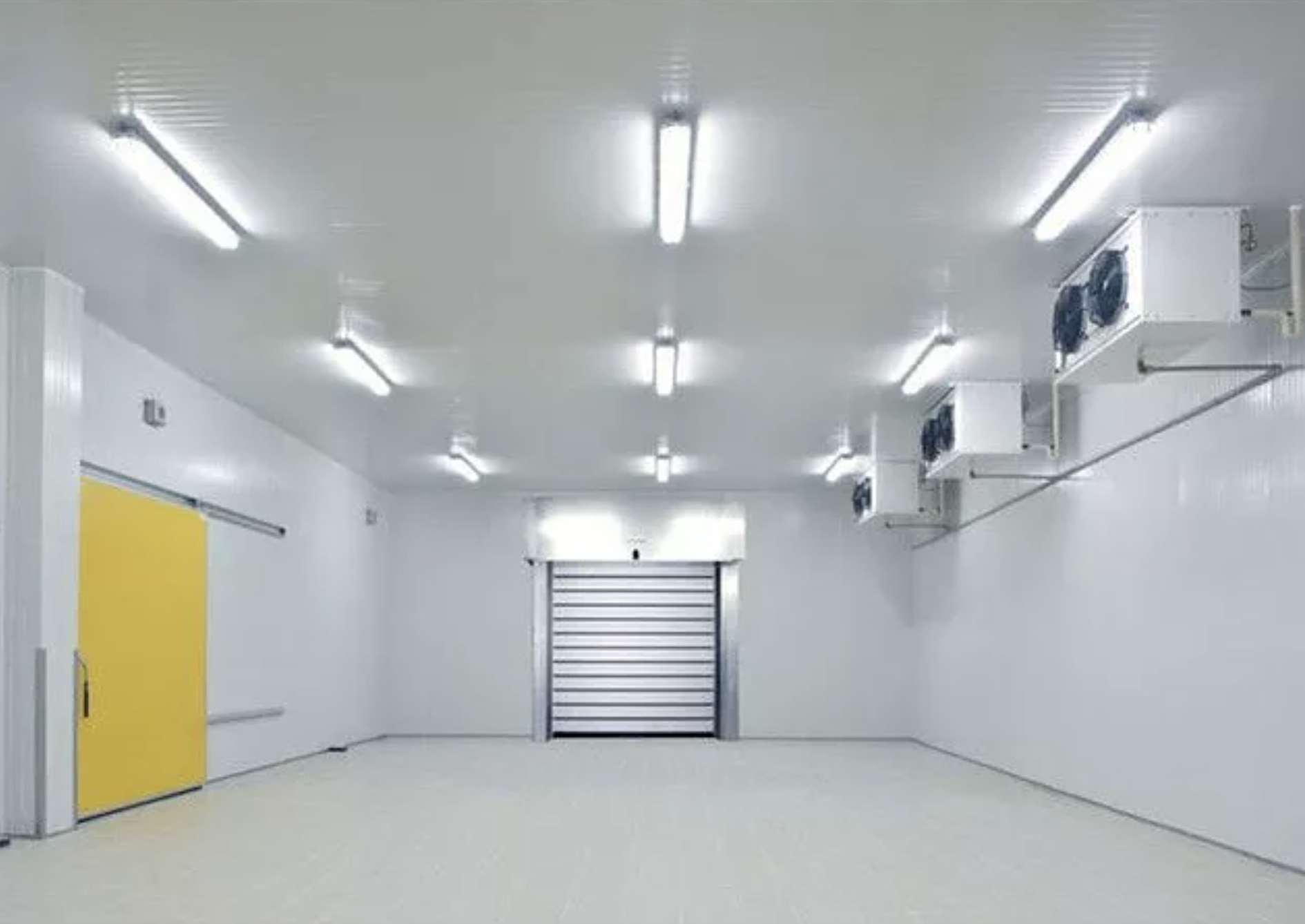
How to Source Cold Room Design Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold room design
In today’s global market, sourcing the right cold room design is a pivotal challenge for businesses aiming to safeguard perishable goods while optimizing operational efficiency. As companies expand their reach across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil—understanding the intricacies of cold room design becomes essential. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of cold rooms tailored for specific applications, from industrial storage to pharmaceutical needs, ensuring that international buyers can make informed decisions.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the critical aspects of cold room design, including temperature specifications, structural considerations, and environmental controls. We will also address the importance of supplier vetting to ensure compliance with industry standards and the latest technological advancements. Additionally, the guide will provide insights into cost implications and financing options, empowering businesses to weigh their investment against expected returns.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert knowledge, this guide serves as a valuable resource for navigating the complexities of cold room design. Whether you are looking to enhance your supply chain resilience or comply with strict storage regulations, our detailed analysis will help you identify solutions that align with your operational goals.
Understanding cold room design Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Temperature Cold Rooms | Operate between 0°C to 15°C; humidity control essential | Food storage, pharmaceuticals, floral preservation | Pros: Maintains freshness; versatile applications. Cons: Limited to specific products. |
| Negative Temperature Cold Rooms | Categorized by temperature ranges; includes medium, low, ultra-low | Frozen food storage, pharmaceuticals, chemicals | Pros: Essential for long-term storage; preserves product integrity. Cons: Higher energy costs. |
| Modular Cold Rooms | Prefabricated panels; customizable sizes and configurations | Quick deployment in various industries | Pros: Flexible design; faster installation. Cons: May require specialized assembly. |
| Controlled Atmosphere Storage | Maintains specific gas compositions; ideal for sensitive goods | High-value perishables, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Extends shelf life; reduces spoilage. Cons: Complex setup; higher initial investment. |
| Mobile Cold Rooms | Portable units; can be used for temporary storage solutions | Events, food distribution, emergency response | Pros: Flexibility and mobility; quick setup. Cons: Limited storage capacity; may lack temperature precision. |
What Are Positive Temperature Cold Rooms and Their Applications?
Positive temperature cold rooms maintain temperatures between 0°C to 15°C, making them ideal for storing a variety of perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, and pharmaceuticals. The ability to control humidity levels is crucial for preserving the quality of these items. B2B buyers should consider the specific temperature and humidity requirements of their products, as well as the potential for energy efficiency in these systems.
How Do Negative Temperature Cold Rooms Support Various Industries?
Negative temperature cold rooms are essential for industries requiring storage of frozen goods. They are categorized into medium, low, and ultra-low temperature ranges, catering to different product needs. These cold rooms play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals during storage and transport. Buyers must evaluate their specific storage needs and the potential energy consumption associated with maintaining these lower temperatures.
What Advantages Do Modular Cold Rooms Offer to Businesses?
Modular cold rooms are constructed using prefabricated panels, allowing for customizable sizes and configurations. This design facilitates quicker installation and adaptability to various operational needs. They are particularly beneficial for businesses that require temporary or expandable cold storage solutions. Buyers should assess their space limitations and future growth plans when considering modular options.
Why Choose Controlled Atmosphere Storage for Sensitive Goods?
Controlled atmosphere storage is designed to maintain specific gas compositions, which is particularly beneficial for high-value perishables and pharmaceuticals. This technology can significantly extend the shelf life of products by reducing spoilage. However, the complexity and cost of setup may be a consideration for buyers, who should weigh the benefits against their budget and product sensitivity.
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Mobile Cold Rooms?
Mobile cold rooms provide a flexible solution for temporary storage needs, making them suitable for events, food distribution, and emergency responses. Their portability allows for quick setup and adaptability to various locations. However, potential buyers should consider the limited storage capacity and possible challenges in maintaining precise temperature control compared to stationary cold rooms.
Key Industrial Applications of cold room design
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Cold Room Design | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Storage of Perishable Goods | Extends shelf life and maintains product quality | Compliance with food safety standards, energy efficiency |
| Pharmaceuticals | Vaccine and Drug Storage | Ensures efficacy and safety of temperature-sensitive products | Regulatory compliance, precise temperature control |
| Agriculture | Controlled Atmosphere Storage for Produce | Preserves freshness and reduces spoilage | Humidity control capabilities, scalability |
| Biotechnology and Research | Sample Preservation in Laboratories | Maintains integrity of biological samples | Customization for specific research needs, reliability |
| Floral Industry | Cold Storage for Flowers | Prolongs freshness and aesthetic quality | Temperature and humidity regulation, accessibility |
How is Cold Room Design Applied in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, cold room design is crucial for the storage of perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, dairy, and meats. These facilities maintain optimal temperatures and humidity levels to extend the shelf life of products and prevent spoilage. For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions with varying climates, it is essential to ensure compliance with local food safety regulations and select cold rooms that are energy-efficient to reduce operating costs.
What Role Does Cold Room Design Play in Pharmaceuticals?
Cold room design is vital in the pharmaceutical industry for the storage of vaccines and temperature-sensitive medications. These cold rooms must maintain precise temperature ranges to ensure the efficacy and safety of products. Buyers should focus on sourcing solutions that meet stringent regulatory compliance standards, such as those outlined by the WHO or local health authorities. Additionally, advanced monitoring systems for temperature and humidity are critical to maintain product integrity throughout the storage period.
How Can Cold Room Design Benefit Agriculture?
For the agricultural sector, controlled atmosphere storage cold rooms are employed to preserve the freshness of produce during transportation and storage. By regulating temperature and humidity, these facilities help reduce spoilage and maintain the quality of fruits and vegetables. Buyers in Africa and South America, where agricultural exports are significant, should consider scalability and the capability to adapt to different types of produce when sourcing cold room solutions.
Why is Cold Room Design Important for Biotechnology and Research?
In biotechnology and research, cold rooms are essential for preserving samples, including biological materials that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. These facilities must be designed to meet specific requirements, such as maintaining a constant low temperature and humidity levels. Buyers should prioritize customization options that cater to unique research needs, as well as reliability in temperature control systems to ensure sample integrity over time.
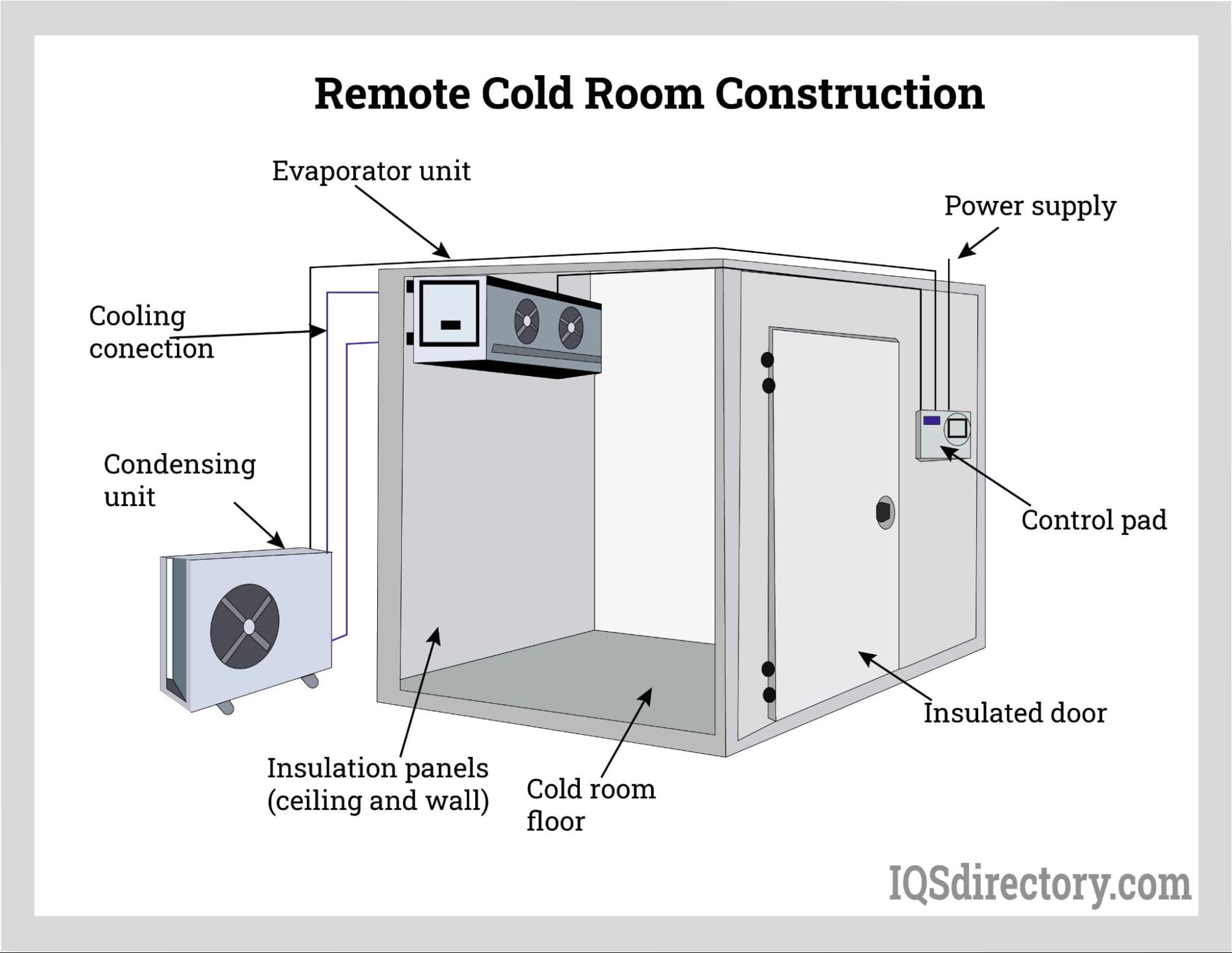
Illustrative image related to cold room design
How Does Cold Room Design Support the Floral Industry?
The floral industry relies on cold room design for the storage of flowers and plants, which require specific temperature and humidity conditions to stay fresh. These cold rooms help prolong the aesthetic quality of floral arrangements, making them more appealing to consumers. For B2B buyers, particularly those in Europe and the Middle East, it is essential to source cold room solutions that offer precise climate control and easy access to inventory to enhance operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold room design’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Temperature Control in Cold Rooms
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges faced by B2B buyers in cold room design is ensuring consistent temperature control. Fluctuations in temperature can lead to spoilage of sensitive goods, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals and food. Buyers often report issues related to inadequate insulation, poor refrigeration systems, or improper placement of temperature sensors, which can compromise product integrity and lead to substantial financial losses. The pressure to comply with stringent regulatory standards adds another layer of complexity, as any failure in maintaining temperature can result in legal repercussions and damage to reputation.
The Solution: To overcome temperature control issues, it is crucial to invest in high-quality insulation materials and advanced refrigeration systems that are tailored to the specific needs of the stored products. Consider using insulated panels with high thermal resistance ratings to minimize heat transfer. Additionally, implementing a redundancy system—such as backup compressors or emergency power sources—can safeguard against system failures. Regular maintenance schedules should be established to ensure that all equipment is functioning optimally. Moreover, utilizing advanced monitoring technology, such as IoT-enabled sensors, can provide real-time temperature data and alerts, allowing for immediate corrective actions if any deviations occur.
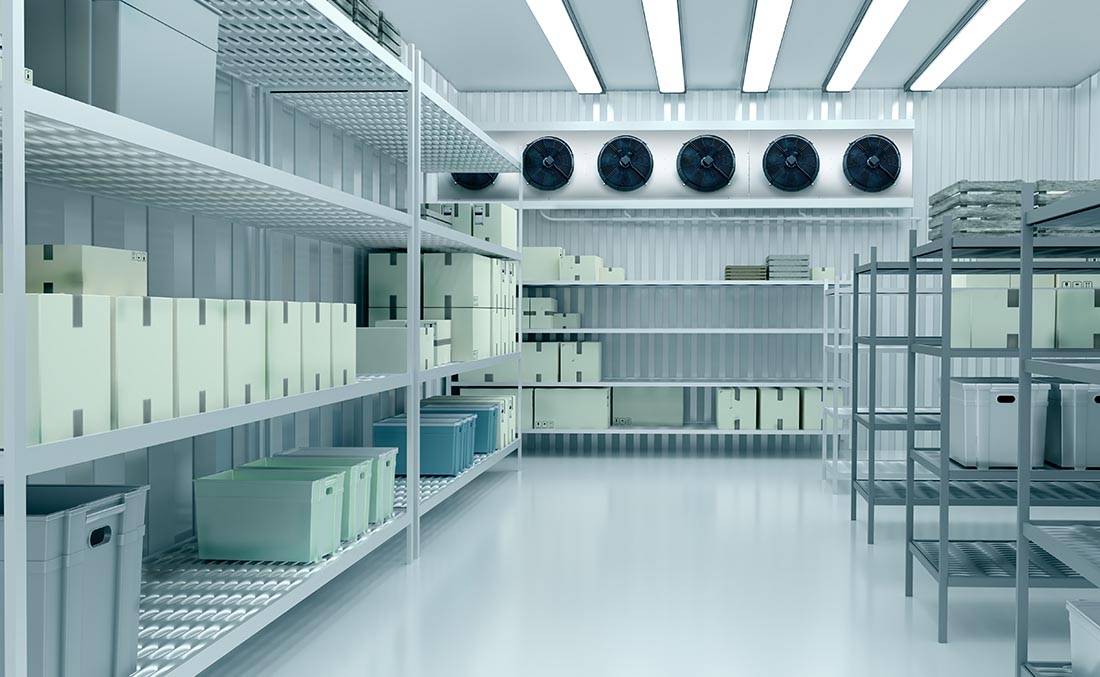

Illustrative image related to cold room design
Scenario 2: Space Optimization and Layout Design Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with maximizing the available space within cold rooms. Inefficient layouts can lead to wasted storage capacity, hinder operational workflows, and increase the time required for product retrieval. This is particularly critical for businesses that operate in sectors like grocery distribution or pharmaceuticals, where timely access to products is essential for maintaining supply chain efficiency. Buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by various shelving options and stacking methods, unsure of how to best utilize vertical space without compromising accessibility.
The Solution: To optimize space effectively, it is advisable to conduct a thorough analysis of the product types and volumes that will be stored. Employing a combination of adjustable shelving and mobile racking systems can allow for flexible storage solutions that adapt to changing inventory needs. Consider implementing a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to enhance accessibility and reduce spoilage. Additionally, leveraging software solutions for inventory management can streamline operations by providing insights into stock levels and turnover rates, ultimately guiding layout decisions. Collaborating with a cold room design specialist can also help tailor a layout that maximizes space while ensuring operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Compliance with Industry Regulations and Standards
The Problem: Navigating the complex landscape of regulations and industry standards can be a daunting task for B2B buyers involved in cold room design. Different regions have varying requirements regarding temperature control, hygiene, and safety protocols, which can create confusion and increase the risk of non-compliance. This is especially true for industries like food service and pharmaceuticals, where adherence to strict guidelines is not only mandatory but also critical for consumer safety. Buyers may find it challenging to stay updated on changes in regulations, leading to potential fines and loss of business licenses.
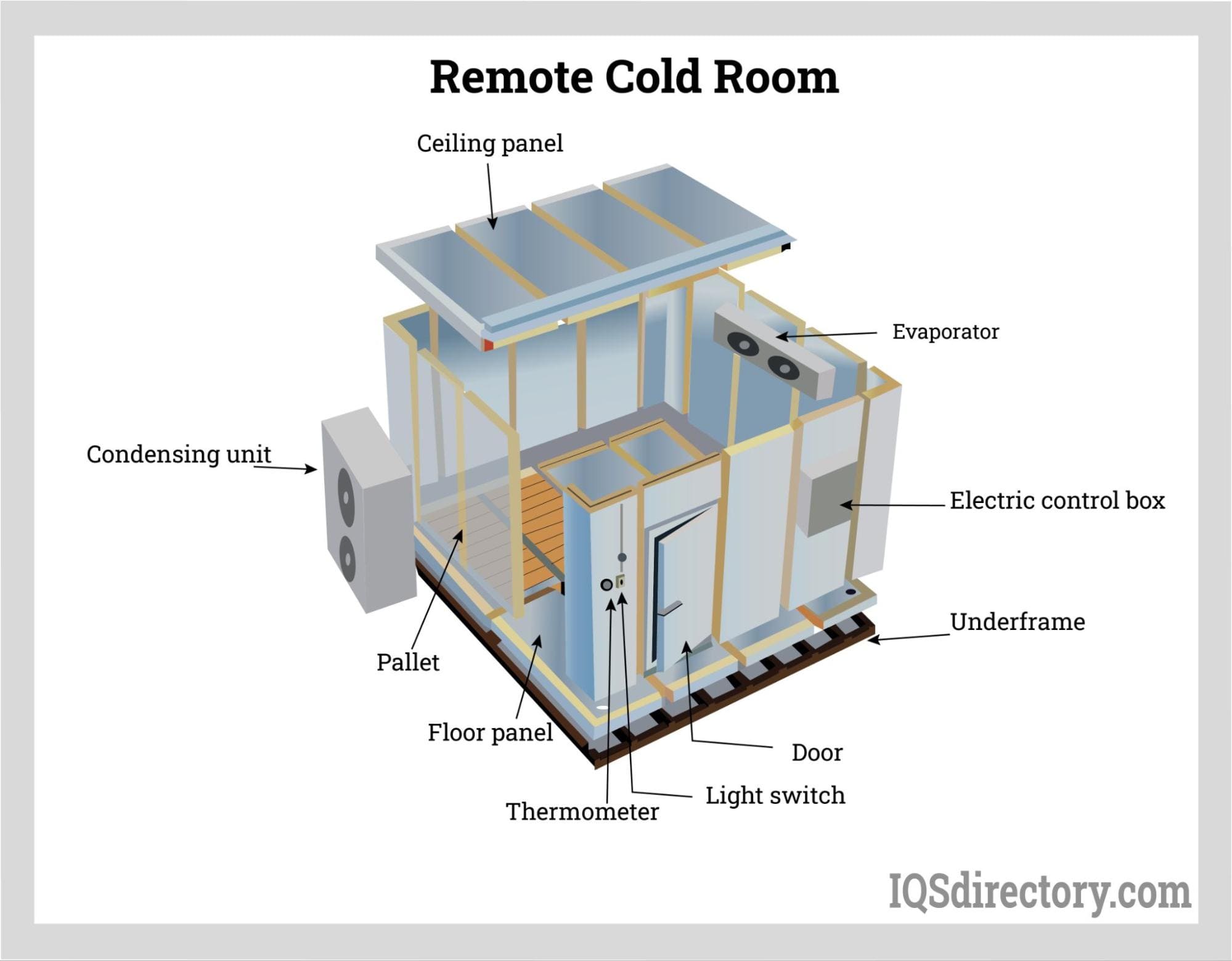
Illustrative image related to cold room design
The Solution: To ensure compliance, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest regulations relevant to their industry and region. Engaging with regulatory consultants or industry associations can provide valuable insights and resources. When designing a cold room, incorporating features that meet or exceed these standards—such as antimicrobial surfaces, proper drainage systems, and easy-to-clean materials—can simplify compliance. Additionally, implementing comprehensive training programs for staff on hygiene practices and regulatory requirements can foster a culture of compliance within the organization. Regular audits and assessments can also help identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing adherence to necessary standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold room design
What Are the Key Materials for Cold Room Design?
When designing a cold room, selecting the right materials is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in cold room construction: polyurethane panels, stainless steel, fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), and concrete. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact the effectiveness of a cold room.
How Do Polyurethane Panels Perform in Cold Room Applications?
Polyurethane panels are widely favored for cold room insulation due to their excellent thermal resistance. They typically have a temperature rating of up to -40°F (-40°C) and provide a high R-value, which measures thermal resistance. The primary advantage of polyurethane is its lightweight nature, which simplifies installation and reduces structural load.
Pros: Polyurethane panels offer superior insulation, are easy to handle, and have a smooth surface that facilitates cleaning. They are also resistant to moisture and mold, making them suitable for humid environments.
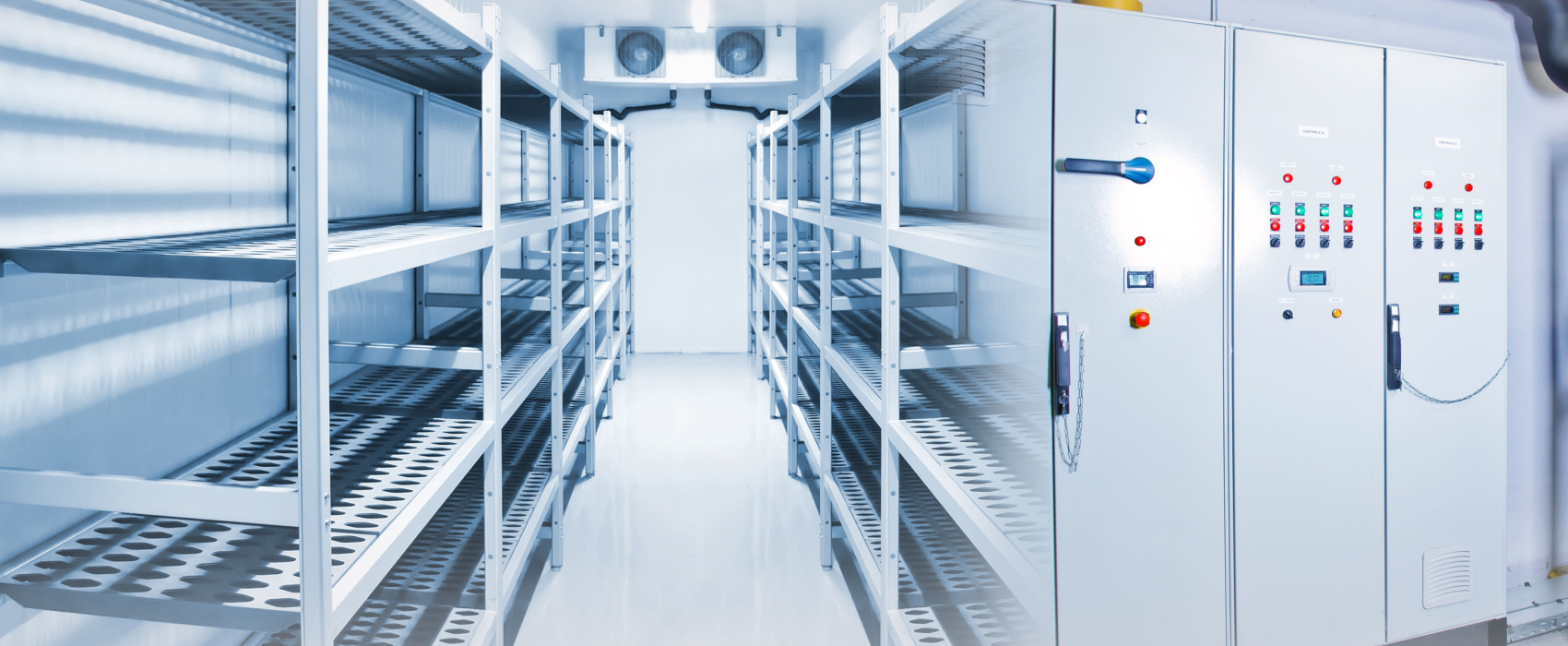

Illustrative image related to cold room design
Cons: The primary drawback is their susceptibility to physical damage, which can compromise insulation. Additionally, while they are cost-effective in terms of energy savings, the initial investment can be higher compared to other materials.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with local building codes and standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of these panels in their region to avoid supply chain disruptions.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Cold Room Construction?
Stainless steel is another popular choice for cold room design, particularly for surfaces that require high durability and corrosion resistance. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is often used for shelving, doors, and walls in cold storage facilities.
Pros: Stainless steel is highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and easy to clean, making it ideal for food storage applications. Its aesthetic appeal also enhances the overall look of the cold room.
Cons: The primary limitation of stainless steel is its higher cost compared to other materials. Additionally, it has a lower insulating value, which may necessitate additional insulation layers to maintain temperature control.
For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, ensuring compliance with food safety standards and regulations is paramount. Stainless steel should meet specific grades (e.g., 304 or 316) to ensure it is suitable for food contact.
How Does Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Compare in Cold Room Design?
Fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) is known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It is often used in environments where moisture is prevalent, making it suitable for cold rooms that handle perishable goods.
Pros: FRP is resistant to chemicals and moisture, making it an excellent choice for cold rooms storing pharmaceuticals or food products. It is also easy to install and maintain.
Cons: One of the downsides is that FRP can be less durable than metal options, leading to potential damage from heavy loads. Additionally, its insulating properties may not be as effective as polyurethane.
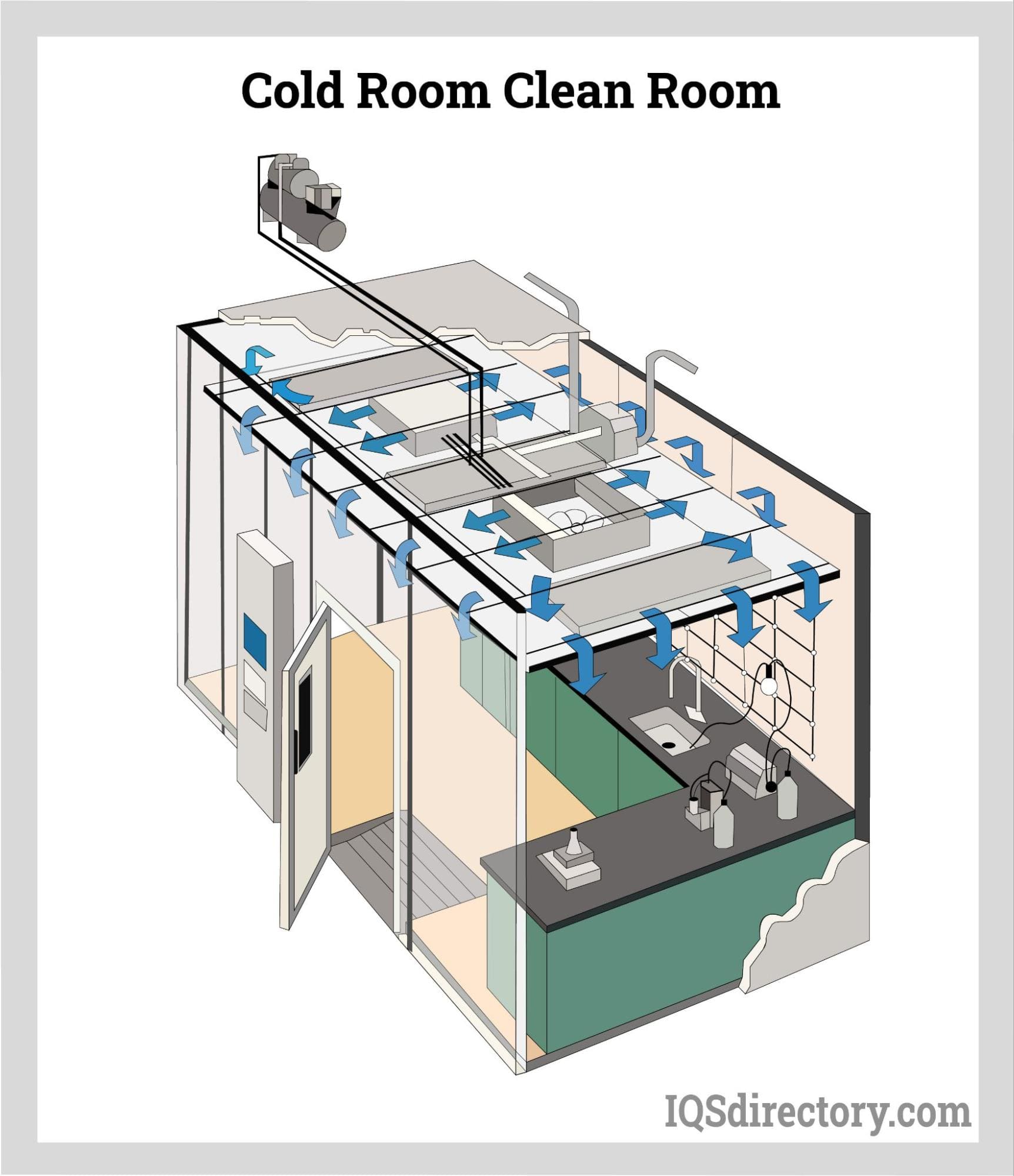
Illustrative image related to cold room design
International buyers should consider the specific environmental conditions of their regions, such as humidity levels, when selecting FRP. Compliance with local regulations regarding materials used in food storage is also critical.
What Role Does Concrete Play in Cold Room Construction?
Concrete is often used for larger cold storage facilities due to its strength and durability. It provides excellent thermal mass, which helps in maintaining stable temperatures.
Pros: Concrete is highly durable, fire-resistant, and can support heavy loads, making it suitable for large-scale operations. It also offers good thermal performance when properly insulated.
Cons: The main drawback of concrete is its weight and the complexity of installation, which can lead to higher labor costs. Additionally, it requires insulation to achieve the desired temperature control.
For buyers in regions like Brazil and Vietnam, understanding local building codes and the availability of skilled labor for concrete construction is essential. Ensuring that the concrete meets specific standards for thermal performance is also crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Cold Room Design
| Material | Typical Use Case for cold room design | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane Panels | Insulation for walls and ceilings | Excellent thermal resistance | Susceptible to physical damage | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Shelving and structural components | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and lower insulation value | High |
| Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic | Walls and surfaces in humid environments | Moisture and chemical resistance | Less durable under heavy loads | Medium |
| Concrete | Large-scale cold storage facilities | High durability and thermal mass | Heavy and complex installation | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights to make informed decisions when designing cold rooms tailored to their specific needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold room design
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cold Room Design?
The manufacturing process of cold rooms involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the rigorous standards required for temperature-controlled environments. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking to invest in cold room solutions.
Material Preparation: How Are Cold Room Components Selected?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves selecting high-quality materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and humidity. Common materials include insulated panels made from polyurethane or polystyrene, which offer excellent thermal insulation properties. Additionally, stainless steel is often used for surfaces due to its resistance to corrosion and ease of cleaning. Suppliers should provide material certifications that confirm compliance with international standards, ensuring they are fit for purpose.
What Techniques Are Utilized in the Forming Stage of Cold Room Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the selected materials into components that will comprise the cold room. This includes cutting insulated panels to size, fabricating refrigeration units, and assembling structural frames. Advanced techniques such as CNC machining and laser cutting are commonly employed to achieve precise dimensions, minimizing thermal bridges and ensuring optimal insulation. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturing technology used, as modern techniques contribute significantly to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the cold room.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Cold Room Design?
Once the components are formed, they proceed to the assembly stage. This phase is critical as it involves integrating various systems, including refrigeration, electrical wiring, and control systems. A modular approach is often adopted, allowing for easier installation and maintenance. During assembly, it is essential to ensure that all seals are airtight to prevent leaks, which can compromise temperature control. B2B buyers should ask about the assembly protocols and the experience of the technicians involved, as skilled assembly is crucial for long-term performance.
Illustrative image related to cold room design
What Finishing Techniques Are Important for Cold Rooms?
The finishing stage of cold room manufacturing focuses on quality enhancements and aesthetic considerations. This may include painting, applying protective coatings, and installing insulation covers. Finishing techniques not only improve the appearance but also enhance the durability of the cold room. Buyers should verify that the finishes used are suitable for the specific environmental conditions of their intended applications, particularly in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments.
What International Standards Should Cold Room Designs Comply With?
Quality assurance in cold room manufacturing is paramount, and compliance with international standards is a significant aspect of this process. Standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems) are essential for ensuring that suppliers maintain consistent quality throughout their manufacturing processes. Compliance with these standards can be a crucial factor for B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as they demonstrate a commitment to quality and reliability.
How Do Industry-Specific Certifications Impact Cold Room Quality?
In addition to general quality standards, cold room manufacturers may also need to comply with industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European market or API standards for pharmaceutical applications. These certifications assure buyers that the cold rooms meet specific safety and performance criteria. Buyers should request documentation of these certifications to ensure that the supplier’s products are suitable for their intended use.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Cold Room Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the cold room manufacturing process, with several critical checkpoints established to monitor quality at different stages.
What Are the Stages of Quality Control in Cold Room Manufacturing?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers should conduct tests to ensure that materials meet specified standards and requirements.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to verify that components are being produced according to design specifications. This may include monitoring temperature and humidity levels during assembly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the cold room is fully assembled, a comprehensive final inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing of refrigeration systems, insulation integrity checks, and ensuring compliance with all relevant standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure they are making a sound investment. Here are several methods to achieve this:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, processes, and adherence to quality standards firsthand. This also provides an opportunity to review documentation related to past audits and certifications.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for regular quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks. These reports can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can also help verify compliance with international standards.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from different regions, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing cold rooms.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Cold Room Design and Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying regulations and standards that affect cold room design. For instance, European buyers must adhere to stringent EU regulations, while those in Africa may encounter less formalized standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers can meet these specific requirements.

Illustrative image related to cold room design
What Role Does Cultural Understanding Play in Supplier Relationships?
Cultural differences can impact communication and expectations regarding quality assurance. Building strong relationships with suppliers through clear communication and understanding of local practices is essential. This can foster trust and facilitate smoother negotiations regarding quality standards and compliance.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Cold Room Design
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for cold room design is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, manufacturing techniques, and compliance with international standards, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Verifying supplier quality control processes through audits, reports, and third-party inspections will further ensure the reliability and performance of cold room solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold room design’
To assist B2B buyers in successfully procuring cold room design services, this guide outlines essential steps and considerations. This checklist will help ensure that the cold room you design meets your specific operational requirements and complies with industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the first and most crucial step in the cold room design process. Consider factors such as the type of goods to be stored, required temperature ranges, and humidity levels. This information will guide your design decisions and ensure that the facility is tailored to your needs.
- Type of Goods: Different products require varying temperature settings; for example, pharmaceuticals need ultra-low temperatures, while fruits may need a positive temperature environment.
- Space Requirements: Assess the physical dimensions of the cold room to ensure it can accommodate your storage volume.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Understanding and adhering to local and international regulations is vital for cold room design. Non-compliance can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions.
- Local Standards: Investigate the regulations governing food safety, pharmaceuticals, or specific industry standards in your region.
- International Guidelines: If you operate globally, familiarize yourself with international standards such as ISO or HACCP that may apply to your cold storage solutions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, a thorough evaluation is essential. This step ensures you choose a partner capable of meeting your technical and regulatory requirements.
- Request Documentation: Ask for company profiles, certifications, and case studies relevant to your industry.
- Seek References: Connect with other businesses that have utilized the supplier’s services to understand their reliability and quality of work.
Step 4: Assess Design Flexibility and Scalability
The ability to adapt your cold room design as your business grows is crucial. Inquire about the potential for future expansions or modifications.
- Modular Designs: Explore suppliers that offer modular cold room solutions, which can be easily expanded or reconfigured.
- Technological Upgrades: Consider whether the design can accommodate technological advancements in refrigeration or monitoring systems in the future.
Step 5: Review Energy Efficiency Options
Energy consumption is a significant ongoing cost in cold room operations. Selecting energy-efficient designs can lead to substantial long-term savings.
- Energy Ratings: Look for equipment and materials that have high energy efficiency ratings to minimize operational costs.
- Sustainable Practices: Evaluate suppliers who employ sustainable practices in their design and manufacturing processes.
Step 6: Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Before finalizing your decision, perform a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis of the proposed designs and suppliers. This analysis will help you weigh the initial investment against the expected return on investment.
- Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Savings: Consider both upfront costs and potential savings from energy efficiency and reduced spoilage.
- Maintenance and Operational Costs: Factor in ongoing maintenance and operational expenses to ensure the cold room remains cost-effective over time.
Step 7: Finalize Design and Installation Plans
Once you’ve selected a supplier and finalized your design, work closely with them on the installation process. Ensure all parties are clear on timelines, responsibilities, and quality assurance measures.
- Installation Timeline: Develop a detailed schedule for installation to minimize disruption to your operations.
- Quality Checks: Establish quality assurance checkpoints throughout the installation process to ensure compliance with your specifications.
By following this step-by-step checklist, you will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of cold room design and procurement, ensuring a solution that meets your business needs efficiently and effectively.

Illustrative image related to cold room design
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold room design Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Cold Room Design?
When considering the costs associated with cold room design, several critical components contribute to the overall expenditure:
-
Materials: The selection of insulation materials, refrigeration units, flooring, and wall structures significantly influences costs. High-performance insulation materials can reduce energy consumption, impacting long-term operational costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor for installation and assembly is essential. Labor costs can vary based on geographic location and complexity of the cold room design. Regions with a high availability of skilled labor may offer more competitive rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs related to production, including utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with efficient processes can reduce overhead, potentially lowering prices.
-
Tooling: Specific designs may require custom tooling, which adds to initial costs. However, investing in quality tooling can enhance production efficiency and product quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that cold rooms meet industry standards requires rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with testing and certification can vary depending on the complexity and regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Transporting cold room components requires careful planning, particularly for international shipments. Factors like shipping distance, mode of transport, and local customs regulations can significantly impact logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and ensure sustainability. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cold Room Design Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of cold room designs, making it essential for buyers to understand these nuances:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk often leads to significant discounts. Buyers should consider their storage needs to optimize order quantities for better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed cold rooms tailored to specific requirements can incur higher costs. Standardized designs may offer cost savings, so buyers should weigh their customization needs against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials directly affects both upfront costs and long-term operational efficiency. Certified materials may command a premium but can lead to lower energy costs and longer lifespans.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service levels can impact pricing. Engaging with established suppliers often provides assurance of quality and support, but may come at a higher price.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery can help buyers manage costs effectively. Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, influencing the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Cold Room Design?
To maximize value in cold room design sourcing, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engaging in discussions with suppliers regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules can yield favorable terms. Building strong relationships can lead to better deals over time.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial costs, buyers should assess the TCO, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A more efficient cold room may have a higher upfront cost but lower operational expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and tariffs that can affect total costs. Collaborating with local experts can mitigate risks.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize digital tools for cost comparison and supplier evaluation. Online platforms can provide insights into market trends and help identify competitive pricing.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly updating knowledge about industry standards, technological advancements, and market conditions can empower buyers to make informed decisions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Pricing in the cold room design sector can fluctuate based on various market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional economic factors. The figures discussed herein are indicative and should be verified through direct consultations with suppliers for accurate and up-to-date pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold room design With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Cold Room Design
In the realm of temperature-controlled storage solutions, cold room design stands as a prominent choice for preserving perishable goods. However, various alternatives exist that can also meet the needs of businesses across different sectors. This section compares cold room design with two viable alternatives: Modular Refrigerated Containers and Blast Chillers. Each option has unique strengths and weaknesses that can influence the decision-making process for B2B buyers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Room Design | Modular Refrigerated Containers | Blast Chillers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for long-term storage | Good for transport and short-term storage | Rapid cooling for immediate use |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate cost, lower than cold rooms | Lower initial cost, but higher operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex setup and installation | Quick to deploy and relocate | Easy to operate but requires additional space |
| Maintenance | Regular checks and upkeep needed | Low maintenance; portable units | Requires frequent cleaning and monitoring |
| Best Use Case | Long-term storage of bulk items | Transporting goods over distances | Rapid cooling of fresh goods prior to storage |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Modular Refrigerated Containers
Modular refrigerated containers offer a flexible and portable solution for temperature-sensitive goods. These containers can be easily transported and set up at various locations, making them ideal for businesses that require mobility, such as event catering or pop-up markets. The moderate cost and relatively low maintenance make them an attractive option. However, their performance may not match that of fixed cold rooms for long-term storage, as they are designed primarily for transport and short-term use.
Blast Chillers
Blast chillers are specialized equipment designed to rapidly lower the temperature of food products to ensure freshness and safety. They are particularly beneficial in food service industries where immediate cooling is necessary, such as restaurants and catering services. The lower initial cost and ease of operation make blast chillers appealing; however, they may incur higher operational costs due to energy consumption and require additional space for installation. They are not suitable for long-term storage, which limits their functionality compared to cold rooms.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between cold room design and its alternatives, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific requirements, including the type of goods being stored, budget constraints, and operational flexibility. Cold rooms excel in long-term storage for bulk items, while modular refrigerated containers offer portability, and blast chillers provide rapid cooling solutions. By evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that best align with their logistical needs and operational goals.
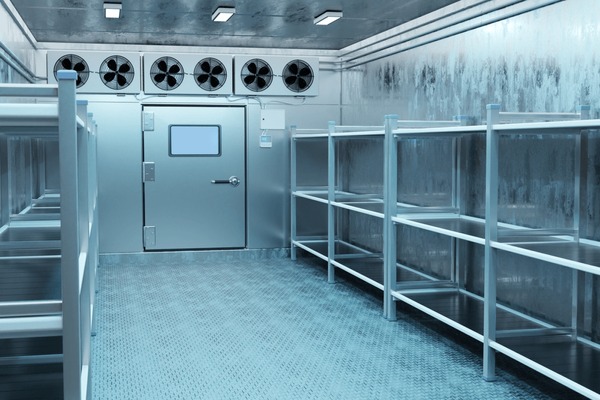

Illustrative image related to cold room design
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold room design
What Are the Essential Technical Properties for Cold Room Design?
When designing a cold room, several critical technical properties must be considered to ensure optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. Below are key specifications that play a vital role in cold room design:
-
Insulation Material and Thickness
– Definition: Insulation material refers to the type of substance used to minimize heat transfer, while thickness indicates the depth of this material.
– B2B Importance: Proper insulation is crucial for maintaining desired temperatures and energy efficiency. High-quality insulation reduces energy costs and enhances product preservation, making it a critical factor in ROI assessments. -
Temperature Range
– Definition: This specification outlines the operational temperature limits of the cold room, typically categorized into positive and negative temperature ranges.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the required temperature range is essential for selecting appropriate refrigeration systems and ensures that stored goods, such as pharmaceuticals or perishables, remain within safe limits to avoid spoilage or degradation. -
Humidity Control
– Definition: Humidity control refers to the mechanisms in place to maintain desired moisture levels within the cold room.
– B2B Importance: Excess humidity can lead to mold growth and spoilage of products. Effective humidity control is vital for industries such as food storage and pharmaceuticals, where product integrity is paramount. -
Load Capacity
– Definition: Load capacity indicates the maximum weight and volume of products that the cold room can accommodate.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the load capacity helps in planning storage logistics and maximizing space utilization, ultimately affecting storage costs and operational efficiency. -
Energy Efficiency Rating
– Definition: This rating measures the energy consumption of the cold room relative to its output.
– B2B Importance: Energy-efficient systems reduce operating costs and are increasingly important for sustainability initiatives. B2B buyers often seek energy-efficient designs to comply with regulations and improve their corporate social responsibility profiles. -
Construction Materials
– Definition: This refers to the types of materials used in the structure of the cold room, such as steel, aluminum, or specialized panels.
– B2B Importance: The choice of construction materials affects durability, maintenance costs, and overall performance. High-quality materials can enhance the lifespan of the cold room and reduce long-term operational costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Cold Room Design?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the cold room design sector. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Explanation: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– B2B Context: Buyers often work with OEMs to obtain high-quality components tailored to specific cold room designs, ensuring compatibility and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Explanation: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– B2B Context: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for businesses looking to scale operations without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Explanation: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific goods or services.
– B2B Context: Utilizing RFQs can help businesses compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive the best value for their investments. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Explanation: These are predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– B2B Context: Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses navigate shipping, delivery, and risk management, particularly when sourcing cold room components from international suppliers. -
Cold Chain Logistics
– Explanation: Cold chain logistics refers to the temperature-controlled supply chain required for transporting perishable goods.
– B2B Context: Understanding cold chain logistics is vital for businesses involved in food and pharmaceutical sectors, as it directly impacts product safety and compliance with health regulations. -
Blast Freezer
– Explanation: A blast freezer rapidly lowers the temperature of food products to preserve freshness and quality.
– B2B Context: Incorporating a blast freezer into a cold room design is essential for businesses in the food industry to ensure that products remain safe and high-quality during storage and transportation.
By grasping these essential properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality in cold room design.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold room design Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Cold Room Design?
The cold room design sector is experiencing significant growth driven by globalization, increased demand for perishable goods, and advancements in refrigeration technology. International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly active, as they seek reliable cold storage solutions to meet both local and export needs. Key trends include the adoption of modular cold room systems, which allow for rapid deployment and scalability, catering to fluctuating demand. In addition, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technology is transforming cold room management, enabling real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity levels, thus ensuring compliance with health regulations and enhancing operational efficiency.
Emerging markets are witnessing a shift toward energy-efficient designs, prompted by rising energy costs and stringent environmental regulations. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in developing regions where energy supply can be inconsistent. Furthermore, as e-commerce continues to expand, cold chain logistics are becoming increasingly crucial, creating a robust demand for sophisticated cold storage solutions. Buyers must remain vigilant about these dynamics, as they directly influence sourcing strategies and investment decisions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Cold Room Design?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of cold room design, with an emphasis on reducing the environmental impact of refrigeration systems. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly refrigerants and energy-efficient designs. This shift is not only beneficial for the environment but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are seeking transparency in the supply chain. This includes ensuring that materials used in cold room construction adhere to ‘green’ certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or ISO 14001 for environmental management. By selecting suppliers who prioritize ethical practices, businesses can mitigate risks associated with labor exploitation and environmental degradation. Moreover, implementing sustainable practices can lead to significant cost savings over time, particularly through reduced energy consumption and waste.
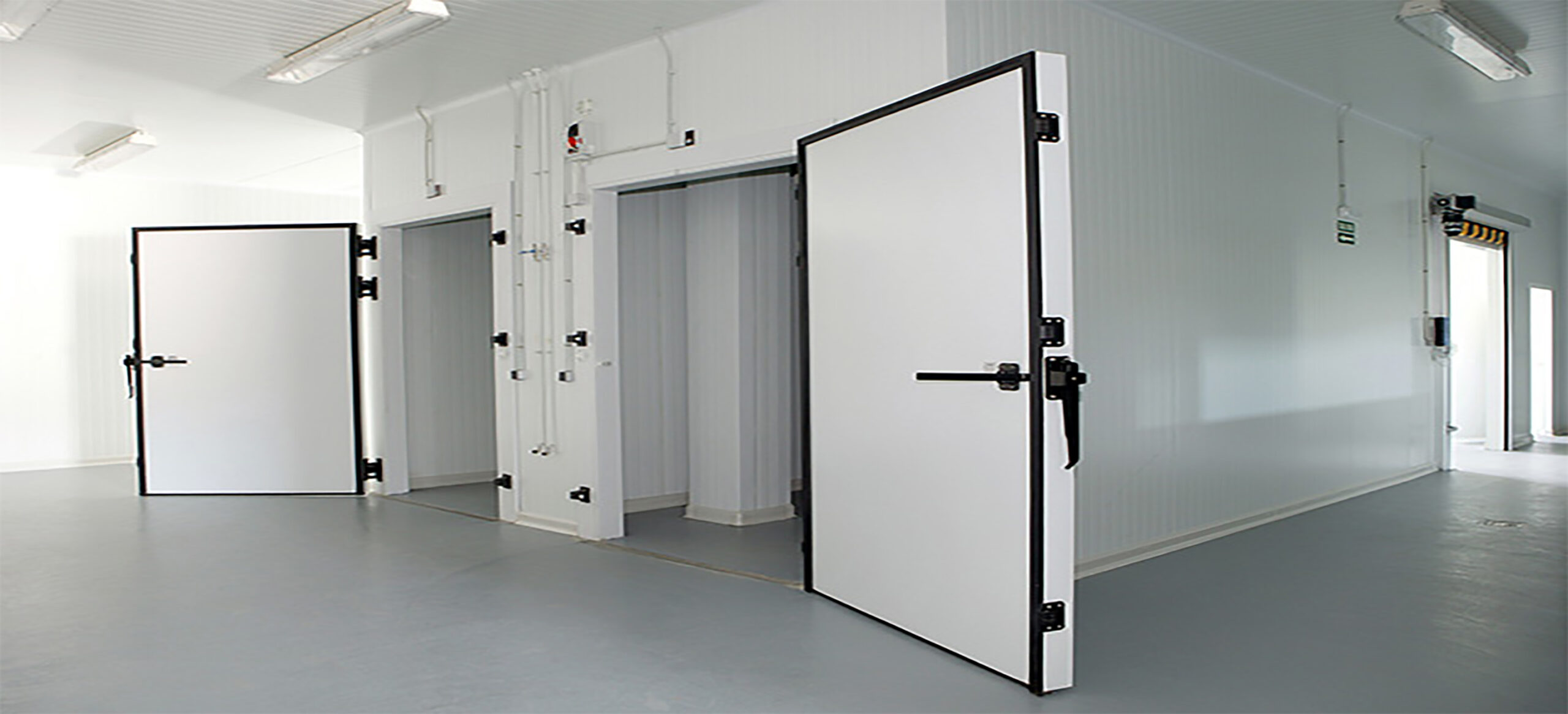

Illustrative image related to cold room design
What Has Been the Evolution of Cold Room Design?
The evolution of cold room design can be traced back to the early days of refrigeration technology in the late 19th century. Initially, cold storage facilities were basic, relying on ice and natural cooling methods. However, the development of electric refrigeration in the 20th century revolutionized the industry, allowing for precise temperature control and enhanced storage capabilities.
In recent decades, advancements in materials and technology have further transformed cold room design. The introduction of insulated panels and energy-efficient refrigeration systems has significantly improved performance and reduced operational costs. Today, cold rooms are not only designed for functionality but also for sustainability and adaptability, reflecting the changing needs of global markets and consumer preferences. As technology continues to advance, the future of cold room design promises even greater efficiency and innovation, making it a vital consideration for B2B buyers in various sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold room design
-
How do I select the right cold room design for my business needs?
Choosing the appropriate cold room design begins with identifying the specific requirements of your business, including the type of products you plan to store, their temperature and humidity needs, and the volume of goods. Consider factors like the space available, the desired temperature range (positive or negative), and whether a modular or custom-built solution is more suitable. Consulting with a professional cold room designer can provide insights tailored to your operational goals, ensuring compliance with local regulations and industry standards. -
What are the key features to consider in a cold room design?
When evaluating cold room designs, prioritize features such as insulation quality, refrigeration system efficiency, temperature control options, and humidity regulation. Additionally, assess the layout for optimal space utilization, accessibility for loading and unloading, and safety measures like alarm systems and emergency exits. Customization options may also be vital, depending on the unique requirements of your stored products, such as airflow patterns and shelving configurations. -
What are the typical lead times for cold room design and installation?
Lead times for cold room design and installation can vary significantly based on the complexity of the project and the supplier’s capabilities. Generally, standard modular cold rooms may take 4 to 6 weeks for delivery and installation, while custom-built solutions can take longer, often 8 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss timelines upfront with potential suppliers to align your project schedule and avoid delays that could impact your operations. -
What are the payment terms commonly offered by cold room suppliers?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upfront (often 30% to 50%) followed by payment upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or installment plans for larger projects. Ensure you clarify payment expectations, including any potential penalties for late payments or discounts for early settlement, before finalizing contracts. -
How can I ensure quality assurance during the cold room installation process?
To guarantee quality assurance, it’s essential to vet your supplier thoroughly. Look for suppliers with certifications, such as ISO or industry-specific accreditations, and check their track record through client testimonials and case studies. Implement a quality control plan that includes regular inspections during installation, adherence to local building codes, and post-installation evaluations to confirm that the cold room meets the specified requirements. -
What international shipping considerations should I be aware of when sourcing cold room components?
When sourcing cold room components internationally, consider factors such as customs regulations, shipping costs, and lead times. Ensure that the supplier can provide all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including commercial invoices and certificates of origin. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs or import duties that may apply based on your location. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in handling cold chain logistics can streamline this process. -
What customization options are available for cold room designs?
Customization options for cold room designs can include temperature zones, shelving configurations, door types, and specialized insulation materials. Some suppliers offer bespoke solutions tailored to specific industry needs, such as additional humidity control for perishable goods or enhanced security features for sensitive pharmaceuticals. Discuss your specific requirements with suppliers to explore available customization options that align with your operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cold room projects?
Minimum order quantities for cold room projects can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the design. Some suppliers may have no MOQ for modular solutions, while custom installations may require a minimum order based on material costs and design specifications. It’s important to clarify MOQ requirements upfront to ensure that your project scope aligns with supplier capabilities and pricing structures.
Top 6 Cold Room Design Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cold Storage Solutions – Smart Monitoring System
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Cold storage room, concrete walls, concrete floor, carbon dioxide levels, humidity levels, larder, north-west orientation, screened cold air intake, zoned system for different produce, Raspberry Pi for monitoring, sealing off area from the house, size considerations.
2. Danfoss – Optyma™ iCO₂ 20MT/10LT
Domain: danfoss.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Danfoss offers a wide range of solutions for cold rooms and walk-in refrigeration, including:
1. **Optyma™ iCO₂ 20MT/10LT** – A robust and low-noise condensing unit compatible with natural refrigerant R744.
2. **Optyma™ Condensing Units** – Versatile units suitable for small to mid-size cold rooms, display cabinets, and more, compatible with low-GWP and natural refrigerants.
3. **Optyma™ iCO₂ 4.6…
3. FrigoSys – Industrial Cold Storage Solutions
Domain: frigosys.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Cold Storage Design – Industrial Cold Room & Equipments includes: Controlled Atmosphere Cold Storage, Fish Cold Storage and Blast Freezing, Meat and Meatfoods Storage, Fruit and Vegetable Storage, Banana Ripening Room, Spiral Freezer. Products offered: Cold Room, Cold Room Doors (Industrial Doors, Service Door, High Speed PVC Door, Hinged Cold Room Door, Sliding Cold Room Door), Cold Room Panels (…
4. Pinterest – Cold Room DIY Solutions
Domain: ca.pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Cold room, DIY basement root cellar, food storage, plans to convert standard cold room into working root cellar, maintaining temperatures in the mid 30’s F, efficient food preservation, related interests include root cellar plans, cold storage room design, and basement remodeling.
5. Cold Room China – Comprehensive Guide to 25 Cold Room Types
Domain: coldroom-china.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: 25 Types of Cold Rooms: A Comprehensive Guide includes various types of cold rooms categorized by temperature, size, purpose, function, and structure. Key types include: 1. Positive Temperature Cold Rooms (32°F to 59°F) for fruits, vegetables, flowers, and pharmaceuticals. 2. Negative Temperature Cold Rooms: Medium-Low (-0.4°F to 32°F) for seafood and meats; Low (-22°F to 0°F) for food and pharmac…
6. Eng-Tips – Cold Storage Design Essentials
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cold storage facility design considerations include unique building codes, material properties of concrete and steel, shrinkage of concrete, and the impact of low temperatures on material strength. Specific design elements mentioned are: 1) Use of double columns for thermal separation, 2) Hardwood insulation pads under column baseplates, 3) Insulated slabs with glycol coolant systems, 4) Considera…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold room design
In today’s competitive marketplace, the strategic sourcing of cold room design is essential for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and ensure product integrity. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting the right type of cold room—whether for pharmaceuticals, food storage, or industrial applications—tailored to specific environmental requirements. Understanding the nuances of temperature control, humidity management, and energy efficiency will empower international buyers to make informed decisions that align with both regulatory standards and market demands.
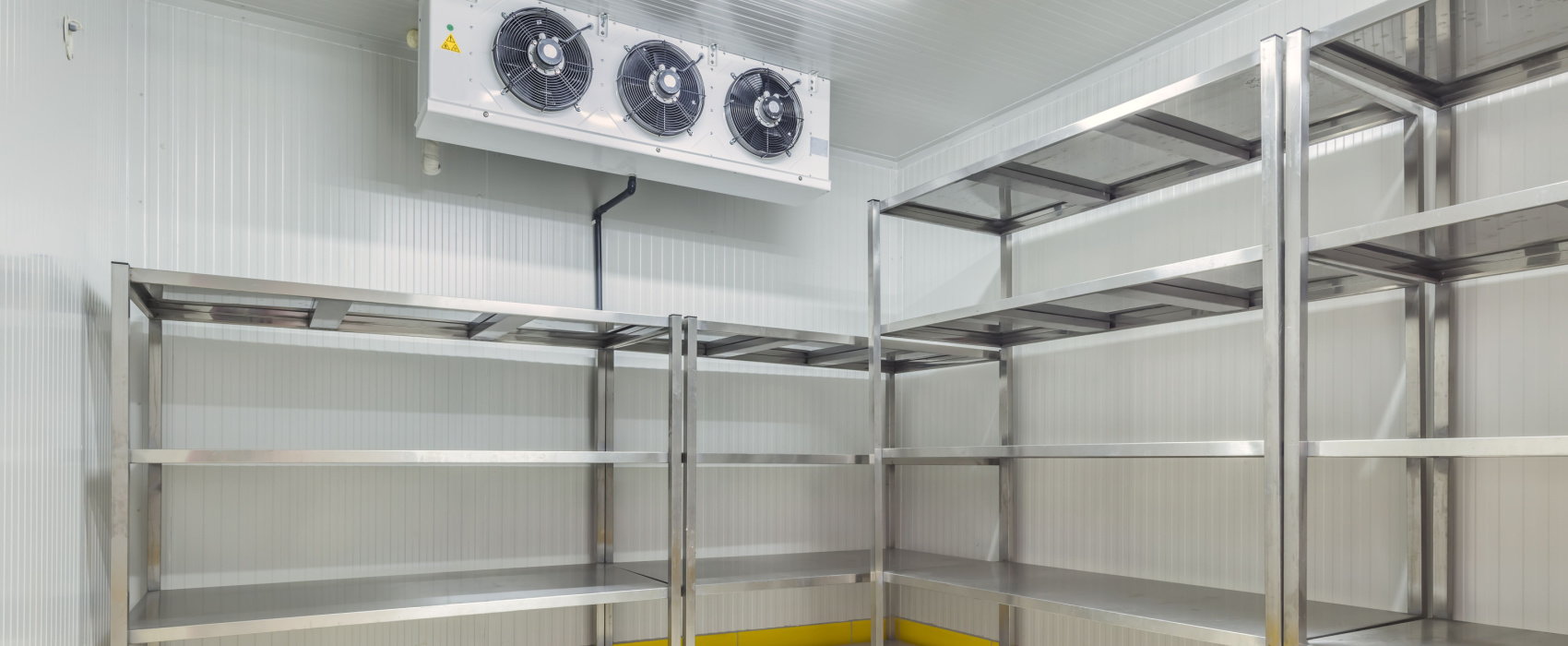

Illustrative image related to cold room design
Investing in innovative cold room solutions not only safeguards perishable goods but also contributes to sustainability efforts by reducing energy consumption. As the global cold chain logistics landscape evolves, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a significant opportunity for businesses to leverage advanced technology and modular designs to optimize their cold storage capabilities.
Looking ahead, we encourage international B2B buyers to prioritize strategic partnerships with reputable suppliers who can provide tailored solutions and support in navigating the complexities of cold room design. By doing so, companies can enhance their supply chain resilience, meet growing consumer expectations, and ultimately drive business growth in an ever-changing environment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to cold room design