How to Source Components Of A Water Filter Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for components of a water filter
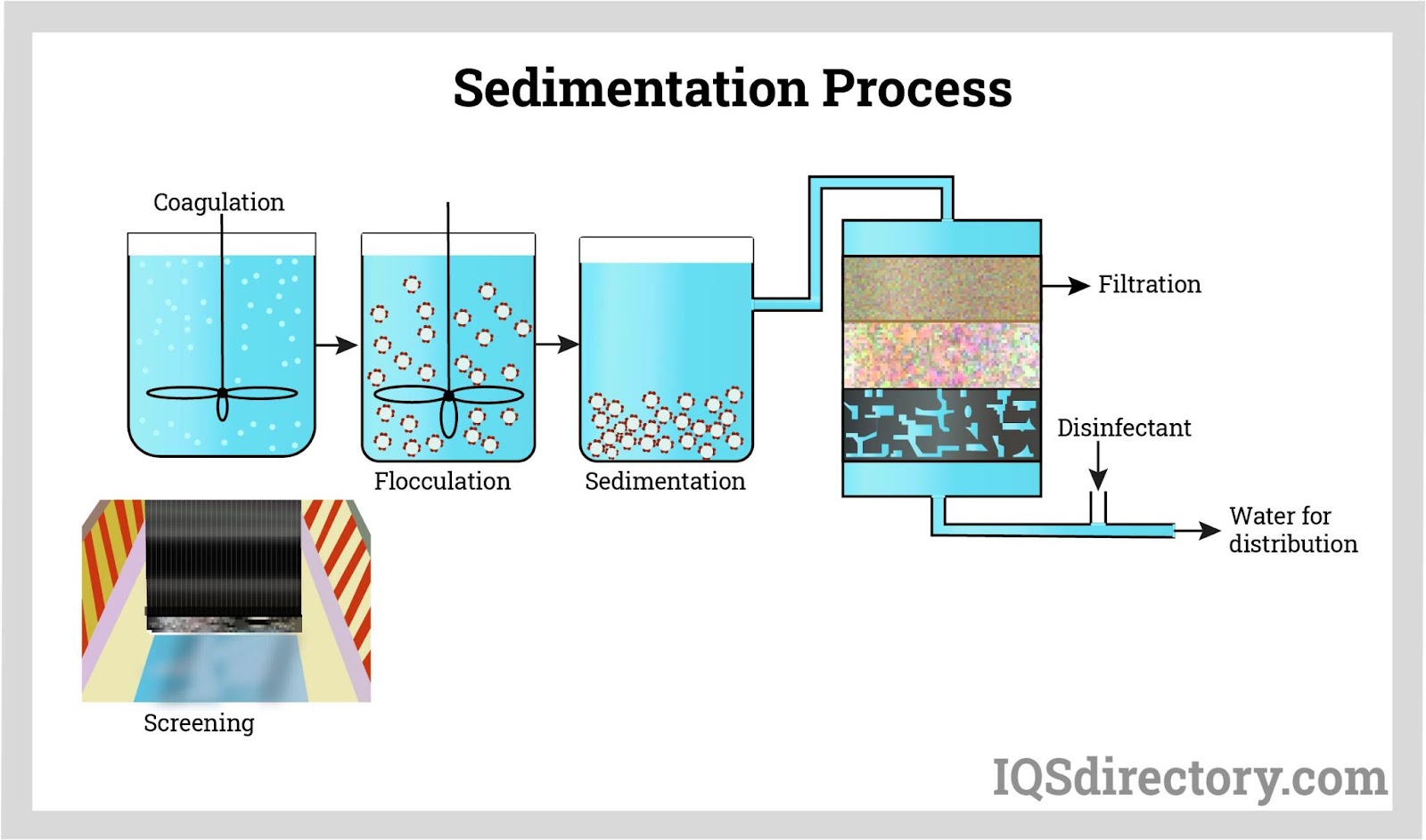
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing reliable components of a water filter poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With increasing concerns about water quality and safety, businesses must ensure that the filtration systems they procure not only meet regulatory standards but also provide effective solutions for local water issues. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential components of water filtration systems, including sediment filters, reverse osmosis membranes, and carbon filters, while exploring various applications tailored to diverse regional needs.
The guide is designed to empower international buyers by offering insights into supplier vetting processes, pricing structures, and the latest technological advancements in water filtration. By understanding the functionality and importance of each component, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints.
Furthermore, this resource highlights best practices for maintaining water filtration systems, ensuring longevity and optimal performance. Whether you are a distributor, manufacturer, or end-user, the knowledge contained within this guide will equip you with the necessary tools to navigate the complexities of the water filter component market, ultimately leading to improved product offerings and customer satisfaction.
Understanding components of a water filter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse Osmosis (RO) System | Multi-stage filtration, including sediment and carbon filters | Industrial water purification, food and beverage processing | Pros: Highly effective at removing contaminants. Cons: Higher initial cost and maintenance requirements. |
| Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection | Uses UV light to eliminate bacteria and viruses | Water treatment in healthcare and food industries | Pros: Chemical-free disinfection. Cons: Ineffective against particulate matter. |
| Activated Carbon Filter | Adsorbs chemicals and impurities from water | Residential and commercial water filtration | Pros: Improves taste and odor. Cons: Limited lifespan and requires regular replacement. |
| Membrane Filtration | Utilizes semi-permeable membranes for particle separation | Pharmaceutical manufacturing, water recycling | Pros: High efficiency in contaminant removal. Cons: Can be costly and complex to install. |
| Gravity Filters | Simple design, uses gravity to filter water through media | Rural and emergency water supply solutions | Pros: Low cost and easy to use. Cons: Slower filtration rate and less effective against dissolved solids. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems for B2B buyers?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are characterized by their multi-stage filtration process, which includes sediment filters, carbon filters, and a semi-permeable membrane. This system is suitable for industries requiring high purity water, such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and maintenance costs, as RO systems often require regular filter replacements and membrane maintenance. However, the effectiveness in removing a wide range of contaminants makes them a preferred choice for critical applications.
Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
How does Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection work and where is it applied?
Ultraviolet (UV) disinfection systems utilize UV light to effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms, making it a critical component in water treatment for sectors such as healthcare, food processing, and municipal water systems. The technology is chemical-free, ensuring that water remains free from harmful residues. B2B buyers should evaluate the system’s ability to integrate with existing filtration processes, as UV systems do not remove particulate matter or chemical contaminants. This makes them an excellent addition to multi-barrier water treatment systems.
What are the advantages and limitations of Activated Carbon Filters in B2B applications?
Activated carbon filters are designed to adsorb impurities and chemicals from water, thereby improving taste and odor. They are widely used in both residential and commercial settings, including restaurants and hotels. While these filters are cost-effective and easy to install, they have a limited lifespan and require regular replacement to maintain effectiveness. B2B buyers should consider the specific contaminants present in their water supply, as activated carbon filters may not be suitable for all types of pollutants.
What role does Membrane Filtration play in industrial applications?
Membrane filtration employs semi-permeable membranes to separate particles and contaminants from water, making it highly efficient for applications in pharmaceuticals, water recycling, and industrial processes. This technology can handle a variety of contaminants, including bacteria and dissolved solids. However, the complexity and cost of installation can be a barrier for some buyers. It is crucial for B2B buyers to assess the long-term operational costs and potential need for skilled personnel to manage these systems effectively.
Why are Gravity Filters considered for rural and emergency water supply solutions?
Gravity filters are simple systems that utilize gravity to filter water through various media, making them an affordable option for rural areas and emergency situations. They are easy to use and require minimal maintenance, which is beneficial in remote locations. However, their slower filtration rate and limited effectiveness against dissolved solids may not meet the needs of all B2B applications. Buyers should weigh the cost-effectiveness against the specific water quality requirements of their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of components of a water filter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of components of a water filter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Use of reverse osmosis membranes and carbon filters to purify water for production. | Ensures high-quality water, meeting health standards and improving product taste. | Compliance with food safety regulations, durability, and efficiency of components. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Implementation of UV disinfection systems and sediment filters in water treatment. | Guarantees sterile water for drug formulation, reducing contamination risks. | Certification of components, reliability under high purity requirements. |
| Agriculture | Sediment and carbon filters in irrigation systems to ensure clean water supply. | Enhances crop yield and reduces soil contamination from harmful substances. | Local sourcing of components for compatibility with existing systems, cost-effectiveness. |
| Manufacturing | Utilizing water filtration systems in cooling processes and equipment cleaning. | Reduces equipment wear and tear, improving operational efficiency and longevity. | Availability of high-pressure components, adaptability to different manufacturing environments. |
| Residential and Commercial | Installation of reverse osmosis systems in homes and offices for drinking water. | Provides safe drinking water, improving health and customer satisfaction. | Compact design for space constraints, ease of maintenance, and local service support. |
How Are Components of a Water Filter Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, components like reverse osmosis membranes and activated carbon filters are crucial for ensuring that water used in production is free from impurities. This is vital for meeting health regulations and enhancing the taste of products. For international buyers, sourcing components that comply with local food safety standards is essential, as is ensuring that the filtration systems are durable and efficient to minimize downtime in production.
What Role Do Water Filters Play in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
Pharmaceutical companies rely heavily on ultra-pure water for drug formulation. Components such as UV disinfection systems and sediment filters are employed to eliminate any potential contaminants. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the products. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing certified components that meet stringent quality standards to ensure that their water treatment processes are reliable and effective.
How Can Water Filter Components Benefit Agricultural Practices?
In agriculture, clean water is vital for irrigation to prevent soil contamination and promote healthy crop growth. Sediment and carbon filters are often integrated into irrigation systems to ensure that water is free from harmful pollutants. B2B buyers should consider local sourcing options for these components to ensure compatibility with existing systems and to keep costs manageable while maximizing crop yield.
Why Are Water Filtration Systems Important in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing processes, especially those involving cooling and cleaning, benefit from high-quality water filtration systems. Components of water filters help reduce equipment wear and tear, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and extending the lifespan of machinery. When sourcing these components, businesses should look for options that can withstand high-pressure environments and are adaptable to various manufacturing setups.
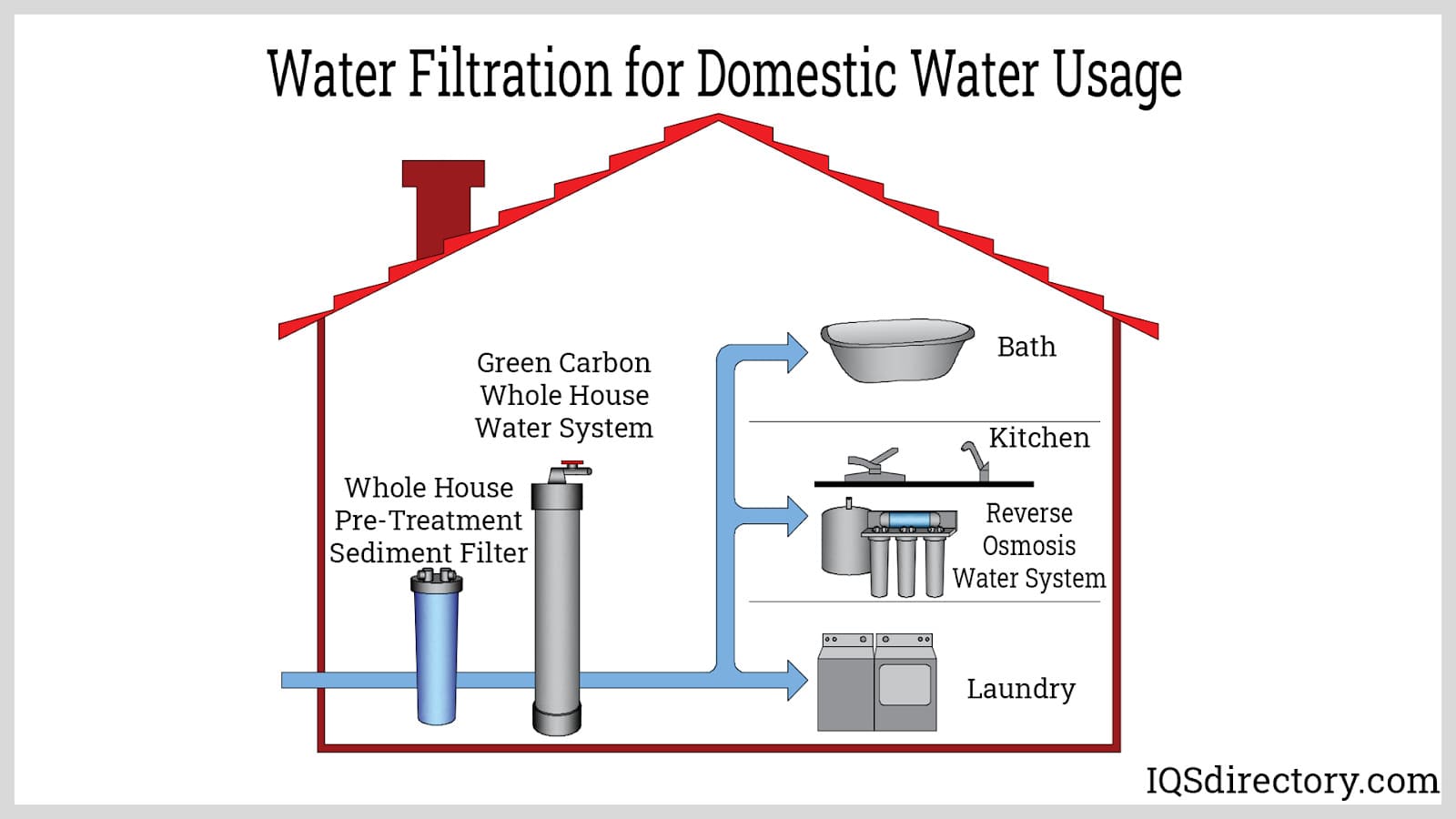
What Are the Advantages of Water Filtration for Residential and Commercial Applications?
In residential and commercial settings, reverse osmosis systems are increasingly popular for providing safe drinking water. These systems incorporate multiple filtration components to ensure high water quality, which is essential for health and customer satisfaction. International buyers should focus on sourcing compact and easy-to-maintain systems, as well as ensuring access to local service support for installation and repairs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘components of a water filter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Sediment Clogging in Water Filters
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa or South America where water quality can be poor, often face the challenge of sediment clogging the filters in water purification systems. This issue can lead to reduced flow rates and diminished water quality, causing interruptions in service and increased maintenance costs. Buyers might purchase high-quality reverse osmosis (RO) systems only to find that sediment pre-filters require more frequent replacement than anticipated, leading to dissatisfaction and unexpected expenses.
The Solution: To mitigate sediment clogging, it is essential to properly assess the water quality before installation. B2B buyers should conduct comprehensive water testing to determine the sediment load and select pre-filters that can handle the specific contaminants present. Investing in high-quality sediment filters rated for fine particles (down to 5 microns) can significantly enhance the lifespan of the system. Additionally, establishing a routine maintenance schedule that includes regular filter replacement can prevent clogging issues. Suppliers should also provide clear guidelines on the expected lifespan of different filter types based on water quality, enabling buyers to plan their inventory effectively.
Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
Scenario 2: Deterioration of RO Membrane Due to Chlorine Exposure
The Problem: In regions where municipal water is heavily chlorinated, B2B buyers may encounter the issue of rapid deterioration of reverse osmosis membranes. Chlorine is known to degrade the membrane material, leading to increased total dissolved solids (TDS) levels in the purified water. This not only affects the quality of the water but also necessitates costly premature membrane replacements, impacting operational budgets.
The Solution: To protect the RO membrane, buyers should prioritize the installation of high-quality carbon filters designed to remove chlorine effectively. It is advisable to source filters that offer a longer contact time for chlorine removal, such as those rated specifically for chloramine as well. Implementing a two-stage carbon filtration system can provide an additional layer of protection against chlorine exposure. Furthermore, regular monitoring of water quality using TDS meters will allow buyers to assess the performance of their filtration systems and make timely adjustments or replacements when necessary. Suppliers should educate buyers on the importance of these components and provide recommendations on optimal filter configurations based on local water conditions.
Scenario 3: Inefficiencies Due to Incorrect Pressure Regulation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating water pressure, face inefficiencies in their water filtration systems due to improper pressure regulation. High water pressure can damage filter housings and membranes, while low pressure can reduce water output significantly. This inconsistency can lead to operational challenges, such as inadequate supply for drinking water or increased waste water production, ultimately affecting customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To address pressure-related issues, B2B buyers should invest in a pressure regulator as part of their water filter system. This component ensures that the incoming water pressure is kept within the optimal range for the entire system, preventing damage to sensitive components. It is crucial to select regulators that are adjustable to accommodate various incoming pressures, especially in regions where supply pressure can vary. Additionally, buyers should consider incorporating a pressure booster pump to enhance performance in low-pressure situations, ensuring consistent water delivery. Regular maintenance checks should include monitoring pressure readings to detect any anomalies early, allowing for proactive adjustments and reducing the risk of system failures. Suppliers should assist buyers by providing detailed installation guides and recommendations tailored to specific regional conditions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for components of a water filter
What Are the Key Materials Used in Water Filter Components?
When selecting materials for components of water filters, various factors such as performance, durability, and compliance with international standards must be considered. Below is an analysis of three common materials used in water filter components, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Polypropylene Perform in Water Filter Components?
Key Properties:
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance and ability to withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F). It has a low density, making it lightweight and easy to handle.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of polypropylene is notable, as it resists cracking and is not prone to corrosion. However, its lower temperature tolerance compared to other materials may limit its use in high-heat applications. Additionally, while it is generally cost-effective, the manufacturing complexity can increase with specialized designs.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is commonly used in sediment filters and housings due to its compatibility with various media and its ability to filter out particulate matter effectively.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the polypropylene used complies with local health and safety standards, such as ASTM or ISO certifications, to guarantee product safety and efficacy.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Water Filter Systems?
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is renowned for its high corrosion resistance, strength, and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures, often exceeding 200°C (392°F).
Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and longevity, making it ideal for components like storage tanks and fittings. However, it comes with a higher cost compared to plastics, and its manufacturing process can be more complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is suitable for high-pressure applications and is often used in water storage tanks and piping systems, where it can maintain water quality without leaching harmful substances.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, compliance with standards such as EN or ASTM is crucial. Additionally, the availability of stainless steel grades that meet local regulations should be verified.
Why Is Activated Carbon Essential in Water Filtration?
Key Properties:
Activated carbon is characterized by its high surface area and porosity, which enhance its adsorption capabilities. It is effective at removing chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other contaminants.

Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of activated carbon is its effectiveness in improving water taste and odor. However, it has a limited lifespan and requires regular replacement, which can increase long-term operational costs.
Impact on Application:
Activated carbon is widely used in pre-filters and post-filters to enhance water quality by removing contaminants that can affect taste and safety.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the sourcing of activated carbon to ensure it meets local environmental regulations and standards. In regions like Vietnam and Nigeria, it is essential to confirm that the carbon used is sustainably sourced and free from contaminants.
Summary of Material Selection for Water Filter Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for components of a water filter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | Sediment filters and housings | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited temperature tolerance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Storage tanks and piping systems | High corrosion resistance and strength | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Activated Carbon | Pre-filters and post-filters | Effective in removing taste and odor | Limited lifespan requiring regular replacement | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials used in water filter components, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional compliance standards.
Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for components of a water filter
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Water Filter Components?
The manufacturing process of water filter components is intricate and involves several critical stages, each playing a vital role in ensuring the quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable components.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first stage in manufacturing water filter components is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality raw materials such as activated carbon, polypropylene, or specialized membrane materials like polyamide. Manufacturers often conduct thorough supplier assessments to ensure that materials meet specific performance standards.
Once selected, raw materials undergo processing, which can include grinding, heating, or chemical treatment to enhance their filtering capabilities. For instance, activated carbon may be treated with steam or chemicals to increase its porosity and surface area, thereby improving its adsorption properties.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Manufacturing Water Filter Components?
Forming is the next stage where raw materials are shaped into usable components. Various techniques are employed depending on the type of component being produced.
-
Molding: Commonly used for plastic components, this process involves heating plastic granules until they melt and then injecting them into molds. This technique is crucial for creating parts such as filter housings and connectors.
-
Extrusion: Used for continuous shapes, such as membranes and filter media, extrusion involves forcing materials through a die to create long, uniform profiles. This method is efficient and allows for precise control over the dimensions of the components.
-
Sintering: In the case of ceramic or metallic components, sintering is used to fuse particles together under heat without melting them. This process is essential for creating durable filters that can withstand high pressures.
How Are Water Filter Components Assembled and Finished?
The assembly stage involves combining individual components to create a complete water filter unit. This process often requires skilled labor and automated systems to ensure precision and efficiency. During assembly, manufacturers pay close attention to the alignment and sealing of components to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance.
Finishing processes may include surface treatments such as coating or polishing to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. For instance, components may be coated with antimicrobial substances to prevent bacterial growth, which is particularly important in regions where water quality is compromised.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Water Filter Component Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that components meet international standards and customer expectations. Manufacturers typically follow a multi-tiered QC approach that includes several checkpoints.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Water Filter Components?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are crucial for ensuring consistent quality across manufacturing processes. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a manufacturer’s commitment to quality management and continuous improvement. In addition to ISO, industry-specific certifications like CE (for European markets) and API (for petroleum and natural gas applications) may also be relevant.
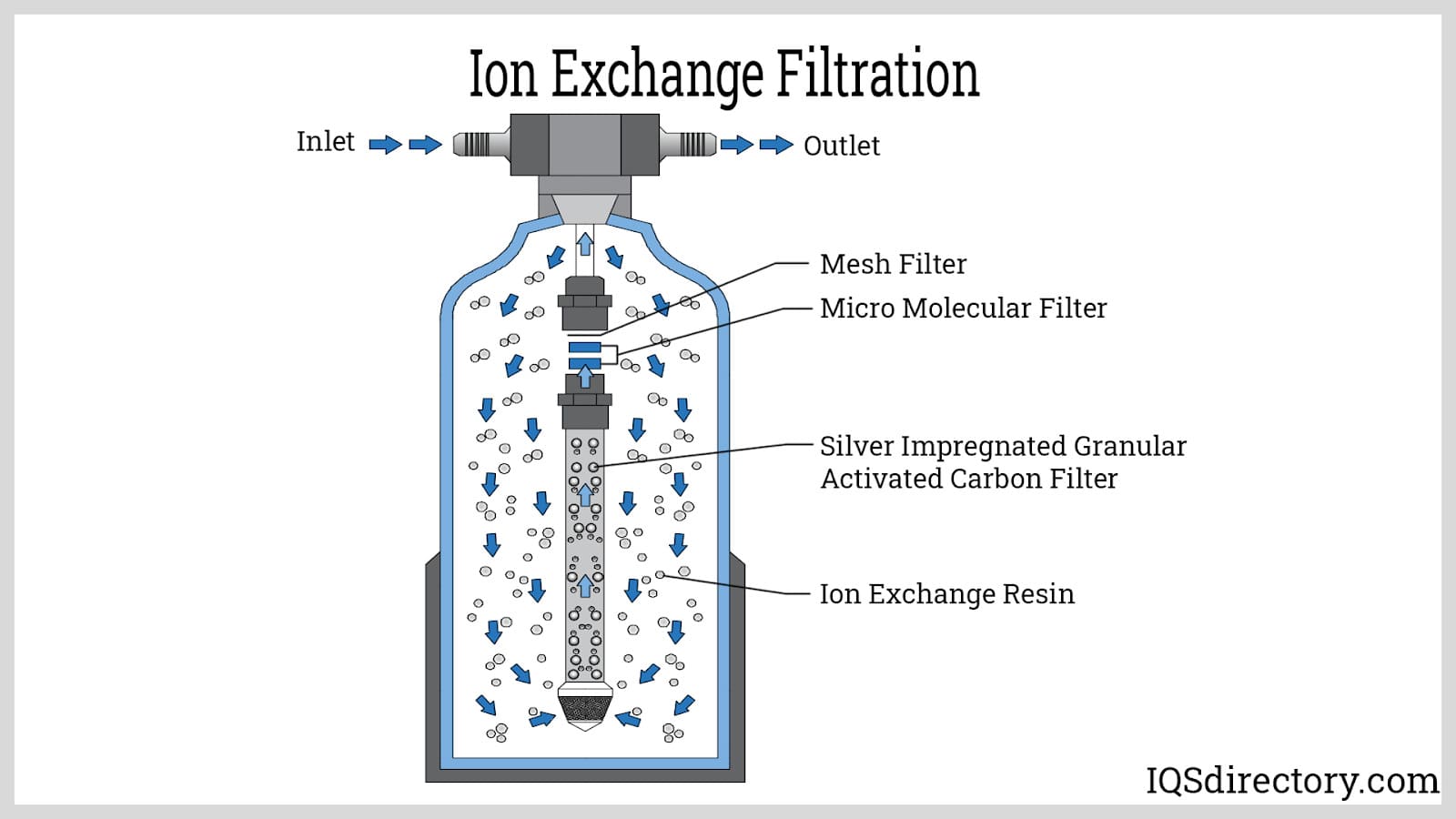
Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each component meets specified standards:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint occurs when raw materials arrive at the facility. Materials are inspected for quality, and any non-conforming items are rejected.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to monitor processes and identify any deviations from quality standards. This includes testing the dimensions and performance of components at various stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the components are assembled, a final inspection is performed. This may involve functional testing, pressure testing, and performance evaluations to ensure that the finished product operates as intended.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the performance of water filter components. Common testing methods include:
-
Flow Rate Testing: Measures the volume of water that passes through the filter over a specified period, ensuring that it meets production specifications.
-
Contaminant Removal Efficiency Testing: Assesses how effectively a filter removes specific contaminants, such as chlorine or heavy metals, from water.
-
Durability and Pressure Testing: Ensures that components can withstand operational pressures without failure, which is critical for maintaining safety and performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. Here are several actionable approaches:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, QC checkpoints, and compliance with international standards firsthand.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed QC reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC tests. These documents provide insight into the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of certain nuances in quality control. Differences in regulatory standards, cultural expectations, and logistical challenges can impact the sourcing process.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international standards relevant to their markets. This may involve understanding specific regulations regarding water quality and safety in their target regions.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding cultural differences can improve communication and collaboration with suppliers, enhancing the quality of partnerships and the final product.
-
Logistical Considerations: Buyers must consider the logistics of transporting components across borders, including potential delays that may affect product quality. It’s advisable to establish clear timelines and quality benchmarks in contracts to mitigate risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for water filter components, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they source high-quality products that meet their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘components of a water filter’
In the competitive landscape of water filtration, sourcing the right components is crucial for ensuring efficiency and reliability in your products. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure the essential components of a water filter, enabling informed decision-making and fostering successful supplier relationships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the specific requirements of your water filtration system is the foundation of successful sourcing. Identify the type of contaminants you aim to remove, the expected flow rate, and the desired water quality standards. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure compatibility with your existing systems.
Step 2: Research Essential Components
Familiarize yourself with the key components required in a water filter, such as:
– Sediment Filters: These remove larger particles like sand and silt to protect downstream components.
– Carbon Filters: Important for removing chlorine and other chemicals that can damage membranes.
– Reverse Osmosis Membranes: The heart of the filtration system, responsible for rejecting dissolved solids.
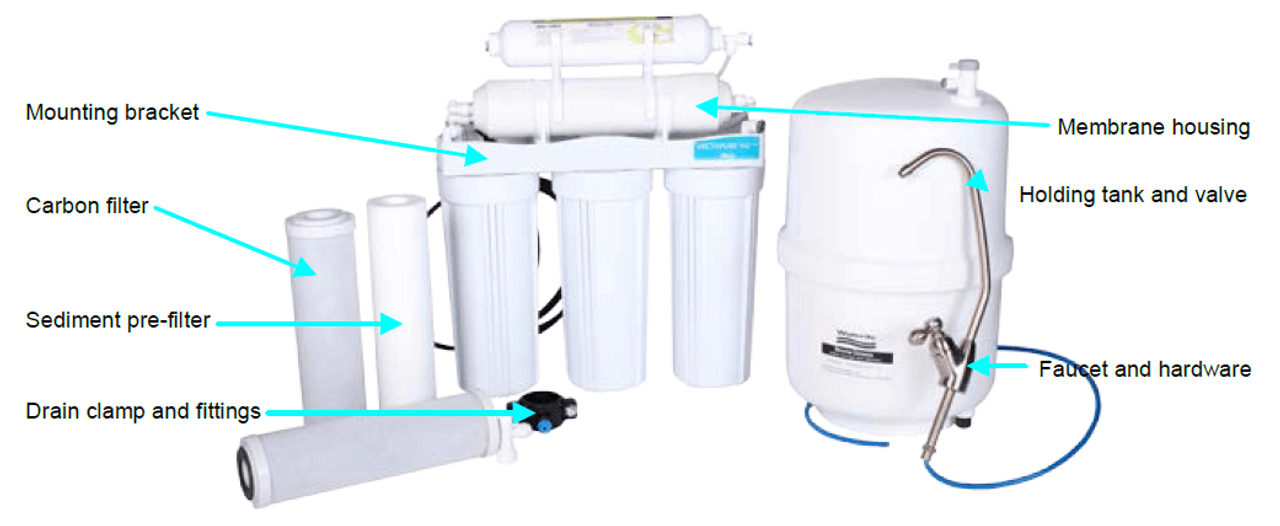

Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
Understanding these components will enable you to make informed choices about quality and performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing your procurement, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, certifications, and product specifications. Look for suppliers with proven track records in the industry, and consider requesting references from other B2B buyers in your region or sector to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the components you are sourcing comply with relevant local and international standards for water quality and safety. This may include certifications such as NSF/ANSI for drinking water treatment units. Compliance not only assures product quality but also enhances marketability in various regions.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather and compare pricing from multiple suppliers, keeping in mind that the lowest price does not always equate to the best value. Consider payment terms, shipping costs, and warranties offered. A well-structured payment agreement can enhance cash flow and provide added security in your procurement process.
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Before making bulk purchases, request samples of critical components for testing. This step allows you to assess the quality and performance of the components in real-world conditions. Testing can reveal potential issues that may not be apparent from specifications alone.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is vital for successful supplier relationships. Establish clear lines of communication regarding order status, delivery schedules, and technical support. A proactive communication plan helps address any issues promptly, ensuring that your supply chain remains uninterrupted.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing water filter components more effectively, leading to better product performance and customer satisfaction.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for components of a water filter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Water Filter Components?
When sourcing components for water filters, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly impacts cost. For example, high-grade plastics for housings or specialized membranes made from polyamide can be more expensive than standard materials. Sourcing materials locally can reduce costs, but may compromise quality.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as Vietnam or Nigeria, manufacturing can be cheaper, but this may come at the expense of quality or adherence to international standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes factory costs such as utilities, rent, and salaries of administrative staff. Efficient manufacturing processes can help in reducing overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be high, especially for custom components. However, once amortized over larger production runs, the cost per unit can decrease significantly.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure product reliability, especially for critical components like RO membranes. While this may increase upfront costs, it can reduce long-term expenses associated with warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including customs duties and insurance, can vary widely based on the destination. Understanding local regulations can help mitigate unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up prices to cover their costs and profit. Buyers should be aware of standard margins in the industry to ensure they are getting competitive pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Component Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of water filter components:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to lower per-unit costs. Establishing minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom components or specific certifications (like NSF or ISO) can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the added expense.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can lead to higher prices. However, investing in quality often pays off in terms of durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, influencing total costs.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers?
To optimize costs and ensure favorable terms, consider the following negotiation strategies:
-
Establish Relationships: Building a rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Strong relationships often facilitate negotiations on both sides.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When negotiating, emphasize the long-term savings associated with higher quality components. A higher upfront cost may result in lower maintenance and replacement costs.
-
Consider Local vs. International Sourcing: While international suppliers might offer lower prices, consider the potential for higher shipping and customs costs. Local suppliers may provide better service and quicker delivery.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding market conditions, material availability, and pricing trends can give buyers leverage in negotiations.
-
Be Clear on Specifications: Ensure that all specifications are clearly defined to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to increased costs.
What Should International Buyers Consider in Pricing Nuances?
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, pricing nuances can significantly affect sourcing decisions:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be mindful of exchange rates, as they can affect the final cost. Consider locking in prices or negotiating contracts in stable currencies.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understand the import duties applicable in your country, as these can add to the total cost. Researching trade agreements can also provide benefits.
-
Cultural Differences: Negotiation styles and business practices vary by region. Being aware of cultural nuances can facilitate smoother negotiations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that all components meet local regulations. Non-compliance can lead to fines or increased costs for modifications.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
All prices referenced in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier pricing strategies, and currency fluctuations. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing when sourcing components for water filters.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing components of a water filter With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Water Filtration Solutions
In the quest for clean and safe drinking water, various technologies and methods have emerged as alternatives to traditional water filter components, particularly reverse osmosis (RO) systems. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for international B2B buyers who aim to select the most suitable water treatment solution for their specific environments and applications. This section compares the components of a water filter against two viable alternatives: ultraviolet (UV) disinfection systems and activated carbon filtration.
Comparison Table of Water Filtration Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Components Of A Water Filter | UV Disinfection System | Activated Carbon Filtration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficacy in removing TDS, contaminants, and pathogens | Effective against bacteria and viruses; does not remove TDS | Good for removing chlorine, taste, and odor; limited effectiveness against pathogens |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to multiple components | Moderate; typically lower than RO systems but higher than carbon filters | Generally lower initial cost; maintenance costs can vary |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation; space-intensive | Relatively easy to install; requires electricity | Simple installation; often a DIY option |
| Maintenance | Regular filter changes; system checks needed | Low maintenance; UV lamp replacement every 12 months | Regular replacement of carbon filters; less frequent than RO |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for areas with high TDS and diverse contaminants | Best for municipal water sources with biological concerns | Suitable for improving taste and odor in treated water |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of UV Disinfection Systems?
UV disinfection systems utilize ultraviolet light to kill or inactivate microorganisms, making them an effective solution for biological contaminants. The primary advantage of UV systems is their ability to treat water without adding chemicals, preserving the water’s taste and quality. However, they do not remove dissolved solids or improve taste, which can be a drawback in regions with high TDS levels. Additionally, these systems require a continuous power supply and can be less effective if water is turbid or contains high levels of particulates, necessitating pre-filtration.
How Does Activated Carbon Filtration Work and What Are Its Benefits?
Activated carbon filtration is a popular method for improving water quality by removing chlorine, sediment, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Its advantages include lower cost and ease of installation, making it a preferred choice for residential applications. However, activated carbon filters do not effectively remove minerals, salts, or pathogens, which limits their use in areas with severe water quality issues. Regular maintenance is required to replace carbon filters, which can lead to increased operational costs over time.

Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Water Filtration Solution
For international B2B buyers, selecting the right water filtration solution involves evaluating specific needs, including water quality, available space, budget, and maintenance capabilities. While components of a water filter, such as reverse osmosis systems, offer comprehensive filtration, alternatives like UV disinfection systems and activated carbon filtration can provide effective solutions for specific issues. Conducting a thorough analysis of these options will help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and the unique challenges presented by their local water sources.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for components of a water filter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Water Filter Components?
When sourcing components for water filtration systems, understanding the technical specifications is vital for ensuring product quality and performance. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type and quality of materials used in manufacturing water filter components. Common materials include polypropylene for sediment filters, activated carbon for filtration, and food-grade plastics for housing. Selecting high-grade materials ensures durability, resistance to corrosion, and compliance with health standards, which is particularly important for international buyers who must adhere to stringent regulations in their markets.
2. Filtration Efficiency
Filtration efficiency is a measure of a component’s ability to remove contaminants from water. This is often expressed in microns for particulate filters (e.g., a 5-micron filter removes larger particles, while a 0.5-micron filter targets smaller contaminants). For B2B buyers, understanding filtration efficiency is crucial for meeting specific water quality standards and customer requirements, particularly in regions facing severe water quality issues.
3. Flow Rate
Flow rate indicates the volume of water that can be filtered in a specific time frame, usually measured in gallons per minute (GPM). This property impacts the system’s overall performance and is critical for high-demand applications. Buyers need to assess flow rates to ensure the system meets their operational needs without causing bottlenecks.

Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
4. Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum operating pressure that components can withstand, typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). Components like pressure regulators and membranes need to be able to handle varying water pressures without failure. Understanding pressure ratings helps buyers avoid system malfunctions, especially in regions with fluctuating water supply conditions.
5. Replacement Cycle
The replacement cycle refers to how often components, such as filters and membranes, need to be replaced to maintain optimal performance. This can vary significantly based on the component type and water quality. B2B buyers should factor in replacement cycles when evaluating total cost of ownership and maintenance needs for their water filtration systems.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Water Filtration Industry?
Navigating the water filtration industry requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are some key terms that are essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the water filtration industry, buyers often collaborate with OEMs to customize filtration components according to their specifications. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers ensure they receive quality products tailored to their needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. It’s a critical factor for B2B buyers as it impacts inventory management and initial investment costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their market demand and financial capabilities, especially in emerging markets where demand may fluctuate.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is essential for buyers looking to procure components for water filtration systems, as it helps them compare prices and terms across multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. Familiarity with terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is crucial for buyers to understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
5. TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)
TDS refers to the total concentration of dissolved substances in water, including salts, minerals, and organic matter. Understanding TDS levels is essential for selecting appropriate filtration technologies and ensures that buyers meet local water quality standards.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate better deals, and ensure the successful integration of water filtration components into their systems.
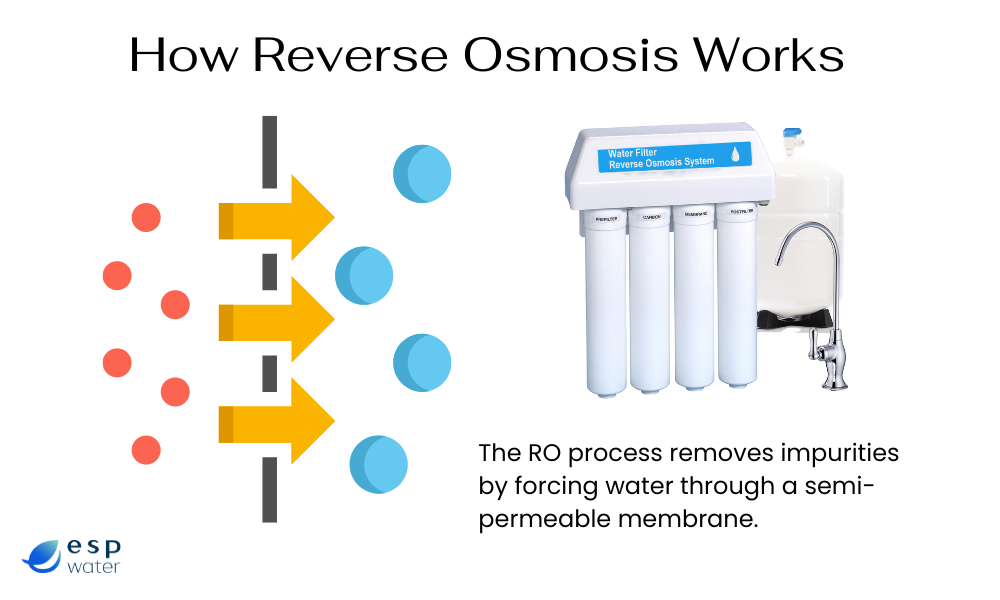
Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the components of a water filter Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Components of Water Filters?
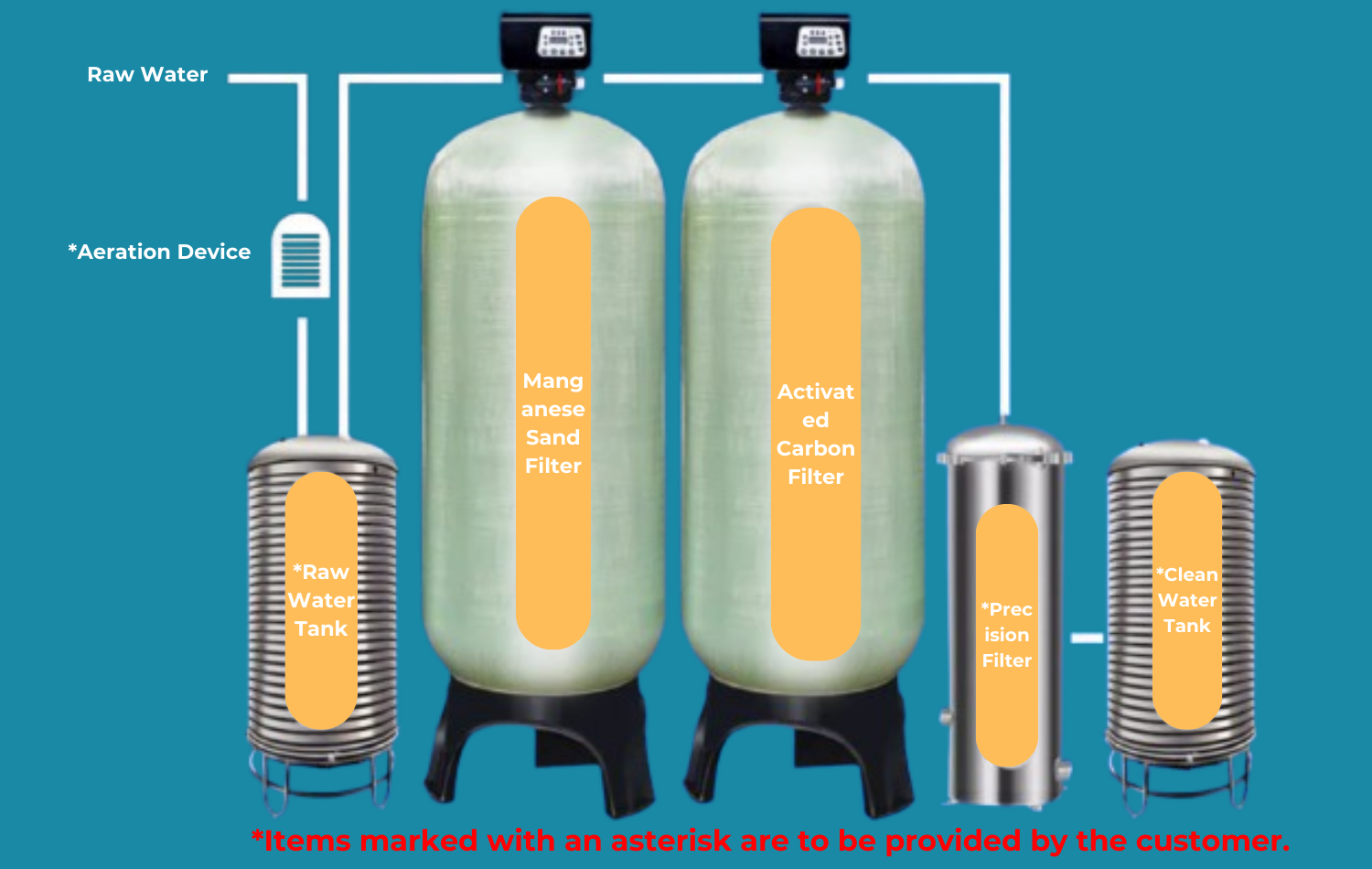
The components of water filtration systems, particularly reverse osmosis (RO) systems, are increasingly shaped by global drivers such as the rising demand for clean drinking water, stringent water quality regulations, and advancements in filtration technology. Regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and parts of Europe are experiencing rapid urbanization and industrialization, which intensifies the need for efficient water purification solutions. For B2B buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends include the integration of smart technology into filtration systems. IoT-enabled devices that monitor water quality and filter performance in real-time are becoming more prevalent. Additionally, there is a growing focus on modular systems that allow for easy upgrades and maintenance, appealing to buyers looking for cost-effective long-term solutions. These innovations not only enhance efficiency but also align with the increasing consumer demand for transparency and control over water quality.
International buyers should also be aware of the competitive landscape, which is seeing increased participation from local manufacturers in emerging markets. This shift provides opportunities for partnerships and sourcing agreements that can lead to reduced costs and improved supply chain resilience. As buyers navigate these market dynamics, they must prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality, innovation, and customer service.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Water Filter Components Sector?
The environmental impact of water filtration systems cannot be overlooked, especially as global awareness of sustainability increases. Components such as membranes, filters, and housing materials often contribute to waste and pollution if not sourced responsibly. B2B buyers are increasingly recognizing the importance of ethical supply chains that minimize environmental footprints. This includes evaluating suppliers based on their production processes, waste management practices, and adherence to environmental regulations.
Furthermore, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise. Components made from recyclable materials or those that utilize environmentally friendly manufacturing processes are becoming more appealing to buyers looking to bolster their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. Certifications such as NSF/ANSI for drinking water treatment and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are crucial markers that buyers should look for when sourcing components.
Investing in sustainable components not only aligns with ethical considerations but can also enhance brand reputation and consumer trust. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, B2B buyers who prioritize sustainability in their sourcing strategies will likely gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
How Has the Components of Water Filters Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of water filtration technology has been marked by significant milestones that have transformed the industry. Initially, water purification methods were rudimentary, primarily relying on sedimentation and basic filtration techniques. However, the introduction of reverse osmosis technology in the 1970s revolutionized the sector by providing a more efficient method for removing contaminants and impurities.
Over the years, advancements in materials science have led to the development of high-performance membranes and filters that enhance the efficacy and lifespan of water filtration systems. Modern systems now incorporate multi-stage filtration processes, combining sediment filters, carbon filters, and advanced RO membranes to ensure superior water quality.
Today, the sector continues to innovate with smart technologies and sustainable practices, catering to the evolving needs of global markets. As B2B buyers engage with suppliers, understanding this historical context can help them appreciate the technological advancements that have paved the way for the efficient, reliable water filtration systems available today.

Illustrative image related to components of a water filter
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of components of a water filter
-
How do I solve issues with low water pressure in my water filtration system?
Low water pressure can be caused by several factors, including clogged filters, a malfunctioning pressure regulator, or inadequate incoming water pressure. Begin by checking the sediment and carbon filters for blockages; replace them if necessary. If the pressure regulator is present, ensure it is functioning correctly. Additionally, consider installing a pressure booster pump to enhance water flow, especially in regions with generally low supply pressure. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of components are essential for optimal performance. -
What is the best reverse osmosis membrane for high TDS water sources?
When dealing with high total dissolved solids (TDS), a thin-film composite (TFC) reverse osmosis membrane is recommended. TFC membranes are designed to remove over 96% of TDS, making them effective for tough water conditions. Ensure that the membrane is rated for the specific TDS levels of your water source. Additionally, consider membranes with higher rejection rates or those specifically designed for challenging contaminants, which can be sourced from reputable suppliers who provide detailed product specifications. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for water filter components?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, experience, and certifications, such as ISO or ANSI standards. Request product samples to assess quality and performance. Evaluate their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your demand. Additionally, inquire about their customer service policies and after-sales support. A thorough background check, including customer reviews and case studies, can provide insights into their reliability and trustworthiness in the international market. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for water filter components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary widely based on the supplier and the specific component. For standard components like sediment filters or carbon filters, MOQs may range from 100 to 1,000 units. Custom components or specialized products might have higher MOQs due to production setup costs. Always clarify MOQs during negotiations and consider potential bulk discounts to optimize your purchasing strategy, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers. -
How can I ensure the quality of water filter components sourced internationally?
To ensure quality, request certificates of analysis (CoA) and compliance from your suppliers, which demonstrate that products meet specific industry standards. Conduct periodic quality audits and consider third-party inspections before shipment. Establish clear quality assurance (QA) criteria and communicate these expectations to your suppliers. Building long-term relationships with trusted suppliers can also enhance accountability and quality consistency over time. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted in international B2B transactions for water filter components?
Common payment terms include letters of credit (LC), telegraphic transfers (T/T), and PayPal for smaller transactions. Many suppliers may request a deposit (usually 30% to 50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate favorable terms that protect both parties and facilitate smooth transactions. Always confirm payment methods that align with your financial capabilities and assess any associated transaction fees. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing water filter components?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods (air or sea freight), customs regulations, and import duties specific to your country. Choose reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling water filter components to ensure timely delivery. Understand the documentation required for customs clearance, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Additionally, factor in lead times for shipping and customs processing when planning your inventory levels. -
Can I customize water filter components to meet specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for water filter components, such as size, material, and filtration specifications. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and limitations. Customization may involve additional costs and longer lead times, so it’s essential to plan accordingly. Ensure that any customizations comply with local regulations and standards to maintain product efficacy and safety.
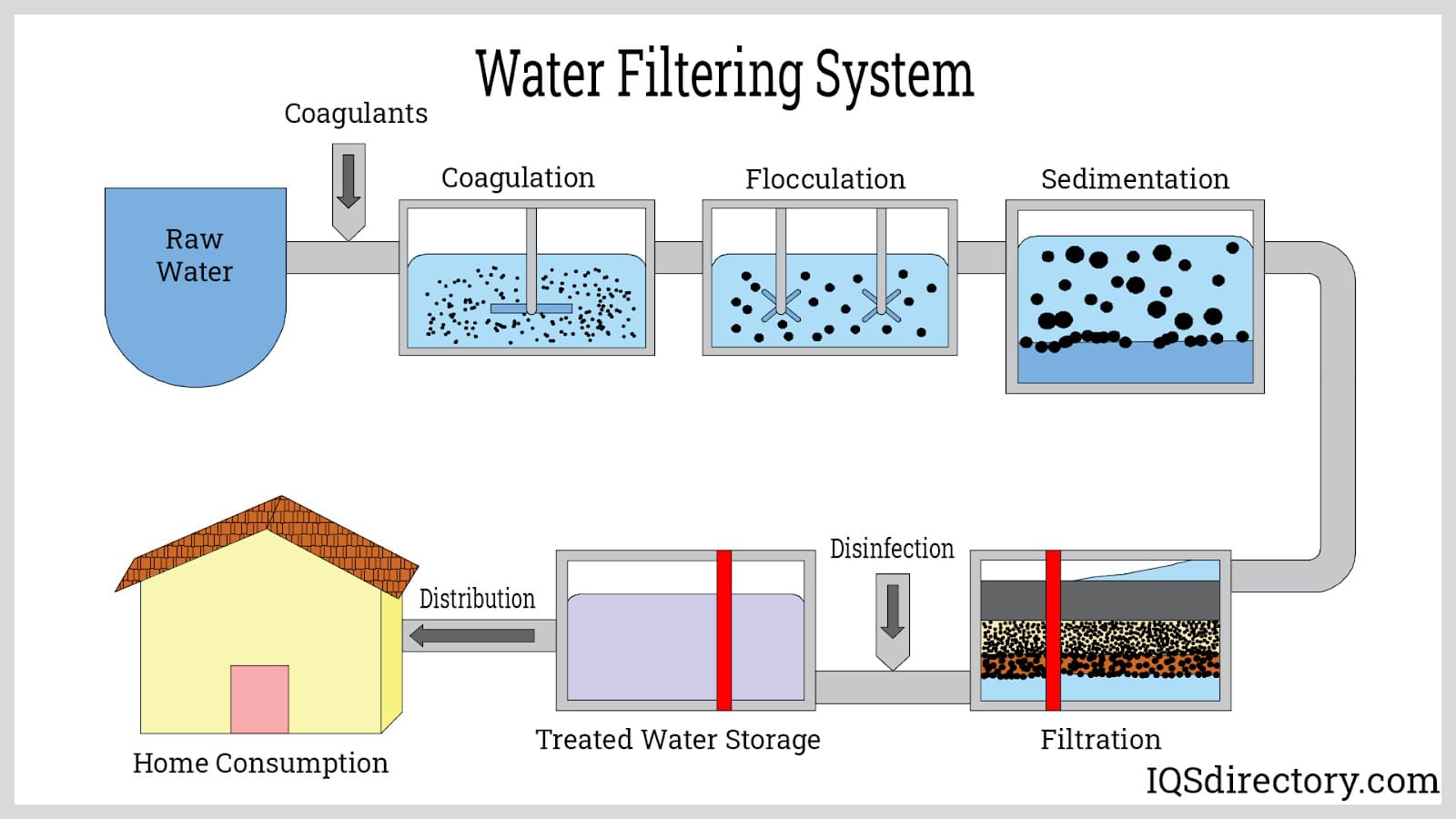
Top 8 Components Of A Water Filter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Water Filter Guru – Key Components of RO Systems
Domain: waterfilterguru.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: The main parts of a reverse osmosis (RO) water purifier system include: a sediment filter, two carbon filters, a reverse osmosis membrane, a water supply connector, a shut-off valve, a check valve, a drain line, a flow restrictor, and a drinking water faucet. Optional components may include a water storage tank, a pressure booster pump, a pressure regulator, a remineralization filter, a UV disinfe…
2. Boshart – Traditional Water Filter Components
Domain: support.boshart.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Traditional Water Filter Components:
– Filter Body: FPT inlet connection for unfiltered water, top knife type seal, mounting pads, air release button.
– Filter Bowl: Cannister holding the filter cartridge, threaded into the filter body, sealed with an O-Ring, available in clear or opaque colors.
– Filter Cartridge: Actual filtering component, various cartridges available for different applicati…
3. IQS Directory – Water Filtering Systems
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
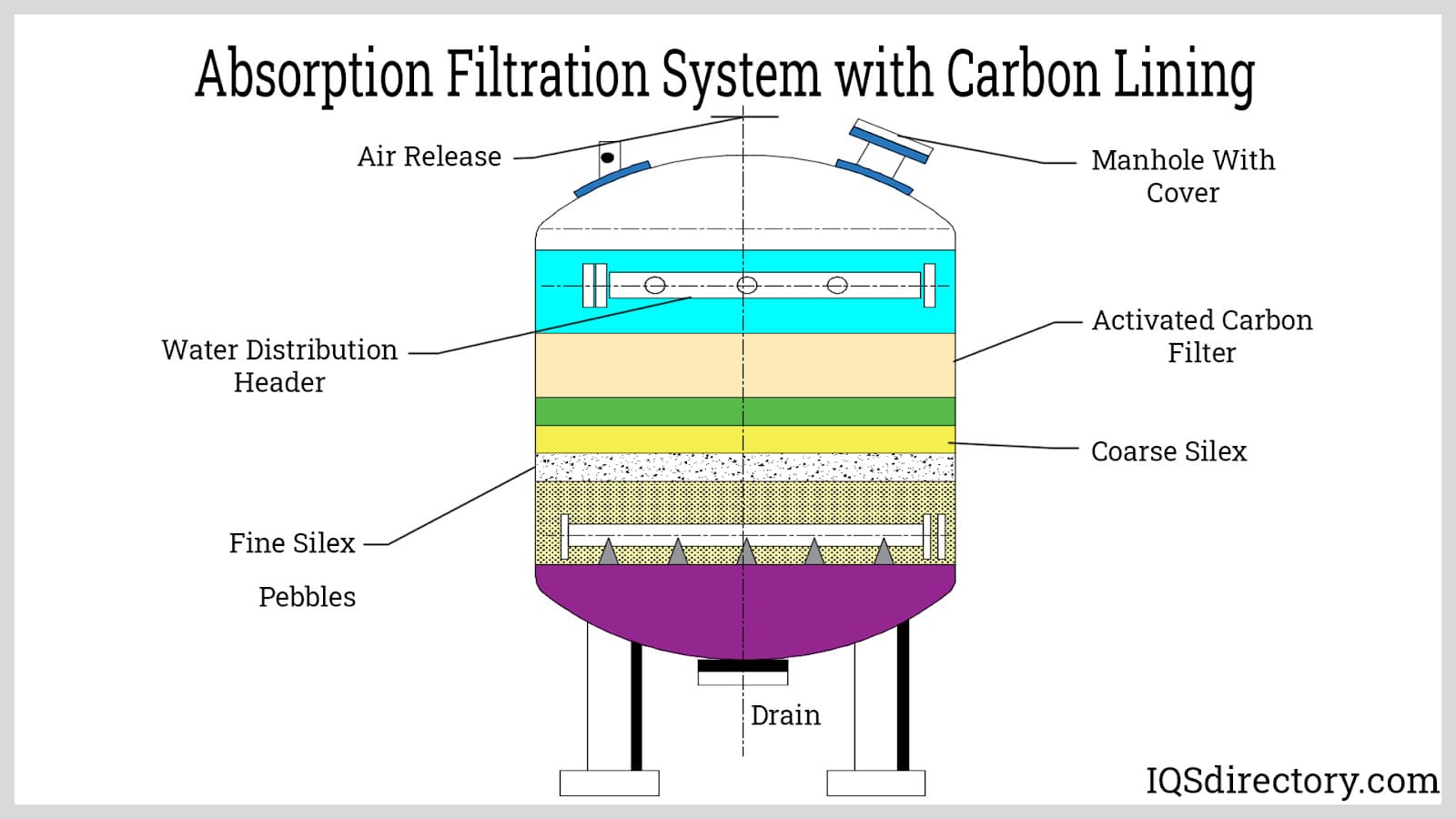
Introduction: Types of Water Filtering Systems: 1. Absorption Water Filtration System – Utilizes carbon to trap contaminants, effective in eliminating bad tastes and odors. 2. Ion Exchange Water Filtration System – Softens hard water by swapping magnesium and calcium ions with sodium or hydrogen ions. 3. Mechanical Water Filtering System – Rated by micron size for capturing particles; typical ratings include 5 …
4. Aquaboon – Water Filtration Products
Domain: filterway.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Aquaboon O-Ring – $7.79
Replacement Cartridge For Aquaboon Spin Down Sediment Water Pre Filter – $9.79
Aquaboon Nipel Connector – $7.99
Aquaboon Micron Spin Down Sediment PreFilter, Reusable Whole House Sediment Water Pre Filter, 1″ MNPT + 3/4″ FNPT – $42.99
Brass Reducer Bushing 1″ х 3/4″ – $11.99
Replacement UV Light Bulb for Aquaboon UV Filtration System – $59.79
Aquaboon Pressure Gauge – $12.9…
5. H2O Distributors – Water Filtration Components
Domain: h2odistributors.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Filtration Water System Components & Parts from H2O Distributors include a variety of products such as:
– Drinking Water Faucets
– Filter Housings
– Filter Heads
– Fittings, Valves & Tubing
– Reverse Osmosis Components
– Tools
– Filtration Media
– Replacement Water Filters & Cartridges
Key brands include Aquatec, Everpure, Pentek, and Watts. The products are categorized by size, capacity, color, …
6. Aqua Cure – Water Filters
Domain: aquacure.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
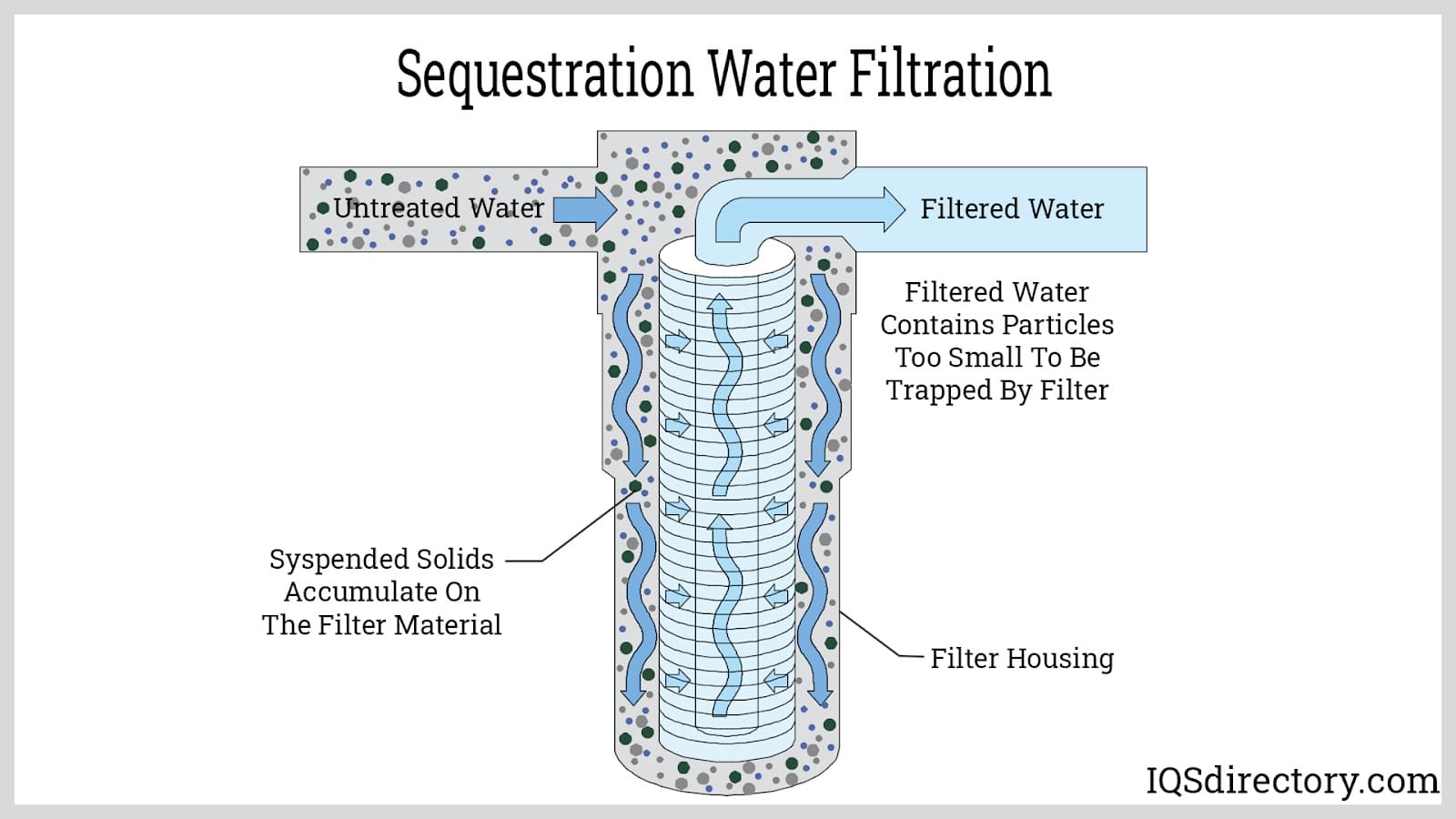
Introduction: Water filters remove unwanted impurities from water such as sediment, taste and odour, hardness, and bacteria. There are five types of water filters: Mechanical Filters, Absorption Filters, Sequestration Filters, Ion Exchange Filters, and Reverse Osmosis Filters. Mechanical filters physically remove particles using barriers, with micron ratings indicating effectiveness. Absorption filters, often u…
7. AquaScience – Water Filtration Parts & Accessories
Domain: aquascience.net
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Water Filtration Replacement Parts, Tools & Accessories including Neoprene Sweat Jackets, Tank Accessories, Filter Wrenches, Filter O-Rings, Filter Mounting Brackets, Quick Connect Flex Tubes and Accessories. Oxygen Chamber Systems (AIO) for Hydrogen Sulfide removal, Centaur Carbon Water Filtration for taste and odor removal, GreensandPlus Water Filtration for iron and manganese removal, Katalox L…
8. Window Cleaning Warehouse – Water Filtration Systems
Domain: windowcleaningwarehouse.co.uk
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Water Filtration Components Explained: The text discusses two primary types of filtration systems for window cleaning: RO/DI Filtration (four-stage system) and DI Only Filtration (single-stage system). It highlights the role of Pre-Filters in RO/DI systems, which are used to filter specific contaminants before the reverse osmosis membrane to prolong its life. Pre-filters vary in size, type, and qu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for components of a water filter
As the demand for high-quality water filtration solutions continues to grow globally, the strategic sourcing of components for water filters has become increasingly crucial. By understanding the critical elements such as sediment filters, carbon filters, and reverse osmosis membranes, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies. These components not only ensure effective purification but also contribute to the longevity and efficiency of water filtration systems.
Building strong partnerships with reliable suppliers is vital for securing the best materials at competitive prices, thus optimizing the overall supply chain. As regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe grapple with varying water quality challenges, investing in advanced filtration technologies becomes a priority.
Looking ahead, businesses that prioritize strategic sourcing will not only meet regulatory standards but also foster customer trust and satisfaction. We encourage B2B buyers to explore innovative sourcing solutions and collaborate with manufacturers who can provide tailored components for their specific market needs. Embrace the opportunity to lead in water filtration technology by investing in high-quality components today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.