics, aerospace, and metallurgy is a significant driver. Graphite bars, known for their excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, are becoming indispensable in manufacturing processes that require precision and durability. Emerging technologies, particularly in renewable energy, are propelling the demand for graphite components in batteries and fuel cells, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where mineral resources are abundant.
International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for sourcing, enabling a more streamlined procurement process. Innovations such as AI-driven supply chain management tools are enhancing transparency and efficiency, allowing buyers to track the sourcing journey from raw material extraction to finished products. Additionally, customization is a growing trend; buyers are seeking tailored solutions to meet specific operational requirements, leading manufacturers to adopt flexible production processes.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in the Graphite Bar Industry?
Sustainability has emerged as a cornerstone of the graphite bar supply chain, influenced by growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. The extraction and processing of graphite can have significant ecological impacts, prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers with sustainable practices. This includes minimizing water usage, reducing carbon footprints, and ensuring responsible mining practices that protect local ecosystems.
Ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly important as buyers seek to align with suppliers who are committed to social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade practices are critical indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Companies that invest in ‘green’ materials and processes not only enhance their brand reputation but also attract environmentally conscious buyers, making ethical sourcing a competitive advantage in the graphite bar sector.
How Has the Graphite Bar Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the graphite bar sector can be traced back to its historical use in various applications, from pencils to high-temperature industrial components. Initially recognized for its lubricating properties, graphite has transformed into a critical material in advanced technologies, including nuclear reactors and semiconductor manufacturing. The advent of modern processing techniques has allowed for the production of high-purity graphite bars, catering to the increasing demand in specialized industries.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing the performance characteristics of graphite bars through innovation and research. This includes the development of composite materials and specialized treatments that improve durability and performance in extreme conditions. As the industry continues to evolve, the emphasis on customization and sustainability will shape the future of graphite bar sourcing, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about market trends and technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of graphite bar
-
How do I choose the right graphite bar for my application?
Selecting the appropriate graphite bar depends on various factors, including the specific application, desired purity level, and physical properties required. For high-temperature environments, opt for bars with a high-temperature resistance rating, typically above 2000°C. Consider the bar’s electrical conductivity if used in electrochemical applications. Additionally, consult with suppliers about customization options to ensure the bar meets your technical specifications and industry standards. -
What are the common applications of graphite bars in industry?
Graphite bars are utilized across various sectors, including metallurgy, electronics, and chemical processing. In metallurgy, they serve as electrodes in smelting processes for aluminum and copper. In the electronics industry, they are used to manufacture components like transistors and tubes. Their high thermal and electrical conductivity makes them ideal for heating applications and as stirring rods in molten metal processes. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for graphite bars?
When vetting suppliers, evaluate their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and certifications. Request samples to assess the quality of their graphite bars. It’s also essential to inquire about their experience in international trade, particularly in your region, and their ability to meet delivery timelines. Additionally, check customer reviews and references to gauge their reliability and after-sales support. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for graphite bars?
The MOQ for graphite bars can vary significantly based on the supplier and the customization required. Generally, standard sizes may have lower MOQs, often ranging from 50 to 100 pieces. For customized orders, suppliers may require larger quantities to justify production costs. Always discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate if necessary. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of graphite bars?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but most will offer options such as upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, or payment upon delivery. International transactions may involve letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties. It is advisable to clarify payment terms upfront and ensure they align with your cash flow requirements and risk management strategies. -
How can I ensure the quality of graphite bars I receive?
To guarantee the quality of graphite bars, request a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from the supplier, which provides detailed information about the material’s composition and properties. Additionally, consider conducting third-party inspections or quality audits before shipment. Establishing a clear return policy in case of non-compliance with agreed specifications can also help mitigate risks. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing graphite bars?
When importing graphite bars, consider shipping methods, customs duties, and import regulations specific to your country. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in handling industrial materials to ensure timely delivery. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping, especially if sourcing from international suppliers, to avoid delays in your operations. -
Can I customize graphite bars to suit specific industry requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for graphite bars, allowing you to specify dimensions, purity levels, and additional properties such as thermal resistance or electrical conductivity. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to determine their capabilities and any associated costs. Custom solutions can enhance the performance of your applications, making it worthwhile to invest time in this process.
Top 5 Graphite Bar Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Graphite Store – Graphite Plates, Rods & Tubes
Domain: graphitestore.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Graphite Store – Graphite Plates, Rods & Tubes, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. McMaster-Carr – Graphite Bars
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster-Carr – Graphite Bars, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. USA Industrials – Graphite Bar
Domain: fixsupply.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Graphite Bar”, “Dimensions”: {“Thickness”: “1/4 inch”, “Width”: “1 inch”, “Length”: “12 inches”}, “Brand”: “USA Industrials”, “Item Number”: “AD7121”, “Manufacturer Model Number”: “BULK-GS-18”, “Color”: “Black”, “Electrical Properties”: {“Conductive”: true, “Electrical Resistivity”: “0.00054 ohms-in”}, “Grain Size”: “0.00047 inch”, “Maximum Temperature”: “800° F”, “Maximum Vacuum…
4. East Carb – Graphite Bars
Domain: eastcarb.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Graphite Bar is a solid section made from graphite material with varying cross-section shapes such as square, rectangular, or hexagonal. Commonly referred to as graphite rods, they are associated with solid sections having round or circular cross-sections. Benefits include self-lubricating properties, low friction coefficient, chemical inertness, high electrical and thermal conductivity, resistanc…
5. Goodfellow – Graphite Carbon Rods
Domain: goodfellow.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: {“Grade”:”Graphite”,”Formula”:”C”,”Form”:”Rod”,”Material”:”Carbon”,”CAS Number”:”7440-44-0″,”Commodity”:”Metals”,”Description”:”Graphite Carbon Rods are used in high-temperature, inert, or vacuum environments for electrochemical applications like fuel cells, batteries, and electrolysis. They serve as electrodes and heating elements in furnaces and thermal analysis equipment due to their high elect…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for graphite bar
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of graphite bars presents a valuable opportunity for businesses across diverse industries, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Graphite bars are essential for high-temperature applications, electrical conductivity, and chemical stability, making them a critical component in manufacturing processes ranging from metallurgy to electronics. By partnering with reliable suppliers, companies can ensure access to high-quality products tailored to their specific needs, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and product performance.
As global demand for graphite continues to rise, driven by advancements in technology and sustainable practices, it is vital for international buyers to prioritize strategic sourcing. This approach not only mitigates supply chain risks but also fosters long-term relationships with manufacturers who can adapt to evolving market requirements.
Looking ahead, we encourage B2B buyers to explore innovative sourcing solutions and engage with suppliers who offer customized graphite bar options. By doing so, businesses can position themselves advantageously in a competitive landscape, ultimately driving growth and success in their respective markets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.