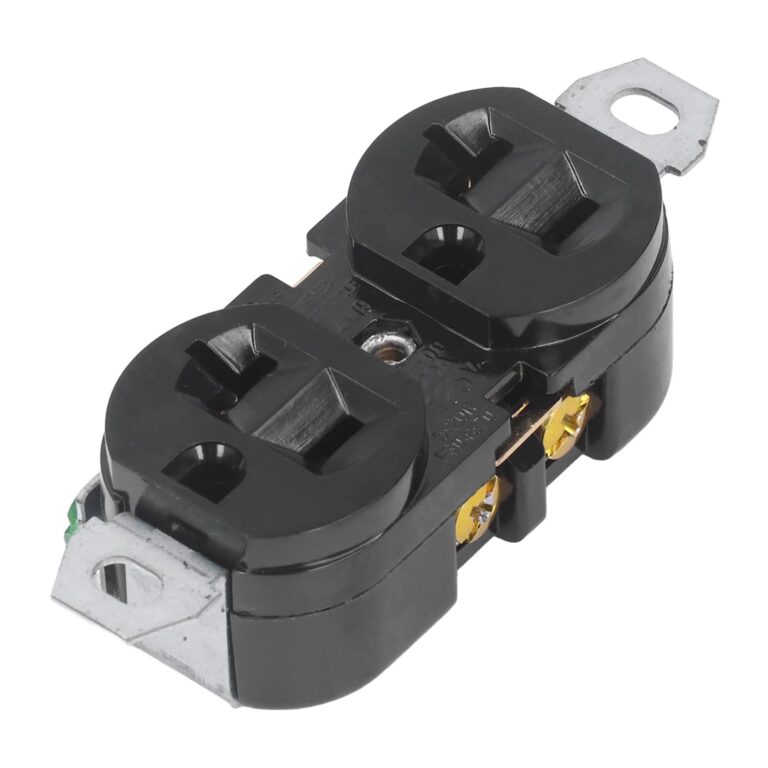
How to Source Gas Valve Coils Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gas valve coils
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing gas valve coils can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With the growing demand for reliable heating solutions across various industries, understanding the intricacies of gas valve coils is essential. These components play a critical role in the functionality of gas appliances, including dryers and heating systems, by controlling the flow of gas to burners. Navigating this complex market requires not only knowledge of the different types of coils available but also an awareness of their applications, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam—by providing actionable insights into the gas valve coil market. We will explore various types of coils, their specific applications, and best practices for supplier vetting to ensure quality and compliance with international standards. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations and potential pitfalls to avoid, enabling you to make informed purchasing decisions.
By leveraging this guide, you can streamline your sourcing process, mitigate risks, and ultimately enhance your operational efficiency. Whether you are a seasoned buyer or new to the market, understanding the nuances of gas valve coils will position your business for success in an ever-evolving global economy.
Understanding gas valve coils Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Wire Gas Valve Coil | Simple design; typically used in basic gas systems. | Residential dryers, basic heating systems | Pros: Cost-effective; easy to replace. Cons: Limited functionality; not suitable for advanced systems. |
| 3-Wire Gas Valve Coil | More complex; includes a holding coil for continuous operation. | Industrial dryers, advanced heating systems | Pros: Improved performance; better gas flow control. Cons: Higher cost; requires more technical knowledge for installation. |
| Booster Coil | Enhances gas flow; used in high-demand applications. | Commercial dryers, industrial ovens | Pros: Increases efficiency; suitable for high volume. Cons: More expensive; potential for overuse if not monitored. |
| Export Model Coils | Designed for specific voltage and frequency (e.g., 50 Hz). | International markets, export appliances | Pros: Tailored for specific regions; complies with local standards. Cons: Limited availability; may require special ordering. |
| OEM Replacement Coils | Original equipment manufacturer parts; ensure compatibility. | All appliance types requiring gas valves | Pros: Guaranteed fit and performance; usually backed by warranty. Cons: Higher price point compared to generic options. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 2-Wire Gas Valve Coils?
2-wire gas valve coils are the most basic type of gas valve coil, designed primarily for simple gas systems. They operate by opening the gas valve when energized, allowing gas flow to the burner. Their straightforward design makes them a cost-effective solution for residential applications, such as dryers and basic heating systems. However, their limited capabilities mean they may not be suitable for more complex or high-demand systems.
How Do 3-Wire Gas Valve Coils Improve Performance?
3-wire gas valve coils include an additional holding coil, which allows for continuous operation once the valve is opened. This design is particularly beneficial in industrial applications where consistent gas flow is essential, such as in commercial dryers and advanced heating systems. While they provide better control and efficiency, they come at a higher cost and may require specialized installation knowledge.
Why Are Booster Coils Important in High-Demand Applications?
Booster coils are specialized components designed to enhance gas flow in systems that require higher demand, such as commercial dryers and industrial ovens. By improving gas delivery, they significantly increase efficiency and performance. However, buyers should be aware of their higher price point and the necessity for monitoring to avoid potential overuse, which could lead to system failures.
Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
What Should Buyers Know About Export Model Coils?
Export model coils are specifically designed to meet the voltage and frequency requirements of international markets, such as those that operate on 50 Hz. These coils are essential for compliance with local regulations and standards in regions like Africa and South America. While they offer tailored solutions for specific applications, buyers may face challenges in availability and may need to place special orders.
Why Choose OEM Replacement Coils for Gas Valve Needs?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) replacement coils are designed to match the specifications of the original parts, ensuring compatibility and reliability. They are suitable for all types of gas appliances that require gas valves. While they generally come with a higher price tag, the assurance of fit and performance, along with warranty backing, makes them a preferred choice for many B2B buyers looking for long-term solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of gas valve coils
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gas valve coils | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Gas valve coils in industrial dryers for textile production | Ensures consistent drying, enhancing efficiency | OEM compatibility, voltage specifications, and durability |
| Food Processing | Gas valve coils in commercial ovens and fryers | Improves cooking consistency and safety | Temperature ratings, corrosion resistance, and certification |
| HVAC and Refrigeration | Gas valve coils in heating systems | Enhances energy efficiency and cost savings | Compliance with local regulations, energy ratings, and reliability |
| Automotive | Gas valve coils in automotive heating systems | Ensures passenger comfort and safety | Temperature tolerance, electrical specifications, and OEM compatibility |
| Oil and Gas | Gas valve coils in gas flow control systems | Enhances safety and operational efficiency | Material compatibility, pressure ratings, and certification |
How are Gas Valve Coils Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, gas valve coils are vital components in industrial dryers used for textile production. These coils control the gas flow to the burner, ensuring optimal drying conditions. A malfunctioning coil can lead to inconsistent drying, affecting product quality and increasing operational costs. Buyers in this sector must consider OEM compatibility and durability, especially in high-volume environments, to maintain efficiency and minimize downtime.

Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
What Role Do Gas Valve Coils Play in Food Processing?
In food processing, gas valve coils are integral to the operation of commercial ovens and fryers. They regulate gas flow, allowing for precise temperature control, which is crucial for cooking consistency and food safety. A defective gas valve coil can lead to uneven cooking or safety hazards, impacting product quality and compliance with health regulations. Buyers should prioritize temperature ratings and corrosion resistance, particularly in environments with high moisture or grease.
How Are Gas Valve Coils Essential for HVAC and Refrigeration?
Gas valve coils are essential in HVAC systems, particularly in gas-powered heating units. They manage the gas flow necessary for heating air, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs. Inconsistent heating can lead to discomfort and increased energy bills. B2B buyers must ensure compliance with local regulations and consider energy ratings to optimize system performance and reliability, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
Why Are Gas Valve Coils Important in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, gas valve coils are used in heating systems to ensure passenger comfort. They regulate gas flow to the heater core, providing consistent heat output. A faulty coil can lead to inadequate heating, compromising safety and comfort. Buyers should focus on temperature tolerance and electrical specifications to ensure compatibility with various vehicle models, especially for international markets where vehicle standards may vary.
How Do Gas Valve Coils Enhance Safety in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas industry, gas valve coils are crucial for controlling gas flow in various applications, including pipeline monitoring and gas processing. They enhance safety by ensuring that gas is only released under safe conditions, preventing leaks and potential hazards. Buyers should consider material compatibility and pressure ratings to ensure reliable operation under varying conditions, particularly in regions with fluctuating environmental factors.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gas valve coils’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Gas Valve Coils
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in sourcing gas valve coils that meet specific quality and compatibility requirements. This is particularly true for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local suppliers may not stock the necessary OEM parts or may offer generic alternatives that do not perform reliably. The lack of standardization in products can lead to frequent breakdowns and increased operational costs, making it essential for buyers to ensure they are obtaining high-quality components.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should develop relationships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers who specialize in gas valve coils. It is advisable to prioritize suppliers that offer OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts, as these are designed to meet the exact specifications of the original equipment. Conduct thorough research and read reviews or case studies from other businesses in similar sectors. Additionally, leveraging online platforms that provide detailed specifications and compatibility information can help buyers make informed decisions. Establishing a robust supply chain with reliable partners ensures timely access to quality components, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Heating Performance in Equipment
The Problem: Another common issue faced by B2B buyers is inconsistent heating performance in gas-powered appliances, such as dryers or industrial heating equipment. Often, this inconsistency can be traced back to faulty or worn gas valve coils, which can lead to inefficient gas flow. This not only affects the performance of the equipment but can also increase energy consumption and operational costs. Buyers may find that their appliances heat intermittently, resulting in delayed processes and frustrated end-users.
Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
The Solution: To address inconsistent heating performance, it is critical for buyers to implement regular maintenance checks and testing protocols for gas valve coils. Establish a routine inspection schedule that includes testing the coils for continuity and functionality. Buyers should invest in quality diagnostic tools to facilitate this process. When sourcing replacements, choose coil kits that are specifically designed for the equipment in use, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance. Training maintenance personnel on the importance of these checks can help preemptively identify issues before they escalate into significant operational disruptions.
Scenario 3: High Replacement Costs Due to Frequent Failures
The Problem: Frequent failures of gas valve coils can lead to unexpectedly high replacement costs and affect the overall operational budget for B2B buyers. This is especially problematic in industries that rely heavily on gas-powered machinery, where prolonged downtime translates to lost revenue. Buyers may struggle to find cost-effective solutions that do not compromise on quality, leading to a cycle of expensive repairs and replacements.
The Solution: To mitigate high replacement costs, buyers should consider investing in high-quality, durable gas valve coils that are designed for longevity. This includes researching and selecting products with proven performance records and warranties that cover premature failures. Additionally, implementing a proactive maintenance strategy can significantly reduce the frequency of failures. By training staff to recognize early warning signs of coil issues—such as inconsistent heating or unusual noises—buyers can act before a complete failure occurs. Establishing a long-term partnership with a reliable supplier for bulk purchasing can also provide cost savings and ensure consistent availability of high-quality parts.

Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gas valve coils
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Gas Valve Coils?
Gas valve coils are critical components in gas appliances, responsible for controlling the flow of gas to the burner. The selection of materials for these coils significantly impacts their performance, durability, and overall efficiency. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of gas valve coils, considering their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Copper: A Traditional Choice for Gas Valve Coils
Copper is a widely used material for gas valve coils due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications in gas dryers and other heating appliances.
Pros:
– High electrical and thermal conductivity ensures efficient operation.
– Good corrosion resistance, especially when coated or treated.
– Relatively easy to manufacture and shape.
Cons:
– Higher cost compared to some alternatives.
– Susceptible to oxidation if not properly protected, which can affect performance.
Impact on Application:
Copper coils are compatible with a range of gases and are often used in environments where high temperatures and pressures are present.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B75 for copper tubing and be aware of any specific regulations in their region regarding copper usage.
Stainless Steel: A Durable Alternative
Stainless steel is another popular choice for gas valve coils, particularly in environments where corrosion resistance is paramount. Its ability to withstand harsh conditions makes it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros:
– Exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in humid or corrosive environments.
– High strength-to-weight ratio enhances durability.
– Can handle high temperatures and pressures effectively.
Cons:
– More expensive than copper and other materials.
– Manufacturing processes can be more complex, leading to higher production costs.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel coils are ideal for applications involving aggressive gases or environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel and consider local preferences for specific grades, such as 304 or 316 stainless steel.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Option
Aluminum is increasingly being used for gas valve coils due to its lightweight and cost-effective nature. While not as conductive as copper, it offers a good balance of properties for many applications.
Pros:
– Lightweight, which can reduce overall appliance weight.
– Cost-effective compared to copper and stainless steel.
– Good thermal conductivity, although not as high as copper.
Cons:
– Lower strength and durability compared to stainless steel and copper.
– More susceptible to corrosion unless treated or coated.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum coils are suitable for low to moderate temperature applications and are often used in consumer appliances where weight is a consideration.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions and be aware of local regulations regarding aluminum use in gas appliances.
Plastic Composites: An Emerging Material
Plastic composites are gaining traction in the manufacturing of gas valve coils, particularly in applications where weight and cost are critical factors. These materials can be designed to withstand specific environmental conditions.
Pros:
– Lightweight and cost-effective, reducing overall production costs.
– Can be engineered for specific applications, including resistance to certain gases.
– Lower thermal conductivity can be beneficial in certain designs.
Cons:
– Limited temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals.
– Potential concerns regarding long-term durability and performance under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites may be suitable for specific low-pressure applications but are generally not recommended for high-temperature or high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards for plastic materials and ensure that the chosen composites are suitable for the gases being used.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Gas Valve Coils
| Material | Typical Use Case for gas valve coils | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Gas dryers, heating appliances | High conductivity and durability | Higher cost, oxidation risk | High |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments, industrial use | Excellent corrosion resistance | More complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Consumer appliances | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower strength, corrosion risk | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Low-pressure applications | Lightweight, customizable | Limited temperature ratings | Low |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the material selection for gas valve coils, enabling informed decisions based on application needs, compliance requirements, and cost considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gas valve coils
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Gas Valve Coils?
The manufacturing process of gas valve coils involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial for ensuring that the coils meet performance and safety standards required in various applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, typically copper or aluminum for the coil windings, and durable insulation materials. Suppliers must ensure that these materials comply with international standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications. Rigorous testing of raw materials for conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion is standard practice.
-
Forming: In this stage, the metal wires are shaped into coils. Advanced winding machines are used to ensure precision in the number of turns and the tightness of the coils. This step often employs CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology to enhance accuracy and reduce human error. Additionally, the forming process may include heat treatment to improve the mechanical properties of the coils, ensuring they can withstand operational stresses.
-
Assembly: Following the forming stage, coils are assembled with other components such as plungers and housing units. This assembly is usually done in a clean environment to prevent contamination. Automated assembly lines may be used to enhance efficiency, but manual assembly is also common for quality-sensitive components. Each assembly is checked to ensure proper alignment and fit.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves applying protective coatings or treatments to enhance resistance to environmental factors such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. Finishing techniques may include varnishing, anodizing, or applying other protective films. This stage is critical for the longevity of the coils, especially in harsh operational environments.
What International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers must be aware of various international standards and industry-specific certifications that ensure the quality and safety of gas valve coils. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures a consistent approach to quality across all manufacturing processes. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has robust quality management systems in place.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking demonstrates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is vital for establishing the product’s marketability in Europe.
-
API Standards: For coils used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial. These standards ensure that products can withstand the demanding conditions of the industry.
-
UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification is essential for electrical components, indicating that the coils have been tested for safety and performance under specific conditions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing Gas Valve Coils?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets required specifications. Key QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. Testing may include dimensional checks, material composition analysis, and verification of supplier certifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC involves monitoring the production process. This includes regular inspections of the winding process, assembly accuracy, and adherence to operational parameters. Any deviations from standard operating procedures can be corrected immediately.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the final product. This may include electrical resistance tests, functionality tests, and environmental testing to ensure the coils can operate effectively under expected conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure reliability and performance. Here are effective strategies to achieve this:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s quality management practices. This includes reviewing documentation, observing production processes, and evaluating the training of staff involved in QC.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, testing methods, and results. Regular reporting on defect rates and corrective actions taken can help buyers assess ongoing performance.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies to evaluate the supplier’s processes and products can provide an unbiased assessment of quality. These agencies often have established protocols to ensure compliance with international standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Gas Valve Coils?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that gas valve coils function correctly and meet safety standards. Common tests include:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes resistance measurements to ensure that coils operate within specified electrical parameters. Insulation resistance tests may also be performed to prevent electrical failures.
-
Functional Testing: Coils are tested in simulated operational conditions to confirm that they activate the gas valve correctly. This often involves cycling the coil under load and monitoring performance.
-
Environmental Testing: Coils may undergo exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and corrosive environments to assess their durability and performance over time. This testing is critical for applications in harsh conditions.
What Nuances in Quality Control Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must consider various nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the local manufacturing culture and practices can influence quality perceptions. Buyers should engage in open communication to clarify expectations regarding quality standards.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Each region may have specific regulatory requirements that impact quality assurance. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and ensure that their suppliers comply with these regulations.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Delays in shipping or customs clearance can affect product quality. Buyers should establish clear logistics protocols with suppliers to mitigate risks associated with transportation and storage.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing gas valve coils, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gas valve coils’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring gas valve coils, this step-by-step checklist outlines the essential actions to ensure a smooth sourcing process. Following these guidelines will help you find reliable suppliers and secure quality products suited to your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline the technical requirements for the gas valve coils you need. This includes understanding the voltage, resistance, and compatibility with your existing equipment. Identify the specific models or OEM parts required to ensure you receive the correct components that meet your operational standards.
- Voltage and Resistance: Check the specifications of your existing coils to match voltage ratings and resistance levels.
- Model Compatibility: Ensure the coils are compatible with the brands and models of gas appliances you are servicing.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers in the gas valve coil market. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of companies that specialize in gas valve coils. This step is crucial for establishing a pool of potential partners who can meet your sourcing needs.
- Industry Directories: Websites like ThomasNet and Alibaba can provide valuable leads.
- Trade Shows: Attend industry events to meet suppliers and view their products firsthand.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
It is imperative to verify the certifications and compliance of potential suppliers. Look for ISO certifications or other industry-standard qualifications that indicate the supplier’s adherence to quality and safety regulations. This step minimizes risks associated with sourcing low-quality or non-compliant products.
- ISO Certifications: Check for ISO 9001 or similar certifications that ensure quality management systems.
- Local Compliance: Ensure suppliers comply with local regulations in your target market regions, such as CE marking in Europe.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the gas valve coils for testing. Testing samples allows you to assess the quality, compatibility, and performance of the coils with your equipment. This step helps prevent costly mistakes associated with bulk orders of unsuitable products.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate the coils under operational conditions to ensure they meet heating and safety standards.
- Material Inspection: Check for build quality and materials used to ensure durability and reliability.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers and compare pricing alongside other terms such as lead times and payment options. While price is an important factor, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes shipping, warranty, and after-sales support.
- Total Cost Analysis: Factor in shipping costs and potential tariffs or taxes for international orders.
- Payment Terms: Look for flexible payment options that suit your cash flow needs, such as net terms or discounts for early payment.
Step 6: Assess Customer Support and After-Sales Service
Evaluate the level of customer support and after-sales service offered by suppliers. Reliable suppliers should provide robust customer service, including assistance with installation, troubleshooting, and warranty claims. This support is vital for minimizing downtime in your operations.
- Response Times: Assess how quickly potential suppliers respond to inquiries and their willingness to assist.
- Technical Support: Verify if they offer technical guidance or resources for installation and maintenance.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Place Orders
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review and finalize contracts before placing your order. Ensure all agreed-upon terms are documented clearly to avoid misunderstandings. This step provides legal protection and ensures both parties are aligned on expectations.
- Contract Review: Involve legal counsel if necessary to review terms and conditions.
- Order Confirmation: Confirm all details of the order, including quantities, delivery dates, and payment terms, before finalizing.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for gas valve coils, ensuring they select high-quality products from reputable suppliers while minimizing risks and costs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gas valve coils Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Gas Valve Coils?
When sourcing gas valve coils, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:

Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used, such as copper wire for coils and durable plastics or metals for housing, significantly influence the price. Higher-quality materials generally lead to better performance and longevity, impacting the total cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the region of production. Countries with higher labor costs may produce gas valve coils at a premium, while regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs, which can be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for manufacturing gas valve coils can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs are amortized over a larger production run to reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the coils meet safety and performance standards. While this adds to the overall cost, it can prevent costly defects and warranty claims in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including freight, customs duties, and insurance, can significantly affect the final price. International buyers should account for these expenses when evaluating offers from suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their prices to include a profit margin. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Gas Valve Coil Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of gas valve coils:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk usually results in lower per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can provide leverage for negotiating discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom coils designed to specific requirements may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly outline their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Coils made from premium materials or those that comply with international quality standards (like ISO certifications) may come at a higher price but often offer better reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a crucial role. Well-established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery (like FOB, CIF, etc.) is vital for calculating total costs. Different Incoterms can shift responsibility and costs between buyers and suppliers, affecting the overall price.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Gas Valve Coils?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips for effective negotiations:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough research on prevailing market prices and competitor offerings. This knowledge can provide a strong basis for negotiation.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Rather than just the purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs. Suppliers who offer warranties or better service may justify a higher initial price.
-
Long-term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to more favorable pricing terms over time. Regular orders can encourage suppliers to provide better rates.
-
Flexibility on Specifications: If possible, be open to using standard models instead of custom designs. This can significantly reduce costs as suppliers often have existing inventory for standard parts.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. It’s worth exploring regional manufacturers who meet quality standards.
While prices for gas valve coils can vary widely, understanding the underlying cost components and price influencers can empower buyers to make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved supplier relationships.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gas valve coils With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Gas Valve Coils in Industrial Applications
In the realm of industrial heating systems, gas valve coils play a crucial role in regulating gas flow to burners. However, businesses may also explore alternative solutions that can achieve similar objectives, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their operational needs and budget constraints.
Comparison of Gas Valve Coils and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Gas Valve Coils | Electric Heating Elements | Pressure Switches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable, effective in gas systems | Quick heating, consistent output | Offers safety and control |
| Cost | Moderate ($30 – $130) | Varies ($25 – $150 depending on type) | Low to moderate ($20 – $100) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific installation skills | Generally easy to install | Simple installation |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular checks needed | Low; minimal maintenance | Low; infrequent replacement |
| Best Use Case | Gas dryers and industrial burners | Electric dryers and heating systems | Safety control in gas systems |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Heating Elements?
Electric heating elements are a popular alternative to gas valve coils, especially in environments where gas supply is limited or safety concerns are paramount. They provide a quick and consistent heat output, making them ideal for electric dryers and heating systems. However, they may not be as energy-efficient in large-scale industrial applications, leading to higher operating costs over time. Additionally, electric elements require a reliable electricity supply, which may not be feasible in all regions, especially in areas with unstable power infrastructure.
How Do Pressure Switches Offer a Viable Solution?
Pressure switches serve as another alternative, primarily focusing on safety and control within gas systems. They monitor gas pressure and can shut off the gas supply if it exceeds safe levels, preventing potential hazards. While pressure switches are not a direct substitute for gas valve coils in terms of heating, they can be integrated into systems that use gas valve coils to enhance safety. Their installation is generally straightforward, and they require minimal maintenance, making them a reliable choice for businesses prioritizing safety.
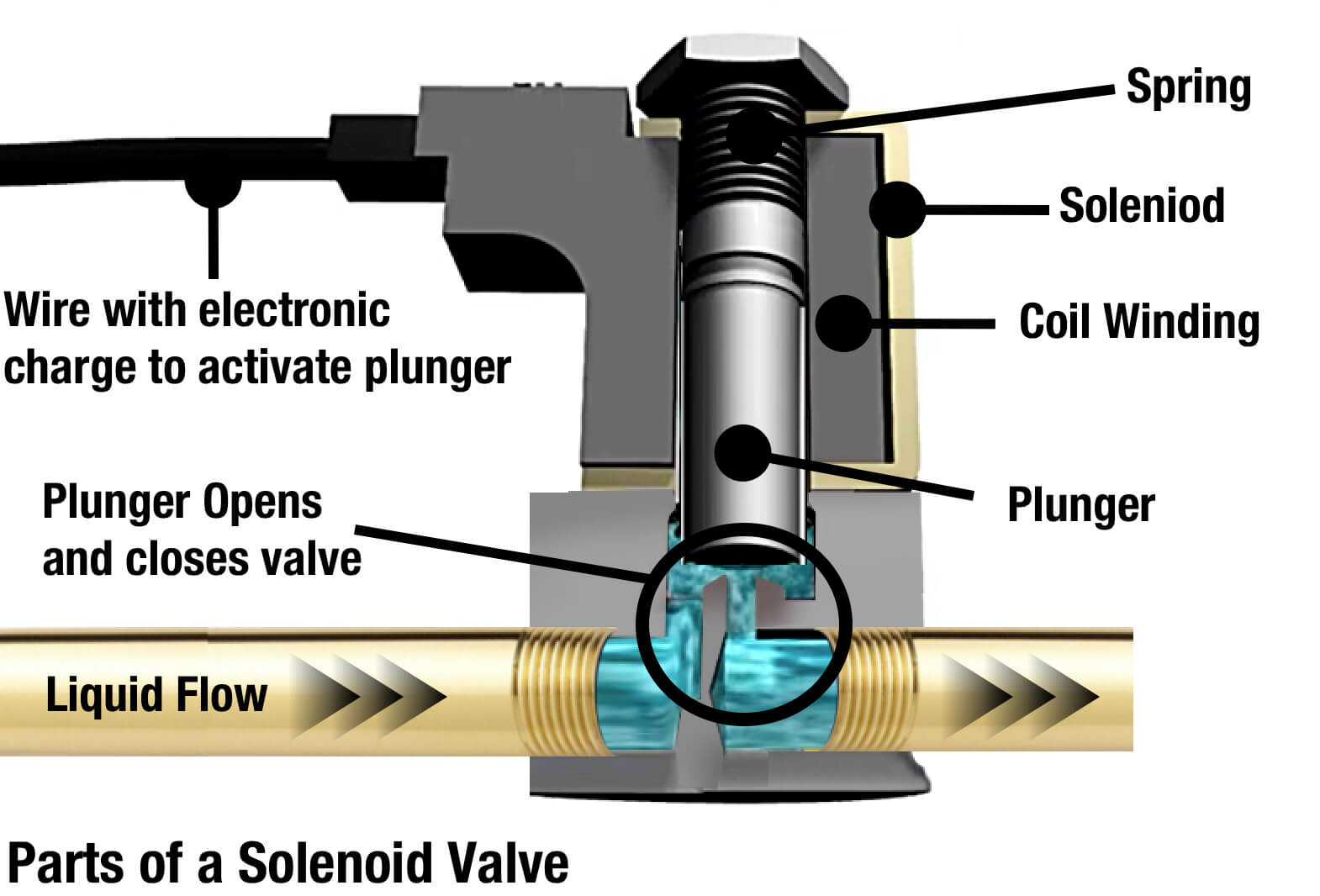
Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When evaluating whether to utilize gas valve coils or explore alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, ease of installation, and maintenance needs. For businesses operating in regions with stable gas supplies, gas valve coils may offer the best performance for heating applications. Conversely, if safety and ease of use are top priorities, electric heating elements or pressure switches may prove more beneficial. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific operational context and long-term goals of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gas valve coils
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gas Valve Coils?
Understanding the technical properties of gas valve coils is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when selecting components for industrial applications. Here are several essential specifications that impact performance and reliability:
1. Material Grade
Gas valve coils are typically made from copper or other conductive materials. The choice of material affects electrical conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and overall durability. For example, high-grade copper coils provide better conductivity and longevity, which is vital for applications in harsh environments. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer coils made from materials that meet industry standards for their specific use cases.
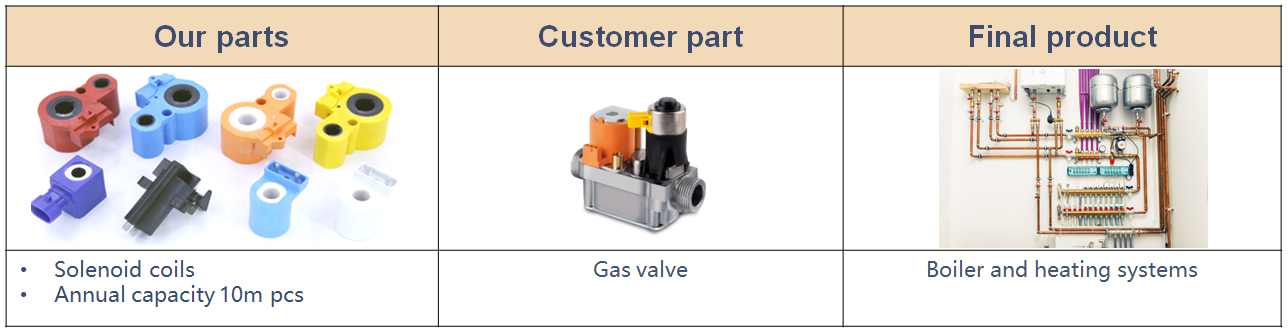
Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
2. Voltage Rating
Voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the coil can safely handle without failure. Most gas valve coils operate on standard voltages, such as 120V or 240V, depending on the application. Selecting a coil with the appropriate voltage rating ensures compatibility with existing systems and reduces the risk of electrical malfunctions, which can lead to costly downtime.
3. Resistance
The resistance of a gas valve coil is a key indicator of its efficiency and functionality. Typically measured in ohms, the resistance affects how much current flows through the coil when energized. Coils with low resistance values are preferred for rapid activation of the gas valve, which is essential for timely heating in gas appliances. Buyers should ensure that the resistance specifications align with their operational requirements.
4. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the coil’s physical dimensions and electrical characteristics. Tight tolerances are critical in applications where precise performance is necessary. For instance, in industrial settings, a coil that deviates from specified tolerances may not function correctly, leading to safety hazards or equipment failure. Thus, understanding the tolerance levels offered by manufacturers can help buyers make informed decisions.
5. Coil Configuration
Coil configurations, such as the number of wires (e.g., 2-wire or 3-wire setups), play a significant role in compatibility with different gas valve systems. The configuration dictates how the coil connects to the valve and influences the functionality of the gas flow mechanism. Buyers must consider the specific configuration required by their equipment to ensure seamless integration.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Gas Valve Coils?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms relevant to gas valve coils:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components or products that are used in another company’s end product. When sourcing gas valve coils, buyers often look for OEM parts to ensure compatibility and quality. These components are designed to meet the exact specifications of the original equipment, reducing the risk of malfunction.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers need to evaluate their demand and negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing strategy to avoid overstocking or production delays.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products. Submitting an RFQ for gas valve coils allows buyers to gather competitive quotes and assess supplier capabilities. This step is vital for making informed purchasing decisions and securing favorable terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and costs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping arrangements and manage logistics effectively. For instance, terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate the point at which the responsibility for the goods transfers from seller to buyer.
In summary, grasping the technical properties and trade terminology associated with gas valve coils empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring compatibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Illustrative image related to gas valve coils
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gas valve coils Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Gas Valve Coils Sector?
The global gas valve coils market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand in the appliance and HVAC sectors. As industries evolve, the need for efficient and reliable gas management systems has heightened, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. International B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality gas valve coils that comply with stringent safety standards and regulations.
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies into gas valve systems, allowing for enhanced monitoring and control. This shift towards automation is particularly relevant for buyers seeking to optimize operational efficiency and reduce downtime in their production processes. Additionally, as energy costs continue to rise, manufacturers are prioritizing the development of coils that improve energy efficiency, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Supply chain dynamics are also shifting, with a noticeable move towards localized sourcing to mitigate risks associated with global logistics. This trend is especially pertinent for buyers in developing markets, such as Nigeria and Vietnam, where infrastructure challenges can impact delivery timelines. Buyers are encouraged to establish strong relationships with local suppliers who understand regional market nuances and can offer timely support.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Gas Valve Coils Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the gas valve coils sector. B2B buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact associated with manufacturing processes and are seeking suppliers committed to reducing their carbon footprints. The use of eco-friendly materials and production techniques not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also meets the growing demand for sustainable products from end consumers.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally critical, as buyers prioritize suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and maintain transparent supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are becoming essential criteria for suppliers aiming to gain a competitive edge. By choosing suppliers with these certifications, businesses can ensure compliance with international standards while enhancing their brand reputation.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials in the production of gas valve coils is gaining traction. Buyers should look for coils made from recyclable materials or those that meet low-emission standards. This not only contributes to environmental sustainability but also positions businesses as leaders in responsible sourcing within their industries.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Gas Valve Coils in B2B Context?
The evolution of gas valve coils can be traced back to the early 20th century when they were primarily used in industrial applications. Initially, these coils were simple mechanical devices, but advancements in technology have transformed them into sophisticated components integral to modern gas appliances. The introduction of electronic ignition systems in the 1980s marked a significant turning point, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of gas delivery systems.
Today, gas valve coils are essential in various applications, from residential dryers to large-scale industrial burners. Their development has paralleled advancements in material science and electronics, leading to the creation of more durable and efficient coils. As the market continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these historical advancements to make educated sourcing decisions that align with current technological capabilities and market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gas valve coils
-
How do I solve heating issues in gas dryers related to valve coils?
Heating problems in gas dryers are often linked to faulty gas valve solenoid coils. To diagnose the issue, check if the igniter glows without igniting the gas; this typically indicates a defective coil. If the dryer fails to heat, consider replacing both the primary and secondary coils to ensure optimal functionality. Always source OEM parts for reliability and performance. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can help identify early signs of wear, preventing unexpected downtime. -
What is the best gas valve coil for commercial dryers?
The best gas valve coils for commercial dryers depend on the specific model and operational requirements. Look for OEM parts from reputable manufacturers, as they are designed to meet strict quality standards. Kits that include both 2 and 3 wire coils are ideal for flexibility in various applications. Always consult the dryer’s manual or a parts specialist to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing gas valve coils internationally?
When sourcing gas valve coils internationally, consider factors like product quality, supplier reliability, and compliance with local regulations. Verify the supplier’s certifications and past performance through references or reviews. Additionally, assess the logistics capabilities, including shipping times, customs duties, and potential tariffs. Language barriers and payment methods should also be discussed upfront to avoid miscommunication. -
How can I vet suppliers for gas valve coils?
Vetting suppliers for gas valve coils involves several key steps. Start by researching their business history and reputation in the industry. Look for certifications such as ISO or industry-specific standards that ensure product quality. Request samples to evaluate the quality firsthand and ask for references from existing clients. Regular communication and a thorough understanding of their production capabilities will also aid in establishing trust. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gas valve coils?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for gas valve coils can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific product. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 100 units for standard items, while specialized or custom coils may have higher MOQs. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs with suppliers based on your purchasing needs and inventory management strategy, particularly if you are entering a new market or testing a new product line. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing gas valve coils?
Payment terms for gas valve coils can vary by supplier and geographic region. Common terms include payment upon order confirmation, 30% deposit with the balance due before shipment, or net 30/60 days after delivery. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfers, letters of credit) and ensure that terms are documented in the purchase agreement. Consider discussing options for bulk purchases to negotiate better terms. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for gas valve coils?
To ensure quality assurance for gas valve coils, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your supplier. Implement a quality control process that includes pre-shipment inspections to verify that parts meet your standards. Establish a clear return policy for defective items and maintain open communication with the supplier to address any quality issues promptly. Regular audits and feedback loops can also enhance product consistency over time. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing gas valve coils?
When importing gas valve coils, logistics considerations include shipping methods, transit times, and customs clearance processes. Assess whether air freight or sea freight is more suitable based on urgency and cost. Understand the import regulations in your country, including tariffs and duties, to avoid unexpected expenses. Collaborating with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the logistics process, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with all legal requirements.
Top 1 Gas Valve Coils Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Aspen Appliance Parts – Gas Valve Coils
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gas valve coils
In summary, strategic sourcing of gas valve coils is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and reliability in gas-powered appliances. As the backbone of the burner assembly, these coils directly influence the performance of gas dryers, making their quality and availability critical for manufacturers and suppliers. By prioritizing partnerships with reputable suppliers, B2B buyers can ensure access to high-quality, OEM-compliant components, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Furthermore, with the growing demand in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is an increasing opportunity for suppliers to expand their market reach. Buyers should consider not only the immediate cost of procurement but also the long-term value of investing in dependable products that minimize failure rates and enhance customer satisfaction.
As we look to the future, the gas valve coil market is poised for growth. International B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage this trend by seeking out innovative sourcing solutions that align with their operational needs. By doing so, they can position themselves competitively in their respective markets while ensuring the consistent performance of their gas appliances.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.