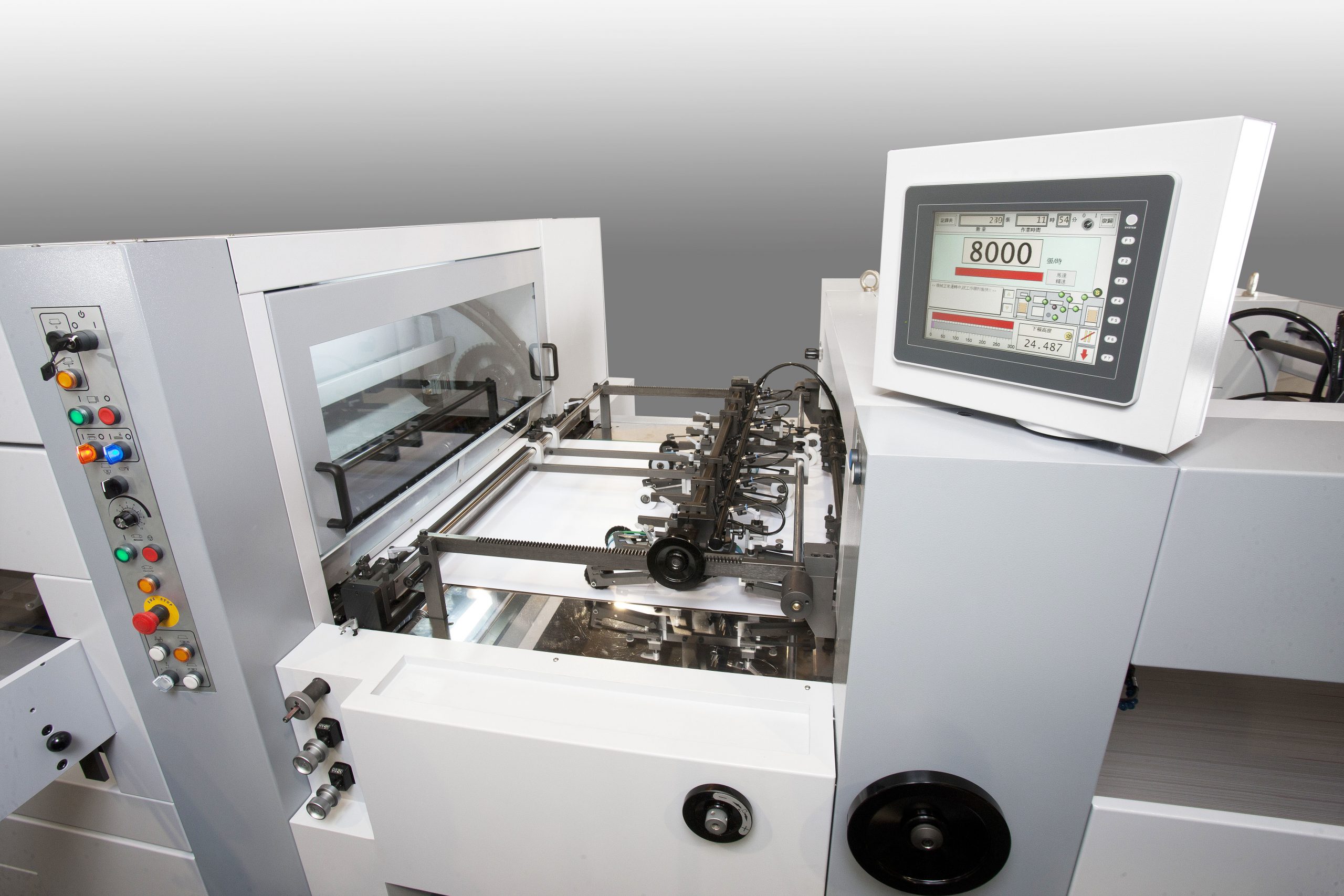
How to Source Die Cutting Technology Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for die cutting technology
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing die cutting technology presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets like Africa and South America, as well as established regions such as Europe and the Middle East. With various methods and machines available, selecting the right die cutting solution can be daunting. This guide is designed to demystify the complexities of die cutting technology, offering a comprehensive overview of types, applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting.
We delve into the nuances of die cutting processes—from flatbed to rotary methods—highlighting their unique advantages and the materials they best accommodate. Buyers will also gain insights into the cost structures associated with different machines and the factors influencing pricing in various regions. With detailed sections on how to assess potential suppliers, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this resource aims to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that companies can confidently invest in die cutting technology that meets their production demands. Whether you’re in Brazil, Saudi Arabia, or elsewhere, understanding the global market for die cutting is vital for maintaining a competitive edge and driving growth in your industry.
Understanding die cutting technology Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flatbed Die Cutting | Uses a flat surface to press material onto a die; ideal for larger items. | Custom packaging, textiles, and metal parts | Pros: Versatile for various materials; good for low-volume runs. Cons: Slower production speed; not ideal for intricate designs. |
| Rotary Die Cutting | Utilizes rollers for continuous cutting; suitable for high-speed production. | Labels, packaging, and flexible materials | Pros: High efficiency; excellent for large volumes. Cons: Higher initial investment; limited to specific material types. |
| Semi-Rotary Die Cutting | Combines rotary and flatbed techniques; allows for intricate cuts. | Specialty labels and custom shapes | Pros: Versatile; good for detailed designs. Cons: More complex setup; may require skilled operators. |
| Digital Die Cutting | Employs digital technology for precise cutting; no physical die required. | Prototyping, short runs, and custom designs | Pros: Flexibility in design; quick turnaround for small batches. Cons: Limited material types; higher cost per unit for large runs. |
| Steel Rule Die Cutting | Uses steel rule dies for cutting; adaptable for various applications. | Packaging, promotional materials, and crafts | Pros: Cost-effective for medium to high volumes; can handle multiple materials. Cons: Setup time can be lengthy; not suitable for complex shapes without additional costs. |
What Are the Characteristics of Flatbed Die Cutting?
Flatbed die cutting is characterized by its use of a flat surface to press material onto a die, making it suitable for larger items and various materials, including textiles and metals. This method is particularly beneficial for custom packaging solutions, allowing for unique shapes that can enhance product appeal. Buyers should consider the slower production speed and limitations on intricate designs when evaluating flatbed die cutting for their needs.
How Does Rotary Die Cutting Enhance Production Efficiency?
Rotary die cutting features rollers that facilitate continuous cutting, making it ideal for high-speed production environments. This method excels in applications such as labels and flexible packaging, where efficiency and volume are paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment against the significant throughput potential, while also noting that rotary die cutting is limited to specific materials, which could affect material sourcing strategies.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Why Choose Semi-Rotary Die Cutting for Intricate Designs?
Semi-rotary die cutting merges the benefits of both rotary and flatbed techniques, allowing for intricate cuts that are ideal for specialty labels and custom shapes. This method is particularly advantageous for businesses seeking to produce visually appealing products without sacrificing efficiency. However, buyers should be aware of the more complex setup and potential need for skilled operators to manage the process effectively.
What Advantages Does Digital Die Cutting Offer for Customization?
Digital die cutting utilizes advanced technology to create precise cuts without the need for physical dies, making it perfect for prototyping and short runs of custom designs. This flexibility allows businesses to quickly adapt to market changes and customer preferences. While the ability to handle diverse designs is a significant advantage, B2B buyers should consider the limitations on material types and the higher cost per unit for larger production runs.
How Does Steel Rule Die Cutting Balance Cost and Versatility?
Steel rule die cutting employs durable steel dies that are adaptable for various applications, including packaging and promotional materials. This method is cost-effective for medium to high-volume production, making it appealing for businesses looking to balance quality and expense. However, buyers should account for potential setup time and the challenges associated with producing complex shapes, which may require additional investment in tooling.
Key Industrial Applications of die cutting technology
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of die cutting technology | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Custom packaging inserts for fragile products | Enhanced product protection and reduced shipping costs | Material durability, design complexity, and volume |
| Automotive | Die-cut gaskets and seals | Improved sealing performance and reduced assembly time | Material compatibility, precision requirements, and lead time |
| Electronics | Insulation components for circuit boards | Increased product reliability and safety | Material specifications, compliance standards, and cost-effectiveness |
| Textiles | Die-cut patterns for garment manufacturing | Streamlined production and reduced fabric waste | Fabric type, cutting precision, and order volume |
| Medical Devices | Custom die-cut components for devices | Enhanced functionality and compliance with regulations | Material certifications, customization options, and delivery timelines |
How is Die Cutting Technology Used in the Packaging Industry?
In the packaging sector, die cutting technology is employed to create custom inserts that protect fragile products during transit. This process allows manufacturers to design tailored solutions that fit specific items, thereby minimizing movement and potential damage. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable materials that can withstand diverse shipping conditions is critical. Additionally, companies must consider the design intricacies and production volume to optimize costs and efficiency.
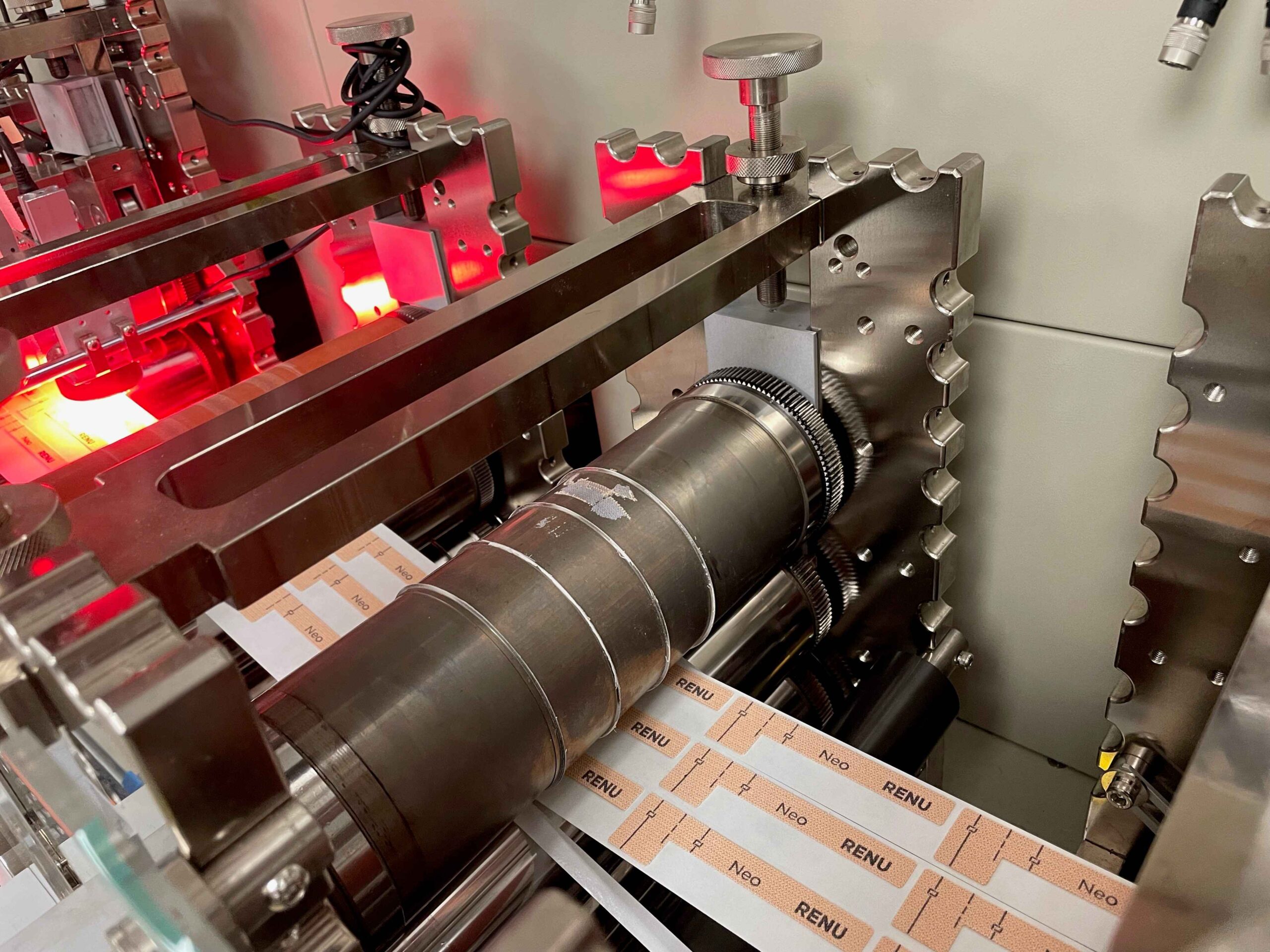
Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
What Role Does Die Cutting Play in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, die cutting is essential for producing gaskets and seals that ensure optimal performance and durability. These components must fit precisely to prevent leaks and maintain the integrity of various systems within the vehicle. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing materials that meet stringent industry standards for durability and heat resistance. Precision in cutting is also crucial, as any deviations can lead to costly assembly delays and performance issues.
How is Die Cutting Beneficial for Electronics Manufacturing?
Die cutting technology is widely used in electronics manufacturing to create insulation components for circuit boards. These components play a vital role in enhancing product reliability and safety by preventing short circuits and electrical failures. For B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, it is essential to ensure that the sourced materials meet relevant compliance standards, such as RoHS or UL certification. Cost-effectiveness and the ability to handle complex designs are also key considerations when selecting a die-cutting partner.
Why is Die Cutting Important in the Textile Industry?
In the textile sector, die cutting is utilized to produce patterns for garment manufacturing, streamlining the cutting process and reducing fabric waste. This technology enables manufacturers to achieve intricate designs quickly and efficiently, which is particularly beneficial for high-volume production runs. Buyers in Europe and South America must consider the type of fabric being used, as different materials may require specific die-cutting techniques to achieve the desired outcome. Additionally, understanding the supplier’s capacity to handle varying order sizes is crucial for maintaining production schedules.
How Does Die Cutting Enhance Medical Device Manufacturing?
Die cutting technology is critical in the medical device industry for creating custom components that meet stringent regulatory requirements. These components must not only be functional but also comply with health and safety standards. International buyers must prioritize sourcing materials that are certified for medical use, ensuring compliance with regulations such as ISO 13485. Customization options and reliable delivery timelines are also vital, as delays in sourcing can impact product launches and patient safety.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘die cutting technology’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Production Costs in Die Cutting Projects
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers, especially in industries like packaging and printing, is managing production costs associated with die cutting technology. High initial costs for custom dies can strain budgets, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that require frequent design changes or low-volume runs. Additionally, unexpected costs arising from material waste, machine maintenance, and labor can further complicate financial planning.
The Solution: To address these concerns, buyers should consider investing in flexible die options, which are more cost-effective for short runs or intricate designs. Flexible dies are generally less expensive than solid steel dies and can be used with various materials, thereby reducing waste. Furthermore, implementing a robust project management system can help track costs and material usage, allowing for real-time adjustments to avoid overruns. Buyers should also evaluate their supplier relationships—negotiating for bulk discounts or exploring partnerships with manufacturers who offer die rental services can significantly reduce financial burdens. By strategically managing the production process and leveraging modern technology, businesses can maintain quality while optimizing costs.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Precision and Quality in Die Cutting
The Problem: Quality control is crucial in die cutting, as inaccuracies can lead to product defects and increased rework, which are particularly detrimental in competitive markets. B2B buyers often struggle with ensuring that the die cutting process maintains high precision, especially when scaling production or utilizing multiple machines. Inconsistent results can frustrate customers and harm brand reputation.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
The Solution: To enhance precision and quality, buyers should invest in advanced die cutting machines equipped with laser or digital cutting technology. These machines offer superior accuracy and can handle intricate designs without compromising material integrity. Additionally, establishing a rigorous quality assurance protocol is essential. This includes regular calibration of machines and thorough inspection of die cuts at various production stages. Utilizing computer-aided design (CAD) software for die design can also help identify potential issues before production begins, ensuring that designs are feasible and align with quality standards. Training staff on best practices for operating die cutting machinery will further reinforce quality control measures.
Scenario 3: Navigating Material Compatibility Issues in Die Cutting
The Problem: A significant pain point for B2B buyers is navigating the compatibility of various materials with die cutting processes. Different materials, such as paper, plastic, and metals, require specific die types and cutting techniques. Buyers may face challenges in selecting the right materials for their products, leading to complications like poor cutting performance, increased wear on dies, and ultimately, product failures.
The Solution: To overcome material compatibility issues, buyers should conduct thorough research on the properties of the materials they intend to use for die cutting. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in die cutting technology can provide valuable insights into material behavior and the most suitable dies for each application. It is also advisable to create a material database that includes test results and performance metrics for various combinations of materials and dies. This resource can serve as a reference for future projects, streamlining the decision-making process. Additionally, collaborating with experienced die cutting engineers during the design phase can help identify potential material-related challenges early on, ensuring a smoother production process and higher quality outcomes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for die cutting technology
When selecting materials for die cutting technology, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations, especially from a B2B perspective. This guide analyzes four common materials used in die cutting: paper, cardboard, plastics, and metals. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its suitability for various applications, particularly for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Paper in Die Cutting?
Paper is one of the most commonly used materials in die cutting, especially for applications such as labels, greeting cards, and packaging. Key properties include its weight (measured in grams per square meter), thickness, and finish. Paper can be easily die-cut into intricate shapes, making it ideal for detailed designs.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Pros: Paper is cost-effective, readily available, and versatile, allowing for a wide range of finishes and textures. It is also lightweight, which can reduce shipping costs.
Cons: While paper is suitable for many applications, it can be less durable than other materials, especially in high-moisture environments. Additionally, its performance can vary based on the weight and type of paper used.
Impact on Application: Paper is compatible with various printing techniques, enhancing its utility for custom designs. However, international buyers should be aware of local preferences for paper quality and sustainability standards.
How Does Cardboard Compare in Die Cutting Applications?
Cardboard, particularly corrugated and chipboard, is frequently used in packaging and structural applications. Its key properties include strength, rigidity, and insulation.
Pros: Cardboard is robust and can withstand significant pressure, making it suitable for shipping and storage. It is also recyclable, aligning with eco-friendly practices.
Cons: The thickness of cardboard can complicate the die-cutting process, requiring more powerful machines. Additionally, it may not provide the same level of detail as thinner materials.
Impact on Application: Cardboard is often used for packaging designs that require structural integrity. Buyers should consider compliance with local packaging regulations and standards, such as those set by ASTM or ISO.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastics in Die Cutting?
Plastics, including PVC, PET, and polycarbonate, are increasingly popular in die cutting due to their versatility and durability. Key properties include chemical resistance, flexibility, and temperature tolerance.
Pros: Plastics can be die-cut into complex shapes and are resistant to moisture and chemicals, making them suitable for various applications, including labels and industrial components.
Cons: The cost of high-quality plastics can be significantly higher than paper or cardboard. Additionally, the die cutting of certain plastics may require specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for applications demanding durability and resistance to environmental factors. International buyers must consider local regulations regarding plastic use and recycling, particularly in regions emphasizing sustainability.
What Role Do Metals Play in Die Cutting Technology?
Metal die cutting is primarily used for industrial applications, such as automotive parts and electronic enclosures. Key properties include strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Pros: Metals are incredibly durable and can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for long-lasting applications. They also provide precision in cutting, essential for intricate designs.
Cons: The cost of metal materials is typically higher, and the die cutting process can be more complex and time-consuming. Additionally, specialized machinery is often required.
Impact on Application: Metal die cutting is crucial for industries where strength and precision are paramount. Buyers must ensure compliance with international standards, such as DIN and JIS, which govern material specifications.
Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Summary Table of Material Selection for Die Cutting Technology
| Material | Typical Use Case for die cutting technology | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | Labels, greeting cards, packaging | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable in high-moisture environments | Low |
| Cardboard | Packaging, structural applications | Strong and recyclable | Thickness complicates die cutting | Medium |
| Plastics | Labels, industrial components | Chemical and moisture resistant | Higher cost and specialized equipment needed | High |
| Metals | Automotive parts, electronic enclosures | Durable and precise | Higher cost and complex processing | High |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for die cutting technology involves evaluating the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option. Understanding these factors can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific applications and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for die cutting technology
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing in Die Cutting Technology?
The manufacturing process for die cutting technology is structured into several key stages, each crucial for achieving high-quality results. Understanding these stages enables B2B buyers to assess suppliers effectively and ensure that they meet industry standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process involves selecting and preparing the right materials. Common materials for die cutting include paper, cardboard, plastic, metal, and fabric. The choice of material significantly affects the cutting process and the final product quality.
Material preparation includes:
- Material Selection: Choose materials based on durability, thickness, and application.
- Pre-Processing: Materials may require treatments such as coating or laminating to enhance performance or aesthetics.
- Quality Checks: Initial inspections ensure that materials meet specified standards, such as thickness and consistency.
2. Forming
The forming stage involves the actual die cutting process, where the prepared materials are shaped into the desired designs. This can be achieved through various die cutting methods, including flatbed, rotary, and semi-rotary cutting.
Key techniques in the forming stage include:
- Die Creation: Using CAD software, manufacturers design dies that will cut the material into specified shapes.
- Cutting Methods: Different methods are employed based on the material and the complexity of the design. Flatbed machines are suited for thicker materials, while rotary cutters excel with flexible materials.
- Precision Cutting: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines enhance accuracy, ensuring that the cuts are clean and consistent.
3. Assembly
Once the cutting is completed, the next stage is assembly, where the cut pieces are combined if necessary. This is particularly relevant for products that require multiple components, such as packaging or complex designs.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Assembly processes typically involve:
- Joining Techniques: Depending on the final product, techniques such as gluing, stitching, or fastening may be employed.
- Quality Control Checks: Ensure that all components fit together correctly and meet design specifications.
4. Finishing
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing, which includes any additional processes that enhance the product’s appearance or functionality.
Finishing processes may include:
- Trimming and Edging: Removing excess material and refining edges for a polished look.
- Coating or Lamination: Applying finishes that protect the product and improve aesthetics.
- Final Quality Inspections: A thorough check is conducted to ensure that the products meet all quality standards before packaging and shipping.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant to Die Cutting Technology?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in die cutting technology, ensuring that products not only meet customer expectations but also comply with international standards.
International Standards
Several international quality standards are crucial for die cutting manufacturers:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, emphasizing a process approach to enhance customer satisfaction through effective system implementation.
- ISO 14001: Pertaining to environmental management, this standard is important for companies aiming to minimize their environmental impact during manufacturing.
- ISO 45001: This standard focuses on occupational health and safety, ensuring that manufacturers provide a safe working environment.
Industry-Specific Standards
Depending on the application, additional certifications may be required:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), ensuring they meet health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for die cutting in the oil and gas sector, these standards ensure that products meet specific performance and safety criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Die Cutting?
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet the established standards. Here are the key QC checkpoints:
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC involves the inspection of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This process ensures that materials meet predefined specifications before they are used in production.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Common IQC practices include:
- Material Verification: Checking certificates of compliance and performing physical inspections.
- Sampling: Random sampling of materials to assess quality and consistency.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC focuses on monitoring the production activities to catch defects early. Techniques used in this phase include:
- Real-time Monitoring: Utilizing sensors and software to track cutting accuracy and machine performance.
- Periodic Inspections: Regular checks at different stages of the process to ensure adherence to quality standards.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC is conducted after the manufacturing process is complete. This stage involves a comprehensive assessment of the finished products to ensure they meet customer specifications and quality standards.
FQC procedures typically include:
- Dimensional Checks: Measuring the final products against design specifications.
- Functional Testing: Verifying that products perform as intended in their application.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Here are some strategies to verify supplier QC processes:
1. Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits of suppliers provide insight into their quality management systems and manufacturing processes. During an audit, buyers can:

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
- Evaluate the supplier’s adherence to quality standards.
- Review documentation related to quality processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC records.
2. Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the results of inspections and tests performed throughout the manufacturing process. These reports should include:
- Data on defect rates.
- Information about corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
3. Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality processes. These services can include:
- Pre-shipment inspections to verify that products meet specifications.
- Random sampling of products for quality assurance.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control and Certification for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial, especially when sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
- Regional Standards: Buyers must be aware of local regulations and standards that may differ from international norms. For instance, compliance with local health and safety regulations is essential when sourcing from regions with specific legal requirements.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding cultural attitudes toward quality and manufacturing practices can help buyers foster better relationships with suppliers.
- Language Barriers: Communication regarding quality expectations may be affected by language differences. Clear documentation and potentially using local intermediaries can help mitigate misunderstandings.
By understanding these aspects of the manufacturing process and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for die cutting technology, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘die cutting technology’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of die cutting technology can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This step-by-step checklist is designed to help you make informed decisions, ensuring you acquire the right technology that meets your operational needs and quality standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your requirements. Consider the types of materials you will be cutting (e.g., paper, metal, plastic) and the volume of production needed. This will guide you in selecting the appropriate die cutting machine, whether it’s a manual, digital, or industrial model.
Step 2: Research Available Die Cutting Methods
Familiarize yourself with the various die cutting methods such as flatbed, rotary, and semi-rotary. Each method has distinct advantages depending on your application. For example, rotary die cutting is ideal for high-speed production of labels, while flatbed cutting is better suited for larger items or low-volume projects.
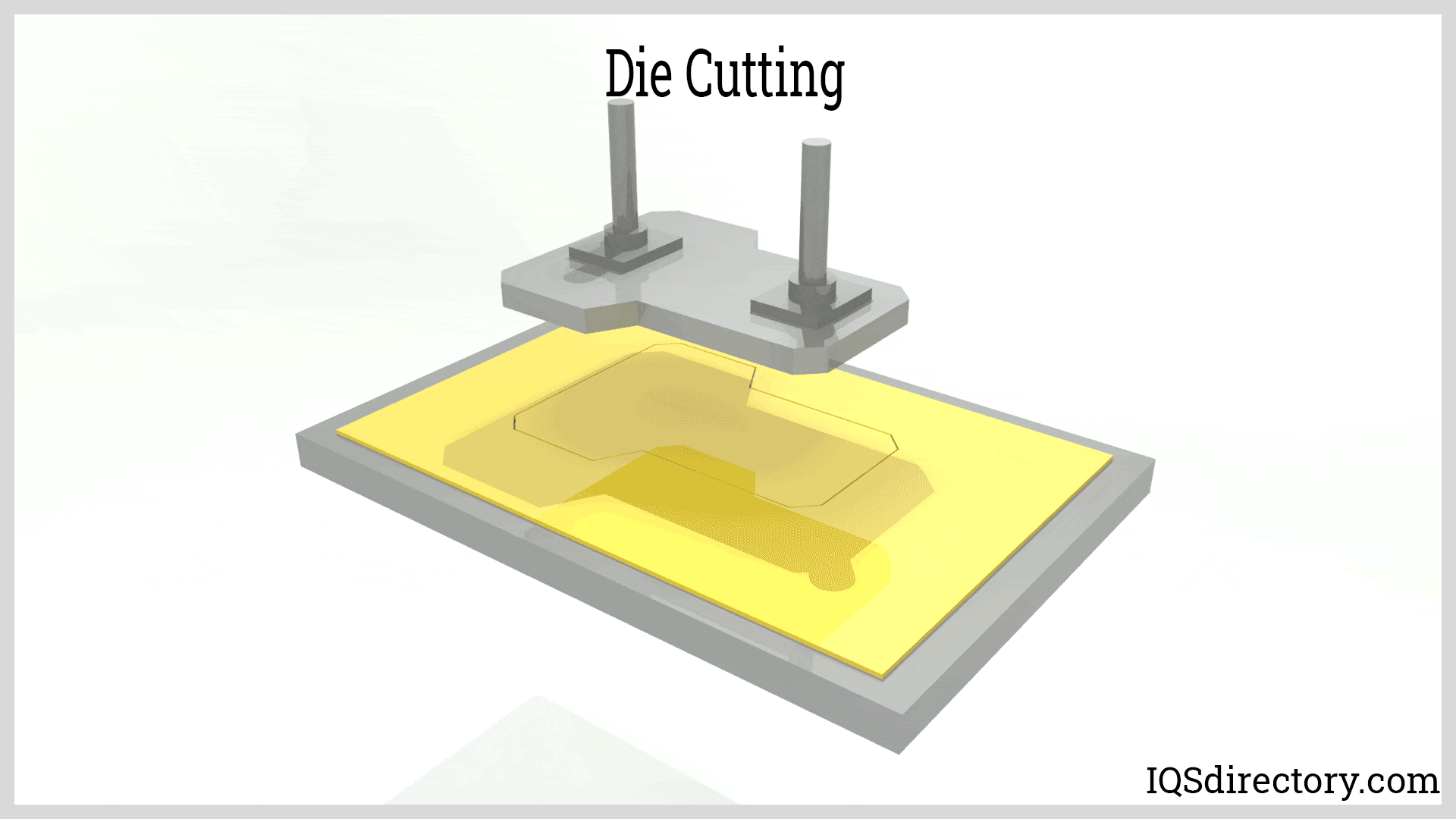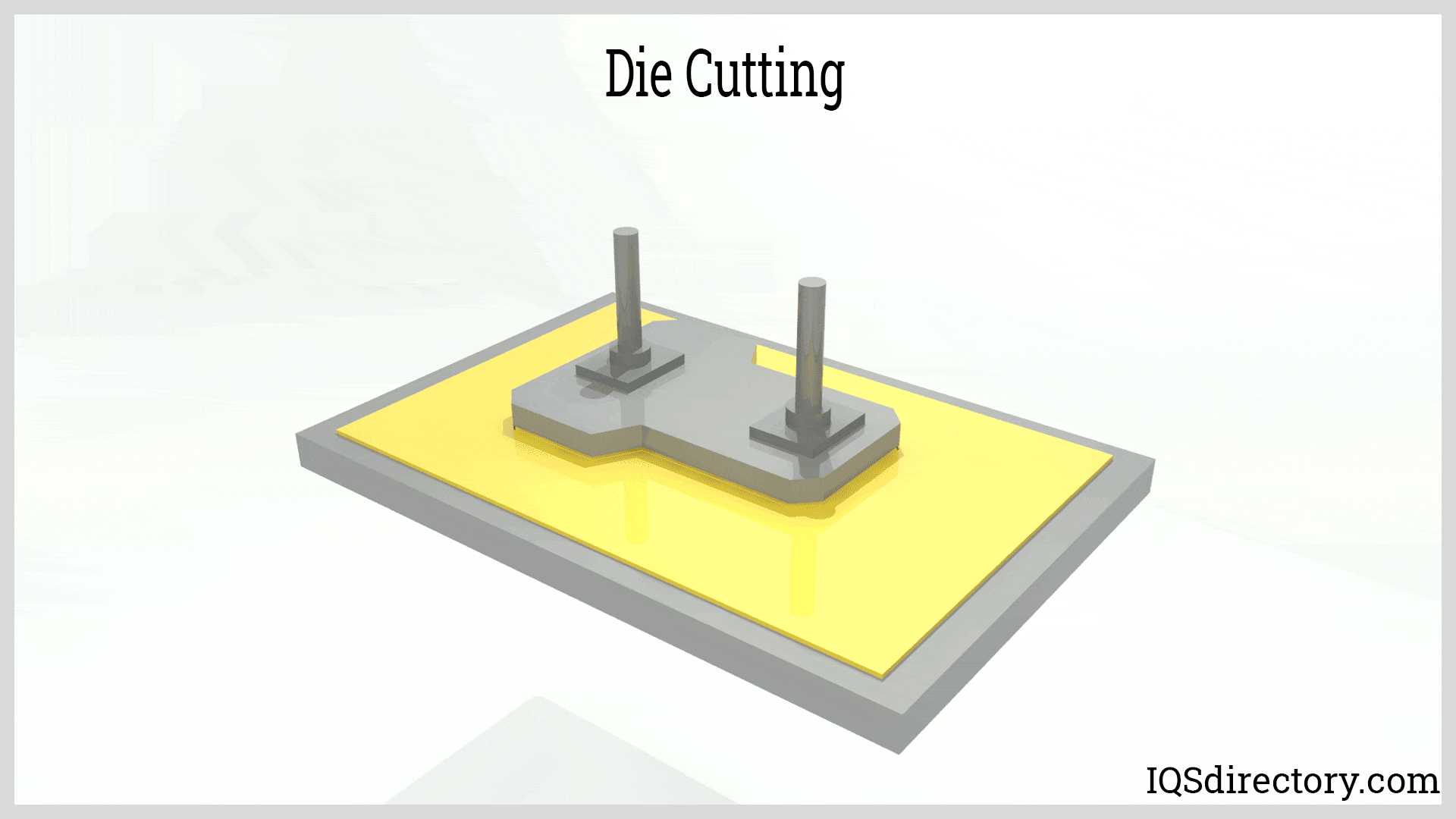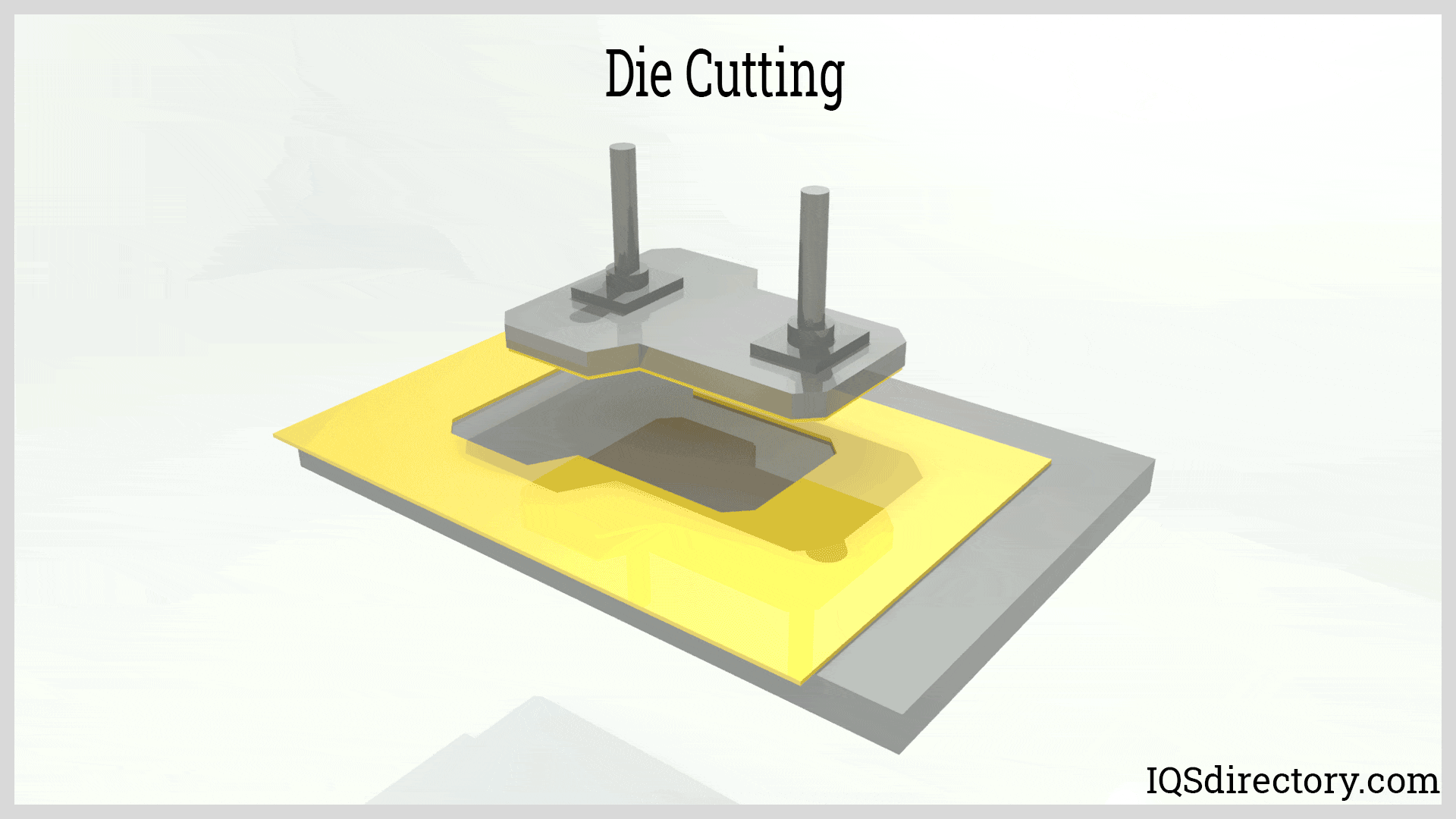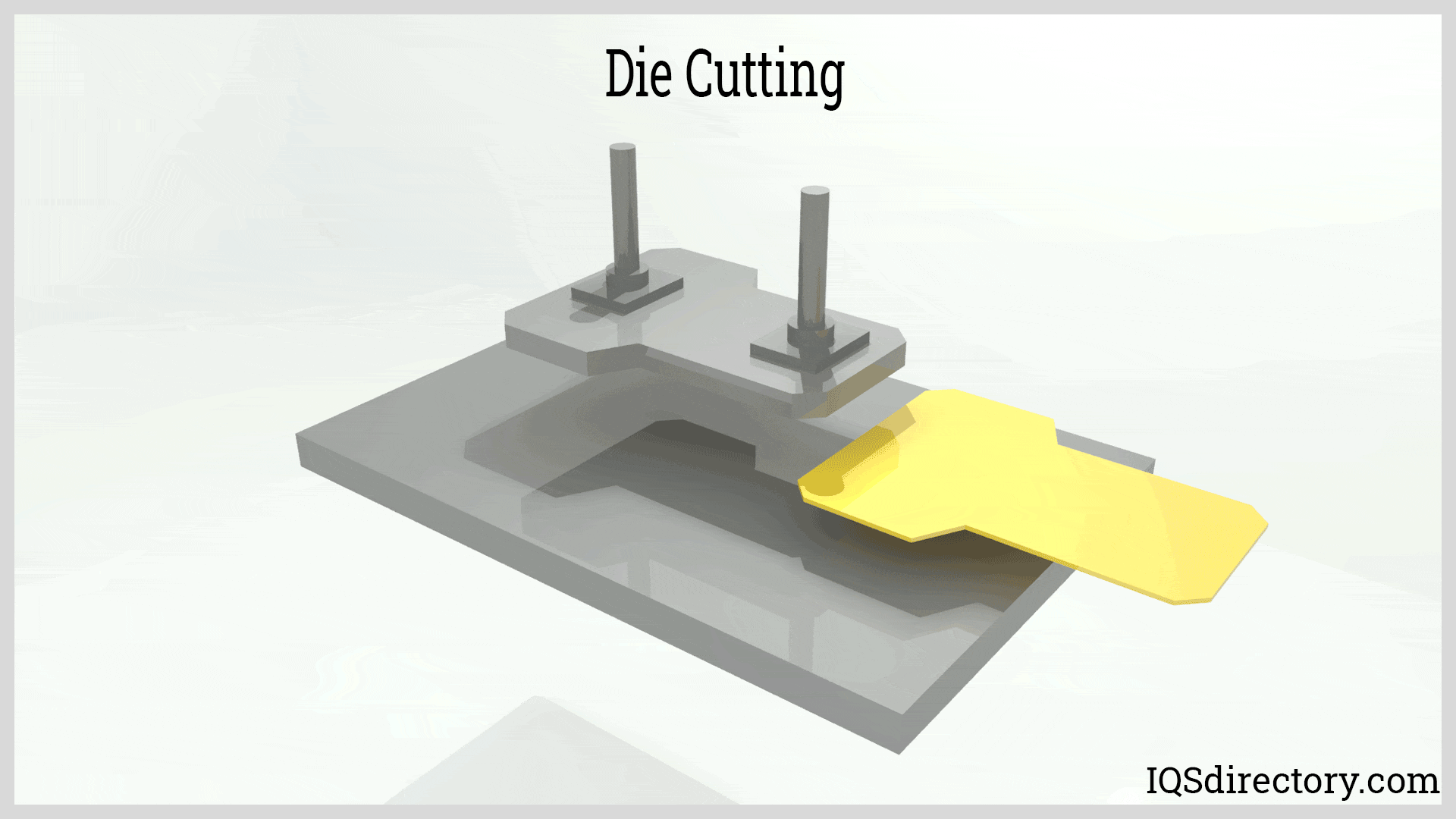
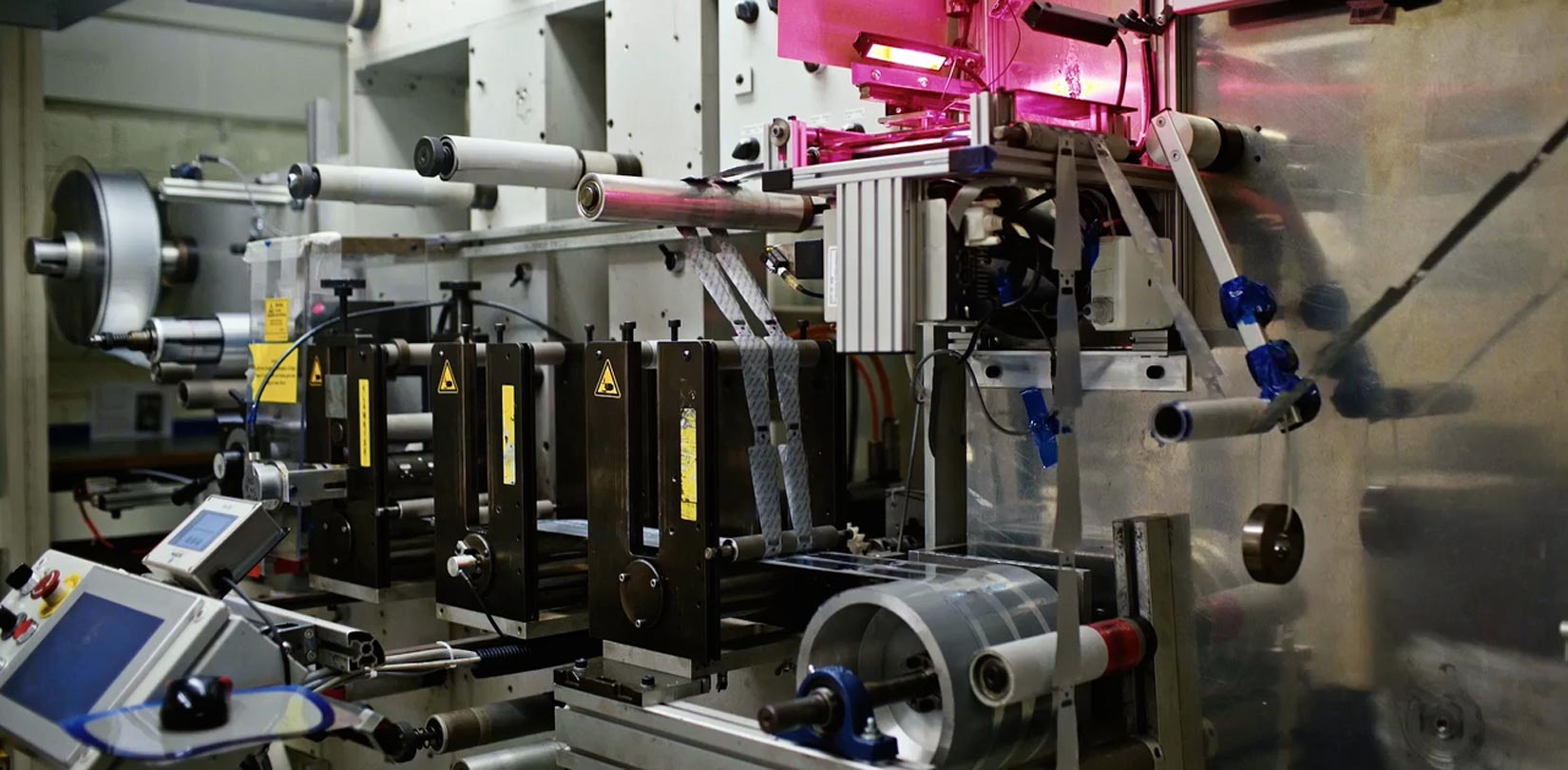
Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, conduct a thorough assessment of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from existing clients in similar industries. Ensure that the supplier has a proven track record in delivering reliable and quality die cutting solutions.
- Check for certifications: Verify any industry certifications (e.g., ISO) that indicate adherence to quality standards.
- Review customer testimonials: Seek feedback specifically related to product performance and customer service.
Step 4: Request Samples and Demonstrations
Ask suppliers to provide samples of their die cutting capabilities. This is essential for evaluating the quality of cuts and the precision of shapes produced. Additionally, request a demonstration of the equipment to assess ease of use and operational efficiency.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance Services
Investigate the level of after-sales support offered by the supplier. Reliable maintenance services can significantly impact the longevity and performance of your die cutting machines. Ensure that the supplier provides adequate training, spare parts availability, and responsive customer service.
- Inquire about warranty terms: Understand the warranty period and what it covers.
- Ask about training programs: Confirm if training is included for your staff on machine operation and maintenance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms. Discuss pricing structures, payment options, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the final agreement includes all necessary details to prevent misunderstandings later on.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan for Integration
After agreeing on terms, finalize your order and plan for the integration of the new technology into your existing operations. Consider logistics, installation, and any required adjustments to your workflow to ensure a seamless transition.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for die cutting technology, ensuring they select the best solutions to enhance their production capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for die cutting technology Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Die Cutting Technology?
Understanding the cost structure of die cutting technology is essential for B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials can vary significantly based on the type and quality. Common materials used in die cutting include paper, cardboard, plastic, and metal. The choice of material will influence both the unit price and the overall project cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled operators who run die cutting machines and oversee production processes. Depending on the region, labor costs can fluctuate, impacting the final pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help mitigate overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the creation and maintenance of dies and other cutting tools. Custom dies, which are often necessary for specific projects, can be expensive and should be factored into the total cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing quality control processes ensures that products meet specified standards. This can add to the labor and overhead costs but is crucial for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are significant, especially for international buyers. The choice of shipping method and distances can affect lead times and overall expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s business model.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Die Cutting Technology Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in die cutting technology, particularly for B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling and materials. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can greatly influence pricing. Premium materials may yield better quality products but come at a higher cost.
-
Quality and Certifications: Certifications for quality assurance can add to the cost but are often necessary for compliance with international standards. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and relationship history can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability and quality assurances.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affects logistics and pricing. Buyers should understand the responsibilities and costs associated with different terms to optimize total costs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Die Cutting Technology?
When sourcing die cutting technology, international B2B buyers should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms, especially for bulk orders. Leverage competitive quotes to drive down prices.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the total cost of ownership, including all associated costs such as maintenance, logistics, and potential wastage. This holistic view helps in making more cost-effective decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to labor and material costs.
-
Supplier Relationship Management: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Regular communication and feedback can foster collaboration and drive down costs over time.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to compare multiple suppliers. Understanding the market landscape can provide insights into competitive pricing and innovation in die cutting technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, pricing influencers, and effective buyer strategies is crucial for B2B buyers in the die cutting technology sector. By considering these factors, international buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions and achieve better value for their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing die cutting technology With Other Solutions
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses often face the challenge of choosing the right technology for their production processes. Die cutting technology is a popular choice for various industries, but it’s essential to consider alternative methods that may better suit specific needs. This section compares die cutting with two viable alternatives: laser cutting and rotary cutting. Each method has unique advantages and drawbacks, making it crucial for B2B buyers to analyze which solution aligns best with their operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Die Cutting Technology | Laser Cutting | Rotary Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed production of uniform shapes | Excellent precision with intricate designs | Efficient for continuous cutting of long materials |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment with low operational costs | Higher initial costs, but cost-effective for complex designs | Lower setup costs, but more suitable for high-volume runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific dies and setup | Requires skilled operators and software | Easier setup with less need for specialized training |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of dies and machines | Minimal maintenance, but requires calibration | Regular maintenance of rollers and blades |
| Best Use Case | Bulk production of specific shapes | Custom designs with intricate details | High-volume runs of flexible materials |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting technology offers remarkable precision and the ability to create intricate designs that die cutting may struggle with. It employs a focused laser beam to cut materials, allowing for detailed and complex shapes. However, it comes with a higher initial investment and operational costs, making it less suitable for bulk production of simpler shapes. Additionally, laser cutting may be slower than die cutting for high-volume runs, particularly in thicker materials.
How Does Rotary Cutting Compare to Die Cutting?
Rotary cutting is a method that utilizes a circular blade to cut materials continuously, making it highly efficient for long runs. This technique is particularly well-suited for flexible materials such as textiles and films. Its setup costs are generally lower than die cutting, especially for high-volume productions. However, rotary cutting may not achieve the same level of detail as laser cutting or die cutting, particularly for intricate designs, which could limit its applications in certain industries.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Cutting Technology?
When selecting between die cutting technology and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific production needs. Consider factors such as the complexity of designs, volume requirements, and budget constraints. Die cutting excels in producing high volumes of consistent shapes, making it ideal for standard applications. In contrast, laser cutting is best for intricate designs, while rotary cutting offers efficiency in continuous production. By assessing these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for die cutting technology
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Die Cutting Technology?
Understanding the essential technical properties of die cutting technology is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in this manufacturing process. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and type of material used for die cutting, which can include metals, plastics, paper, and textiles. The grade impacts durability, flexibility, and the finished product’s overall quality. For instance, high-grade steel is preferred for dies due to its ability to withstand repetitive cutting without losing sharpness. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the die can handle the intended production volume and complexity, thus minimizing costs related to die wear and replacement.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the die-cut item. It is critical in ensuring that the cut items meet specific design requirements. For example, tighter tolerances are necessary for intricate designs that require precise alignment in assembly processes. In B2B applications, maintaining the right tolerance levels can significantly affect product quality and performance, which is vital for customer satisfaction and compliance with industry standards.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
3. Die Life Cycle
The die life cycle is the expected operational lifespan of a cutting die before it needs replacement or re-sharpening. This property is influenced by the material used for the die, the cutting speed, and the thickness of the material being cut. A longer die life cycle reduces operational costs and downtime, making it a key consideration for manufacturers looking to optimize production efficiency.
4. Cutting Speed
Cutting speed is the rate at which the die cutting machine can process material. This property directly impacts production efficiency and capacity. High cutting speeds can lead to shorter lead times and increased output, which is particularly advantageous for businesses operating in competitive markets. Understanding the cutting speed of different machines helps B2B buyers choose equipment that aligns with their production goals.
5. Die Configuration
Die configuration pertains to the design and layout of the cutting die itself. This includes factors like shape, size, and the arrangement of cutting edges. The right die configuration is essential for achieving desired product shapes and optimizing material usage, thereby reducing waste. In B2B scenarios, selecting the appropriate die configuration can lead to significant cost savings and enhance product customization options.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Die Cutting Technology?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology helps B2B buyers navigate the die cutting market effectively. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In die cutting, this term is significant when sourcing machinery or components, as it indicates the reliability and quality of the products being offered.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to gauge inventory levels and cost-effectiveness. It helps in planning purchases and managing budgets, especially for businesses that may have fluctuating demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This term is crucial in the procurement process, as it allows buyers to compare offers from different suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers engaged in international trade, as they can affect overall costs and risk management.
5. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD refers to the use of computer software to create precise drawings and technical illustrations. In die cutting, CAD is essential for designing dies and ensuring accuracy in the cutting process. Knowledge of CAD capabilities can help B2B buyers evaluate the technical resources of potential suppliers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality in die cutting technology.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the die cutting technology Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Die Cutting Technology Sector?
The die cutting technology sector is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors, particularly among international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The increasing demand for customized products in industries such as packaging, textiles, and automotive is a primary market driver. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for solutions that enhance production efficiency while allowing for creative designs. Automation in die cutting processes, such as the rise of digital die cutters, is a notable trend, facilitating faster production cycles and reducing labor costs.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling predictive analytics for better inventory management and demand forecasting. Furthermore, the integration of eco-friendly materials and sustainable practices is gaining traction, as companies recognize the importance of environmental responsibility in their sourcing decisions. For B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics and trends is crucial for staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Die Cutting Technology Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the die cutting technology sector. B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their procurement choices, which has led to a demand for suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and waste reduction techniques. Suppliers that can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability often gain a competitive advantage in the market.

Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as B2B buyers seek to build supply chains that are transparent and responsible. Certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and ISO 14001 signal a supplier’s commitment to environmentally friendly practices. Utilizing materials with such certifications not only enhances a company’s brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer expectation for corporate responsibility. For buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, establishing partnerships with suppliers who uphold these values is essential for long-term success and market acceptance.
How Has the Die Cutting Technology Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of die cutting technology can be traced back over a century, transitioning from manual processes to highly automated systems. Initially, die cutting involved labor-intensive methods that required skilled artisans to create dies and execute cuts. However, with advancements in technology, the introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines revolutionized the industry, allowing for precision and efficiency that were previously unattainable.
In recent years, the adoption of digital die cutting has further transformed the landscape, enabling manufacturers to produce intricate designs with minimal setup time. This shift not only caters to the rising demand for customization but also supports rapid prototyping, which is invaluable in today’s fast-paced market. As the technology continues to advance, B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about innovations that can enhance their operational capabilities and product offerings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of die cutting technology
-
How do I choose the right die-cutting technology for my business needs?
Choosing the right die-cutting technology depends on several factors, including the types of materials you plan to cut, the complexity of your designs, and your production volume. For high-volume manufacturing, consider investing in industrial die-cutting machines that offer automation and precision. If you are looking for flexibility and customization, digital die-cutters may suit your needs. Assess your budget, evaluate the specific applications within your industry, and consult with suppliers to identify the best fit for your business. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting die-cutting suppliers?
When vetting die-cutting suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Verify their manufacturing capabilities, including the types of machines they use and their production capacity. It’s crucial to assess their quality assurance processes to ensure consistent product quality. Additionally, inquire about their lead times, delivery schedules, and after-sales support. Engaging in direct communication with potential suppliers can help you gauge their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your specific requirements. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for die-cutting services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for die-cutting services can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the designs. Typically, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Suppliers may establish MOQs to cover setup costs and ensure production efficiency. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your business needs and budget, especially if you are a smaller enterprise or testing new products. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing die-cutting technology internationally?
Payment terms for international die-cutting technology can vary, but common practices include upfront deposits (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established clients. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, and to review any additional fees related to currency exchange or international transactions. Ensure that all terms are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in my die-cutting products?
To ensure quality assurance in die-cutting products, establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier before production begins. Request samples or prototypes to evaluate the cutting precision, material quality, and overall design. Implement regular inspections during the manufacturing process, and consider third-party quality control services if necessary. Additionally, maintain open communication with your supplier throughout production to address any potential issues promptly and ensure adherence to your quality requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing die-cutting technology?
When importing die-cutting technology, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your country. Choose a reliable freight forwarder to manage logistics, including documentation and compliance with international shipping laws. Evaluate the total landed cost, which includes shipping, duties, and any additional fees, to ensure it fits within your budget. Planning for potential delays at customs and ensuring that all necessary paperwork is in order can help streamline the import process. -
Can I customize die-cutting designs to meet specific product requirements?
Yes, most suppliers offer customization options for die-cutting designs to meet specific product requirements. You can work with their design team to create custom dies based on your unique specifications. This includes adjusting dimensions, shapes, and even material choices. Providing detailed design files and collaborating closely with your supplier will facilitate a smoother customization process. Ensure that you discuss any additional costs or lead times associated with custom designs upfront. -
What materials are suitable for die-cutting in various industries?
Die-cutting can accommodate a wide array of materials, making it versatile across various industries. Common materials include paper, cardboard, plastics, and textiles for packaging and stationery. In the automotive and aerospace sectors, metals and composites are frequently used. When selecting materials, consider their thickness, flexibility, and compatibility with your die-cutting technology. Consulting with your supplier about material options can help you achieve the desired quality and performance for your specific applications.
Top 7 Die Cutting Technology Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Interwell – Die Cutting Solutions
Domain: interwell.cn
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Die cutting is a process used in various industries, including metalworking, printing, and packaging, to cut, shape, and shear sheets of stock material into unique designs using a specialized tool called a die. Key product details include:
– Types of dies: Nesting Dies, Corner Dies, Edgeable Dies.
– Types of die-cutting machines: Manual, Digital, Industrial.
– Die-cutting methods: Blanking, Dra…
2. JBC-Tech – Precision Die-Cutting Solutions
Domain: jbc-tech.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: JBC-West specializes in precision die-cutting and flexible materials converting, offering high-quality custom components from specialty engineered materials such as FDA-compliant silicone rubber, Teflon, and 3M thermal gap pads. Key services include:
– Precision Die-Cutting: High-speed presses for small parts and large format presses for parts up to 72″.
– Clean Room Manufacturing: ISO 8/Class 100…
3. Crafter’s Companion – Colour Creation Powder
Domain: crafterscompanion.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Crafter’s Companion – Colour Creation Powder – 8pc $24.95
4. Sizzix – Big Shot Machine
Domain: sizzix.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Die-Cutting Machines from Sizzix are designed for both beginners and experienced crafters, making cardmaking, papercrafting, and DIY projects easier. Key products include: 1. Sizzix Big Shot Machine Only – SKU: #667085, Price: $169.99 2. Sizzix Big Shot Machine Starter Kit – SKU: #667086, Price: $229.99 3. Sizzix Big Shot Switch Plus Machine Starter Kit – Sorbet – SKU: #665595, Price: $299.99 4. S…
5. xTool – Innovative Laser Solutions
Domain: xtool.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: xTool P3: 80W CO2 Laser Cutter with Intelligent Automation; xTool P2S: Improved Desktop CO2 Laser; xTool P+F Duo: Productive Business Duo; xTool F2 Ultra: 60W MOPA & 40W Diode Laser with AI; xTool F1 Ultra: 20W Fiber & 20W Diode Laser; xTool S1: Best choice for beginners; xTool S1 + 1064nm IR Laser Kit: Ultimate performance on wood-working; xTool M1 Ultra: World’s First 4-in-1 Craft Machine; xTool…
6. Tonic Studios – Tangerine Die Cutting Machine
Domain: tonic-studios.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Tonic Studios offers a manual die cutting machine called the Tangerine. A die is a piece of metal with a raised edge used to cut shapes out of card and other materials like thin craft foam, metal, and some fabrics. Die cutting machines apply pressure to the die to cut shapes from card. The die cutting process involves using a “die-cutting sandwich,” which consists of plates and the die. Recommende…
7. Interstate SP – Precision Die Cutting Services
Domain: interstatesp.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Precision die cutting services for custom gaskets and die cut parts, supporting tight tolerances, small and large part sizes, and various production volumes. Capabilities include rotary die cutting, digital knife cutting, slitting & laminating, cleanroom converting, and component prototyping. Utilizes high-quality tooling and state-of-the-art equipment in a Made in the USA facility. Offers solid m…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for die cutting technology
In conclusion, the die cutting technology landscape offers significant opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various die cutting methods, such as flatbed and rotary systems, enables businesses to choose the most suitable solutions for their production needs. Strategic sourcing of die cutting equipment and materials can lead to enhanced operational efficiency, cost savings, and improved product customization.
As industries increasingly demand precision and uniqueness, the value of die cutting technology cannot be overstated. By leveraging advanced die cutting processes, companies can streamline their production and create innovative products that stand out in competitive markets.
Illustrative image related to die cutting technology
For B2B buyers looking to enhance their offerings, now is the time to invest in die cutting solutions that align with market trends and consumer preferences. Embrace the potential of this technology to drive growth and elevate your product portfolio. Engage with trusted suppliers and partners who can provide the expertise and support necessary to navigate this evolving landscape. Your strategic sourcing decisions today will shape the success of your business tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.