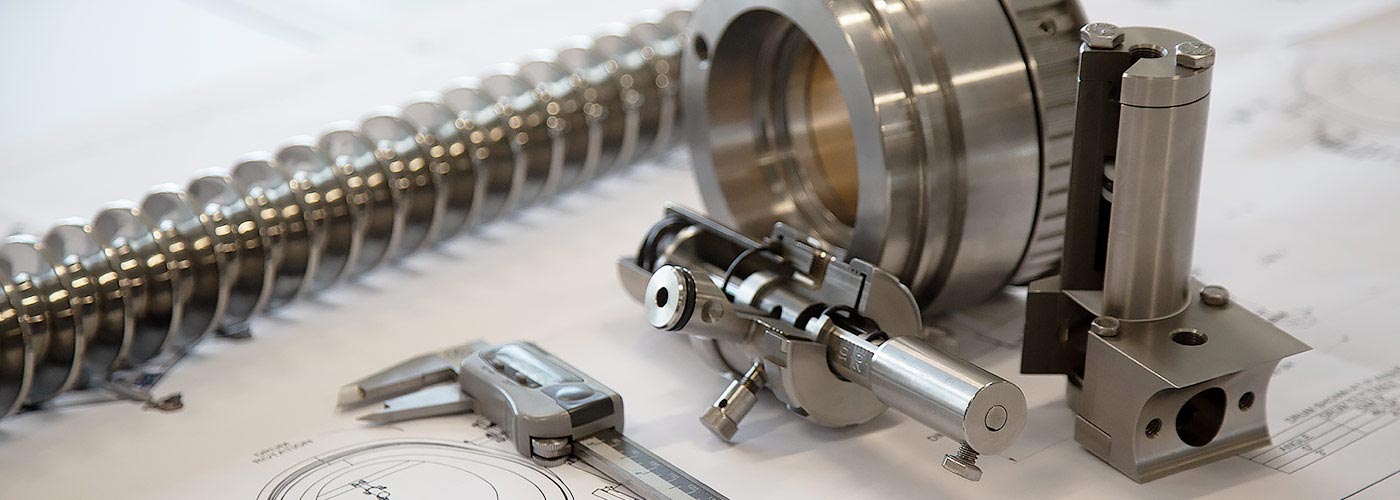
Heat Parts: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heat parts
Navigating the global market for heat parts presents unique challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With diverse applications ranging from residential heating systems to industrial solutions, sourcing the right heating components can be a daunting task. This guide addresses the critical need for reliable information on various types of heat parts, including replacement components for gas, electric, and hydronic systems, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will explore essential topics such as the different categories of heating parts, their applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting. We will also provide insights into pricing strategies and cost factors, enabling international buyers to optimize their procurement processes. By offering actionable insights and expert guidance, this guide empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of the heat parts market confidently.
Whether you’re in Germany seeking efficient heating solutions or in Nigeria looking for durable components, understanding the nuances of the global supply chain is crucial. Our aim is to equip you with the knowledge necessary to enhance your purchasing strategy, streamline operations, and ultimately, ensure that your heating systems run efficiently and reliably.
Understanding heat parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Burners | Convert fuel into heat, available in gas, oil, and electric | Industrial heating, commercial kitchens | Pros: High efficiency; Cons: Requires precise installation and maintenance. |
| Blowers | Facilitate air circulation, crucial for heating efficiency | HVAC systems, gas stoves, fireplaces | Pros: Enhances heating performance; Cons: Can be noisy and may require regular servicing. |
| Thermostats | Regulate temperature, programmable and non-programmable | Residential and commercial heating systems | Pros: Energy savings through automation; Cons: May need calibration for accuracy. |
| Heat Exchangers | Transfer heat between fluids, key for system efficiency | Industrial processes, HVAC systems | Pros: Improves energy efficiency; Cons: Can be costly to replace or repair. |
| Ignition Systems | Initiate combustion in heating units, includes pilot lights | Gas heaters, boilers, furnaces | Pros: Reliable starting mechanism; Cons: Can fail and require timely replacement. |
What Are the Characteristics of Burners in Heating Systems?
Burners are essential components that convert various fuel types into heat energy. They come in several forms, including gas, oil, and electric burners, each suited to different applications. In B2B contexts, they are widely used in industrial heating and commercial kitchens. Buyers should consider the efficiency ratings and compatibility with existing systems, as improper selection can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased costs.
How Do Blowers Enhance Heating Efficiency?
Blowers are integral to heating systems as they facilitate air circulation, ensuring that warm air is distributed evenly throughout a space. They are commonly used in HVAC systems, gas stoves, and fireplaces. When purchasing blowers, B2B buyers should assess their noise levels and energy consumption, as these factors can impact overall system performance and user comfort. Regular maintenance is also crucial to sustain optimal airflow.
Why Are Thermostats Important for Temperature Regulation?
Thermostats play a vital role in maintaining desired temperature levels within heating systems. They can be programmable or non-programmable, allowing for varying degrees of control over heating schedules. In B2B applications, they are essential for both residential and commercial heating systems. Buyers should consider the ease of use, compatibility with existing systems, and energy-saving features when selecting thermostats to optimize heating efficiency and reduce costs.
What Role Do Heat Exchangers Play in System Efficiency?
Heat exchangers are key components that transfer heat between two or more fluids, significantly enhancing system efficiency. They are commonly found in industrial processes and HVAC systems. B2B buyers should focus on the material quality and design of heat exchangers, as these factors influence their longevity and performance. While they can be a significant investment, their ability to improve energy efficiency often justifies the cost.
How Do Ignition Systems Function in Heating Units?
Ignition systems are critical for initiating combustion in various heating units, including gas heaters and boilers. They typically consist of pilot lights or electronic igniters. For B2B buyers, reliability and safety are paramount when selecting ignition systems. Regular checks and timely replacements are necessary to prevent failures that could lead to downtime or safety hazards. Understanding the specific requirements of heating units can help buyers make informed decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of heat parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of heat parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Heating systems for production lines | Enhanced efficiency and reduced downtime | Quality certifications, local regulations, and lead times |
| Agriculture | Greenhouse heating systems | Improved crop yields and extended growing seasons | Energy efficiency, durability in harsh conditions |
| Oil & Gas | Wellhead heating and pipeline heating | Prevention of freeze damage and increased operational uptime | Compatibility with existing systems and safety certifications |
| Hospitality | Heating solutions for hotels and restaurants | Increased guest comfort and energy cost savings | Availability of replacement parts and energy efficiency ratings |
| Automotive | Engine block heaters for vehicle assembly | Improved production efficiency and reduced labor costs | Supplier reliability and part compatibility |
How Are Heat Parts Used in Manufacturing Processes?
In the manufacturing sector, heat parts are integral to heating systems that maintain optimal temperatures for production lines. They help in controlling the environment for processes such as molding and curing, thus enhancing efficiency and minimizing downtime. International buyers, particularly from regions with fluctuating temperatures, must consider the quality certifications of these parts to ensure compliance with local regulations and standards.
What Role Do Heat Parts Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, heat parts are used in greenhouse heating systems to create a controlled climate for plant growth. These systems improve crop yields and allow for extended growing seasons by ensuring that temperatures remain stable, even in colder climates. Buyers from Africa and South America should focus on energy efficiency and the durability of these parts, as they often face extreme weather conditions that can impact performance.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
How Are Heat Parts Essential in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, heat parts are crucial for heating wellheads and pipelines to prevent freeze damage and maintain operational uptime. These components are designed to withstand harsh environments and ensure that the flow of materials remains uninterrupted. Buyers need to ensure compatibility with existing systems and verify that all components meet safety certifications to mitigate risks associated with hazardous materials.
Why Are Heat Parts Important for the Hospitality Industry?
The hospitality industry relies heavily on heating solutions to maintain guest comfort in hotels and restaurants. Efficient heating systems not only enhance the customer experience but also contribute to energy cost savings. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize the availability of replacement parts and energy efficiency ratings to ensure long-term operational sustainability and guest satisfaction.
How Are Heat Parts Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, heat parts such as engine block heaters are essential for ensuring that vehicles are assembled efficiently, particularly in cold climates. These heaters help reduce labor costs by minimizing the time required for engines to reach optimal operating temperatures. Buyers should consider supplier reliability and the compatibility of parts with various vehicle models to streamline their procurement processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heat parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions for Heat Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when sourcing heat parts, particularly in regions with unstable supply chains. For instance, companies in Africa or South America might experience delays in receiving essential components like blowers or igniters, leading to prolonged downtimes in heating systems. This not only affects operational efficiency but can also result in financial losses and dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain disruptions, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions. Diversifying the supplier base can reduce dependency on a single source and enhance resilience against local disruptions. Additionally, leveraging technology, such as inventory management systems, can help track parts availability and predict when restocking is necessary. Implementing a just-in-time inventory approach may also minimize excess stock while ensuring that critical components are on hand when needed. Engaging with suppliers that offer expedited shipping options can further alleviate delays.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Identifying the Right Heat Parts for Specific Models
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the confusion surrounding the identification of the correct heat parts for specific equipment models. For example, a maintenance manager may struggle to find the right thermocouple for a particular gas stove model, risking compatibility issues that could lead to system failures or safety hazards.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should invest time in understanding the specifications of their heating systems and the associated parts. Maintaining an organized database of equipment models and corresponding part numbers can streamline the ordering process. Moreover, utilizing supplier resources such as part finders and technical support can provide crucial assistance. Many suppliers offer online tools where users can input model numbers to receive accurate part recommendations. Regular training for staff on product knowledge can also empower teams to make informed decisions, reducing the likelihood of errors in ordering.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs While Ensuring Quality in Heat Parts Procurement
The Problem: Budget constraints are a frequent concern for B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets where cost competitiveness is critical. Buyers may find themselves torn between opting for cheaper heat parts, which might compromise quality, and investing in higher-quality components that ensure longevity and reliability.
The Solution: To balance quality and cost, buyers should adopt a value-based procurement approach rather than solely focusing on the lowest price. Conducting a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis can help in understanding the long-term implications of purchasing decisions. This involves evaluating factors such as the lifespan of heat parts, maintenance costs, and energy efficiency. Additionally, establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers who offer warranties and after-sales support can enhance confidence in the quality of purchased parts. Buyers should also explore bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts that may offer discounts while ensuring consistent quality. Regularly assessing market trends and innovations can also uncover opportunities for cost-effective, high-quality alternatives.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heat parts
When selecting materials for heat parts, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific applications. This guide will analyze four common materials used in heat parts: stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and carbon steel. Each material has its unique characteristics that can significantly influence performance, manufacturing processes, and compliance with international standards.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
What are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel for Heat Parts?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and durability. It typically withstands temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C) and maintains structural integrity under pressure. Stainless steel’s resistance to oxidation and scaling makes it suitable for applications involving steam, water, and various chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and minimal maintenance requirements, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, it is more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to machine, which may increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including water, steam, and gases, making it versatile for heating systems. Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or DIN 1.4301, particularly in regions like Germany and Europe.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Material for Heat Parts?
Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent thermal conductivity, and is resistant to corrosion. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 600°F (315°C) and is often used in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in portable heating devices.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, allowing for complex shapes and designs. However, it is less durable compared to stainless steel and can be prone to deformation under high pressure or temperatures.
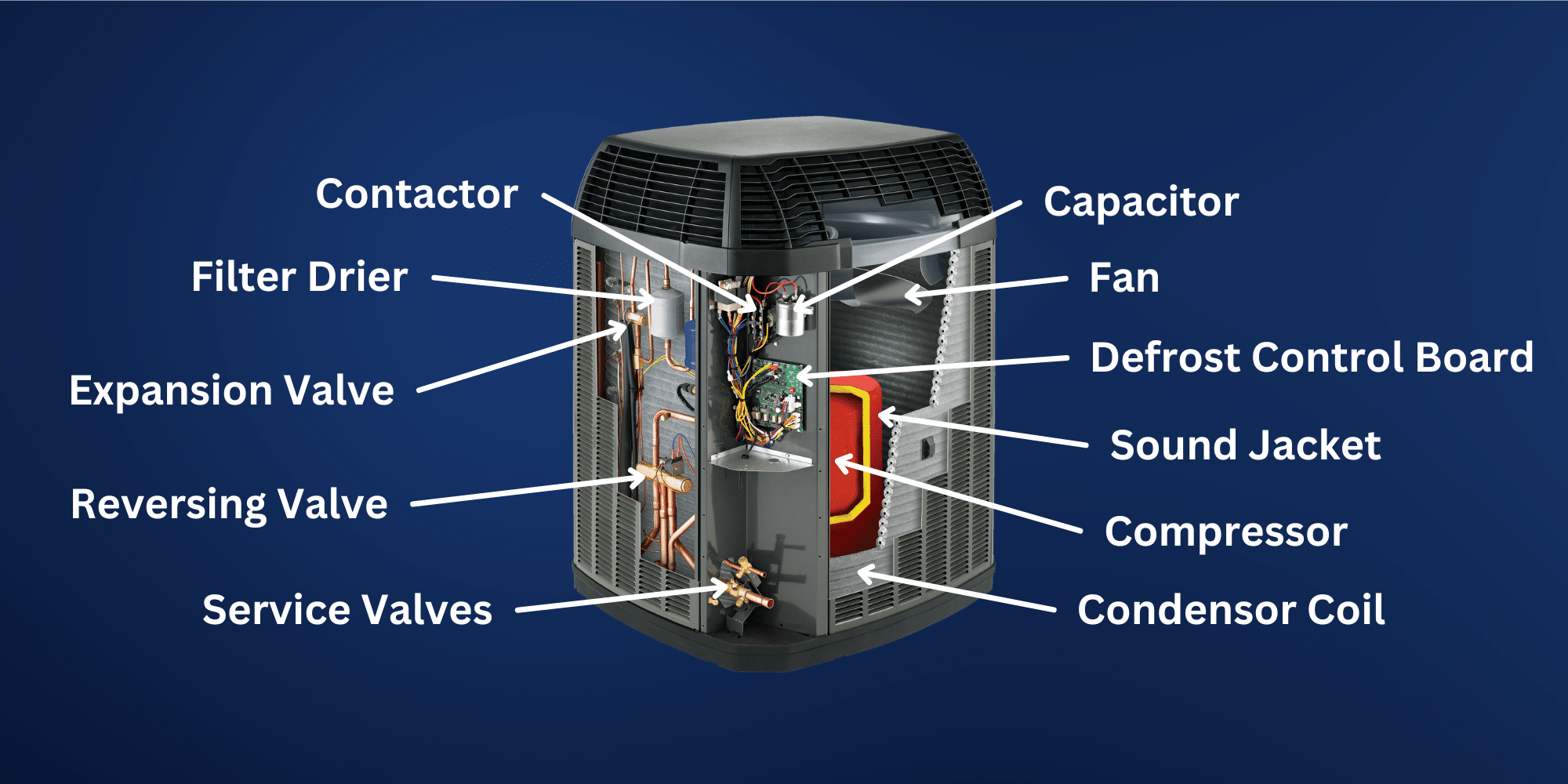
Illustrative image related to heat parts
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various heating media but may not be suitable for high-temperature applications. Buyers in regions with specific thermal and pressure standards, such as JIS in Japan or ASTM in the U.S., should verify compliance.
What are the Benefits of Using Copper in Heat Parts?
Copper is favored for its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for heat exchangers and components requiring efficient heat transfer. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,500°F (815°C) and has good corrosion resistance, especially when treated.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its superior heat transfer properties, which enhance system efficiency. However, it is relatively expensive and can be susceptible to corrosion in certain environments, particularly in the presence of chlorides.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with water and other fluids makes it a popular choice for heating systems. International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM B280, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where copper is widely used.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Heat Parts?
Carbon steel is known for its strength and ability to withstand high pressures, making it suitable for boilers and heat exchangers. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C) and can handle various media, including steam and oil.
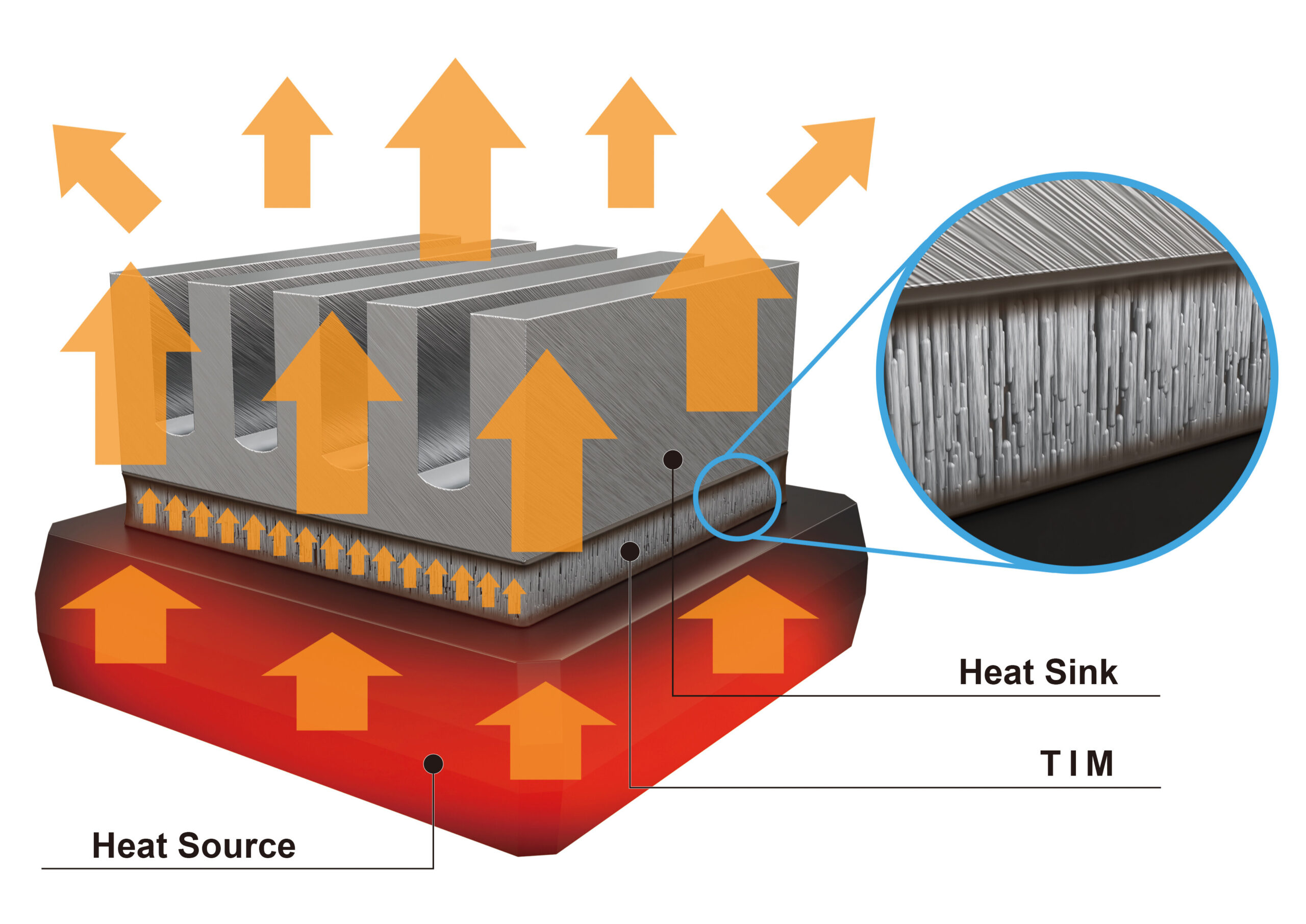
Illustrative image related to heat parts
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and high strength-to-weight ratio. However, it is prone to corrosion, which may require protective coatings or treatments, adding to maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is widely used in industrial applications, but buyers must consider local regulations and standards, such as DIN 17100 in Europe, to ensure compliance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Heat Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for heat parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High-temperature boilers and heat exchangers | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Portable heaters and lightweight components | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Less durable at high temperatures | Medium |
| Copper | Heat exchangers and electrical components | Superior thermal conductivity | Expensive and corrosion-prone | High |
| Carbon Steel | Industrial boilers and heat exchangers | High strength and low cost | Prone to corrosion | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heat parts
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heat Parts?
The manufacturing of heat parts involves several critical stages that ensure both the functionality and durability of the final product. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing components.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first stage in manufacturing heat parts is material preparation. Common materials include high-grade metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, which are favored for their heat conductivity and resistance to corrosion. These materials must undergo rigorous quality checks before production. They are often sourced from certified suppliers who adhere to international standards, ensuring that the raw materials meet the necessary specifications for thermal resistance and structural integrity.
How Are Heat Parts Formed?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This can involve various techniques, including:

Illustrative image related to heat parts
- Casting: Molten metal is poured into molds to create complex shapes.
- Machining: Precision tools are used to cut, shape, or finish the materials.
- Stamping: A mechanical press is used to shape metal sheets into desired forms.
These techniques allow manufacturers to create parts that fit specific designs and requirements. The choice of forming technique often depends on the part’s complexity, volume, and material properties.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Following the forming stage, the assembly process comes into play. This is where individual components are brought together to create a functional unit. For heat parts, this may include the installation of elements such as burners, ignitors, and heat exchangers.
Manufacturers may use automated assembly lines for efficiency, or manual assembly for more intricate components. Quality assurance during assembly is crucial; each step must be monitored to ensure that components fit correctly and function as intended.
How Are Heat Parts Finished for Optimal Performance?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetics of heat parts. Common finishing techniques include:

Illustrative image related to heat parts
- Coating: Applying protective layers to prevent corrosion and improve heat resistance.
- Polishing: Enhancing surface smoothness to improve heat transfer efficiency.
- Testing: Conducting performance tests to ensure the part meets specified thermal and mechanical properties.
These finishing touches are vital in ensuring that the heat parts will perform reliably in their intended applications.
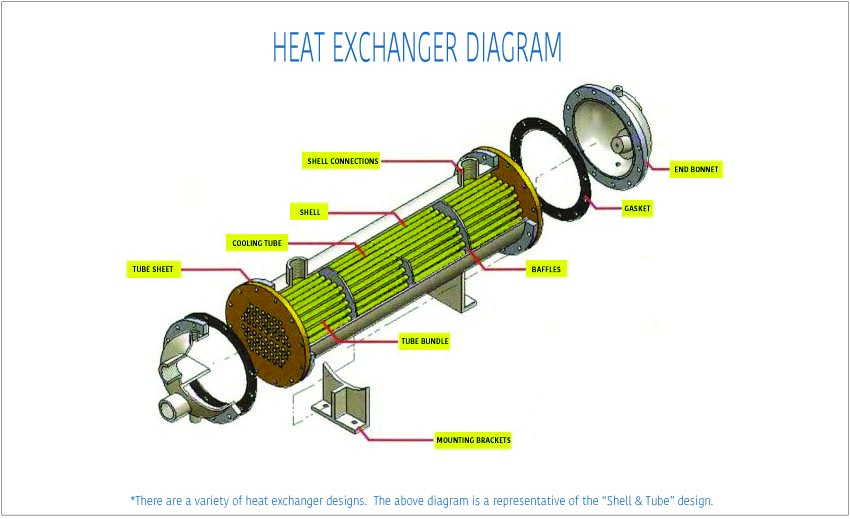
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Heat Parts?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing heat parts, as it ensures that products meet both industry standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with the various QA measures employed in the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Adhering to international quality standards is essential for manufacturers of heat parts. The ISO 9001 standard is widely recognized and focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 signifies that a manufacturer has established a robust quality management framework that consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards may apply. For instance, the CE mark is crucial for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. In the oil and gas sector, the American Petroleum Institute (API) standards are critical for ensuring the reliability and safety of components.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that any deviations from quality standards are addressed promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, finished products undergo rigorous testing to confirm they meet all specifications and standards.
These checkpoints are crucial for identifying potential defects early in the process, thereby reducing waste and ensuring high-quality outcomes.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Assurance Processes of Suppliers?
Verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is vital for B2B buyers, particularly in international markets. Here are some effective methods:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is a proactive way to assess a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. Buyers should request access to quality management documentation, including:
- Quality manuals
- Inspection reports
- Certificates of compliance with international standards
Audits can either be performed by the buyer or facilitated through third-party services, ensuring an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s practices.
How Can Buyers Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services?
Third-party inspection services can provide an additional layer of verification. These independent organizations assess the manufacturer’s processes, materials, and final products against established standards. This is particularly important for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary significantly from international standards.
What Are the Quality Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers must navigate various certification requirements when sourcing heat parts globally. Understanding the nuances of these certifications is essential:
- Regional Variability: Quality standards may differ between regions. For instance, while CE marking is essential for the European market, UL certification may be required for products entering North America.
- Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation, including certificates of compliance and traceability reports for materials used in production.
By being diligent in assessing quality assurance measures and understanding regional certification nuances, B2B buyers can establish long-lasting partnerships with reliable suppliers, ensuring that they receive high-quality heat parts tailored to their market needs.
Illustrative image related to heat parts
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heat parts’
To ensure a successful procurement process for heating parts, it’s essential to approach sourcing methodically. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist tailored for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, you can streamline your sourcing efforts and secure high-quality components for your heating systems.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is foundational for sourcing heating parts. Specify the type of heating system and the exact components needed, such as blowers, thermocouples, or igniters. This clarity will help suppliers understand your needs and provide the correct parts that meet your operational standards.
- Key Considerations:
- Model numbers and compatibility with existing systems.
- Environmental factors such as temperature ranges and humidity levels.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in heating parts. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of potential vendors. Focus on their market presence and reputation within your region.
- Where to Look:
- Online marketplaces and manufacturer websites.
- Reviews and testimonials from previous customers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management systems, which is critical for reliability in heating parts.
- What to Check:
- Documentation of quality assurance processes.
- Compliance with local and international safety standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Product Specifications
Once you shortlist potential suppliers, request samples of the heating parts you intend to purchase. This step allows you to assess the quality and compatibility of the parts with your systems.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
- What to Evaluate:
- Build quality and material specifications.
- Performance under various operational conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in negotiations with your selected suppliers to discuss pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Establishing clear terms early on can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Compare quotes from multiple suppliers to gauge market rates.
- Discuss bulk purchase discounts or long-term partnership options.
Step 6: Assess Supply Chain Reliability
Investigate the supplier’s logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery. A reliable supply chain is essential to avoid production delays and maintain operational efficiency.
- Key Questions:
- What are their lead times for orders?
- Do they have contingency plans for disruptions?
Step 7: Build Long-term Relationships
Once you have procured your heating parts, focus on building a long-term relationship with your supplier. This can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products or technologies as they become available.
- Ways to Foster Relationships:
- Maintain open lines of communication.
- Provide feedback on product performance and service quality.
By following this checklist, you can enhance your procurement strategy for heating parts, ensuring that you secure the best components for your business needs while fostering valuable supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heat parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Heat Parts Sourcing?
When sourcing heat parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing heat parts, such as metals, plastics, and electrical components, significantly impact overall costs. The quality and sourcing of these materials can vary widely, affecting both price and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers involved in the manufacturing process. Regions with higher labor costs may influence the pricing of heat parts, while countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs down.
-
Tooling: The cost of tools and equipment needed to produce heat parts can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized components. This cost is often amortized over production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the heat parts meet safety and performance standards. While this adds to initial costs, it can reduce long-term expenses by preventing defects and product returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the distance, mode of transport, and volume of parts. Efficient logistics management can minimize these costs and impact lead times.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their costs and generate profit. Understanding the expected margins in different regions can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Heat Parts Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat parts, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a reliable relationship with suppliers can help secure favorable pricing for larger orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts or those requiring specific certifications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to receive accurate quotes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of higher-quality parts against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium but can offer peace of mind.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade can help buyers manage costs effectively. Incoterms dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the total cost of ownership.
What Are the Best Practices for International B2B Buyers Sourcing Heat Parts?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power to negotiate better prices and terms. Establish long-term relationships with suppliers to enhance bargaining positions.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond initial purchase prices. Assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and durability of parts over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations and regional economic conditions that may affect pricing. This understanding can lead to better timing for purchases.
-
Conduct Due Diligence: Research potential suppliers thoroughly. Verify their credentials, review customer feedback, and assess their compliance with international quality standards.
-
Plan for Logistics: Factor in shipping times and costs when placing orders. Choose suppliers with efficient logistics capabilities to minimize delays and additional costs.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of heat parts sourcing requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components and pricing influencers. By employing strategic negotiation tactics and focusing on total cost of ownership, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budgetary constraints. Understanding these dynamics will empower international buyers, particularly in emerging markets, to enhance their purchasing strategies and achieve optimal results.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heat parts With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Heat Parts: What Are Your Options?
In the realm of heating solutions, understanding alternatives to traditional heat parts can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions. Whether you’re considering replacement parts for existing heating systems or evaluating new technologies, several options exist that may align with your business objectives. This analysis compares heat parts with two viable alternatives: electric heating systems and hydronic heating solutions.
| Comparison Aspect | Heat Parts | Electric Heating Systems | Hydronic Heating Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable but may require regular replacements | Quick heating; consistent temperature control | Efficient, even heating; can be slow to respond |
| Cost | Typically lower upfront costs | Higher initial installation costs | Moderate to high initial setup costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward installation | Can be complex; may require professional help | Requires plumbing expertise for installation |
| Maintenance | Moderate; parts need regular checks | Low; minimal upkeep required | High; system requires regular maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Residential and commercial settings | Small spaces or specific rooms | Large facilities needing uniform heat distribution |
What Are Electric Heating Systems and Their Advantages?
Electric heating systems utilize electric resistance to generate heat, providing a quick and efficient way to warm up spaces. These systems are often installed in homes or businesses where rapid temperature adjustments are needed.
Pros: They offer immediate warmth and are typically easier to install in existing structures without extensive modifications. Moreover, they tend to require less maintenance compared to traditional heating systems.
Cons: However, the initial installation costs can be significant, especially for larger areas or commercial applications. Additionally, reliance on electricity can lead to higher operational costs, particularly in regions with fluctuating energy prices.
Understanding Hydronic Heating Solutions: Benefits and Drawbacks
Hydronic heating systems circulate heated water through pipes to radiators or underfloor heating systems, providing even and efficient heating throughout a space. This method is particularly effective in larger buildings.
Pros: Hydronic systems are known for their energy efficiency and the comfort they provide, as they maintain a consistent temperature. They are also quieter than forced-air systems and can be powered by renewable energy sources, making them eco-friendly options.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
Cons: The complexity of installation can be a drawback, requiring specialized plumbing skills. Additionally, maintenance can be higher due to the need for regular inspections of the water system to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance.
How to Choose the Right Heating Solution for Your Business?
Selecting the appropriate heating solution ultimately depends on your specific needs, budget, and operational context. For businesses focused on cost-effectiveness and simplicity, heat parts remain a reliable choice, particularly for existing systems requiring occasional replacements. However, if your business values efficiency and sustainability, investing in electric or hydronic heating solutions may yield long-term benefits despite higher initial costs.
When evaluating options, consider factors such as performance requirements, installation complexity, and maintenance capabilities. Consulting with experts or conducting a cost-benefit analysis can further refine your decision-making process, ensuring you choose the heating solution that best aligns with your operational goals and financial framework.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heat parts
In the procurement of heating parts, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here’s a concise breakdown of the key specifications and jargon relevant to B2B buyers.
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of Heating Parts?
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade indicates the quality and type of materials used in manufacturing heating parts, such as metals (e.g., stainless steel, brass) or composites.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the right material grade is essential for durability, heat resistance, and overall performance. It ensures that the parts can withstand the specific thermal and mechanical stresses of their application, reducing the likelihood of failure and costly replacements. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension or measurement in manufacturing processes.
– B2B Importance: Precise tolerances are critical for ensuring that parts fit correctly in systems, which is vital for efficiency and safety. Parts that do not meet required tolerances can lead to system malfunctions, increased energy consumption, and potential safety hazards. -
Thermal Conductivity
– Definition: Thermal conductivity measures a material’s ability to conduct heat, usually expressed in watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K).
– B2B Importance: High thermal conductivity is desirable for parts that need to transfer heat efficiently, such as heat exchangers and burners. Understanding this property helps buyers select parts that optimize energy use and system performance. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: Pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure that a heating part can safely handle, often specified in psi (pounds per square inch).
– B2B Importance: Knowing the pressure rating is essential for safety and compliance with industry standards. Using parts that exceed the rated pressure can lead to catastrophic failures, impacting safety and reliability. -
Wattage and Output Capacity
– Definition: Wattage refers to the power consumption or output of heating elements, typically measured in watts (W).
– B2B Importance: Understanding wattage helps businesses calculate energy costs and ensure that heating systems meet their operational needs without excessive energy consumption.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers of Heating Parts Understand?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM produces parts that are used in the manufacturing of a final product.
– Significance: OEM parts are often preferred for their compatibility and reliability, ensuring that replacements meet the original specifications of the equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Significance: Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers must balance the need for parts against potential excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products.
– Significance: RFQs facilitate competitive bidding, enabling buyers to compare offers and make cost-effective purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade.
– Significance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, delivery responsibilities, and risk management, which are critical for international procurement. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Significance: Knowing the lead time is essential for planning and ensuring that heating systems remain operational without unexpected downtime. -
Compatibility
– Definition: Compatibility refers to whether a part will function correctly with existing systems or components.
– Significance: Ensuring compatibility is vital for seamless integration, reducing the risk of operational disruptions and enhancing overall system efficiency.
By grasping these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing heating parts effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Illustrative image related to heat parts
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heat parts Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Heat Parts Market?
The heat parts sector is witnessing significant transformations driven by several global factors. Increasing energy efficiency regulations and the push for sustainable energy sources are key drivers reshaping market dynamics. Countries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are investing in cleaner technologies, influencing international B2B buyers to seek innovative heating solutions that meet stringent environmental standards.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled heating systems, are gaining traction, allowing for real-time monitoring and optimization of energy usage. This trend not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with the growing demand for smart home solutions. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who offer technologically advanced products that provide both functionality and sustainability.
Furthermore, the supply chain landscape is evolving, with a shift toward localized sourcing to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Nigeria and Germany, this means collaborating with suppliers who demonstrate agility and responsiveness to changing market conditions. The rise of e-commerce platforms is also facilitating easier access to a diverse range of heat parts, allowing buyers to compare products and prices more efficiently than ever before.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing Decisions in Heat Parts?
The environmental impact of manufacturing and sourcing heat parts cannot be understated. As awareness of climate change grows, businesses are increasingly held accountable for their environmental footprint. Ethical sourcing has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the heat parts sector. Companies are now looking for suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or adopting green manufacturing processes.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications, such as ENERGY STAR or ISO 14001, into sourcing decisions is becoming standard practice. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also provide assurance to buyers about the environmental integrity of their purchases. Moreover, businesses that align with sustainable practices often experience long-term cost savings through improved energy efficiency and reduced waste.
The importance of ethical supply chains is further emphasized by consumer demand for transparency. Buyers are increasingly seeking information about the origin of materials and the ethical practices employed by manufacturers. This trend encourages businesses to engage with suppliers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability, fostering a more responsible industry overall.
What Is the Historical Context of the Heat Parts Sector?
The heat parts sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional heating methods, the industry has adapted to technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. The shift towards more efficient heating solutions began in the late 20th century as environmental concerns gained prominence.
As the demand for energy-efficient products grew, manufacturers began developing innovative heat parts, including smart thermostats and advanced heat exchangers. This evolution has paved the way for a more competitive marketplace where international buyers can access a wider array of products tailored to their specific needs.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
In summary, understanding the historical trajectory of the heat parts sector provides valuable context for current trends and sourcing strategies, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with both market demands and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heat parts
-
1. How do I solve issues with heating part compatibility?
To address compatibility issues with heating parts, first, ensure you have the exact model number of your heating system. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications or manuals for the correct part numbers. If you’re unsure, reach out to your supplier with detailed information about your system, including brand, model, and any other relevant data. A reputable supplier will have a knowledgeable team that can assist in verifying compatibility and suggesting suitable alternatives if necessary. -
2. What is the best heating part for improving efficiency in my system?
The best heating part for improving system efficiency depends on the specific heating system you have. For many systems, upgrading to high-efficiency thermostats or variable-speed blowers can significantly enhance performance. Additionally, consider investing in quality heat exchangers and well-insulated piping to reduce energy loss. Consulting with an HVAC professional can provide tailored recommendations that align with your system’s requirements and your efficiency goals. -
3. What should I consider when vetting suppliers for heating parts?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation and experience in the industry. Check for customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies to gauge reliability. Confirm that the supplier offers a wide range of parts from reputable manufacturers and provides transparent information about sourcing and quality assurance processes. Additionally, inquire about their return policy and customer support services, as responsive and knowledgeable support is crucial for resolving any issues that may arise. -
4. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for heating parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between suppliers and product types. Some suppliers may impose MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness, while others might offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for international buyers. Always clarify MOQ policies before placing an order, as this will help you manage inventory effectively and avoid overcommitting to stock that may not be needed. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing heating parts internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely based on the supplier and your location. Common options include payment in advance, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., 30 or 60 days). It’s essential to establish clear payment expectations upfront to avoid potential disputes. Discuss currency options as well, as fluctuations can affect overall costs. Utilizing secure payment methods can also provide additional protection against fraud. -
6. How do I ensure quality assurance for heating parts sourced from abroad?
To ensure quality assurance, request certifications and compliance documents from your supplier that verify the parts meet international standards. Conducting factory audits or requesting samples for testing can also provide insights into product quality. Establishing a quality control process, including inspections upon arrival, will help identify any issues early. Consider working with suppliers who have established quality management systems to further mitigate risks. -
7. What logistics considerations are important when importing heating parts?
When importing heating parts, consider shipping methods, transit times, and customs regulations. Choose reliable logistics partners who are experienced in handling international shipments, especially for bulky or sensitive items. Be aware of any import duties or taxes that may apply and factor these into your total cost. Timely communication with your supplier and logistics provider can help ensure smooth operations and minimize delays. -
8. How can I customize heating parts for my specific applications?
Many suppliers offer customization options for heating parts to meet specific operational needs. Engage in discussions with your supplier about your requirements, including dimensions, materials, and performance specifications. Providing detailed technical drawings or prototypes can facilitate the customization process. Keep in mind that custom orders may have longer lead times and higher costs, so plan accordingly to align with your project timelines.
Top 7 Heat Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Heater Parts Central – Replacement Heater Parts
Domain: heaterpartscentral.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Heater Parts Central offers a wide range of heater replacement parts including Electric Appliance Parts (Blower/Heater Assemblies, Misc. Electric Appliance Parts, Remotes), Indoor Gas Heating Parts (Blowers, Floor Stands & Mounting Brackets, Gas Install Kits, Ignitors/Piezos, Knobs, Log Set Replacements, Misc. Gas Parts, ODS Assemblies, Orifices, Regulators, Remotes & Receivers, Thermocouples, Val…
2. Pool Heater Parts – Top Brands
Domain: parts4heating.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Parts4Heating.com offers a wide range of heating system parts, water heater parts, and pool heater parts from top manufacturers. Key product categories include: 1. Pool Heater Parts: Brands include Hayward, Jandy, Lochinvar, Pentair, Raypak, Rheem, Sta-Rite, Teledyne Laars, and Zodiac. 2. Water Heater Parts: Brands include A.O. Smith, Baxi, Bradford White, Camus, HYDRO-SMART, IBC, Lochinvar, NTI, …
3. All Parts Inc – Heating Parts and Accessories
Domain: allpartsinc.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Heating parts sales, repair parts and technical information. The store carries parts from top heating brands including Mr. Heater, Dyna Glo, Lennox, Empire, and more. The catalog includes gas heaters, gas and electric fireplaces, and gas stove fireplace parts. Many heating parts are original components used by manufacturers, with some replacement parts available for out-of-production items. Refere…
4. Century HVAC – Electrical Heating Parts
Domain: centuryhvac.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Electrical Heating Parts include: Watt Restrictors, Sequencers, Heat Cables, Electrical Elements, Electric Heat Elements, Zone Control Controllers, Motorized Dampers, Valves (Refrigeration and Plumbing), Chilled Water Controls, Boiler Controls and Parts, Pressure Relief Valves, and Smart Devices. Subcategories under Electrical Heating Parts consist of Watt Restrictors, Sequencers, Heat Cables, and…
5. Spa Depot – Key Heating System Parts
Domain: spadepot.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Hot Tub & Spa Heating System Parts available at SpaDepot.com. Key products include: 1. Pressure Switch – Adjustable, SPST-NO, Stainless Steel 3029 – $31.95 2. Pressure Switch – Adjustable, SPST-NO, 3902 – $21.95 3. Pressure Switch – Adjustable, SPST-NO 34-0178C-K – $24.95 4. Pressure Switch – Adjustable, SPST-NO, 4010P – $19.95 5. Balboa Pressure Switch Cable 21223 – $15.95 6. Flow Switch 3/4″ Bar…
6. Ferguson – HVAC Repair Parts & Maintenance
Domain: ferguson.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: HVAC Repair Parts & Maintenance, including capacitors, motors, HVAC compressors, maintenance chemicals, electrical relays, contactors, pipe fittings, pipe & tubing, and fasteners.
7. Water Heater Parts – Factory Approved Service Components
Domain: waterheaterparts.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Factory approved water heater service and repair parts; Brands: A.O. Smith, Takagi, Reliance; Installation, troubleshooting, instructional videos, and printable guides available at www.hotwater101.com; Hours of operation: Monday – Friday 7am – 5pm CST; Orders after 4 pm CST considered next business day; Ground orders have a 2 to 3 day lead time; Sales limited to shipments within the United States;…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heat parts
In the rapidly evolving market for heat parts, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. By leveraging reliable suppliers and understanding regional market dynamics, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and ensure the timely availability of essential components. Key takeaways include the importance of establishing strong relationships with reputable manufacturers and distributors, which can lead to cost savings and improved supply chain resilience.
Moreover, as global demand for heating solutions increases, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses must remain agile and adaptable. Buyers should prioritize sourcing strategies that focus on quality assurance and the ability to fulfill specific needs, such as energy efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Looking ahead, the landscape for heat parts will continue to be shaped by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. Now is the time for international buyers to capitalize on these trends by exploring diverse sourcing options and investing in partnerships that align with their long-term goals. Engage with suppliers who share your vision for sustainability and innovation to stay ahead in this competitive market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.

Illustrative image related to heat parts
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.