Glass Homogenizer: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for glass homogenizer
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right glass homogenizer is a critical challenge for businesses aiming to achieve precise and efficient sample preparation. With various types available, from Dounce to Ten Broeck homogenizers, understanding the nuances of each can significantly impact research outcomes across industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and food science. This comprehensive guide addresses the essential aspects of glass homogenizers, including their applications, types, and the key factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Vietnam and Saudi Arabia, face unique challenges in navigating global markets. This guide empowers these buyers by providing actionable insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and quality assurance measures. By equipping you with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions, we aim to streamline your procurement process, ensuring you select the right equipment that meets your research needs while adhering to budget constraints.
Ultimately, understanding the intricacies of glass homogenizers not only enhances laboratory efficiency but also supports the pursuit of innovative solutions in scientific research and product development. Let us navigate this essential market together, ensuring you stay ahead of the curve in your industry.
Understanding glass homogenizer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dounce Tissue Grinder | Borosilicate glass, large reservoir, dual pestle options | Biochemical studies, cell lysis, DNA/RNA extraction | Pros: High precision, easy to clean; Cons: Manual operation may be labor-intensive. |
| Ten Broeck Homogenizer | Interchangeable parts, low-speed motor compatibility | Small sample grinding, pathological studies | Pros: Versatile, suitable for various sample sizes; Cons: Requires careful handling to avoid damage. |
| Glass Tissue Grinder (Pack) | Ergonomic design, multiple sizes, non-reactive material | Research labs, enzyme assays, tissue fractionation | Pros: Cost-effective in packs, easy to sterilize; Cons: Limited to manual use without motor. |
| Homogenizer with Pour Spout | Designed for easy decanting, smooth grinding action | Sample preparation for PCR, gel electrophoresis | Pros: Reduces contamination risk, efficient sample transfer; Cons: Glass fragility requires careful handling. |
| Motorized Glass Homogenizer | Motor-driven, friction release mechanism | High-throughput applications in industrial settings | Pros: Increased efficiency for large volumes; Cons: Higher initial investment, maintenance needs. |
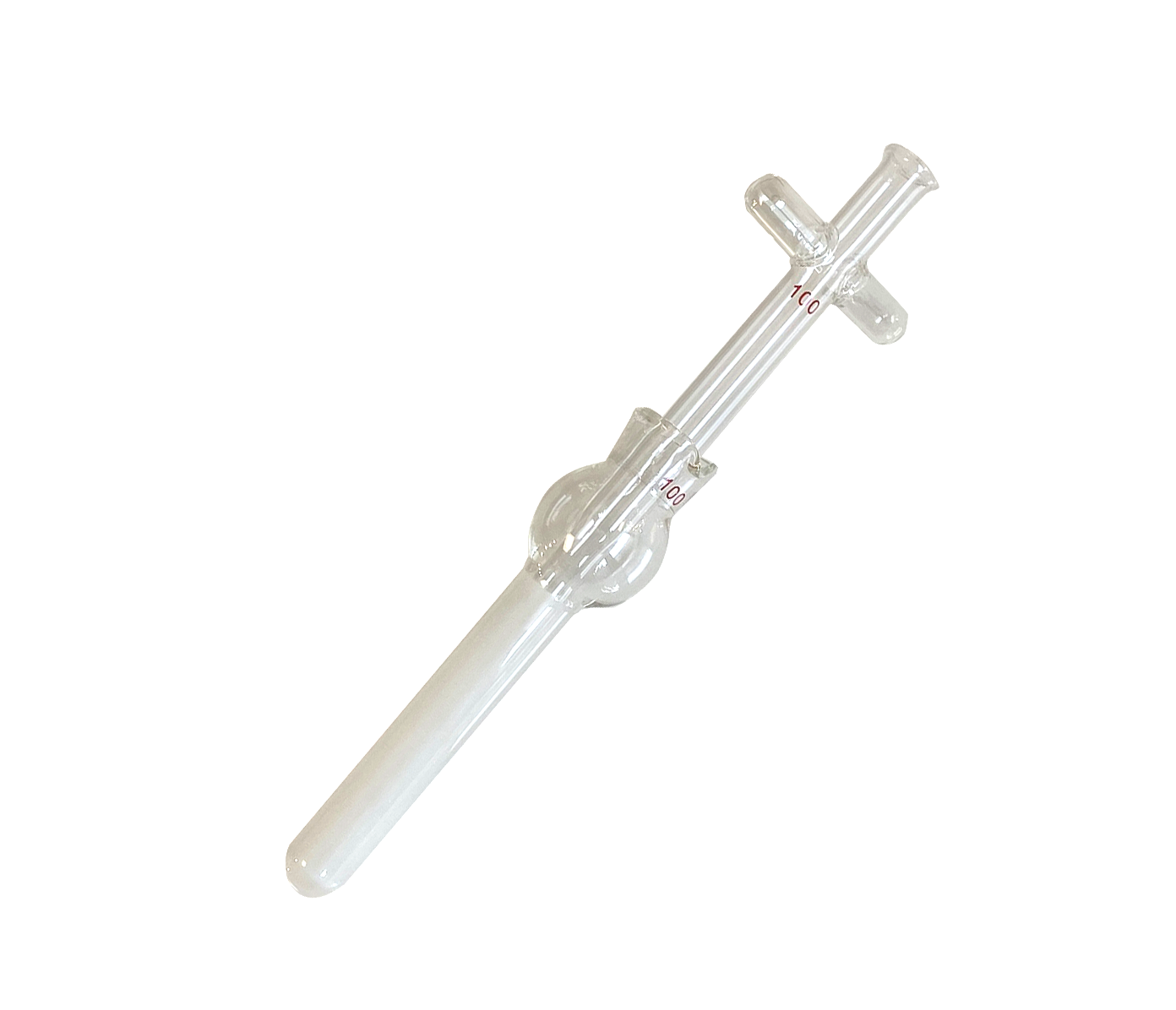
What Are the Key Characteristics of Dounce Tissue Grinders?
Dounce tissue grinders are notable for their borosilicate glass construction, which offers excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability. They feature a large reservoir and come with both loose and tight pestles, allowing for customizable grinding based on sample consistency. Primarily used in biochemical studies and for cell lysis, these grinders are ideal for extracting DNA and RNA. Buyers should consider the manual operation’s labor intensity versus the precision achieved, especially in high-throughput environments.
How Do Ten Broeck Homogenizers Stand Out?
The Ten Broeck homogenizer is characterized by its interchangeable mortar tubes and pestles, designed for grinding small samples. Its compatibility with low-speed motor devices enhances usability while providing a consistent clearance for effective homogenization. This type is particularly suited for pathological studies and small-scale biochemical research. B2B buyers should weigh the versatility and small footprint against the need for careful handling to prevent damage to the glass components.
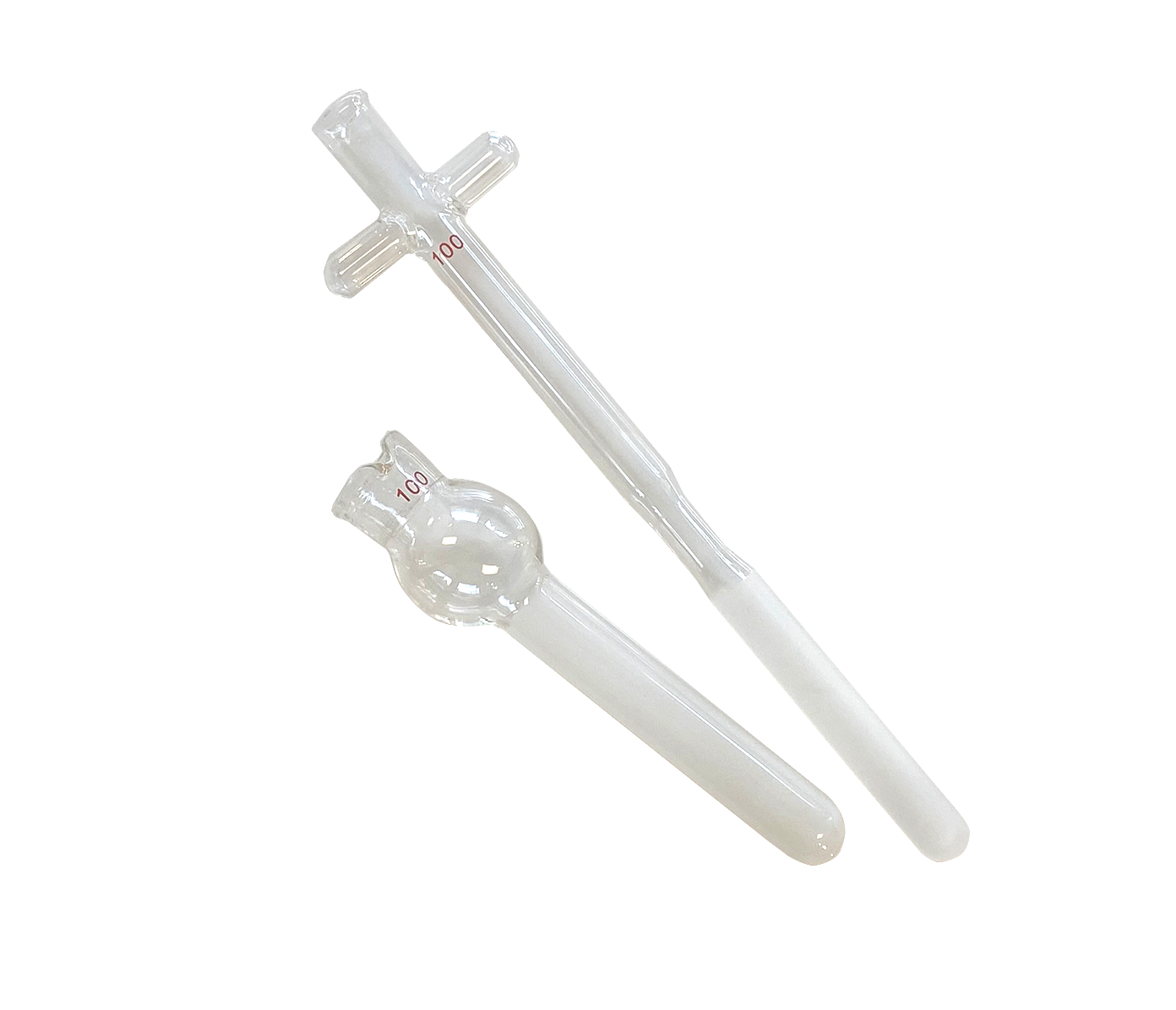

Illustrative image related to glass homogenizer
Why Choose Glass Tissue Grinders Sold in Packs?
Glass tissue grinders available in packs are designed for efficiency and convenience in laboratory settings. They feature an ergonomic pestle design and are made from non-reactive borosilicate glass, ensuring sample integrity during homogenization. These grinders are suitable for a range of applications, including enzyme assays and tissue fractionation. While they offer a cost-effective solution for labs, buyers should note their manual operation, which may limit throughput compared to motorized options.
What Are the Benefits of Homogenizers with Pour Spouts?
Homogenizers with pour spouts are engineered for easy decanting and smooth grinding, making them ideal for sample preparation tasks such as PCR and gel electrophoresis. Their design reduces the risk of contamination during sample transfer, enhancing the reliability of results. While these homogenizers provide significant advantages in usability, buyers must be cautious about the fragility of glass, necessitating careful handling and storage.
When to Consider Motorized Glass Homogenizers?
Motorized glass homogenizers are tailored for high-throughput applications, featuring a friction release mechanism to protect against damage during operation. They are particularly beneficial in industrial settings where large sample volumes are processed regularly. While the efficiency and speed of these machines can significantly enhance productivity, B2B buyers should consider the higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance requirements as part of their purchasing decision.
Key Industrial Applications of glass homogenizer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of glass homogenizer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biotechnology | DNA, RNA, and Protein Extraction | Ensures high yield and purity of nucleic acids and proteins, critical for research accuracy. | Buyers should prioritize quality of borosilicate glass and ease of cleaning to prevent contamination. |
| Pharmaceutical | Drug Formulation and Development | Facilitates uniform distribution of active ingredients, enhancing drug efficacy and safety. | Consider sourcing suppliers with certifications for material safety and compliance with industry standards. |
| Food and Beverage | Nutritional Analysis and Quality Control | Provides reliable homogenization for consistent product quality and compliance with safety standards. | Look for glass homogenizers with a range of sizes to accommodate different sample volumes and types. |
| Environmental Science | Soil and Water Sample Analysis | Enhances the accuracy of contaminant analysis by ensuring thorough sample homogenization. | Ensure suppliers offer robust support for international shipping and compliance with local regulations. |
| Veterinary Medicine | Diagnostic Testing | Improves the reliability of test results by ensuring consistent sample preparation from biological materials. | Buyers should assess the availability of sterilizable options to maintain laboratory hygiene standards. |
How is a glass homogenizer utilized in biotechnology for DNA, RNA, and protein extraction?
In biotechnology, glass homogenizers are essential for breaking down biological tissues to release DNA, RNA, and proteins for further analysis. The precision of these tools allows researchers to achieve high yields of nucleic acids and proteins, which is crucial for experiments such as PCR and gel electrophoresis. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality borosilicate glass homogenizers that are easy to clean and sterilize is vital to prevent contamination and ensure reproducibility in results.
What role does a glass homogenizer play in pharmaceutical drug formulation?
In the pharmaceutical industry, glass homogenizers are used to create homogenous mixtures of active ingredients and excipients in drug formulations. This uniformity is critical for ensuring the efficacy and safety of medications. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider suppliers that provide glass homogenizers with certifications that meet regulatory standards, as this will facilitate compliance with stringent pharmaceutical guidelines and enhance product reliability.
How do glass homogenizers contribute to food and beverage quality control?
Glass homogenizers are pivotal in the food and beverage sector for conducting nutritional analyses and ensuring product quality. By providing consistent homogenization, these tools help in accurately measuring nutritional components and contaminants, which is essential for regulatory compliance. B2B buyers in this sector should seek suppliers that offer a variety of sizes to accommodate different sample types and ensure that the homogenizers are made from durable, non-reactive materials to maintain sample integrity.
Why are glass homogenizers important in environmental science?
In environmental science, glass homogenizers are utilized for preparing soil and water samples for contaminant analysis. Their ability to ensure thorough homogenization leads to more accurate and reliable test results. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee robust shipping options and compliance with local environmental regulations, especially in developing regions where access to high-quality laboratory equipment may be limited.
How does a glass homogenizer enhance diagnostic testing in veterinary medicine?
In veterinary medicine, glass homogenizers are used to prepare biological samples for diagnostic tests, improving the accuracy of results. By ensuring consistent sample preparation, these tools help in identifying pathogens or analyzing patient samples effectively. Buyers should evaluate the availability of sterilizable glass homogenizers to uphold hygiene standards in laboratories, particularly in regions where veterinary services are expanding, such as in parts of Africa and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘glass homogenizer’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Sample Homogenization
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter the challenge of inconsistent results when using glass homogenizers for sample preparation. This inconsistency can arise from various factors, such as the choice of pestle clearance, the grinding technique employed, or even the size and type of the biological samples being processed. For instance, researchers in pharmaceutical companies may struggle to obtain uniform cell lysis when preparing samples for enzyme assays, which can lead to erroneous data and compromised experimental outcomes.
The Solution: To ensure consistent homogenization, it is crucial to select the appropriate type of glass homogenizer based on the specific application. Buyers should carefully consider the pestle clearance options available—loose or tight pestles—and how these affect the grinding process. For example, using a loose pestle may be beneficial for softer tissues, while a tight pestle is more suited for harder samples. Additionally, implementing standardized operating procedures (SOPs) for sample preparation can greatly enhance reproducibility. This includes maintaining consistent grinding speeds and times, as well as ensuring that the homogenizer is thoroughly cleaned and sterilized between uses to prevent cross-contamination. Investing in higher-quality homogenizers with ergonomic designs can also reduce the risk of operator fatigue, leading to more reliable results.
Scenario 2: Concerns About Sample Contamination
The Problem: In the realm of biological research, sample purity is paramount. B2B buyers often face the risk of contamination during the homogenization process, particularly when using glass homogenizers that are not designed for easy cleaning or sterilization. This issue is particularly critical in industries such as pharmaceuticals and diagnostics, where even trace amounts of contaminants can skew results and lead to significant financial losses.
The Solution: To mitigate contamination risks, buyers should prioritize glass homogenizers made from high-quality, non-reactive materials, such as borosilicate glass. These types of homogenizers not only maintain the integrity of the samples but are also easier to clean and sterilize. Implementing a rigorous cleaning protocol after each use is essential; this can include autoclaving the homogenizers or using chemical sterilants as recommended by the manufacturer. Additionally, acquiring homogenizers with features such as smooth surfaces and modular designs can facilitate thorough cleaning and reduce the likelihood of sample carryover. Regular training sessions for laboratory personnel on proper cleaning techniques and contamination prevention can further enhance sample integrity.
Scenario 3: Limited Versatility for Diverse Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find that their glass homogenizers lack the versatility needed to handle a wide range of sample types and volumes. This limitation can hinder research progress, especially in facilities that conduct diverse studies, from microbiology to food science. For example, a laboratory may need to switch between homogenizing plant tissues for DNA extraction and animal tissues for protein analysis, but a one-size-fits-all homogenizer may not provide optimal results for both applications.
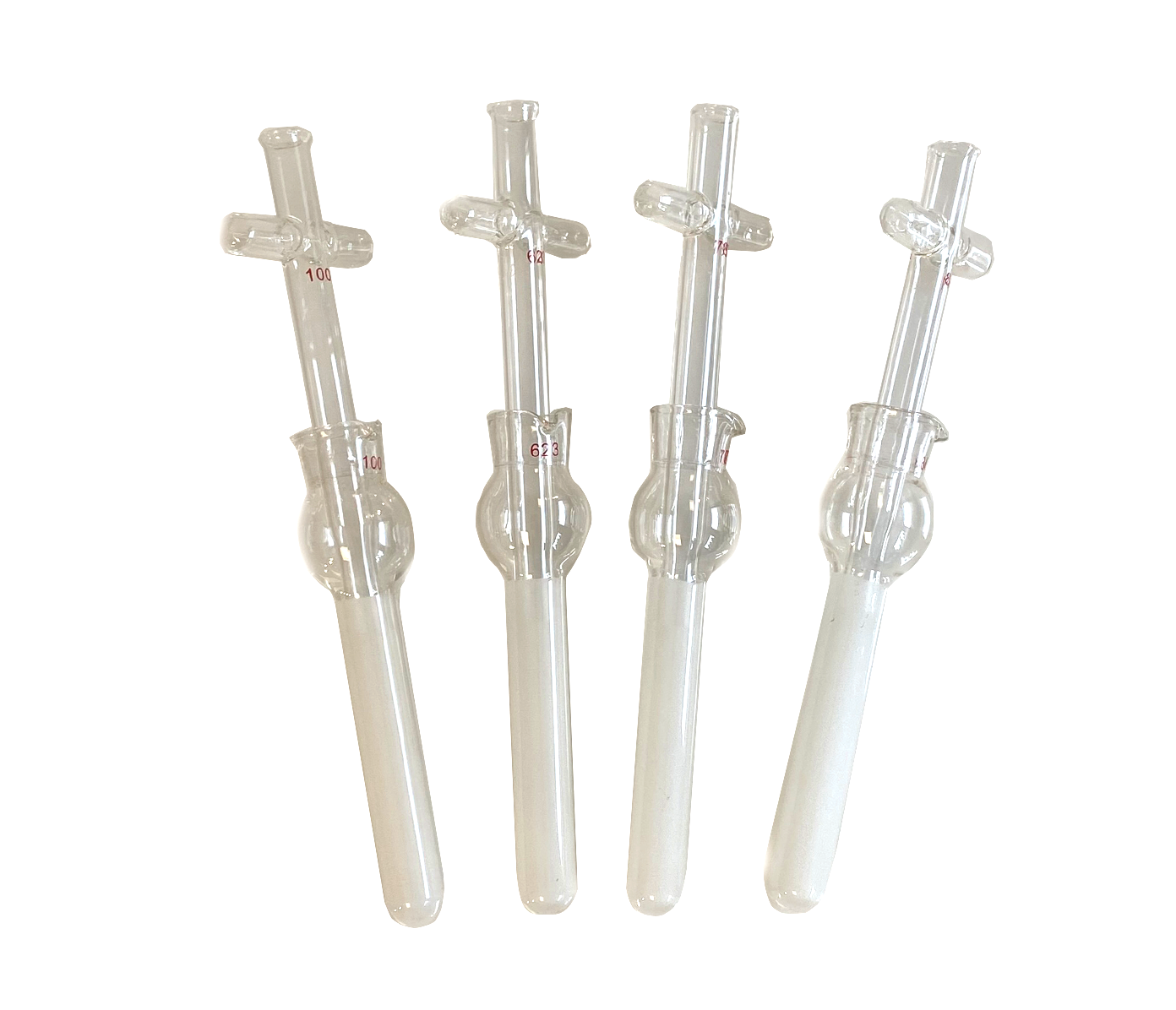

Illustrative image related to glass homogenizer
The Solution: To address this versatility issue, buyers should look for glass homogenizers that offer a variety of sizes and pestle types. Selecting homogenizers that come in multiple capacities (such as 2mL, 10mL, and 40mL) allows for flexibility in processing different sample sizes without sacrificing performance. Additionally, buyers should consider homogenizers designed to accommodate both manual and motor-driven operations, enabling them to adapt to different research needs. When sourcing these products, it’s beneficial to partner with suppliers who offer comprehensive product lines and can provide guidance on selecting the right homogenizer for specific applications. Investing in a diverse set of homogenizers can ultimately streamline workflows and improve the quality of research outputs across various scientific disciplines.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for glass homogenizer
When selecting materials for glass homogenizers, it is crucial to consider their properties and how they align with the specific applications and requirements of international B2B buyers. Below are analyses of three common materials used in the construction of glass homogenizers, focusing on their performance, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for buyers from diverse regions.
What Are the Key Properties of Borosilicate Glass in Glass Homogenizers?
Borosilicate glass is a widely used material in glass homogenizers due to its excellent thermal and chemical resistance. It can withstand temperature fluctuations up to 500°C and has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, reducing the risk of breakage. Additionally, borosilicate glass is resistant to many corrosive substances, making it suitable for a variety of biological and chemical applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of borosilicate glass is its durability and resistance to thermal shock, which is essential for maintaining sample integrity during homogenization. However, it can be more expensive than other glass types, and its brittleness poses a risk of breakage during handling or transport.
Impact on Application: Borosilicate glass is compatible with a wide range of media, including organic solvents and aqueous solutions, making it ideal for applications in molecular biology, biochemistry, and pharmaceuticals.
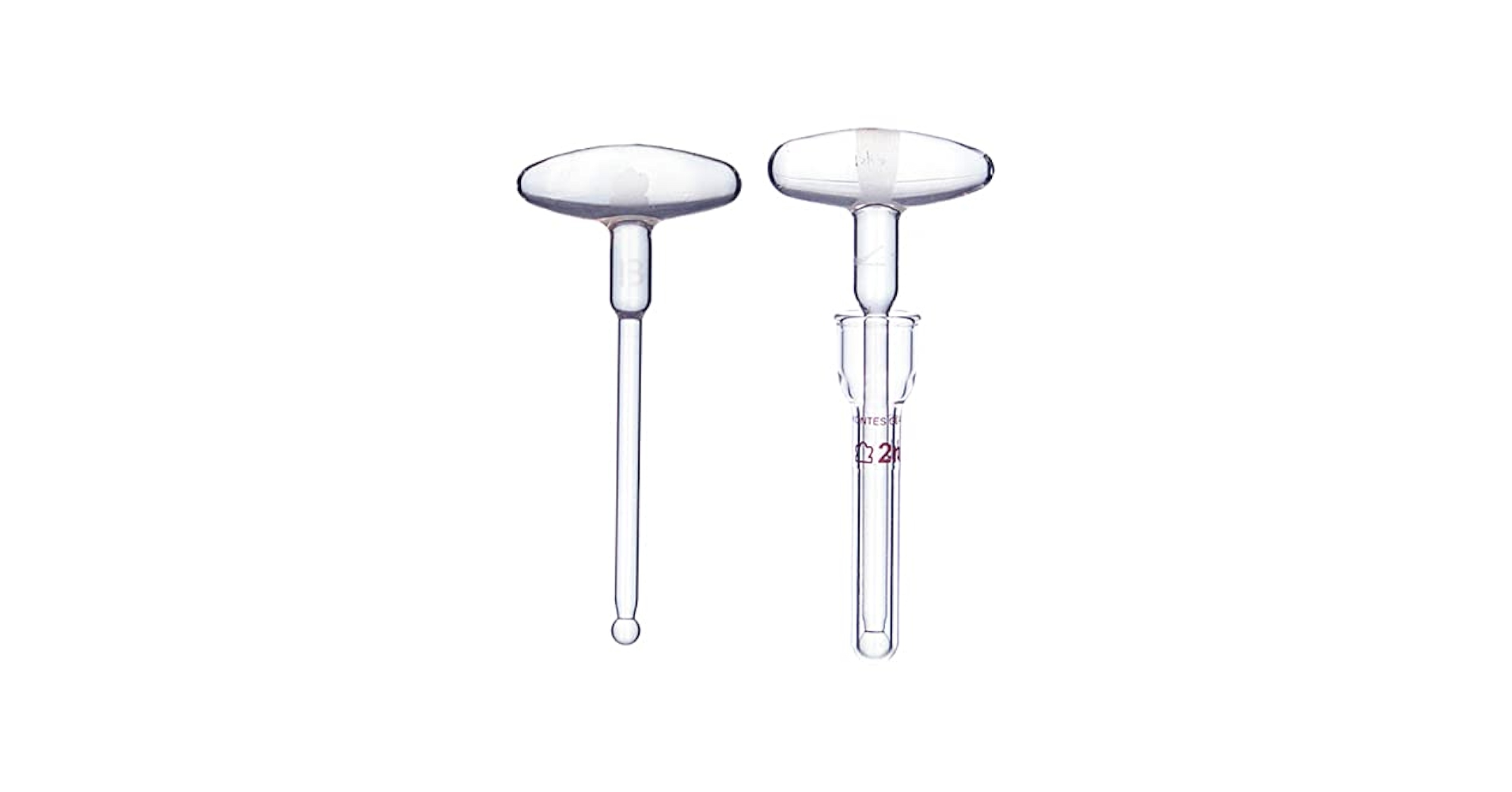
Illustrative image related to glass homogenizer
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that borosilicate glass homogenizers comply with international standards such as ASTM E438 or DIN 12592. This compliance is particularly important in regions like Europe and North America, where regulatory standards are stringent.
How Does Soda-Lime Glass Compare for Use in Glass Homogenizers?
Soda-lime glass is another common material used in glass homogenizers, primarily due to its lower cost compared to borosilicate glass. While it is suitable for many laboratory applications, its thermal and chemical resistance is not as robust.
Pros & Cons: The cost-effectiveness of soda-lime glass makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers. However, its lower resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion limits its use in more demanding applications. It is also less durable, which can lead to higher replacement costs over time.
Impact on Application: Soda-lime glass homogenizers are best suited for non-corrosive media and lower-temperature applications, such as general sample preparation in educational or low-stakes laboratory settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with less stringent regulatory environments may find soda-lime glass homogenizers acceptable. However, they should still verify compliance with local standards to avoid issues related to quality and safety.
What Are the Advantages of Quartz Glass in Glass Homogenizers?
Quartz glass offers exceptional optical clarity and chemical resistance, making it a premium choice for specialized applications. It can withstand high temperatures exceeding 1000°C and is highly resistant to thermal shock.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of quartz glass is its ability to maintain sample integrity under extreme conditions, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as high-temperature chemical reactions. However, quartz is significantly more expensive and can be more challenging to manufacture, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application: Quartz glass homogenizers are particularly beneficial in applications involving high-temperature reactions or where sample purity is critical, such as in certain pharmaceutical and materials science research.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that quartz glass products meet relevant international quality standards, such as ISO 3585, especially in regions like Europe and North America, where high-quality materials are mandated.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Glass Homogenizers
| Material | Typical Use Case for glass homogenizer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borosilicate Glass | Molecular biology, biochemistry | Excellent thermal and chemical resistance | Higher cost and brittleness | High |
| Soda-Lime Glass | General sample preparation | Cost-effective for basic applications | Lower thermal and chemical resistance | Low |
| Quartz Glass | High-temperature and purity-critical applications | Exceptional thermal stability and clarity | Very high cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on the specific needs of their applications and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for glass homogenizer
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Glass Homogenizers?
The manufacturing of glass homogenizers involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality, reliable instruments suitable for laboratory use. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who prioritize quality and performance in their procurement processes.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Glass Homogenizers?
The primary material used in the manufacturing of glass homogenizers is borosilicate glass, known for its durability, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion. This type of glass is chosen for its ability to withstand high temperatures and varying pH levels without altering the sample’s integrity. During the material preparation stage, raw materials are sourced, typically from reputable suppliers, ensuring they meet industry standards for quality and safety.
How Are Glass Homogenizers Formed?
The forming stage involves shaping the borosilicate glass into the required components, such as the mortar and pestle of the homogenizer. This process often employs techniques such as precision molding and glass blowing. Advanced machinery is utilized to create uniform thickness and dimensions, which are essential for achieving the correct clearance between the pestle and mortar. Ensuring the right fit is critical, as it affects the efficiency of the homogenization process.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
Once the individual components are formed, they undergo an assembly process. This typically involves manual labor, where skilled technicians fit the pestle into the mortar and ensure that any necessary features, such as pouring spouts, are integrated seamlessly. The assembly stage is critical for ensuring that the final product functions as intended, with attention paid to detail to avoid any potential issues during use.
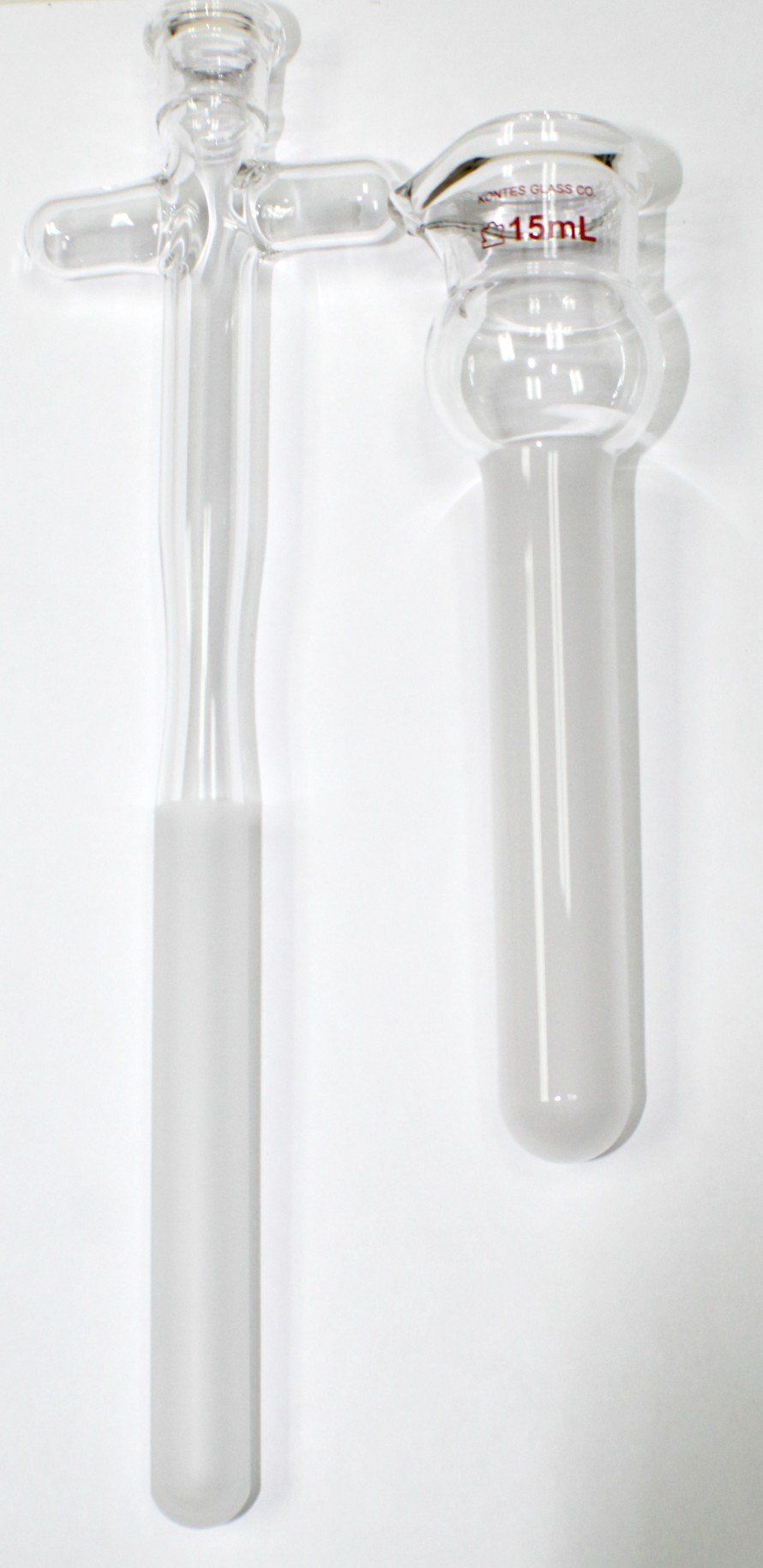

Illustrative image related to glass homogenizer
How Is the Finishing of Glass Homogenizers Done?
Finishing involves polishing the glass surfaces to eliminate any imperfections and enhance clarity. This step is essential for ensuring that researchers can visually monitor the homogenization process. In some cases, the glass may be treated with coatings to enhance its chemical resistance. Rigorous cleaning processes are also implemented to prepare the products for sterilization before packaging.
What Quality Control Measures Are Standard in Glass Homogenizer Production?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of glass homogenizers, ensuring that each product meets stringent performance and safety standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with the quality control measures that manufacturers implement throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of glass homogenizers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which sets the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates that the manufacturer has a systematic approach to managing quality, which can significantly reduce the risk of defects.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may apply, depending on the intended use of the homogenizers. These certifications provide assurance that the products comply with European and international safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control is typically organized into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards before being used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, components are regularly inspected for dimensional accuracy and surface quality to catch any issues early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the homogenizers are assembled, they undergo final inspections, including functional tests and visual examinations, before being packaged and shipped.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods for glass homogenizers include dimensional checks, pressure tests, and thermal shock tests. Dimensional checks ensure that components fit together correctly, while pressure tests may be used to assess the durability of the glass under stress. Thermal shock tests evaluate the glass’s ability to withstand rapid temperature changes, which is critical for laboratory applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Procedures?
When sourcing glass homogenizers, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures employed by potential suppliers. Here are some strategies:
What Role Do Audits Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting audits of suppliers can provide invaluable insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control protocols. Buyers should look for suppliers who welcome third-party audits and can provide documentation of their adherence to relevant quality standards.
How Important Are Quality Reports and Certifications?
Requesting quality reports and certifications is essential for understanding a supplier’s commitment to quality. Buyers should ask for documentation that outlines the results of quality tests, compliance with international standards, and any certifications relevant to the product. This information not only helps verify quality but also builds trust in the supplier relationship.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s important to consider the nuances of quality control. Different markets may have varying standards and regulations that affect the acceptance of products. Buyers should ensure that the products they import comply with local regulations and that suppliers can provide the necessary documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with glass homogenizers is crucial for B2B buyers. By being informed about material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and quality control measures, buyers can make educated decisions and select suppliers that uphold high standards of quality. This knowledge not only helps in sourcing reliable products but also contributes to the overall success of their laboratory operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘glass homogenizer’
When sourcing a glass homogenizer, a systematic approach can help ensure you choose a product that meets your laboratory’s needs and enhances your research capabilities. This checklist outlines essential steps for B2B buyers to follow during the procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical before you begin your search. Consider the sample types you will be homogenizing, the required volume capacity, and whether you need features like a pour spout or specific pestle designs. This clarity will guide you in identifying models that suit your particular applications, such as DNA extraction or enzyme assays.
Step 2: Research Material Quality and Design
The material and design of the homogenizer can significantly impact your results. Opt for homogenizers made from high-quality borosilicate glass, as it offers superior chemical resistance and durability. Additionally, examine the geometry of the mortar and pestle; a well-designed pestle tip ensures efficient disruption of tissues, which is crucial for achieving optimal yields of cellular components.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before committing to a supplier, check their certifications and compliance with industry standards. Look for suppliers that provide quality certifications demonstrating that their products meet established specifications. This step is essential to ensure product reliability and to minimize risks associated with laboratory work, especially in regulated environments.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Reputation
Assess the supplier’s experience in providing glass homogenizers. A reputable supplier will have a history of serving customers in your industry or region. Request case studies and references from similar buyers to gauge their satisfaction with the product quality and service. This insight can help you avoid potential pitfalls and ensure a smooth procurement process.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
While price is a significant factor, consider the value offered at different price points. Compare similar products from multiple suppliers to determine the best balance between cost and features. Additionally, evaluate the payment terms and conditions, as flexible payment options can ease cash flow concerns, especially for larger orders.
Step 6: Inquire About Warranty and Support Services
A solid warranty can provide peace of mind regarding your investment. Check the warranty terms and what they cover, including parts and repairs. Furthermore, inquire about the supplier’s customer support services, such as technical assistance and product training, which can be invaluable in maximizing the use of your homogenizer.
Step 7: Plan for Post-Purchase Considerations
After selecting your glass homogenizer, consider your post-purchase needs. This includes establishing a cleaning and maintenance protocol to ensure longevity and performance. Also, keep in mind the potential need for additional accessories or consumables, such as pestle replacements or cleaning solutions, which may be required for optimal operation.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for glass homogenizers more effectively, ensuring they acquire a product that meets their laboratory’s specific needs and contributes to successful research outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for glass homogenizer Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Glass Homogenizers?
When sourcing glass homogenizers, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary components influencing costs include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: Glass homogenizers are primarily made from high-quality borosilicate glass, known for its durability and resistance to thermal shock. The quality of the glass used significantly impacts the overall cost. Suppliers may offer variations in glass type, which can affect both performance and price.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. Given the precision required in crafting glass homogenizers, labor costs can be substantial. This factor can vary by region, with countries offering lower labor costs potentially providing a competitive advantage.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which is crucial for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery for producing glass homogenizers can be significant. Custom designs or specialized features may require additional tooling, which can drive up costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each unit meets stringent quality standards involves additional costs. Certification processes and testing are vital, especially for international buyers who may require compliance with specific regulations.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely depending on the origin of the product and the destination. For international buyers, understanding the implications of freight costs and potential tariffs is crucial.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Glass Homogenizer Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of glass homogenizers, particularly for international buyers. Key influencers include:

Illustrative image related to glass homogenizer
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide better pricing for bulk purchases or minimum order quantities (MOQ). Higher volumes can lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific dimensions may increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and recognized certifications can enhance the price. Buyers should assess the importance of these factors based on their intended use.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for determining responsibility for shipping costs, risks, and insurance. This can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing glass homogenizers and achieve cost efficiency, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially for bulk orders. Suppliers may offer discounts or flexible terms to secure larger contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, operation, and potential replacements. A lower initial price may not equate to overall savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and customs duties that may apply when importing glass homogenizers. These factors can significantly alter the final cost.
-
Research and Comparison: Conduct thorough research on multiple suppliers to compare not just prices but also service, quality, and delivery times. This can help in making an informed decision.
-
Understand Market Trends: Keep an eye on market trends and pricing fluctuations. Being informed can help in timing purchases to secure better deals.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for glass homogenizers can vary based on multiple factors, including supplier, region, and specific product specifications. The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may change over time. Buyers should obtain current quotes from suppliers to ensure accurate budgeting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing glass homogenizer With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Homogenization
When it comes to homogenizing biological samples, selecting the right equipment is crucial for achieving reliable and reproducible results. While glass homogenizers are a popular choice due to their precision and ability to maintain sample integrity, other alternatives also exist that may better suit specific laboratory needs, budget constraints, or operational workflows. This analysis explores viable alternatives to glass homogenizers, including mechanical homogenizers and bead mills, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their unique requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Glass Homogenizer | Mechanical Homogenizer | Bead Mill Homogenizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; suitable for soft tissues | Effective for hard and soft samples | Excellent for tough samples; high throughput |
| Cost | Moderate; varies by size and brand | Higher initial investment | Generally high due to consumables |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires manual operation; simple setup | More complex; requires training | Moderate complexity; setup needed |
| Maintenance | Low; easy to clean and sterilize | Moderate; requires regular servicing | Moderate; cleaning can be labor-intensive |
| Best Use Case | DNA/RNA extraction, cell lysis | Large sample volumes, tough tissues | Industrial applications, high-throughput needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Mechanical Homogenizer
Mechanical homogenizers utilize blades or rotors to disrupt cells and tissues, making them suitable for a variety of sample types, including both soft and hard materials. One of the primary advantages is their ability to process larger sample volumes quickly, which is particularly beneficial in high-throughput environments. However, they require more complex setups and operator training to ensure optimal performance and safety. Additionally, the initial cost can be significantly higher than that of glass homogenizers, which may deter smaller laboratories or those with limited budgets.
Bead Mill Homogenizer
Bead mills employ a combination of beads and mechanical action to efficiently disrupt cells, making them a preferred choice for tough samples such as plant tissues or bacteria. They are particularly effective for high-throughput applications, allowing for simultaneous processing of multiple samples. However, they come with higher operational costs due to the need for consumables like beads and can require more extensive maintenance. The cleaning process can also be labor-intensive, which may not be ideal for every laboratory setting.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Homogenization Solution
For B2B buyers, the choice between a glass homogenizer, mechanical homogenizer, and bead mill homogenizer should be guided by specific laboratory needs and operational considerations. Glass homogenizers offer precision and simplicity, making them ideal for applications involving delicate biological samples. In contrast, mechanical and bead mill homogenizers provide solutions for larger volumes and tougher materials, albeit with increased costs and complexity. Understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each option will empower buyers to select the most suitable homogenization technology for their research or production processes, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and research outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for glass homogenizer
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a Glass Homogenizer?
When sourcing glass homogenizers for laboratory use, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
Glass homogenizers are typically made from borosilicate glass, known for its high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. This property is vital in laboratory settings where samples may react with different chemicals or experience temperature fluctuations. The use of high-grade materials ensures durability, reducing the risk of breakage and contamination, which can compromise experimental integrity. -
Pestle Clearance Tolerance
The clearance between the pestle and the mortar is a critical specification, usually ranging from 0.025 mm to 0.15 mm depending on the application. This tolerance affects the efficiency of homogenization; tighter clearances are ideal for fine homogenization of delicate samples, while looser clearances may be suitable for coarser grinding. Understanding these tolerances helps buyers select the right homogenizer for specific sample types and desired outcomes. -
Volume Capacity
Glass homogenizers come in various sizes, typically ranging from 2 mL to 40 mL. Selecting the appropriate volume capacity is essential for optimizing sample preparation without waste. For laboratories handling small samples, smaller capacities may be sufficient, whereas larger capacities may be necessary for bulk processing or industrial applications. This consideration ensures efficient use of resources and time. -
Autoclavable Features
Many glass homogenizers are designed to be autoclavable, allowing for sterilization between uses. This feature is crucial in preventing cross-contamination, especially in labs conducting sensitive experiments. Buyers should prioritize homogenizers that can withstand autoclaving, ensuring compliance with laboratory safety and hygiene standards. -
Ease of Cleaning
The design of glass homogenizers should facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance. A smooth glass surface minimizes the risk of residue buildup and allows for thorough sterilization. For laboratories that frequently change sample types, ease of cleaning is essential to maintain sample integrity and avoid contamination. -
Compatibility with Motorized Systems
Some glass homogenizers can be motor-driven, provided they include friction-release mechanisms to protect the apparatus from damage. This compatibility offers versatility in laboratory operations, allowing for higher throughput and efficiency in sample processing. Understanding this feature can help buyers align their homogenizer choice with their operational needs.
What Are the Common Trade Terminology and Concepts Associated with Glass Homogenizers?
Navigating the procurement of glass homogenizers also involves familiarizing oneself with industry jargon. Here are some essential terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another brand’s name. In the context of glass homogenizers, working with OEMs can ensure that buyers receive high-quality, branded products that meet specific standards. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers evaluate product quality and reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers who need to manage budgets and stock levels. Knowing the MOQ can aid in planning purchases, especially for companies looking to maintain a steady supply of glass homogenizers without excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. For buyers, issuing an RFQ for glass homogenizers allows them to compare options and negotiate better deals. It’s a strategic step in the procurement process that can lead to cost savings and better supplier relationships. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers sourcing glass homogenizers from global suppliers, as they clarify shipping, insurance, and delivery obligations, helping to avoid disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is vital for planning purposes, especially in research and production environments where timely access to equipment can impact project timelines. -
Quality Assurance (QA)
QA encompasses the processes and measures taken to ensure that products meet certain standards before they reach the buyer. Buyers should inquire about the QA practices of suppliers to ensure that the glass homogenizers they purchase adhere to necessary quality and safety standards, thereby safeguarding their research outcomes.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when procuring glass homogenizers, ensuring that they meet their laboratory needs effectively and efficiently.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the glass homogenizer Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Glass Homogenizer Sector?
The glass homogenizer sector is witnessing a transformative phase driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for precision in biological and biochemical research is propelling growth, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As international B2B buyers seek reliable solutions for sample preparation, the emphasis is on high-quality materials like borosilicate glass that ensure purity and minimize contamination. Furthermore, a shift towards automation in laboratories is leading to the integration of motor-driven homogenizers, which can significantly enhance efficiency and reproducibility in sample processing.
Emerging technologies, such as improved pestle designs and ergonomic features, are gaining traction. These innovations not only facilitate easier use but also reduce the risk of heat buildup during homogenization, thereby preserving sensitive biomolecules. Additionally, the growing trend of personalized medicine is driving the need for customized laboratory equipment, including glass homogenizers tailored to specific research applications. As a result, suppliers are focusing on offering diverse product ranges that cater to various sample volumes and types.
The competitive landscape is also evolving, with suppliers leveraging digital platforms for global outreach. E-commerce has become a vital channel for international buyers, enabling them to compare prices, specifications, and certifications easily. This trend is particularly pronounced in developing markets, where buyers are increasingly looking for cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Glass Homogenizer Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the glass homogenizer sector. The environmental impact of laboratory equipment production is prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials and minimizing waste during manufacturing processes. Borosilicate glass, commonly used in homogenizers, is not only durable but also recyclable, making it an attractive option for environmentally conscious buyers.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. International buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the origins of their products, seeking manufacturers who adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming essential in supplier selection processes. These certifications assure buyers of the manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability and quality, thereby reducing risks associated with procurement.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ certifications is rising, as laboratories aim to minimize their ecological footprint. Suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with international environmental standards are more likely to gain a competitive edge in the market. As the pressure to adopt sustainable practices intensifies, the glass homogenizer sector is poised to evolve towards more responsible sourcing, appealing to the values of modern B2B buyers.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of Glass Homogenizers in B2B Markets?
The evolution of glass homogenizers dates back to their early use in biological and biochemical research, where the need for precise sample preparation was paramount. Initially, these tools were manually operated, relying on the skill of the researcher to achieve desired results. Over the decades, advancements in material science, particularly the development of borosilicate glass, revolutionized their design and functionality. This material’s resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion made it the standard for laboratory equipment.
With the advent of automation and technology, glass homogenizers have seen significant enhancements, including ergonomic designs and the ability to integrate with motorized systems. This evolution has not only improved the efficiency of homogenization processes but also expanded their applications across various scientific fields, from molecular biology to pharmacology. As research demands grow more complex, the glass homogenizer continues to adapt, ensuring it remains a vital tool in laboratories worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of glass homogenizer
-
How do I choose the right glass homogenizer for my laboratory needs?
Selecting the appropriate glass homogenizer involves considering the sample types and volumes you frequently work with. For biological applications, look for homogenizers made from high-quality borosilicate glass to ensure chemical resistance and thermal stability. Additionally, assess the pestle design (loose vs. tight) to match your homogenization requirements. Compatibility with motor-driven devices can also enhance efficiency. Evaluate product specifications and user reviews to ensure you choose a homogenizer that meets your research needs. -
What are the benefits of using a glass homogenizer over plastic alternatives?
Glass homogenizers offer several advantages, including superior chemical resistance and the ability to withstand high temperatures during sterilization. They minimize the risk of sample contamination, which is crucial for accurate results in sensitive experiments. The smooth glass surface allows for easier cleaning and sterilization, reducing the potential for cross-contamination. Moreover, glass homogenizers typically provide better sample visibility, enabling researchers to monitor the homogenization process effectively. -
What should I consider when sourcing glass homogenizers internationally?
When sourcing glass homogenizers internationally, focus on the supplier’s reputation, product quality certifications, and compliance with international standards. Verify that they have experience exporting to your region and understand local regulations. Ensure clear communication regarding delivery timelines, customs documentation, and import duties. Additionally, consider the supplier’s ability to provide after-sales support and warranty services to address any issues that may arise post-purchase. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for glass homogenizers?
Minimum order quantities for glass homogenizers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and your specific needs. Generally, MOQs range from 10 to 100 units, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and the product’s complexity. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a smaller research facility or startup. Some suppliers may offer flexibility in MOQs for first-time orders or trial purchases. -
How can I ensure the quality of glass homogenizers from a supplier?
To ensure the quality of glass homogenizers, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Look for compliance with industry standards such as ISO or ASTM, which indicate adherence to quality management practices. Consider asking for samples to assess the product’s performance and durability firsthand. Additionally, review customer testimonials and seek references from other buyers to gauge the supplier’s reliability and product quality. -
What payment terms are typically offered for international orders of glass homogenizers?
Payment terms for international orders can vary widely among suppliers. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, and net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days). Some suppliers may require a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon shipment. It’s essential to clarify payment methods, currency, and any additional fees upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate more favorable payment terms over time. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing glass homogenizers?
When importing glass homogenizers, consider shipping methods, transit times, and potential customs duties. Glass products are fragile, so ensure that the supplier uses adequate packaging to prevent damage during transport. Familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, including any required documentation for customs clearance. Collaborating with a logistics provider experienced in handling laboratory equipment can help streamline the import process and reduce the risk of delays. -
Can glass homogenizers be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for glass homogenizers to meet specific research requirements. Customizations may include variations in size, pestle design, and additional features like pour spouts or specific markings. When discussing customization, clearly articulate your needs and any specific applications you intend to use the homogenizers for. This dialogue can lead to tailored solutions that enhance efficiency and effectiveness in your laboratory processes.
Top 6 Glass Homogenizer Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. WHEATON® – Dounce Tissue Grinder
Domain: dwk.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: WHEATON® Dounce Tissue Grinder manufactured from borosilicate glass 3.3. Retains high percentage of cell nuclei and mitochondria in soft tissues or from cell cultures. Tube has large reservoir and pouring lip for easy decanting. Pestle ball encircled in liquid to avoid heat build-up by reducing friction. Contains both loose and tight pestles with clearance ranges: Loose pestle clearance range: 0.0…
2. Merck – Glass Tissue Homogenizers
Domain: sigmaaldrich.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Merck – Glass Tissue Homogenizers, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. 4ES – Glass Homogenizer 10-20mL Dounce/TenBroeck Style
Domain: 4es-usa.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Glass Homogenizer 10-20mL Dounce/TenBroeck Style – 4 Pack”,”price”:”$39.00″,”type”:”homogenizer”,”availability”:”in stock”},{“name”:”Mortar and Pestle Sets”,”price”:”$21.00″,”type”:”mortar & pestle”,”availability”:”in stock”},{“name”:”Handheld Rotor-Stator Homogenizer”,”price”:”$618.00″,”type”:”homogenizer”,”availability”:”in stock”},{“name”:”Bead Mill Homogenizer”,”price”:”C…
4. Corning – PYREX® Ten Broeck Homogenizer
Domain: ecatalog.corning.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: Product Name: PYREX® Ten Broeck Homogenizer with Pour Spout
Key Features: Designed for hand grinding small samples for pathological or biochemical studies; can be motor driven at low speed with friction release; interchangeable mortar tubes and pestles; clearance between parts is approximately 0.15 mm; medium grind for well homogenized samples; made in accordance with Federal Specification NNN-T-3…
5. Bellco – Tenbroeck Homogenizer 2ml Glass
Domain: bellcoglass.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Tenbroeck Homogenizer 2ml Glass”, “material”: “glass”, “capacity”: “2ml”, “features”: [“used for homogenizing samples”, “durable construction”, “easy to clean”], “applications”: [“laboratory use”, “biological samples”, “chemical samples”]}
6. SciLogex – Glass Homogenizers
Domain: scilogex.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Glass Homogenizers include various models such as General Purpose Homogenizers (available in 5ml, 10ml, 15ml, 30ml, and 55ml sizes), Duo-Form Homogenizers (Hand Type and Plain Rod Style, 15ml), and Ground Glass Round Body Homogenizers (Tenbroeck Style, available in 5ml, 10ml, 15ml, 30ml, and 55ml sizes). Prices range from $80.00 to $176.00 depending on the model and specifications.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for glass homogenizer
In the dynamic landscape of laboratory equipment, glass homogenizers stand out as essential tools for a variety of applications in biological and biochemical research. Their ability to deliver precise homogenization while maintaining sample integrity is invaluable, particularly in fields such as genomics, proteomics, and drug development. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize their laboratory processes, understanding the nuances of strategic sourcing becomes paramount.
Investing in high-quality glass homogenizers not only enhances the reliability of research outcomes but also ensures compliance with stringent quality standards. By collaborating with reputable suppliers who prioritize innovation and sustainability, organizations can secure a competitive edge.
Looking ahead, the demand for glass homogenizers is expected to grow, driven by advancements in research methodologies and an increasing focus on quality control across various industries. As you consider your sourcing strategy, prioritize suppliers who can provide not only exceptional products but also comprehensive support and expertise. Embrace the opportunity to elevate your laboratory capabilities and drive your research forward—partner with trusted manufacturers today to ensure your success in an ever-evolving market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.