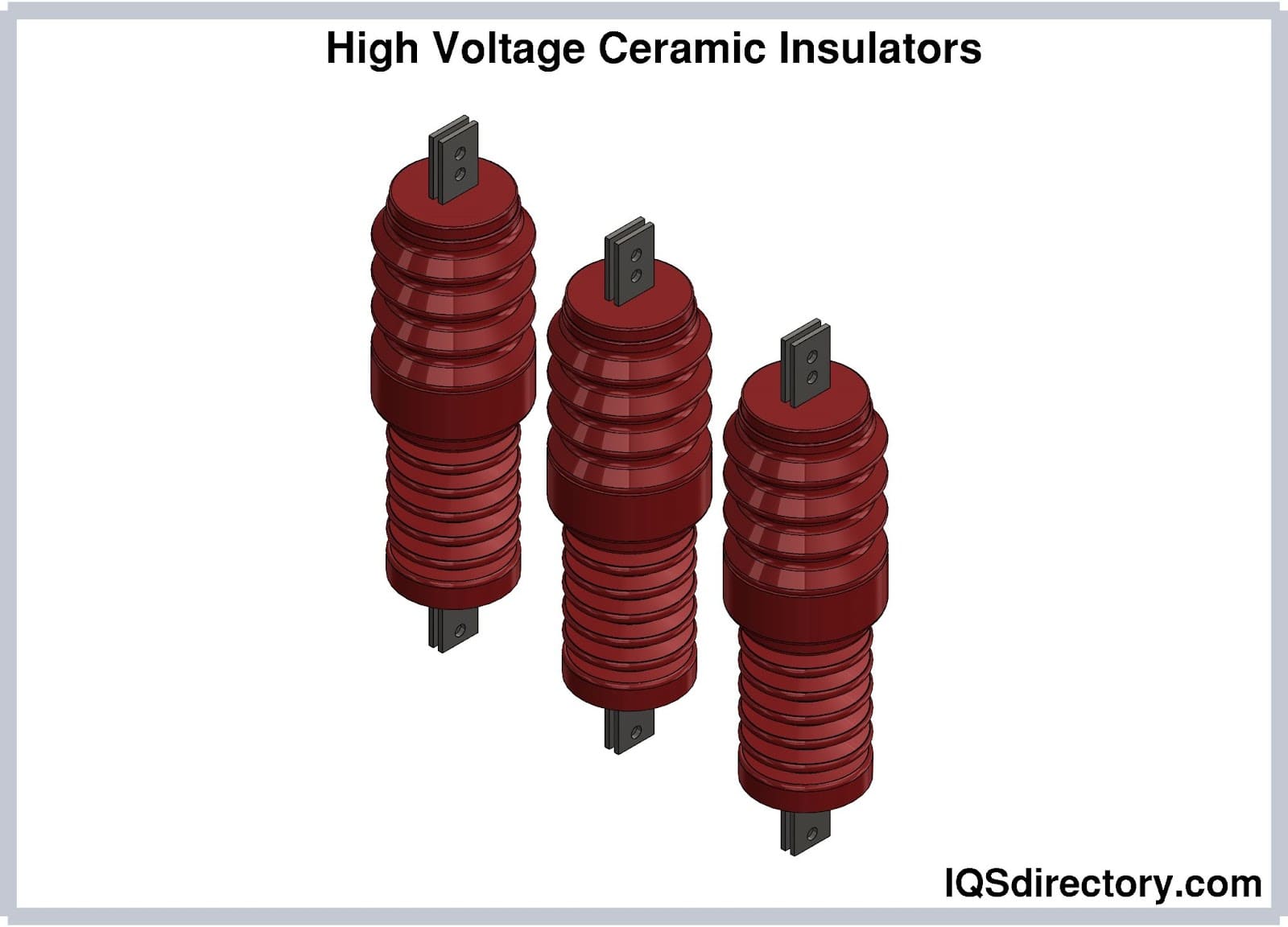
High Voltage Ceramic Insulator: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high voltage ceramic insulator
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing high voltage ceramic insulators presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse environments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including nations like Vietnam and Germany. The need for reliable, durable insulators that can withstand extreme conditions while ensuring safety and efficiency is paramount. This guide aims to equip businesses with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the global market for high voltage ceramic insulators, addressing critical aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
High voltage ceramic insulators are essential components in electrical power transmission and distribution systems, providing the necessary insulation to prevent current leakage and electrical failures. Understanding the various types—such as porcelain, glass, and composite insulators—along with their specific applications, is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, we delve into the intricacies of supplier evaluation to help you identify trustworthy manufacturers and distributors that meet your quality and compliance standards.
By leveraging the insights provided in this guide, B2B buyers can navigate the global landscape with confidence, ensuring that their selections not only meet operational demands but also align with budgetary constraints and long-term strategic goals. Empower your purchasing strategy with comprehensive knowledge and make informed decisions that drive efficiency and reliability in your electrical infrastructure.
Understanding high voltage ceramic insulator Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain Insulators | High mechanical and dielectric strength | Power transmission (11 kV to 400 kV) | Pros: Durable, high performance; Cons: Heavier, more fragile than composites. |
| Polymeric Insulators | Lightweight and flexible, resistant to UV | Urban areas, renewable energy projects | Pros: Easy installation, low maintenance; Cons: Limited lifespan in extreme conditions. |
| Glass Insulators | Transparent, high resistance to environmental stress | Low to medium voltage applications | Pros: Proven reliability; Cons: Susceptible to breakage. |
| Composite Insulators | Made of glass fiber and epoxy resin | High voltage applications (up to 800 kV) | Pros: Lightweight, high mechanical strength; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Feed Through Insulators | Designed for mounting through panels | RF applications, industrial equipment | Pros: Versatile installation options; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Porcelain Insulators?
Porcelain insulators are the most traditional type used in high voltage applications, known for their robust mechanical and dielectric strength. They are particularly suitable for environments where durability is crucial, such as in power transmission lines ranging from 11 kV to 400 kV. When purchasing porcelain insulators, B2B buyers should consider their weight and fragility; while they offer excellent performance, their heavier nature can complicate installation and transport.
How Do Polymeric Insulators Compare in Performance?
Polymeric insulators have gained popularity due to their lightweight and flexible properties, making them ideal for urban installations and renewable energy projects. They are resistant to UV radiation and can offer significant cost savings in terms of installation and maintenance. However, buyers should be aware that their lifespan may be limited in extreme environmental conditions, necessitating periodic replacements.
What Advantages Do Glass Insulators Offer?
Glass insulators are recognized for their transparency and high resistance to environmental stressors, making them a reliable choice for low to medium voltage applications. Their proven track record in the field enhances their attractiveness to B2B buyers. However, one must consider their susceptibility to breakage, which can lead to higher maintenance costs over time.

Illustrative image related to high voltage ceramic insulator
Why Choose Composite Insulators for High Voltage Applications?
Composite insulators, made from glass fiber and epoxy resin, are designed for high voltage applications up to 800 kV. They provide a lightweight alternative to traditional insulators without compromising mechanical strength. When considering composite insulators, buyers should weigh the initial investment against their long-term benefits, as they tend to have a higher upfront cost but can offer better performance and longevity in challenging environments.
What Are the Specific Uses of Feed Through Insulators?
Feed through insulators are specialized components designed for mounting through panels, commonly used in RF applications and various industrial equipment. Their versatility allows for multiple installation options, making them a practical choice for B2B buyers looking to optimize their setups. However, their functionality is limited to specific applications, which necessitates careful consideration during the purchasing process to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Key Industrial Applications of high voltage ceramic insulator
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of high voltage ceramic insulator | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Generation | Insulation in high voltage power plants | Ensures reliable power transmission and minimizes outages | Voltage ratings, thermal stability, and mechanical strength |
| Transmission and Distribution | Use in overhead power lines | Enhances system reliability and reduces maintenance costs | Creepage distance, environmental resistance, and durability |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in wind and solar energy systems | Supports sustainable energy solutions while ensuring safety | Compatibility with existing systems and installation ease |
| Telecommunications | Insulators for RF transmission lines | Improves signal quality and reduces interference | Material properties, size specifications, and cost efficiency |
| Rail Transportation | Insulation in electrified rail systems | Enhances safety and operational efficiency | Compliance with international standards and load ratings |
How are high voltage ceramic insulators utilized in power generation?
In power generation, high voltage ceramic insulators are crucial for insulating components within power plants, specifically in areas where high voltage equipment operates. They help maintain system integrity by preventing electrical breakdown, thereby reducing the risk of outages. International buyers should focus on sourcing insulators with high dielectric strength and thermal stability to ensure optimal performance in diverse climates, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
What role do high voltage ceramic insulators play in transmission and distribution?
In transmission and distribution networks, these insulators are employed in overhead power lines to secure conductors while providing electrical isolation from the supporting structures. This application is vital for enhancing system reliability and minimizing maintenance costs. Buyers should consider the creepage distance and environmental resistance of the insulators to ensure they can withstand local conditions, particularly in areas prone to contamination or severe weather.
How do high voltage ceramic insulators support renewable energy initiatives?
High voltage ceramic insulators are increasingly being integrated into renewable energy systems, such as wind and solar farms. They ensure safe and efficient transmission of electricity generated from renewable sources, which is crucial for supporting global sustainability efforts. Buyers in emerging markets should prioritize insulators that offer compatibility with existing energy infrastructures and ease of installation to facilitate the rapid deployment of renewable projects.
In what ways do telecommunications benefit from high voltage ceramic insulators?
In telecommunications, high voltage ceramic insulators are utilized in RF transmission lines to enhance signal quality and minimize interference. This application is essential for maintaining the integrity of communication networks. When sourcing insulators for this purpose, buyers should focus on the material properties and size specifications to ensure they meet the technical requirements for optimal performance in various communication systems.
Why are high voltage ceramic insulators important for rail transportation?
In electrified rail systems, high voltage ceramic insulators provide the necessary insulation for overhead lines, enhancing safety and operational efficiency. They help prevent electrical faults that could disrupt service. Buyers need to ensure that the insulators comply with international safety standards and possess adequate load ratings to withstand the operational demands of rail transportation, especially in regions with varying rail infrastructure.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high voltage ceramic insulator’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Ensuring Long-Term Durability in Harsh Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant challenges when selecting high voltage ceramic insulators for installations in extreme environmental conditions. Insulators are exposed to various pollutants, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, which can lead to premature failure. For instance, insulators in coastal areas may suffer from salt contamination, while those in desert regions could face issues with dust and sand accumulation. This not only compromises the electrical integrity but also results in increased maintenance costs and potential downtime.
The Solution: To ensure long-term durability, buyers should prioritize ceramic insulators specifically designed for harsh environments. Look for products with enhanced resistance to environmental factors, such as higher creepage distances and specialized coatings that promote self-cleaning. It’s crucial to collaborate with manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and testing results related to their insulators’ performance in extreme conditions. Additionally, consider implementing a regular inspection and maintenance schedule to identify early signs of wear or contamination. Investing in high-quality insulators and proactive maintenance can significantly reduce the total cost of ownership and enhance system reliability.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complex Installation Requirements
The Problem: The installation of high voltage ceramic insulators can often be a complex process, especially in existing infrastructure where space is limited and the risk of damaging surrounding components is high. Buyers may face challenges in ensuring that the insulators fit properly while meeting all safety and performance standards. Misalignment or incorrect installation can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, and costly repairs.
The Solution: To navigate these complexities, it is essential to engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive installation guides and technical support. Buyers should also request customized solutions that consider the specific dimensions and requirements of their existing setups. Utilizing insulators with features designed for easier installation, such as lighter materials or modular designs, can facilitate smoother integration. Additionally, training installation teams on best practices and potential pitfalls can mitigate risks associated with improper installation. By prioritizing these proactive measures, buyers can enhance the reliability of their installations and avoid unforeseen issues.
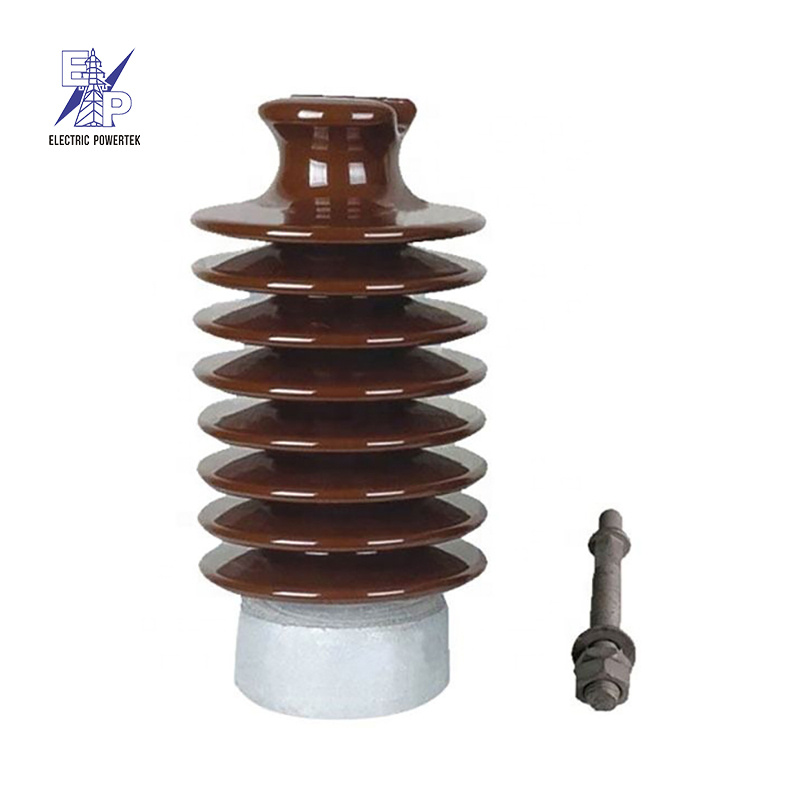

Illustrative image related to high voltage ceramic insulator
Scenario 3: Managing Cost-Effectiveness Without Compromising Quality
The Problem: Balancing the cost of high voltage ceramic insulators with their quality and performance is a common pain point for B2B buyers. With budget constraints often in place, there is pressure to select the most cost-effective options. However, opting for lower-quality insulators can lead to frequent replacements, increased downtime, and ultimately higher overall costs. This dilemma can create tension between procurement and engineering teams regarding the best choices for long-term operational success.
The Solution: To effectively manage cost while ensuring quality, buyers should adopt a value-based procurement approach. This involves evaluating insulators not just on their initial purchase price but also on their lifespan, maintenance needs, and performance under specific operational conditions. Consider suppliers who provide warranties or performance guarantees, which can serve as a safety net against premature failures. Additionally, conducting a total cost of ownership analysis can help in identifying the most economical options in the long run. By focusing on quality-driven purchasing decisions, companies can achieve better reliability and lower maintenance costs, aligning budgetary constraints with operational excellence.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high voltage ceramic insulator
What Are the Key Materials Used in High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
When selecting materials for high voltage ceramic insulators, it is crucial to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option. The following analysis focuses on four common materials: porcelain, glass, composite materials, and polymer ceramics. Each material presents unique characteristics that influence their performance in various applications.
How Does Porcelain Perform as a Material for High Voltage Insulators?
Porcelain is one of the most widely used materials for high voltage insulators, particularly in applications ranging from 11 kV to 400 kV. Its key properties include high dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and excellent thermal stability. Porcelain insulators can withstand extreme weather conditions and have a long service life, making them suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros: Porcelain insulators are highly durable and resistant to environmental degradation. They also offer good resistance to thermal and electrical stress, ensuring reliable performance over time.
Cons: The primary drawback is their weight, which can complicate installation and increase transportation costs. Additionally, porcelain can be brittle, making it susceptible to cracking during handling.
Impact on Application: Porcelain insulators are particularly effective in areas with high humidity or pollution, as they resist contamination. However, their weight may limit their use in regions with strict installation guidelines.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and IEC is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe and South America should ensure that the porcelain used meets these standards to avoid regulatory issues.
What Are the Advantages of Glass Insulators in High Voltage Applications?
Glass insulators, made from tempered glass, have been a staple in the industry for many years. They are known for their high mechanical strength and excellent dielectric properties, making them suitable for voltages up to 33 kV.

Illustrative image related to high voltage ceramic insulator
Pros: Glass insulators are highly resistant to UV radiation and can self-clean in rainy conditions, reducing maintenance needs. Their transparency allows for easy visual inspections for cracks or contamination.
Cons: While they are durable, glass insulators can be heavier than their porcelain counterparts, and their fragility can lead to breakage during installation or transport.
Impact on Application: Glass insulators are ideal for environments where visual monitoring is essential. However, their weight and fragility may limit their application in areas with challenging installation conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of glass materials, particularly in regions with seismic activity. Compliance with standards like DIN is also crucial for ensuring product safety and reliability.
How Do Composite Materials Compare in High Voltage Insulator Applications?
Composite insulators, typically made from glass fiber reinforced polymer, have gained popularity due to their lightweight and high mechanical strength. They can be used in high voltage applications up to 800 kV.
Pros: The primary advantage of composite insulators is their lightweight design, which simplifies installation and reduces transportation costs. They also offer excellent resistance to contamination and environmental degradation.
Cons: Composite materials may have a shorter lifespan compared to porcelain or glass, particularly in extreme temperatures. Additionally, their performance can be affected by UV exposure if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Composite insulators are particularly suitable for regions with high pollution levels, as they resist contamination effectively. However, their longevity in harsh environments must be considered.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that composite insulators comply with international standards such as IEC and ASTM. Understanding local environmental conditions will help in selecting the right composite material.
What Role Do Polymer Ceramics Play in High Voltage Insulation?
Polymer ceramics combine the benefits of ceramics and polymers, offering high dielectric strength and flexibility. They are increasingly used in high voltage applications due to their innovative properties.
Pros: These materials are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to various environmental factors, including UV and thermal degradation. They can also be manufactured in various shapes, making them versatile for different applications.
Cons: The primary limitation is their relatively higher cost compared to traditional materials like porcelain or glass. Additionally, long-term performance data is still being gathered, which may concern some buyers.
Impact on Application: Polymer ceramics are ideal for applications requiring flexibility and lightweight solutions, such as in urban environments where space is limited.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that polymer ceramics meet local and international standards to guarantee safety and performance. Understanding the specific environmental conditions in regions like Africa and the Middle East is also essential for optimal material selection.
Summary Table of Material Selection for High Voltage Ceramic Insulators
| Material | Typical Use Case for High Voltage Ceramic Insulator | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | 11 kV to 400 kV power lines | High durability and thermal stability | Heavy and brittle | Medium |
| Glass | Up to 33 kV transmission lines | Self-cleaning and UV resistance | Heavier and fragile | Medium |
| Composite | Up to 800 kV applications | Lightweight and contamination resistant | Shorter lifespan in extreme temperatures | High |
| Polymer Ceramics | Flexible applications in urban environments | Versatile and resistant to environmental factors | Higher cost and limited long-term data | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with actionable insights for choosing the right high voltage ceramic insulator material based on specific application needs and regional considerations.

Illustrative image related to high voltage ceramic insulator
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high voltage ceramic insulator
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
The manufacturing of high voltage ceramic insulators involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the production of high-quality, durable products suitable for demanding electrical environments. The primary stages of manufacturing include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
The first step in manufacturing high voltage ceramic insulators is the preparation of raw materials. Typically, this involves sourcing high-purity alumina and kaolin, which are essential for the production of high-quality porcelain. The materials are then mixed with additives, such as feldspar, to enhance the electrical and mechanical properties of the insulators.
The mixture undergoes a grinding process to achieve a uniform particle size, which is crucial for ensuring consistent quality in the final product. Once ground, the materials are screened and blended to ensure homogeneity before moving to the forming stage.
What Techniques are Used in Forming High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
Forming is a critical stage where the prepared material is shaped into the desired insulator form. Common techniques include:
-
Pressing: In this method, the mixture is placed into a mold and subjected to high pressure, forming the insulator’s shape. This technique is widely used for its efficiency and ability to produce complex geometries.
-
Extrusion: This technique involves forcing the material through a die to create long shapes, which are then cut to size. Extrusion is beneficial for producing insulators with specific dimensions and profiles.
-
Casting: For more intricate designs, casting techniques may be employed. This involves pouring the liquid mixture into molds, allowing it to set and then removing the formed insulator.
Each of these techniques requires careful control of parameters such as temperature and pressure to ensure the integrity of the insulator.
How is Assembly Conducted in High Voltage Ceramic Insulator Production?
Following the forming stage, the next step is assembly. This typically involves attaching metal fittings or hardware to the ceramic components. These fittings are crucial for ensuring that the insulators can be securely mounted onto transmission lines and other structures.
Quality checks are often performed during assembly to ensure that all components fit together properly and that there are no defects that could compromise performance. The assembly process may also include the application of protective coatings to enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used for High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
The finishing stage is where the insulators are prepared for their final use. This includes:
-
Drying and Firing: After forming, insulators are dried to remove moisture before being fired in a kiln. Firing at high temperatures (up to 1400°C) is crucial, as it enhances the mechanical strength and dielectric properties of the ceramic.
-
Glazing: A glaze may be applied to improve the surface finish and increase resistance to environmental contaminants. This step is essential for ensuring long-term performance, particularly in harsh conditions.
-
Final Inspection: Before packaging, each insulator undergoes a thorough final inspection to ensure it meets all design specifications and quality standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the manufacturing of high voltage ceramic insulators. It ensures that products meet both international and industry-specific standards, which is vital for maintaining safety and performance.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are fundamental for ensuring consistent quality management systems. This certification indicates that the manufacturer adheres to international best practices in quality assurance.
Additionally, specific standards such as the CE marking for products sold in Europe, and API standards for certain applications, may apply. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold relevant certifications to ensure compliance with these standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality criteria.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted at various stages to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and that defects are minimized.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the insulators are completed, they undergo rigorous testing, including visual inspections, dielectric strength tests, and mechanical load tests to ensure they meet performance specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing results and compliance with standards can help buyers assess supplier reliability.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices and product quality.
-
Certifications and Compliance Documents: Buyers should request copies of relevant certifications and compliance documents to verify that the supplier meets international standards.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Assurance?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of regional variations in quality standards and practices. This includes understanding local regulations, cultural differences in business practices, and potential language barriers that may affect communication about quality expectations.
Buyers should also consider the logistics of shipping and handling, as insulators are often large and fragile. Ensuring that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping procedures is essential to avoid damage during transit.
By understanding these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and build strong partnerships with suppliers of high voltage ceramic insulators. This approach not only ensures the procurement of high-quality products but also contributes to the reliability and safety of electrical power transmission systems.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high voltage ceramic insulator’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure high voltage ceramic insulators. Understanding the complexities involved in sourcing these critical components will ensure you make informed decisions, optimize costs, and secure reliable products for your electrical power transmission and distribution systems.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful procurement process. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, dielectric strength, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. This ensures that the insulators you select will meet the operational demands of your specific applications and environmental conditions.
Step 2: Research Different Types of Insulators
Familiarize yourself with the various types of high voltage ceramic insulators available in the market. Common types include porcelain, composite, and polymer insulators, each offering distinct advantages based on their material properties. Understanding these differences will help you select the right type that aligns with your application needs and environmental conditions.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s critical to conduct thorough evaluations. Look for established companies with a proven track record in manufacturing high voltage insulators. Request case studies, product certifications, and references from previous clients in similar industries or regions. This step helps to ensure that your supplier can meet your technical and quality standards.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the insulators comply with international and local standards, such as IEC or ANSI. Compliance not only guarantees product safety and reliability but also protects your investment in the long term. Ask for certifications and test reports to validate that the products meet these stringent requirements.
Step 5: Assess Product Durability and Maintenance Requirements
High voltage insulators should be durable enough to withstand environmental factors such as contamination, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stress. Inquire about the expected lifespan and maintenance requirements of the insulators. Selecting products that are easy to maintain can significantly reduce operational costs and downtime.
Step 6: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the insulators for testing under your specific operational conditions. This practical evaluation can reveal how well the insulators perform in real-world scenarios. Ensure that they meet your specifications for dielectric strength and mechanical performance before making a bulk purchase.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier and validated the product, negotiate the terms of purchase. Discuss pricing, delivery schedules, warranty options, and return policies. Clear agreements will minimize risks and ensure that both parties understand their responsibilities, leading to a smoother procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing high voltage ceramic insulators with confidence, ensuring that they select the most suitable products for their electrical infrastructure needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high voltage ceramic insulator Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
When sourcing high voltage ceramic insulators, understanding the cost structure is critical for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials, primarily high-quality ceramic, significantly influence the cost. The purity and type of ceramic used can vary, impacting both performance and price. For instance, insulators made from specialized ceramics designed for extreme conditions typically command higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs include the wages for skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. These costs can vary significantly based on geographic location, with regions offering lower labor costs potentially providing a more competitive pricing structure.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead and result in lower pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. Buyers should consider how these upfront costs can be amortized over larger orders to minimize the per-unit price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes ensure that insulators meet safety and performance standards. While these QC measures increase costs, they are crucial for preventing failures that could lead to costly downtime or safety hazards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, as well as the chosen shipping method. Understanding logistics costs is essential for calculating the total landed cost of insulators.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Impact High Voltage Ceramic Insulator Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of high voltage ceramic insulators:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to significant discounts. Understanding the supplier’s MOQ can help buyers negotiate better pricing based on their projected needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized insulators designed for specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly outline their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects performance but also impacts cost. Buyers should evaluate whether premium materials are necessary for their application or if more economical options will suffice.
-
Quality Certifications: Insulators that meet international standards or come with certifications may have a higher price. However, these certifications often justify the expense by ensuring reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium, while newer or less reputable suppliers might offer lower prices but at higher risk.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade can significantly affect overall costs. Understanding the responsibilities of both the buyer and supplier under different Incoterms can help in evaluating total costs, including insurance, freight, and customs duties.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Negotiate Better Pricing for High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
To achieve cost-efficiency in sourcing high voltage ceramic insulators, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with suppliers to explore pricing flexibility. Highlighting potential long-term relationships or larger order volumes can provide leverage.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost, including installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. This holistic view can justify investing in higher-quality insulators that may be more expensive upfront but save costs in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, being aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local regulations can provide insights into total costs. Additionally, understanding local market conditions can help in negotiating favorable terms.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices for high voltage ceramic insulators are subject to fluctuation based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier pricing strategies. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high voltage ceramic insulator With Other Solutions
Introduction to High Voltage Insulator Alternatives
When considering high voltage insulators for electrical power transmission and distribution systems, it’s essential to explore various alternatives that can meet specific operational needs. This analysis compares high voltage ceramic insulators with two prominent alternatives: polymeric insulators and glass insulators. Each of these solutions presents unique advantages and challenges that can influence decision-making for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse geographical markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | High Voltage Ceramic Insulator | Polymeric Insulator | Glass Insulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent dielectric strength; high resistance to contamination | Good dielectric properties; lightweight | Reliable; proven performance under various conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; longer lifespan can offset costs | Moderate cost; competitive pricing | Generally lower cost; shorter lifespan |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires careful handling during installation | Easy to install; flexible design | Straightforward installation; heavier than polymers |
| Maintenance | Low; durable and long-lasting | Low; minimal upkeep required | Moderate; can be susceptible to breakage |
| Best Use Case | High voltage applications in harsh environments | Urban settings with space constraints | General use in moderate voltage applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Polymeric Insulators
Polymeric insulators are becoming increasingly popular due to their lightweight and flexible nature. They offer good dielectric properties and can be engineered to meet specific environmental conditions, making them ideal for urban installations where space is limited. The moderate cost of polymeric insulators is appealing, especially for projects with budget constraints. However, while they exhibit low maintenance requirements, they may not withstand extreme environmental conditions as well as ceramic insulators. This makes them less suitable for high voltage applications in harsh climates.
Glass Insulators
Glass insulators, a traditional choice for electrical installations, are valued for their reliability and proven performance. They are typically less expensive than ceramic insulators, making them an attractive option for projects with tighter budgets. Their straightforward installation process and established track record are significant advantages. However, glass insulators can be heavier and more susceptible to breakage, which may lead to higher maintenance costs over time. While they work effectively in moderate voltage applications, they may not be the best choice for high voltage scenarios, particularly where durability is a concern.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Insulator Solution
Selecting the appropriate insulator for high voltage applications requires careful consideration of various factors, including performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific requirements of their projects—such as environmental conditions, voltage levels, and budget constraints—is crucial. High voltage ceramic insulators provide superior performance and longevity, making them ideal for demanding applications. In contrast, polymeric and glass insulators may offer cost-effective solutions for less severe conditions or urban environments. Ultimately, aligning the insulator choice with the operational context will lead to optimal performance and cost efficiency in electrical power transmission and distribution systems.

Illustrative image related to high voltage ceramic insulator
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high voltage ceramic insulator
High voltage ceramic insulators are critical components in electrical power transmission and distribution systems. Understanding their essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those involved in procurement and supply chain management across various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Technical Properties of High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
1. Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength refers to the maximum electric field that a material can withstand without breaking down. For high voltage ceramic insulators, this property is vital as it ensures the insulator can operate safely under high voltage conditions, preventing electrical failure. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide insulators with high dielectric strength ratings to ensure reliability in critical applications.
2. Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength denotes the ability of the insulator to withstand physical stress, including wind, ice, and the weight of conductors. High mechanical strength is essential to avoid breakage during installation and operation. Buyers should look for insulators with documented mechanical strength specifications, ensuring they meet the demands of their specific environments.
3. Creepage Distance
Creepage distance is the shortest path between two conductive parts along the surface of an insulator. Adequate creepage distance is crucial to prevent arcing and flashover, especially in polluted environments. B2B buyers must verify that the insulators they procure meet the creepage distance requirements for their specific voltage levels and environmental conditions.
4. Thermal Stability
Thermal stability indicates the insulator’s ability to maintain performance under varying temperature conditions. Insulators with high thermal stability can resist deformation and degradation, ensuring long-term durability. Buyers should assess thermal stability ratings, particularly for regions with extreme temperature fluctuations.
5. Resistance to Contamination
High voltage insulators are often exposed to environmental contaminants such as dust, pollution, and moisture. Resistance to these contaminants is essential for maintaining dielectric properties and preventing failures. Buyers should consider insulators designed with self-cleaning surfaces or those treated to enhance contamination resistance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the High Voltage Ceramic Insulator Market?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers as it can influence product quality, warranty, and support. Buyers should seek manufacturers with strong OEM credentials to ensure reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B transactions as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their project needs and budgetary constraints.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. This term is vital in procurement processes, allowing buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to better deals and more favorable contract terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers to ensure clarity regarding shipping costs, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, ultimately minimizing disputes.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from placing an order to its delivery. In the context of high voltage ceramic insulators, understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and coordination. Buyers should always confirm lead times with suppliers to ensure timely delivery for their projects.
By focusing on these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding high voltage ceramic insulators, ensuring they select the best products for their specific needs and operational contexts.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high voltage ceramic insulator Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
The high voltage ceramic insulator market is experiencing significant growth driven by the global increase in electricity demand, urbanization, and the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure. As countries invest in upgrading their power transmission systems, the need for reliable, high-performance insulators becomes paramount. This trend is particularly evident in emerging markets in Africa and South America, where electrification initiatives are underway. In Europe and the Middle East, aging infrastructure is being modernized, creating opportunities for suppliers of high voltage ceramic insulators.
Technological advancements are reshaping the sourcing landscape. The adoption of smart grid technologies and IoT-enabled devices is enhancing the monitoring and management of insulators, leading to improved maintenance and reduced downtime. Additionally, the integration of advanced materials—such as composite insulators—provides enhanced performance characteristics, including greater dielectric strength and resistance to environmental degradation. For international B2B buyers, this means sourcing strategies must adapt to include innovative materials and technologies that align with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Buyers should also be aware of regional sourcing trends. For instance, European buyers are increasingly focused on suppliers who can demonstrate compliance with EU standards, while Middle Eastern buyers may prioritize suppliers that can ensure timely delivery amidst the region’s rapid infrastructure development. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions in the high voltage ceramic insulator market.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the High Voltage Ceramic Insulator Industry?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for international B2B buyers in the high voltage ceramic insulator sector. The environmental impact of production processes and materials is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. High voltage ceramic insulators, traditionally made from clay and other natural materials, can be produced with reduced carbon footprints by utilizing energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
Buyers are increasingly interested in sourcing insulators that are certified green or contain recycled materials. These certifications not only enhance a company’s brand image but also align with global sustainability goals and regulatory requirements. Ethically sourced materials ensure that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and environmental stewardship, which are becoming non-negotiable for many buyers.
Moreover, the shift towards renewable energy sources is influencing the demand for sustainable insulators. As solar and wind power installations expand, there is a growing need for insulators that can withstand diverse environmental conditions while minimizing ecological impact. Buyers who prioritize sustainability can not only contribute to environmental conservation but also position themselves competitively in a market that increasingly values corporate responsibility.
What Is the Historical Context of High Voltage Ceramic Insulators?
The history of high voltage ceramic insulators dates back to the early days of electrical power transmission in the late 19th century. Initially, insulators were primarily made from glass and porcelain, materials chosen for their electrical insulating properties and mechanical strength. As the demand for electricity surged, particularly in urban areas, the design and manufacturing of insulators evolved to meet higher voltage requirements and more challenging environmental conditions.
The introduction of composite materials in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point. These materials offered superior performance characteristics, such as lighter weight and enhanced resistance to pollution and weathering, compared to traditional ceramics. This evolution has led to a diverse range of insulator types, catering to various applications in power transmission and distribution networks worldwide.
Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the advancements in technology and materials that have shaped the current market. As the industry continues to innovate, staying informed about these developments will be essential for making strategic sourcing decisions in the high voltage ceramic insulator sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high voltage ceramic insulator
-
What are the key characteristics to consider when sourcing high voltage ceramic insulators?
When sourcing high voltage ceramic insulators, it’s crucial to consider characteristics such as dielectric strength, mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to environmental contamination. These factors ensure that the insulator can withstand high voltages and extreme weather conditions. Additionally, evaluate the installation and maintenance ease, as this can impact long-term operational costs. Understanding the specific requirements of your application, including voltage rating and environmental conditions, will guide your selection process. -
How can I ensure the quality of high voltage ceramic insulators from suppliers?
To ensure quality, it’s essential to vet suppliers rigorously. Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications and a proven track record in producing high voltage ceramic insulators. Request samples and conduct independent testing to verify their performance under specified conditions. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, including compliance with international standards. Establishing a long-term relationship with a reliable supplier can also provide reassurance regarding product consistency and quality. -
What are the common applications for high voltage ceramic insulators?
High voltage ceramic insulators are widely used in power transmission and distribution systems, particularly in substations and along overhead power lines. They are suitable for voltages ranging from 11 kV to 800 kV, making them ideal for critical infrastructure such as renewable energy systems, industrial plants, and urban power grids. Their durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions make them a preferred choice in various sectors, including telecommunications, railways, and utility companies. -
What factors influence the pricing of high voltage ceramic insulators?
Pricing for high voltage ceramic insulators is influenced by several factors, including material costs, manufacturing processes, and customization options. Bulk orders typically benefit from lower unit costs, while specialized designs may incur additional charges. Geographic location can also impact shipping and logistics costs. It’s advisable to compare quotes from multiple suppliers and consider total cost of ownership, which includes installation and maintenance expenses, when evaluating pricing. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for high voltage ceramic insulators?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for high voltage ceramic insulators can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs for standard products, while customized insulators might require larger orders to justify production costs. It’s beneficial to communicate your specific needs with suppliers, as they may accommodate smaller orders, especially for long-term partnerships or pilot projects. -
How can I customize high voltage ceramic insulators for specific applications?
Customization of high voltage ceramic insulators involves specifying dimensions, voltage ratings, and material properties tailored to your application needs. Engage directly with manufacturers to discuss your requirements, including environmental factors such as pollution levels and temperature extremes. Many suppliers offer engineering support to assist in designing insulators that meet your exact specifications. Be prepared to provide details about installation conditions and any unique challenges your project may face. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of high voltage ceramic insulators?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include net 30, 60, or 90 days after delivery, depending on the buyer’s creditworthiness and the supplier’s policies. Some suppliers may also require a deposit upfront, especially for large orders or custom products. It’s important to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that offer protection for both parties. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing high voltage ceramic insulators?
When importing high voltage ceramic insulators, consider logistics factors such as shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your preferred shipping method and that they understand the regulations of your destination country. It’s also advisable to work with logistics partners experienced in handling industrial equipment to mitigate risks during transport. Proper packaging is crucial to prevent damage during transit, so confirm that your supplier follows best practices in this regard.
Top 6 High Voltage Ceramic Insulator Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Poinsa – High Voltage Insulators
Domain: poinsa.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: High voltage insulators are essential for electrical power transmission and distribution systems, designed to isolate electrical conductors from towers and the ground. Key types include: 1. Porcelain Insulators: Used for voltage lines from 11 kV to 400 kV, made of fired clay with high mechanical and dielectric strength. 2. Polymeric Insulators: Meet demanding requirements, facilitating assembly an…
2. eBay – High Voltage Insulators
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: High Voltage Insulator In Collectible Insulators for sale on eBay. Featured refinements include Glass Insulator, Telephone Insulators, Electric Insulator, Ceramic Insulator, Carnival Glass Insulator, Porcelain Insulator, and Purple Insulator. Products available include various types of insulators such as: High Voltage Ceramic Insulator, Porcelain Insulator, Vintage Electrical Insulators, and more….
3. MGS4U – Feed Through Insulator Ceramic
Domain: mgs4u.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Feed Through Insulator Ceramic”, “price”: “$7.95”, “quantity_discounts”: [{“quantity_range”: “1-9”, “price”: “$7.95”}, {“quantity_range”: “10-24”, “price”: “$7.16”}, {“quantity_range”: “25-99”, “price”: “$6.36”}, {“quantity_range”: “100+”, “price”: “$5.57”}], “sku”: “FT-IN-01”, “voltage_rating”: “14 kV”, “screw_length”: “2.095 in”, “screw_diameter”: “.183 in”, “screw_material”: “Stainles…
4. Morgan Technical Ceramics – High Voltage Ceramic Insulators
Domain: morgantechnicalceramics.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: High Voltage Ceramic Insulators are precision-made for analytical applications, lasers, power tubes, and high voltage bushings. They are designed to withstand extremely high voltages, corrosive atmospheres, and extreme thermal shock. Made from 95% alumina, these insulators offer excellent electrical properties and are suitable for precision machining, brazing, and metallisation. The company emphas…
5. IQS Directory – Ceramic Insulators
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Ceramic insulators are insulating materials made from clay, available in red, brown, or white, characterized by a porous texture. They efficiently separate electronic components, offering outstanding dielectric properties, exceptional resistance to electrical currents, and low energy dissipation. They are easy to maintain, highly resistant to staining and residue buildup, and have been favored for…
6. Etsy – High Voltage Insulators
Domain: etsy.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: This company, Etsy – High Voltage Insulators, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high voltage ceramic insulator
In the evolving landscape of electrical power transmission, high voltage ceramic insulators remain pivotal for ensuring reliability and efficiency. Their unique characteristics, including high dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and resistance to environmental degradation, make them indispensable in various applications across continents. For B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of these insulators is crucial. By leveraging a deep understanding of the different types—such as porcelain, glass, and composite insulators—buyers can tailor their procurement strategies to meet specific operational needs and environmental challenges.
As the demand for energy continues to rise globally, investing in high-quality insulators can significantly enhance system performance and reduce long-term operational costs. Moreover, fostering partnerships with reputable manufacturers can ensure access to innovative solutions that meet evolving industry standards.

Illustrative image related to high voltage ceramic insulator
Looking ahead, companies are encouraged to stay abreast of technological advancements and market trends in insulator manufacturing. By doing so, they can make informed purchasing decisions that not only meet current demands but also position their operations for future growth. Engage with suppliers today to explore tailored solutions that will empower your infrastructure and drive efficiency in your energy distribution systems.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.