How to Source 1-1 Heat Exchanger Effectively: A 2025 Checklist
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 1-1 heat exchanger
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right 1-1 heat exchanger can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications across industries—ranging from energy production to chemical processing—understanding the intricacies of these essential components is crucial. This guide is designed to demystify the complexities of the global market for 1-1 heat exchangers, offering insights into various types, applications, and the factors influencing costs.
We will explore the critical aspects of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable manufacturers and distributors, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia. By providing detailed information on performance specifications, material considerations, and maintenance requirements, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchases that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Moreover, we will address common pitfalls and best practices in procurement, enabling buyers to navigate potential challenges effectively. Whether you are looking to enhance energy efficiency in your operations or seeking innovative solutions for heat transfer applications, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge necessary to optimize your sourcing strategy and ultimately drive business success.
Understanding 1-1 heat exchanger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
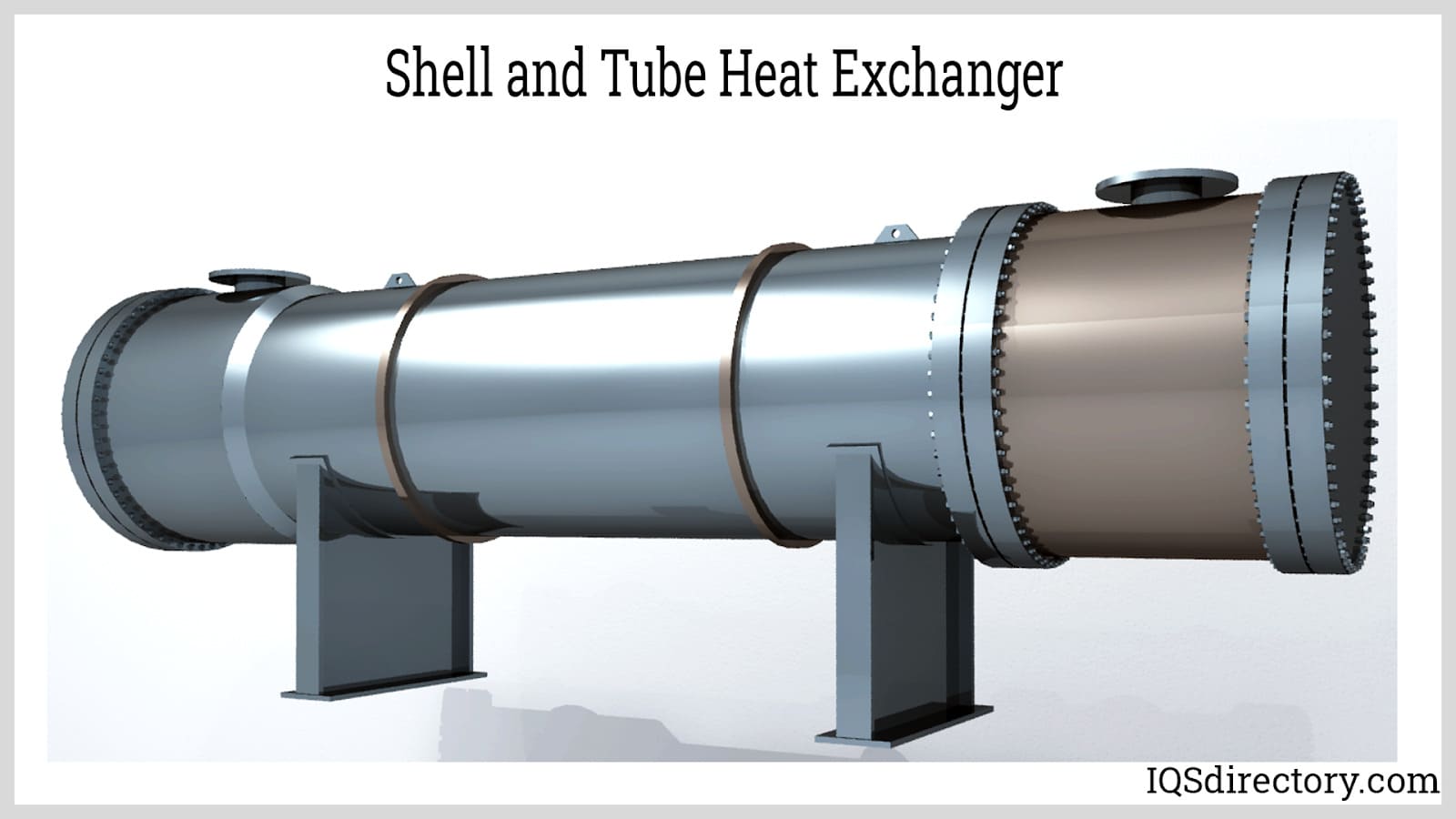
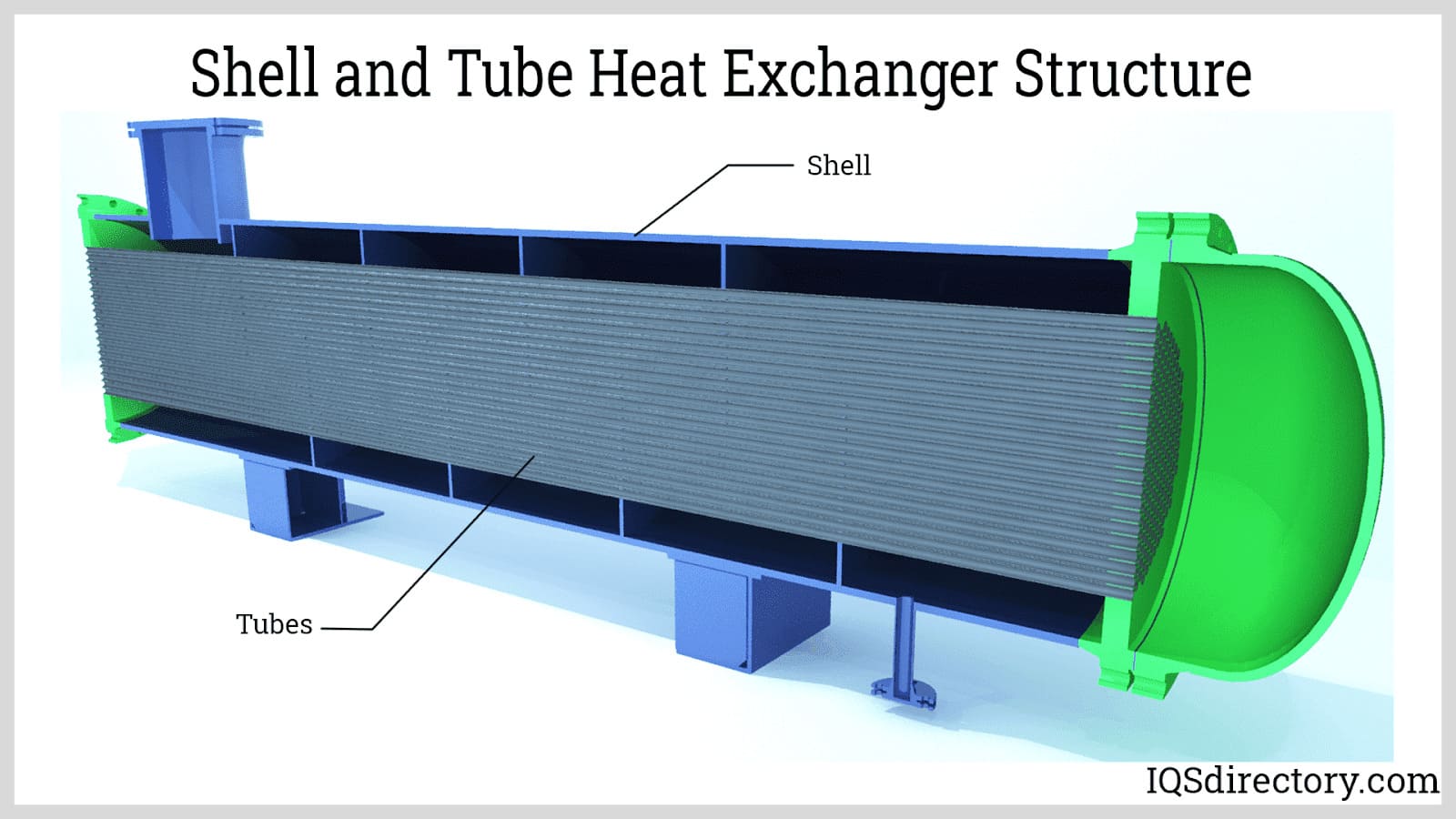
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger | Multiple tubes in a shell; flexible design | Oil and gas, chemical processing | Pros: High efficiency, customizable. Cons: Larger footprint, potential for fouling. |
| Plate Heat Exchanger | Thin plates for heat transfer; compact design | HVAC, food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Space-efficient, high heat transfer. Cons: Sensitive to pressure variations. |
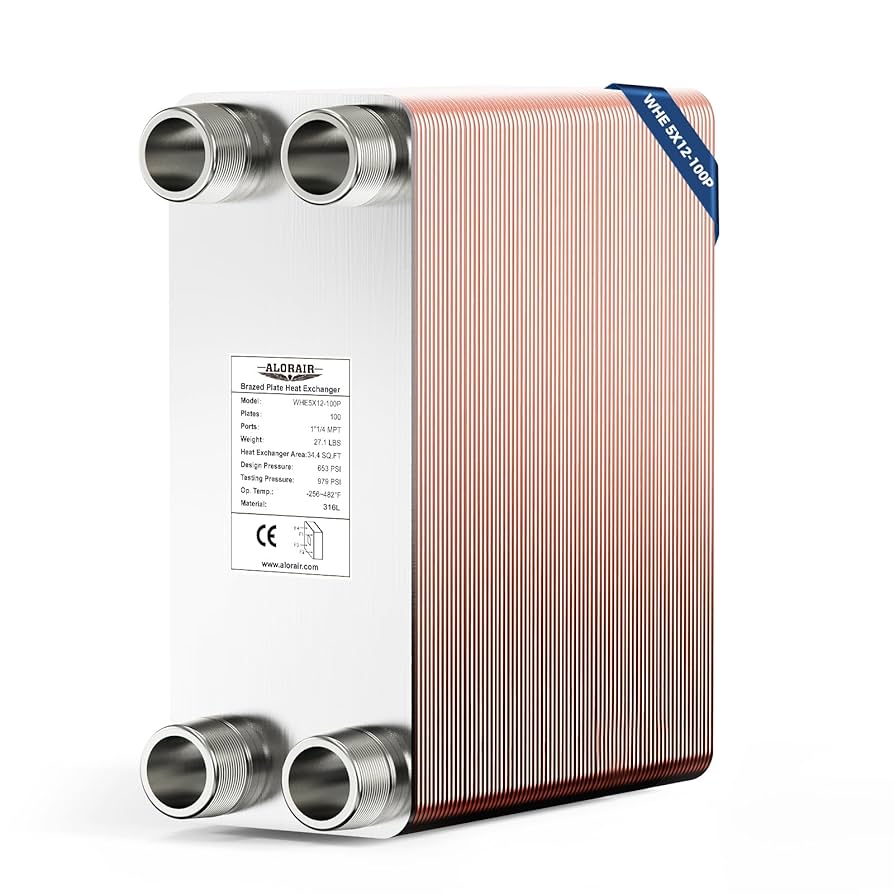
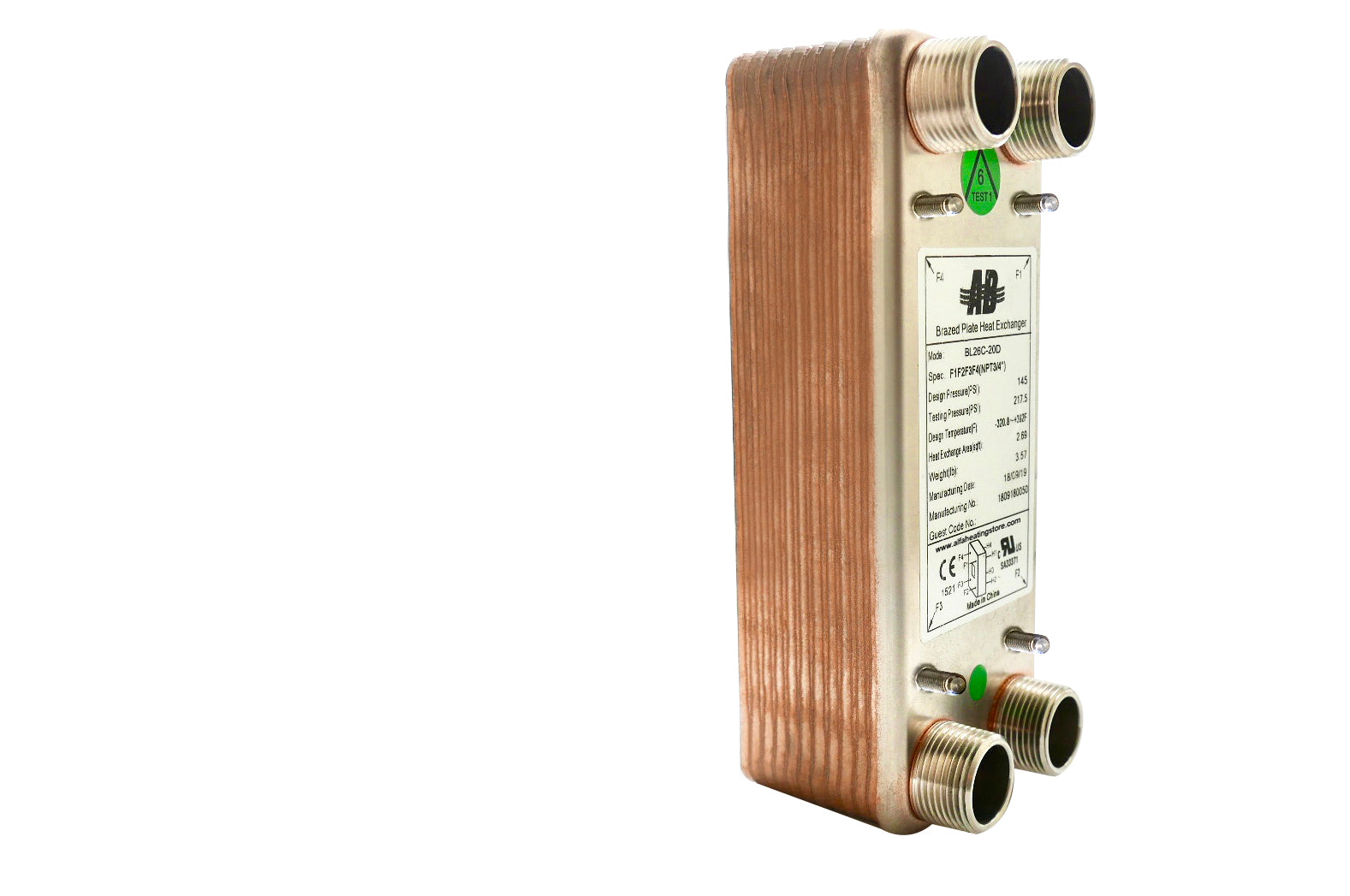
| Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger | Plates permanently joined; optimized for compactness | Residential heating, outdoor wood stoves | Pros: High pressure tolerance, efficient. Cons: Limited to lower temperature applications. |
| Spiral Heat Exchanger | Spiral design for enhanced flow; compact and efficient | Swimming pools, HVAC systems | Pros: Space-saving, effective for viscous fluids. Cons: More complex to manufacture. |
| Double Pipe Heat Exchanger | Two pipes; one for hot fluid, one for cold; simple design | Power plants, industrial heating | Pros: Simple design, easy maintenance. Cons: Less efficient than other types. |
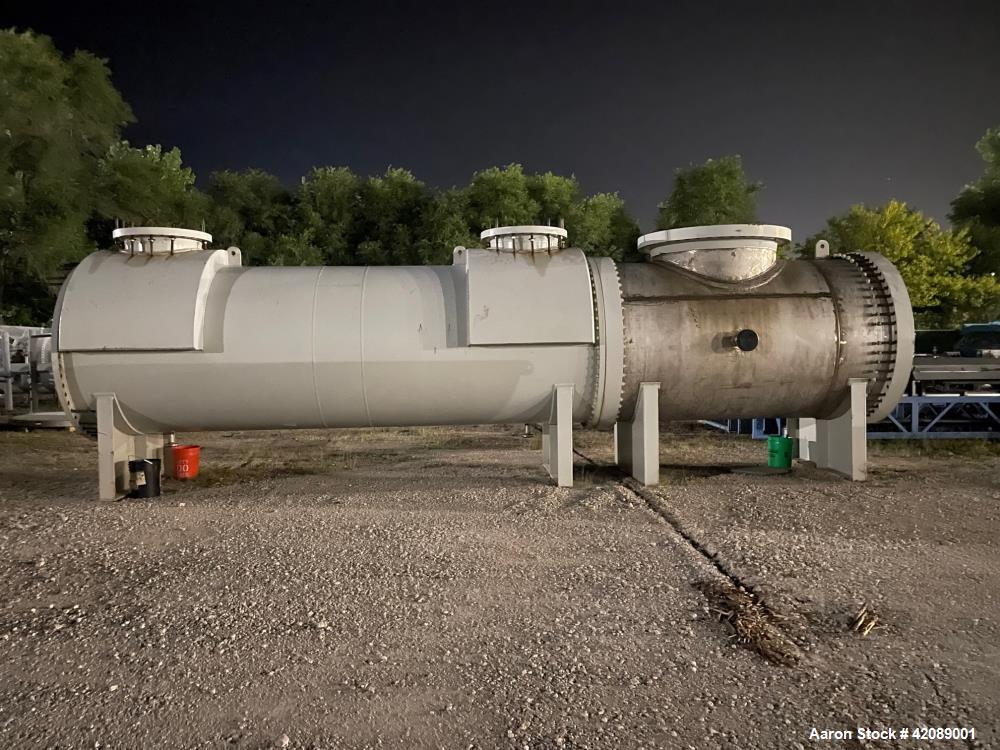
What are the Characteristics of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
Shell and tube heat exchangers consist of a series of tubes, one set carrying the hot fluid and the other the cold fluid. This design allows for high thermal efficiency and flexibility in handling varying flow rates. They are suitable for applications in oil and gas, as well as chemical processing, where robust heat transfer capabilities are essential. When purchasing, buyers should consider the size, material compatibility, and maintenance requirements, as fouling can affect performance.
How Do Plate Heat Exchangers Stand Out?
Plate heat exchangers utilize a series of thin plates to transfer heat between two fluids. Their compact design makes them ideal for applications in HVAC systems and food processing, where space is a premium. They offer high heat transfer efficiency but can be sensitive to pressure changes, making it crucial for buyers to evaluate the operational conditions and fluid characteristics before purchase.
What Benefits Do Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers Offer?
Brazed plate heat exchangers are characterized by their durable construction, with plates permanently joined to optimize space and efficiency. They are widely used in residential heating and for connecting outdoor wood stoves to indoor systems. Buyers should note their high pressure tolerance and efficient heat transfer capabilities, but must also consider the limitations on operating temperatures, which can restrict some applications.
Why Choose Spiral Heat Exchangers?
Spiral heat exchangers feature a unique spiral design that enhances flow efficiency and minimizes footprint. They are particularly effective in applications involving viscous fluids, such as swimming pools and HVAC systems. While they are efficient and space-saving, the complexity of manufacturing may lead to higher initial costs, necessitating a thorough cost-benefit analysis for potential buyers.
What Are the Advantages of Double Pipe Heat Exchangers?
Double pipe heat exchangers consist of two concentric pipes, allowing one fluid to flow through the inner pipe and another through the outer pipe. This simple design is easy to maintain and is commonly used in power plants and industrial heating applications. While they are less efficient compared to other heat exchanger types, their straightforward operation and maintenance make them an attractive option for buyers prioritizing reliability and ease of use.
Key Industrial Applications of 1-1 heat exchanger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 1-1 heat exchanger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy & Power Generation | Heat recovery systems in power plants | Increases overall energy efficiency and reduces operational costs | Compliance with local regulations, materials suitable for high temperatures |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Cooling and heating processes in reactors | Enhances process control, safety, and product quality | Material compatibility with chemicals, size and capacity specifications |
| Food & Beverage | Pasteurization and temperature control in food processing | Ensures food safety and quality while optimizing energy use | Hygiene standards, ease of maintenance, and sanitation requirements |
| HVAC Systems | Integration in heating and cooling systems for buildings | Improves energy efficiency and reduces heating/cooling costs | Local climate considerations, energy ratings, and installation requirements |
| Marine & Offshore | Heat exchange in marine engines and systems | Enhances performance and longevity of equipment | Corrosion resistance, material choices for seawater applications |
How is a 1-1 Heat Exchanger Used in Energy & Power Generation?
In the energy sector, 1-1 heat exchangers are essential for heat recovery systems in power plants. They facilitate the transfer of heat from exhaust gases to water, enhancing overall thermal efficiency. This application addresses the challenge of energy loss during power generation, ultimately leading to reduced operational costs. Buyers in this sector must consider compliance with local regulations and ensure that materials can withstand high temperatures and pressures common in power generation environments.
What Role Does a 1-1 Heat Exchanger Play in Chemical Manufacturing?
In chemical manufacturing, 1-1 heat exchangers are utilized for cooling and heating processes in reactors. By providing efficient heat transfer, these exchangers enhance process control, ensuring safety and maintaining product quality. International buyers need to pay attention to material compatibility with various chemicals and the specific size and capacity requirements based on their production processes.
How Are 1-1 Heat Exchangers Beneficial in the Food & Beverage Industry?
The food and beverage industry employs 1-1 heat exchangers primarily for pasteurization and temperature control during processing. This ensures food safety while optimizing energy use, which is crucial for maintaining product quality. Buyers in this sector must adhere to strict hygiene standards, emphasizing the need for easy maintenance and sanitation features in their heat exchangers.
In What Ways Do 1-1 Heat Exchangers Improve HVAC Systems?
1-1 heat exchangers are integrated into HVAC systems to enhance heating and cooling efficiency in buildings. By facilitating effective heat transfer, they help reduce energy consumption and associated costs. For buyers, especially in varying climates, it’s important to consider local climate conditions, energy ratings, and specific installation requirements to ensure optimal performance.
How Are 1-1 Heat Exchangers Used in Marine & Offshore Applications?
In marine and offshore applications, 1-1 heat exchangers are critical for heat exchange in engines and various systems. They improve the performance and longevity of marine equipment by efficiently managing heat. Buyers must prioritize corrosion resistance and select materials suitable for seawater applications to ensure durability and reliability in harsh marine environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘1-1 heat exchanger’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sizing and Selecting the Right 1-1 Heat Exchanger
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with accurately sizing and selecting the appropriate 1-1 heat exchanger for their specific applications. This challenge can arise from a lack of clarity about flow rates, temperature differentials, and the specific thermal requirements of their processes. Misjudging these parameters can lead to inefficient heat transfer, increased energy costs, and even equipment failure, which can have significant financial repercussions.
The Solution: To effectively size and select a 1-1 heat exchanger, buyers should start by gathering comprehensive data on the operating conditions. This includes determining the maximum and minimum flow rates of both the hot and cold fluids, as well as their inlet and outlet temperatures. Using this data, consult with manufacturers or distributors who can provide heat transfer calculations and recommendations based on industry standards. Additionally, leveraging software tools or consulting with thermal engineers can help simulate various scenarios to ensure the selected model meets the specific application needs. Always consider options for adjustable or modular systems that can be fine-tuned after installation, providing flexibility as operational demands change.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance and Downtime Costs
The Problem: Frequent maintenance and unexpected downtime are persistent pain points for businesses utilizing 1-1 heat exchangers. Common issues include fouling, corrosion, and mechanical failures, which not only interrupt production schedules but also lead to increased operational costs. For international buyers, particularly in harsh environments, the risk of accelerated wear can be exacerbated by factors such as temperature fluctuations and the quality of the fluids being processed.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance issues, it is crucial to select heat exchangers made from durable materials suitable for the specific application environment. For instance, titanium models are highly resistant to corrosion in saltwater applications, making them ideal for coastal regions. Regular maintenance schedules should be established, including routine inspections and cleaning protocols to prevent fouling. Implementing real-time monitoring systems can also provide valuable data on the operational efficiency and condition of the heat exchanger, allowing for proactive maintenance before issues lead to costly downtimes. Partnering with suppliers who offer comprehensive service packages, including maintenance training for staff, can further enhance operational reliability.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Integration into Existing Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties when integrating new 1-1 heat exchangers into existing heating or cooling systems. This challenge often arises from compatibility issues with existing equipment, such as mismatched flow rates or differing pressure requirements, which can lead to inefficiencies and operational challenges. Without proper integration, the expected performance benefits may not be realized, and the overall system could suffer.
The Solution: To ensure seamless integration, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their existing systems before purchasing a 1-1 heat exchanger. This analysis should include flow characteristics, pressure drops, and temperature profiles. Engage with suppliers who have experience with system integration and can provide tailored solutions, such as custom fittings or control systems that align with existing infrastructure. It is also advisable to consider modular heat exchangers that can be easily adjusted or reconfigured as needed. Collaborating with engineers or consultants who specialize in thermal systems can also provide insights and strategies to optimize the integration process, enhancing overall system performance and reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 1-1 heat exchanger
What Are the Common Materials Used in 1-1 Heat Exchangers?
When selecting materials for 1-1 heat exchangers, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. Below are four common materials used in the manufacturing of these heat exchangers, tailored for B2B buyers across diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grades like 316L, offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it resists rust and degradation over time. However, it is relatively more expensive than other materials and may involve complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of fluids, including aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A312 is essential. Buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia may also need to consider local regulations regarding material specifications.
2. Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, particularly in freshwater applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its high thermal efficiency, which can enhance the overall performance of a heat exchanger. However, copper is less durable than stainless steel and can be susceptible to corrosion in saline environments, limiting its use in marine applications.
Impact on Application: Copper heat exchangers are often used in HVAC systems and refrigeration. They are particularly effective in applications where quick heat transfer is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B280. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa and South America, additional protective coatings may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
3. Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is recognized for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of titanium is its ability to withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. However, it is one of the most expensive materials, and its manufacturing can be complex, leading to longer production times.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly suited for applications in the chemical processing and marine industries, where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B348 is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East, where oil and gas applications are prevalent, may find titanium particularly beneficial despite its higher cost.
4. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is a cost-effective option with good mechanical properties and moderate corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The affordability of carbon steel makes it an attractive choice for many applications. However, its susceptibility to corrosion limits its use in applications involving aggressive fluids or extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is commonly used in power generation and oil refining processes, where cost efficiency is a priority.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings or linings to enhance corrosion resistance. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A106 is essential for ensuring quality and safety.
Summary Table of Material Selection for 1-1 Heat Exchangers
| Material | Typical Use Case for 1-1 Heat Exchanger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | HVAC systems, refrigeration | High thermal conductivity | Less durable in saline environments | Medium |
| Titanium | Chemical processing, marine applications | Outstanding corrosion resistance | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Steel | Power generation, oil refining | Cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on performance, application compatibility, and regional compliance requirements.
Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 1-1 heat exchanger
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a 1-1 Heat Exchanger?
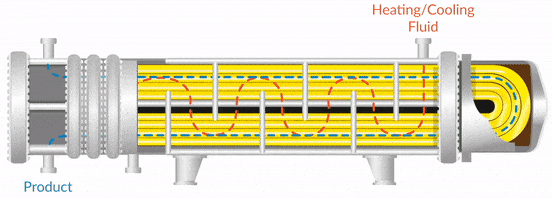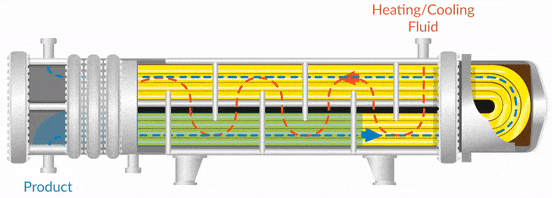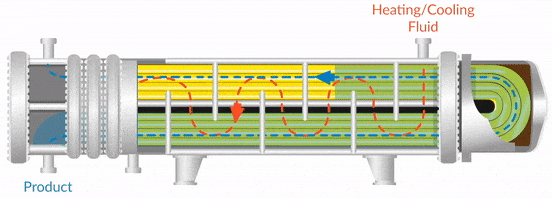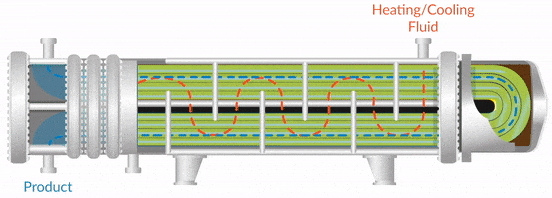
Manufacturing a 1-1 heat exchanger involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the product meets both performance and quality standards. The typical process includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, commonly stainless steel or titanium, which are essential for durability and corrosion resistance. The materials are subjected to stringent inspection to verify their chemical composition and physical properties. This stage may also involve cutting the raw materials to precise dimensions, ensuring they are suitable for subsequent processes.
Forming: Following material preparation, the forming stage shapes the components of the heat exchanger. This can involve various techniques such as stamping or rolling for plates, and bending or machining for tubes. Advanced technologies like laser cutting may also be employed for precision. This phase is crucial as it directly impacts the heat transfer efficiency and overall integrity of the heat exchanger.
Assembly: Once the components are shaped, they are assembled, often using welding or brazing techniques. Brazed plate heat exchangers, for instance, utilize copper brazing for excellent thermal conductivity and strength. The assembly must ensure that there is no leakage between the fluids, which is critical for maintaining operational efficiency and safety.

Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatment, which may include polishing or coating to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Quality checks are performed at this stage to ensure that all parts are free from defects and meet the specified standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of 1-1 Heat Exchangers?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of manufacturing heat exchangers, as it ensures that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Several key components of QA include adherence to international standards, implementing quality control checkpoints, and utilizing various testing methods.
Relevant International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which outline requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards helps ensure consistent quality in production processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe or API standards in oil and gas applications further enhance product credibility.

Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
Quality Control Checkpoints: Effective quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducts inspections during various stages of production, checking for dimensional accuracy and adherence to process specifications.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection assesses the completed heat exchanger for overall performance and compliance with technical specifications.
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and reliability of heat exchangers. These include:
– Hydrostatic Testing: To ensure there are no leaks in the system.
– Thermal Performance Testing: To verify heat transfer efficiency under specified conditions.
– Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are several actionable strategies:
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing facilities and QA practices directly. This includes reviewing documentation related to quality control processes and certifications.
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports that outline the manufacturing processes, testing methods, and outcomes. This documentation provides insight into the reliability and consistency of the supplier’s products.
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality standards. These services can assess compliance with international standards and provide certifications that are recognized globally.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances that may impact their purchasing decisions. Understanding these nuances can significantly affect operational efficiency and product reliability.
Regional Standards and Certifications: Different regions may have distinct standards and certifications that affect product acceptance. For example, CE marking is mandatory for products sold in the European Union, while API certifications are essential for oil and gas applications. Buyers must ensure that the products they source comply with the relevant standards in their operational regions.
Cultural and Regulatory Considerations: Buyers should be aware of cultural differences and regulatory environments that may affect quality expectations. For instance, certain regions may prioritize environmental sustainability or energy efficiency more than others, influencing the type of heat exchangers preferred.
Communication and Transparency: Establishing clear communication with suppliers regarding quality expectations and standards is vital. Transparency in production practices, material sourcing, and quality assurance processes fosters trust and ensures that buyers receive products that meet their specifications.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for 1-1 heat exchangers are integral to delivering reliable and efficient products to international B2B buyers. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, the importance of quality control, and how to verify supplier practices, buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘1-1 heat exchanger’
In the competitive landscape of international B2B procurement, sourcing a 1-1 heat exchanger requires a strategic approach. This guide outlines essential steps to ensure you make informed decisions, ultimately leading to successful procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial to ensure the heat exchanger meets your operational needs. Consider factors such as capacity (BTU ratings), materials (e.g., stainless steel vs. titanium), and the type of fluids being exchanged. This step will guide your supplier selection and help you avoid costly mismatches.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay updated on the latest market trends and technological advancements in heat exchangers. Understanding the innovations, such as improved thermal efficiency designs or eco-friendly materials, can provide a competitive edge. This knowledge will also help you assess which features are essential for your specific applications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s vital to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, product certifications, and case studies that demonstrate their experience in your industry. Additionally, seek references from other businesses that have utilized their products to gauge reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Check supplier reviews: Look for feedback from other international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Assess after-sales support: Ensure that the supplier offers robust customer support, including installation guidance and maintenance services.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Gather detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Ensure that the quotes include all relevant costs, such as shipping, installation, and potential warranties. This comparison will help you identify the best value while also considering the quality of the product.

Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
- Consider total cost of ownership: Look beyond the initial purchase price; factor in long-term operational costs, including energy efficiency and maintenance requirements.
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the heat exchangers you are considering meet relevant industry standards and certifications. Compliance with regulations not only guarantees product quality but also enhances safety and reliability.
- Look for certifications: Check for certifications such as UL, CE, or ISO, which indicate adherence to international safety and quality standards.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Delivery Options
Understanding lead times is critical for project planning. Confirm with suppliers about their production timelines and delivery options. Delays can significantly impact your operations, so it’s essential to align supplier capabilities with your project deadlines.
- Discuss logistics: Evaluate whether the supplier can handle international shipping efficiently, especially if you’re operating in remote areas.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review and finalize the contract. Ensure that all terms, including payment schedules, warranty conditions, and service agreements, are clearly outlined. A well-defined contract protects both parties and establishes a foundation for a successful partnership.
Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
By following this checklist, you can navigate the complexities of sourcing a 1-1 heat exchanger with confidence, ensuring you select a solution that aligns with your operational needs and strategic goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 1-1 heat exchanger Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in 1-1 Heat Exchanger Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of 1-1 heat exchangers is crucial for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials include stainless steel, titanium, and various alloys, each with different price points and corrosion resistance properties. For instance, titanium, while more expensive, is preferable for applications involving saltwater due to its durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the region and the complexity of the heat exchanger design. Automated manufacturing processes can reduce labor costs but may require a higher initial investment.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and indirect labor associated with the production process. Depending on the supplier’s location, these costs can fluctuate, affecting the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized designs can lead to higher upfront costs. However, investing in efficient tooling can lower per-unit costs in larger production runs.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes ensure that the heat exchangers meet industry standards and certifications. This can add to the cost but ultimately protects buyers from future failures and associated costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, particularly for international buyers, can significantly affect the total cost. Factors such as shipping distance, weight, and mode of transport play a role.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This margin can vary based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect 1-1 Heat Exchanger Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of 1-1 heat exchangers, making it essential for buyers to be aware of these elements:

Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to discounts. Suppliers typically offer tiered pricing based on order size, encouraging bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Standardized models may be more cost-effective, while bespoke designs will require more time and resources.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, UL) often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certifications against their project needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence price. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but offer better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for cost estimation. Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for 1-1 Heat Exchangers?
For international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance purchasing efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage competition among suppliers to negotiate better prices or terms. Consider discussing volume discounts or payment terms that can ease cash flow.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy efficiency, and replacement. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to lower operational costs over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and economic conditions that may affect supplier pricing strategies. Factors such as currency fluctuations and local demand can influence costs.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better service, pricing, and terms. Long-term partnerships often yield better negotiating power.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices for 1-1 Heat Exchangers
Prices for 1-1 heat exchangers can vary widely based on the factors discussed. The costs outlined above are indicative and may not reflect current market rates. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 1-1 heat exchanger With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Heat Transfer Solutions
In the quest for efficient thermal management, various technologies can serve as alternatives to the 1-1 heat exchanger. Each solution has its unique strengths and weaknesses, making it crucial for B2B buyers to understand their options. This analysis compares the 1-1 heat exchanger against two viable alternatives: the brazed plate heat exchanger and the shell-and-tube heat exchanger. Understanding these alternatives can assist buyers in selecting the best solution tailored to their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 1-1 Heat Exchanger | Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger | Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Efficient for direct heat transfer | High thermal efficiency; compact size | Versatile with varying flow rates |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Generally lower cost | Higher initial and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific installation setup | Easy to install; flexible designs | More complex installation; requires space |
| Maintenance | Low; minimal wear and tear | Low; robust materials | Moderate; requires periodic cleaning |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small-scale applications | Best for residential or light commercial | Suited for heavy industrial applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger
Brazed plate heat exchangers are designed for high efficiency in a compact form. They utilize a series of thin plates that create a large surface area for heat transfer. The primary advantage is their compact design, which allows for installation in tighter spaces, making them ideal for residential heating systems or applications with limited space. However, while they are generally cost-effective, they may not withstand extreme pressures and temperatures as effectively as other options, limiting their use in heavy industrial settings.
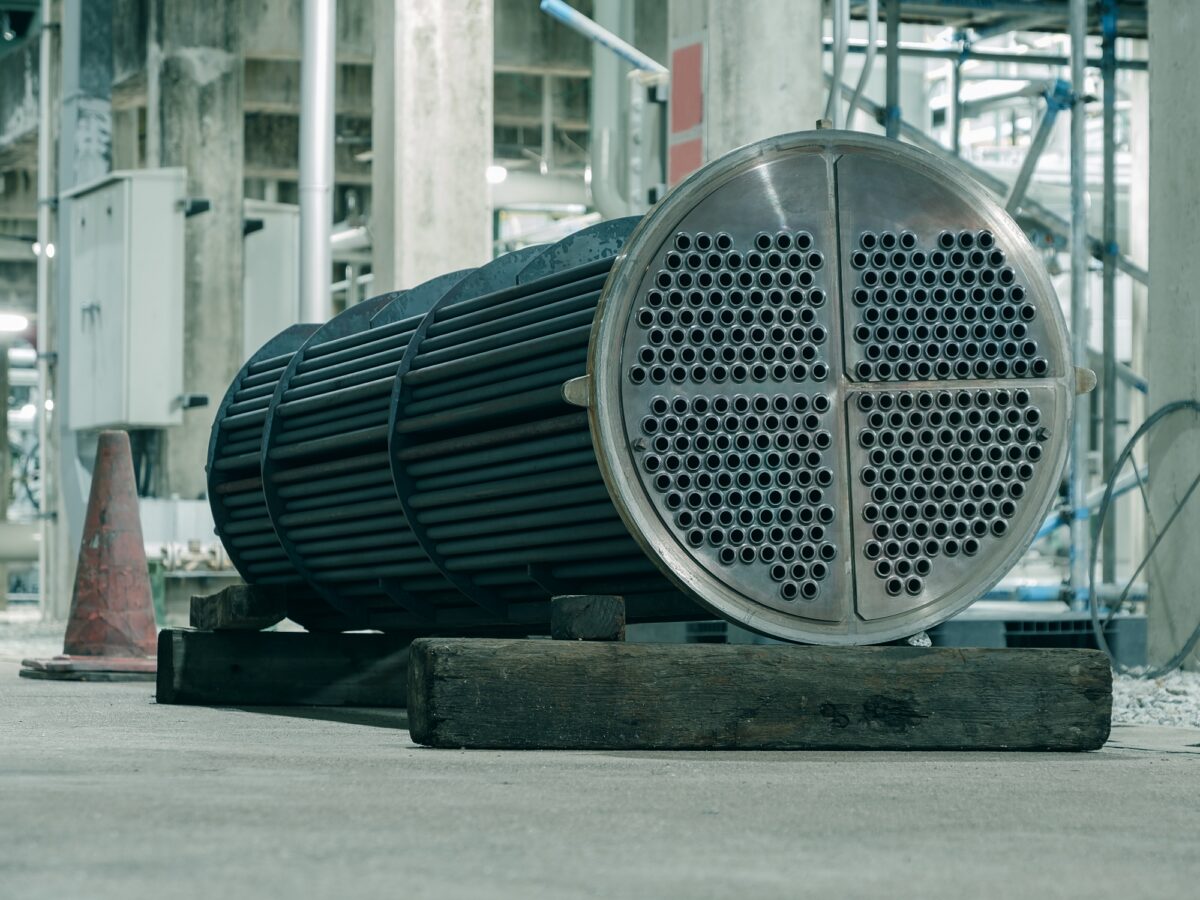
Shell-and-Tube Heat Exchanger
Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are renowned for their versatility and ability to handle a wide range of flow rates and pressures. These systems consist of a series of tubes enclosed within a shell, allowing them to facilitate heat transfer between two fluids efficiently. Their primary advantage is their scalability and ability to adapt to various operational requirements. However, they typically require more space and are more complex to install and maintain, which can lead to higher overall costs. They are best suited for heavy industrial applications where high capacity and durability are essential.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right heat exchanger solution hinges on understanding the specific needs of your operation. If you’re looking for an efficient, cost-effective solution for smaller applications, the 1-1 heat exchanger or a brazed plate heat exchanger may be suitable. For larger, industrial needs where versatility and high capacity are paramount, a shell-and-tube heat exchanger could be the best choice. Evaluating performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your operational goals and budget.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 1-1 heat exchanger
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a 1-1 Heat Exchanger?
Understanding the essential technical properties of a 1-1 heat exchanger is critical for B2B buyers, particularly when evaluating performance, reliability, and compatibility with existing systems. Here are several key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The choice of material significantly influences the heat exchanger’s durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel (e.g., 316L) and titanium. Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion and can handle high temperatures, making it suitable for various applications. Titanium is particularly advantageous in saltwater environments due to its superior resistance to corrosion. -
Heat Transfer Capacity (BTU/hr)
This specification indicates the maximum amount of heat the exchanger can transfer per hour. For instance, a 1-1 heat exchanger may have a capacity ranging from 128,000 BTU/hr to 155,000 BTU/hr. Understanding this capacity is vital for ensuring the heat exchanger meets the thermal demands of your system, thereby enhancing efficiency and performance. -
Pressure Ratings (Design and Test Pressure)
The design pressure refers to the maximum pressure the heat exchanger can safely handle, while the test pressure is the level at which the unit is tested for leaks and structural integrity. For example, a unit might have a design pressure of 190 psi and a test pressure of 285 psi. Selecting a heat exchanger with appropriate pressure ratings ensures safety and longevity in high-pressure applications. -
Flow Rates
Flow rates (measured in gallons per minute, GPM) determine how effectively the heat exchanger can transfer heat between fluids. For instance, a heat exchanger designed for a hot water flow volume of 8.46 GPM can efficiently manage thermal loads in heating systems. Proper flow rates are essential to maintain optimal thermal exchange and system efficiency. -
Temperature Range
The operating temperature range indicates the minimum and maximum temperatures the heat exchanger can withstand. A typical range might be from -19°F to 406°F. This specification is crucial for ensuring that the heat exchanger can operate effectively in varying environmental conditions without risking damage or failure. -
Connection Types
The type and size of connections (e.g., 1″, 1-1/4″ MPT) are important for compatibility with existing plumbing and systems. Ensuring that the connections match your setup will facilitate easier installation and reduce the risk of leaks or inefficiencies.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with 1-1 Heat Exchangers?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to heat exchangers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing quality parts compatible with their systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially for international buyers looking to import heat exchangers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. It is a fundamental step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms used in international sales contracts to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for navigating logistics and ensuring compliance. -
LMTD (Log Mean Temperature Difference)
This term is used in heat exchanger calculations to determine the temperature driving force for heat transfer. It helps in optimizing the design and efficiency of heat exchangers. -
BTU (British Thermal Unit)
A BTU measures the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is a critical unit of measure for evaluating the heating capacity of heat exchangers.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting and negotiating the purchase of 1-1 heat exchangers, ensuring they meet their specific operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 1-1 heat exchanger Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing the 1-1 Heat Exchanger Sector?
The global 1-1 heat exchanger market is experiencing robust growth driven by several factors, including increasing energy efficiency demands, the rise of renewable energy sources, and technological advancements in heat exchange systems. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focusing on sourcing heat exchangers that not only meet performance standards but also align with sustainability goals.
Emerging trends include the adoption of advanced materials such as titanium and high-grade stainless steel, which enhance durability and efficiency, especially in harsh environments such as coastal areas where saltwater corrosion is a concern. Additionally, innovations like spiral-twisted corrugated tube designs are gaining traction, as they maximize thermal efficiency while minimizing energy consumption. The market is also witnessing a shift towards integrated systems that facilitate seamless operation across different applications, from HVAC to industrial processes, ensuring versatility and improved return on investment.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on smart technology integration is reshaping procurement strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that offer heat exchangers equipped with IoT capabilities for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, further enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.

Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing for B2B Buyers in the 1-1 Heat Exchanger Market?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the B2B purchasing decision-making process. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their sourcing choices and are actively seeking suppliers who prioritize ethical practices and sustainable materials. In the 1-1 heat exchanger sector, this translates to sourcing products that feature certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or are made from recyclable materials.
The use of eco-friendly manufacturing processes is also a significant consideration. Suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing carbon footprints and minimizing waste during production are more likely to attract discerning B2B buyers. Furthermore, the incorporation of energy-efficient designs and technologies not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also promises long-term cost savings for businesses operating in energy-intensive industries.
Ethical sourcing extends beyond materials; it encompasses fair labor practices and transparency in supply chains. B2B buyers are increasingly interested in understanding the origins of their products, ensuring that their suppliers adhere to ethical standards throughout the production process. This focus on sustainability and ethics not only enhances brand reputation but also fosters customer loyalty and trust.

Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
How Has the 1-1 Heat Exchanger Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the 1-1 heat exchanger sector reflects broader trends in industrial efficiency and technological advancement. Historically, heat exchangers were primarily constructed from basic materials and designed for straightforward applications. However, as industries began to recognize the critical role of heat transfer efficiency in reducing operational costs, the demand for more sophisticated designs emerged.
In recent decades, the introduction of advanced materials like titanium and specialized alloys has transformed the market. These materials not only offer superior corrosion resistance but also enable heat exchangers to operate at higher temperatures and pressures, catering to diverse industrial needs. Additionally, the shift towards energy-efficient solutions has led to the development of compact and modular heat exchangers, which are easier to install and maintain.
Today, the market is characterized by a focus on innovation, with manufacturers continually refining designs to enhance performance and sustainability. As global energy policies evolve, the 1-1 heat exchanger sector remains poised for further transformation, aligning with the needs of environmentally-conscious B2B buyers seeking reliable and efficient solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 1-1 heat exchanger
-
How do I select the right 1-1 heat exchanger for my application?
Choosing the right 1-1 heat exchanger involves assessing your specific application requirements, including flow rates, temperature ranges, and the type of fluids involved. Consider the heat exchanger’s capacity, material compatibility (e.g., stainless steel for corrosive fluids), and design (such as shell-and-tube or plate). Additionally, consult with manufacturers for performance data and recommendations based on your operational conditions to ensure efficient heat transfer and longevity of the unit. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing 1-1 heat exchangers internationally?
When sourcing 1-1 heat exchangers internationally, consider factors such as supplier reputation, certifications (e.g., ISO, UL), and compliance with local regulations. Evaluate the supplier’s production capabilities, lead times, and experience in your specific industry. Additionally, assess logistics considerations, including shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines to ensure timely and cost-effective procurement. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering a 1-1 heat exchanger?
Lead times for ordering a 1-1 heat exchanger can vary significantly based on factors such as the supplier’s location, manufacturing capacity, and the complexity of the design. Standard models may have lead times ranging from 2 to 6 weeks, while customized units could take longer. It’s advisable to communicate directly with the supplier to get precise timelines and discuss any potential delays due to international shipping. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 1-1 heat exchangers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for 1-1 heat exchangers can vary by manufacturer and product type. Generally, MOQs can range from one unit for standard models to larger quantities for custom designs. When negotiating, consider your budget and operational needs, and inquire if the supplier offers flexibility on MOQs for first-time orders or trial purchases. -
Can I customize the specifications of my 1-1 heat exchanger?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for 1-1 heat exchangers. Customization can include adjustments to size, material, connection types, and thermal performance characteristics. It’s crucial to provide detailed specifications and discuss your requirements with the manufacturer to ensure that the final product meets your operational needs and complies with relevant industry standards. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international orders of heat exchangers?
Payment terms for international orders of heat exchangers can vary widely. Common practices include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or financing options for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms in advance to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from a reputable supplier?
A reputable supplier should implement rigorous quality assurance measures, including regular inspections, testing of materials, and adherence to industry standards. Look for suppliers who provide certifications, such as ISO 9001, which demonstrate their commitment to quality management. Additionally, inquire about their warranty policies and after-sales support to ensure that you receive a reliable product. -
What are the best practices for shipping 1-1 heat exchangers internationally?
When shipping 1-1 heat exchangers internationally, ensure that the units are adequately packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use shock-absorbent materials and secure the exchangers in sturdy crates. Collaborate with logistics experts to navigate customs requirements and select reliable shipping methods. Consider insurance for high-value items and track shipments to stay informed about delivery status and potential delays.
Top 9 1-1 Heat Exchanger Manufacturers & Suppliers List
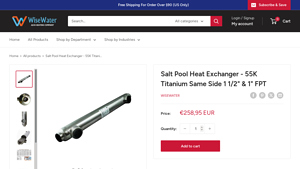
1. Alfa Heating – SP-55KTI-S-2 Heating System
Domain: alfaheating.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “SP-55KTI-S-2”, “type”: “Heating System”, “features”: [“High efficiency”, “Compact design”, “Easy installation”, “Durable construction”], “dimensions”: {“height”: “24 inches”, “width”: “18 inches”, “depth”: “12 inches”}, “weight”: “50 lbs”, “power”: “55,000 BTU”, “fuel_type”: “Natural Gas”, “warranty”: “5 years”}
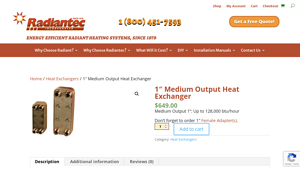
2. Radiantec – Medium Output Heat Exchanger
Domain: radiantec.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 1″ Medium Output Heat Exchanger
Price: $649.00
Output: Up to 128,000 BTU/hour
Weight: 12 lbs
Description: Designed to transfer heat from one fluid to another without mixing. Features flat plates pressed together with a tube for warm water from the heater and another tube for the heating fluid. Allows the addition of glycol to the radiant system without mixing with domestic water. Used in Radiantec…
3. ResearchGate – Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger 1-1
Domain: researchgate.net
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Performance of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger 1–1 Counter Current Formalin (Shell) – Water (Tube) Fluid Systems in Industry. Key specifications include: 1. Type: Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger 1-1. 2. Fluids: Formalin (Shell) and Water (Tube). 3. Flow rates of cold fluid (water): 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0 liters/minute. 4. Hot fluid (formalin) inlet temperatures: 40, 50, 60 °C. 5. Concentration of hot…
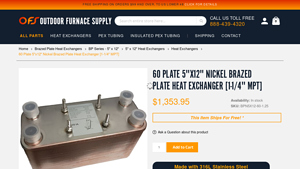
4. Outdoor Furnace Supply – 60 Plate Nickel Brazed Heat Exchanger
Domain: outdoorfurnacesupply.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “60 Plate 5’x12′ Nickel Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger [1-1/4′ MPT]”, “SKU”: “BPN5X12-60-1.25”, “Price”: “$1,353.95”, “Availability”: “In stock”, “Material”: “316L Stainless Steel plates with 99.9% nickel brazing”, “Type”: “Liquid to Liquid”, “Connections”: “1-1/4′ MPT Ports”, “Design Pressure”: “145 psi”, “Test Pressure”: “217 psi”, “Design Temperature”: “-256F – 437F”, “BTU Rating”…
5. Thermopedia – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: thermopedia.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are popular for their flexibility in handling a wide range of pressures and temperatures. They are categorized into two main types: those used in the petrochemical industry, governed by TEMA standards, and those used in the power industry, such as feedwater heaters and condensers. The main components include: Front Header (fluid entry), Rear Header (fluid exit), Tube…
6. Chere Resources – Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Domain: cheresources.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: 1:1 Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger; Temperature Correction Factor (F) is 1.0 for a 1 shell pass, 1 tube pass configuration; Used in refining, hydrocarbons, oil, and gas applications.
7. IQS Directory – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Shell and tube heat exchangers (STHE) are devices engineered for thermal energy exchange, comprising a cylindrical shell housing numerous parallel tubes for heat transfer between two fluids. Key components include the shell, tubes, channel, tube sheet, baffles, and nozzles. They are constructed from materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and special alloys to withstand high pressures and te…
8. STERIS – HEAT EXCHANGER 1-1/2NPT
Domain: shop.steris.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “HEAT EXCHANGER 1-1/2\”NPT P338523522”, “catentry_id”: “3512720”}
9. Everhot – 70-Plate Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger
Domain: pexuniverse.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: {“name”:”70-Plate, 5\” x 12\” Brazed Plate Heat Exchanger, 1-1/4\” MNPT”,”brand”:”Everhot”,”part_number”:”BT5x12C-70″,”in_stock”:”Yes”,”delivery_estimate”:”Usually ships within 1 business day”,”description”:”Designed for use in a variety of liquid-to-liquid heat transfer applications, where a reliable, efficient and compact heat exchanger is needed.”,”applications”:[“Radiant Heating and Snow Melt …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 1-1 heat exchanger
In the competitive landscape of industrial heating solutions, the strategic sourcing of 1-1 heat exchangers emerges as a critical factor for success. These systems provide efficient heat transfer while maintaining the integrity of separate fluids, making them essential for various applications across sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and HVAC. By investing in high-quality 1-1 heat exchangers—whether utilizing brazed plate or shell-and-tube designs—businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce energy costs, and comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing these vital components can lead to significant competitive advantages. Consider factors such as material durability, warranty offerings, and supplier reliability when making procurement decisions. Engaging with reputable suppliers who prioritize innovation and customer support will ensure access to cutting-edge technology tailored to your specific needs.

Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger
Looking ahead, the demand for efficient thermal solutions is poised to grow, driven by sustainability initiatives and evolving industrial standards. Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategy for 1-1 heat exchangers and position your business for future success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Illustrative image related to 1-1 heat exchanger