How to Source Check Valve Internals Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for check valve internals
In the complex landscape of industrial operations, sourcing high-quality check valve internals can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Often misunderstood and misapplied, check valves are essential components that prevent backflow in a variety of fluid systems, yet they are frequently blamed for operational failures when used incorrectly. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify check valve internals by exploring their various types, applications, and the critical factors to consider during the procurement process.
Buyers will gain insights into the different styles of check valves—such as swing, piston, and poppet types—each suited for specific applications across industries including oil and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing. Furthermore, the guide addresses the importance of proper supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable manufacturers who meet their unique operational needs. We will also delve into cost considerations, helping businesses make informed purchasing decisions that align with their budgetary constraints.
Designed specifically for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—this guide empowers you to navigate the global market with confidence. By providing actionable insights and expert recommendations, we aim to enhance your procurement strategies, ensuring that you select the most effective check valve internals for your operational requirements.
Understanding check valve internals Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swing Check | Hinged disc design, gravity-assisted closure | Water, wastewater, and HVAC systems | Pros: Good flow capacity, easy maintenance. Cons: Not suitable for vertical flow; prone to water hammer. |
| Piston/Poppet Check | Spring-assisted disc, silent operation | Pump discharge, chemical processing | Pros: Fast-closing, minimizes water hammer. Cons: Best for clean media only; requires specific installation. |
| Ball Check | Spherical disc that seals against a seat | Oil and gas, petrochemical industries | Pros: Compact design, reliable sealing. Cons: Limited to certain flow rates; can be prone to clogging. |
| Tilting Disc Check | Disc tilts to close, allowing for higher flow rates | Fire protection systems, HVAC | Pros: High flow capacity, effective sealing. Cons: Not suitable for low backpressure; requires horizontal installation. |
| Dual Plate Check | Two plates that open and close with flow direction | Marine, power generation, and HVAC systems | Pros: Compact, lightweight, and quick response. Cons: More complex design may increase maintenance needs. |
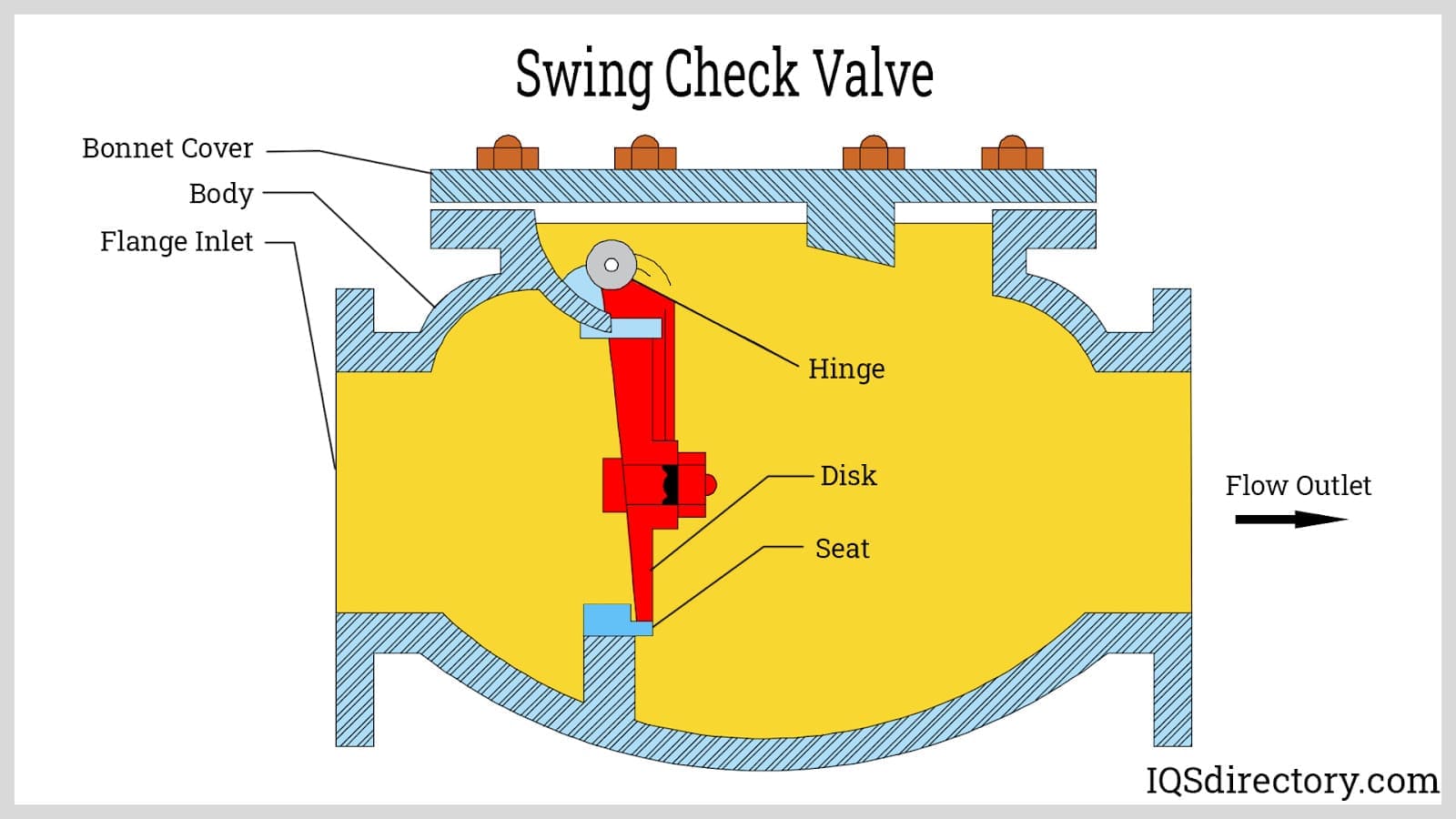
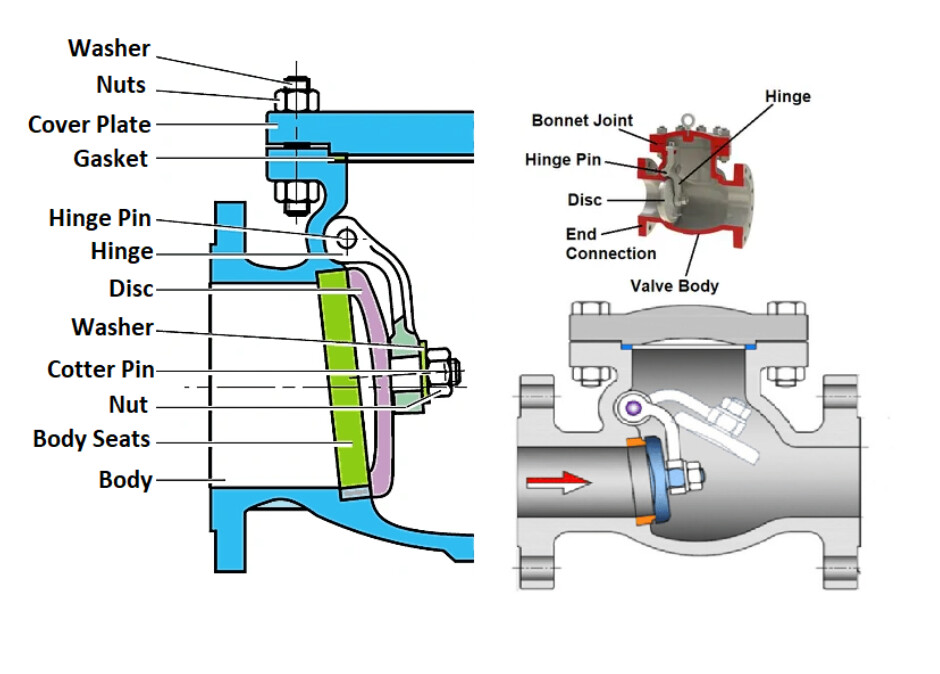
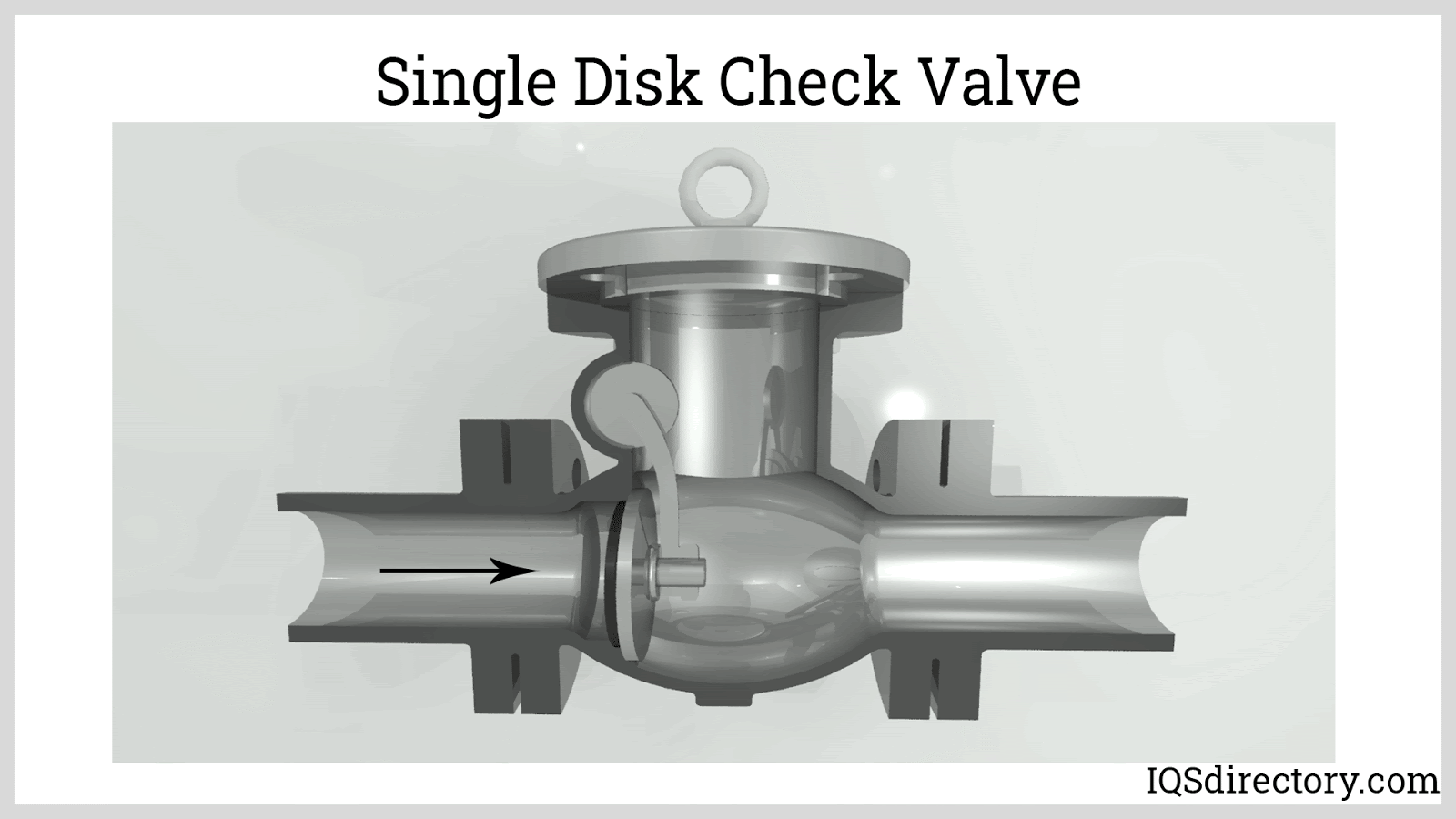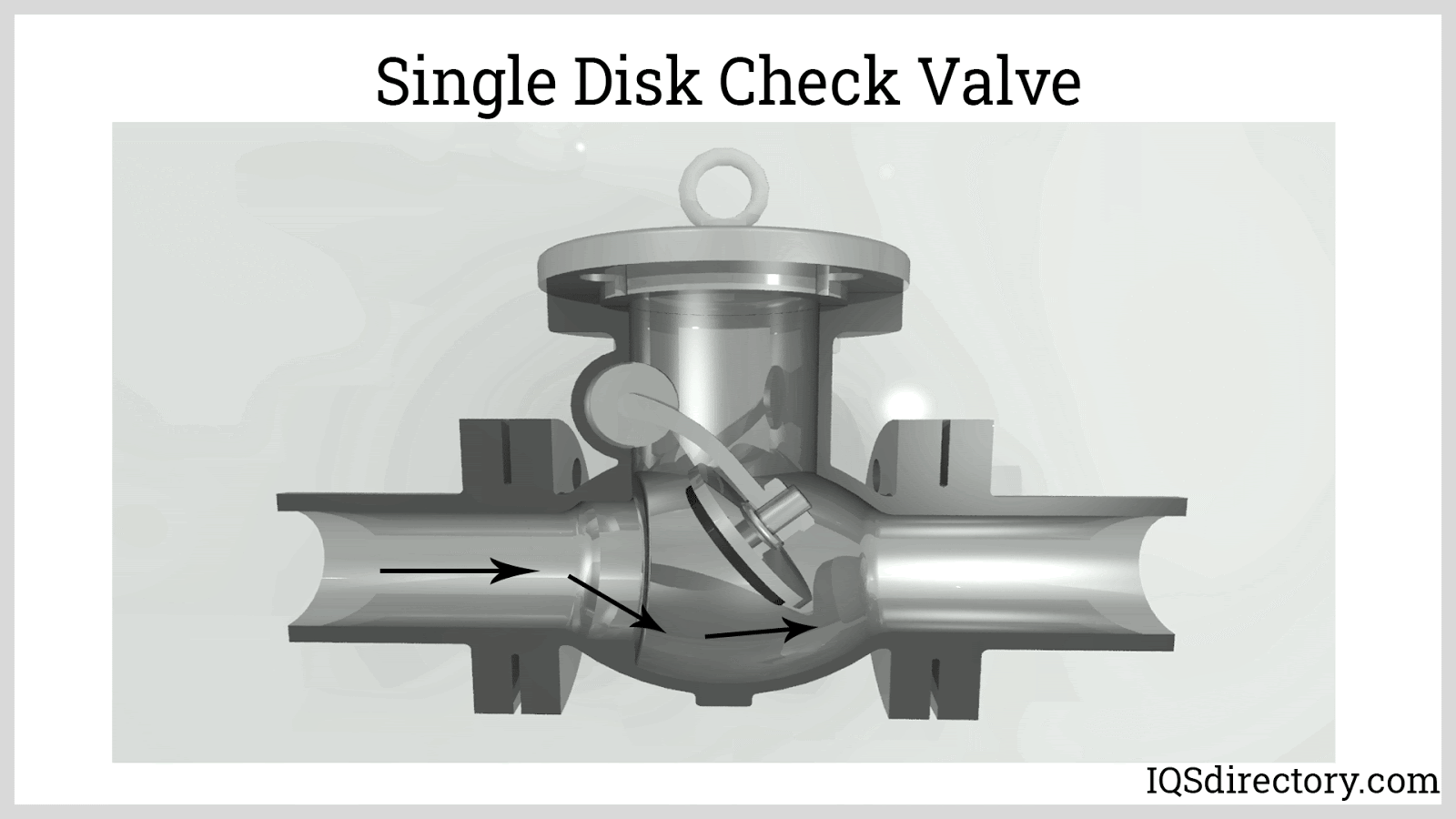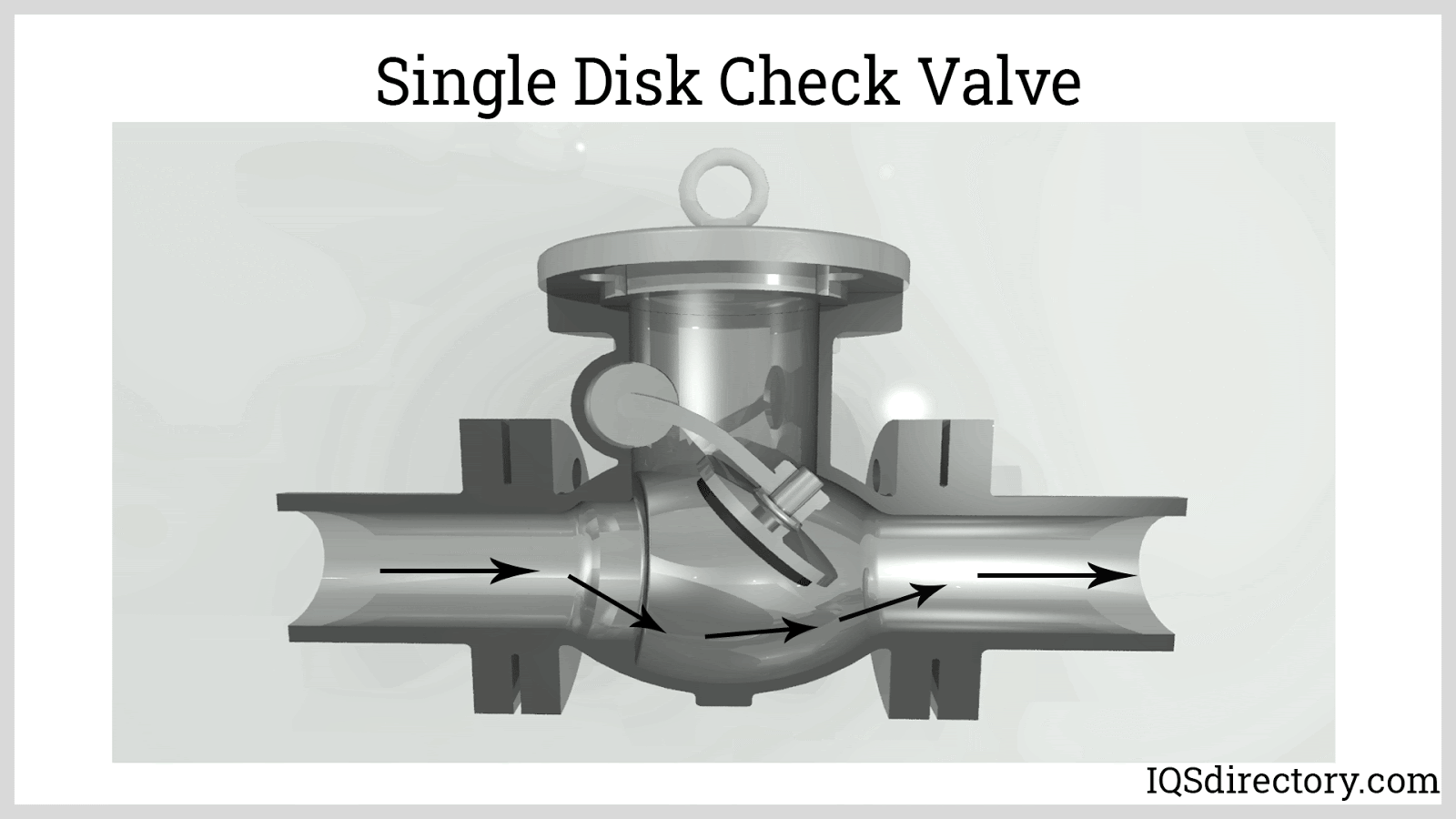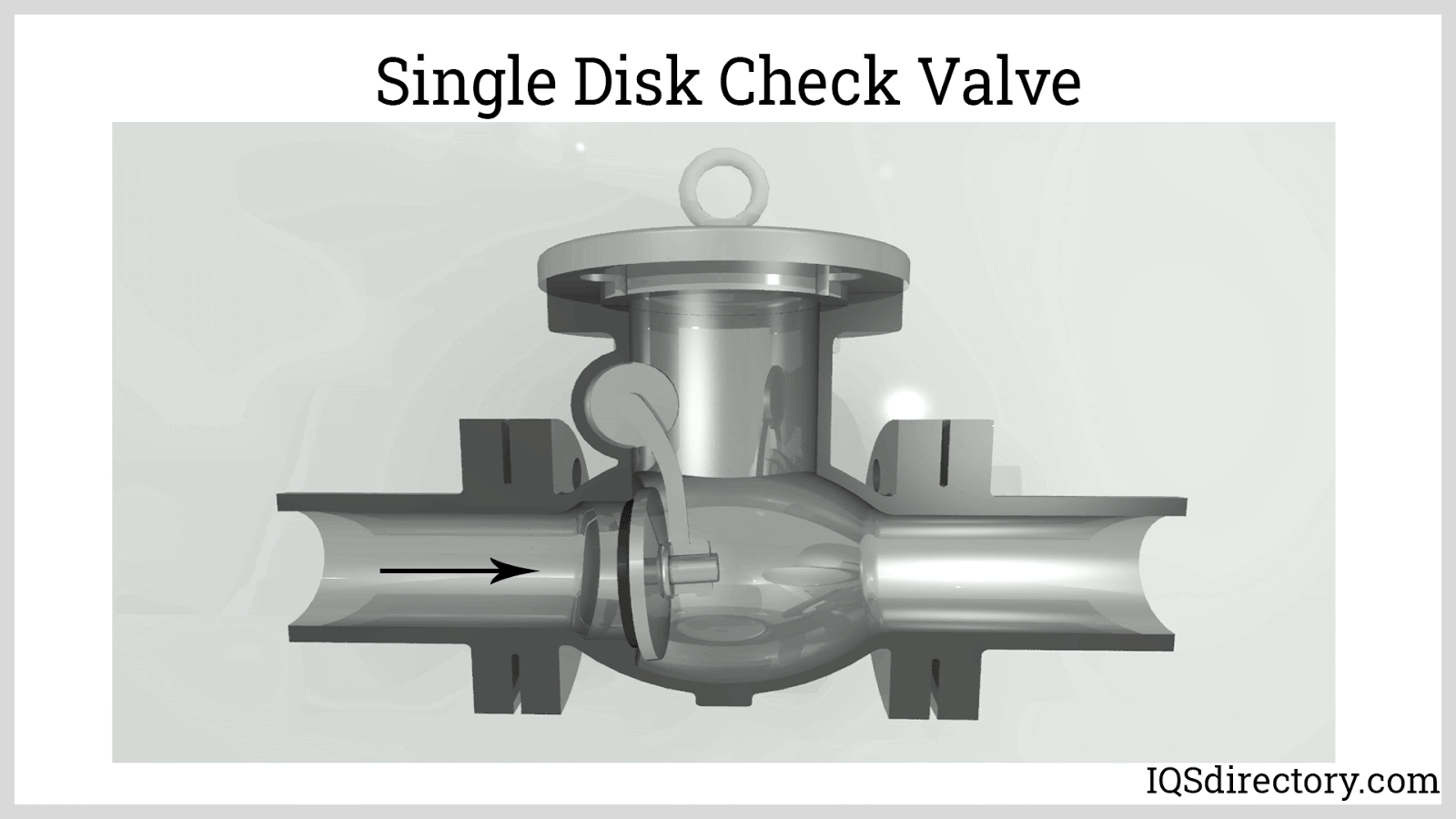
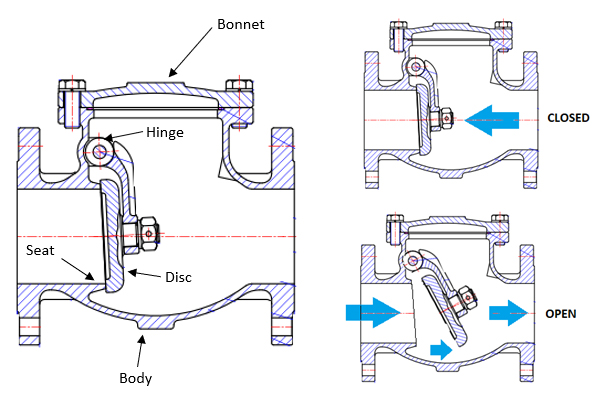
What Are the Characteristics of Swing Check Valves?
Swing check valves feature a disc attached to a hinge, allowing it to swing open with forward flow and close against reverse flow, aided by gravity. They are primarily used in water and wastewater applications, as well as HVAC systems. Buyers should consider installation orientation, as these valves function best in horizontal positions. While they offer easy maintenance and good flow capacity, they are susceptible to water hammer and may not seal effectively in low backpressure situations.
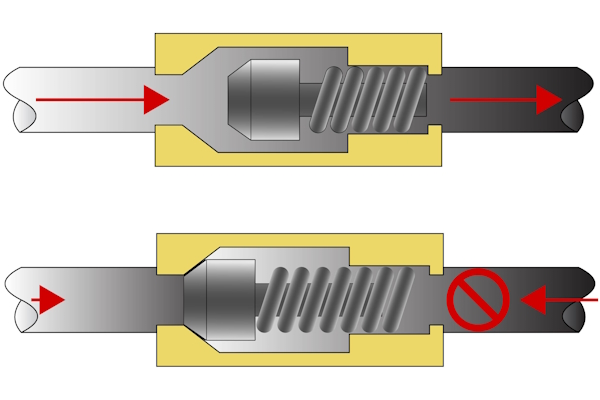
How Do Piston/Poppet Check Valves Operate?
Piston or poppet check valves utilize a spring-assisted disc that opens with flow and closes quickly to prevent backflow, minimizing the risk of water hammer. They are suitable for pump discharge and chemical processing applications, where maintaining system integrity is crucial. When purchasing, consider the media type, as these valves are ideal for clean applications. Their rapid closure can be advantageous, but installation specifics must be adhered to for optimal performance.
What Makes Ball Check Valves Unique?
Ball check valves utilize a spherical disc that seals against a seat to prevent backflow. Their compact design makes them suitable for oil and gas applications, as well as petrochemical industries. When considering a ball check valve, it’s essential to evaluate the expected flow rates, as they may not perform well under all conditions. While they provide reliable sealing, potential clogging issues should be noted, especially with viscous or particulate-laden media.
Why Choose Tilting Disc Check Valves?
Tilting disc check valves feature a disc that tilts rather than swings, allowing for higher flow rates and effective sealing. Commonly used in fire protection and HVAC systems, they offer significant advantages in high-flow scenarios. However, they must be installed horizontally and may not perform well under low backpressure. Buyers should assess the specific application requirements and flow characteristics to ensure compatibility and optimal functionality.
Illustrative image related to check valve internals
What Are the Advantages of Dual Plate Check Valves?
Dual plate check valves consist of two plates that open and close in response to flow direction, making them suitable for marine, power generation, and HVAC systems. Their lightweight and compact design allows for easy installation and quick response to flow changes. However, the complexity of their design may lead to increased maintenance requirements, which should be factored into purchasing decisions. Assessing the operational environment will help ensure that dual plate check valves meet the intended application needs effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of check valve internals
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of check valve internals | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water and Wastewater | Pump discharge systems | Prevents backflow, ensuring system integrity and efficiency | Material compatibility with water and waste, pressure ratings, and maintenance ease |
| Oil and Gas | Pipeline flow management | Ensures safe, reliable operation by preventing reverse flow | High-pressure ratings, material durability in corrosive environments, and compliance with industry standards |
| Food and Beverage | Processing and bottling lines | Maintains hygiene and prevents contamination | Compliance with food safety regulations, material certifications, and ease of cleaning |
| Chemical Processing | Chemical feed systems | Protects equipment from backflow, reducing downtime | Chemical compatibility, pressure and temperature ratings, and reliability under varying flow conditions |
| HVAC Systems | Condensate drainage | Prevents system damage from reverse flow | Size and type for specific applications, pressure requirements, and ease of installation |
How Are Check Valve Internals Utilized in Water and Wastewater Applications?
In water and wastewater treatment facilities, check valve internals are crucial for pump discharge systems. They allow for the unidirectional flow of water while preventing backflow, which can compromise system integrity and efficiency. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, must consider the compatibility of materials with various water qualities and ensure that the valves can withstand the pressure ratings typical in these applications. Regular maintenance access is also a significant factor to reduce downtime.
What Role Do Check Valve Internals Play in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, check valve internals are integral to pipeline flow management. They prevent reverse flow, thereby ensuring safe and reliable operation of the pipelines. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing valves with high-pressure ratings and materials that are durable in corrosive environments. Compliance with industry standards is critical to avoid operational risks and costly failures.
How Are Check Valve Internals Essential in Food and Beverage Processing?
In food and beverage processing, check valve internals are vital in processing and bottling lines. They help maintain hygiene by preventing contamination from backflow, which is essential for food safety. B2B buyers in Europe and Africa need to ensure that the valves comply with food safety regulations and possess the necessary material certifications. Furthermore, ease of cleaning is a crucial consideration to maintain operational efficiency and product quality.
What Benefits Do Check Valve Internals Provide in Chemical Processing?
Check valve internals in chemical processing applications are essential for chemical feed systems. They protect equipment from backflow, which can lead to downtime and costly repairs. Buyers must prioritize chemical compatibility when sourcing these valves, as well as ensure they meet pressure and temperature ratings specific to their processes. Reliability under varying flow conditions is also a key factor in selecting the right check valve internals.
How Are Check Valve Internals Used in HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, check valve internals are used primarily in condensate drainage applications. They prevent system damage caused by reverse flow, which can lead to inefficiencies or failures. For international buyers, particularly in regions with varying climates, selecting the appropriate size and type of check valve for specific applications is crucial. Additionally, understanding the pressure requirements and installation ease can significantly impact the overall system performance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘check valve internals’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment in Application and Valve Selection
The Problem: A manufacturing plant in Nigeria recently installed several check valves to prevent backflow in its piping system. However, after a few months, operators noticed frequent valve failures and increased maintenance costs. The check valves were misapplied in a low-pressure system where their design was not suitable. Many personnel blamed the valves themselves, believing they were faulty, not realizing the root cause was improper selection based on application requirements. This misalignment not only led to operational inefficiencies but also wasted financial resources on replacements and repairs.
The Solution: To prevent such costly mistakes, it is crucial to perform a thorough application analysis before selecting check valve internals. B2B buyers should engage with manufacturers or valve specialists to assess specific requirements, including pressure ranges, flow characteristics, and the nature of the media being transported. When selecting check valves, consider their operating conditions, such as whether they will handle clean liquids or corrosive chemicals. Utilizing flow simulations or consulting engineering guidelines can help ensure the selected valve type—be it swing, piston, or poppet—is ideal for the application. Additionally, regular maintenance schedules should be established to monitor valve performance and identify potential issues before they escalate.
Scenario 2: Pressure Drop and Flow Restriction Issues
The Problem: A company in Saudi Arabia was facing challenges with inconsistent flow rates in their industrial process, leading to production delays. After investigation, it was found that the installed check valves were causing significant pressure drops due to improper sizing. The valves were selected based on line size rather than flow requirements, resulting in partial opening under lower flow conditions. This scenario not only hampered the overall efficiency of the system but also increased operational costs due to energy inefficiencies.
The Solution: To address pressure drop issues, B2B buyers should prioritize correct sizing when sourcing check valve internals. It is essential to calculate the Cv (flow coefficient) needed based on the specific flow rates of the application rather than defaulting to the line size. Engaging with valve manufacturers for flow analysis and selecting valves with appropriate flow characteristics can mitigate these challenges. Implementing a comprehensive testing phase, where flow rates are monitored post-installation, can further ensure that the chosen valves perform effectively. If pressure drop issues persist, consider exploring alternative valve designs or integrating bypass systems to enhance flow stability.
Scenario 3: Longevity and Wear of Valve Internals
The Problem: A water treatment facility in Brazil experienced frequent failures of check valve internals due to wear and tear, leading to costly downtime. The facility used elastomer-seated valves that were not compatible with the chemical media they were treating. As a result, the seats degraded quickly, causing leaks and allowing backflow, which disrupted operations and jeopardized the treatment process. The facility’s management was frustrated, as they had not anticipated the chemical compatibility issues affecting the longevity of their valve internals.
The Solution: To enhance the longevity of check valve internals, B2B buyers must conduct a thorough compatibility assessment of materials against the media they will handle. When sourcing check valves, it is essential to inquire about the materials used for seats and seals, ensuring they are suitable for the specific chemical environment. Consulting with manufacturers for expert recommendations on materials like PTFE or specific elastomers can significantly improve durability. Regular inspections should be scheduled to monitor wear patterns and replace components proactively before they lead to failure. Additionally, creating a feedback loop with operators can help identify any recurring issues related to valve performance, allowing for timely adjustments and replacements.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for check valve internals
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Check Valve Internals?
When selecting materials for check valve internals, understanding the properties and performance characteristics of each material is critical. The most commonly used materials include stainless steel, brass, cast iron, and various polymers. Each of these materials has unique attributes that make them suitable for specific applications.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Check Valve Internals?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, making it a preferred choice for check valve internals in harsh environments. With a temperature rating that can exceed 200°C and pressure ratings up to 1500 psi, stainless steel is suitable for a wide range of applications, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment.
Pros: Stainless steel offers durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements. It is also compatible with various media, including corrosive fluids, which makes it versatile.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to other materials, which may be a concern for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for specialized machining processes.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, especially in regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria, compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes is essential. Buyers should also consider the local availability of this material to avoid delays.
What Advantages Does Brass Provide for Check Valve Internals?
Brass is another common material used in check valve internals, particularly for smaller valves. It exhibits good corrosion resistance and can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, typically up to 120°C and 300 psi.
Illustrative image related to check valve internals
Pros: Brass is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, making it a cost-effective option for manufacturers. Its excellent sealing properties make it suitable for applications involving water and low-pressure gas.
Cons: However, brass is less durable than stainless steel and may not perform well in highly corrosive environments. It is also susceptible to dezincification, which can weaken the material over time.
Impact on Application: For buyers in South America and the Middle East, it’s crucial to ensure that brass components meet local standards, such as ASTM B16 for brass fittings. Understanding the specific media compatibility is also vital to prevent premature failure.
Why Is Cast Iron a Popular Choice for Check Valve Internals?
Cast iron is often used for larger check valves due to its strength and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. It can handle pressures up to 250 psi and temperatures around 200°C, making it suitable for water and wastewater applications.
Pros: The durability of cast iron makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, and it is generally more affordable than stainless steel.
Cons: However, cast iron is prone to corrosion and may require protective coatings, which can add to manufacturing complexity. It is also heavier, which can be a disadvantage in certain installations.
Impact on Application: Buyers in Europe and Africa should be aware of the need for compliance with standards such as EN 10204 for material certification. Additionally, the weight of cast iron may impact transportation and installation costs.
How Do Polymers Compare for Check Valve Internals?
Polymers, such as PTFE and PVC, are increasingly used in check valve internals, particularly in applications involving corrosive media. These materials can handle temperatures up to 100°C and pressures of around 150 psi.

Illustrative image related to check valve internals
Pros: Polymers are lightweight, resistant to a wide range of chemicals, and often provide excellent sealing capabilities. They are also cost-effective for specific applications.
Cons: However, polymers may not withstand high temperatures or pressures as effectively as metals. Their mechanical strength is also lower, which can limit their use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, especially in developing regions, ensuring compliance with standards such as ASTM D1784 for PVC is essential. Buyers should also consider the specific chemical compatibility of the polymer with the media being used.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Check Valve Internals
| Material | Typical Use Case for check valve internals | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, chemical processing | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | Water and low-pressure gas applications | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Water and wastewater applications | Durable and affordable | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Polymers | Corrosive media applications | Lightweight and chemical resistant | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for check valve internals
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Check Valve Internals?
The manufacturing process for check valve internals involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure quality and performance. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The selection of materials is crucial in manufacturing check valve internals, as they must withstand various pressures and corrosive environments. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, carbon steel, and specialized alloys such as Hastelloy or Inconel. The preparation phase involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, which are then inspected for compliance with industry standards. This includes checking for mechanical properties, chemical composition, and surface integrity.
-
Forming: The forming process can vary depending on the type of valve being produced. Techniques such as casting, forging, or machining are commonly employed. For instance, precision machining is often used to create the internal components like discs and seats, ensuring that they fit perfectly together to prevent leaks. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining are utilized to achieve high precision and repeatability, which is essential for maintaining consistent quality.
-
Assembly: After the individual components are formed, they undergo an assembly process. This stage may include installing seals, springs, and other internal mechanisms necessary for the valve’s operation. Care is taken to ensure that each component is installed correctly to avoid issues such as disc chatter or improper sealing. Automated assembly lines may be used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
-
Finishing: The finishing stage includes surface treatments such as polishing, coating, or plating to enhance corrosion resistance and improve durability. Processes like passivation are often employed for stainless steel components to remove free iron and enhance corrosion resistance. This stage is vital, especially for valves that will be used in harsh environments, as it significantly affects the overall longevity and reliability of the valve.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Check Valve Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each check valve meets stringent performance and safety standards. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA process.
-
International Standards: Compliance with ISO 9001 is critical for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate a commitment to quality management systems. This standard outlines requirements for consistent quality in product design, development, production, installation, and service. Manufacturers are encouraged to adopt a continuous improvement mindset to enhance quality and customer satisfaction.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: In addition to ISO standards, check valve manufacturers often adhere to industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for valves used in the oil and gas sector. These certifications provide assurance that the products meet essential health, safety, and environmental protection requirements.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated into the manufacturing process. These typically include:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected for conformity to specifications before being accepted into the production process.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections are conducted throughout the manufacturing stages to detect any deviations from quality standards early on.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished products undergo rigorous testing, including pressure testing, leakage testing, and functional testing to ensure that they meet the required specifications before shipping.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Check Valve Internals?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the performance and reliability of check valve internals. These methods help identify any defects or inconsistencies that could lead to failures in real-world applications.
-
Hydraulic Testing: This involves subjecting the valve to a specified pressure to ensure it can withstand operational conditions without leaking. Hydraulic tests are essential for verifying the integrity of seals and joints.
-
Leak Testing: Various methods, such as bubble testing or pressure decay testing, are utilized to check for leaks in the valve assembly. Ensuring a leak-tight seal is crucial, especially for applications involving fluids under pressure.
-
Functional Testing: This test simulates the operational conditions of the valve to ensure it opens and closes correctly. Functional tests help confirm that the internal mechanisms, such as discs and springs, are working as intended.
-
Material Testing: Additional tests, including tensile testing, hardness testing, and corrosion resistance testing, are performed on raw materials and finished components. These tests ensure that the materials used in manufacturing meet the necessary specifications for strength and durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure product reliability.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing facilities, quality control processes, and adherence to international standards. Audits can reveal a supplier’s commitment to quality and highlight areas for improvement.
-
Reviewing Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken. These reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s quality assurance processes and the performance of their products.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can be particularly beneficial for international buyers who may not have the capacity to conduct their audits.
-
Certifications Verification: Buyers should verify the authenticity of any certifications claimed by the supplier. This can often be done through the certifying body or by requesting copies of the certificates and checking their validity.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances in quality control when sourcing check valve internals. Understanding these nuances can significantly impact procurement decisions.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations regarding valve standards. Buyers must ensure that the products comply with local regulations and standards in their respective countries, which may require additional certifications or testing.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Language and cultural differences can affect the clarity of communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear specifications and maintaining open lines of communication can help mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Transporting check valves across borders can introduce risks, including damage during shipping or delays that affect product quality. Buyers should consider working with suppliers who have robust logistics capabilities and are experienced in international shipping.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Building a long-term relationship with suppliers can enhance trust and facilitate better quality control. Suppliers who understand the specific needs and challenges of their clients are more likely to prioritize quality and reliability in their products.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for check valve internals, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure product reliability and operational efficiency.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘check valve internals’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring check valve internals effectively, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. Understanding the intricacies of check valve internals will help you make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and minimize long-term costs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the check valve internals you need. Consider factors such as the media type, pressure, temperature, and flow rates. These specifications will guide your search and ensure compatibility with your existing systems.
- Media Type: Identify whether you will be handling liquids, gases, or slurries, as this influences material choice.
- Pressure and Temperature Ratings: Specify the maximum allowable pressure and temperature to ensure the internals can withstand operational conditions.
Step 2: Assess Material Compatibility
Select materials that are compatible with the media and environment in which the check valves will operate. The choice of materials affects durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance.
- Common Materials: Evaluate options like stainless steel, bronze, and specialized alloys based on your application needs.
- Elastomers: For sealing components, consider elastomer compatibility with the media to prevent premature failure.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your technical and operational requirements. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing check valve internals.
- Experience and Reputation: Request case studies and references, particularly from industries similar to yours.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO or API standards, to ensure quality compliance.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Before finalizing an order, request samples or detailed specifications of the check valve internals. This allows you to assess the quality and suitability of the components for your application.
- Quality Assurance: Evaluate the samples for material integrity, precision in design, and adherence to your specifications.
- Documentation: Ensure that the supplier provides comprehensive documentation, including material safety data sheets (MSDS) and technical drawings.
Step 5: Inquire About Testing and Quality Control Procedures
Understand the supplier’s testing protocols and quality control measures to ensure the reliability of their products. This step is crucial in preventing future operational issues.
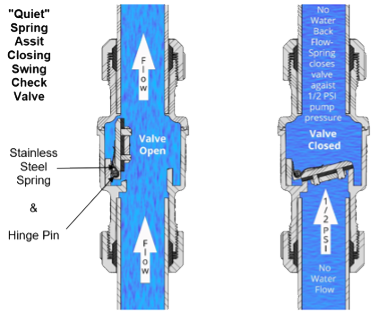
Illustrative image related to check valve internals
- Testing Standards: Ask about the standards used for testing, such as MSS SP-61 for pressure testing.
- Quality Control: Inquire about their quality assurance processes during production to minimize defects.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate terms that cover pricing, delivery schedules, and warranty options. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and ensure timely delivery.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment options that align with your budget and financial processes.
- Warranty Coverage: Ensure that warranty terms cover manufacturing defects and provide recourse for any failures.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Maintenance
Consider the logistics of installation and ongoing maintenance when sourcing check valve internals. Proper planning can enhance the longevity and performance of your valve systems.
- Installation Guidelines: Ensure that the supplier provides detailed installation instructions and support.
- Maintenance Schedule: Establish a maintenance routine to monitor performance and address issues proactively.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for check valve internals, ensuring that they select the best components for their specific applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for check valve internals Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Check Valve Internals?
When sourcing check valve internals, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialized alloys like Hastelloy or Inconel. Each material has different price points based on availability and market demand. For example, high-performance alloys may be necessary for corrosive environments but will increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for precision machining and assembly, particularly for custom designs. These costs can vary by region, with labor rates in Africa or South America potentially differing significantly from those in Europe or the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs, which is a critical factor in pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom internals. Tooling costs should be amortized over the production run, which means larger orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and safety of check valve internals requires rigorous QC processes. This includes testing for leaks, pressure tolerance, and material integrity. The costs associated with QC can vary depending on the standards required, such as ISO certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely based on the distance and mode of transport. Incoterms also play a role in determining who bears these costs, impacting the overall price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin on top of their costs. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, competition, and perceived value of their products.
What Influences Pricing for Check Valve Internals?
Several factors can affect the pricing of check valve internals:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can significantly influence pricing. Suppliers often offer better rates for larger orders, which can be beneficial for buyers looking to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can lead to higher costs. It’s essential to clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality: As mentioned, the choice of materials directly affects pricing. Additionally, certifications for quality and compliance with international standards can add to the cost.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can influence prices. Established suppliers may charge more for their reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms can shift costs and responsibilities between the buyer and supplier, affecting the total cost of acquisition.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Prices?
When negotiating prices for check valve internals, consider the following tips:
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms. Trust and reliability can often result in discounts and improved service.
-
Leverage Volume: If possible, consolidate purchases to meet MOQs or negotiate for bulk discounts. Suppliers are often willing to provide better rates for larger orders.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the initial purchase price but also maintenance, downtime, and potential replacement costs. A lower-priced valve that requires frequent replacements may end up being more expensive in the long run.
-
Research Market Trends: Staying informed about market conditions and material costs can provide leverage during negotiations. If material costs are rising, suppliers may be less inclined to offer discounts.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers can provide a better understanding of the market and help negotiate more favorable terms.
Why Is It Important to Be Aware of Pricing Nuances in International Markets?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding pricing nuances is essential. Exchange rates, local market conditions, and tariffs can all impact the final cost. Moreover, cultural differences in negotiation styles and business practices may affect interactions with suppliers. Being aware of these factors can lead to more informed purchasing decisions and ultimately better value for your investment.
Disclaimer: The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing check valve internals With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Check Valve Internals in Fluid Control Systems
In the realm of fluid control systems, check valve internals serve a crucial function by allowing flow in one direction while preventing backflow. However, various alternative solutions exist that may better suit specific applications or operational needs. This section explores these alternatives, providing insights into their respective advantages and disadvantages.
| Comparison Aspect | Check Valve Internals | Piston/Poppet Check Valves | Swing Check Valves |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective in preventing backflow; flow-sensitive, can lead to chatter if not sized correctly | Fast-closing, reduces water hammer; suitable for varying flow rates | Simple design, good flow capacity, but not ideal for low backpressure |
| Cost | Generally moderate; varies with material and design | Higher initial costs due to complexity | Typically lower cost; simpler design reduces manufacturing expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise sizing and installation; can be complex for maintenance | Can be installed in multiple positions; maintenance may require line removal | Easy to install and maintain; generally allows for in-line repairs |
| Maintenance | May require frequent checks for wear and tear; susceptible to clogging | Requires regular inspection; potential for spring failure | Minimal maintenance; easy to repair or replace |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications with stable flow rates; common in various industries | Best for applications requiring quick closure to prevent water hammer | Suitable for horizontal installations with less sensitivity to pressure fluctuations |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Piston/Poppet Check Valves?
Piston or poppet check valves are known for their quick-closing mechanisms, which help mitigate issues like water hammer. These valves operate with a spring-assisted disc that ensures minimal travel distance, allowing them to respond swiftly to changes in flow. While they are versatile in installation positions, their complexity may lead to higher upfront costs. Furthermore, maintenance can be more demanding due to potential spring failures, but their effectiveness in preventing reverse flow makes them a strong alternative to traditional check valve internals.
How Do Swing Check Valves Compare?
Swing check valves feature a straightforward design, utilizing a hinged disc that closes due to gravity when flow reverses. They are particularly effective in horizontal applications and are generally more cost-effective than other solutions due to their simpler manufacturing process. However, they may not perform well under low backpressure conditions and are prone to issues like water hammer. Maintenance is relatively easy, often allowing repairs without removing the valve from the line. Their simplicity makes them a popular choice, but their limitations in specific scenarios should be carefully considered.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between check valve internals and alternative solutions like piston/poppet or swing check valves, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements. Consider factors such as the nature of the media being controlled, pressure conditions, and installation constraints. It’s crucial to evaluate not only the initial costs but also long-term maintenance implications and performance reliability. Engaging with manufacturers for tailored advice can further enhance decision-making, ensuring the chosen solution aligns with both technical specifications and budgetary constraints. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing performance needs with cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for check valve internals
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Check Valve Internals?
Understanding the essential technical properties of check valve internals is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure optimal performance and longevity in their applications. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The choice of material for check valve internals significantly influences durability and compatibility with various media. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and specialized alloys like Hastelloy and Inconel. Selecting the right material prevents corrosion, erosion, and wear, ensuring reliable operation in demanding environments such as oil and gas or chemical processing. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the acceptable variation in dimensions and fit of valve components. High tolerance levels ensure precise alignment of moving parts, reducing wear and tear while enhancing performance. In B2B contexts, tighter tolerances can lead to less maintenance, lower operational costs, and improved safety, making it a crucial specification in procurement decisions. -
Pressure Rating
This specification defines the maximum pressure a check valve can withstand without failing. Understanding the pressure requirements of the application ensures the selected valve can handle operational conditions, preventing catastrophic failures. For industries like water treatment or petrochemical, where pressure fluctuations are common, selecting valves with appropriate pressure ratings is essential for system integrity. -
Flow Coefficient (Cv)
The flow coefficient quantifies the flow capacity of the valve, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) at a specific pressure drop. A higher Cv indicates better flow performance. Understanding the Cv is vital for B2B buyers to ensure that the valve will not restrict flow in applications such as pumping systems, where efficiency is paramount. -
Seat Material
The material of the valve seat directly affects sealing capability and leakage rates. Common seat materials include elastomers like Buna-N and Viton for tight sealing or metals for more robust applications. The choice of seat material is particularly important in industries dealing with gases or volatile liquids, where leakage can lead to safety hazards or product loss.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Check Valve Internals?
Navigating the procurement of check valve internals also requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products that are used as components in another company’s product. In the context of check valves, buyers often seek OEMs for reliable, high-quality parts that meet specific performance standards, ensuring compatibility and reliability in their systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively. This term can impact purchasing decisions, especially for smaller companies or those testing new applications. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products. For check valves, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, specifications, and delivery times, facilitating informed decision-making. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B transactions involving check valves, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk management, and costs associated with transportation and delivery. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving it. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and maintaining operational efficiency, particularly in industries with strict timelines and regulatory compliance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting check valve internals, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and reducing long-term costs.
Illustrative image related to check valve internals
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the check valve internals Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Check Valve Internals Sector?
The check valve internals sector is undergoing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. Global initiatives aimed at enhancing infrastructure in emerging economies such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are fostering a robust demand for reliable fluid control systems. The rise of automation in manufacturing processes is another crucial factor, with B2B buyers increasingly favoring smart, IoT-enabled check valves that provide real-time data on flow conditions and valve performance. This trend is particularly evident in the oil and gas, water treatment, and industrial manufacturing sectors.
Moreover, the trend towards modularity in design is gaining traction. B2B buyers are looking for customizable solutions that can be adapted to specific applications, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime. Supply chain disruptions have prompted businesses to diversify their sourcing strategies, seeking suppliers that can guarantee both quality and timely delivery. As a result, international partnerships are being formed, allowing companies from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to access a wider array of products and technologies.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Check Valve Internals Market?
Sustainability has become a central theme in the sourcing of check valve internals. Environmental regulations are tightening globally, pushing companies to adopt more sustainable practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications and utilize eco-friendly materials in their products. This shift not only mitigates environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation among consumers who are increasingly conscious of corporate responsibility.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining importance, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where local communities are often affected by industrial activities. Buyers are encouraged to collaborate with suppliers that adhere to ethical labor practices and invest in local economies. Transparent supply chains are becoming a competitive advantage, as businesses recognize that ethical considerations directly impact customer loyalty and long-term profitability.
What Is the Historical Context of Check Valve Internals in the B2B Sector?
The history of check valves dates back to ancient times, with early versions used in various engineering applications. However, the modern check valve, as we know it today, emerged in the 19th century alongside the industrial revolution, which necessitated efficient fluid control systems. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of diverse check valve designs, including swing check, piston, and ball check valves.
In the B2B context, this evolution has been marked by a growing emphasis on performance and reliability. Initially used in waterworks and steam applications, check valves have found their way into a myriad of sectors such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and food and beverage. This diversification has not only expanded the market but has also necessitated a focus on tailored solutions that meet the specific needs of different industries, paving the way for a more complex and dynamic check valve internals market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of check valve internals
-
How do I solve issues with check valve performance?
To address performance issues with check valves, first ensure the valve is suitable for the application. Common problems arise from improper sizing or installation. Check for flow rates and pressure conditions; if the valve doesn’t fully open, it may lead to chattering or premature wear. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to identify wear on internal components. Consulting with the manufacturer can provide insights into specific issues and help determine if a different valve type or size is necessary for optimal performance. -
What is the best check valve type for high-pressure applications?
For high-pressure applications, piston or poppet check valves are often the best choice due to their design, which allows for quick closure and minimizes the risk of water hammer. They can effectively prevent backflow while maintaining flow efficiency. Additionally, ensure that the valve materials can withstand the specific pressures and media involved. Always consult with a manufacturer or supplier to confirm the specifications match your operational requirements. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing check valve internals?
When sourcing check valve internals, consider the material compatibility with the media, pressure ratings, and temperature limits. Assess the supplier’s reputation and ability to provide certifications that meet industry standards. Additionally, inquire about customization options and whether the supplier can accommodate specific designs or sizes. It’s also important to evaluate the supplier’s lead times and logistics capabilities, especially for international shipments. -
How can I ensure the quality of check valve internals?
Quality assurance can be ensured by selecting suppliers that adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001. Request documentation of their quality control processes, including material certifications and testing procedures. Additionally, consider conducting audits or site visits to verify their manufacturing practices. Utilizing third-party inspection services can also provide an added layer of confidence in the quality of the check valve internals being sourced. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for check valve internals?
MOQs for check valve internals vary by supplier and depend on the type of valve and customization required. Some manufacturers may have low MOQs for standard products, while custom designs could require larger orders to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to find a balance between your order size and their production capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing check valve internals internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly between suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%) with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms after delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms early in negotiations and ensure they are documented in the purchase agreement. Be aware of any additional fees related to currency exchange or international transactions. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of check valve internals?
Logistics and shipping are crucial when sourcing check valve internals, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations can affect delivery schedules. Ensure the supplier has experience in international shipping and can provide accurate shipping estimates. Consider working with a freight forwarder to navigate customs and ensure timely delivery, especially in regions with complex import regulations. -
Can I customize check valve internals to fit my specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for check valve internals to meet specific application requirements. Customizations can include size, material, and design modifications. When considering customization, it’s vital to communicate your specific needs clearly to the manufacturer. Collaborating closely with them can lead to tailored solutions that enhance performance and reliability in your unique application environment.
Top 3 Check Valve Internals Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tameson – Check Valves
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Check valves allow liquid and air to flow in only one direction and prevent backflow, which can lead to contamination, equipment damage, and increased maintenance costs. They are used in various applications, including plumbing, industrial systems, and household appliances. Key types include inline spring-loaded, swing, ball, lift, and Y-shape check valves, made from materials like stainless steel…
2. Check-All – Inline Check Valves
Domain: checkall.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Inline check valves utilize a check mechanism that functions in the fluid line or media pathway of a process piping system. They are compact in design for space-saving and ease of installation. Check-All inline check valves use a spring-loaded check mechanism, allowing installation in vertical or horizontal orientations. Key styles include:
– Flange Insert Check Valve: Fits ANSI class 150, 300, o…
3. Tork Systems – Check Valves
Domain: torksystems.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Check valves are designed to automatically shut off when pressure reduces or changes direction, preventing backflow of fluids or gases. Key components include the body, seat, disc, and cover. Types of check valves include:
1. Swing Check: Features a disc that opens with flow pressure and closes with backflow pressure.
2. Lift Check: Similar to swing checks but flow moves upward against the disc,…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for check valve internals
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of check valve internals is critical for ensuring reliability, efficiency, and longevity in various industrial applications. Understanding the different types of check valves, such as swing checks and piston/poppet designs, empowers B2B buyers to select the most suitable option for their specific needs. Proper selection and installation not only mitigate the risk of premature failure and costly downtime but also enhance overall system performance.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, fostering strong relationships with manufacturers can lead to valuable insights and support in navigating the complexities of valve selection. As the global market continues to evolve, prioritizing quality and compatibility with local conditions will be paramount.
Illustrative image related to check valve internals
Looking ahead, consider engaging with trusted suppliers and leveraging technological advancements to optimize your valve procurement processes. By doing so, you can ensure that your operations remain resilient and competitive in an increasingly dynamic industrial landscape. Embrace strategic sourcing as a pathway to innovation and operational excellence in your projects.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.