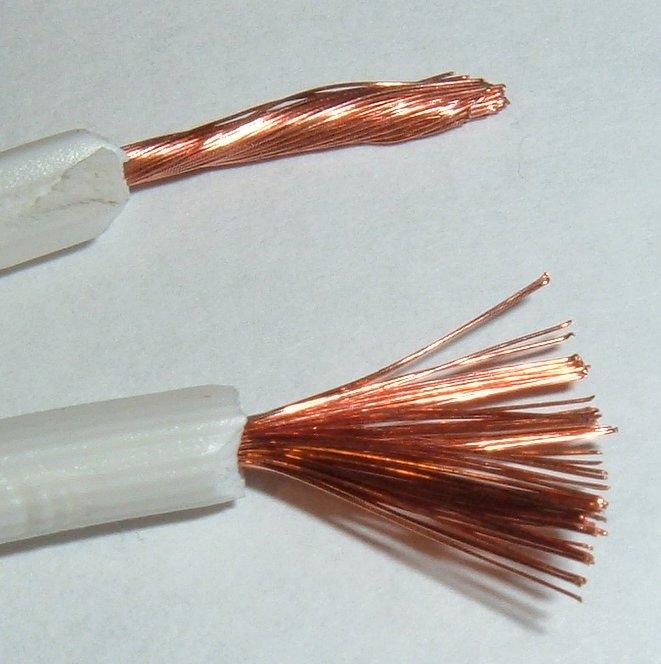
Everything You Need to Know About What Is A Stranded Wire Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for what is a stranded wire
Stranded wire is a critical component in modern electrical systems, yet sourcing the right type for your specific application can be a challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re working on intricate electronic devices in Germany or setting up robust electrical infrastructure in South America, understanding the nuances of stranded wire is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring safety. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of stranded wire, their applications, and key factors to consider when sourcing from suppliers.
As you navigate the complexities of the global market, this guide equips you with actionable insights on how to evaluate stranded wire options based on criteria such as flexibility, current capacity, and cost-effectiveness. We will also cover best practices for vetting suppliers, ensuring that you partner with manufacturers who meet international quality standards and can cater to your specific regional requirements.
With a focus on empowering B2B buyers from Africa, the Middle East, Europe, and South America, this resource provides the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your project goals. By understanding the distinctions between stranded and solid wire, as well as their respective advantages and disadvantages, you can enhance your procurement strategy and drive successful outcomes in your electrical projects.
Understanding what is a stranded wire Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Stranded Wire | Composed of numerous fine strands twisted together, offering high flexibility. | Electronic devices, automotive wiring, robotics. | Pros: Excellent flexibility and bendability. Cons: Higher cost and potential for corrosion. |
| Litz Wire | Made from many thin, insulated strands to minimize skin effect at high frequencies. | RF applications, audio equipment, high-frequency circuits. | Pros: Reduced skin effect, better performance at high frequencies. Cons: More complex to manufacture and terminate. |
| Flexible Stranded Wire | Features a high strand count for maximum flexibility, often with PVC insulation. | Mobile equipment, machinery, and tight spaces. | Pros: High flexibility, ideal for dynamic applications. Cons: Lower current capacity compared to solid wire. |
| Tinned Stranded Wire | Stranded wire coated with tin to enhance corrosion resistance. | Marine applications, outdoor installations, automotive. | Pros: Improved corrosion resistance, longer lifespan. Cons: Slightly higher cost due to tin coating. |
| Silicone Insulated Stranded Wire | Features silicone insulation for high-temperature applications. | Aerospace, high-temperature electronics, automotive. | Pros: High thermal resistance, flexible at extreme temperatures. Cons: Higher price point compared to standard insulation types. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Multi-Stranded Wire for B2B Buyers?
Multi-stranded wire is designed for applications requiring flexibility and resilience. Its construction allows it to bend easily, making it ideal for electronic devices, automotive wiring, and robotics. When selecting this type of wire, buyers should consider the required flexibility versus the cost, as multi-stranded wire tends to be more expensive than solid alternatives. Additionally, its susceptibility to corrosion can be a concern in certain environments, necessitating protective measures.
Why is Litz Wire a preferred choice for high-frequency applications?
Litz wire is specifically engineered for minimizing the skin effect, which is crucial in high-frequency applications like RF transmission and audio equipment. It consists of numerous thin, insulated strands that are twisted together, allowing for efficient current flow at higher frequencies. B2B buyers in industries such as telecommunications should prioritize Litz wire for its superior performance, albeit at a higher manufacturing complexity and cost. Understanding the application requirements is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
How does Flexible Stranded Wire perform in dynamic applications?
Flexible stranded wire is characterized by a high strand count, providing exceptional flexibility that is particularly beneficial in mobile equipment and machinery where movement is frequent. This wire type is ideal for tight spaces and applications where bending is necessary. However, buyers should be aware that while it offers increased flexibility, it may have a lower current capacity than solid wire. Evaluating the application’s specific requirements is critical for selecting the right wire type.
What advantages does Tinned Stranded Wire offer in harsh environments?
Tinned stranded wire is coated with tin to enhance its resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for marine applications and outdoor installations. This wire type is often used in automotive wiring as well, where exposure to moisture and harsh conditions is common. While the tin coating increases the lifespan of the wire, it does come at a slightly higher cost. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced durability against budget constraints when considering this wire type.
Why choose Silicone Insulated Stranded Wire for high-temperature applications?
Silicone insulated stranded wire is designed to withstand extreme temperatures, making it ideal for aerospace applications and high-temperature electronics. Its flexibility at elevated temperatures is a significant advantage, allowing it to be used in environments where standard insulation would fail. B2B buyers should consider the higher price point of silicone insulated wire as a worthwhile investment for applications requiring reliability and performance under challenging conditions.
Key Industrial Applications of what is a stranded wire
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of what is a stranded wire | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Circuit boards and electronic devices | Enhanced flexibility for compact designs, reducing space and weight in devices | Ensure compatibility with specific electronic components and standards. Consider insulation materials for safety. |
| Automotive | Vehicle wiring harnesses | Reliable connections for various automotive systems, enhancing performance and safety | Look for high-temperature resistance and durability to withstand harsh conditions. |
| Telecommunications | Data transmission cables | High flexibility and reduced signal loss, improving data integrity over distances | Verify the wire gauge and material to meet specific transmission standards. |
| Renewable Energy | Solar panel connections | Efficient power transfer from solar panels to inverters, maximizing energy yield | Consider corrosion resistance and UV protection for outdoor applications. |
| Industrial Equipment | Machinery control systems | Ability to withstand vibrations and movements, ensuring operational reliability | Assess the wire’s ampacity and flexibility for ease of installation and maintenance. |
How is Stranded Wire Utilized in Electronics?
In the electronics sector, stranded wire is commonly employed in circuit boards and electronic devices due to its superior flexibility. This characteristic allows for effective routing in compact spaces, making it ideal for intricate designs where movement and vibration are prevalent. B2B buyers in this industry must consider compatibility with specific electronic components and adherence to safety standards, including insulation materials that prevent short circuits.
Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
What Role Does Stranded Wire Play in the Automotive Industry?
Stranded wire is vital in automotive wiring harnesses, connecting various systems within vehicles, such as lighting, sensors, and entertainment systems. Its flexibility allows for easy installation in confined spaces, while its durability ensures reliable performance under harsh conditions. Buyers in this sector should prioritize wires with high-temperature resistance and durability to withstand vibrations and environmental challenges, ensuring long-term reliability and safety.
How Does Stranded Wire Benefit Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, stranded wire is utilized in data transmission cables, where its flexibility and reduced signal loss enhance data integrity over long distances. This application is critical for maintaining high-quality communication channels. B2B buyers should verify the wire gauge and material to comply with specific transmission standards, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in data-driven environments.
Why is Stranded Wire Important for Renewable Energy Applications?
Stranded wire is essential for connecting solar panels to inverters, facilitating efficient power transfer and maximizing energy yield. Its flexibility and resistance to environmental factors make it suitable for outdoor installations. Buyers in the renewable energy sector should consider wires that offer corrosion resistance and UV protection, ensuring longevity and efficiency in energy generation systems.
How is Stranded Wire Used in Industrial Equipment?
In industrial settings, stranded wire is used in machinery control systems, where it must withstand vibrations and movements without compromising performance. This application is crucial for ensuring operational reliability in demanding environments. B2B buyers should assess the stranded wire’s ampacity and flexibility to ensure ease of installation and maintenance, which can significantly reduce downtime and improve productivity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘what is a stranded wire’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Flexibility Needs of Stranded Wire in Tight Spaces
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the right type of wire for applications requiring flexibility, particularly in compact electronic assemblies. Stranded wire is known for its superior flexibility compared to solid wire; however, buyers may struggle with determining whether the stranded wire will adequately meet their specific needs in environments where space is limited, such as in circuit boards or intricate electronic devices. There is a risk of misjudging the wire’s ability to withstand bending and twisting, leading to potential failures that can disrupt operations and incur additional costs.
The Solution: To effectively address these flexibility concerns, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their specific application requirements. Begin by assessing the bending radius needed for your application—this will help determine the gauge and strand count necessary for optimal performance. When sourcing stranded wire, prioritize suppliers who provide detailed specifications, including the wire’s flexibility ratings and its performance in dynamic environments. Additionally, consider investing in sample testing of different stranded wire types in your intended application to validate their performance before committing to a bulk purchase. This proactive approach ensures that the wire will withstand the necessary movements without compromising electrical connectivity.
Scenario 2: Managing Corrosion Risks in Stranded Wire Applications
The Problem: Stranded wire can present unique challenges related to corrosion, especially when used in harsh environments such as coastal regions or industrial settings with high humidity. B2B buyers may find that while stranded wire offers flexibility, it is more susceptible to corrosion due to the multiple strands that can trap moisture. This can lead to decreased conductivity over time, increased resistance, and ultimately, failure of the electrical system, which can be costly and time-consuming to repair.
The Solution: To mitigate corrosion risks, buyers should focus on selecting stranded wire that is specifically designed for environmental resilience. Look for wires that have been treated with corrosion-resistant coatings or are made from materials such as tinned copper, which provides better protection against oxidation. When specifying stranded wire, it is also beneficial to consult with manufacturers regarding the environmental conditions the wire will face. They can often provide insights into the best practices for installation and maintenance, such as ensuring proper sealing and drainage in installations to reduce moisture accumulation. Implementing these strategies will enhance the longevity of the stranded wire and maintain the integrity of the electrical systems.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Voltage Drop Challenges in Long-Distance Applications
The Problem: Another common issue faced by B2B buyers is the voltage drop associated with using stranded wire over long distances. Stranded wire, while flexible and suitable for certain applications, can exhibit higher resistance compared to solid wire, especially when dealing with high currents. This can result in significant voltage drops, leading to inefficient power delivery and potential operational issues in systems where consistent voltage is critical.
The Solution: To effectively manage voltage drop concerns, buyers should calculate the expected voltage drop for their specific application before selecting stranded wire. Utilize voltage drop calculators available online or consult with electrical engineers to determine the appropriate wire gauge that compensates for the length of the run and the expected current load. When purchasing stranded wire, ensure you select a wire gauge that is larger than the minimum requirement to account for the increased resistance. Additionally, consider using solid wire for longer runs where voltage drop is a critical factor, reserving stranded wire for shorter connections or areas where flexibility is paramount. This strategic approach will help maintain efficiency and performance across your electrical installations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for what is a stranded wire
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Stranded Wire?
When selecting stranded wire for various applications, the choice of material is critical. Different materials offer distinct properties that can significantly influence performance, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in stranded wire manufacturing: copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and tinned copper.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper Stranded Wire?
Copper is the most widely used material for stranded wire due to its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C (392°F) and can handle high amperage loads, making it ideal for electrical applications.
Pros: Copper stranded wire is highly durable, flexible, and resistant to corrosion, ensuring long-term performance in various environments. Its superior conductivity allows for efficient energy transmission, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper stranded wire is its cost, which is higher than that of other materials like aluminum. Additionally, copper is susceptible to oxidation, which can affect its conductivity over time if not properly insulated.
Impact on Application: Copper stranded wire is compatible with a wide range of media and environments, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Its high conductivity is particularly beneficial in power distribution systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and Europe should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and IEC. In markets like Germany, adherence to DIN standards is crucial for quality assurance.
How Does Aluminum Stranded Wire Compare?
Aluminum is another common material for stranded wire, particularly in applications where weight is a concern. It has a lower density than copper, making it lighter and easier to handle.
Pros: Aluminum stranded wire is cost-effective and offers good conductivity, particularly when using larger gauge sizes. It is also resistant to corrosion, especially when anodized or treated.

Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
Cons: While aluminum has decent conductivity, it is not as efficient as copper, requiring a larger gauge to achieve the same current capacity. Additionally, aluminum is more prone to mechanical fatigue and can break under repeated flexing.
Impact on Application: Aluminum stranded wire is often used in overhead power lines and other applications where weight savings are critical. Its compatibility with various environmental conditions makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regional standards such as JIS in Japan and various European standards that govern aluminum wire specifications. Compliance with these standards ensures reliability and safety.
What Are the Benefits of Stainless Steel Stranded Wire?
Stainless steel is less common but is used in specialized applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating similar to copper and aluminum, depending on the specific alloy used.
Pros: Stainless steel stranded wire is exceptionally durable and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments, such as marine or industrial applications. Its strength allows it to withstand significant mechanical stress.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of stainless steel is its lower electrical conductivity compared to copper and aluminum, which can limit its use in electrical applications. Additionally, it is generally more expensive to produce.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel stranded wire is suitable for applications requiring mechanical strength, such as in construction and heavy machinery. However, its lower conductivity makes it less ideal for power transmission.
Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM and other international standards is essential for stainless steel wire applications. Buyers should also consider the specific alloy grades that meet their industry needs.
Why Choose Tinned Copper Stranded Wire?
Tinned copper stranded wire is copper wire coated with a layer of tin, enhancing its corrosion resistance and solderability. It is particularly useful in marine and outdoor applications.
Pros: The tin coating provides excellent protection against corrosion, making it suitable for environments exposed to moisture. Tinned copper also retains the excellent conductivity of copper.

Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
Cons: The main drawback is the additional cost associated with the tin coating, which can make tinned copper stranded wire more expensive than standard copper wire. Additionally, the tin layer may wear off over time in harsh conditions.
Impact on Application: Tinned copper stranded wire is ideal for applications in marine environments, automotive wiring, and other situations where moisture exposure is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that tinned copper wire meets relevant standards, such as UL and IEC, to guarantee quality and performance in specific applications.

Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
Summary Table of Material Selection for Stranded Wire
| Material | Typical Use Case for what is a stranded wire | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Electrical applications, power distribution | Excellent conductivity and durability | Higher cost and oxidation susceptibility | High |
| Aluminum | Overhead power lines, lightweight applications | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Marine and industrial applications | High strength and corrosion resistance | Lower conductivity and higher cost | High |
| Tinned Copper | Marine and outdoor applications | Corrosion resistance and solderability | Higher cost and potential wear of tin | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for stranded wire, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for what is a stranded wire
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Stranded Wire?
The manufacturing process of stranded wire involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality stranded wire.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The journey of stranded wire begins with the careful selection of raw materials, typically copper or aluminum. The purity of the metal is paramount, as impurities can significantly impact conductivity and overall wire performance. Raw metal is usually in the form of rods or bars, which are then drawn into thinner wires. This drawing process involves pulling the metal through a series of dies to achieve the desired gauge and diameter.
Once the wire is drawn, it undergoes annealing, a heat treatment process that enhances its ductility and flexibility. This is particularly important for stranded wire, as it will be twisted into strands that need to maintain their integrity and flexibility during usage.
How Are Strands Formed and Assembled in Stranded Wire Production?
The next stage involves forming the strands. Multiple smaller wires are twisted together to create a single stranded wire. This process is performed using specialized machinery that ensures uniform twisting and tension, which is crucial for maintaining the wire’s structural integrity. The twisting technique can vary; for example, some manufacturers use a helical twist, while others may opt for a more complex configuration to enhance flexibility.
Following the twisting, the stranded wire is insulated with non-conductive materials, such as PVC or rubber, to prevent short circuits and enhance durability. The insulation process is critical, as it protects the wire from environmental factors and ensures safe operation in various applications.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented During Stranded Wire Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of stranded wire manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both international standards and specific industry requirements.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with several international standards that govern the quality of stranded wire. ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Additionally, compliance with CE marking indicates that the product meets European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
In sectors like oil and gas, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards is crucial, especially for applications involving high levels of stress and environmental challenges. Understanding these standards can help buyers ensure that they are sourcing stranded wire that is not only reliable but also compliant with regional regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Stranded Wire Production?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, typically encompassing Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): During this initial phase, raw materials are inspected for quality and compliance with specifications. Any defects found at this stage can significantly reduce the likelihood of issues arising later in the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various parameters such as wire diameter, tensile strength, and flexibility are monitored. This real-time assessment allows manufacturers to make necessary adjustments to maintain product quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the stranded wire is complete, a final inspection is conducted. This may include electrical testing, visual inspections, and verification of insulation integrity. Random sampling methods are often employed to ensure a representative quality check.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Stranded Wire Quality?
Testing methods are crucial for verifying the performance and reliability of stranded wire. Common methods include:

Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
- Electrical Conductivity Tests: These tests assess the wire’s ability to conduct electricity, ensuring it meets required standards.
- Tensile Strength Tests: By applying force until the wire breaks, manufacturers can determine its strength and durability.
- Flexibility Tests: Stranded wires are subjected to bending and twisting to evaluate their flexibility and resistance to fatigue over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify a Supplier’s Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring that the stranded wire meets their specific requirements. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures in place. This firsthand observation can provide invaluable insights into the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can offer transparency regarding testing results and compliance with international standards. These reports should include data on past production runs and any issues encountered.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control measures. These inspections can serve as a safeguard, particularly for international transactions.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements. Understanding these can help buyers avoid potential legal and operational issues.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across regions. Establishing clear lines of communication regarding quality expectations is vital to successful partnerships.
-
Logistical Considerations: Transporting stranded wire across borders may introduce additional quality control challenges. Buyers should consider how shipping and handling can affect product integrity.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for stranded wire is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable and compliant products. By focusing on the stages of production, quality control checkpoints, and testing methods, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing stranded wire for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘what is a stranded wire’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure stranded wire for their electrical and electronic applications. Stranded wire, known for its flexibility and durability, is essential for various industries, including electronics, automotive, and renewable energy. Understanding how to source the right stranded wire can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of your projects.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as amperage load, wire gauge, and environmental conditions. This ensures that the stranded wire you select meets your project’s specific needs, such as flexibility for tight spaces or durability for outdoor applications.
- Amperage Load: Determine the current your application will require to avoid overheating or inefficiency.
- Wire Gauge: Select the appropriate gauge based on your electrical specifications to ensure optimal performance.
Step 2: Research Material Types
Stranded wire can be made from various metals, with copper and aluminum being the most common. Each material has its own properties, including conductivity, weight, and corrosion resistance, which can affect performance and cost.
- Copper vs. Aluminum: Copper offers superior conductivity and durability, while aluminum is lighter and often less expensive.
- Corrosion Resistance: Consider whether your application will be exposed to harsh environments, which may necessitate corrosion-resistant coatings.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
When sourcing stranded wire, verifying supplier certifications is crucial to ensure product quality and compliance with international standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, RoHS, and UL, which indicate adherence to quality management and safety regulations.
- ISO 9001: Ensures consistent quality management processes.
- RoHS Compliance: Confirms that the wire is free from hazardous substances, making it suitable for various applications.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing a supplier, request samples of the stranded wire for testing. This step allows you to evaluate the wire’s performance in real-world conditions and confirm that it meets your specifications.
- Testing for Flexibility: Assess how well the wire bends and retains its shape under stress.
- Current Capacity Tests: Measure how the wire performs under load to ensure it meets your amperage requirements.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Delivery Options
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and delivery options. Consider factors such as minimum order quantities, lead times, and shipping costs, which can significantly impact your overall budget.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk orders, which can provide substantial savings.
- Lead Times: Ensure that suppliers can meet your project timelines to avoid delays in production.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Finally, evaluate the after-sales support and warranty offered by the supplier. A reliable supplier should provide assistance with installation, troubleshooting, and any issues that may arise post-purchase.
- Technical Support: Confirm that the supplier offers technical assistance for product-related queries.
- Warranty Terms: Review warranty coverage to ensure protection against defects or performance issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing stranded wire, ensuring that they select products that meet their technical needs and project requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for what is a stranded wire Sourcing
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis for sourcing stranded wire is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis encompasses various cost components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips that can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Stranded Wire Production?
-
Materials: The primary component is the raw material cost, typically copper or aluminum. The price of these metals fluctuates based on global market conditions. Additional materials include insulation and protective coatings, which also add to the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs include wages for skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. Stranded wire production requires more complex handling and assembly than solid wire, which can increase labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs associated with facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Stranded wire manufacturing generally involves more sophisticated machinery and processes, contributing to higher overhead.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, particularly for custom specifications. Investment in specialized equipment for twisting and insulating the wires is essential, affecting the pricing structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the stranded wire meets industry standards and certifications incurs additional costs. Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are vital to ensure reliability and safety, particularly in sectors like automotive and electronics.
-
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs can vary significantly based on the geographic location of suppliers and buyers. International shipping, customs duties, and local regulations must be factored into the overall pricing.
-
Margin: Manufacturers and suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary widely based on their market positioning and competition.
What Factors Influence the Pricing of Stranded Wire?
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer significant discounts for large quantities, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs accurately.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom stranded wire solutions tailored to specific applications will typically cost more due to the added complexity in production and design.
-
Materials: The choice of conductive material (copper vs. aluminum) and the quality of insulation can greatly affect pricing. Higher quality materials generally lead to enhanced performance but at an increased cost.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet stringent quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO, UL, RoHS) often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and customer service can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better guarantees on quality and delivery.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade can significantly impact the final cost. Understanding whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties is vital for accurate budgeting.
How Can Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Stranded Wire?
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing, especially for bulk orders. Leverage your position as a repeat customer to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate the long-term performance and reliability of stranded wire to avoid costly replacements.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and market conditions is essential. Currency fluctuations and import tariffs can significantly impact overall costs.
-
Supplier Diversification: Avoid reliance on a single supplier by exploring multiple options. This can lead to better pricing and terms, as well as mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion
In summary, a thorough understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers for stranded wire is essential for B2B buyers. By applying strategic negotiation and cost management techniques, businesses can optimize their sourcing process and ensure they receive the best value for their investment. While indicative pricing may vary, these insights will help guide informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing what is a stranded wire With Other Solutions
When considering electrical wiring solutions, it is essential to evaluate the alternatives to stranded wire. Stranded wire, characterized by its flexibility and malleability, is often favored in applications requiring intricate routing. However, other wire types may offer different advantages that could better suit specific project requirements. This analysis compares stranded wire with solid wire and aluminum wire, providing actionable insights for B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | What Is A Stranded Wire | Solid Wire | Aluminum Wire |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High flexibility; suitable for dynamic applications | Higher current capacity; less flexible | Lightweight; decent conductivity but higher resistance |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to complex manufacturing | Lower production costs; more economical | Cost-effective; lower material costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful handling for termination | Easy to install; straightforward connections | Requires special connectors and techniques |
| Maintenance | Prone to corrosion; requires regular checks | Durable and low maintenance | Susceptible to oxidation; needs protective coatings |
| Best Use Case | Indoor applications; electronic devices | Outdoor installations; high-current applications | Budget-sensitive projects; lightweight structures |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Solid Wire?
Solid wire is a single-core conductor that is thicker and more robust than stranded wire. Its primary advantage lies in its higher current capacity, making it ideal for outdoor applications where durability and low voltage drop are critical. However, solid wire is less flexible, which can limit its use in applications requiring intricate bends or routing around obstacles. Additionally, while solid wire is less expensive to produce, it can be susceptible to damage if subjected to excessive bending.
Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
How Does Aluminum Wire Compare?
Aluminum wire is another alternative, known for its lightweight properties and lower material costs. It is often used in overhead power lines and in applications where weight is a critical factor. However, aluminum has a higher electrical resistance than copper, which can lead to greater energy loss over distance. Its installation requires specialized connectors and careful handling to avoid issues related to oxidation, which can compromise performance over time.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Wire Solution?
Selecting the appropriate wire solution depends on various factors including application requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions. For projects requiring flexibility and adaptability in tight spaces, stranded wire may be the best choice. In contrast, solid wire is preferable for high-current outdoor applications where durability is essential. Meanwhile, aluminum wire can serve as a cost-effective solution in projects with weight considerations. B2B buyers should assess their specific needs against these characteristics to make an informed decision that aligns with both performance expectations and financial considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for what is a stranded wire
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Stranded Wire That B2B Buyers Should Know?
When sourcing stranded wire, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:

Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
1. Material Grade
Stranded wire is typically made from copper or aluminum, with copper being the preferred choice due to its superior conductivity. The material grade affects electrical performance, resistance to corrosion, and overall durability. For applications requiring high conductivity, look for wires made from high-purity copper, often rated as C11000 or C10200.
2. Wire Gauge
Wire gauge refers to the thickness of the stranded wire, measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG) or metric sizes. The gauge determines the wire’s current-carrying capacity, resistance, and flexibility. A lower gauge number indicates a thicker wire, which can handle more current but is less flexible. Understanding the appropriate gauge for your application is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency.
3. Stranding Configuration
The configuration of the strands (e.g., 7×19 or 19×7) indicates how many wires are twisted together and their arrangement. A higher number of smaller strands generally increases flexibility and reduces the risk of breakage during movement. This property is especially important for applications in tight spaces or where frequent bending occurs.
4. Current Capacity (Ampacity)
Ampacity is the maximum amount of electric current a wire can safely carry without overheating. Stranded wire typically has a lower ampacity compared to solid wire of the same gauge due to its increased surface area and air gaps. Understanding the ampacity is vital for preventing overheating and ensuring compliance with electrical codes.
5. Flexibility and Bend Radius
Flexibility refers to how easily the wire can be bent and manipulated without breaking. Stranded wire is significantly more flexible than solid wire, making it ideal for applications that require routing around obstacles or frequent movement. The minimum bend radius is a critical specification that indicates how tightly the wire can be bent without damage.
6. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating signifies the maximum voltage the wire can handle safely. This is critical for ensuring that the wire is suitable for your specific electrical application, especially in high-voltage environments. Selecting a wire with an adequate voltage rating is essential to avoid electrical failures or hazards.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Stranded Wire Purchases?
Understanding industry jargon can greatly facilitate B2B transactions. Here are some common terms that buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of stranded wire, OEMs often require specific wire specifications for their products, making it essential to understand their needs for compatibility and performance.
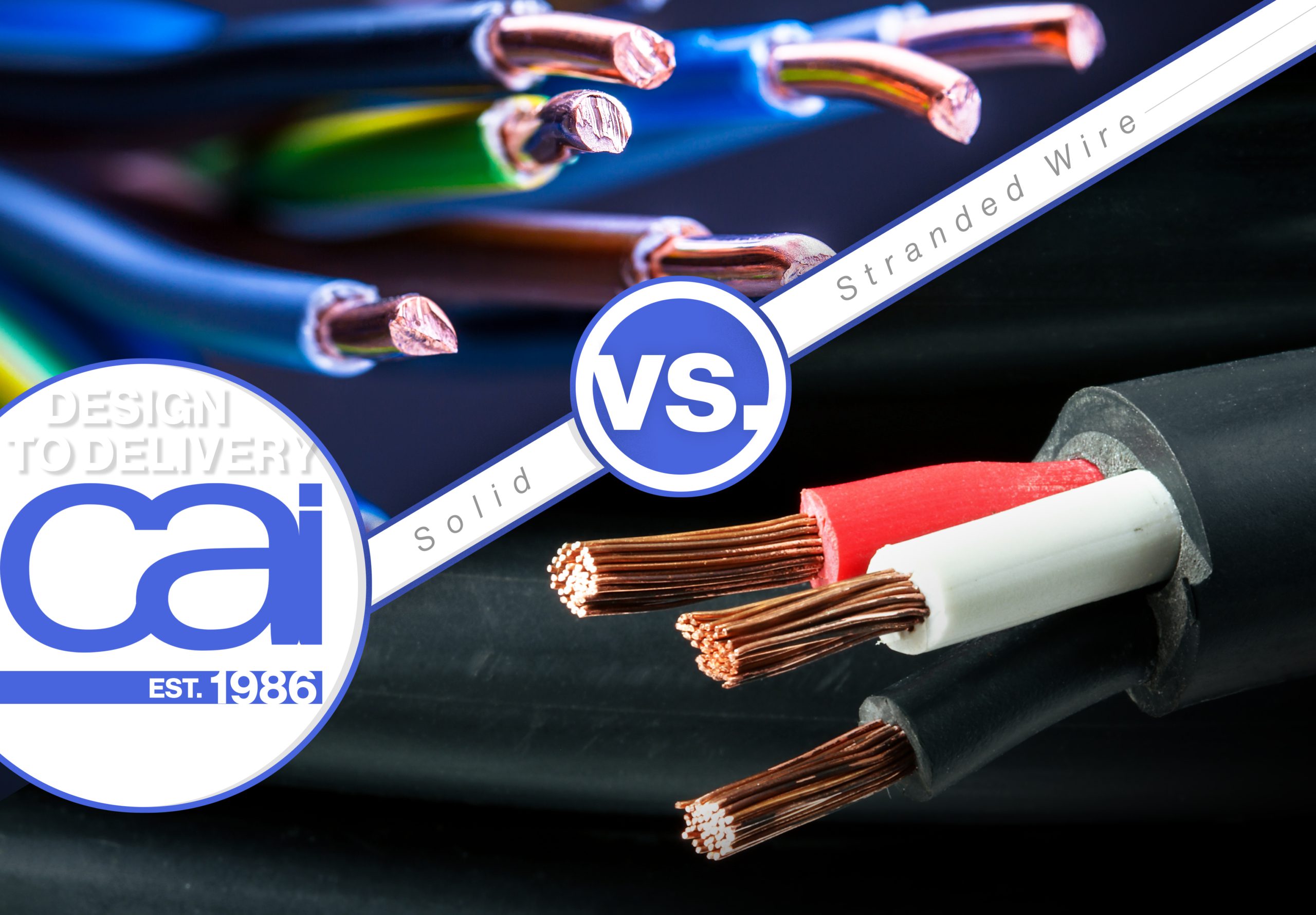
Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly relevant for stranded wire, as different applications may require varying lengths and quantities. Understanding MOQ can help buyers budget and plan their inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for a specific product. When sourcing stranded wire, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, terms, and lead times from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping costs, insurance, and risk management when purchasing stranded wire from global suppliers.
5. UL (Underwriters Laboratories) Certification
UL certification indicates that a product has been tested for safety and meets specific standards. For stranded wire, UL certification ensures compliance with safety regulations, making it a vital consideration for buyers in regulated industries.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing stranded wire, ensuring that they select the right products for their specific applications.

Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the what is a stranded wire Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Stranded Wire Market?
The global stranded wire market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors including automotive, electronics, and renewable energy. As industries worldwide strive for greater efficiency and performance, stranded wire is favored for its flexibility, durability, and ability to withstand high amperage loads. Emerging markets in Africa and South America are seeing a surge in infrastructure development, necessitating reliable electrical solutions.
Additionally, technological advancements in manufacturing processes are enhancing the quality and performance of stranded wire, making it a compelling choice for B2B buyers. The trend towards miniaturization in electronics means that more compact and versatile wiring solutions are needed, which stranded wire provides. Moreover, the transition to renewable energy sources is driving demand for stranded wire in solar and wind applications, as these setups often require flexible wiring solutions that can adapt to diverse environmental conditions.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Stranded Wire Industry?
As global awareness of environmental issues grows, sustainability has become a critical factor for B2B buyers in the stranded wire sector. The production of stranded wire can have significant environmental impacts, particularly when it comes to resource extraction and manufacturing processes. Ethical sourcing practices are increasingly prioritized, as companies seek to minimize their carbon footprints and ensure that materials are sourced responsibly.
Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and RoHS for hazardous substances. These certifications indicate a commitment to sustainable practices and can enhance a company’s reputation among environmentally-conscious consumers. Additionally, many manufacturers are exploring the use of recycled materials in stranded wire production, contributing to a circular economy. This trend not only addresses environmental concerns but also appeals to cost-conscious buyers looking for competitive pricing without compromising on quality.
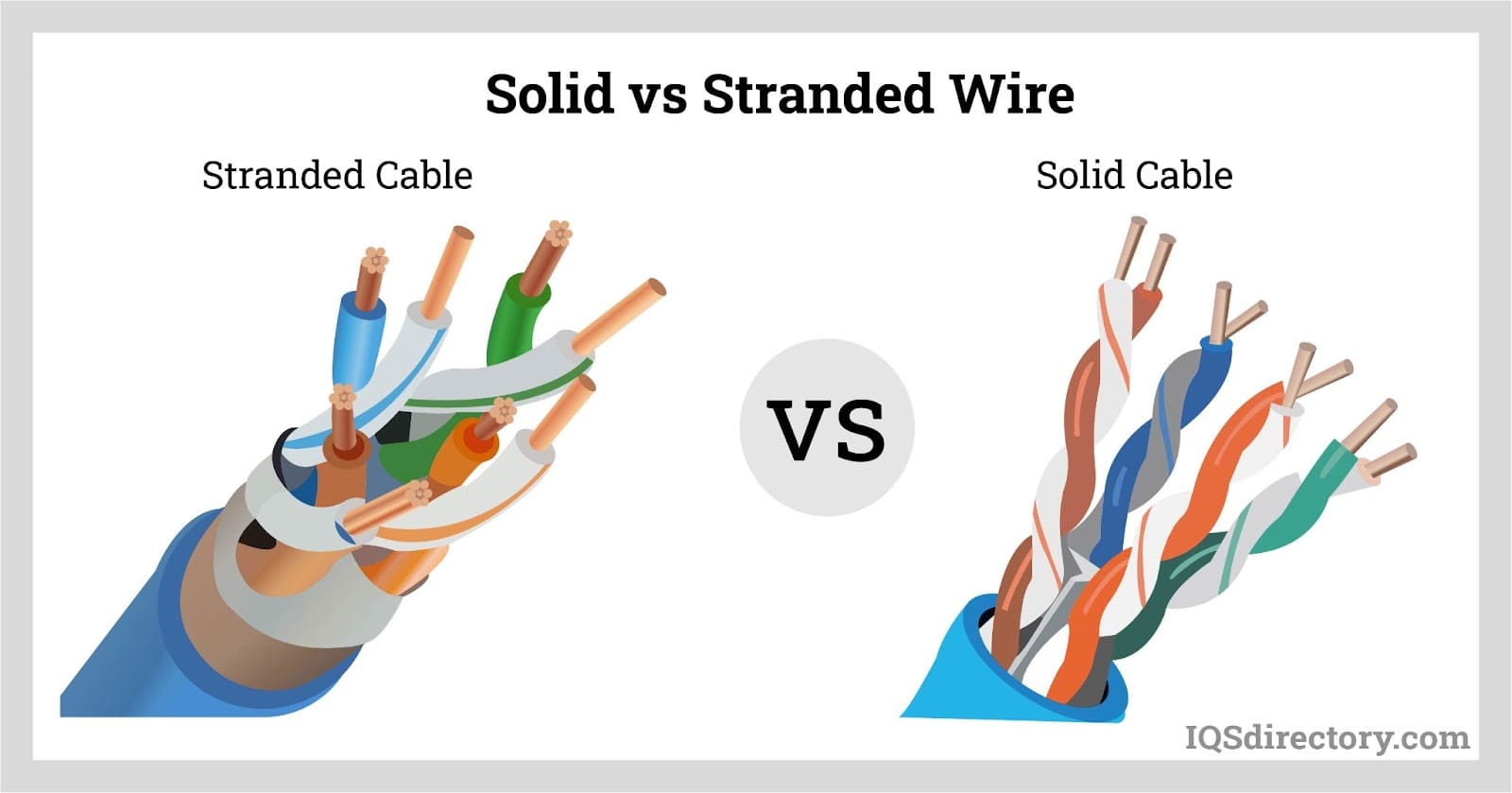
Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
What Is the Evolution of Stranded Wire Technology and Its Relevance Today?
The evolution of stranded wire technology dates back to the early 19th century when electrical systems began to emerge. Initially, solid wire was the standard due to its simplicity and lower production costs. However, as electrical applications became more complex, the need for flexibility and adaptability led to the development of stranded wire, which consists of multiple thinner wires twisted together. This construction allows for greater flexibility and durability, making it suitable for a range of applications, from intricate electronic devices to robust outdoor installations.
Today, stranded wire continues to evolve with advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques. The introduction of high-performance alloys and improved insulation materials has expanded its applications, particularly in high-tech and renewable energy sectors. For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of stranded wire can provide insights into its current capabilities and potential future developments, enabling more informed purchasing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of what is a stranded wire
-
How do I determine if stranded wire is suitable for my application?
To assess if stranded wire meets your needs, consider factors such as flexibility, current capacity, and environmental conditions. Stranded wire is ideal for applications requiring bending and movement, like in electronics or tight spaces. However, if your project demands high current capacity over long distances, solid wire may be preferable. Evaluate the specific requirements of your project, including the wire gauge and metal type, to make an informed decision. -
What are the advantages of using stranded wire over solid wire in electrical applications?
Stranded wire offers several advantages, particularly in terms of flexibility and durability. Its construction of multiple thin strands allows for easier routing around obstacles and better performance in dynamic environments, such as machinery or mobile devices. Additionally, stranded wire tends to resist breaking under stress, making it suitable for applications with vibration or movement. However, it generally has a lower current capacity than solid wire, so consider your specific needs before selecting the type. -
What customization options are available for stranded wire?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for stranded wire, including variations in gauge, strand count, insulation materials, and lengths. Depending on your specific requirements, you may choose specialized insulation for added durability or flexibility. Be sure to communicate your project specifications clearly to potential suppliers, as this will help ensure that you receive a product tailored to your needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for stranded wire?
Minimum order quantities for stranded wire can vary significantly by supplier and the specifics of your order. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred meters to several kilometers, depending on the manufacturer’s production capabilities and the complexity of your customization requests. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to find a partner that can accommodate your desired order size. -
How can I vet suppliers of stranded wire for international trade?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications (ISO, RoHS, CE, etc.) and industry reputation. Look for reviews or testimonials from other B2B clients, especially those in your region, to gauge their reliability. Request samples of stranded wire to assess quality and performance before placing larger orders. Additionally, inquire about their logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery to your location. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing stranded wire internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, often influenced by factors such as order size and relationship with the buyer. Common terms include upfront deposits, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms early in the negotiation process to avoid misunderstandings. Be sure to assess any potential currency exchange risks and consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in stranded wire products?
Quality assurance is crucial when sourcing stranded wire. Look for suppliers that follow strict quality control processes, including material inspections and testing for electrical performance. Certifications such as UL and CE can also indicate compliance with international safety standards. Request documentation of their QA procedures and inquire about warranties or guarantees on their products to ensure you receive reliable wire for your applications. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of stranded wire?
Logistics and shipping play a significant role in the timely delivery of stranded wire. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs requirements based on your location. It’s beneficial to partner with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to navigate potential challenges. Clear communication regarding delivery schedules and tracking can help ensure that your materials arrive on time and in good condition.
Top 6 What Is A Stranded Wire Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Stranded & Braided Wire Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Stranded Wire: Consists of multiple thin wires bundled together, covered with insulating material, enhancing flexibility for tight spaces. Braided Wire: Mesh-like shielding woven around a cable to protect from electromagnetic interference, enhancing mechanical strength. Wire Strands: Wires wound concentrically in a helix, can be made from materials like stainless steel or precious metals. Types of…
2. SparkFun – Wire Types: Solid Core & Stranded Core
Domain: learn.sparkfun.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Wire types: Solid Core and Stranded Core. Solid Core: Composed of a single piece of metal wire, commonly used for prototyping circuits on breadboards and PCB due to ease of insertion. Stranded Core: Composed of multiple pieces of solid wire, offering greater flexibility, suitable for applications requiring movement (e.g., robot arms). Tips for using stranded wire: twist and tin the tips for better…
3. Titan WNC – Stranded Wire Solutions
Domain: titanwnc.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Stranded wire is a type of electrical wire that consists of multiple thin strands of conductive material bundled together to act as a single conductor. Key benefits include: 1. Flexibility: Stranded wire is extremely flexible, allowing for bending and turning without breaking, unlike solid core wire. 2. Inexpensive: Typically costs less than solid core wire due to easier manufacturing processes. 3…
4. Reddit – Solid vs Stranded Wire
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Solid wire is primarily used in the U.S. for electrical installations, while stranded wire is more common in other countries like Germany. Solid wire is preferred for its ease of termination, as it does not have loose strands that can complicate connections. It is also quicker to work with and provides better stability in terminals. Stranded wire, while flexible, can lead to issues such as losing …
5. Scott Precision Wire – Stranded vs Solid Wire
Domain: scottprecisionwire.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Stranded Wire vs Solid Wire: Stranded wire is more flexible, can withstand thermal expansion, but is more expensive and harder to terminate. Solid wire is cheaper, easier to terminate, and fits neatly in panels, but is less flexible and suitable only for fixed installations. Both types can be used for thermocouple and resistance wires.
6. AWC Wire – MIL-Spec Conductor Stranding Products
Domain: awcwire.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Conductor Stranding includes various MIL-Spec products such as M22759, M25038, M5086, M81044, M81381, M85485, and others. Specific part numbers include M22759 – Raychem Spec 44 (44A0111, 44A0112, 44A0114, etc.), M22759 – Raychem Spec 55 (55A0111, 55A0112, 55A0113, etc.), M25038 (M25038/1, M25038/3), M5086 (M5086/1, M5086/2, etc.), and M81044 (M81044/10, M81044/11, etc.). Additional categories incl…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for what is a stranded wire
In the evolving landscape of electrical applications, understanding the unique characteristics of stranded wire is vital for strategic sourcing decisions. Stranded wire, composed of multiple thinner strands, offers unparalleled flexibility, making it ideal for complex installations and environments requiring frequent movement. This adaptability allows for efficient routing in tight spaces, essential for modern electronic devices and intricate circuit designs. However, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits against potential drawbacks, such as higher costs and lower current capacity compared to solid wire.
Illustrative image related to what is a stranded wire
As international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate sourcing strategies, recognizing the specific needs of their applications will enhance decision-making. Prioritizing quality and reliability in suppliers can lead to long-term partnerships that not only meet immediate project demands but also foster innovation and growth.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced electrical solutions will only increase. Buyers are encouraged to engage with reputable manufacturers who can provide tailored solutions, ensuring that their projects are supported by the best materials available. By doing so, they can position themselves at the forefront of industry advancements while maximizing the value of their investments.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.