How to Source Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ceramics size reduction equipment
The global market for ceramics size reduction equipment presents a complex challenge for international B2B buyers seeking efficient and effective solutions. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe increasingly demand high-quality ceramic products, the need for reliable size reduction machinery becomes paramount. This guide aims to illuminate the intricacies of sourcing ceramics size reduction equipment, addressing critical aspects such as types of machinery, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
Understanding the various equipment options—from crushers and grinders to pulverizers—allows buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific production needs. Additionally, this guide delves into cost considerations, ensuring that businesses can balance quality with budgetary constraints while navigating a diverse supplier landscape. By providing actionable insights and expert recommendations, this resource empowers B2B buyers to streamline their purchasing processes and enhance operational efficiency.
Whether you are a manufacturer in Vietnam or a distributor in Saudi Arabia, this comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge needed to confidently invest in ceramics size reduction equipment that meets your operational demands and drives business growth. The right machinery not only optimizes production but also positions your organization for success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Understanding ceramics size reduction equipment Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jaw Crushers | Heavy-duty, ideal for primary crushing of large ceramic materials. | Mining, ceramics manufacturing | Pros: High efficiency, robust design. Cons: Limited to larger particle sizes. |
| Ball Mills | Utilizes grinding balls for fine grinding; suitable for wet and dry processes. | Fine ceramics production, pigments | Pros: Versatile, achieves very fine particle sizes. Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Hammer Mills | Employs high-speed rotating hammers for size reduction. | Recycling, ceramic tile production | Pros: Quick processing, handles various materials. Cons: May generate heat, affecting material properties. |
| Vibratory Disc Mills | Uses vibration to achieve fine grinding; suitable for small samples. | Laboratory analysis, research | Pros: Efficient for small batches, precise control. Cons: Limited capacity for large volumes. |
| Cutting Mills | Employs mechanical cutting methods for soft to medium-hard materials. | Food industry, ceramics with fibrous content | Pros: Effective for fibrous materials, easy to clean. Cons: Not suitable for very hard materials. |
What are Jaw Crushers and Their Applications in Ceramics Size Reduction?
Jaw crushers are heavy-duty machines designed for the primary crushing of large ceramic materials. They operate by compressing the material between two jaws, one stationary and one moving. This equipment is particularly suitable for initial size reduction in mining and ceramics manufacturing, where large feed sizes are common. When considering a jaw crusher, buyers should assess the hardness and size of the materials they will be processing, as these factors influence the efficiency and output quality.
How Do Ball Mills Contribute to Fine Grinding in Ceramics?
Ball mills are versatile size reduction machines that use grinding balls to achieve fine particle sizes. They can operate in both wet and dry conditions, making them suitable for various applications, including fine ceramics production and pigment processing. For B2B buyers, key considerations include energy consumption and the desired fineness of the final product. While ball mills are effective for achieving very fine particles, their higher energy requirements may impact operational costs.
Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
What Are the Benefits of Using Hammer Mills in Ceramic Processing?
Hammer mills utilize high-speed rotating hammers to reduce the size of materials quickly. They are particularly effective for recycling and ceramic tile production, where a variety of materials may need processing. Buyers should consider the heat generated during operation, as it may affect the properties of heat-sensitive ceramics. Despite this, hammer mills offer quick processing times and flexibility, making them a popular choice in the ceramics industry.
Why Choose Vibratory Disc Mills for Laboratory Analysis?
Vibratory disc mills are specialized for fine grinding using vibration, making them ideal for small sample sizes in laboratory settings. They are widely used for research and quality control in ceramics and other materials. B2B buyers should evaluate the mill’s capacity and the precision required for their applications. While these mills provide excellent control over particle size, their limited capacity for larger batches may necessitate additional equipment for high-volume production.
What Are Cutting Mills and Their Role in Size Reduction?
Cutting mills employ mechanical cutting methods to reduce soft to medium-hard materials, making them suitable for ceramics with fibrous components. They are commonly used in the food industry and can efficiently handle materials that require shredding rather than grinding. When considering cutting mills, buyers should focus on the types of materials they will process and the required output size. While cutting mills offer ease of cleaning and effective processing for fibrous materials, they may not be suitable for very hard ceramics.
Key Industrial Applications of ceramics size reduction equipment
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ceramics size reduction equipment | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramics Manufacturing | Grinding raw materials like kaolin and feldspar | Improved particle size distribution for better product quality | Material compatibility, energy efficiency, and scalability |
| Construction Materials | Producing fine aggregates for concrete and mortar | Enhanced strength and durability of construction materials | Compliance with local construction standards and regulations |
| Electronics | Pulverizing ceramics for capacitors and insulators | Higher performance and reliability of electronic components | Precision in particle size and material purity |
| Pharmaceuticals | Size reduction of ceramic powders for drug formulation | Enhanced bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy | Contamination control and material specifications |
| Environmental Remediation | Processing ceramic waste for recycling | Sustainable waste management and reduced environmental impact | Equipment adaptability to various waste types |
How is Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment Used in Ceramics Manufacturing?
In the ceramics manufacturing industry, size reduction equipment is essential for grinding raw materials like kaolin, feldspar, and quartz into fine powders. This process ensures a uniform particle size distribution, which is crucial for producing high-quality ceramic products. International buyers must consider the compatibility of the equipment with specific materials and the energy efficiency of operations, especially in regions like Africa and South America where energy costs can significantly impact production.
What Role Does Size Reduction Equipment Play in Construction Materials?
For the construction materials sector, ceramics size reduction equipment is used to produce fine aggregates that enhance the properties of concrete and mortar. By achieving the desired particle size, manufacturers can improve the strength, workability, and durability of their products. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing equipment that meets local construction standards and regulations, ensuring compliance while optimizing production efficiency.
Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
Why is Size Reduction Important in Electronics?
In the electronics industry, ceramics size reduction equipment is utilized to pulverize materials used in capacitors, insulators, and other electronic components. Achieving a fine particle size is critical for enhancing the performance and reliability of these products. B2B buyers must prioritize precision in particle size and material purity when selecting equipment, as these factors directly influence the quality and functionality of electronic devices.
How Does Size Reduction Equipment Contribute to Pharmaceuticals?
Size reduction of ceramic powders in pharmaceuticals is vital for drug formulation, as it increases the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of active ingredients. This process allows for better absorption and effectiveness of medications. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the equipment offers strict contamination controls and adheres to specific material specifications to maintain product integrity and compliance with health regulations.
What is the Importance of Size Reduction in Environmental Remediation?
Ceramics size reduction equipment plays a crucial role in processing ceramic waste for recycling in environmental remediation efforts. By reducing waste to manageable sizes, businesses can implement sustainable waste management practices and minimize environmental impact. Buyers should consider the adaptability of the equipment to handle various types of waste materials, ensuring versatility and efficiency in recycling operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ceramics size reduction equipment’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Particle Size Leading to Product Quality Issues
The Problem: A ceramics manufacturer is facing challenges with inconsistent particle sizes during the grinding process. This inconsistency leads to variability in the final product quality, affecting not only the aesthetic appeal but also the mechanical properties of ceramics. In a competitive market, such variations can result in increased rejection rates and customer dissatisfaction, ultimately impacting profitability and brand reputation. The buyer is unsure whether the issue lies with the size reduction equipment or the operational parameters being used.
The Solution: To address this problem, it is essential to conduct a thorough assessment of both the size reduction equipment and the operational parameters. First, evaluate the equipment to ensure it is suitable for the specific type of ceramics being processed. For example, using a ball mill may be ideal for achieving a finer particle size, while a hammer mill may be more appropriate for larger particles. Next, consider implementing a closed-loop system with continuous monitoring of particle size distribution. This can be achieved through real-time analytical tools that assess particle size, allowing for immediate adjustments to the grinding process. Additionally, training operators to understand the importance of maintaining consistent feed rates and adjusting the grinding media according to the material properties can lead to significant improvements in product quality.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Equipment
The Problem: A company engaged in ceramics production is experiencing high operational costs, particularly in energy consumption and equipment maintenance. The buyer suspects that the current size reduction equipment is outdated and not optimized for energy efficiency, leading to excessive wear and tear, increased downtime, and ultimately higher costs. They are looking for ways to reduce operational expenses without compromising productivity.
The Solution: The first step in mitigating high operational costs is to conduct a comprehensive audit of the current size reduction equipment to identify inefficiencies. Upgrading to modern, energy-efficient equipment can significantly reduce energy consumption and improve processing times. For instance, investing in variable speed drives and advanced control systems can optimize energy use based on the material properties and desired particle size. Furthermore, consider implementing preventive maintenance schedules to minimize unexpected breakdowns and extend the equipment’s lifespan. By analyzing the total cost of ownership, including energy savings, maintenance costs, and productivity gains, buyers can make informed decisions about upgrading their equipment. Additionally, exploring options for financing or leasing new machinery can spread out the initial investment and provide immediate cost savings.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Handling Diverse Material Types
The Problem: A ceramics manufacturer specializes in producing a wide range of products, which requires processing various types of raw materials with different properties. The buyer struggles to find size reduction equipment that can efficiently handle this diversity without compromising performance or requiring frequent equipment changes. This situation leads to increased downtime and complexity in the production process.
The Solution: To effectively manage the processing of diverse materials, buyers should consider investing in modular size reduction equipment that offers flexibility and adaptability. Equipment such as multi-purpose mills can accommodate various grinding methods, allowing for easy switching between different materials and particle size requirements. Additionally, employing a combination of pre-crushing and fine grinding equipment can optimize the process for different materials. For example, using a crusher to break down larger chunks before feeding them into a specialized mill can ensure efficient size reduction. Furthermore, it is crucial to work closely with equipment manufacturers to customize the machinery based on specific material properties, ensuring that the equipment can handle variations in hardness, moisture content, and abrasiveness. Implementing these strategies can streamline operations, reduce downtime, and enhance overall productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ceramics size reduction equipment
What Are the Key Materials Used in Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
When selecting materials for ceramics size reduction equipment, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in this context: steel, tungsten carbide, zirconium oxide, and agate. Each material has unique characteristics that influence performance and suitability for various applications.
How Does Steel Perform in Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
Steel is a widely used material in the manufacturing of size reduction equipment due to its strength and durability. It typically has a high-temperature tolerance and can withstand significant pressure, making it suitable for various grinding applications. However, steel is prone to corrosion, especially when processing abrasive or chemically reactive materials.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and readily available, making it a cost-effective option for many manufacturers. Its durability ensures a long service life under normal operating conditions.
Cons: The susceptibility to corrosion can lead to contamination of the processed material, which is a critical concern in industries requiring high purity, such as pharmaceuticals or food processing.
Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with a wide range of materials but may not be ideal for applications requiring minimal contamination or high chemical resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN for material specifications, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East where regulations can be stringent.
What Are the Benefits of Tungsten Carbide in Size Reduction Equipment?
Tungsten carbide is favored for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for grinding very hard materials. It can handle high temperatures and pressures without significant degradation, ensuring consistent performance over time.
Pros: The high density of tungsten carbide allows for effective size reduction, as it generates greater energy input during the grinding process. This material is also resistant to abrasion, which is beneficial for maintaining equipment longevity.

Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
Cons: Tungsten carbide is more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing process can be complex, potentially leading to longer lead times for equipment delivery.
Impact on Application: Tungsten carbide is particularly suitable for applications involving hard ceramics and minerals, where traditional materials may fail.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the cost-benefit ratio, especially in regions with budget constraints like parts of Africa and South America, where lower initial costs may be prioritized.

Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
Why Choose Zirconium Oxide for Ceramics Size Reduction?
Zirconium oxide is recognized for its high wear resistance and chemical inertness, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring minimal contamination. It can withstand high temperatures and is often used in wet grinding processes.
Pros: This material is neutral to analysis, ensuring that it does not interfere with the properties of the processed materials. It is particularly effective for grinding ceramics and other sensitive materials.
Cons: Zirconium oxide is generally more expensive than both steel and tungsten carbide, which could limit its use in cost-sensitive applications.
Impact on Application: Its compatibility with a wide range of materials makes zirconium oxide ideal for industries where purity is paramount, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with specific industry standards is crucial, especially in regions like Europe where quality assurance is heavily regulated.
Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
What Role Does Agate Play in Size Reduction Equipment?
Agate is a natural stone that is often used in laboratory settings for its low contamination risk and excellent grinding properties. It is particularly suitable for small-scale operations and research applications.
Pros: Agate is chemically inert and provides a high degree of purity, making it ideal for sensitive applications. Its natural properties allow for effective size reduction without introducing foreign materials.
Cons: The fragility of agate can limit its use in high-volume or industrial applications, as it may not withstand the same pressures as synthetic materials.
Impact on Application: Agate is best suited for laboratory environments where sample integrity is critical, making it less suitable for large-scale industrial processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of agate and its associated costs, particularly in regions where natural resources may be limited.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment
| Material | Typical Use Case for ceramics size reduction equipment | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | General grinding and size reduction | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion and contamination | Low |
| Tungsten Carbide | Grinding hard ceramics and minerals | High wear resistance and effective size reduction | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Zirconium Oxide | Wet grinding and high-purity applications | Chemically inert and minimal contamination | Higher cost compared to steel | Medium |
| Agate | Laboratory grinding for sensitive materials | Low contamination risk and high purity | Fragile and not suitable for high-volume use | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in ceramics size reduction equipment, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ceramics size reduction equipment
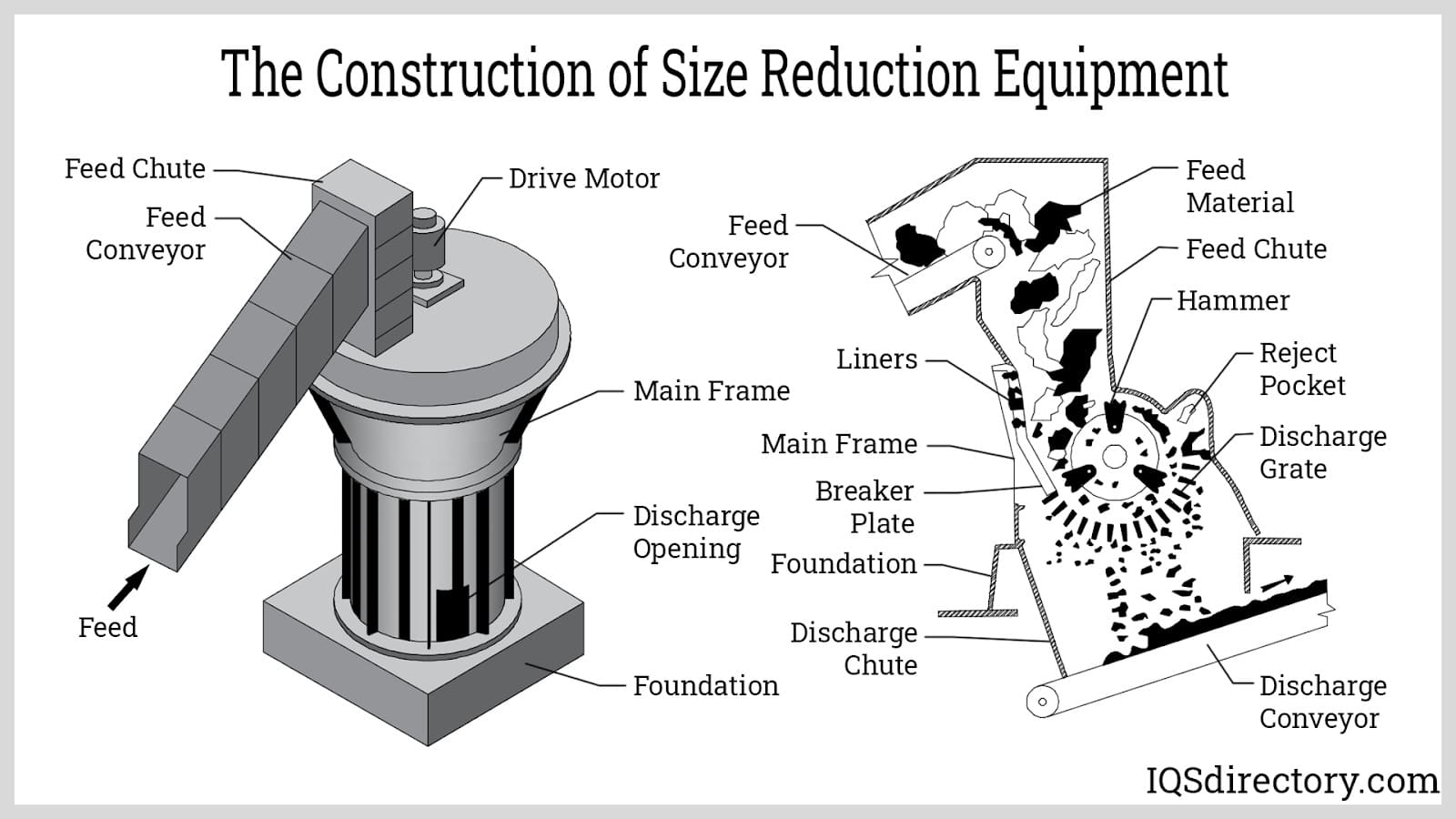
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
The manufacturing of ceramics size reduction equipment involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the rigorous demands of various industries. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers evaluate the equipment’s reliability and performance.
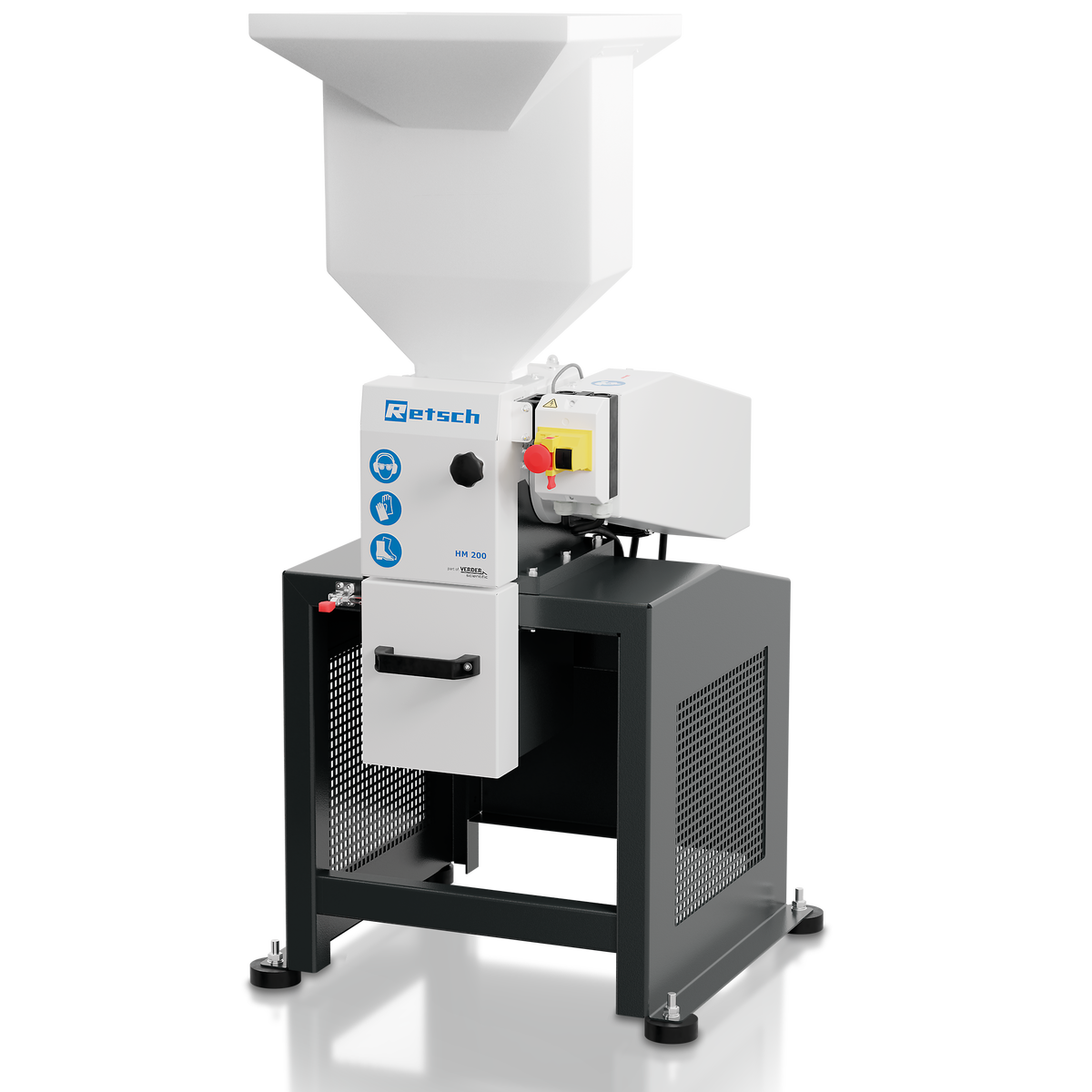

Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in manufacturing ceramics size reduction equipment is the selection and preparation of raw materials. High-quality ceramics, such as zirconium oxide or tungsten carbide, are typically chosen for their hardness and wear resistance. These materials undergo initial processing, which may include crushing and milling to achieve a uniform particle size. This uniformity is crucial as it directly impacts the performance and durability of the final equipment.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape the Equipment?
Once the materials are prepared, they are shaped using various forming techniques. Common methods include:
-
Pressing: This involves compacting the powdered ceramics into molds under high pressure. This method is widely used due to its efficiency and the ability to produce complex shapes.
-
Injection Molding: For more intricate designs, injection molding may be utilized. This method involves injecting the ceramic slurry into a mold, allowing for precise shapes and sizes.
-
Slip Casting: In this technique, a liquid ceramic mixture (slip) is poured into a porous mold. The water is absorbed, leaving a solid layer that can be removed and fired.
Each method has its advantages, and the choice depends on the desired properties of the final product and the complexity of the design.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into the Final Product?
After forming, the components are assembled. This may involve attaching different parts of the size reduction equipment, such as grinding chambers, motors, and feed systems. Precision during assembly is critical, as any misalignment can lead to decreased efficiency and increased wear.
Automated assembly lines are often employed to ensure consistency and speed, but manual assembly may still be necessary for intricate components. During this stage, engineers may also conduct preliminary tests to verify the functionality of individual components before proceeding to the next phase.
Finishing: What Quality Enhancements Are Applied?
The finishing stage includes various treatments to enhance the performance and aesthetic qualities of the equipment. Common finishing processes include:
-
Sintering: This involves heating the shaped components to a temperature below their melting point, allowing them to fuse and strengthen without losing their shape.
-
Surface Treatment: Techniques such as polishing or coating may be applied to improve surface smoothness and reduce friction during operation.
These finishing processes not only improve the equipment’s performance but also extend its lifespan.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring that ceramics size reduction equipment meets industry standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant international and industry-specific standards that govern quality.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is the most widely recognized quality management standard globally. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality control processes throughout the production cycle. Additionally, industry-specific standards, such as CE marking in Europe and API standards for certain applications, may also apply. These certifications indicate that the equipment meets specific safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential for maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection focuses on raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis or other documentation to verify material quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to ensure that the processes meet predefined specifications. This may include monitoring dimensions, material consistency, and adherence to production schedules.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the complete equipment undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it functions correctly. This may involve performance tests, stress tests, and safety checks.
These QC checkpoints help identify defects early, reducing the risk of costly errors later in the production process.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular on-site audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the supplier’s quality management practices. Buyers should look for adherence to ISO 9001 and other relevant standards during these audits.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should be willing to provide detailed documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports, compliance certificates, and testing results.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: For added assurance, buyers can enlist third-party inspection services to conduct independent assessments of the equipment. These services can provide unbiased evaluations of both the manufacturing process and the final product.
What Are the QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Different regions may have varying standards and expectations regarding quality.
-
Cultural Awareness: Buyers should be aware of cultural differences that may affect communication and business practices. Establishing clear lines of communication can help mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations regarding equipment safety and performance. This knowledge can guide their selection process and ensure compliance with regional standards.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: The quality of equipment can be affected by logistics and transportation conditions. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that products are packaged and transported in ways that minimize damage.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing ceramics size reduction equipment, ensuring that they choose reliable suppliers capable of meeting their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ceramics size reduction equipment’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring ceramics size reduction equipment, this guide offers a structured checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select the right equipment that meets their operational needs and enhances productivity.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for identifying suitable size reduction equipment. Consider factors such as the type of ceramics being processed, the desired particle size, and the production capacity required. This clarity will help in narrowing down options and communicating effectively with suppliers.
- Material Properties: Assess the hardness, brittleness, and moisture content of the ceramics.
- Desired Outcomes: Specify the final particle size and distribution needed for your application.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Understanding the market landscape is essential before making a purchase. Research various manufacturers and their offerings to get a sense of the available technologies and innovations in ceramics size reduction equipment.
- Competitor Analysis: Identify what equipment your competitors use and evaluate its performance.
- Trends and Innovations: Stay informed about new technologies that could improve efficiency or reduce costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step helps ensure that you choose a reputable supplier with a proven track record.
- Quality Assurance: Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards.
- Customer Feedback: Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients to gauge satisfaction levels.
Step 4: Request Product Demonstrations
Seeing the equipment in action can provide invaluable insights into its capabilities. Arrange for product demonstrations or trial periods to assess performance under real operational conditions.
- Test Performance: Evaluate the equipment’s ability to achieve the desired particle size and processing speed.
- Ease of Use: Observe the user interface and maintenance requirements during the demonstration.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance
After-sales support is a critical factor that can impact long-term satisfaction with the equipment. Ensure that the supplier offers robust support services, including maintenance and training.
- Service Agreements: Inquire about warranty terms and the availability of service contracts for ongoing maintenance.
- Training Programs: Check if the supplier provides training for your staff on equipment operation and troubleshooting.
Step 6: Compare Total Cost of Ownership
When evaluating options, consider not just the initial purchase price but the total cost of ownership over the equipment’s lifecycle. This includes operating costs, maintenance expenses, and potential downtime costs.
- Energy Efficiency: Assess the energy consumption of the equipment, as this can significantly affect long-term costs.
- Replacement Parts: Investigate the availability and cost of replacement parts to avoid unexpected expenses.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected the right supplier and equipment, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in a purchase agreement. This should include delivery timelines, payment terms, and any warranties or service commitments.
- Documentation: Ensure all technical specifications and compliance standards are documented in the agreement.
- Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms that better suit your operational budget and needs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing ceramics size reduction equipment, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ceramics size reduction equipment Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure of ceramics size reduction equipment is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. The pricing of such equipment is influenced by a variety of factors that can significantly impact the total expenditure. Here, we break down the key cost components, price influencers, and offer valuable buyer tips to optimize sourcing strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a primary factor. High-quality materials, such as ceramics (e.g., tungsten carbide or zirconium oxide), significantly influence pricing due to their durability and performance in grinding applications. The choice of material impacts not only the initial purchase price but also the longevity and efficiency of the equipment.
-
Labor: Labor costs are associated with the manufacturing and assembly of the equipment. Skilled labor is often required for precision engineering, which can lead to higher costs. Suppliers in regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing, but this can vary based on local labor regulations and expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs of production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower these overhead costs, thus influencing the final price of the equipment.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications adds to the initial cost. Buyers should consider whether they require standard or custom solutions, as custom tooling often incurs additional design and manufacturing expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the equipment meets industry standards and performance specifications. The cost of implementing these quality measures can be reflected in the pricing, making it crucial for buyers to assess the certifications and standards upheld by suppliers.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary based on the origin of the equipment and the destination market. Buyers should account for potential tariffs, import duties, and shipping delays when evaluating overall costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins also factor into pricing. Understanding the market dynamics and competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
What Influences the Pricing of Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help buyers negotiate better pricing based on projected usage.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized equipment tailored to specific needs can significantly increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Equipment that meets international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) may command higher prices but often results in better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and reliability play a crucial role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and customer service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the total landed cost. Buyers should be aware of the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) on pricing and risk allocation.
How Can Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Strategy?
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures. Understanding their cost components can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial purchase price, but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. High-quality equipment may have a higher upfront cost but lower TCO.
-
Explore Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing locally can reduce logistics costs and lead to quicker delivery times.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and technological advancements in ceramics size reduction equipment. This knowledge can assist in making timely purchasing decisions and identifying cost-effective solutions.
-
Be Mindful of Pricing Nuances: Understand that pricing can fluctuate based on market demand, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors. This is particularly important for international transactions.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ceramics size reduction equipment With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment
In the landscape of size reduction technology, ceramics size reduction equipment offers unique advantages, but it is essential to consider alternative solutions that may better suit specific operational needs. Different technologies can achieve similar goals of particle size reduction, each with its own set of benefits and challenges. Below, we present a comparative analysis of ceramics size reduction equipment against two viable alternatives: Hammer Mills and Roller Mills.
| Comparison Aspect | Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment | Hammer Mills | Roller Mills |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for hard and brittle materials, achieving fine particle sizes | High throughput, effective for coarse to medium grinding | Provides uniform particle size, ideal for moderate hardness materials |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; long-term cost-effective due to durability | Lower upfront cost; operational costs can rise with wear | Moderate cost; efficient but may require more energy |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled personnel for setup and operation | Relatively easy to install and operate | Requires precise alignment and setup, which can be complex |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance; specific parts may need replacement | Generally lower maintenance needs, but wear parts must be frequently checked | Maintenance can be labor-intensive; regular inspections needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for ceramics and similar materials requiring fine particle size | Best for processing large volumes of softer materials | Suited for producing uniform granules in food and pharmaceutical industries |
How Do Hammer Mills Compare to Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
Hammer Mills are versatile machines that utilize high-speed rotating hammers to crush materials. They excel in producing coarse to medium particle sizes and can process a wide variety of materials, including soft and fibrous substances. The initial investment for hammer mills is generally lower than that for ceramics size reduction equipment, making them an attractive option for businesses with tighter budgets. However, operational costs can escalate due to the wear of hammers and screens, necessitating frequent replacements. Hammer mills are best suited for applications where high throughput and lower particle size precision are acceptable.
What Advantages Do Roller Mills Offer Over Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
Roller Mills use a series of rotating cylindrical rollers to crush and grind materials. They are known for their ability to produce uniform particle sizes, making them ideal for industries such as food and pharmaceuticals. While roller mills can handle moderate hardness materials efficiently, they may not be suitable for very hard substances like ceramics. The initial costs are moderate, but the need for precise alignment and maintenance can add complexity. Their best use case is in scenarios where product consistency and uniformity are critical, even if it means sacrificing some versatility in material types.
Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Size Reduction Equipment?
When selecting size reduction equipment, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including the nature of the material being processed, the desired particle size, and the operational budget. Ceramics size reduction equipment shines in applications requiring fine, consistent sizes from hard materials, while hammer and roller mills offer cost-effective and versatile alternatives for softer substances. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing performance requirements with cost, maintenance capabilities, and the specific operational context. Careful evaluation of these aspects will lead to an optimal investment in size reduction technology that meets business objectives effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ceramics size reduction equipment
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
When selecting ceramics size reduction equipment, understanding its technical properties is essential for ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and composition of the materials used in the construction of size reduction equipment. For ceramics, this could include high-alumina, zirconia, or other specialized ceramics. The right material grade enhances durability, resistance to wear, and chemical stability, which is crucial for processing abrasive ceramic materials. Selecting equipment made from appropriate material grades minimizes maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of the machinery.
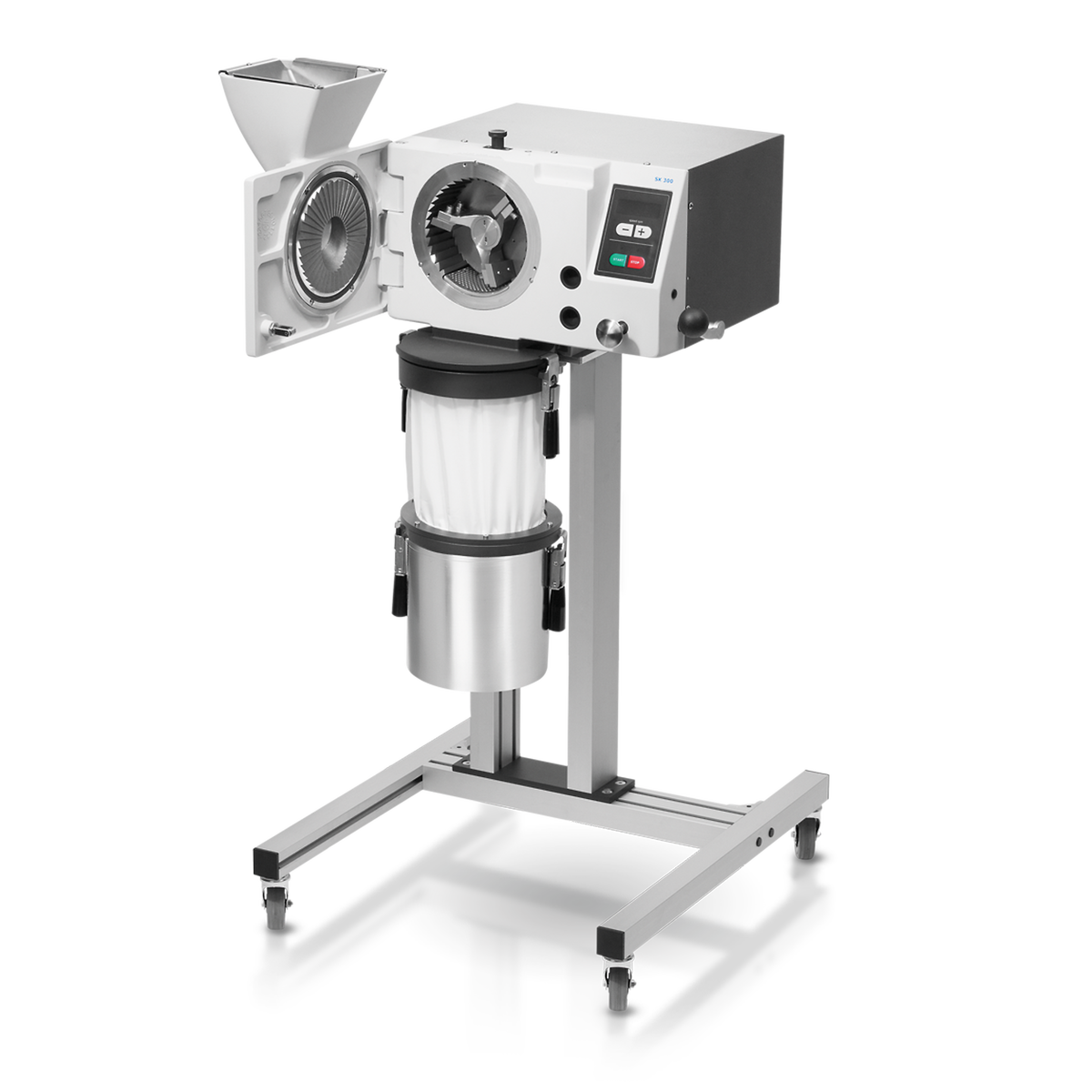

Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels indicate the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the equipment’s design and manufacturing. In ceramics processing, precise tolerances are critical for achieving the desired particle size and uniformity. High tolerance levels ensure that the size reduction equipment operates efficiently, reducing the likelihood of product inconsistency. This is particularly important in industries where product specifications are stringent, such as pharmaceuticals and high-tech ceramics.
3. Grinding Capacity
Grinding capacity refers to the volume of material that the equipment can process within a specified time frame. It is typically measured in kilograms per hour (kg/h). Understanding the grinding capacity helps businesses gauge whether the equipment can meet production demands. A higher grinding capacity often translates to improved efficiency and lower operational costs, making it a vital consideration for B2B buyers focused on productivity.
4. Energy Consumption
Energy consumption metrics indicate the power requirements of the size reduction equipment during operation. Lower energy consumption not only reduces operational costs but also contributes to sustainable practices. Buyers should consider energy-efficient models that maintain performance while minimizing electricity use, particularly in regions where energy costs are high.
5. Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance requirements encompass the frequency and type of upkeep needed to keep the equipment in optimal working condition. Equipment that is easier to maintain can lead to reduced downtime and lower overall costs. B2B buyers should evaluate the maintenance demands of ceramics size reduction equipment and consider service agreements or warranties that can provide additional peace of mind.
Which Trade Terminology Is Essential for Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment?
Understanding industry-specific terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some common terms relevant to ceramics size reduction equipment:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce equipment that may be sold under another company’s brand name. In ceramics size reduction, buyers may prefer to work with OEMs known for quality and reliability. This designation can affect pricing, warranty conditions, and service agreements.
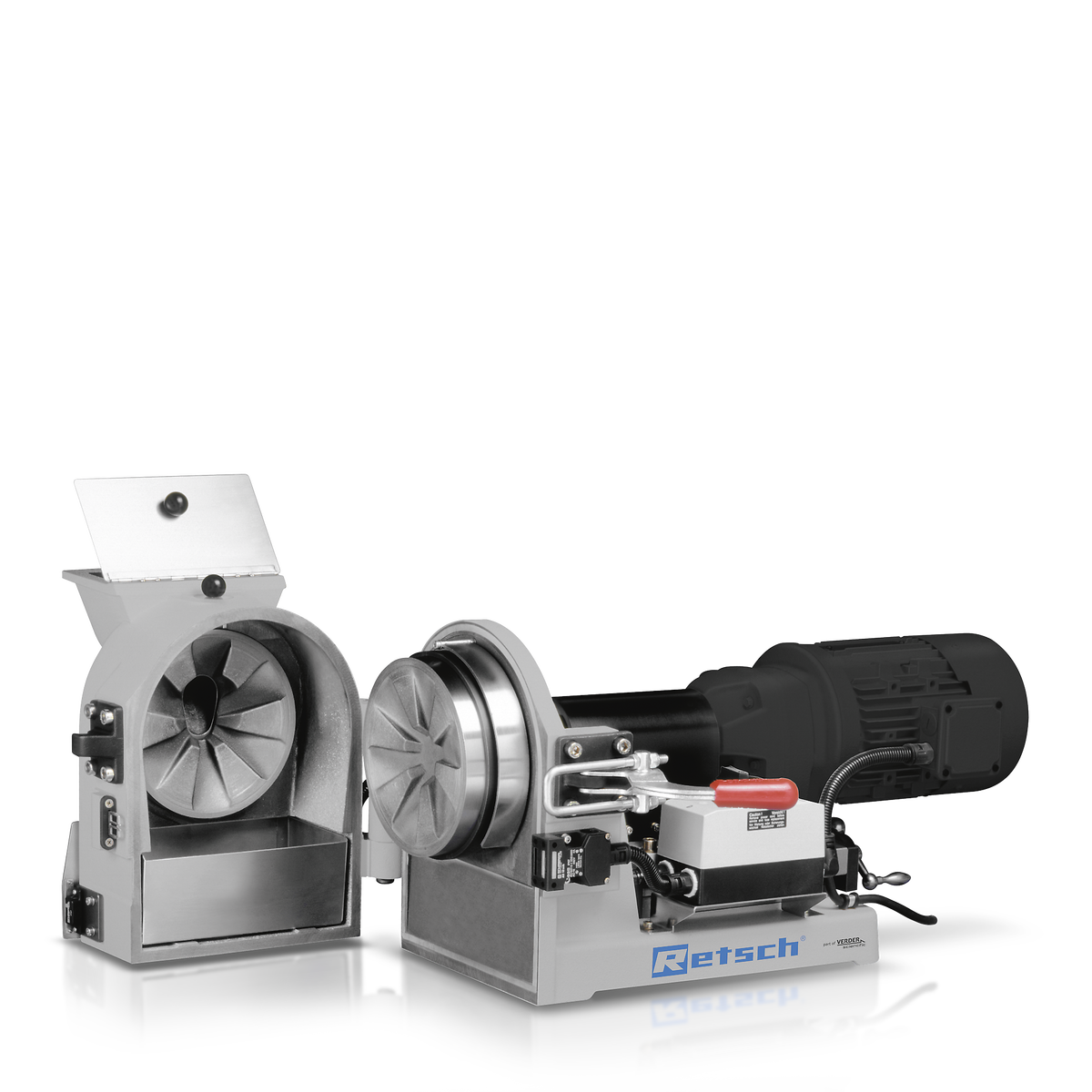

Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In the ceramics industry, understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers must negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules while ensuring they meet supplier requirements.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific equipment or services. In the context of ceramics size reduction equipment, a well-crafted RFQ can help buyers compare offerings from different suppliers and negotiate better terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global procurement, as they influence shipping costs, insurance, and risk management during the transport of ceramics size reduction equipment.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from the initiation of an order to its delivery. Understanding lead times is critical for planning production schedules and managing inventory. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating contracts to ensure that equipment arrives when needed.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the ceramics industry can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ceramics size reduction equipment Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment Sector?
The ceramics size reduction equipment market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand in various industries such as construction, electronics, and automotive. Key market drivers include the need for enhanced material properties and efficient production processes. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a rising focus on technological advancements in size reduction equipment, including automation and smart technologies that improve operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Emerging trends include the adoption of high-efficiency grinding technologies, such as jet mills and cryogenic grinding systems, which cater to the specific requirements of ceramics processing. International buyers are increasingly seeking equipment that can deliver precise particle size distribution and improve material homogeneity, which is critical for high-quality end products. Moreover, the integration of Industry 4.0 principles is reshaping sourcing strategies, with advanced analytics and IoT-enabled machinery providing real-time data for improved decision-making.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional manufacturing capabilities and the availability of raw materials. For instance, countries like Vietnam and Saudi Arabia are ramping up production capabilities to meet local and export demands, while addressing challenges such as supply chain disruptions and fluctuating raw material prices. International B2B buyers should keep abreast of these trends to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the ceramics size reduction equipment sector. As environmental regulations tighten globally, companies are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly practices in their operations. The production and use of ceramics can have significant environmental impacts, from raw material extraction to energy consumption during processing. Therefore, B2B buyers are urged to consider suppliers who are committed to reducing their carbon footprint and implementing sustainable manufacturing practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are increasingly concerned about the provenance of their materials and the conditions under which they are produced. This has led to a demand for suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with international labor standards and environmental certifications. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential in supplier evaluations.
Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials in the manufacturing of size reduction equipment is gaining traction. Buyers should look for suppliers who utilize sustainable materials, such as recycled metals or eco-friendly coatings, to minimize environmental impact. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international B2B buyers can not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile but also improve their competitive edge in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Has Been the Evolution of Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment Over Time?
The evolution of ceramics size reduction equipment has been marked by significant technological advancements and a growing understanding of material properties. Initially, traditional grinding methods dominated the sector, focusing on basic crushing and milling techniques that often fell short of meeting the precise requirements of modern ceramics processing.
Over the decades, the introduction of advanced milling technologies, such as high-energy ball mills and jet mills, revolutionized the industry. These innovations allowed for finer particle sizes and improved material homogeneity, essential for high-performance ceramics. The development of computer-controlled equipment further enhanced efficiency and precision, enabling operators to achieve consistent results.
As the demand for high-quality ceramics continues to rise, the focus on energy efficiency and sustainability has also shaped the evolution of size reduction equipment. Today, manufacturers are integrating smart technologies and automation to streamline processes and reduce waste, ensuring that the ceramics industry remains competitive in a global market. This historical context is vital for international buyers as they navigate sourcing decisions, emphasizing the importance of selecting equipment that not only meets current operational needs but is also adaptable to future demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ceramics size reduction equipment
-
How do I choose the right ceramics size reduction equipment for my application?
Choosing the right ceramics size reduction equipment involves considering several factors, including the material’s properties (hardness, moisture content, and brittleness), desired particle size, and throughput requirements. Conduct a thorough analysis of the material to determine its breaking behavior, which can influence the equipment type—crushers for large particles and mills for finer sizes. Additionally, consider the scalability of the equipment for future production needs and the compatibility of the equipment with your existing production line. -
What is the best equipment for grinding ceramics to a fine powder?
For grinding ceramics into a fine powder, ball mills are often the best choice due to their ability to achieve very fine particle sizes and excellent homogeneity. Other options include vibratory disc mills, which are effective for brittle materials, and high-energy mills that can achieve nanoscale fineness. It’s essential to choose equipment that minimizes contamination risk and optimizes energy input for effective size reduction, ensuring that the final product meets your quality standards. -
What are the key quality assurance measures for ceramics size reduction equipment?
Quality assurance in ceramics size reduction equipment involves regular maintenance checks, calibration of machinery, and adherence to industry standards. Ensure that your supplier provides documentation of compliance with relevant international standards, such as ISO certifications. It’s also beneficial to request samples or trial runs to verify equipment performance and output quality, helping you make an informed purchasing decision. -
How can I vet suppliers of ceramics size reduction equipment?
Vetting suppliers requires thorough research and due diligence. Start by checking their industry reputation, years of experience, and client testimonials. Request case studies or references from similar industries and inquire about their after-sales support, warranty policies, and availability of spare parts. Additionally, visiting their facilities or attending trade shows can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and operational capabilities. -
What are typical payment terms for purchasing ceramics size reduction equipment?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier and region, but typical arrangements may include a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by the balance due prior to shipment. Some suppliers might offer flexible financing options or payment plans, especially for large orders. It’s crucial to clarify these terms upfront, including any penalties for late payments, to ensure a smooth transaction and avoid misunderstandings. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for ceramics size reduction equipment?
The minimum order quantity for ceramics size reduction equipment varies by supplier and the type of equipment. Generally, suppliers may have a MOQ ranging from one unit to several, depending on production capabilities and the complexity of the machinery. When sourcing, inquire about the possibility of smaller orders or pilot equipment to evaluate the machinery’s effectiveness before committing to a larger purchase. -
How does logistics impact the procurement of ceramics size reduction equipment?
Logistics plays a critical role in the procurement process, particularly for international buyers. Consider shipping options, delivery times, and the costs associated with customs duties and taxes in your region. Ensure your supplier is experienced in handling international shipments and can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. Additionally, discuss the potential for local support or installation services, as this can affect operational efficiency once the equipment arrives. -
What customization options are available for ceramics size reduction equipment?
Many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific operational needs, such as altering the size, configuration, or features of the equipment. Customizations can include modifications to accommodate different materials, enhanced safety features, or integration with existing production lines. When discussing your requirements with potential suppliers, be clear about your needs and ask for examples of past custom projects they have successfully completed to gauge their capability in this area.
Top 5 Ceramics Size Reduction Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Stedman Machine Company – Industrial Crushers
Domain: stedman-machine.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Stedman Machine Company offers industrial clay, brick, and ceramic crushers designed for size reduction in the brick, clay, and ceramic industries. Key products include: Mega Slam HSI, Grand Slam HSI, V-Slam Impactor VSI, various Cage Mills and Pulverizers, Hammer Mill Crushers, and Lump Breakers. These machines are engineered to improve productivity, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance safety i…
2. IQS Directory – Size Reduction Equipment
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Size Reduction Equipment includes devices engineered to crush and grind materials, effectively reducing their size. Key types include pulverizers, which handle a wide range of materials such as coal, shale, brick, concrete, wood, limestone, and plastics. The equipment is designed for specific throughput or grinding capacity based on the Hardgrove Grindability Index (HGI) value, considering factors…
3. Digital Fire – Particle Size Reduction Solutions
Domain: digitalfire.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Particle size reduction refers to the process of pulverizing ceramic materials, particularly clays, into fine powders. Common technologies used for this process include: 1. Hammer Mills: These mills feed material into a grinding chamber where a rapidly rotating rotor with hammers strikes the material. They are simple in design, have low initial costs, high energy consumption, and low wear (except …
4. MSE Supplies – 3D Mixers
Domain: msesupplies.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 3D Mixers: MSE PRO 5L Lab Scale 3D Movement Powder Mixer – $8,311.95; MSE PRO 15L Lab Scale 3D Movement Powder Mixer – $9,235.95; MSE PRO 20L Lab Scale 3D Movement Powder Mixer – $10,291.95; High Performance Dr. Fritsch 3D Powder Shaker Mixer – Request a Quote.
5. Munson Machinery – Size Reduction Equipment
Domain: munsonmachinery.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“size_reduction_equipment”: {“large_bulk”: [“CX Heavy Duty Cutters”, “De-Clumper™ Lump Breakers”, “Titan™ Shredders”, “Maxum™ Crushers”], “coarse”: [“SCC™ Screen Classifying Cutters”, “Magnum™ Cutters”, “Laboratory Mini Cutters”, “Security Destructor”, “Rotary Knife Cutters”, “Pin Mills”], “fine”: [“Pin Mills”, “Attrition Mills”, “HammerHead™ Hammer Mills”]}, “material_requirements”: [“Powders”, …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ceramics size reduction equipment
In the dynamic landscape of ceramics size reduction equipment, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal strategy for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. Understanding the diverse types of size reduction machinery—ranging from crushers to grinders—enables buyers to align their equipment choices with specific material properties and processing requirements. By prioritizing equipment that not only meets immediate production needs but also supports future scalability, companies can optimize their investment and improve overall performance.
For international buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the importance of selecting reliable suppliers cannot be overstated. Building strong partnerships with manufacturers that offer tailored solutions and robust after-sales support is essential for mitigating risks associated with equipment procurement.
As the market evolves, technological advancements in ceramics size reduction equipment promise to drive efficiency and sustainability in production processes. By staying informed about these trends and leveraging strategic sourcing practices, businesses can position themselves competitively. Engage with reputable suppliers and explore innovative solutions that will not only meet current demands but also pave the way for future growth. Investing wisely today ensures your operations remain at the forefront of the ceramics industry tomorrow.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to ceramics size reduction equipment
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.