How to Source Cold Forging Aluminum Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold forging aluminum
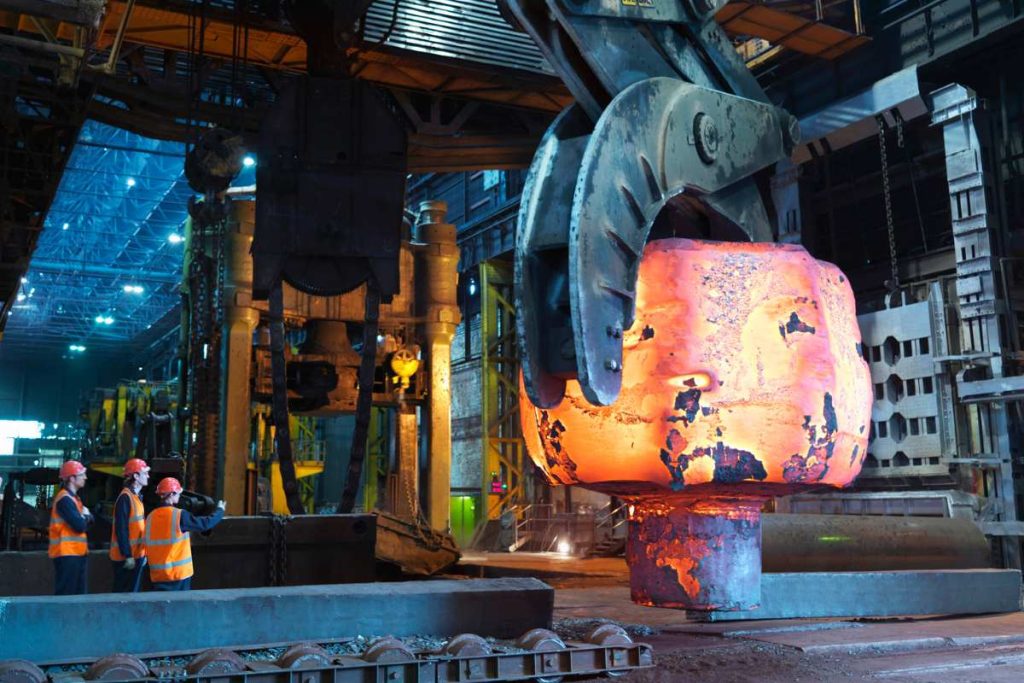
In an increasingly competitive global landscape, sourcing high-quality cold forged aluminum components presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. This guide aims to demystify the cold forging aluminum process, addressing critical aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations. As manufacturers seek to reduce production costs while maintaining high standards of quality and precision, understanding the nuances of cold forging becomes essential.
Cold forging is particularly advantageous for producing intricate parts with narrow tolerances and superior surface finishes, making it a preferred choice in sectors like automotive and aerospace. However, with the diverse landscape of suppliers spanning Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in regions like Germany and Brazil—navigating this market can be daunting.
This comprehensive resource empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights and detailed information necessary for informed purchasing decisions. From exploring the latest developments in aluminum alloys to evaluating supplier capabilities and understanding cost implications, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make strategic choices that align with your business needs. By leveraging this expertise, you can ensure that your sourcing of cold forged aluminum components not only meets quality standards but also drives operational efficiency and competitive advantage in your market.
Understanding cold forging aluminum Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward Cold Forging | Involves a single-direction die movement for forming shapes. | Automotive parts, brackets, and fittings | Pros: High precision, good surface finish; Cons: Limited to simpler geometries. |
| Backward Cold Forging | Uses a reverse motion to shape materials, allowing for complex forms. | Aerospace components, intricate parts | Pros: Capable of complex shapes; Cons: Higher tooling costs. |
| Multi-Stage Cold Forging | Combines several forging operations to achieve complex geometries. | High-strength automotive components | Pros: Efficient for complex designs; Cons: Longer production time and setup. |
| Tubular Cold Forging | Specifically designed for forming tubular components with high concentricity. | Pipe fittings, automotive exhaust parts | Pros: Excellent concentricity; Cons: Requires specialized equipment. |
| Warm Forging | Slightly elevated temperatures improve formability and reduce loads. | Aerospace, automotive, and structural components | Pros: Reduces forging load, enhances ductility; Cons: More energy-intensive than cold forging. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Forward Cold Forging?
Forward cold forging is characterized by the movement of the die in a single direction, compressing the aluminum stock into the desired shape. This method is particularly suitable for manufacturing simpler components such as automotive brackets and fittings, where high precision and surface finish are crucial. For B2B buyers, the advantages of forward cold forging include cost-effectiveness and efficiency for straightforward designs. However, its limitation lies in its inability to accommodate more complex geometries, potentially necessitating additional manufacturing processes for intricate parts.
How Does Backward Cold Forging Differ from Other Methods?
Backward cold forging utilizes a reverse motion to shape materials, making it ideal for producing complex and intricate parts, especially in the aerospace sector. This method allows for greater design flexibility and can achieve high tolerances and surface quality. B2B buyers should consider the higher tooling costs associated with backward cold forging, which can impact overall project budgets. However, the ability to create detailed shapes may justify the investment for projects requiring precision-engineered components.
What Advantages Does Multi-Stage Cold Forging Offer?
Multi-stage cold forging involves a series of forging operations that progressively shape the aluminum material into complex geometries. This technique is particularly advantageous for producing high-strength automotive components that require both durability and intricate designs. B2B buyers should weigh the efficiency of multi-stage processes against the longer production times and setup requirements. While this method can significantly enhance design capabilities, it may also lead to increased lead times and costs.
Why Choose Tubular Cold Forging for Specific Applications?
Tubular cold forging is tailored for creating tubular components, ensuring high concentricity and dimensional accuracy. This technique is commonly used for applications such as pipe fittings and automotive exhaust parts. For buyers in industries requiring precise tubular shapes, the benefits of excellent concentricity and surface finish are paramount. However, the need for specialized equipment may represent a barrier for some manufacturers, making it essential for B2B buyers to evaluate their production capabilities before committing.
What Benefits and Challenges Are Associated with Warm Forging?
Warm forging operates at slightly elevated temperatures, enhancing the formability of aluminum and allowing for reduced forging loads. This method is advantageous in producing components for sectors like aerospace and automotive, where both strength and ductility are essential. For B2B buyers, the primary considerations include the increased energy consumption associated with warm forging compared to traditional cold methods. However, the trade-off can be worthwhile for projects that demand superior material properties and complex geometries.
Key Industrial Applications of cold forging aluminum
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cold forging aluminum | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing of high-strength components like brackets and housings | Reduces weight while maintaining strength; enhances fuel efficiency | Need for precision tolerances and surface finish; availability of high-strength aluminum alloys |
| Aerospace | Production of structural components and fittings | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant parts improve overall aircraft efficiency | Certifications for aerospace-grade materials; compliance with strict regulatory standards |
| Electronics | Fabrication of housings and enclosures for devices | Cost-effective production of complex shapes; improved thermal conductivity | Requirement for high-quality finishes and tight tolerances; sourcing from reliable suppliers |
| Machinery & Equipment | Production of gears, shafts, and connectors | Enhanced durability and performance of machinery parts | Focus on material properties and treatment processes; need for reliable supply chains |
| Construction & Building | Creation of structural supports and fixtures | Lightweight solutions reduce overall project costs and improve energy efficiency | Consideration for local sourcing and sustainability practices; adherence to building codes and standards |
How is Cold Forging Aluminum Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, cold forging aluminum is pivotal in creating high-strength components such as brackets and housings. These parts are essential for vehicle assembly, contributing to weight reduction and enhanced fuel efficiency. International buyers need to prioritize suppliers that can meet precise tolerances and surface finishes, as even minor deviations can affect vehicle performance and safety. High-strength aluminum alloys, like AA6082, are often preferred due to their favorable mechanical properties.
What Role Does Cold Forging Aluminum Play in Aerospace Applications?
The aerospace industry utilizes cold forging aluminum for producing lightweight, corrosion-resistant structural components and fittings. These parts contribute significantly to the overall efficiency and performance of aircraft, making cold forging a vital manufacturing process. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must ensure that their suppliers are certified for aerospace-grade materials and adhere to stringent regulatory standards, as safety and reliability are paramount.

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
How is Cold Forging Aluminum Beneficial in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics sector, cold forging aluminum is employed to fabricate housings and enclosures for various devices. This method allows for the cost-effective production of intricate shapes while enhancing thermal conductivity, which is crucial for electronic applications. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who can deliver high-quality finishes and maintain tight tolerances, as these factors directly impact the functionality and aesthetic appeal of electronic products.
What Advantages Does Cold Forging Aluminum Offer in Machinery and Equipment?
Cold forging aluminum is widely used in manufacturing gears, shafts, and connectors for machinery and equipment. The process enhances the durability and performance of these parts, leading to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. When sourcing, businesses must focus on the specific material properties and treatment processes required for their applications, ensuring that suppliers can provide consistent quality and performance.
How is Cold Forging Aluminum Applied in Construction and Building?
In the construction industry, cold forging aluminum plays a crucial role in creating structural supports and fixtures. The lightweight nature of forged aluminum solutions can significantly reduce overall project costs and improve energy efficiency. Buyers in this sector should consider local sourcing options and sustainability practices while ensuring that their materials meet relevant building codes and standards, which can vary by region.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cold forging aluminum’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges in Achieving Precision and Quality in Parts
The Problem:
B2B buyers in industries such as automotive and aerospace often face difficulties in achieving the required precision and quality in cold-forged aluminum components. When tolerances are tight and specifications are stringent, any deviation can lead to costly rework or product failures. This challenge is compounded by the complexity of designs that may require intricate shapes and high concentricity, which are not easily achieved through standard processes. Buyers may find themselves frustrated when their suppliers cannot meet these expectations, resulting in delays and increased costs.
The Solution:
To overcome these challenges, it is crucial to partner with suppliers who specialize in high-precision cold forging techniques. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with advanced technology and expertise in handling high-strength aluminum alloys, such as AA6082. Additionally, conducting thorough pre-production trials can help identify potential issues in achieving the desired specifications. Collaborating closely with engineers during the design phase can also ensure that the designs are optimized for cold forging, taking into account the material properties and process limitations. This proactive approach not only improves the chances of meeting precision requirements but also enhances overall product quality.

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Scenario 2: High Production Costs and Inefficiencies
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers are confronted with rising production costs associated with cold forging aluminum, particularly when dealing with complex geometries that require multiple forming operations. The need for soft annealing between processes can extend production times and increase costs, leading to a competitive disadvantage in the market. Buyers may be disheartened when they realize that what seemed like a cost-effective manufacturing solution is becoming increasingly expensive due to inefficiencies in the process.
The Solution:
To tackle this issue, buyers should explore suppliers that offer warm forging as an alternative to traditional cold forging. This method operates at elevated temperatures, which can reduce the need for multiple forming steps and minimize the reliance on soft annealing, thereby streamlining production. Additionally, investing in technology that allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments during the forging process can further enhance efficiency. By collaborating with suppliers who utilize advanced tooling and die design, buyers can significantly reduce production costs while maintaining the desired quality and performance of the forged parts.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Material Selection for Specific Applications
The Problem:
Selecting the right aluminum alloy for cold forging can be daunting for B2B buyers, especially when specific mechanical properties are required for particular applications. For instance, buyers in the automotive sector may require components that exhibit high strength, ductility, and resistance to fatigue. The challenge lies in the vast array of aluminum alloys available, each with distinct characteristics that can affect the performance of the final product. Making an incorrect choice can lead to failures, safety concerns, and financial losses.
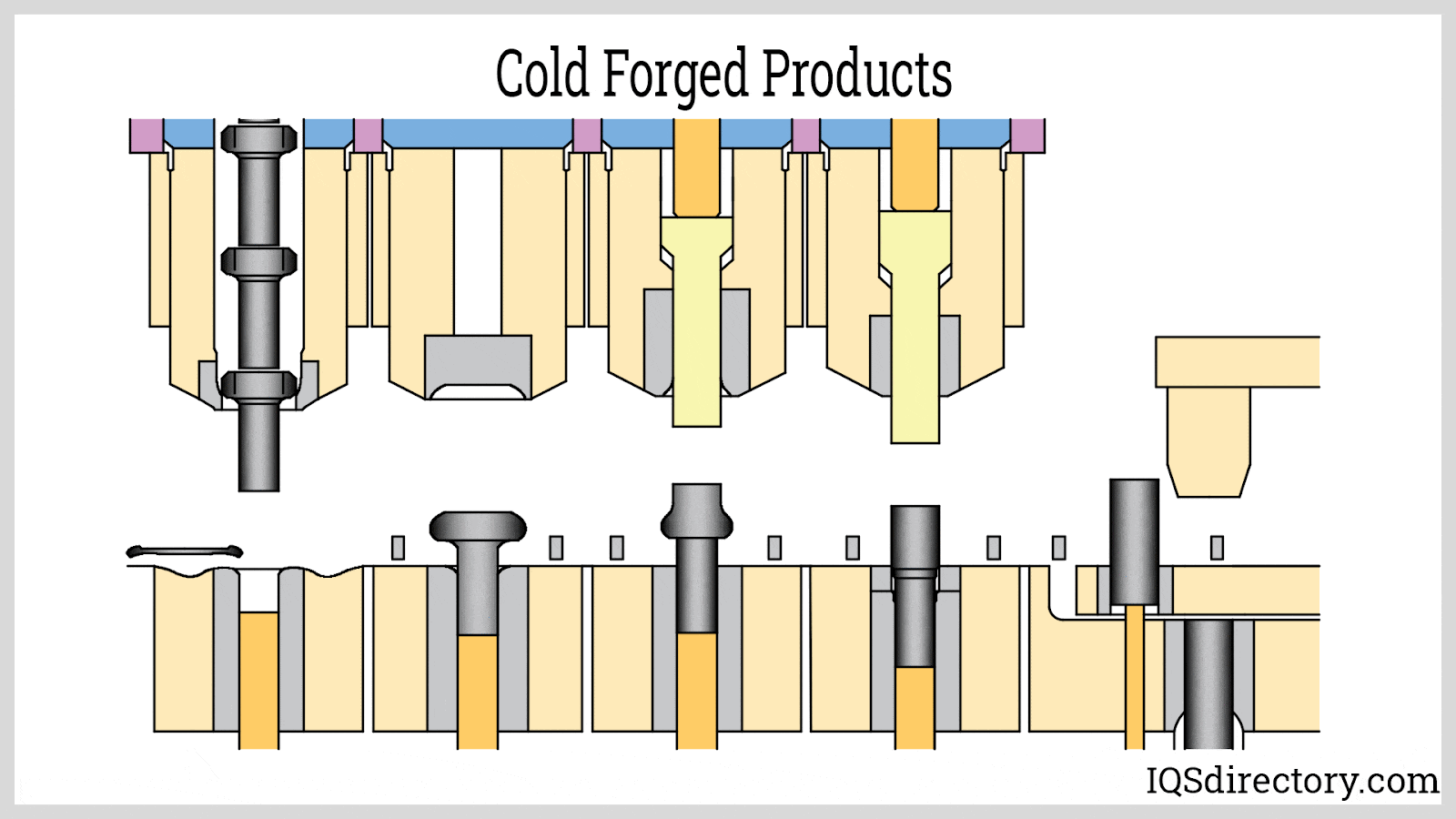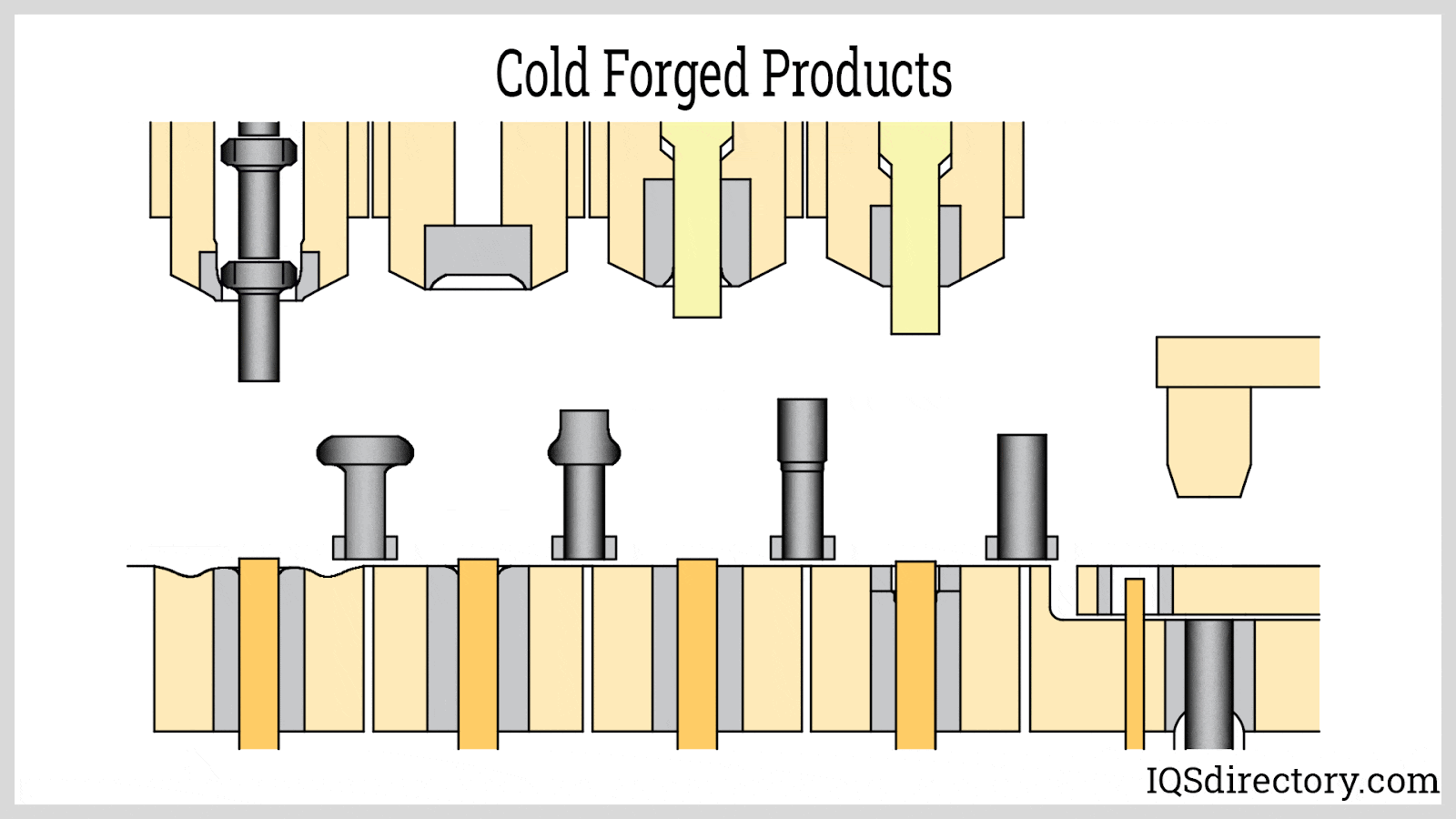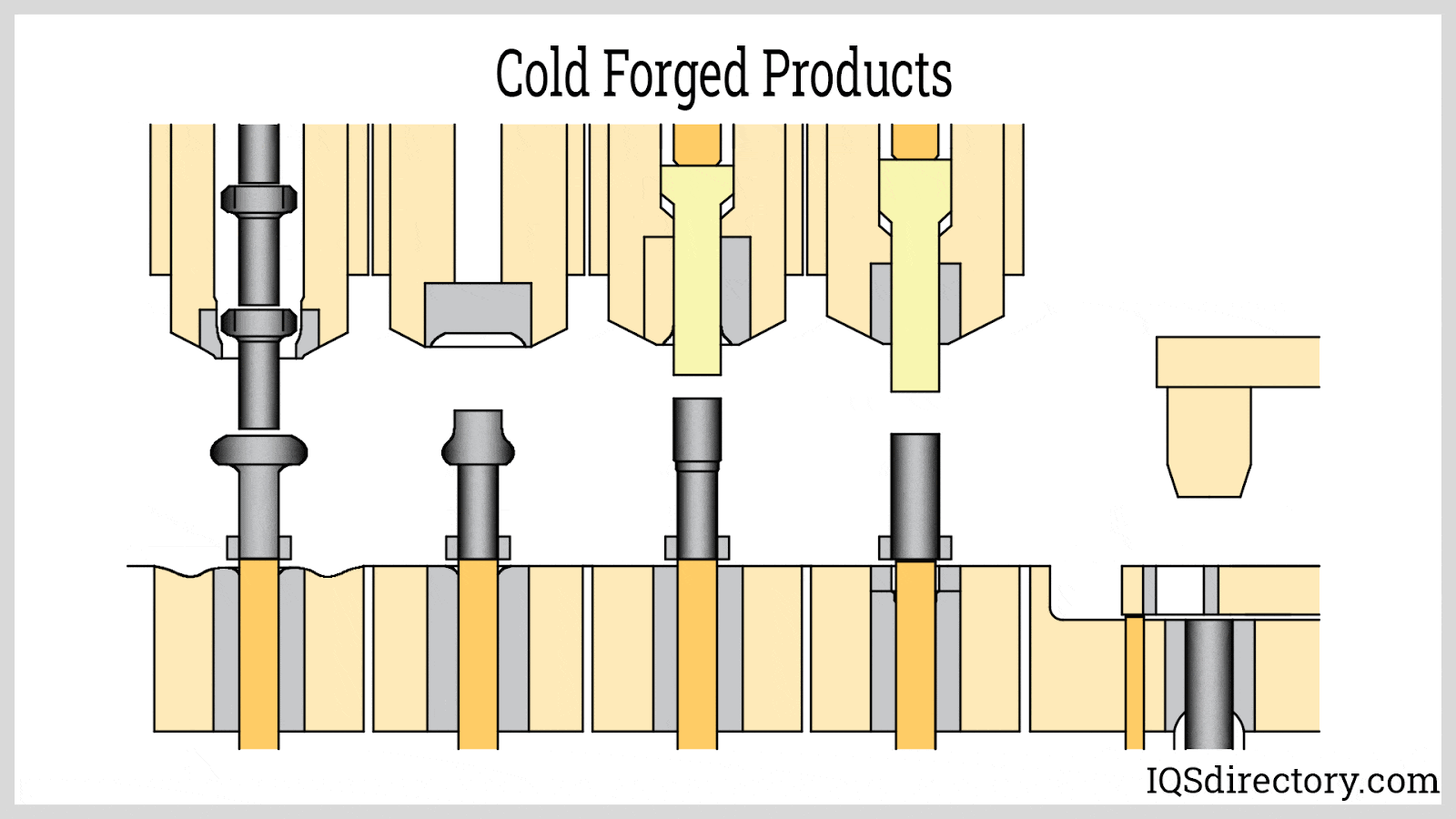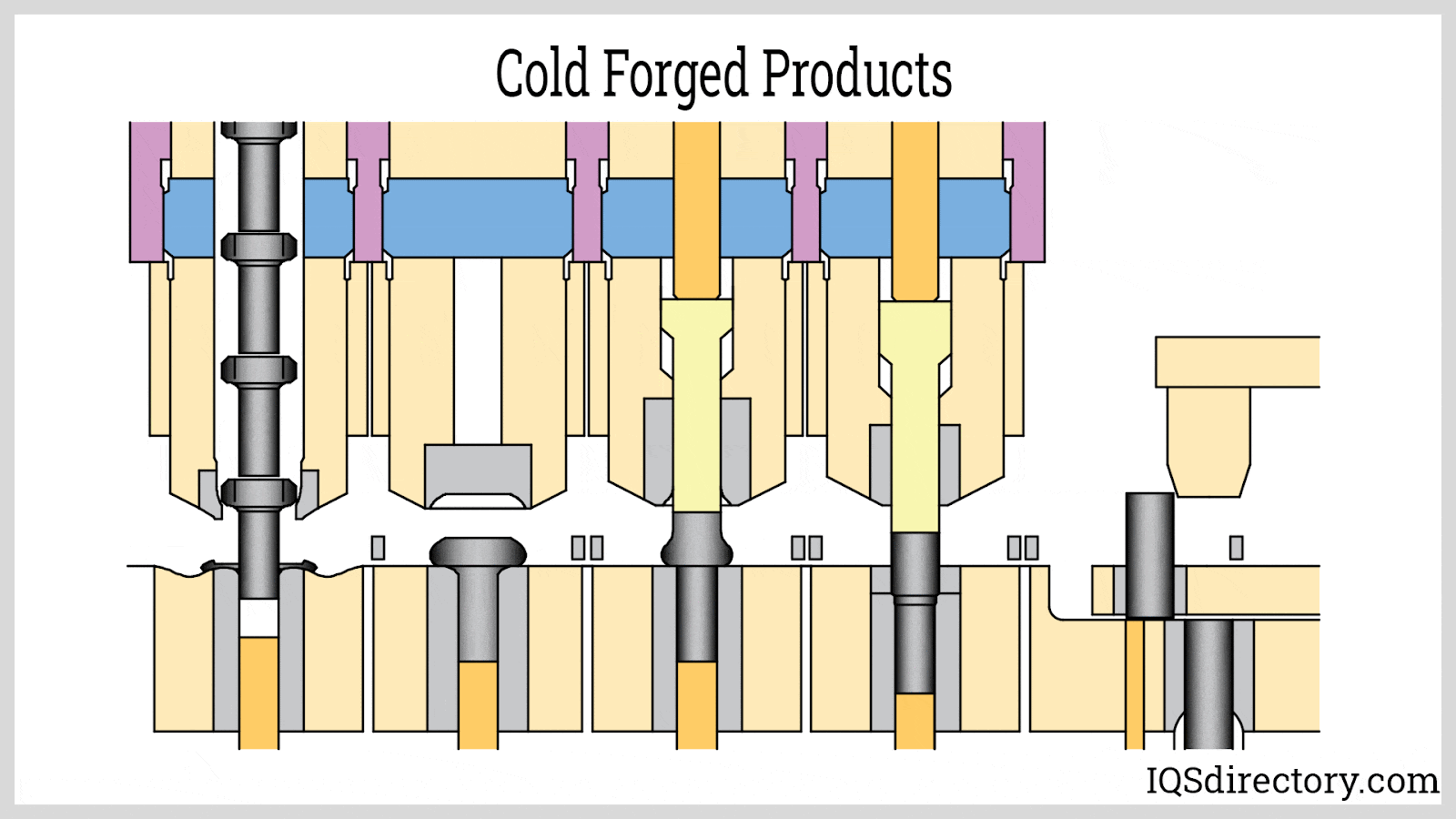
Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
The Solution:
To navigate this complexity, buyers should engage in close collaboration with material scientists and suppliers who have a deep understanding of aluminum alloys and their properties. It is advisable to conduct comprehensive material testing, including assessments of mechanical properties and behavior under stress, to make informed decisions. Additionally, exploring case studies or examples of successful applications can provide valuable insights into which alloys perform best in similar scenarios. By leveraging this knowledge and working with trusted suppliers who can provide recommendations based on their expertise, buyers can ensure that they select the most suitable materials for their cold forging projects, ultimately enhancing product performance and reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold forging aluminum
What Are the Key Materials for Cold Forging Aluminum?
When selecting materials for cold forging aluminum, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and their impact on applications. Here, we analyze four common aluminum alloys used in cold forging: AA6061, AA6082, AA7075, and AA2024. Each alloy presents unique characteristics that can significantly influence the manufacturing process and the performance of the final product.
How Does AA6061 Perform in Cold Forging?
AA6061 is a versatile aluminum alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. It offers a moderate strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive and aerospace components. The alloy can withstand temperatures up to 200°C and has good weldability, which is beneficial for complex assemblies.
Pros: AA6061 is relatively easy to forge, has good machinability, and provides excellent anodizing properties. Its cost is moderate, making it a popular choice among manufacturers.
Cons: While it has decent strength, it may not be suitable for applications requiring extremely high strength compared to other alloys like AA7075. The manufacturing complexity can increase with intricate designs.

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Impact on Application: AA6061 is compatible with various media, including water and mild chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and marine applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is crucial, especially in regions like Europe and North America. Buyers should ensure that the alloy meets local regulatory requirements.
What About AA6082 for Cold Forging Applications?
AA6082 is a high-strength alloy often used in structural applications. It provides excellent corrosion resistance and is known for its good mechanical properties, making it suitable for high-load components. The forging temperature for AA6082 can reach up to 250°C, which helps in achieving better formability.
Pros: This alloy is particularly advantageous for producing parts with narrow tolerances and complex geometries. Its good surface finish and strength make it ideal for automotive and aerospace components.
Cons: The need for soft annealing can complicate the manufacturing process, adding time and cost. Moreover, the alloy may require post-forging heat treatment to achieve optimal mechanical properties.
Impact on Application: AA6082 is suitable for applications exposed to harsh environments, including marine and industrial settings, due to its superior corrosion resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards like DIN and JIS that may apply, especially in European and Asian markets.
Why Choose AA7075 for High-Strength Applications?
AA7075 is one of the strongest aluminum alloys available, making it ideal for applications that require high strength and low weight, such as in aerospace and military applications. It can withstand high temperatures and has excellent fatigue resistance.
Pros: The primary advantage of AA7075 is its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an excellent choice for load-bearing components. It also has good machinability and can be anodized for improved corrosion resistance.
Cons: The alloy is more expensive than other options, which can be a limiting factor for budget-sensitive projects. It is also less ductile, which may restrict its use in complex shapes.
Impact on Application: AA7075 is particularly effective in high-stress environments, making it suitable for aircraft components and other critical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with aerospace standards is crucial, and buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide the necessary certifications.

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Is AA2024 a Viable Option for Cold Forging?
AA2024 is another high-strength alloy commonly used in aerospace applications. It offers excellent fatigue resistance and is often used in aircraft structures. The alloy’s performance is optimized when used in conjunction with heat treatment processes.
Pros: AA2024 has a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent machinability, making it suitable for precision components. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other high-strength alloys.
Cons: The alloy has lower corrosion resistance compared to other aluminum alloys, which may necessitate protective coatings in certain environments. Additionally, its formability can be challenging due to its high strength.
Impact on Application: AA2024 is particularly well-suited for applications requiring high strength and fatigue resistance but may require additional protective measures in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with aerospace industry standards and be aware of the specific requirements in their regions.

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Summary Table of Materials for Cold Forging Aluminum
| Material | Typical Use Case for Cold Forging Aluminum | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA6061 | Automotive and marine components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Moderate strength compared to other alloys | Medium |
| AA6082 | Structural components in aerospace | High strength and good surface finish | Requires soft annealing and post-treatment | Medium |
| AA7075 | Aerospace and military applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and lower ductility | High |
| AA2024 | Aircraft structures | Excellent fatigue resistance | Lower corrosion resistance; may need coatings | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the performance and application of various aluminum alloys in cold forging, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold forging aluminum
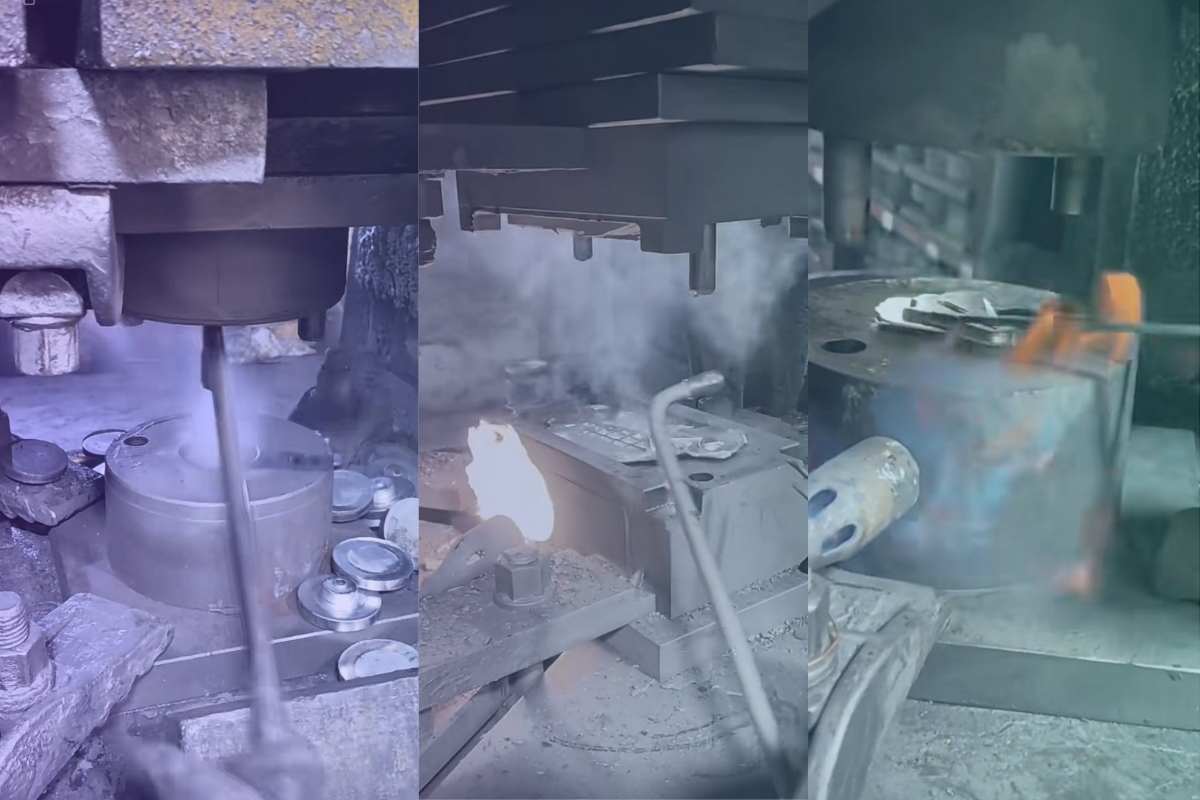
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Cold Forging Aluminum?
The cold forging process for aluminum involves several distinct stages, each critical to ensuring the quality and performance of the final product. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
1. Material Preparation: How Is Aluminum Prepped for Cold Forging?
The first step in cold forging aluminum is selecting the appropriate alloy, often high-strength aluminum alloys like AA6082, which are known for their excellent mechanical properties. The material is typically supplied in the form of bar stock, which is cut to the required lengths and subjected to processes like homogenization to enhance its properties.
Before forging, the aluminum may undergo soft annealing to improve its ductility, making it easier to shape. Lubrication is also applied to minimize friction during the forging process, which can significantly affect the final product’s surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in the Cold Forging Process?
The forming stage is where the actual shaping of the aluminum takes place. Cold forging utilizes high-pressure techniques to shape the material into the desired geometry within a closed die. This process is typically performed at room temperature, ensuring that the material retains its strength and structural integrity.
Common methods include:
- Forward and Backward Forging: This technique involves moving the material in both directions to achieve complex geometries and better material flow.
- Severe Forging Operations: For intricate designs, multiple forging operations may be necessary, sometimes requiring intermediate soft annealing to maintain formability.
- Hydraulic Presses: These are often employed to apply the necessary force for shaping, with the pressure and speed carefully controlled to avoid defects.
3. Assembly: How Are Components Joined After Forging?
Once the components have been forged, they may need to be assembled into larger structures or systems. This could involve welding, riveting, or using fasteners, depending on the application. Quality in this stage is crucial, as any misalignment can compromise the integrity of the final product.
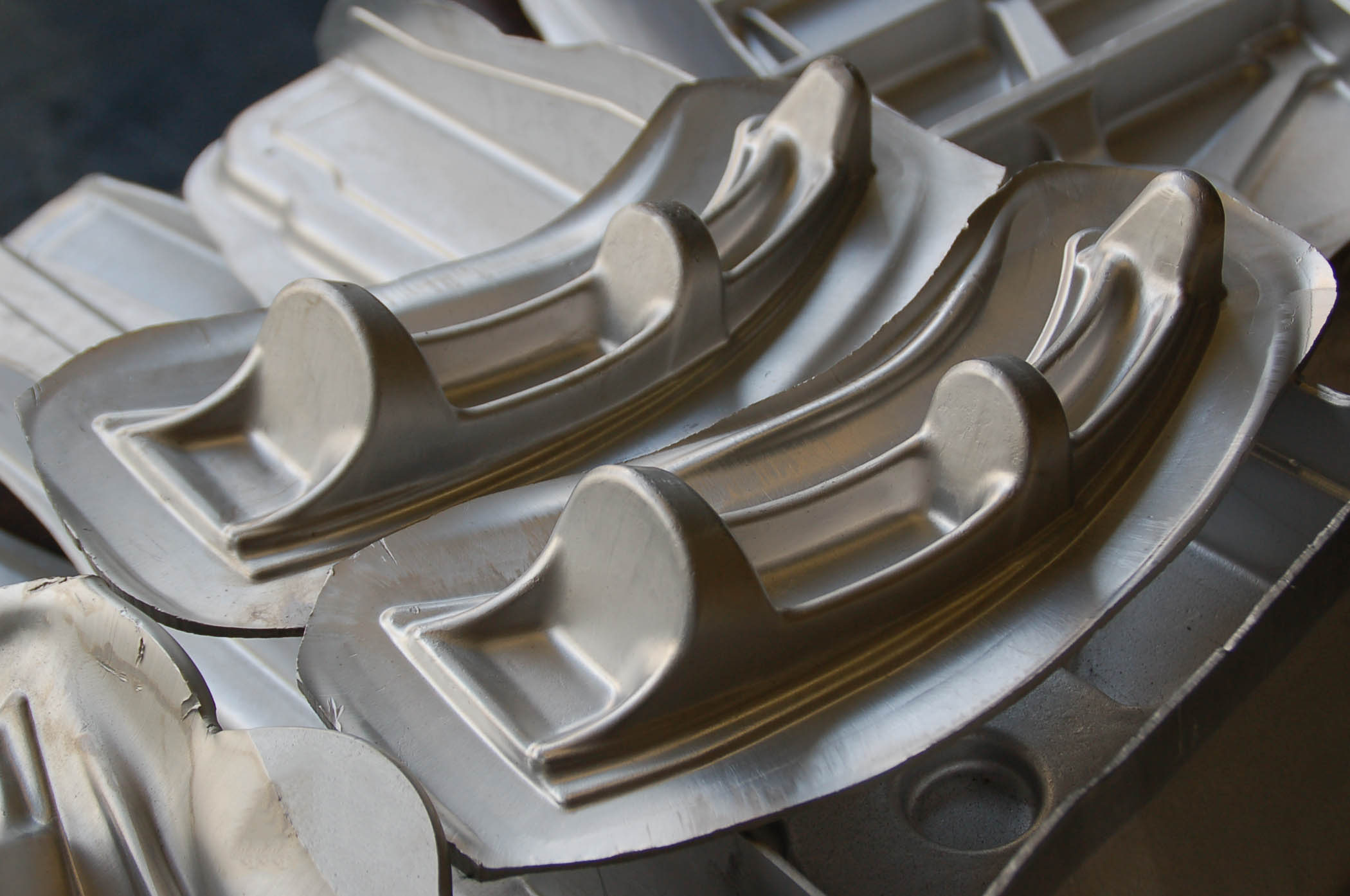
4. Finishing: What Post-Processing Techniques Are Common?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the final product’s surface quality and performance. Common finishing techniques include:
- Machining: This is often necessary to achieve tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
- Anodizing: A process that enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Coating: Various coatings can be applied for aesthetic or functional purposes, such as improving wear resistance.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Cold Forging Aluminum?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that cold-forged aluminum components meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with the key QA measures that suppliers should implement.
1. What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Several international standards govern the quality of forged aluminum components. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard ensures consistent product quality and continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Particularly important in Europe, this indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For components used in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
2. What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Cold Forging?
Quality control checkpoints should be established throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each stage meets established criteria. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves verifying the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the forging process ensures that any deviations are caught early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage involves a thorough inspection of finished components to verify they meet specifications.
3. What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
To ensure quality and performance, several testing methods can be employed, including:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the forged components.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the hardness of the aluminum, which correlates with wear resistance.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Methods such as ultrasonic or X-ray testing can detect internal defects without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
When sourcing cold-forged aluminum components, B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers.
1. What Role Do Audits Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting supplier audits is a vital step in verifying quality control practices. Audits can help assess compliance with international standards and internal QA protocols. Buyers should request access to audit reports or consider third-party audits for an impartial evaluation.
2. How Can Buyers Assess QC Reports?
Buyers should review quality control reports provided by suppliers, focusing on metrics such as defect rates, inspection results, and corrective actions taken. This information provides insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
3. What Are the Nuances of QC Certification for International Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of QC certifications is crucial. Different regions may have varying expectations and standards. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East might focus on compliance with local regulations. It’s essential to ensure that the supplier’s certifications align with the buyer’s market requirements.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in cold forging aluminum are multifaceted and crucial for ensuring high-quality components. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough quality checks, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers across the globe. This not only enhances product performance but also builds trust and reliability in international trade relationships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cold forging aluminum’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing cold forged aluminum components, this guide outlines essential steps to streamline the procurement process. By following this checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right suppliers and materials to meet their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is paramount when sourcing cold forged aluminum. This includes determining the desired alloy type, dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish. Specific requirements help suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensure the final product meets your quality standards.
- Key Considerations:
- Identify the aluminum alloy (e.g., AA6082) that aligns with your application needs.
- Specify tolerances and any critical dimensions to avoid complications during manufacturing.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct comprehensive research to identify suppliers specializing in cold forging aluminum. An effective supplier should have a proven track record in the industry and experience with the specific alloys you require.
- Important Actions:
- Review supplier websites for case studies and product offerings.
- Utilize industry directories and trade shows to discover reputable manufacturers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before finalizing your supplier choice, verify their certifications and quality management systems. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate adherence to international quality standards, ensuring consistent product quality.
- What to Look For:
- Confirm the supplier’s compliance with relevant industry standards.
- Ask for quality assurance documentation to assess their manufacturing processes.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples of the cold forged aluminum components before placing large orders. Testing samples allows you to evaluate the material’s performance, mechanical properties, and surface finish.
- Testing Considerations:
- Assess the samples under conditions that reflect your application.
- Check for dimensional accuracy and surface defects.
Step 5: Discuss Production Capabilities
Engage in discussions with potential suppliers about their production capabilities, including lead times, production volumes, and technologies used. Understanding these aspects ensures that the supplier can meet your demands efficiently.
- Questions to Ask:
- Inquire about their machinery and technology for cold forging.
- Ask about their capacity to scale production as your needs grow.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate pricing and payment terms to establish a mutually beneficial agreement. Be transparent about your budget while ensuring that quality is not compromised.
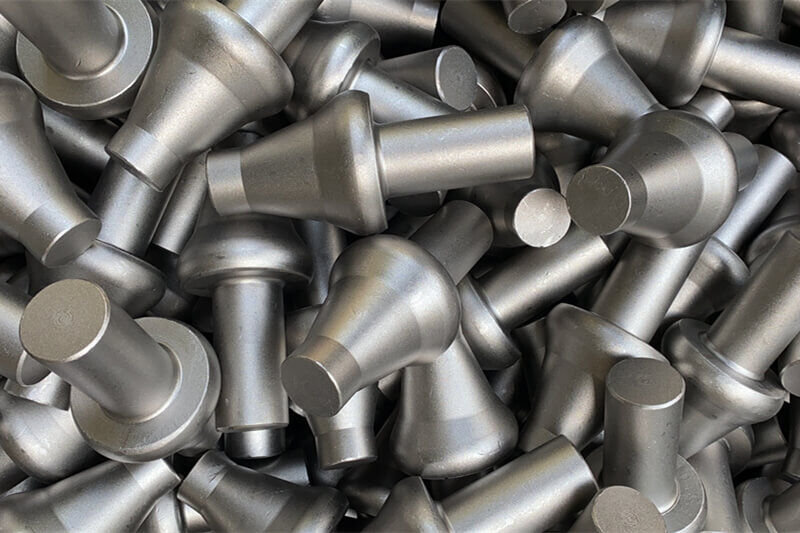

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
- Negotiation Tips:
- Discuss bulk order discounts and long-term partnership options.
- Clarify payment schedules and any additional costs that may arise.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, establish a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier. Effective communication ensures that any issues are addressed promptly and that both parties are aligned throughout the production process.
- Communication Best Practices:
- Set regular check-ins to monitor progress and address concerns.
- Use collaborative tools for sharing updates and documentation.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing cold forged aluminum components, ultimately enhancing product quality and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold forging aluminum Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Cold Forging Aluminum Sourcing?
When sourcing cold forged aluminum components, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials represent one of the most significant expenses in cold forging. The choice of aluminum alloy, such as AA6082, affects both the price and the performance of the finished product. High-strength alloys may incur higher costs but offer better durability and performance, making them suitable for specific applications like automotive components.
Labor costs are influenced by the skill level required for the forging process. Skilled labor can command higher wages but is essential for maintaining quality and efficiency.
Manufacturing overhead encompasses expenses related to the facilities, utilities, and equipment used in the forging process. Efficient manufacturing practices can help reduce these costs, impacting the final pricing structure.
Tooling expenses involve the creation and maintenance of dies and molds used in the forging process. Custom tooling can be costly, especially for unique specifications, but is often necessary for achieving precise geometrical tolerances.
Quality Control (QC) is crucial in ensuring that the forged parts meet industry standards and customer specifications. The cost associated with QC processes can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the components and the level of certification required.
Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Logistics costs include transportation and warehousing, which can vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, especially for international shipments. Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing these costs effectively.
Margins are the final piece of the cost structure, reflecting the supplier’s profit. This margin can vary based on market conditions, supplier reputation, and negotiation dynamics.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Cold Forging Aluminum Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of cold forged aluminum components. Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) are significant; higher volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers often offer tiered pricing structures, encouraging buyers to purchase larger quantities.
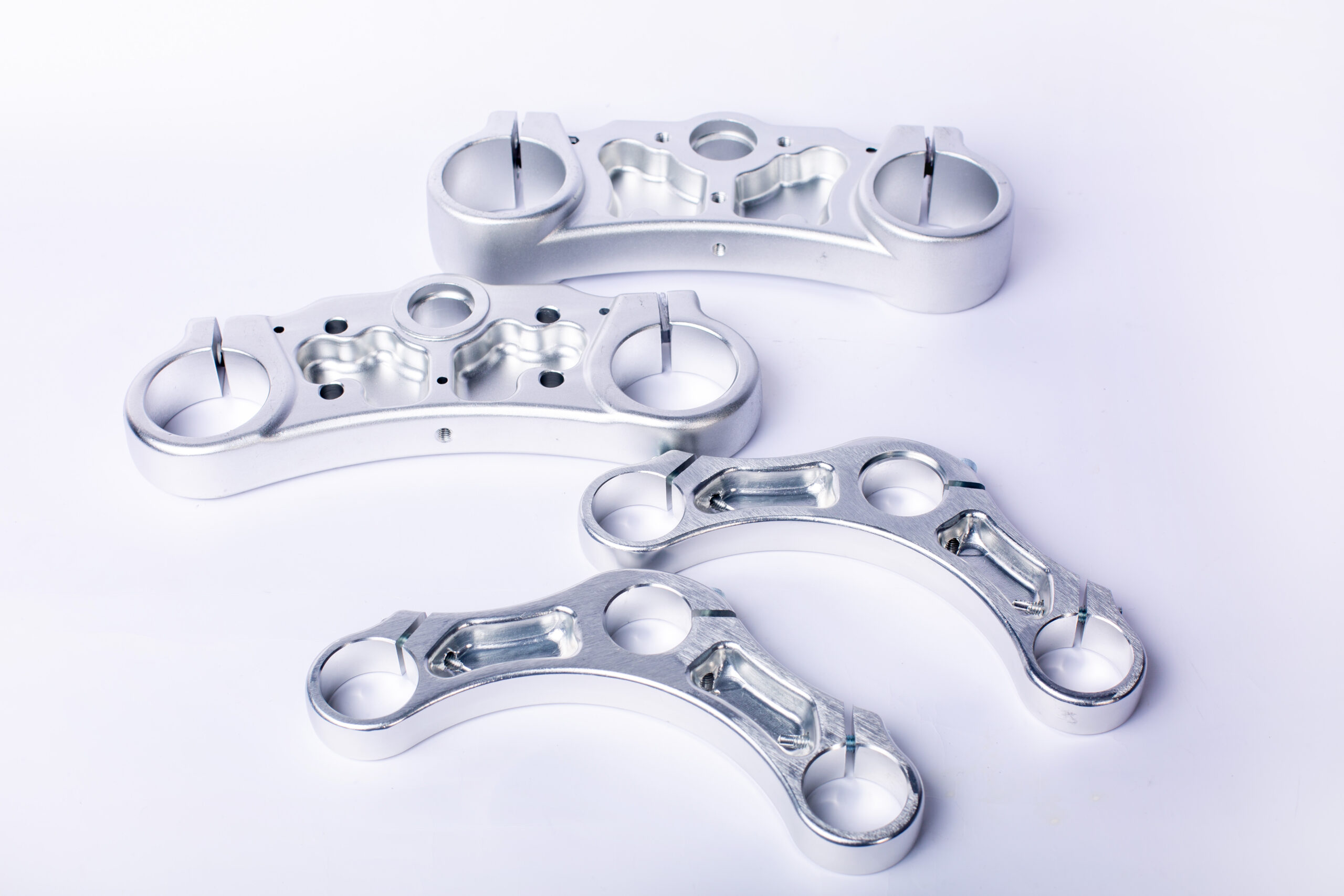

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Specifications and Customization can lead to increased costs. Custom parts require additional tooling and setup time, which can inflate prices. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
Material quality and certifications also play a critical role. Components that require specific quality certifications or meet rigorous industry standards may cost more. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher-quality materials against their budget constraints.
Supplier factors, including their location, reputation, and production capabilities, can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge a premium, but their quality assurance can lead to lower total costs in the long run.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices for Cold Forging Aluminum?
To secure favorable pricing in cold forging aluminum sourcing, buyers can employ several strategies. Negotiation is key; engaging in discussions about volume discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules can yield significant savings.
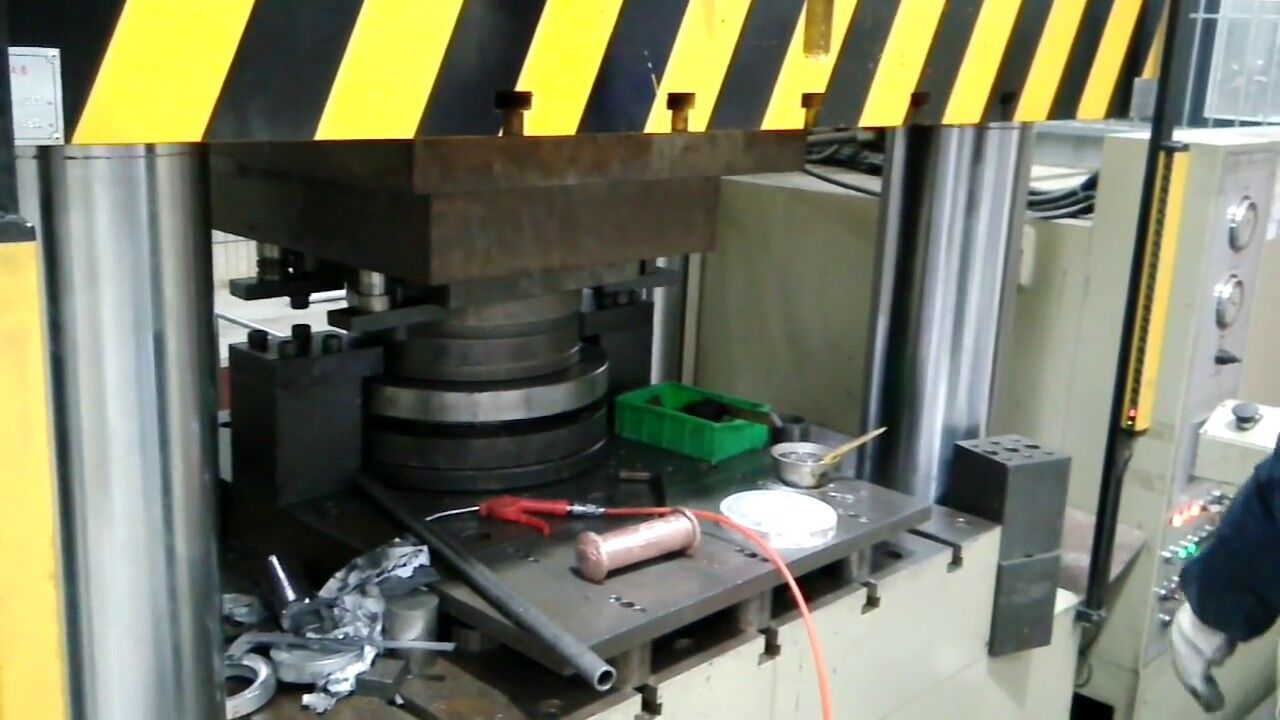

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Focusing on cost-efficiency involves evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also costs related to maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. Buyers should consider how different suppliers’ offerings align with their long-term operational goals.
Understanding pricing nuances for international transactions is essential, especially for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Factors such as currency fluctuations, import duties, and shipping costs can significantly impact overall expenses.
Lastly, buyers should always seek indicative prices rather than fixed quotes, as market conditions can fluctuate. Requesting multiple quotes from different suppliers can help establish a baseline for negotiations and ensure competitive pricing.
By keeping these cost components, price influencers, and negotiation tips in mind, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions in sourcing cold forged aluminum components, ultimately enhancing their supply chain efficiency and profitability.
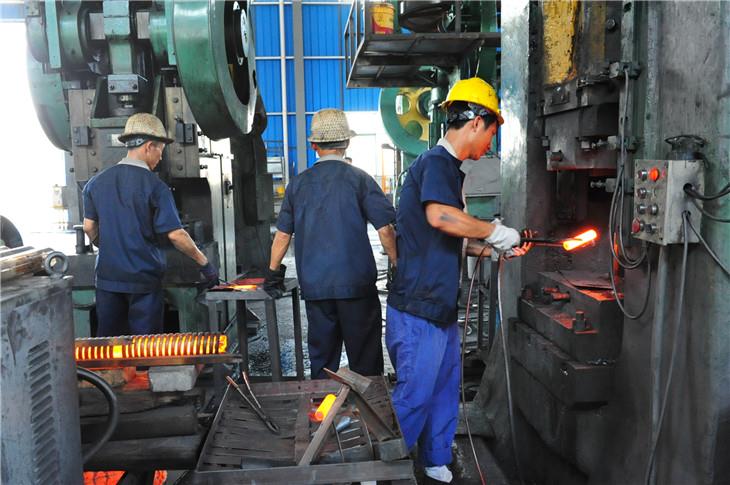

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cold forging aluminum With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Cold Forging Aluminum in Manufacturing
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, businesses are constantly seeking efficient methods to produce high-quality components while managing costs and time. Cold forging aluminum is a well-established technique, but there are several alternative solutions that may offer distinct advantages depending on specific requirements. This analysis compares cold forging aluminum with aluminum casting and warm forming, two viable alternatives in the context of performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Cold Forging Aluminum | Aluminum Casting | Warm Forming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, tight tolerances, good surface finish | Excellent for complex shapes, good surface finish | Good strength and ductility, fewer steps than cold forging |
| Cost | Moderate, lower for mass production | Higher due to material waste and energy costs | Generally lower than cold forging, varies with setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific machinery and tooling | Requires molds and skilled labor | Less complex than cold forging, adaptable machinery |
| Maintenance | Moderate; dies need regular upkeep | High; molds wear out quickly | Moderate; tooling can wear over time |
| Best Use Case | High-strength, precision components (automotive, aerospace) | Complex geometries, intricate designs (industrial applications) | Components needing good strength but simpler shapes |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Aluminum Casting
Aluminum casting is an established method that allows for the creation of intricate shapes and complex geometries. The primary advantage of this method lies in its ability to produce detailed components with minimal finishing work. However, the process can be costly due to material waste and energy consumption associated with melting aluminum. Additionally, it often results in longer lead times compared to cold forging. This method is best suited for applications where complexity outweighs the need for tight tolerances, such as in industrial machinery parts.
Warm Forming
Warm forming involves shaping aluminum at elevated temperatures, typically between room temperature and 300°C. This method strikes a balance between the rigidity of cold forging and the flexibility of hot forging. Warm forming can produce components with good strength and ductility while requiring fewer operations than cold forging. Its primary disadvantage is the need for temperature control, which can complicate the setup. This technique is ideal for producing medium to high-strength parts that require some complexity without the full rigidity of cold forging.
Making the Right Choice for Your Manufacturing Needs
When selecting the appropriate manufacturing method, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their projects, including material properties, design complexity, production volume, and budget constraints. Cold forging aluminum excels in applications that demand high strength and precision, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors. However, if your project involves intricate designs or lower production volumes, aluminum casting or warm forming may present more cost-effective and adaptable solutions. Ultimately, understanding the trade-offs between these methods will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold forging aluminum
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Cold Forged Aluminum?
Understanding the technical properties of cold forged aluminum is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of aluminum alloys, such as 6061, 6063, or 6082. Each grade has unique mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. For instance, the AA6082 alloy is often favored for its high strength and good machinability, making it ideal for automotive components. Knowing the right grade helps in selecting materials that meet specific performance requirements and regulatory standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in a forged part. In cold forging, achieving tight tolerances (often within ±0.01 mm) is essential for ensuring part fit and function, particularly in applications like automotive or aerospace. High tolerance levels can reduce the need for secondary machining operations, leading to cost savings and improved production efficiency.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and quality of the surface of the forged part. A smooth surface finish can enhance aesthetics and reduce friction in mechanical applications. For B2B buyers, specifying surface finish requirements can lead to better performance in terms of wear resistance and corrosion protection, particularly in harsh environments.
4. Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation are crucial for determining how a forged part will perform under stress. Cold forged aluminum typically exhibits enhanced mechanical properties due to work hardening. Buyers should consider these properties to ensure that the forged components can withstand operational demands without failure.

Illustrative image related to cold forging aluminum
5. Production Volume
Production volume, often measured in units per batch, is a critical factor in determining the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of cold forging. Understanding your needs regarding minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help in negotiating better terms and prices with suppliers. High-volume production can lead to economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Cold Forging Aluminum?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts that are used in another company’s end products. For B2B buyers, understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring that the components meet the required specifications and quality standards of the final product.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory and production schedules effectively. It can also affect pricing structures, as larger orders may lead to discounts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is essential for B2B buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. A well-prepared RFQ can also clarify specifications, ensuring that all parties are aligned on requirements.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of predefined commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing shipping costs, risk, and delivery timelines. For instance, terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who is responsible for costs and liabilities at various stages of shipment.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In the context of cold forging aluminum, lead times can vary based on factors such as material availability, production capacity, and complexity of the design. Understanding lead times helps in planning and ensures that project timelines are met.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making process, ensuring they choose the right suppliers and materials for their cold forging aluminum needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cold forging aluminum Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Driving the Cold Forging Aluminum Sector?
The global cold forging aluminum market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand from various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. In particular, the automotive industry is pushing for lighter materials to improve fuel efficiency, making high-strength aluminum alloys an attractive choice. This trend is further fueled by technological advancements that enhance the capabilities of cold forging processes, allowing manufacturers to produce complex geometries with high precision and reduced waste.
Emerging technologies, such as automation and Industry 4.0, are reshaping sourcing strategies within the cold forging sector. For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these shifts is crucial. The adoption of smart manufacturing techniques enables real-time monitoring of production processes, resulting in improved quality control and reduced lead times. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is facilitating better supply chain management, allowing for more accurate demand forecasting and inventory management.
Another trend shaping the market is the move towards near-net-shape production. This approach minimizes material wastage and reduces the need for extensive machining, aligning with cost-reduction strategies sought by buyers. Furthermore, as global competition intensifies, companies are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer both high-quality products and flexible service options to adapt to changing market demands.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing in the Cold Forging Aluminum Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a key consideration for B2B buyers in the cold forging aluminum sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to prioritize sustainable practices. Cold forging, as a process, is inherently more eco-friendly compared to traditional manufacturing methods because it generates less waste and requires less energy, particularly when producing parts with complex shapes.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with buyers increasingly demanding transparency in their supply chains. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers who need to ensure that their suppliers adhere to environmental regulations and ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled aluminum can enhance a supplier’s credibility and appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on circular economy principles is encouraging companies to explore recycled materials for cold forging. Utilizing recycled aluminum not only reduces the carbon footprint but also aligns with the corporate social responsibility goals of many organizations. Buyers who prioritize suppliers with sustainable practices are likely to gain a competitive advantage in their respective markets.
How Has the Cold Forging Aluminum Industry Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the cold forging aluminum industry has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, cold forging was primarily used for simpler shapes and components. However, as industries began to recognize the benefits of aluminum’s lightweight and high-strength properties, the application of cold forging expanded to more complex geometries and high-performance components.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of high-strength aluminum alloys revolutionized the sector, enabling manufacturers to produce parts with improved mechanical properties. The focus shifted towards precision manufacturing, leading to the development of sophisticated die designs and automated processes. This evolution has been particularly beneficial for the automotive and aerospace industries, where safety and performance are paramount.
Today, the cold forging aluminum sector is characterized by a commitment to innovation, sustainability, and efficiency. Continuous research and development efforts are aimed at optimizing processes and materials, ensuring that manufacturers can meet the ever-evolving needs of global markets while adhering to environmental standards. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it highlights the industry’s trajectory and underscores the importance of partnering with suppliers who are at the forefront of these advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold forging aluminum
-
1. How do I choose the right supplier for cold forging aluminum?
Selecting the right supplier involves assessing their experience, quality certifications, and production capabilities. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in aluminum cold forging and those who understand the specific requirements of your industry. Request samples to evaluate their product quality and verify their compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider their ability to provide customization options and their responsiveness to inquiries, as these factors can significantly impact your long-term partnership. -
2. What are the common applications of cold forged aluminum?
Cold forged aluminum is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries due to its lightweight and high-strength properties. Common applications include structural components, brackets, connectors, and intricate parts requiring precise tolerances. The method is particularly favored for parts that demand a smooth surface finish and enhanced mechanical properties. Understanding your application needs will help in selecting the right alloy and forging process to meet performance specifications. -
3. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for cold forged aluminum products?
MOQs for cold forged aluminum can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Typically, suppliers may set MOQs ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. Factors influencing MOQ include material costs, production setup times, and the specific requirements of your order. Always discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your project demands. -
4. How can I ensure quality assurance in cold forged aluminum products?
Implementing a robust quality assurance (QA) process is crucial for maintaining product integrity. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 from your supplier, which demonstrates their commitment to quality management. Additionally, inquire about their in-house testing capabilities, including dimensional checks, mechanical property evaluations, and surface finish inspections. Regular communication and audits can also help ensure that quality standards are consistently met throughout the production process. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing cold forged aluminum?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers and may include options such as upfront deposits, net 30/60/90 days, or letters of credit. It’s common to negotiate terms based on order size and supplier relationships. Ensure that you understand the implications of each payment method, including any associated fees or risks. Establishing clear payment terms in your contract can help mitigate misunderstandings and foster a trustworthy business relationship. -
6. How does international shipping affect my sourcing of cold forged aluminum?
International shipping can significantly impact lead times and costs. When sourcing cold forged aluminum, consider the logistics involved, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with your supplier to determine the most efficient shipping options, whether by air or sea, to minimize delays. Additionally, factor in insurance for your shipment to protect against potential losses during transit. -
7. Can I customize my cold forged aluminum components?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for cold forged aluminum components, allowing you to specify dimensions, shapes, and finishes according to your requirements. However, the extent of customization may depend on the supplier’s capabilities and the complexity of the design. Providing detailed specifications and collaborating closely with the supplier during the design phase can help ensure that the final product meets your exact needs. -
8. What are the advantages of cold forging aluminum compared to other methods?
Cold forging aluminum offers several advantages, including enhanced strength, improved surface finish, and reduced material waste. The process allows for tight tolerances and complex geometries that are often challenging to achieve with other methods, such as casting or machining. Additionally, cold forging typically requires less energy and results in lower production costs, making it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking efficient and sustainable production methods.
Top 9 Cold Forging Aluminum Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Aluminum Forging Techniques
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Aluminum forging is a method to process aluminum alloys by applying pressure and heat to create durable parts. Key types of aluminum forging include hot forging and cold forging, with advanced techniques such as drop forging, press forging, upset forging, roll forging, rolled ring forging, isothermal forging, open die forging, and closed die forging. Aluminum alloys used for forging include 6061, …
2. iForge Iron – Aluminum Forging Solutions
Domain: iforgeiron.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Forging aluminum is possible, particularly with soft aluminum alloys, but requires careful temperature management. Aluminum melts at around 1350 degrees F, which is lower than iron/steel. Common forging methods include open die forging, closed forging, and ring rolled forging. Precautions should be taken to avoid toxic fumes during the process. Forging can be done cold with plate aluminum, but ove…
3. Reddit – Aluminum Forging Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Forging aluminum parts from billet aluminum using traditional hand hammer and anvil is discussed. The feasibility of this process is questioned, with insights from users who have experience forging aluminum. Key points include: aluminum is temperamental to forge, it can crumble at high temperatures (hot shortness), and commercial forging typically uses dies in presses on cold metal. Users mention …
4. ForceBeyond – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: forcebeyond.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Cold forging products supplied by ForceBeyond for over a decade, serving industries such as energy, automotive, marine, and rail. Cold forging deforms metal at room temperature, ideal for softer metals like aluminum, producing parts with minimal finishing. The process involves inserting bar stock into a die and applying pressure with a second die. Equipment includes vertical presses, either hydrau…
5. Unior Tools – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: uniortools.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Cold forging, also known as cold forming, is a manufacturing process that shapes metal at near room temperature using mechanical or hydraulic presses, or automated multi-station machines. Key advantages include savings in material and final machining, high productivity, excellent dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and improved mechanical properties. Cold forged parts are used in various indust…
6. Thermocool Corp – Cold Forging Heat Sinks
Domain: thermocoolcorp.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Product: Cold Forging Heat Sinks
Materials: Aluminum A1060, Aluminum AL1100, Aluminum A6061, Pure Copper CDA 110
Specifications:
– Max diameter/width: <= 120mm
– Max height: <= 80mm
– Fin height to minimum gap ratio: 25:1
– Fin thickness: >= 0.7 mm
Applications:
– High performance electronics
– Multi-chip modules
– LED cooling
Manufacturing Process: Cold forging using localized compressed f…
7. CX Inforging – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: cxinforging.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Cold forging of aluminum alloys offers several advantages over hot forging, including high workpiece accuracy, good strength, low material and energy consumption, low total processing cost, high production efficiency, and ease of automation. However, it also has challenges such as the need for large tonnage equipment, high mold material strength and toughness, complex mold structures, and a narrow…
8. Bunty LLC – Cold Forging Solutions
Domain: buntyllc.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Bunty LLC – Cold Forging Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
9. Sunrise Metal – Aluminum Forging Solutions
Domain: sunrise-metal.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Aluminum forging is a process that manipulates aluminum alloys at high temperatures and pressure to create durable components for various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and defense. Key details include: 1. **Forging Process**: Involves pre-forging preparation (aluminum alloy selection and billet heating), forging operation (die design, heating, and temperature control), and post-forg…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold forging aluminum
As businesses navigate the complexities of global supply chains, understanding the strategic sourcing of cold forged aluminum becomes increasingly vital. The cold forging process not only enhances the mechanical properties of high-strength aluminum alloys but also ensures precision in manufacturing intricate components. Buyers can leverage these benefits to reduce costs while maintaining high quality and efficiency in production, especially for industries such as automotive and aerospace.
In strategically sourcing cold forged aluminum components, companies should prioritize suppliers that can provide advanced manufacturing capabilities and a commitment to sustainable practices. The ability to produce near-net shape products with tight tolerances means reduced waste and lower overall production costs, which are crucial for maintaining competitiveness in the global market.
Looking ahead, the demand for lightweight, durable materials is set to rise, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. International B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with innovative suppliers who are not only equipped to meet current demands but are also adaptable to future advancements in forging technology. Embrace the potential of cold forging aluminum today to drive your business forward in an ever-evolving landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.