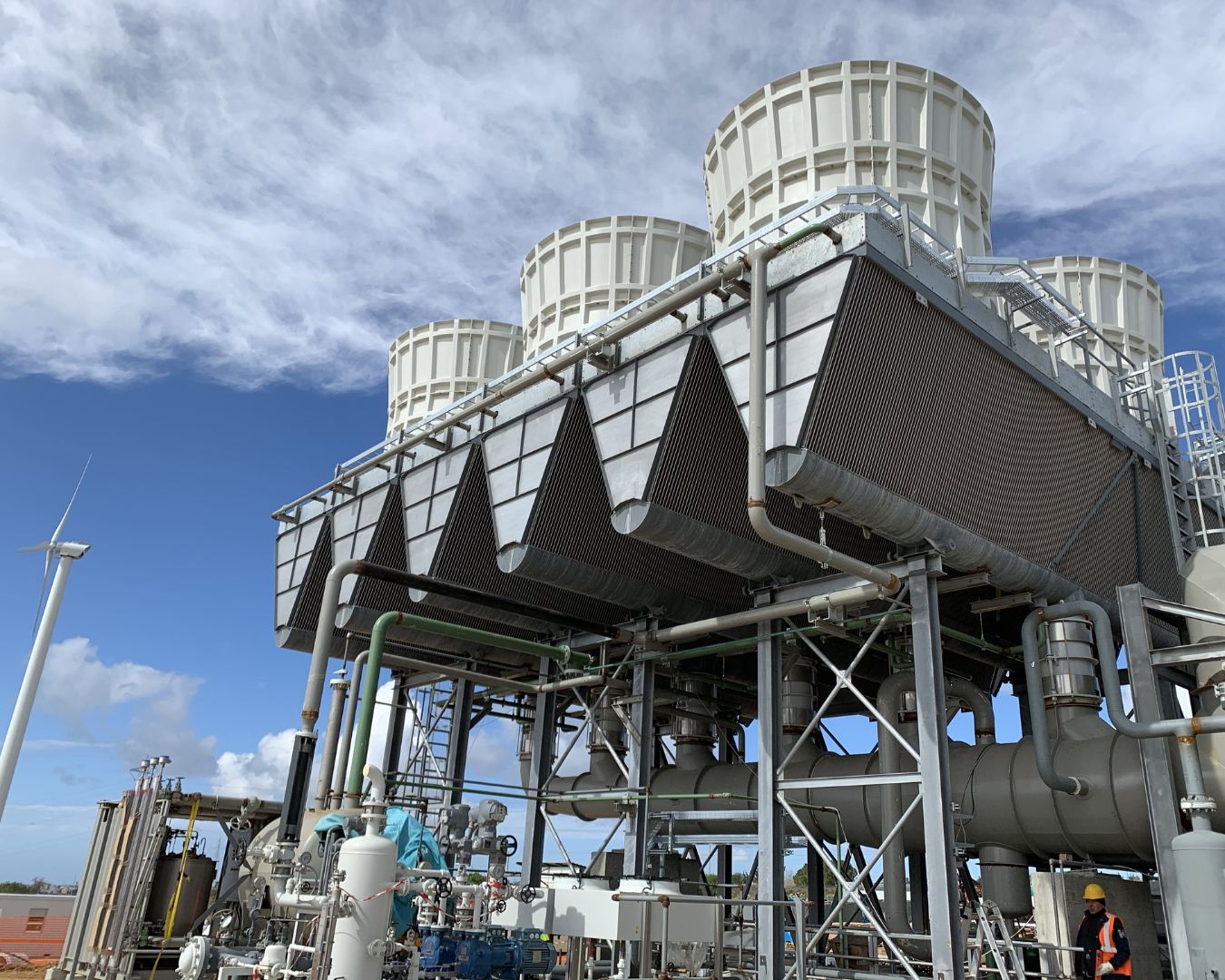
How to Source An Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for an induced draft air cooled condenser
In the quest for efficient thermal management solutions, sourcing an induced draft air cooled condenser (ACC) presents a pivotal challenge for international B2B buyers. These systems, essential for optimizing power plant performance and minimizing water consumption, are increasingly favored in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. However, the complexity of selecting the right technology, assessing supplier reliability, and understanding cost implications can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of induced draft air cooled condensers, covering various types, applications, and the latest innovations in the field. It also addresses critical factors such as supplier vetting processes, maintenance considerations, and cost-benefit analyses, empowering buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals. With a focus on actionable insights, this resource equips international buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market effectively.
As industries strive for sustainability and efficiency, understanding the nuances of induced draft ACCs becomes increasingly vital. This guide not only highlights the advantages of these systems but also provides a roadmap for evaluating potential suppliers and selecting the best fit for specific operational needs. By leveraging this information, buyers can ensure they invest in the most effective solutions, driving both performance and profitability in their projects.
Understanding an induced draft air cooled condenser Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| W-Style® Induced Draft ACC | Unique “W” heat exchanger structure, reduced back pressure | Power plants, industrial cooling | Pros: Lower steel weight, improved maintenance access; Cons: Newer technology may require more research. |
| InAIR® Induced Draft ACC | Fans positioned above heat exchangers, enhanced thermal performance | Renewable energy, petrochemical | Pros: Efficient heat transfer; Cons: Higher fan loading may affect durability. |
| Single-Row Condenser (SRC®) | Utilizes single-row finned tubes for optimal heat exchange | HVAC systems, refrigeration | Pros: Compact design, lower material costs; Cons: Limited capacity compared to multi-row designs. |
| Modular Induced Draft ACC | Prefabricated modules for easy installation | Mining, large-scale industrial use | Pros: Quick setup, customizable; Cons: Transportation costs may be high. |
| Hybrid Induced Draft ACC | Combines air and water cooling for optimal efficiency | Data centers, chemical processing | Pros: Versatile cooling options; Cons: More complex maintenance requirements. |
What are the Characteristics of W-Style® Induced Draft ACC?
The W-Style® Induced Draft Air-Cooled Condenser features a distinctive “W” shaped heat exchanger that optimizes the flow of steam and reduces back pressure. This design minimizes the risk of flow-accelerated corrosion, making it particularly suitable for power plants and industrial cooling applications. Buyers should consider its lower steel weight and improved maintenance access, although the relatively new technology may necessitate additional research to assess long-term performance and reliability.
How Does the InAIR® Induced Draft ACC Stand Out?
The InAIR® Induced Draft ACC is characterized by its fans located above the heat exchangers, allowing for enhanced thermal performance. This type is well-suited for renewable energy projects and petrochemical applications, where efficient heat transfer is crucial. While it offers significant efficiency benefits, buyers should be aware of the higher fan loading, which could impact the longevity of the system and necessitate careful monitoring.

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
What Makes Single-Row Condenser (SRC®) a Viable Option?
The Single-Row Condenser (SRC®) employs single-row finned tubes designed for effective heat exchange in compact spaces, making it ideal for HVAC systems and refrigeration applications. This design leads to lower material costs and a smaller footprint, which can be advantageous for space-constrained installations. However, its capacity limitations compared to multi-row designs may be a consideration for larger projects, prompting buyers to evaluate their specific cooling needs.
Why Consider Modular Induced Draft ACC?
Modular Induced Draft ACCs are prefabricated systems that facilitate quick and easy installation, making them ideal for mining and large-scale industrial applications. Their customizable nature allows for tailored solutions to specific cooling requirements. However, potential buyers should factor in the transportation costs associated with these larger modules, which may impact overall project budgets.
What Advantages and Challenges Does Hybrid Induced Draft ACC Present?
Hybrid Induced Draft ACC systems combine air and water cooling methods, offering versatility for applications such as data centers and chemical processing facilities. This adaptability can lead to optimal cooling performance under varying operational conditions. Nevertheless, the complexity of maintenance for hybrid systems can pose challenges, necessitating skilled personnel and possibly increasing operational costs. Buyers should weigh these factors against their cooling demands and maintenance capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of an induced draft air cooled condenser
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of an induced draft air cooled condenser | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Steam turbine exhaust condensing in thermal power plants | Enhances thermal efficiency and reduces water consumption | Consider local climate, operational temperatures, and maintenance needs |
| Oil & Gas | Gas compression and cooling in processing facilities | Increases operational reliability and reduces downtime | Evaluate corrosion resistance and material durability in harsh environments |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Cooling for exothermic reactions and distillation processes | Improves process safety and energy efficiency | Assess compatibility with chemicals and potential for fouling |
| Mining and Metallurgy | Cooling for ore processing and smelting operations | Reduces water usage and minimizes environmental impact | Ensure compliance with local environmental regulations |
| Food and Beverage | Cooling in pasteurization and refrigeration systems | Enhances product quality and extends shelf life | Focus on hygiene standards and ease of maintenance |
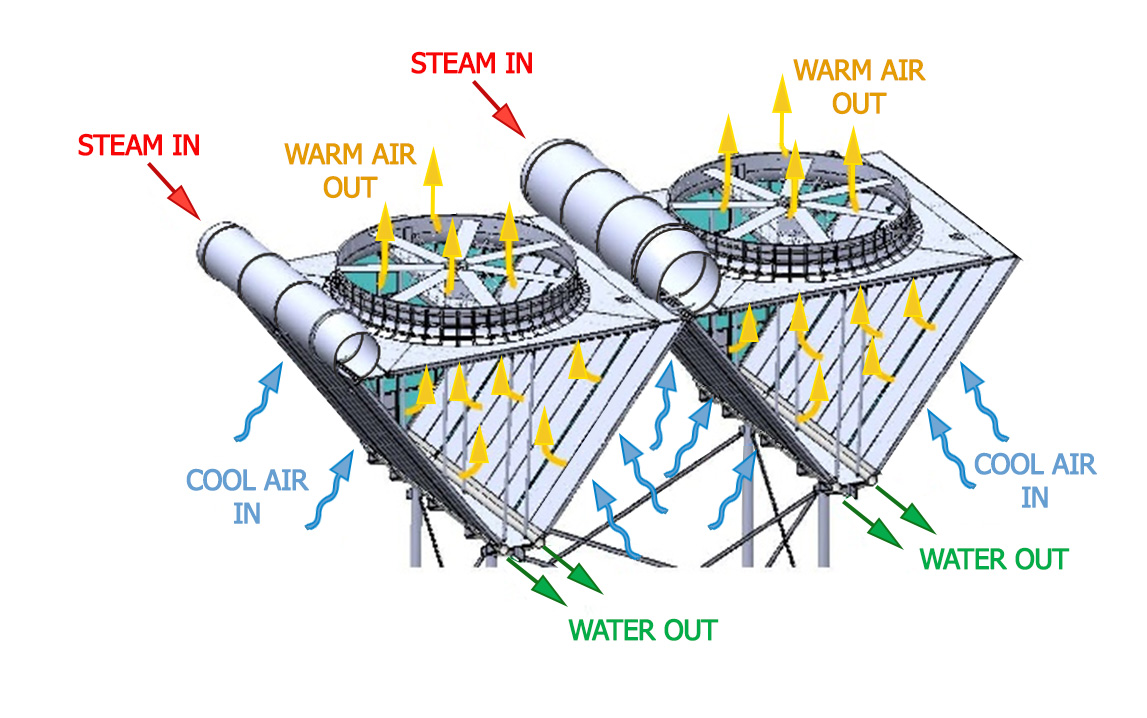
How is an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Used in Power Generation?
In the power generation sector, induced draft air cooled condensers are vital for condensing steam from turbines, allowing for efficient energy recovery. These systems minimize water consumption, a critical factor in areas with limited water resources, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East. Buyers must consider factors such as local climate, as high ambient temperatures can affect cooling efficiency, and the operational requirements of the power plant to ensure optimal performance.
What Role Does an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Play in Oil & Gas?
In the oil and gas industry, induced draft air cooled condensers are employed for cooling gas compressors and other equipment in processing facilities. Their ability to operate effectively in high-temperature environments enhances reliability and reduces the likelihood of equipment failure. Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials with high corrosion resistance and durability to withstand the harsh conditions often found in oil and gas operations, particularly in remote locations in South America and the Middle East.
How Does an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Benefit Chemical Manufacturing?
Chemical manufacturing processes often involve exothermic reactions that require efficient cooling solutions. Induced draft air cooled condensers provide effective temperature control, enhancing process safety and energy efficiency. International buyers in this sector should assess the compatibility of these condensers with various chemicals and consider potential fouling issues that could affect performance, especially in regions with high humidity or dust.
Why is an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Important for Mining and Metallurgy?
In mining and metallurgy, induced draft air cooled condensers are utilized for cooling processes such as ore processing and smelting. These systems help reduce water usage and mitigate environmental impacts, which is increasingly important for compliance with stringent regulations in Europe and beyond. Buyers should ensure that the condensers meet local environmental standards and are designed to operate efficiently in the specific climatic conditions of the mining site.
How Does an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Enhance Food and Beverage Production?
In the food and beverage industry, induced draft air cooled condensers are essential for cooling during pasteurization and refrigeration processes. They improve product quality by maintaining optimal temperatures, thereby extending shelf life. B2B buyers should focus on hygiene standards and ease of maintenance when sourcing these systems, especially in regions where food safety regulations are strict, such as Germany and other European countries.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘an induced draft air cooled condenser’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Heat Transfer Efficiency in Hot Climates
The Problem: In regions with high ambient temperatures, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, B2B buyers often face significant challenges related to heat transfer efficiency when using induced draft air-cooled condensers (ACC). The high air temperatures can lead to reduced cooling capacity and increased operational costs, as the system struggles to maintain optimal performance. Additionally, the risk of overheating in the cooling system can lead to premature equipment failure, causing costly downtime and maintenance issues.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should invest in advanced design features that enhance thermal performance. Specifically, selecting an induced draft air-cooled condenser with a “W” heat exchanger structure can significantly improve heat transfer efficiency. This design minimizes steam velocity and reduces the risk of flow-accelerated corrosion, ensuring better longevity and performance under high temperature conditions. Furthermore, conducting thorough Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis during the design phase can help identify airflow patterns and optimize the placement of the condenser to maximize cooling efficiency. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the fins will also help maintain optimal airflow and cooling performance, particularly in dusty environments.
Scenario 2: Increased Maintenance Needs Due to Environmental Factors
The Problem: Buyers operating in harsh environments, such as coastal regions or areas with high particulate matter, often encounter increased maintenance needs for their induced draft ACCs. Salt, dust, and other contaminants can accumulate on the cooling fins, leading to reduced efficiency and higher energy consumption. Over time, this can escalate maintenance costs and disrupt production schedules.
The Solution: To mitigate these maintenance challenges, it’s crucial to choose an induced draft ACC that offers easy access for cleaning and maintenance. Consider models that feature robust materials resistant to corrosion and fouling, which can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of maintenance required. Implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes inspections and cleaning can help keep the system operating efficiently. Additionally, using protective coatings on the fins can provide an extra layer of defense against environmental contaminants. For buyers, establishing a partnership with a reliable maintenance service provider can ensure that upkeep is performed efficiently and effectively, reducing the risk of unexpected downtimes.
Scenario 3: Concerns About Noise and Vibration Levels
The Problem: Many industrial buyers are concerned about noise and vibration levels associated with induced draft air-cooled condensers. These factors can impact not only the working environment but also compliance with local regulations regarding noise pollution. In densely populated areas or sensitive environments, excessive noise can lead to regulatory challenges or negatively affect community relations.
Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
The Solution: To address noise and vibration concerns, it is essential to select an induced draft ACC that is designed with noise reduction features. Look for models that utilize variable-speed fans and vibration-damping mounts to minimize operational noise. Furthermore, conducting a noise assessment during the installation phase can help identify potential issues before they arise. Buyers should also consider sound barriers or acoustic enclosures if noise levels exceed acceptable limits. Regular monitoring of operational noise levels can help ensure compliance with local regulations and maintain good community relations. Investing in a condenser with advanced engineering solutions can lead to quieter operations and greater overall satisfaction among stakeholders.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for an induced draft air cooled condenser
What Are the Key Materials Used in Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
When selecting materials for an induced draft air cooled condenser (ACC), it is crucial to consider properties such as temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. Here, we analyze four common materials: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP). Each material presents unique advantages and limitations that can impact performance and suitability for specific applications.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle significant pressure loads.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and strength, making it suitable for large structural components. However, it is prone to corrosion, especially in humid environments, which can lead to a shorter lifespan without protective coatings. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as carbon steel can be easily welded and formed.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with various media but requires protective measures against corrosion, especially in regions with high humidity or saline environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local environmental conditions that may affect carbon steel’s durability.
What About Stainless Steel for Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 1,500°F (815°C) depending on the grade. It is also resistant to pitting and oxidation.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and low maintenance, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it is significantly more expensive than carbon steel, which can impact overall project budgets. The manufacturing process is more complex, requiring specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications involving corrosive media or environments, ensuring a longer service life.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 for pipes and tubes is critical. Buyers in Europe, such as Germany, often prefer stainless steel for its durability and compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, with a temperature rating of about 400°F (204°C). It is also resistant to corrosion, particularly in non-saline environments.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for easier handling and installation, reducing structural support requirements. However, its lower strength compared to steel can be a limitation in high-pressure applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, but care must be taken in high-pressure scenarios.
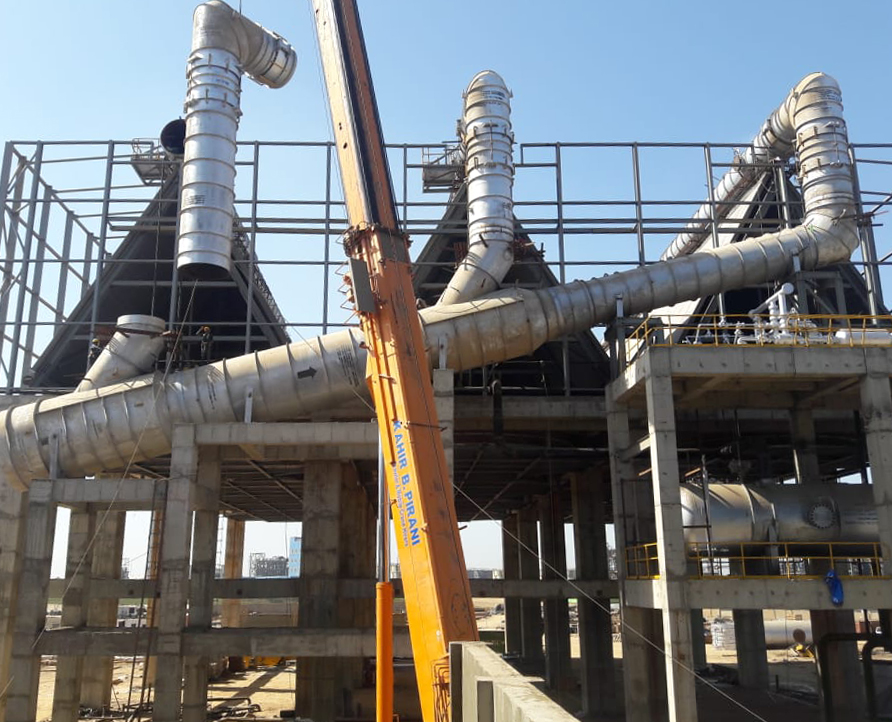

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM B221. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures can be a concern, aluminum’s thermal properties can be advantageous.
What Role Does Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Play in Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Key Properties: FRP is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 200°F (93°C). It is lightweight and has good insulating properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of FRP is its resistance to corrosion and chemical attack, making it ideal for aggressive environments. However, it has lower mechanical strength compared to metals and may not be suitable for all structural applications. Manufacturing can be complex, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: FRP is particularly effective in applications involving corrosive media, such as in coastal areas or chemical processing plants.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties is crucial. Buyers in regions like South America may find FRP beneficial for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers
| Material | Typical Use Case for an induced draft air cooled condenser | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components and supports | Cost-effective and strong | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments and high-temperature applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight structures and non-corrosive environments | Lightweight and good thermal conductivity | Lower strength under high pressure | Medium |
| Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic | Corrosive media applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This guide provides valuable insights into material selection for induced draft air cooled condensers, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for an induced draft air cooled condenser
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for an Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser?
The manufacturing of an induced draft air cooled condenser (ACC) involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets performance and durability standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Manufacturing an Induced Draft ACC?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where high-quality materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are sourced. These materials are selected based on their thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Once sourced, the materials undergo rigorous inspection to confirm they meet predefined specifications. This step may involve testing for mechanical properties and chemical composition.
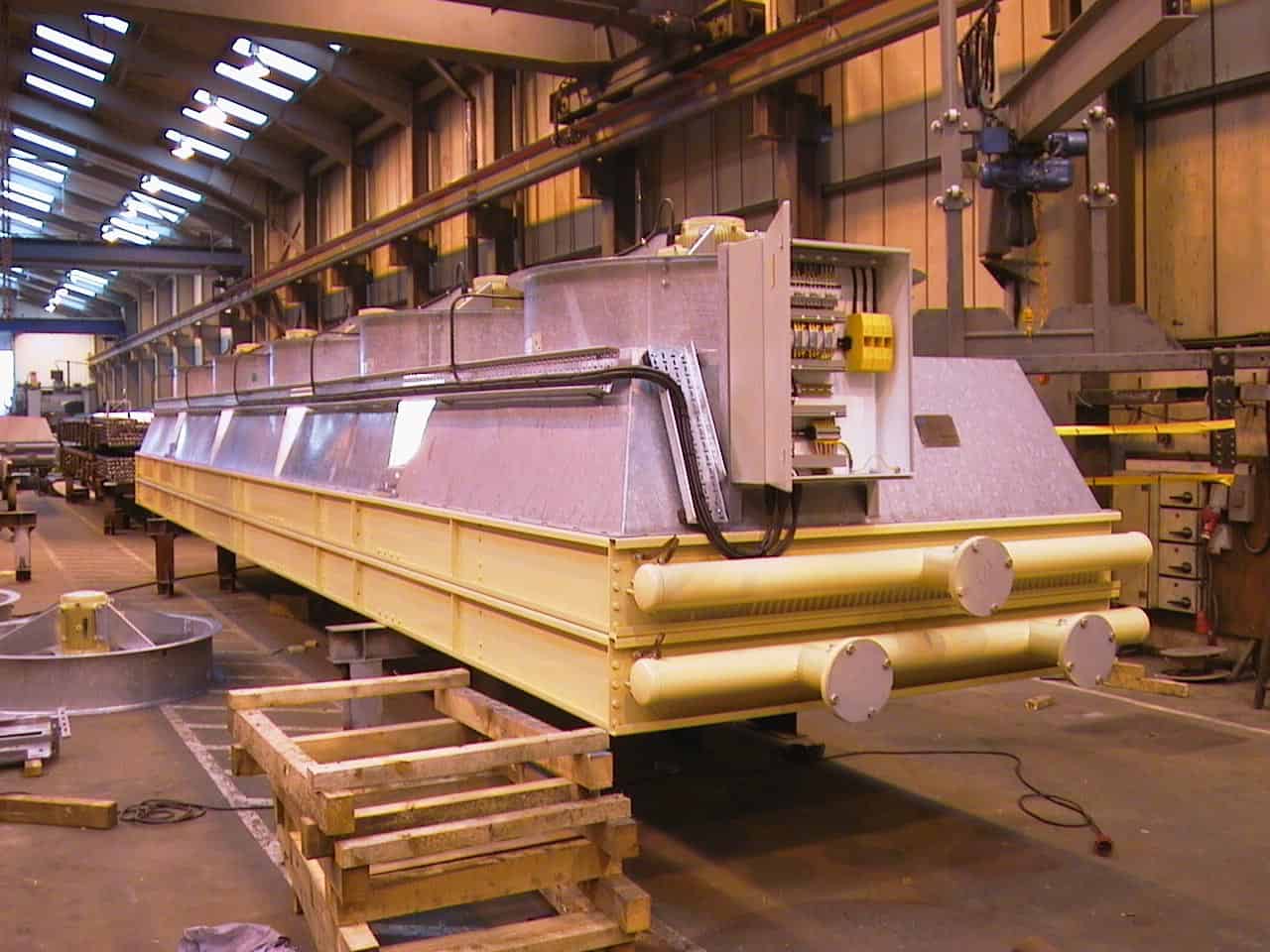

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
What Techniques Are Used in Forming the Components?
After material preparation, the forming stage begins. This includes cutting, bending, and shaping the materials into the required forms for the heat exchangers, fan systems, and structural components. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are commonly employed to achieve precise dimensions. For the “W” shaped heat exchangers, specialized forming techniques are used to create the unique design that enhances thermal performance while minimizing back pressure.
How is the Assembly of Induced Draft ACC Conducted?
The assembly of the ACC is a critical phase where all components are brought together. This includes the installation of the heat exchangers, fan systems, and steam manifolds. The assembly process is typically performed in a controlled environment to minimize contamination and ensure quality. High-strength fasteners and welding techniques are employed to ensure structural integrity. Throughout this process, operators follow detailed assembly instructions and checklists to maintain consistency.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Enhance Durability?
Finishing processes include surface treatments such as galvanization, powder coating, or painting to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. These treatments not only protect the ACC from environmental factors but also improve its overall lifespan. Quality control measures during this stage include visual inspections and adherence to specific thickness and uniformity standards.

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Induced Draft ACC Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of induced draft air cooled condensers to ensure reliability and efficiency. Several international standards and industry-specific certifications are relevant, including ISO 9001, which establishes a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards assures B2B buyers that the manufacturer has effective processes in place to meet customer requirements consistently.
Which Quality Control Checkpoints Are Critical During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular inspections during the manufacturing process to catch defects early. This may include dimensional checks and performance tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive assessment of the finished product, including functional tests and visual inspections, to ensure it meets all specifications before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and durability of an induced draft ACC. These methods may include:
- Hydrostatic Testing: To ensure there are no leaks in the condenser.
- Thermal Performance Testing: To assess the efficiency of heat exchange under different operating conditions.
- Vibration Analysis: To identify any potential issues with fan and motor systems that could lead to premature failure.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing can be used to detect internal defects without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse international markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and QC measures in place.
- Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can help buyers understand how the supplier tracks and manages quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and product quality.
- Certificates of Compliance: Buyers should request certificates that confirm compliance with relevant international standards and industry-specific certifications.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing induced draft air cooled condensers from international suppliers, buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control and certification. Different countries may have specific regulations or standards that need to be met. For instance, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while those in the Middle East might look for API certifications. Understanding these regional nuances helps ensure compliance and reduces the risk of delays or penalties during importation.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for induced draft air cooled condensers are multifaceted, requiring attention to detail at every stage. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they invest in high-quality, reliable equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘an induced draft air cooled condenser’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring an induced draft air-cooled condenser (ACC). By following this step-by-step checklist, you will ensure that you evaluate the critical aspects of the procurement process, from defining technical specifications to assessing supplier capabilities. This comprehensive approach will help you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital to ensuring that the induced draft ACC meets your operational requirements. Consider factors such as capacity, thermal performance, and the specific environment in which the condenser will operate.
- Performance Metrics: Define the required heat transfer rates, steam flow rates, and back pressure limits.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess factors like temperature extremes, humidity, and potential exposure to corrosive elements.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Compliance
Understanding industry standards and compliance regulations is crucial for ensuring that the equipment meets safety and efficiency benchmarks. Research local and international standards relevant to air-cooled condensers.
- Certifications: Look for suppliers that hold necessary certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the equipment adheres to environmental regulations, particularly concerning emissions and energy efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. This helps mitigate risks associated with equipment reliability and supplier performance.
Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
- Company Profile: Request detailed company profiles, including years in business, expertise in ACC technology, and notable projects.
- References and Case Studies: Seek testimonials and case studies from clients within similar industries or geographical regions to gauge reliability and performance.
Step 4: Assess Technical Support and Maintenance Services
Consider the level of technical support and maintenance services offered by the supplier. A reliable support system is critical for the long-term operation and efficiency of the ACC.
- Maintenance Programs: Inquire about maintenance options, including preventive maintenance schedules and emergency repair services.
- Training and Support: Evaluate whether the supplier provides training for your staff on operation and maintenance procedures.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline all costs associated with the purchase, including installation, commissioning, and ongoing maintenance.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure that the quotations provide a breakdown of costs to avoid hidden charges.
- Comparative Analysis: Use these quotations to perform a comparative analysis to determine the best value for your investment.
Step 6: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Before finalizing your purchase, conduct a comprehensive risk assessment of the proposed solutions. This includes evaluating potential operational risks associated with the installation and use of the ACC.
- Operational Risks: Identify potential issues such as equipment failure, maintenance delays, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Mitigation Strategies: Develop strategies to mitigate identified risks, ensuring continuity of operations.
Step 7: Finalize Contract Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s time to finalize the contract terms. Clear and comprehensive agreements will protect your interests and set expectations for both parties.
- Delivery and Installation Timelines: Specify timelines for delivery, installation, and commissioning to ensure accountability.
- Warranty and Liability Clauses: Ensure that warranty terms and liability clauses are clearly defined to protect against equipment failures and defects.
By following this checklist, you will be well-equipped to source an induced draft air-cooled condenser that meets your technical needs and aligns with your operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for an induced draft air cooled condenser Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
When sourcing an induced draft air cooled condenser (ACC), understanding the cost components is vital for accurate budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
Materials: The cost of raw materials, particularly high-quality steel and specialized components like finned tubes and fans, significantly influences the overall price. Advanced materials that enhance durability and performance may come at a premium, so it’s essential to assess whether the benefits justify the extra cost.
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the manufacturing location. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America or Africa, you may find more competitive pricing. However, the quality of workmanship should not be compromised, as it directly affects the performance and longevity of the equipment.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, facility costs, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs, which can be a negotiation point when discussing prices with suppliers.
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can add to the initial costs. However, leveraging standardized designs can help reduce tooling expenses. It’s advisable to discuss potential cost-saving measures with suppliers who may offer alternatives that meet your specifications without incurring high tooling fees.
Quality Control: Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability and performance, which can add to costs. Certifications such as ISO or industry-specific standards may also be required, impacting the final price. Ensure that the chosen supplier meets relevant certifications to avoid costly issues later.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, including tariffs and insurance, should be factored into the total cost. The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can greatly influence logistics costs and responsibilities, affecting your total expenditure.
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the market landscape and average margins can provide leverage during negotiations.
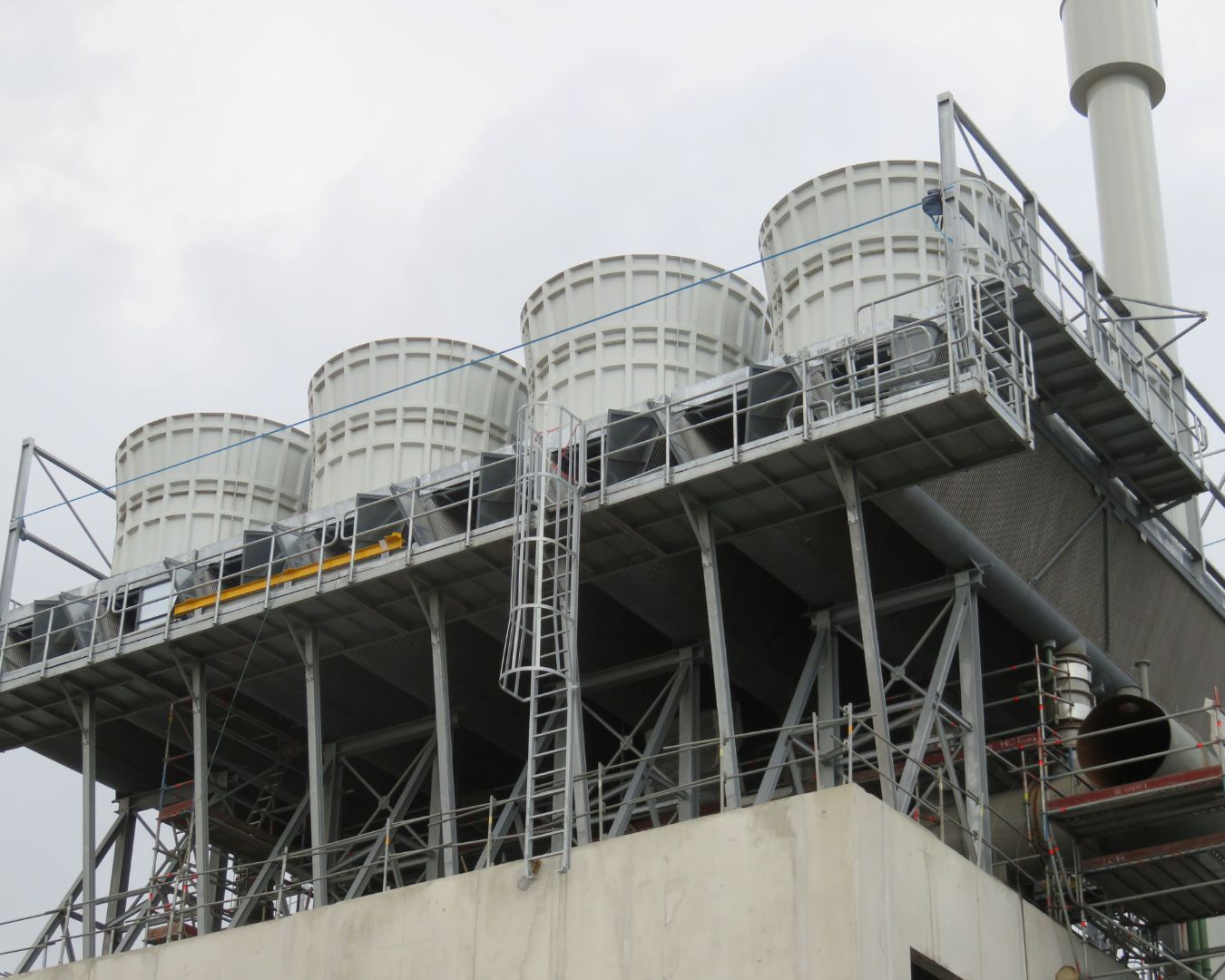

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Several factors influence pricing beyond the basic cost components. These include volume or minimum order quantities (MOQs), specifications and customization, material choices, quality certifications, and supplier factors.
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. If your business anticipates future expansion, discussing potential volume discounts with suppliers can be beneficial.
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized systems may incur additional costs. Clearly defined specifications can streamline the manufacturing process and minimize unexpected expenses. Collaboration with suppliers during the design phase can help identify potential cost savings.

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
Materials and Quality: The choice of materials directly correlates with the performance and longevity of the ACC. Higher quality materials may initially be more expensive but can lead to lower total cost of ownership (TCO) over time due to reduced maintenance and replacement needs.
Supplier Factors: Relationships with suppliers can significantly impact pricing. Established partnerships may yield better pricing and terms, while new suppliers may require more negotiation.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs When Sourcing Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
To maximize your investment in an induced draft air cooled condenser, consider the following strategies:
Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
Negotiation: Always be prepared to negotiate on price, especially if you can leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers. Highlighting your potential for repeat business can also encourage suppliers to offer better terms.
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, not just the initial purchase price. Consider installation, maintenance, and operational costs when making your decision. A slightly higher upfront cost may be justified by long-term savings.
Understanding Pricing Nuances: For international buyers, be aware of currency fluctuations and local market conditions that may affect pricing. Establishing contracts that account for these factors can protect your investment.
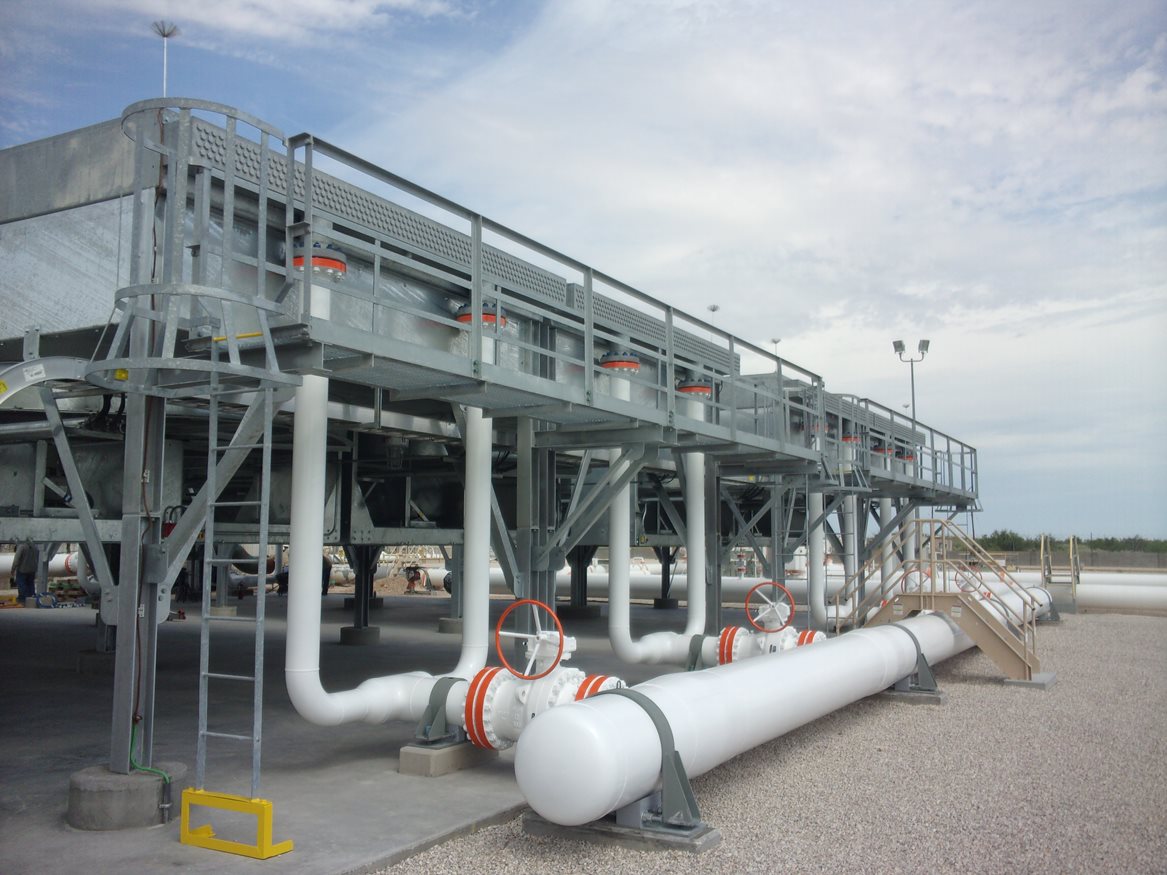

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
Regional Considerations: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions. For instance, buyers in Europe may face different cost dynamics compared to those in Africa or South America. Understanding these nuances can help in negotiating more favorable deals.
Disclaimer: Prices for induced draft air cooled condensers can vary widely based on specifications, market conditions, and supplier factors. Always seek multiple quotes and perform due diligence to ensure you are receiving a fair price.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing an induced draft air cooled condenser With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers
In the realm of thermal management and cooling technologies, businesses often seek the most efficient and cost-effective solutions. An induced draft air cooled condenser (ACC) is one such option, but several alternatives exist that may better suit specific operational needs. Understanding these alternatives can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and budget constraints.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | An Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser | Alternative 1: Forced Draft Air Cooled Condenser | Alternative 2: Wet Cooling Tower |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal efficiency; reduced back pressure and flow accelerated corrosion | Good thermal performance but higher back pressure | Very high efficiency; effective at high heat loads |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower operational costs | Generally lower initial costs; higher energy costs | High initial investment; operational costs can vary based on water availability |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful site planning; compact footprint | Easier to install due to simpler design | More complex installation; requires significant water supply infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized maintenance but less frequent | More frequent maintenance due to fan and motor placement | Regular maintenance of water treatment systems required |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for arid regions with limited water supply | Suitable for various climates with adequate water | Best for regions with abundant water resources |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
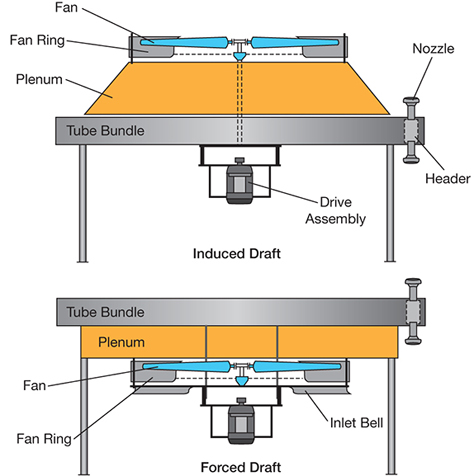
1. Forced Draft Air Cooled Condenser
Forced draft air cooled condensers utilize fans positioned at the front of the unit to push air through the heat exchangers. This design typically offers a lower initial cost compared to induced draft systems, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. However, forced draft condensers can face challenges such as higher back pressure, which may lead to reduced thermal efficiency and increased energy consumption. They are more straightforward to install, but their maintenance can be more frequent due to the placement of mechanical components in the airflow.
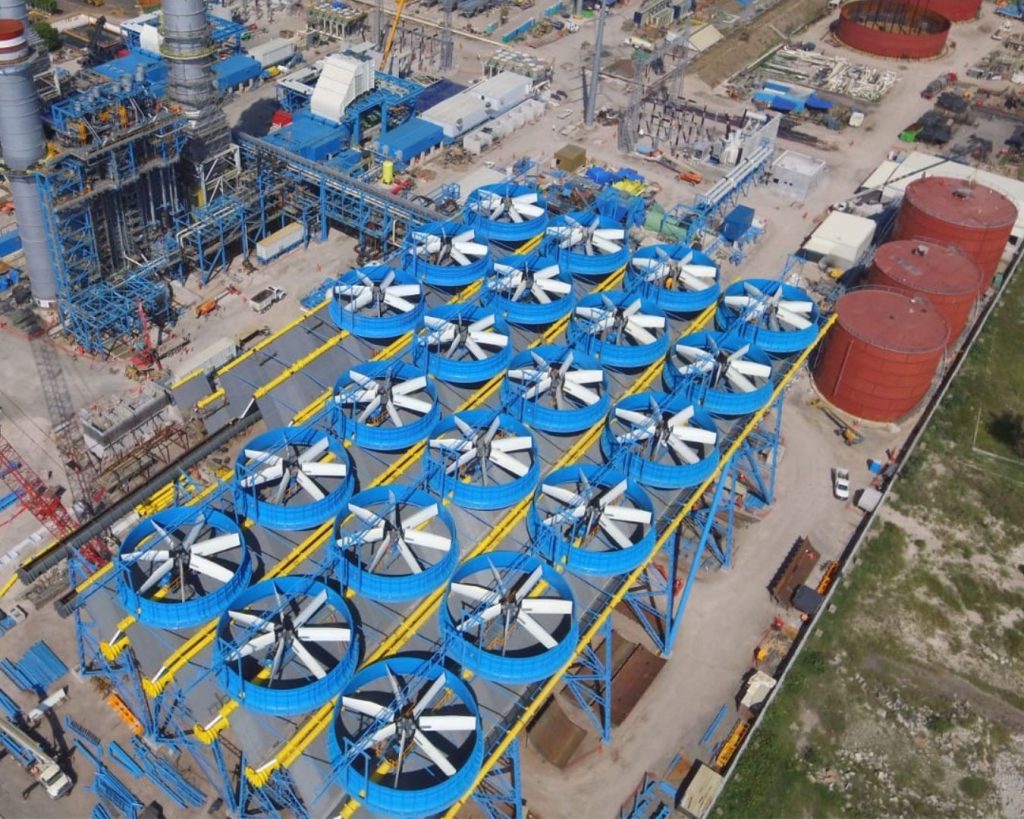

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
2. Wet Cooling Tower
Wet cooling towers leverage the principle of evaporative cooling to dissipate heat. They are highly efficient and effective for high heat loads, making them suitable for large industrial applications. However, they require a significant water supply and are subject to operational costs associated with water treatment and maintenance. The initial investment in wet cooling towers can be substantial, especially in regions where water is scarce or costly. Furthermore, they can pose environmental challenges, such as water loss through evaporation and increased risk of microbial growth if not properly managed.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate cooling technology, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance requirements, cost implications, and environmental conditions. An induced draft air cooled condenser may be ideal for operations in arid regions where water conservation is crucial, while forced draft systems might be more economical for projects with fewer constraints on water supply. Conversely, wet cooling towers can provide exceptional efficiency but require careful consideration of water resources and maintenance needs. Ultimately, understanding the unique demands of your project will guide you toward the most suitable solution, ensuring both operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for an induced draft air cooled condenser
What are the Key Technical Properties of Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Induced draft air cooled condensers (ACC) are essential components in power generation and industrial processes. Understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The construction materials typically include carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, each chosen for its corrosion resistance and structural integrity. The material grade impacts durability, maintenance needs, and overall lifespan. For instance, stainless steel is preferred in corrosive environments, while carbon steel is cost-effective for less aggressive applications. Selecting the right material is essential for reducing long-term operational costs. -
Heat Transfer Efficiency
This property measures the condenser’s ability to transfer heat from steam to the ambient air. It is often quantified in terms of the overall heat transfer coefficient (U-value). Higher efficiency results in improved power output and lower operational costs. A more efficient system can also reduce the size and number of units required, providing significant savings in installation and maintenance. -
Back Pressure
Back pressure refers to the resistance against the steam flow within the condenser. Lower back pressure is preferable as it enhances the turbine’s efficiency and overall system performance. A design that minimizes back pressure can lead to increased power generation and reduced fuel consumption, making it a critical specification for buyers focused on efficiency. -
Fan Power Consumption
The power required by the induced draft fans is a key operational cost factor. This specification is influenced by the design and arrangement of the fans, as well as the ambient conditions. Energy-efficient fans can significantly lower operational costs, making it vital for buyers to assess this aspect when evaluating ACC systems. -
Footprint and Height
The physical dimensions of the ACC can impact site layout and installation costs. A reduced footprint allows for more flexible site planning, especially in constrained environments. Additionally, lower height specifications can minimize structural support requirements and reduce costs associated with foundations and permits. -
Vibration Levels
Monitoring and managing vibration levels is essential for equipment longevity and operational reliability. High vibration can lead to mechanical failures and increased maintenance needs. Understanding the vibration specifications can help buyers select a system that aligns with their operational reliability goals.
What are Common Trade Terms Related to Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
In the B2B landscape, familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms relevant to induced draft ACCs:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. When purchasing an ACC, working directly with the OEM can ensure access to high-quality components and expert support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is important for buyers to manage their inventory and budget effectively, especially when considering large-scale installations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific products. For buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and facilitate competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions. -
CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics)
CFD is a simulation tool used to analyze fluid flow and heat transfer in systems like ACCs. Utilizing CFD analysis can help buyers assess performance under various operational conditions, leading to better-informed purchasing decisions. -
NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head)
NPSH is a critical parameter for ensuring that pumps within the ACC system operate efficiently without cavitation. Understanding NPSH requirements can prevent operational issues, ensuring reliable system performance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting induced draft air cooled condensers, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the an induced draft air cooled condenser Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Market?
The induced draft air cooled condenser (ACC) market is witnessing significant growth, driven by several global factors. Increasing energy demands, particularly in developing regions like Africa and South America, are pushing industries to seek efficient cooling solutions. The rise in thermal power generation, alongside stringent regulations for water conservation, has made induced draft ACCs an attractive option due to their ability to condense steam without consuming water. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as the development of innovative designs like the W-Style ACC, are enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Emerging B2B tech trends are also reshaping sourcing strategies. Digital platforms for procurement and supply chain management are becoming vital, allowing buyers to streamline their purchasing processes while gaining access to a broader range of suppliers. Furthermore, the integration of predictive maintenance technologies and IoT in ACC systems is enabling operators to enhance performance and minimize downtime, making these systems more appealing to international buyers.
In terms of market dynamics, buyers from regions such as the Middle East and Europe are increasingly focused on sourcing suppliers that can provide not just competitive pricing but also advanced technical support and maintenance services. The shift towards sustainable practices is also influencing procurement decisions, as buyers seek partners who prioritize environmental stewardship and offer innovative, eco-friendly solutions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the induced draft ACC sector. The environmental impact of cooling systems is under scrutiny, leading to a demand for technologies that minimize carbon footprints and promote resource conservation. Induced draft ACCs are inherently more sustainable than their water-cooled counterparts, as they eliminate water usage, thus addressing global water scarcity concerns.
Ethical sourcing is gaining traction among B2B buyers, especially in Europe and North America, where regulatory frameworks increasingly require transparency in supply chains. Buyers are looking for suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing processes. This includes compliance with environmental standards and certifications such as ISO 14001, which emphasizes effective environmental management systems.
Moreover, the adoption of green materials and technologies in the production of ACCs not only improves sustainability but also enhances the overall performance of the systems. Suppliers that can provide certifications for energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact are likely to stand out in a competitive market, making them more attractive to eco-conscious buyers.

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
What Is the Historical Context of Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
The evolution of induced draft air cooled condensers can be traced back to the need for efficient and sustainable cooling solutions in power generation. Traditional cooling methods, primarily water-cooled systems, have been challenged by increasing water scarcity and environmental regulations. The advent of induced draft systems marked a significant shift, allowing for air cooling without water consumption.
The introduction of innovative designs, such as the W-Style ACC, has further revolutionized the industry by reducing material usage and enhancing operational efficiency. This evolution has not only improved the performance of cooling systems but also made them more adaptable to diverse operational environments, including arid regions prone to high winds and temperature fluctuations. As the market continues to evolve, the focus on efficiency, sustainability, and technological advancements remains paramount, shaping the future of induced draft ACCs in the global landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of an induced draft air cooled condenser
-
How do I select the right induced draft air cooled condenser for my application?
Selecting the right induced draft air cooled condenser (ACC) involves understanding your specific cooling needs, steam flow rates, and site conditions. Consider factors such as the thermal performance requirements, available space, and local environmental conditions (e.g., temperature fluctuations and wind patterns). It’s also crucial to evaluate the design features of the ACC, such as the “W” heat exchanger structure, which can enhance efficiency and reduce corrosion risks. Collaborating with a knowledgeable supplier can provide insights tailored to your operational context. -
What are the key advantages of using an induced draft air cooled condenser over a forced draft system?
Induced draft air cooled condensers offer several advantages, including reduced back pressure on the steam system and lower wind sensitivity, enhancing operational reliability. The unique design minimizes the risk of flow-accelerated corrosion, contributing to longer lifespan and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, the compact structure requires less foundation work, reducing overall installation costs. This makes induced draft systems particularly suitable for environments where space and environmental factors are critical considerations. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for induced draft air cooled condensers?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience and reputation in the industry. Look for suppliers with a proven track record of successful installations and positive customer testimonials. Evaluate their technical support capabilities and after-sales service, including maintenance and spare parts availability. Additionally, verify certifications and compliance with international quality standards to ensure reliability and performance. Engaging in discussions about customization options and understanding their manufacturing processes can also provide valuable insights into their capabilities. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for induced draft air cooled condensers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and project specifications. Generally, manufacturers may have MOQs based on production capacity and material availability. For customized solutions, MOQs may be higher due to the specialized components involved. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your project scale while ensuring cost-effectiveness. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing an induced draft air cooled condenser?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but typical arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by progress payments linked to production milestones. Some suppliers may offer financing options or letter of credit arrangements, especially for international transactions. It’s crucial to clarify all payment terms upfront, including currency, due dates, and any penalties for late payments, to avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing an induced draft air cooled condenser?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation of the manufacturing processes, including quality control measures and testing protocols. Many reputable suppliers adhere to international standards such as ISO certifications. Additionally, you may consider on-site inspections during production or hiring third-party inspectors to verify the quality of materials and workmanship. Establishing clear specifications and performance criteria in your contract can also help maintain quality throughout the project lifecycle. -
What logistical considerations should I be aware of when importing air cooled condensers?
Logistical considerations include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs associated with importing equipment. Assess the lead times for manufacturing and shipping to align with your project schedule. It’s also important to coordinate with your supplier regarding packing and transportation to prevent damage during transit. Engaging a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping can streamline the logistics process and mitigate potential challenges. -
What are the common maintenance requirements for induced draft air cooled condensers?
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance of induced draft air cooled condensers. This typically includes routine inspections of the fans, motors, and heat exchanger surfaces for signs of wear or corrosion. Cleaning the finned tubes to prevent fouling and ensuring proper lubrication of moving parts are also crucial. Establishing a maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and operational conditions will help minimize downtime and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
Top 3 An Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SPG Dry Cooling – W-Style ACC®
Domain: spgdrycooling.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: W-Style ACC® is an Induced Draft Air-Cooled Condenser (ACC) designed for directly condensing steam turbine exhaust flow, returning condensate to the boiler without water loss. Key features include a unique “W” heat exchanger structure that reduces steel usage and overall height, leading to lower back pressure and reduced risk of flow accelerated corrosion. The module utilizes Single-Row Condenser …
2. Enexio – InAIR Air Cooled Condenser System
Domain: enexio.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The InAIR is an innovative and intelligent air cooled condenser system featuring induced draft fans. Key benefits include reduced air inlet and total height, smaller footprint, reduction of steel structure quantities (up to -60%) and weight (up to -50%), reduced construction costs (-10% to -25%), and decreased construction duration (20% to 30% fewer man-hours). It requires no fan bridge, minimizin…
3. SPX Cooling Tech – Cooling Towers & Heat Exchangers
Domain: spxcooling.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: SPX Cooling Tech, LLC is a leading global manufacturer of cooling towers, evaporative fluid coolers, evaporative condensers, and air-cooled heat exchangers. They offer products such as Evaporative Cooling Towers, Evaporative Fluid Coolers, Evaporative Condensers, Industrial Evaporators, Adiabatic Cooling Systems, MarleyGard™ Water Management, Cooling Tower Controls, Plume Abatement, and Recold Pro…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for an induced draft air cooled condenser
Why Should International Buyers Consider Induced Draft Air Cooled Condensers?
Induced draft air cooled condensers (ACC) offer significant advantages for power generation and industrial applications, particularly in regions with water scarcity. The innovative design of systems like the W-Style ACC® reduces back pressure and minimizes flow accelerated corrosion, enhancing operational efficiency and extending equipment lifespan. This is especially beneficial for international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where energy demands are rising and water resources are increasingly limited.
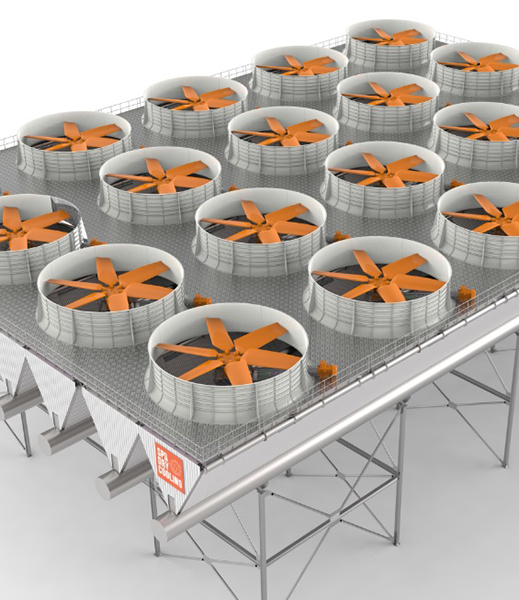

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Procurement Process?
Strategic sourcing is crucial for acquiring high-quality induced draft ACCs. By engaging with reputable suppliers, buyers can ensure they receive not only cutting-edge technology but also comprehensive support services tailored to their specific operational needs. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks associated with equipment downtime but also optimizes long-term investment returns.
What’s Next for Buyers in the Global Market?
As the global landscape evolves, investing in advanced cooling technologies will be vital for maintaining competitive advantage. International buyers should explore partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and sustainability. Embrace the transition towards more efficient cooling solutions and take the first step towards enhancing your operational efficiency today. Consider evaluating your current cooling systems and reaching out to suppliers for tailored solutions that meet your unique requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
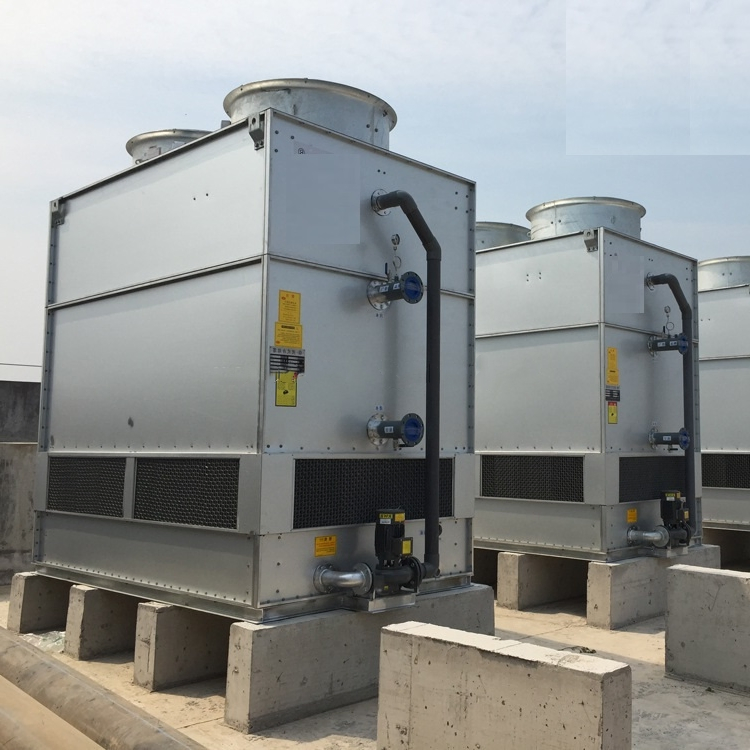

Illustrative image related to an induced draft air cooled condenser