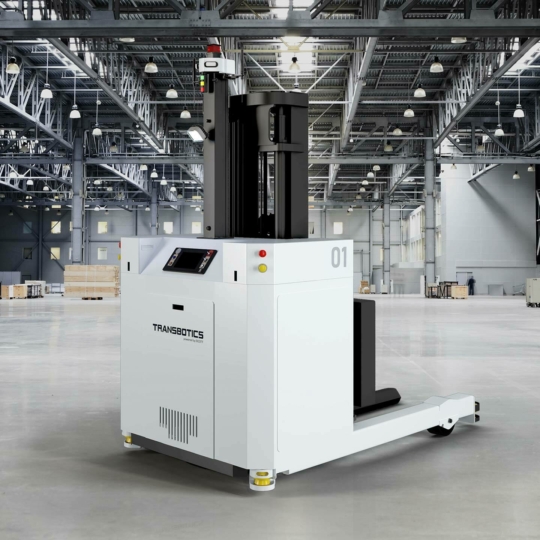
How to Source Forked Agv Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for forked agv
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing the right forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers. Companies must navigate a complex landscape of options, balancing factors like cost, technology, and supplier reliability to optimize their material handling operations. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for stakeholders from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Brazil. By exploring the various types of forked AGVs, their diverse applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting, this guide equips buyers with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of forked AGVs, highlighting their advantages over traditional automated forklifts, such as improved safety, efficiency, and predictable operation. Buyers will gain a clear understanding of cost structures, including potential long-term savings that stem from reduced maintenance and operational risks. Additionally, we will provide actionable tips for assessing suppliers, ensuring that you choose a partner capable of meeting your unique business needs. By empowering decision-makers with knowledge and strategic insights, this guide is designed to facilitate successful investments in forked AGVs, paving the way for enhanced productivity and operational excellence in your organization.
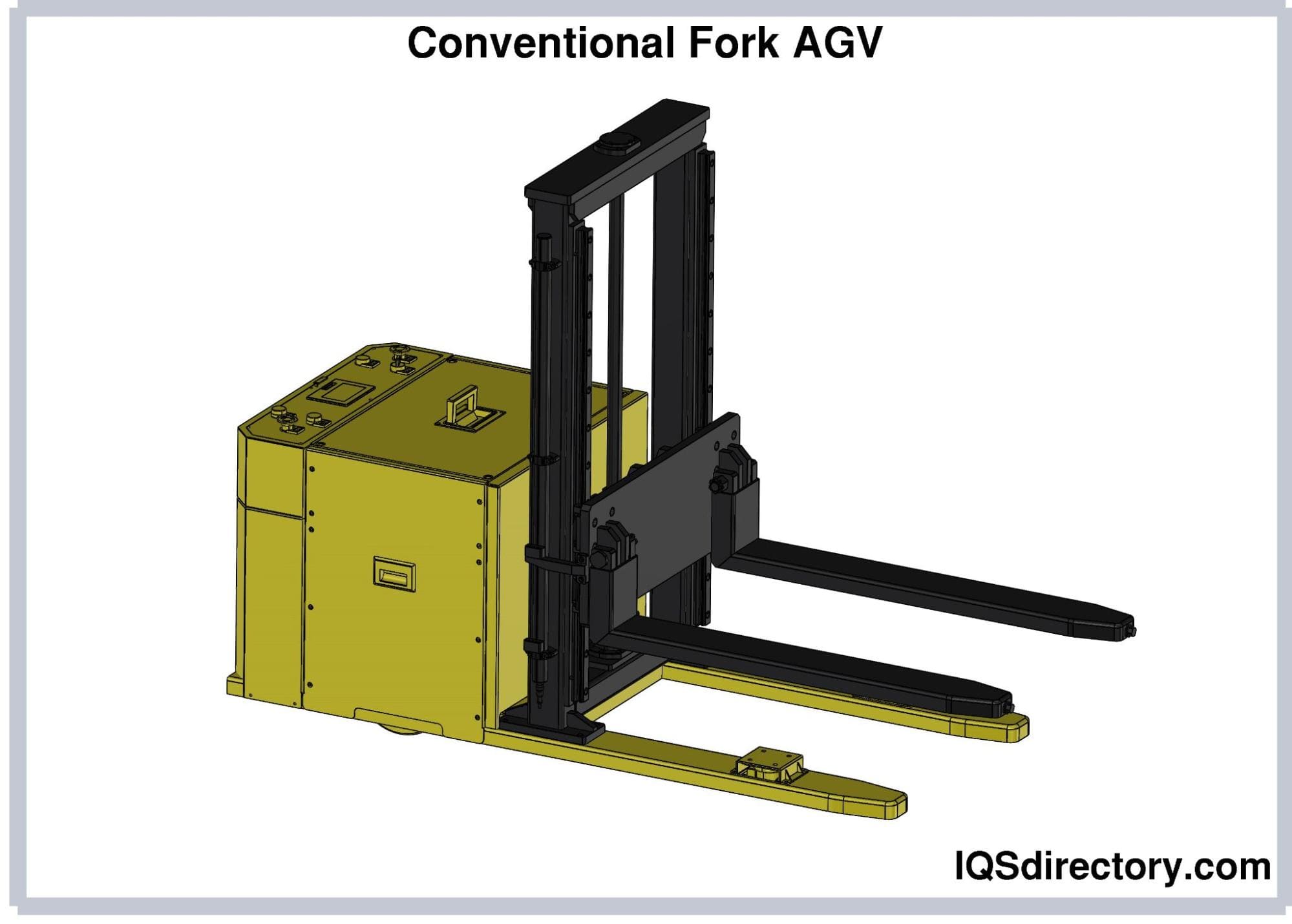
Understanding forked agv Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Counterbalanced Forklift AGV | Features a counterbalance weight for stability; versatile in tight spaces. | Warehousing, distribution centers, retail. | Pros: High maneuverability; efficient in confined areas. Cons: Limited lifting capacity compared to larger models. |
| Straddle Stacker Forklift AGV | Designed to straddle loads; ideal for double-deep storage. | High-density storage environments, manufacturing. | Pros: Maximizes vertical storage; suitable for high racks. Cons: Requires more floor space for operation. |
| Pallet AGV | Specifically designed for transporting pallets; lower profile. | Shipping docks, palletized goods handling. | Pros: Streamlined for pallet handling; reduces manual labor. Cons: Limited to palletized loads; not versatile for other materials. |
| Tugger AGV | Pulls multiple carts or trailers; not equipped for lifting. | Assembly lines, large warehouses. | Pros: Efficient for moving bulk materials; high load capacity. Cons: Cannot lift loads directly; requires additional equipment for loading/unloading. |
| Reach Forklift AGV | Features extendable forks for accessing high storage. | Warehousing, manufacturing with high racks. | Pros: High lifting ability; ideal for maximizing vertical space. Cons: More complex mechanics; higher maintenance costs. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Counterbalanced Forklift AGVs?
Counterbalanced Forklift AGVs are designed with a weight at the back to counterbalance the load, allowing for enhanced stability and maneuverability. These AGVs are particularly suited for operations in tight spaces, making them ideal for warehouses and retail environments where space is at a premium. Buyers should consider their operational layout and the need for flexibility in handling various types of loads, as these AGVs excel in environments requiring quick adjustments and high efficiency.
How Do Straddle Stacker Forklift AGVs Maximize Storage Capacity?
Straddle Stacker Forklift AGVs are engineered to straddle over loads, making them perfect for double-deep storage configurations. This design allows them to handle high-density storage needs, especially in manufacturing and distribution centers. When purchasing, companies should assess their storage strategies and whether they require high vertical reach capabilities, as these AGVs can significantly enhance storage utilization but may require more floor space for operation.
What Are the Benefits of Using Pallet AGVs in Material Handling?
Pallet AGVs are specifically built for the transportation of palletized goods, featuring a lower profile for efficient maneuvering. They are commonly used in shipping docks and facilities handling palletized products, significantly reducing the need for manual labor. B2B buyers should evaluate their material handling processes and consider the volume of palletized goods to determine if investing in pallet AGVs will streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Why Choose Tugger AGVs for Bulk Material Transport?
Tugger AGVs are designed to pull multiple carts or trailers, making them highly efficient for transporting bulk materials across large warehouses or assembly lines. They provide a high load capacity, which can be a significant advantage in environments that require heavy lifting and long-distance transport. Buyers should consider their operational needs for moving large quantities of materials, as these AGVs may require additional equipment for effective loading and unloading.
What Advantages Do Reach Forklift AGVs Offer for High Storage Needs?
Reach Forklift AGVs come equipped with extendable forks, allowing them to access high storage racks effectively. They are particularly beneficial in warehouses and manufacturing facilities that utilize vertical space for storage. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should assess the complexity of their storage systems and the potential for increased maintenance costs associated with more advanced mechanics, but the investment can lead to significant efficiency gains in managing high stacks of goods.
Key Industrial Applications of forked agv
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of forked agv | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated pallet handling in assembly lines | Increased throughput and reduced labor costs | Compatibility with existing systems and load capacity requirements |
| Warehousing | Efficient storage and retrieval of goods | Enhanced space utilization and reduced operational delays | Navigation technology and safety features for high-density areas |
| Retail | Streamlined inventory management and restocking | Improved stock accuracy and faster replenishment cycles | Flexibility in handling various product types and sizes |
| Food & Beverage | Transporting raw materials and finished goods | Minimization of handling damage and improved hygiene | Compliance with safety regulations and temperature control options |
| Logistics & Distribution | Automated loading and unloading of delivery trucks | Reduced labor costs and minimized loading times | Integration with warehouse management systems and real-time tracking |
How is Forked AGV Used in Manufacturing and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the manufacturing sector, forked AGVs are primarily utilized for automated pallet handling along assembly lines. They transport materials and components between workstations, thus increasing throughput and efficiency. By automating these repetitive tasks, businesses can significantly reduce labor costs and minimize human error. Buyers should consider the AGV’s compatibility with existing infrastructure, including load capacities and integration with other automated systems to ensure seamless operations.
What Benefits Does Forked AGV Bring to Warehousing Operations?
In warehousing, forked AGVs excel in the efficient storage and retrieval of goods. They navigate through narrow aisles and can handle various pallet sizes, which enhances space utilization and reduces operational delays. This capability is particularly beneficial in high-density storage environments where maximizing space is crucial. Buyers should evaluate the AGV’s navigation technology, safety features, and ability to operate in confined spaces to meet specific operational requirements.
How Does Forked AGV Enhance Retail Inventory Management?
In the retail sector, forked AGVs streamline inventory management by automating restocking processes. They can transport goods from storage to sales floors, ensuring that shelves are always well-stocked and accurately managed. This leads to improved stock accuracy and faster replenishment cycles, enhancing customer satisfaction. When sourcing AGVs for retail, companies should focus on the flexibility of the vehicle to handle various product types and sizes, as well as its ability to operate in busy retail environments.
What Role Does Forked AGV Play in the Food & Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, forked AGVs are essential for transporting raw materials and finished products while maintaining hygiene standards. They minimize handling damage and facilitate a more sanitary workflow by reducing human contact with products. Compliance with safety regulations is critical in this sector, so buyers must ensure that the AGVs meet industry-specific standards, including temperature control options for sensitive materials.
How Can Forked AGV Optimize Logistics and Distribution?
Forked AGVs are increasingly used in logistics and distribution for automating the loading and unloading of delivery trucks. This application reduces labor costs and minimizes loading times, leading to more efficient operations. Buyers should prioritize AGVs that can integrate with existing warehouse management systems and offer real-time tracking capabilities to enhance visibility throughout the supply chain.

Illustrative image related to forked agv
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘forked agv’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Initial Investment Concerns
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are apprehensive about the high upfront costs associated with forked AGVs. These vehicles often require significant capital investment compared to traditional automated forklifts, making financial decision-makers wary. Buyers may worry about the return on investment (ROI) and whether the operational efficiencies gained will justify the initial expenditure. This concern is particularly pronounced in regions with tighter budgets, such as some areas in Africa and South America, where financial constraints can hinder automation adoption.
The Solution: To address these concerns, businesses should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis that evaluates both immediate and long-term savings. Start by identifying specific operational inefficiencies that forked AGVs could resolve, such as reducing labor costs or minimizing product damage. Additionally, consider utilizing ROI calculators provided by manufacturers to project financial outcomes based on your operational metrics. Engaging with suppliers who offer flexible financing options or leasing agreements can also lower the barrier to entry. By focusing on the potential for enhanced productivity and lower maintenance costs over time, buyers can make a more informed decision that emphasizes the value forked AGVs can bring to their operations.
Scenario 2: Integration with Existing Systems
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers is the seamless integration of forked AGVs into existing warehouse and logistics systems. Companies that rely on traditional material handling methods may find it daunting to shift to automated solutions without disrupting their current workflows. Concerns about compatibility with existing software, machinery, and infrastructure can lead to hesitation in adopting forked AGVs.
Illustrative image related to forked agv
The Solution: To facilitate smooth integration, buyers should prioritize working with suppliers who offer comprehensive support and consultation during the transition phase. This includes assessing current systems to determine compatibility and identifying any necessary upgrades. Request demonstrations or pilot programs to understand how forked AGVs will interact with existing processes before full implementation. Additionally, investing in modular AGVs that can be easily adapted to different tasks or environments can provide the flexibility needed to accommodate changing operational requirements. Collaborating with IT and operations teams to develop a phased integration plan can further ensure that the transition is smooth and minimizes disruptions.
Scenario 3: Safety and Training Issues
The Problem: Safety concerns and the need for adequate training can be significant barriers for businesses considering forked AGVs. B2B buyers may worry about the safety of their workforce during the transition to automation, especially in environments where manual handling has been the norm. There may also be apprehension regarding the training required to operate and maintain these advanced machines properly.
The Solution: To mitigate safety concerns, it is essential to choose forked AGVs equipped with advanced safety features such as obstacle detection systems and emergency stop functions. Buyers should also invest in comprehensive training programs for their staff, which can include hands-on sessions led by the equipment manufacturer. Many manufacturers offer training resources, including detailed manuals and online courses, to help employees become proficient in operating AGVs safely. Additionally, fostering a culture of safety by involving employees in the decision-making process and addressing their concerns can help ease the transition. Regular safety audits and feedback loops can further enhance safety protocols as the organization adapts to the new technology.

Illustrative image related to forked agv
Strategic Material Selection Guide for forked agv
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Forked AGVs?
Selecting the right materials for forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of forked AGVs, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
1. Steel: The Backbone of Forked AGVs
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength, durability, and ability to withstand heavy loads. It has excellent temperature resistance and can endure high-pressure environments, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and resistance to deformation under load. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which can lead to higher maintenance costs over time. Additionally, steel is relatively heavy, which may affect the AGV’s energy efficiency.

Illustrative image related to forked agv
Impact on Application: Steel’s durability makes it ideal for environments where heavy materials are handled, such as warehouses and manufacturing plants. However, its weight can limit the speed and efficiency of the AGV in certain applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for steel quality. In contrast, buyers in Africa and South America may face challenges related to sourcing high-quality steel, impacting lead times and costs.
2. Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio. It performs well in various temperatures and can be anodized for enhanced durability.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which improves energy efficiency and speed. However, it is generally more expensive than steel and may not support as heavy loads, making it less suitable for certain applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring agility and speed, such as in environments with frequent load changes. However, its lower load-bearing capacity may limit its use in heavy-duty scenarios.

Illustrative image related to forked agv
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Germany may prefer aluminum for its lightweight properties, while those in Brazil may need to assess local supply chains for availability. Compliance with international standards is crucial for ensuring quality.
3. Composite Materials: Innovative and Versatile
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, offer high strength while being lightweight. They are resistant to corrosion and can be engineered for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: Composites provide excellent durability and can be tailored to meet specific performance requirements. However, they can be expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which could complicate sourcing.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for specialized applications where weight and corrosion resistance are critical. However, their cost may limit their use in budget-sensitive projects.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from emerging markets may find the cost of composites prohibitive, while European buyers might prioritize them for their performance benefits. Understanding local regulations regarding composite materials is essential.
4. Rubber: Essential for Mobility and Safety
Key Properties: Rubber is flexible, provides excellent traction, and is resistant to wear and tear. It can operate effectively across a range of temperatures and environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: Rubber’s primary advantage is its ability to absorb shocks, which enhances the safety and stability of AGVs. However, it has a limited lifespan compared to metals and may require regular replacement.
Impact on Application: Rubber is crucial for the wheels and bumpers of AGVs, ensuring safe operation in various environments. Its wear over time can lead to increased maintenance costs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of high-quality rubber materials in their region. Compliance with safety standards is critical, especially in industries with stringent regulations.

Illustrative image related to forked agv
Summary Table of Material Selection for Forked AGVs
| Material | Typical Use Case for forked agv | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty material handling in warehouses | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Fast, agile operations in dynamic environments | Lightweight and energy-efficient | Higher cost and lower load capacity | Medium |
| Composite | Specialized applications requiring custom performance | Tailored properties and durability | Expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
| Rubber | Wheels and bumpers for AGVs | Shock absorption and traction | Limited lifespan | Medium |
By carefully considering these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for forked agv
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Forked AGVs?
The manufacturing process for forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is intricate, involving several key stages that ensure the final product meets high standards of quality and functionality. The primary stages of manufacturing include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation:
This initial stage involves sourcing high-quality materials that are essential for the durability and reliability of the forked AGV. Common materials include high-strength steel for structural components, advanced plastics for housing, and lithium-ion batteries for energy efficiency. Manufacturers often engage in rigorous supplier assessments to ensure material quality, which can affect the AGV’s performance and lifespan.
Forming:
In the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into the necessary components using various techniques such as stamping, welding, and machining. For instance, the chassis may be welded together from pre-cut steel sheets, while precision machining is used for components like gears and axles. This stage is crucial as it dictates the structural integrity and operational capabilities of the AGV.
Assembly:
Once the components are formed, they are assembled into the final vehicle. This process typically employs both manual and automated systems to ensure precision. Automated assembly lines may use robotics to install key components, while skilled workers oversee the integration of complex systems such as navigation and safety features. Quality control checks are integrated into this stage to identify any defects early.
Finishing:
The finishing stage involves surface treatment, painting, and final inspections. Surface treatments may include powder coating for corrosion resistance, while painting provides both aesthetics and additional protection. Final inspections assess the AGV’s overall functionality, ensuring that all systems operate as intended before the vehicle is shipped.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of forked AGVs is critical for ensuring reliability and safety. International standards such as ISO 9001 are widely adopted to guarantee quality management systems are in place. This standard emphasizes a process-based approach to manufacturing, ensuring continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Industry-Specific Certifications:
In addition to ISO 9001, forked AGVs may require compliance with industry-specific standards. For instance, the CE marking is essential for products sold in Europe, signifying compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. In certain industries, certifications from organizations like the American Petroleum Institute (API) may also be relevant, particularly for AGVs used in hazardous environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in AGV Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral throughout the manufacturing process of forked AGVs, with several critical checkpoints to ensure quality at every stage.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
This initial checkpoint occurs when materials arrive at the manufacturing facility. IQC involves inspecting the quality of incoming materials against predefined specifications. Suppliers may be required to provide material certificates or reports to verify compliance.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During the manufacturing process, IPQC is implemented to monitor production quality. This includes regular inspections at various stages of assembly and forming. Automated systems may also be employed to detect defects in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
Final Quality Control (FQC):
FQC is the last checkpoint before the forked AGV is shipped to the client. This comprehensive inspection evaluates the complete vehicle for functionality, safety, and compliance with all relevant standards. Test runs may be conducted to assess the AGV’s performance under simulated operational conditions.

Illustrative image related to forked agv
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure the reliability of forked AGVs. Here are several effective strategies:
Audits:
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control systems of suppliers firsthand. This can include reviewing documentation related to quality management systems and observing production practices.
Quality Reports:
Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QC practices. These reports should include data on defect rates, corrective actions taken, and performance against quality standards.
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes. These services often provide comprehensive reports that can help buyers make informed decisions.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various nuances in quality control when sourcing forked AGVs. Here are some considerations:
Regulatory Compliance:
Understanding the regulatory landscape in the buyer’s country is crucial. Different regions may have varying requirements for AGVs, including safety certifications and environmental regulations. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet these local requirements.
Cultural Differences:
Cultural differences can influence communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should establish clear channels of communication with suppliers to ensure that quality standards are understood and adhered to.
Supply Chain Reliability:
The reliability of the supply chain can significantly impact quality. Buyers should assess the supplier’s sourcing practices and logistics capabilities to mitigate risks associated with delays or material shortages.
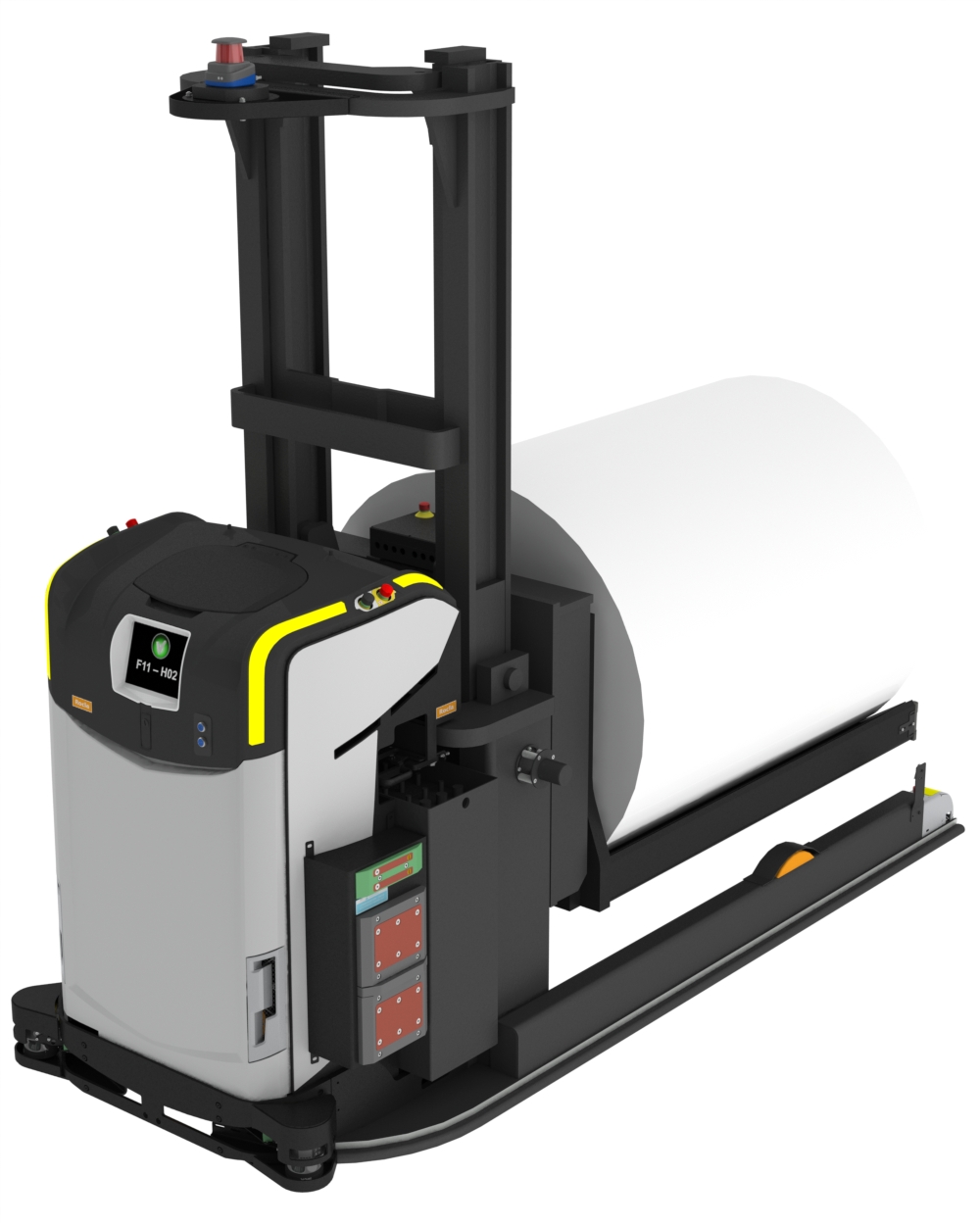

Illustrative image related to forked agv
By paying close attention to these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing forked AGVs, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and safety.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘forked agv’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), this guide outlines essential steps to ensure an informed and effective purchasing decision. The procurement of forked AGVs can significantly enhance operational efficiency and safety in material handling, making it vital to follow a structured approach.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for aligning your needs with the right AGV model. Consider factors such as load capacity, lifting height, and the types of materials to be transported. Additionally, assess the operational environment, including floor conditions and space constraints, to ensure compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
Step 2: Identify Your Budget and Financing Options
Understanding your budget is key to narrowing down your choices. Forked AGVs can have higher upfront costs compared to traditional forklifts, but their long-term savings in maintenance and operational efficiency can justify the investment. Explore financing options, such as leasing or vendor financing, that can ease the initial financial burden.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a solid track record in AGV technology and those that offer comprehensive support services, such as installation and maintenance.
Step 4: Assess Safety Features and Compliance
Safety is paramount when selecting forked AGVs, as they will operate in environments where human workers are present. Evaluate the safety features of the AGVs, such as obstacle detection systems, emergency stop functions, and visibility enhancements. Ensure that the AGVs comply with local and international safety standards relevant to your industry.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Whenever possible, request demonstrations or trial periods for the AGVs you are considering. This hands-on experience allows you to observe the vehicle’s performance in real-time, assess its ease of use, and evaluate how well it integrates with your existing workflows. It also provides an opportunity to identify any potential issues before making a purchase.
Step 6: Consider After-Sales Support and Training
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by the supplier, as ongoing maintenance and training are critical for maximizing the AGV’s operational efficiency. Ensure that the supplier provides comprehensive training for your staff and has a robust support system in place for troubleshooting and repairs. This can greatly reduce downtime and enhance productivity.
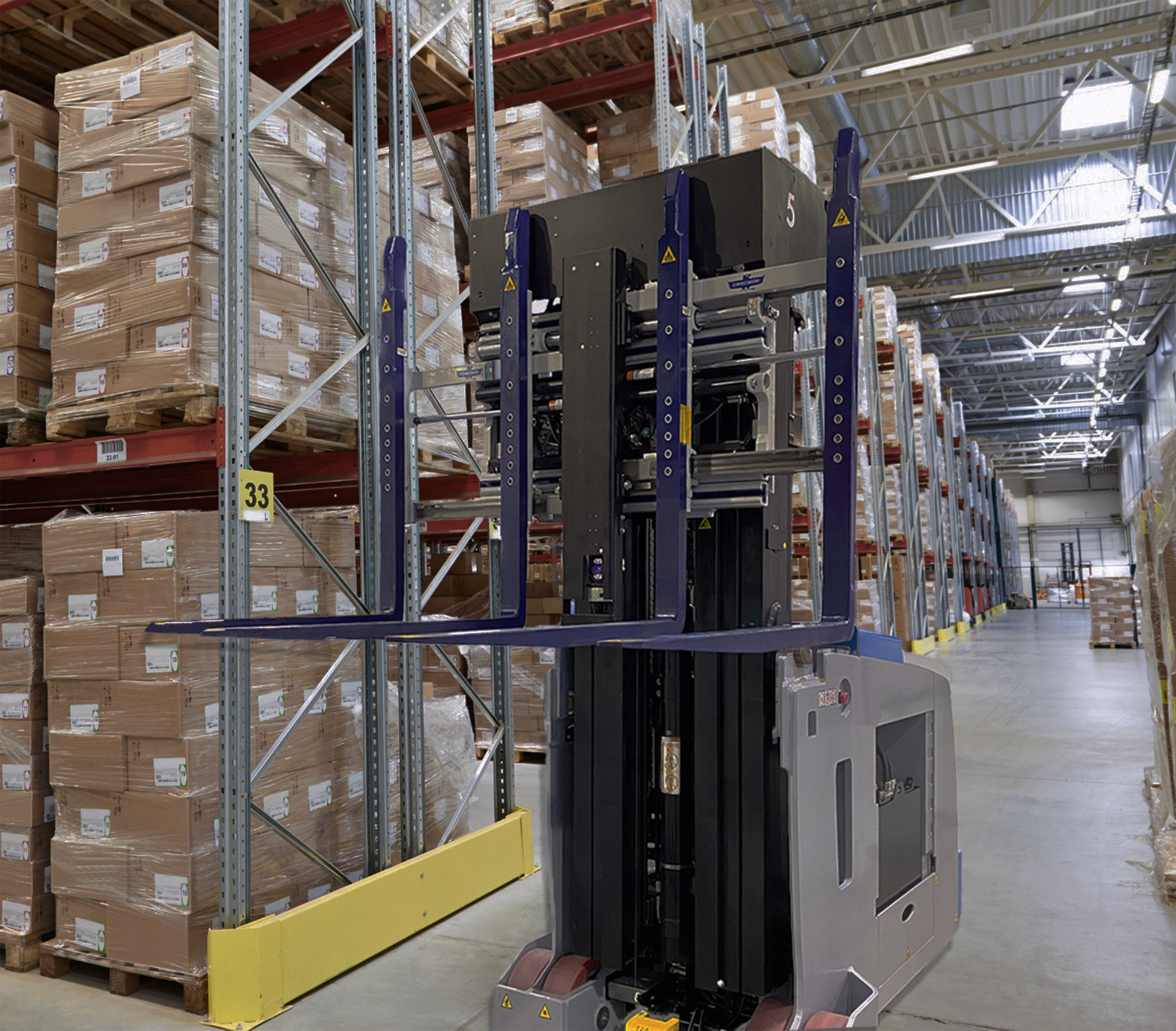

Illustrative image related to forked agv
Step 7: Review Warranty and Maintenance Agreements
Finally, carefully review the warranty and maintenance agreements offered with the AGVs. A strong warranty can protect your investment by covering potential defects and repairs. Additionally, inquire about routine maintenance schedules and costs to ensure that you are prepared for any long-term service needs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing forked AGVs, thereby enhancing their operational capabilities and achieving a strong return on investment.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for forked agv Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components Involved in Sourcing Forked AGVs?
When considering the acquisition of forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The main components that contribute to the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing forked AGVs significantly impact costs. Higher-grade materials may lead to increased durability and lower maintenance costs, which can be a key consideration for long-term investment.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in the design, assembly, and quality control processes. Skilled labor is often required for the assembly of sophisticated AGV systems, which can elevate initial costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the operation of manufacturing facilities, such as utilities, rent, and administrative salaries. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: The cost of specialized tools and equipment necessary for production can be substantial, particularly for customized AGV solutions. Buyers should inquire about the tooling costs associated with their specific requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each forked AGV meets stringent quality standards involves costs associated with testing and inspection. A rigorous QC process may increase upfront costs but can prevent costly failures in the field.
-
Logistics: Transportation of AGVs from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location incurs logistical costs, which can vary based on distance, shipping method, and any additional handling requirements.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary widely based on market competition and the perceived value of the AGV technology.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Forked AGV Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence the pricing of forked AGVs, making it crucial for buyers to understand these dynamics:

Illustrative image related to forked agv
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases can lead to significant discounts. Manufacturers are often willing to negotiate lower prices for larger orders, making it advantageous for companies with extensive material handling needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized AGVs tailored to specific operational needs may incur higher costs due to the additional design and engineering work required. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: AGVs built with high-quality materials that comply with international safety and quality certifications may come at a premium. However, these investments can lead to lower maintenance and operational costs over time.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer better support and assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipping (Incoterms) can greatly affect the total cost. Buyers should understand who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid hidden costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers of Forked AGVs?
For international buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation is key to achieving cost-efficiency:
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Present a TCO analysis to suppliers, highlighting long-term savings on maintenance and operational efficiency. This can justify a higher upfront price if the lifetime costs are lower.
-
Explore Financing Options: Many manufacturers offer financing plans that can ease the initial cash outlay. Inquire about these options to better manage your budget.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Always ask for itemized quotes that break down costs. This transparency allows for better negotiation and understanding of where savings can be made.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Regular communication can foster trust and cooperation.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies for forked AGVs can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions. While the initial investment may be higher compared to traditional forklifts, the long-term benefits often justify the expenditure, particularly in operational efficiency and safety. Always consider the total cost of ownership and engage suppliers in meaningful discussions to optimize your procurement process.
Disclaimer: The prices for forked AGVs can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. Always seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing forked agv With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Forked AGVs in Material Handling
In the rapidly evolving landscape of automation, businesses must consider various solutions that can enhance efficiency, safety, and productivity in material handling. Forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are a prominent choice, but they are not the only option available. This section evaluates forked AGVs against two viable alternatives: Automated Forklifts and Manual Forklifts. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Forked AGV | Automated Forklift | Manual Forklift |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision in repetitive tasks | Good for variable tasks | Versatile but requires skilled operators |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Moderate upfront cost | Lowest upfront cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires integration with existing systems | Easier to integrate in existing setups | Immediate use but less efficient |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance due to fewer parts | Moderate maintenance needs | Higher maintenance due to wear and tear |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume, repetitive tasks | Suitable for varied tasks requiring human judgment | Best for flexible, low-volume environments |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Automated Forklifts?
Automated forklifts are designed to operate autonomously but are often based on traditional manual forklift designs. They provide a hybrid solution, allowing for both automated and manual operation. This flexibility can be advantageous in environments where tasks vary significantly. However, the reliance on a human operator can lead to increased maintenance needs and potential inefficiencies in repetitive tasks. While their initial costs are moderate, the long-term operational costs can accumulate due to the complexity of maintaining a hybrid system.
How Do Manual Forklifts Compare in Terms of Cost and Flexibility?
Manual forklifts are the most traditional solution for material handling, offering a lower initial investment compared to automated options. They are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, making them ideal for businesses that require flexibility in their operations. However, they depend heavily on skilled operators, which can lead to safety issues and variability in performance. Additionally, manual forklifts generally incur higher maintenance costs due to wear and tear from human operation, particularly in high-usage scenarios.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the right material handling solution, B2B buyers should assess their operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Forked AGVs excel in environments that require high efficiency and precision in repetitive tasks, but they come with a higher upfront investment. Automated forklifts offer a balance of automation and flexibility, suitable for diverse tasks but may require more maintenance. Manual forklifts provide the lowest initial costs but depend heavily on human operators and can lead to higher long-term expenses. By carefully considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational strategies and financial plans.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for forked agv
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Forked AGVs That B2B Buyers Should Consider?
Understanding the technical properties of forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is essential for businesses aiming to enhance their material handling operations. Below are critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Load Capacity
The load capacity of a forked AGV indicates the maximum weight it can transport safely. Most AGVs can handle loads ranging from 500 kg to over 3,000 kg. For businesses, selecting an AGV with the appropriate load capacity is crucial to ensure efficient operations without the risk of overloading, which can lead to equipment failure and safety hazards.
2. Battery Technology
The type of battery used in a forked AGV significantly impacts its operational efficiency. Lithium-ion batteries are increasingly popular due to their fast charging times and longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. Understanding battery technology is vital for B2B buyers, as it affects the AGV’s uptime, maintenance costs, and overall productivity.
3. Navigation Technology
Forked AGVs employ various navigation technologies, including laser, magnetic tape, and vision-based systems. Each method has its advantages and suitability for different environments. For example, laser navigation allows for more flexibility in dynamic warehouse settings. Buyers should assess their facility layout and choose AGVs with navigation systems that align with their operational needs.
4. Safety Features
Modern forked AGVs are equipped with advanced safety features such as obstacle detection sensors, emergency stop buttons, and LED warning lights. These features are crucial for preventing accidents and protecting personnel. Understanding the safety mechanisms in place not only ensures compliance with industry standards but also enhances workplace safety, making it a significant consideration for buyers.
5. Dimensions and Maneuverability
The physical dimensions of a forked AGV, including its height, width, and turning radius, determine its ability to operate in constrained spaces. Many AGVs are designed to navigate narrow aisles and tight corners, which is particularly important in warehouses with limited space. B2B buyers must consider these dimensions to ensure the AGV can efficiently operate within their specific environments.
6. Integration Capabilities
Forked AGVs should be compatible with existing warehouse management systems (WMS) and other automation technologies. This capability allows for seamless integration into current operations, enhancing workflow efficiency. Buyers should inquire about the AGV’s ability to interface with other systems to maximize their return on investment.

Illustrative image related to forked agv
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Forked AGVs?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process more effectively. Here are key trade terms related to forked AGVs:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for buyers as it affects warranty support, parts availability, and service agreements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases according to their operational needs and budget constraints.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specific products or services. Buyers should utilize RFQs to gather competitive pricing and ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer. Familiarity with these terms is vital for B2B buyers to understand their obligations and mitigate risks in international transactions.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO is an assessment that includes all costs associated with purchasing and operating an AGV over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. Understanding TCO helps buyers evaluate the long-term value of their investment.
6. SLA (Service Level Agreement)
An SLA is a contract that outlines the expected level of service between a provider and a client. For B2B buyers, having a clear SLA ensures that they receive the expected support and maintenance services for their AGVs, safeguarding their operational uptime.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in forked AGVs, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and productivity.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the forked agv Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Shaping the Forked AGV Market?
The forked Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) sector is undergoing significant transformation, driven by advancements in technology and shifting market demands. One primary driver is the need for increased operational efficiency in manufacturing and logistics, where traditional manual forklifts are being replaced by more reliable and efficient AGVs. In regions like Africa and South America, where labor costs are rising, the automation of material handling processes is becoming a strategic necessity. Additionally, the Middle East and Europe, particularly Germany, are witnessing a surge in demand for AGVs as companies strive to modernize their supply chains and enhance productivity.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced sensor systems are enhancing the capabilities of forked AGVs, enabling them to navigate complex environments and interact seamlessly with other automated systems. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to integrate AGVs into their operations, as these technologies promise reduced operational costs and improved safety. Moreover, the growing emphasis on sustainability is shaping sourcing trends, with companies increasingly seeking AGVs that offer energy-efficient solutions and reduced environmental impact.
The market dynamics are also influenced by the evolving regulatory landscape, especially in Europe, where stricter safety and environmental regulations are driving companies to adopt more sustainable and automated solutions. This regulatory push not only fosters innovation but also creates opportunities for B2B buyers to partner with suppliers who are committed to compliance and sustainability in their product offerings.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Forked AGV Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount considerations for businesses investing in forked AGVs. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of AGVs plays a crucial role in supplier selection. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who utilize sustainable materials and adhere to green manufacturing practices. For instance, the use of recyclable materials in the construction of AGVs not only minimizes waste but also appeals to environmentally conscious customers.
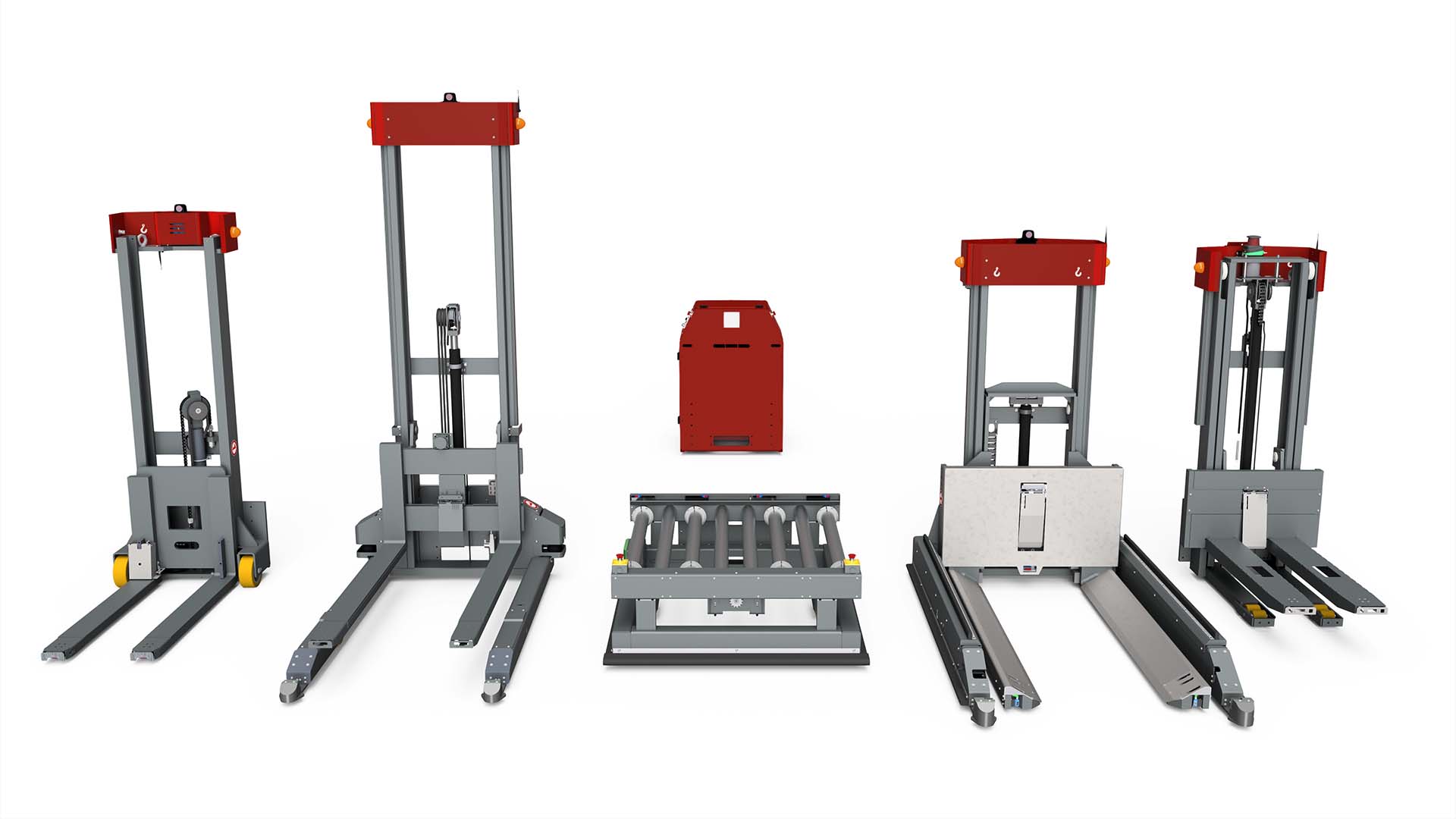

Illustrative image related to forked agv
Ethical supply chains are essential for maintaining corporate responsibility and enhancing brand reputation. B2B buyers must consider suppliers that prioritize transparency in their sourcing processes, ensuring that materials are obtained responsibly and that labor practices comply with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, as businesses face pressure from consumers and stakeholders to adopt more sustainable practices, integrating eco-friendly AGVs can contribute to overall corporate sustainability goals. This transition not only aligns with global sustainability objectives but can also lead to cost savings in energy consumption and waste reduction, enhancing the overall return on investment.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Forked AGVs and Their Impact on B2B Operations?
The evolution of forked AGVs dates back to the early stages of automation in material handling, where the initial focus was on improving efficiency and safety in warehouses and manufacturing facilities. Early models were often limited in functionality, relying on fixed paths and basic navigation systems. However, advancements in robotics and sensor technologies have propelled forked AGVs into a new era of flexibility and capability.
Today’s forked AGVs are designed for autonomous operation, eliminating the need for manual intervention and enabling seamless integration into existing workflows. This evolution has significantly impacted B2B operations by streamlining processes, reducing labor costs, and minimizing the potential for human error. As companies continue to adapt to the demands of modern supply chains, the adoption of forked AGVs is expected to increase, further cementing their role as essential tools in enhancing operational efficiency and safety in diverse industrial settings.
In summary, understanding market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and the historical context of forked AGVs is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to make informed investment decisions in this rapidly evolving sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of forked agv
-
How do I determine if a forked AGV is suitable for my operation?
To assess if a forked Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) fits your needs, evaluate your material handling requirements, including load types, weight, and storage configurations. Analyze your facility’s layout for compatibility, focusing on aisle widths and heights. Additionally, consider factors like the frequency of operations, desired automation level, and existing infrastructure. Engaging with suppliers for a site assessment can provide insights into the most effective AGV solutions tailored to your specific environment. -
What are the key advantages of using forked AGVs over traditional forklifts?
Forked AGVs offer several advantages, including enhanced safety, reduced labor costs, and increased operational efficiency. Unlike traditional forklifts, they are designed for autonomous operation, minimizing human error and accidents. Forked AGVs also provide consistent performance, which reduces wear and tear on equipment and materials. Furthermore, they can operate continuously, maximizing throughput while allowing human operators to focus on higher-value tasks within your business. -
What customization options are available for forked AGVs?
Customization for forked AGVs can include adjustments to payload capacity, fork dimensions, and navigation systems to suit specific operational needs. Some manufacturers offer software customization for integration with existing warehouse management systems, enabling seamless communication and data exchange. Additionally, safety features like light curtains or bumpers can be tailored based on the working environment. Discussing your unique requirements with suppliers can lead to a tailored AGV solution that enhances efficiency and safety. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for forked AGVs?
Minimum order quantities for forked AGVs can vary significantly among manufacturers, often influenced by production capabilities and specific configurations. Generally, MOQs may range from one unit for standard models to several units for custom or specialized AGVs. For larger purchases, negotiating with suppliers may yield better pricing and flexible terms. Engaging with multiple suppliers can also provide a clearer picture of market options and potential savings. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing forked AGVs internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of forked AGVs typically range from upfront payment to net 30 or net 60 days, depending on the supplier and your negotiation leverage. Some suppliers may offer financing options or leasing agreements to ease the initial capital expenditure. It’s crucial to clarify terms in advance, including deposit requirements, currency preferences, and any associated fees for international transactions. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can lead to more favorable terms. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing forked AGVs?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing forked AGVs, request detailed specifications and certifications from suppliers, such as ISO or CE compliance. Conduct site visits or request product demonstrations to evaluate manufacturing practices and quality control processes. Additionally, consider asking for references from previous clients to gauge their satisfaction and performance of the AGVs in real-world scenarios. Establishing clear quality expectations in the contract can help protect your investment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for importing forked AGVs?
Logistics for importing forked AGVs involves several key considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Evaluate the best transport options based on cost, speed, and the AGV’s dimensions and weight. Ensure all necessary documentation, such as commercial invoices and certificates of origin, is prepared for smooth customs processing. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in handling heavy machinery can streamline the import process and mitigate potential delays. -
How do I vet suppliers of forked AGVs for reliability and performance?
Vetting suppliers for forked AGVs requires thorough research and due diligence. Start by checking their industry reputation, customer reviews, and case studies to assess performance history. Request detailed product specifications and warranty information to understand the reliability of their offerings. Engaging in discussions about their manufacturing processes and support services can provide additional insights. Attending trade shows or industry conferences can also facilitate direct interactions with potential suppliers, helping you gauge their capabilities firsthand.
Top 7 Forked Agv Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Scott Automation – Forked AGVs
Domain: scottautomation.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Forked AGVs are suitable for various material handling needs in manufacturing and distribution, including floor to floor, rack, block storage, and double deep operations. They are designed to transport palletized loads, paper products, gaylords, bins, or racks, replacing traditional forklifts and pallet jacks. Key features include:
– Safety features: blue LED directional spotlight, front and side …
2. Toyota – Automated Guided Vehicles
Domain: toyotaforklift.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Toyota’s Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) include automated guided forklifts designed for repetitive warehouse material handling tasks. Key products include: Mouse and Mole Automated Guided Carts, Core Tow Tractor Automated Forklift, Center-Controlled Rider Automated Forklift, CB18 Automated Guided Forklift, M10 Tug Autonomous Vehicle, ML2 Mini Load Autonomous Vehicle, and Key Cart Automated Guide…
3. Go4Robotics – Automated Forklifts & Forked AGVs
Domain: go4robotics.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Automated Forklifts:
– Redeveloped from manual forklifts to work autonomously.
– Often sold as hybrid vehicles (can be driven manually or automatically).
– Established manufacturers with economies of scale.
Forked AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles):
– Designed for autonomous operation from the start (no manual driving controls).
– Also known as automated guided forklifts (AGFs), forklift AGVs, or…
4. RobotShop – ATEAGO L1 Self-Driving Forklift
Domain: robotshop.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: ATEAGO L1 Self-Driving Autonomous Forklift, Warehouse Pallet Mover, Forked AGV, Pallet Lift Truck
5. AGV Network – Automated Forklift Solutions
Domain: agvnetwork.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Automated Forklift (AGV) is a self-driving, computer-controlled forklift designed for material handling without human intervention. Key features include:
– Models: VNR 16(V)-01 Reach Truck AGV, JBT Forklift CB 2500 Compact, Lowy CB- Balyo Stacker, Seegrid Palion Lift CR1.
– Load Capacity: VNR16(V) for indoor/outdoor handling, CB 2500 for 2500 kg up to 6 m height, Lowy CB for 1200 kg payload, See…
6. Bastian Solutions – CB18 Automated Forklift
Domain: bastiansolutions.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The CB18 Automated Forklift is designed for efficient material handling in various environments. It features a load capacity of 4,000 lbs and is equipped with advanced navigation technology, allowing it to operate safely alongside human workers. The forklift can be integrated with existing warehouse management systems and is suitable for transporting goods in manufacturing, distribution, and retai…
7. AGILOX – OCF Omnidirectional AMR
Domain: agilox.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “AGILOX OCF”, “type”: “Omnidirectional AMR with counterweight”, “maximum_lifting_weight”: “1,500 kg (3,306 lbs)”, “maximum_lifting_height”: “1,600 mm (63 in)”, “maximum_station_height”: “1,450 mm (57 in)”, “maximum_speed”: “1.4 m/s (4.6 ft/s)”, “turning_circle”: “3,500 mm (138 in)”, “dead_weight”: “3,600 kg (7,937 lbs)”, “dimensions”: {“length”: “2,784 mm (110 in)”, “width”: “1,20…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for forked agv
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Forked AGVs?
Investing in forked Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) offers substantial long-term benefits for businesses looking to optimize their material handling processes. With their design tailored for autonomous operation, forked AGVs not only enhance efficiency but also reduce the risk of accidents, as they are equipped with advanced safety features. While the initial investment may be higher compared to automated forklifts, the potential for lower maintenance costs and improved operational reliability makes forked AGVs a wise choice for companies seeking to modernize their logistics operations.
How Does Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Operations?
Strategic sourcing is crucial when selecting the right forked AGV for your specific needs. By evaluating suppliers based on cost, technology, and support services, businesses can ensure they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals. Engaging with reputable manufacturers and suppliers can also lead to better pricing, improved product availability, and enhanced after-sales support.
What’s Next for International Buyers?
As global markets evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for innovative material handling solutions will continue to grow. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to explore the potential of forked AGVs to streamline their operations. Embrace this opportunity to transform your material handling processes and position your business for success in an increasingly automated future. Reach out to industry leaders today to discover tailored solutions that can elevate your logistics capabilities.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.