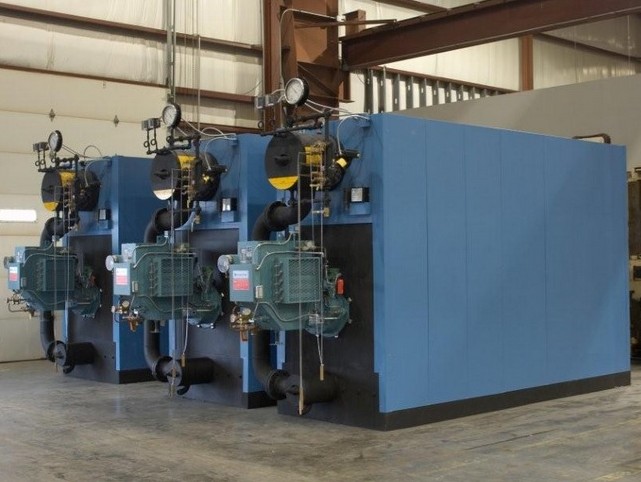
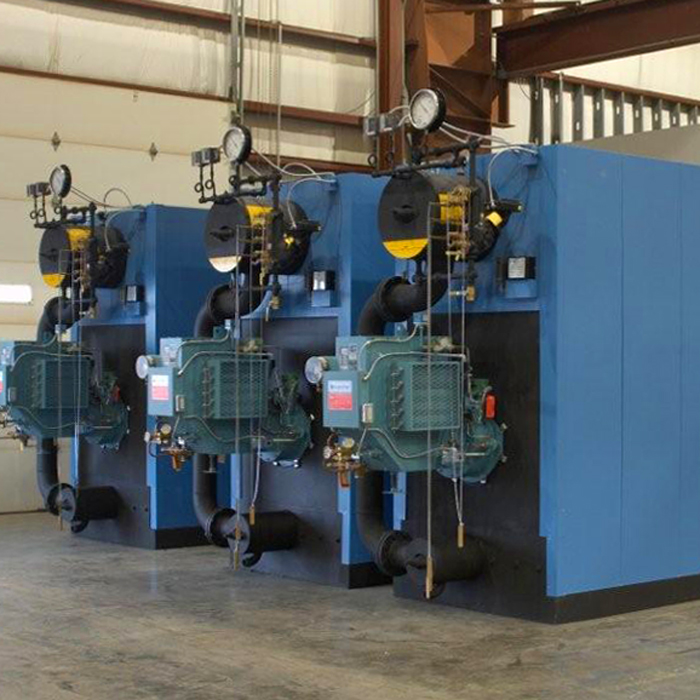
High Pressure Steam Boiler: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for high pressure steam boiler
In an increasingly interconnected world, navigating the global market for high pressure steam boilers presents both challenges and opportunities for international B2B buyers. One of the primary hurdles is sourcing reliable and efficient boiler systems that meet diverse industrial needs while adhering to local regulations and standards. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, covering various types of high pressure steam boilers, their applications across industries, and key considerations for supplier vetting.
Buyers will gain insights into essential factors such as cost implications, maintenance requirements, and the benefits of different fuel types, including natural gas and oil. Additionally, the guide will delve into the advantages of rental solutions, which can provide flexibility during peak demands or emergencies, thus optimizing operational efficiency.
Tailored specifically for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets such as Brazil and Nigeria, this guide empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices. By understanding the nuances of high pressure steam boiler systems, buyers can confidently select the right solutions that enhance productivity and drive profitability in their operations.
Understanding high pressure steam boiler Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Tube Boiler | Features tubes where water circulates, allowing for high pressures | Power generation, chemical processing | Pros: Efficient heat transfer, compact size. Cons: Higher initial cost, complex maintenance. |
| Fire Tube Boiler | Contains tubes filled with hot gases, heating surrounding water | Food processing, textile industries | Pros: Simple design, low maintenance. Cons: Limited pressure capabilities, larger footprint. |
| Modular Boiler | Scalable design with multiple units working together | Industrial heating, large facilities | Pros: Flexibility, redundancy. Cons: Higher upfront investment, requires space for installation. |
| Electric Steam Boiler | Uses electric elements to generate steam | Pharmaceutical, small-scale operations | Pros: Clean energy source, precise control. Cons: Higher operational costs, limited capacity. |
| High-Pressure Steam Boiler | Operates at pressures above 15 psi, delivering high efficiency | Steam turbines, HVAC systems | Pros: High efficiency, rapid steam production. Cons: Safety regulations, potential for high maintenance costs. |
What Are the Characteristics and Applications of Water Tube Boilers?
Water tube boilers are designed with tubes through which water circulates, heated by combustion gases from below. This design allows for high-pressure operation and efficient heat transfer, making them ideal for power generation and chemical processing industries. B2B buyers should consider their efficiency and compact size, which can save space in industrial settings. However, they come with a higher initial investment and more complex maintenance requirements.
How Do Fire Tube Boilers Compare in Terms of Design and Use?
Fire tube boilers operate by filling tubes with hot gases while surrounding water absorbs the heat. This simpler design is well-suited for applications in food processing and textile industries, where reliability is crucial. Buyers appreciate the low maintenance and straightforward operation, but they should be aware of the limitations in pressure capabilities and the larger space these boilers require.
What Advantages Do Modular Boilers Offer for Large Industrial Needs?
Modular boilers consist of multiple smaller units that can operate independently or together to meet varying demands. This scalability makes them perfect for industrial heating applications and large facilities. B2B buyers benefit from the flexibility and redundancy they provide, ensuring continuous operation during maintenance or peak demand. However, the upfront investment can be higher, and adequate installation space is necessary.
Why Choose Electric Steam Boilers for Specific Operations?
Electric steam boilers utilize electric elements to produce steam, making them a clean and efficient option for industries such as pharmaceuticals and small-scale operations. Their precise control over steam production is a significant advantage for processes requiring exact specifications. However, buyers should consider the higher operational costs and limited capacity compared to traditional boilers.
What Should Buyers Know About High-Pressure Steam Boilers?
High-pressure steam boilers operate above 15 psi, delivering rapid steam production and high efficiency, making them vital in steam turbine applications and HVAC systems. Buyers must weigh the benefits of high efficiency against the stringent safety regulations and potentially high maintenance costs associated with these systems. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of high pressure steam boiler
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of high pressure steam boiler | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Steam generation for cooking and sterilization processes | Ensures food safety, quality, and efficiency | Compliance with health regulations and standards |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Heat supply for chemical reactions and distillation | Enhances production efficiency and product yield | Material compatibility and safety certifications |
| Textile Industry | Steam for dyeing, finishing, and washing fabrics | Improves fabric quality and reduces cycle time | Energy efficiency and maintenance support |
| Power Generation | Steam for turbines in electricity generation | Increases energy output and operational reliability | Fuel flexibility and emissions control |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilization of equipment and production processes | Ensures product safety and regulatory compliance | Precision controls and monitoring capabilities |
How is a high pressure steam boiler utilized in the food and beverage industry?
In the food and beverage sector, high pressure steam boilers are essential for various cooking and sterilization processes. They provide the necessary heat for cooking products, ensuring they meet safety standards by eliminating harmful bacteria. Additionally, steam is used in pasteurization to extend shelf life. Buyers in this sector must consider compliance with health regulations, selecting boilers designed for food-grade applications and ensuring they have the capacity to handle peak production demands.
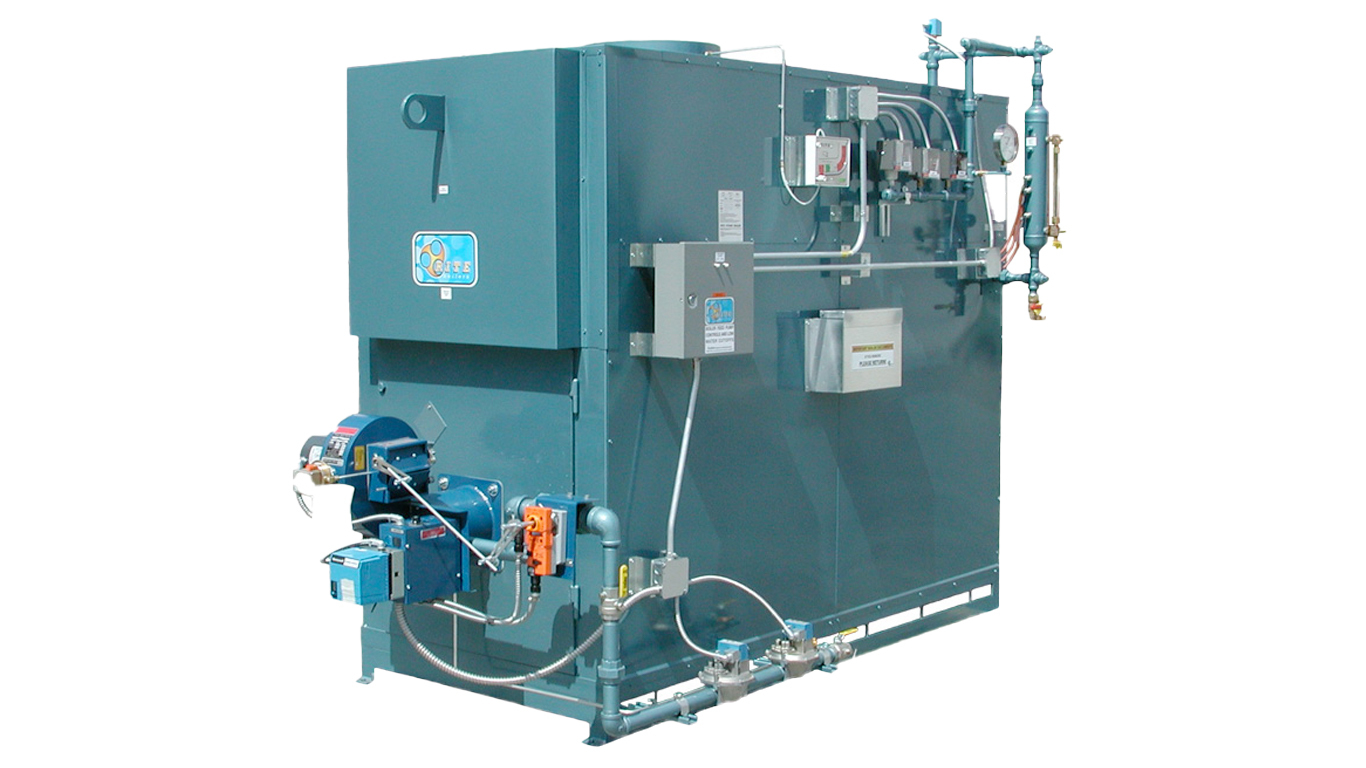

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
What role does a high pressure steam boiler play in chemical manufacturing?
High pressure steam boilers serve a critical function in chemical manufacturing by supplying heat for various chemical reactions and distillation processes. The ability to maintain consistent high temperatures enhances reaction rates and improves overall production efficiency. Buyers should focus on the boiler’s material compatibility with corrosive substances and ensure it meets safety certifications to avoid hazardous situations, especially in regions with strict regulatory frameworks.
How does the textile industry benefit from high pressure steam boilers?
In the textile industry, high pressure steam boilers are utilized for dyeing, finishing, and washing fabrics. The steam provides the required heat for these processes, leading to improved fabric quality and reduced cycle times. Buyers should prioritize energy efficiency and maintenance support when sourcing boilers, as these factors can significantly impact production costs and uptime, especially in competitive markets across Africa and South America.
Why are high pressure steam boilers crucial in power generation?
High pressure steam boilers are vital in power generation, where they produce steam that drives turbines for electricity generation. This process is essential for increasing energy output and ensuring operational reliability. Buyers need to consider the boiler’s fuel flexibility and emissions control technologies to comply with environmental regulations, particularly in regions that are increasingly prioritizing sustainable energy practices.
How do high pressure steam boilers ensure safety in the pharmaceutical industry?
In the pharmaceutical sector, high pressure steam boilers are primarily used for sterilizing equipment and ensuring that production processes meet stringent safety standards. The steam effectively eliminates contaminants, safeguarding product integrity. Buyers in this field must look for boilers with precision controls and robust monitoring capabilities to ensure consistent performance and compliance with regulatory requirements, especially in regions with strict health and safety laws.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘high pressure steam boiler’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Boiler Downtime Due to Maintenance Issues
The Problem:
B2B buyers often grapple with unexpected boiler downtime, which can severely disrupt production schedules. High pressure steam boilers are complex systems that require regular maintenance, and any oversight can lead to equipment failure. For instance, a manufacturing facility in Brazil may find itself unable to produce steam for essential processes due to a malfunctioning pressure control system. This unplanned downtime not only affects output but can also lead to financial losses and strained relationships with clients.
The Solution:
To mitigate maintenance-related downtime, B2B buyers should implement a proactive maintenance strategy. This involves scheduling regular inspections and preventative maintenance checks, ideally through a service agreement with a qualified boiler technician. Buyers should also invest in modern monitoring systems that provide real-time data on boiler performance, allowing for early detection of issues. Additionally, maintaining a stock of critical spare parts can reduce repair time significantly. Establishing a relationship with a reliable supplier for genuine parts ensures that replacements are timely and compatible, further enhancing boiler reliability.
Scenario 2: Rising Operating Costs Due to Inefficient Boiler Performance
The Problem:
Many businesses face escalating operational costs linked to the inefficient performance of their high pressure steam boilers. For example, a food processing plant in Nigeria might experience increased fuel consumption due to poor heat transfer efficiency or outdated technology. This inefficiency not only inflates operating costs but can also impact the plant’s overall competitiveness in the market.
The Solution:
To address rising operational costs, companies should consider conducting a comprehensive energy audit of their steam systems. This audit can help identify inefficiencies and recommend improvements, such as upgrading to a more efficient boiler model or retrofitting existing units with advanced technologies like economizers or variable frequency drives (VFDs). Buyers should also evaluate their fuel options; switching to alternative fuels, such as natural gas or biomass, may yield cost savings and improve efficiency. Collaborating with energy consultants can provide insights into optimizing boiler operations and achieving long-term energy savings.
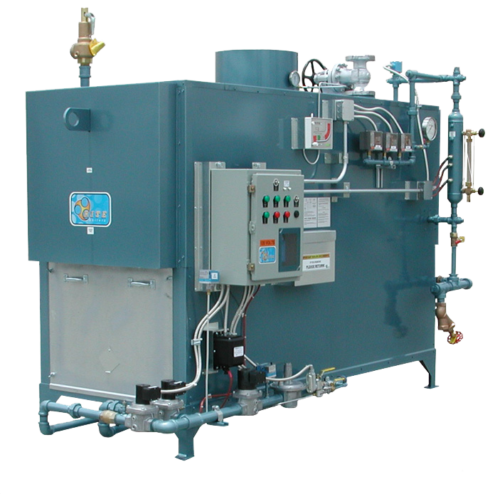

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Scenario 3: Compliance Challenges with Safety and Environmental Regulations
The Problem:
Navigating the complex landscape of safety and environmental regulations is a significant challenge for businesses operating high pressure steam boilers. For instance, a manufacturing facility in Europe may struggle to meet stringent emissions standards, leading to potential fines and increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies. Non-compliance can not only result in financial penalties but can also damage a company’s reputation.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should prioritize compliance by staying informed about the latest regulations affecting their operations. This can be achieved through regular training programs for staff and engaging with industry associations that provide updates on regulatory changes. Investing in modern boiler systems equipped with low NOx burners and advanced emission control technologies can help meet environmental standards. Furthermore, conducting routine compliance audits will ensure that operations align with legal requirements. Establishing a relationship with compliance consultants can offer additional support in navigating these challenges and maintaining adherence to local and international regulations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for high pressure steam boiler
What Are the Key Materials for High Pressure Steam Boilers?
When selecting materials for high pressure steam boilers, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in high pressure steam boiler construction: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel, and Cast Iron.
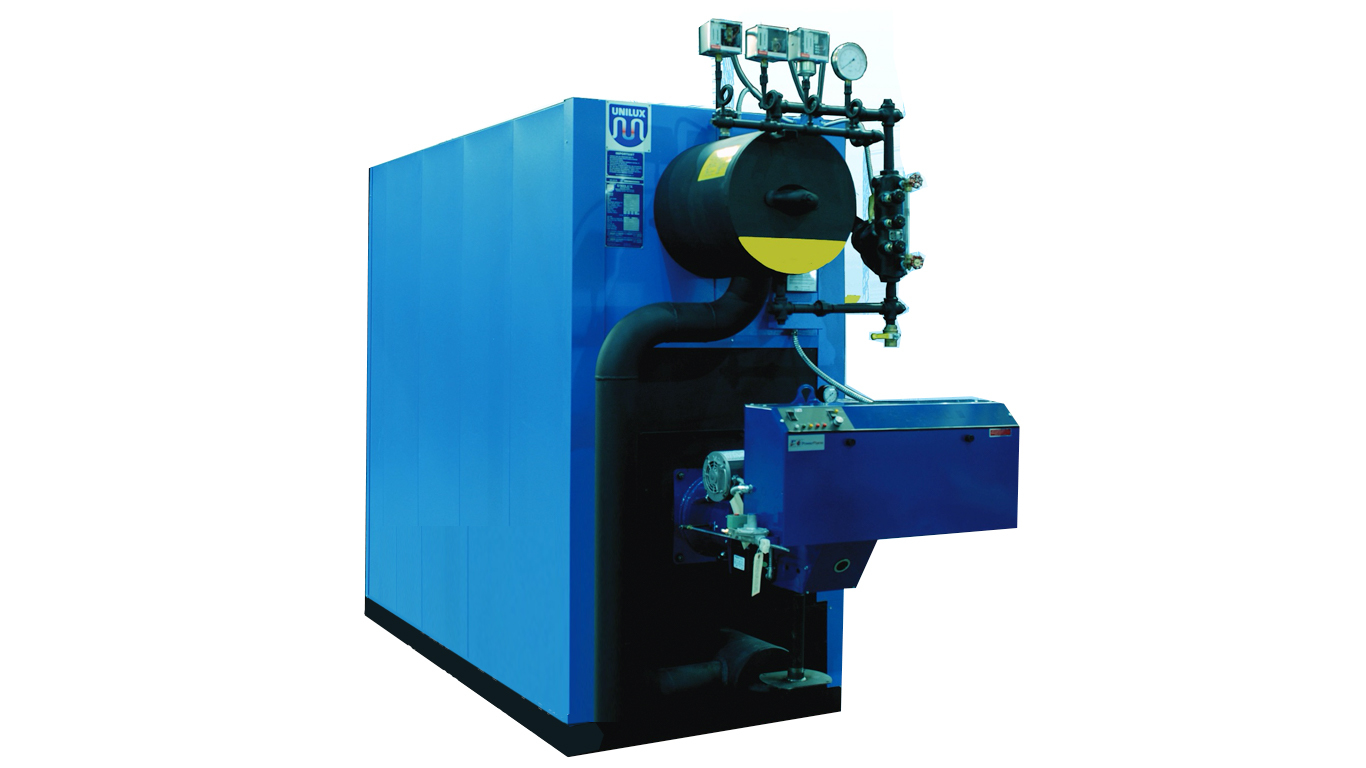

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in High Pressure Steam Boilers?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its excellent strength and toughness at high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 450°C (842°F) and can withstand pressures exceeding 150 psi.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively low-cost and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for many boiler applications. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, particularly in environments with high moisture content. This limitation can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with a variety of steam media but may require protective coatings or treatments to enhance its corrosion resistance in certain applications.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM A106 for seamless carbon steel pipes. Understanding local environmental conditions is essential for determining the suitability of carbon steel.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in High Pressure Steam Boilers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and can handle temperatures up to 800°C (1472°F) with pressure ratings that can exceed 300 psi.
Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to oxidation, which significantly reduces maintenance needs. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine and weld.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications involving aggressive media or environments, such as those found in chemical processing industries.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards like ASTM A312 for stainless steel pipes is crucial. Buyers in Europe may prefer grades like 316L for enhanced corrosion resistance, particularly in coastal regions.
Why Choose Alloy Steel for High Pressure Steam Boilers?
Key Properties: Alloy steel combines elements like chromium and molybdenum to enhance strength and resistance to high temperatures, with capabilities reaching up to 600°C (1112°F) and pressures of 400 psi.
Pros & Cons: The high strength-to-weight ratio makes alloy steel a robust option for high pressure applications. However, it is more expensive than both carbon and stainless steel and can require specialized manufacturing processes.
Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is particularly suitable for high-stress applications, such as in power generation or industrial processes requiring high thermal efficiency.
International Considerations: Buyers should reference standards such as ASTM A335 for seamless alloy steel pipes. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, selecting the right alloy composition is critical for performance.
Is Cast Iron a Viable Option for High Pressure Steam Boilers?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent compressive strength and ability to withstand high temperatures, typically rated up to 400°C (752°F) and pressures around 100 psi.
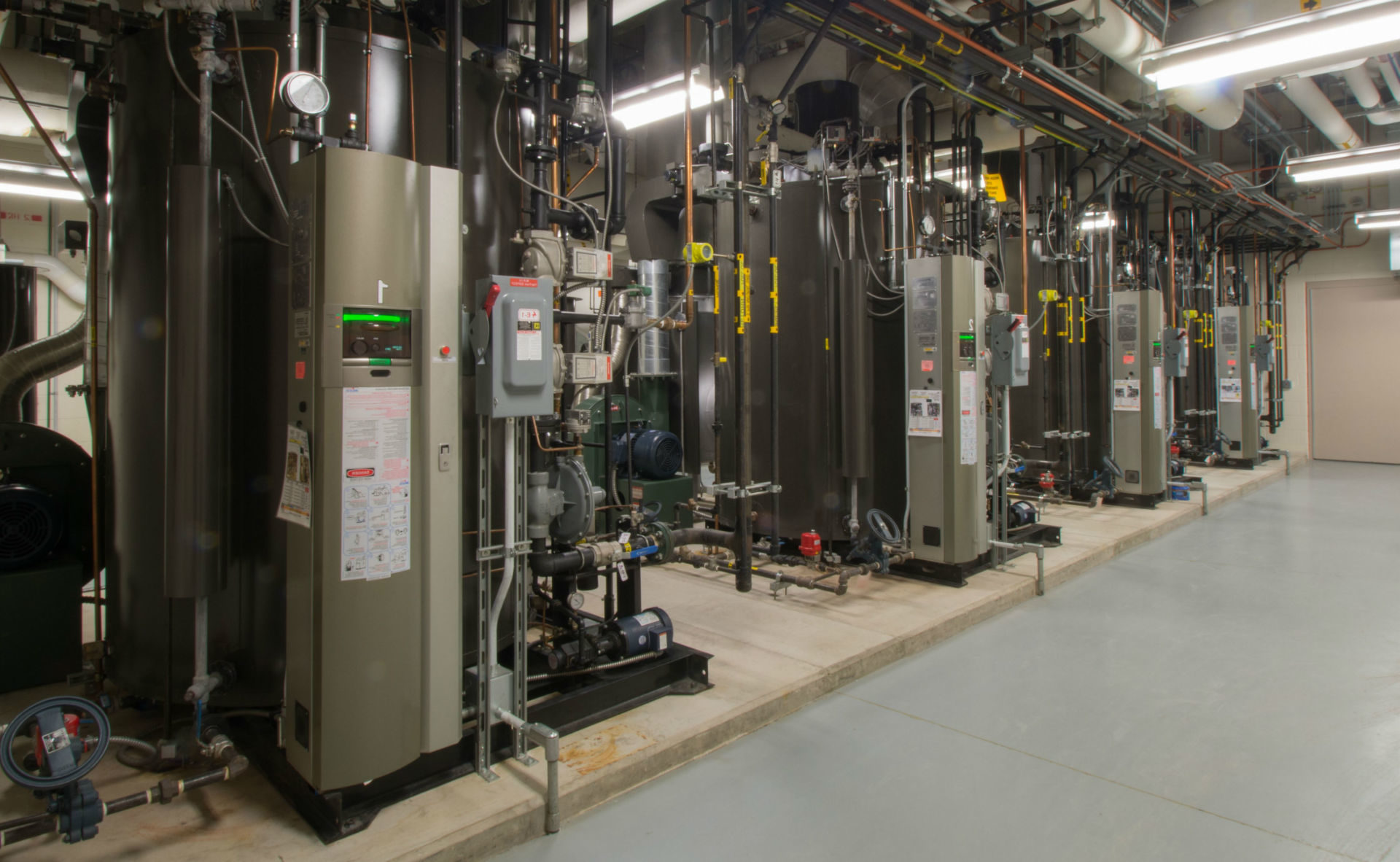

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Pros & Cons: Cast iron is cost-effective and offers good thermal conductivity. However, it is brittle and can crack under high-stress conditions, which limits its application in high pressure scenarios.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is generally used in low to medium pressure steam applications and is less suitable for high pressure systems.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A48 for gray iron castings. In regions with high humidity, the risk of corrosion can be a concern, necessitating protective coatings.
Summary Table of Material Selection for High Pressure Steam Boilers
| Material | Typical Use Case for high pressure steam boiler | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General steam applications | Cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, high corrosion environments | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost, difficult to machine | High |
| Alloy Steel | High-stress applications in power generation | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, specialized manufacturing | Med |
| Cast Iron | Low to medium pressure systems | Good thermal conductivity | Brittle, limited high-pressure use | Low |
This comprehensive analysis of material options provides B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions regarding high pressure steam boiler procurement, ensuring compliance with international standards and suitability for specific applications.

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for high pressure steam boiler
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of High Pressure Steam Boilers?
The manufacturing process for high pressure steam boilers is intricate, requiring precision and adherence to industry standards. Typically, the process can be divided into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The initial stage involves selecting high-quality materials such as carbon steel or stainless steel, which are essential for the durability and efficiency of the boilers. Suppliers often conduct chemical composition tests to ensure that the materials meet the required specifications. The materials are then cut and shaped into suitable sizes for further processing.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials undergo various forming processes such as rolling, bending, and welding. Advanced techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining are frequently employed to achieve precise dimensions. The use of automated machinery enhances accuracy and reduces human error, which is crucial given the safety requirements for high pressure applications.
-
Assembly: After forming, the components are assembled into the boiler structure. This includes the installation of tubes, burners, and control systems. Quality control measures are implemented throughout the assembly process, ensuring that each component fits perfectly and functions as intended. Modular designs are increasingly popular, allowing for easier maintenance and scalability.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatments such as painting, coating, and insulation. These processes not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also improve resistance to corrosion and heat loss. Insulation materials are carefully selected to optimize energy efficiency, which is a significant consideration for B2B buyers looking to minimize operational costs.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for High Pressure Steam Boilers?
Quality control (QC) is critical in the manufacturing of high pressure steam boilers, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and client specifications. Understanding the QC processes involved can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
-
International Standards: Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS), emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for European markets and API standards for oil and gas applications provide further assurance of quality.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: QC is typically structured around three key checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified criteria.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor critical parameters such as dimensions, weld quality, and pressure testing.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the entire unit undergoes rigorous testing for safety and performance. This may include hydrostatic testing, performance evaluations, and safety checks against national and international standards. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability of high pressure steam boilers. Non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques like ultrasonic testing (UT) and radiographic testing (RT) are commonly used to detect defects without damaging the components. Pressure tests are also conducted to confirm that the boiler can withstand operational pressures safely.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must be diligent in verifying the quality control processes of their suppliers to ensure that they are investing in reliable products. Here are some actionable strategies for buyers:
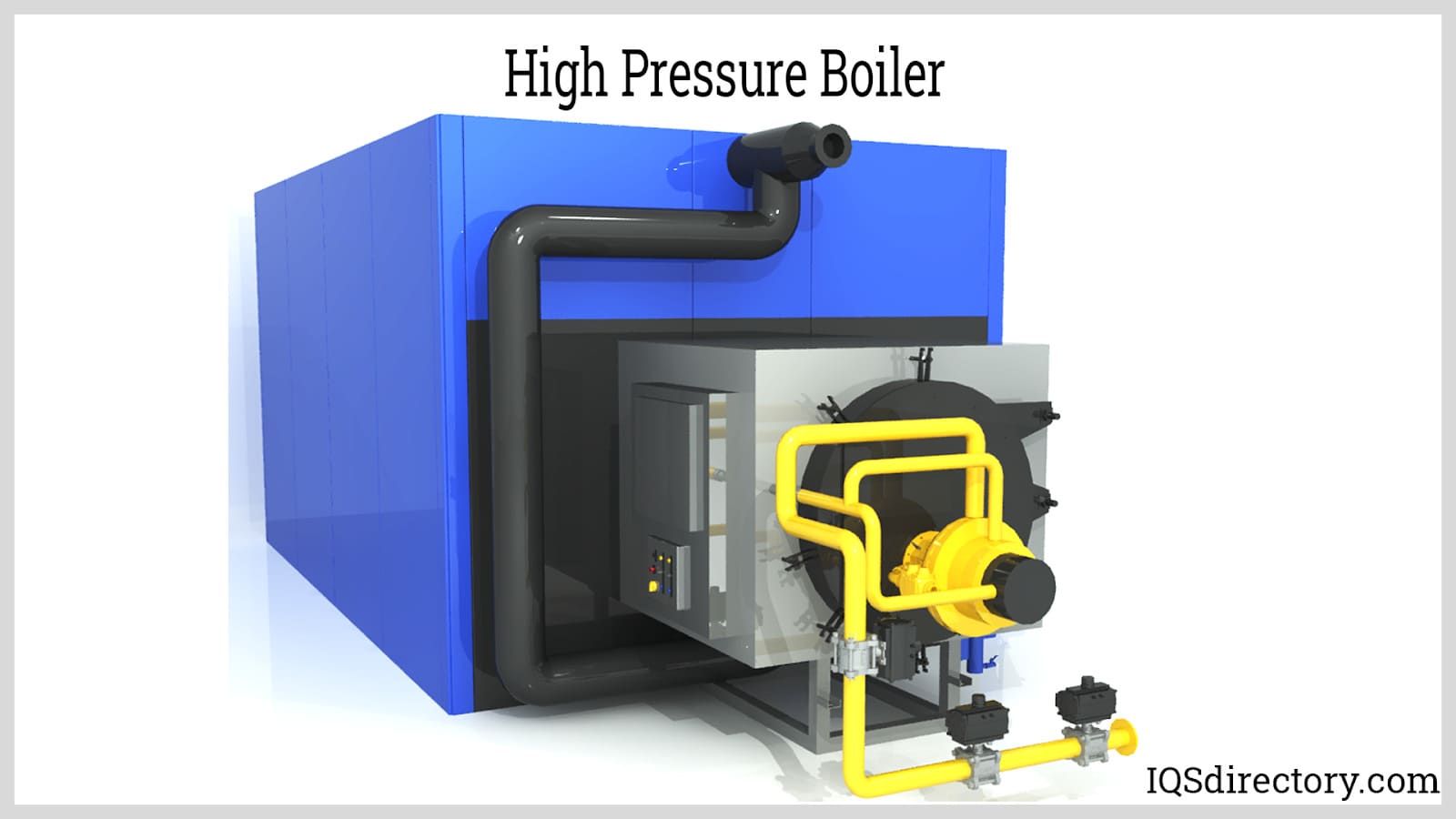
Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. An audit can reveal whether the supplier adheres to international standards and industry best practices.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers can offer transparency regarding their QC processes. These reports should include information on testing methods, results, and compliance with standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing quality. These agencies often have the expertise to evaluate compliance with international standards and can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing from foreign suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges when it comes to quality control in high pressure steam boiler procurement.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have specific regulations governing boiler safety and efficiency. Buyers must ensure that suppliers are compliant with local regulations, which may differ significantly from international standards. Understanding these nuances can help avoid legal and operational issues down the line.
-
Cultural and Language Barriers: Effective communication is vital in ensuring that quality standards are clearly understood and met. Buyers may encounter challenges due to cultural differences and language barriers. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and employing local representatives can help bridge these gaps.
-
Supply Chain Reliability: The reliability of the supply chain can significantly impact the quality of the final product. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s logistics capabilities, including their ability to source quality materials and manage shipping and delivery timelines. A robust supply chain often correlates with better quality assurance practices.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for high pressure steam boilers is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they select reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘high pressure steam boiler’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure high pressure steam boilers. The goal is to facilitate informed decision-making by providing actionable steps and considerations that will help ensure the selection of the right boiler for your operational needs.
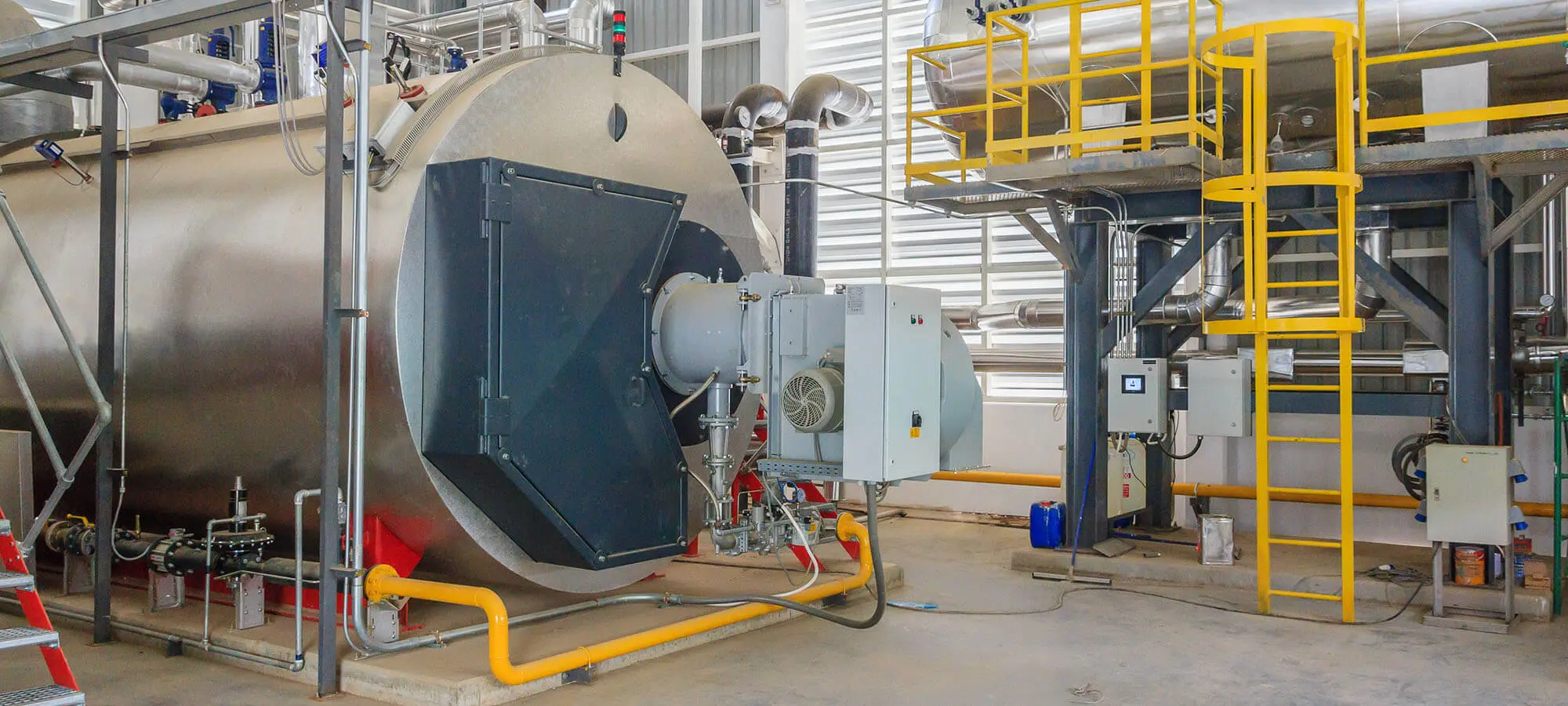

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by establishing the technical requirements for the high pressure steam boiler. This includes determining the desired steam output capacity, pressure ratings, and fuel types.
– Capacity: Assess your operational needs to decide on the appropriate horsepower (HP) or BTU output.
– Pressure Ratings: Consider the maximum pressure required for your processes to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Step 2: Research Different Boiler Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of high pressure steam boilers available in the market, such as water tube and fire tube boilers. Understanding the differences will help you select the most suitable boiler for your application.
– Water Tube Boilers: Typically more efficient for high-pressure applications due to their design.
– Fire Tube Boilers: Often easier to maintain and operate at lower pressures.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your needs. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Certifications: Check for compliance with international standards (e.g., ASME, ISO) to ensure product quality.
– Support Services: Inquire about after-sales support, including maintenance and spare parts availability.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that include not just the boiler price, but also installation, training, and ongoing maintenance costs.
– Breakdown of Costs: Ensure the quotation includes all costs associated with the purchase, including shipping and handling.
– Warranty and Service Agreements: Evaluate warranty terms and available service contracts for maintenance and repairs.
Step 5: Assess Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
As energy costs rise and regulations tighten, it’s crucial to consider the energy efficiency of the boiler and its environmental impact. Look for boilers that meet low NOx emissions standards and have energy-saving features.
– Efficiency Ratings: Investigate the boiler’s thermal efficiency and operational costs to optimize long-term savings.
– Sustainability Practices: Understand the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices and the environmental footprint of their products.
Step 6: Plan for Installation and Training
Consider the logistics of installation and the need for operator training. Ensure that the supplier provides support for both.
– Installation Services: Confirm whether the supplier offers professional installation services to avoid potential issues during setup.
– Training Programs: Look for suppliers that offer training for your staff to ensure safe and efficient operation of the boiler.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision and Negotiate Terms
After evaluating all factors, finalize your decision and negotiate terms with the selected supplier. Ensure clarity on delivery timelines, payment terms, and any contingencies.
– Contract Clarity: Ensure that all agreements are documented clearly to avoid misunderstandings.
– Contingency Plans: Discuss what measures are in place should any issues arise post-installation, such as equipment failures or delays.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing high pressure steam boilers, ensuring they select a product that meets their operational needs while aligning with budgetary and regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for high pressure steam boiler Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in High Pressure Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
When sourcing high pressure steam boilers, understanding the cost structure is essential. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality steel, insulation, and components like burners and controls are critical. Specialty materials, such as low-NOx burners or corrosion-resistant alloys, may incur additional costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for manufacturing, assembly, and installation. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location, with countries in Africa and South America often facing higher labor costs compared to Europe or the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient operations can reduce these costs, positively affecting pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom boiler designs. The complexity of the boiler and the precision required in manufacturing dictate these expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes ensure safety and compliance with international standards. These QC measures, while essential, add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the destination. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties must be factored into the final pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect High Pressure Steam Boiler Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of high pressure steam boilers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchasing can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders, which is beneficial for companies planning to scale operations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific features (like modular systems or unique fuel capabilities) can increase costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of these features against their operational requirements.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Boilers that comply with international certifications (like ASME or CE markings) may command higher prices due to the assurance of safety and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, which often come with warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: The chosen shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can impact overall costs. Buyers should understand how these terms affect their total expenditure, especially in international transactions.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in High Pressure Steam Boiler Sourcing?
To maximize value when sourcing high pressure steam boilers, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to explore discounts for larger orders or long-term contracts. Building a good relationship can lead to better terms over time.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider installation, maintenance, and operational costs. A more expensive boiler with superior efficiency may offer lower long-term costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that can affect pricing. For buyers in Africa or South America, these factors can significantly alter the total cost.
-
Research Local Suppliers: Local manufacturers may provide cost advantages due to reduced shipping and import fees. Additionally, they may offer tailored solutions that meet regional compliance standards.
-
Evaluate Lifecycle Costs: Examine the projected lifespan and maintenance requirements of the boiler. A higher upfront investment might yield better reliability and lower maintenance costs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for high pressure steam boilers can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. Buyers should request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing high pressure steam boiler With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to High Pressure Steam Boilers
In the industrial landscape, high pressure steam boilers are a critical component for various applications, such as power generation and process heating. However, there are alternative solutions that may offer different advantages depending on specific operational needs, budget constraints, and environmental considerations. This analysis compares high pressure steam boilers with two viable alternatives: electric boilers and industrial furnaces.
| Comparison Aspect | High Pressure Steam Boiler | Electric Boiler | Industrial Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, high steam output | Lower output, suitable for smaller applications | High heat capability, versatile in application |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, ongoing fuel costs | Lower installation costs, higher operational costs | Variable costs based on materials and usage |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires significant setup and infrastructure | Easier installation, minimal infrastructure needed | Complex installation, requires skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required, skilled technicians needed | Lower maintenance, easier to service | High maintenance, particularly for fuel systems |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale steam generation for industrial processes | Smaller operations or where electricity is readily available | Heavy-duty applications requiring extreme heat |
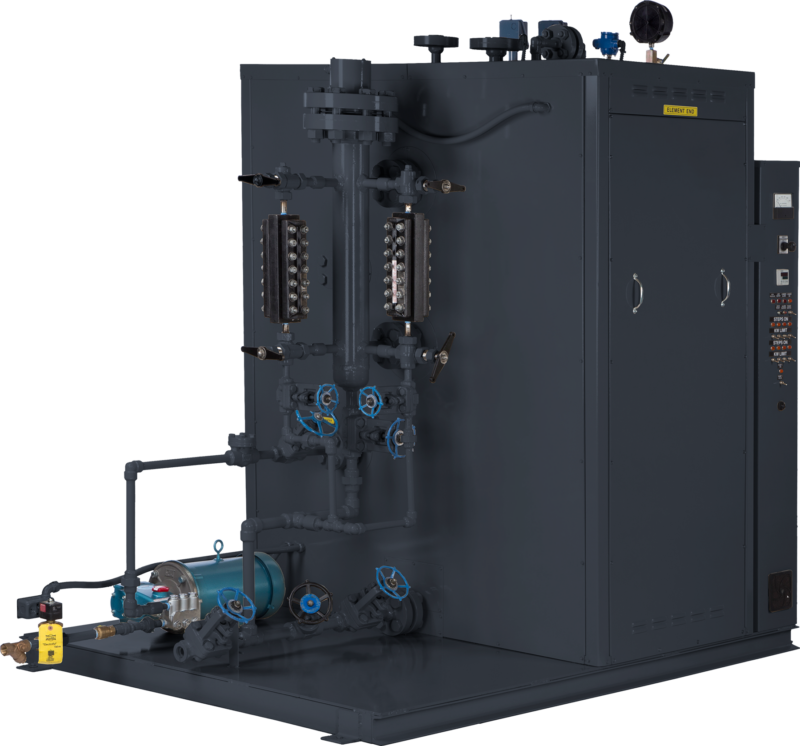
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Boilers?
Electric boilers utilize electricity to generate steam or hot water, making them an attractive alternative for facilities where natural gas is not readily available or where emissions must be minimized.

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Pros:
– Lower Installation Costs: Electric boilers are often easier to install and can be located in smaller spaces.
– Reduced Emissions: They produce no emissions at the point of use, which can be advantageous in environmentally sensitive areas.
Cons:
– Higher Operational Costs: The cost of electricity can be significantly higher than that of natural gas or other fuels, leading to increased operational expenses.
– Limited Output: Electric boilers may not meet the high demand of large industrial applications, making them less suitable for larger operations.
How Do Industrial Furnaces Compare to High Pressure Steam Boilers?
Industrial furnaces are designed for high-temperature applications, commonly used in metal processing, curing, and other heat-intensive processes.
Pros:
– Versatility: They can handle a variety of materials and processes, making them ideal for diverse industrial applications.
– High Temperature Capability: Industrial furnaces can achieve and maintain extremely high temperatures, essential for certain processes.
Cons:
– Complex Installation: The setup of industrial furnaces can be complex and may require specialized skills.
– Maintenance Challenges: Due to the high temperatures and varying fuel types, maintenance can be intensive and costly.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the appropriate solution requires a thorough assessment of your specific operational needs, budget, and environmental impact. High pressure steam boilers excel in large-scale applications with significant steam demands, while electric boilers may be better suited for smaller operations or in regions with strict emission regulations. Industrial furnaces offer versatility and high heat capabilities but come with greater complexity and maintenance demands.
Consider factors such as initial investment, operational costs, and long-term maintenance when making your choice. Engaging with suppliers who understand your industry requirements can also provide valuable insights and help you identify the most effective solution for your business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for high pressure steam boiler
Understanding the technical properties and terminology associated with high-pressure steam boilers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in industries where efficiency and safety are paramount. This section outlines essential specifications and trade terms that will aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Technical Specifications for High-Pressure Steam Boilers?
1. Steam Design Pressure
Steam design pressure refers to the maximum pressure that a steam boiler is engineered to safely handle, typically measured in pounds per square inch (psig). For high-pressure steam boilers, this can range from 15 psig to over 150 psig. Understanding this specification is vital for buyers to ensure that the boiler can meet the demands of their specific applications without risking safety or efficiency.
2. Material Grade
The material grade of a boiler’s components, such as the shell and tubes, significantly influences its durability and performance. Common materials include SA178-A steel for firetubes and stainless steel for corrosion resistance. Selecting the right material grade is essential for buyers to ensure longevity and reduce maintenance costs, particularly in harsh operating environments.
3. Heating Surface Area
The heating surface area refers to the total area available for heat transfer from the combustion gases to the water in the boiler. This specification affects the boiler’s efficiency and output capacity. A larger heating surface area generally allows for more efficient steam production, making it a critical factor for buyers looking to optimize operational efficiency.
4. Fuel Capabilities
High-pressure steam boilers can be designed to operate on various fuels, including natural gas, propane, and oil. Understanding fuel capabilities is crucial for buyers to ensure compatibility with existing fuel supply systems and to assess operational costs. The choice of fuel can also impact emissions and compliance with environmental regulations.
5. Control Systems
Modern high-pressure steam boilers often include sophisticated control systems that manage pressure, temperature, and water levels. These systems can enhance operational efficiency and safety through automation. Buyers should prioritize boilers with advanced control technologies to minimize human error and optimize performance.
6. Safety Features
Safety is a top concern in steam boiler operations. Key safety features include pressure relief valves, low water cut-off devices, and UL-listed components. Buyers should evaluate these safety features to ensure compliance with industry standards and to protect personnel and equipment from potential failures.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the High-Pressure Steam Boiler Industry?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the boiler industry, OEMs provide critical components that ensure the reliability and performance of the boiler system. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and quality products.

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. In the context of high-pressure steam boilers, knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to assess inventory needs and budget constraints. It can also influence purchasing strategies, especially for smaller operations.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. For high-pressure steam boilers, submitting an RFQ can lead to competitive pricing and ensure that buyers receive detailed proposals tailored to their needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms used in international trade, outlining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers in different regions, as they dictate shipping, insurance, and liability, which can significantly affect total costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is delivered. For high-pressure steam boilers, lead times can vary widely based on customization and supplier capabilities. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their operations effectively and avoid downtime.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of high-pressure steam boiler procurement more effectively, ensuring they select the right equipment for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the high pressure steam boiler Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Shaping the High Pressure Steam Boiler Sector?
The high pressure steam boiler sector is experiencing significant transformations driven by globalization, technological advancements, and increasing energy demands. Key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in industrialization, prompting a need for efficient steam generation systems. A notable trend is the rise of modular boiler systems, which offer flexibility and scalability for businesses facing fluctuating demand. These systems allow for quick deployment and can be adjusted as production needs change, making them particularly appealing to industries in regions like Brazil and Nigeria.
In addition, the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled monitoring and control systems, is enhancing operational efficiency. These technologies facilitate real-time data collection and analysis, allowing for predictive maintenance and reduced downtime. International buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer these advanced features, as they align with the broader trend toward automation in manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability is influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are looking for suppliers who not only provide high-quality products but also demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impacts. This shift is driving competition among manufacturers to adopt greener technologies and practices, thereby shaping the market dynamics.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the High Pressure Steam Boiler Market?
The environmental impact of industrial processes, including steam generation, has led to a heightened focus on sustainability within the high pressure steam boiler sector. As businesses face increasing pressure from consumers, regulators, and stakeholders to reduce their carbon footprints, the importance of ethical sourcing has become paramount. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe, are prioritizing suppliers that implement sustainable manufacturing practices and offer energy-efficient products.

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for energy efficiency, are becoming critical criteria in the procurement process. Buyers are not only looking for high pressure steam boilers that meet their operational requirements but also those that contribute to their overall sustainability goals. This trend is evident in the growing demand for boilers that utilize alternative fuels, such as biomass or hydrogen, which can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels.
Moreover, establishing ethical supply chains is vital for mitigating risks associated with environmental compliance and social responsibility. Suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their sourcing practices and commit to fair labor standards are more likely to attract discerning buyers. The focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing is reshaping supplier relationships, encouraging businesses to collaborate with manufacturers who align with their values and goals.
What Is the Historical Context of High Pressure Steam Boilers in B2B?
The history of high pressure steam boilers dates back to the early industrial revolution when steam power became a cornerstone of manufacturing. Initially, these boilers were simple vessels designed to generate steam for driving machinery. Over the years, advancements in engineering and materials science led to the development of more sophisticated designs, such as water tube and fire tube boilers, which improved efficiency and safety.
In the mid-20th century, the introduction of automation and control systems further revolutionized the sector, allowing for better pressure management and energy efficiency. As industries expanded globally, particularly in developing regions, the demand for reliable steam generation systems surged, prompting manufacturers to innovate continuously. Today, high pressure steam boilers represent a critical component of various industries, from energy production to food processing, highlighting their enduring significance in the B2B landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of high pressure steam boiler
-
How do I solve high pressure issues with my steam boiler?
To address high pressure issues, first check the pressure gauge to confirm the readings. If the pressure exceeds the safe operating limits, inspect the pressure control settings and ensure they are properly calibrated. A malfunctioning pressure relief valve may also contribute to excessive pressure; it should be tested and replaced if faulty. Additionally, ensure that the boiler is not overfilled with water, as this can lead to pressure build-up. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are crucial to avoid such problems. -
What is the best type of high pressure steam boiler for industrial applications?
The ideal high pressure steam boiler for industrial use typically depends on the specific application and required steam output. Water tube boilers are often favored for their efficiency and ability to produce high-pressure steam. They have a larger heating surface and can handle fluctuations in demand. Conversely, firetube boilers may be suitable for smaller operations due to their simpler design and lower initial costs. Assess your operational needs, including fuel type and steam requirements, to determine the best fit. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for high pressure steam boilers?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Verify their compliance with international safety standards, such as ASME or ISO. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and customer service. Additionally, evaluate their capacity for customization and support services, including installation and maintenance. Review their financial stability to ensure they can deliver on large orders and consider their logistics capabilities for timely delivery. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for high pressure steam boilers?
Minimum order quantities for high pressure steam boilers can vary significantly based on the supplier and the boiler type. Generally, MOQs can range from one unit for specialized manufacturers to several units for larger industrial suppliers. It is crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility in MOQs for new customers or high-value contracts. Understanding your operational demands will help you negotiate favorable terms. -
What payment terms can I expect when purchasing high pressure steam boilers?
Payment terms for high pressure steam boilers typically include options such as upfront payment, installment payments, or letters of credit. Many suppliers require a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. It is advisable to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. Ensure that all payment terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing steam boilers internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing steam boilers, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Conduct factory audits or third-party inspections to verify manufacturing processes and compliance with safety standards. Establish a clear QA process, including testing for performance and safety before acceptance. Building a relationship with suppliers who prioritize quality can also facilitate better oversight and communication throughout the procurement process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing steam boilers?
When importing steam boilers, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, including bills of lading, commercial invoices, and certificates of origin. Plan for potential delays in shipping and customs clearance, particularly for larger or specialized units. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in heavy machinery can streamline the import process and mitigate risks. -
Can I customize high pressure steam boilers to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for high pressure steam boilers to meet specific operational requirements. Customizations can include adjustments to capacity, fuel type compatibility, and control systems. When discussing your needs with suppliers, clearly outline your operational demands and any special features required. Ensure that the customization options are feasible within your budget and timeline to avoid delays in project implementation.
Top 7 High Pressure Steam Boiler Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – High Pressure Boilers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: High Pressure Boilers operate at pressures of 80 bars or more, primarily used in thermal power plants for electricity generation. They convert water into steam using thermal energy in tubes filled with water. Key characteristics include: 1. Types: Steam generators, electric boilers, fire-tube, water-tube, vertical, horizontal configurations. 2. Heat Sources: Fuels like coal, natural gas, or oil. 3…
2. Cleaver-Brooks – Low and High Pressure Steam Boilers
Domain: cleaverbrooks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Cleaver-Brooks – Low and High Pressure Steam Boilers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Superior Boiler – Triad High Pressure Steam Boiler
Domain: superiorboiler.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Triad High Pressure Steam Boiler”, “Capacity”: “14 – 48 HP”, “Fuel Capabilities”: [“#2 Oil”, “Hydrogen”, “Natural Gas”, “Propane”], “Tube Type”: “Smooth Tubes with Turbulators”, “Steam Design Pressure”: “Up to 150 psig”, “Temperature Range”: “160-210°F”, “Vessel Capacity”: “109 gallons”, “Heating Surface”: “138 sq. ft.”, “Firetube Specifications”: {“Number of Firetubes”: “70”, “D…
4. Unilux – High Pressure Boilers
Domain: industrial-boilers.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: High pressure boilers operate with steam pressure greater than 80 bars and are used primarily in power generation in thermal power plants. They are designed to transfer heat from a source to water or steam while maintaining high internal pressure. Key manufacturers include Unilux Advanced Manufacturing, Fulton, Miura Boiler Co., Ltd., INDECK, California Boiler, Burnham® Commercial, and Nationwide …
5. Reddit – High Pressure Steam Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: High pressure steam is generally considered to be steam over 15 psi, with some definitions stating that anything over 5 psi is classified as pressure equipment. The specific context in the discussion mentions a steam line operating between 100-125 psi.
6. Boiler Specialists – High Pressure Boilers
Domain: boilerspecialists.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: High pressure boiler is defined as having a max allowable working pressure (MAWP) above 15 PSI. Low pressure steam typically runs at a pressure no higher than 2 PSI. Cast iron sectional boilers have an MAWP of 15 PSI steam, making them low pressure boilers. It is important to check that the manufacturer’s MAWP stamp matches or exceeds the safety valve ratings for safety and compliance.
7. PEP – VT Series High Pressure Steam Boilers
Domain: pepboiler.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: VT Series Boilers: High Pressure Steam Boilers by PEP. Features include: ASME 3-Pass design for maximum heat transfer and efficiency, pressure-fired combustion chamber, large steam dome chamber for drier steam, extra-large steam capacity, submerged water-cooled furnace (first in the industry), high efficiency low-high-low and modulating burners available, 3/8″ thick rolled plate shell for long ser…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for high pressure steam boiler
In summary, strategic sourcing of high-pressure steam boilers is essential for international B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. As the demand for reliable steam solutions continues to grow across industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the diverse types of boilers, their capabilities, and the services associated with them—such as rental options—can provide significant competitive advantages.

Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Investing in quality high-pressure steam boilers not only ensures compliance with safety regulations but also improves energy efficiency and minimizes downtime. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive support, including training programs and access to genuine parts, to maximize the longevity and performance of their boiler systems.
As we move into an increasingly dynamic market landscape, it is crucial for businesses to remain adaptable and informed. By leveraging strategic sourcing and fostering strong partnerships with reputable manufacturers, companies can position themselves for success in meeting the evolving demands of their industries.
Now is the time to explore the best options for your steam boiler needs. Engage with experienced suppliers, evaluate your requirements, and take proactive steps to secure the solutions that will drive your business forward.
Illustrative image related to high pressure steam boiler
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.