Everything You Need to Know About Types Of Plug In Cords Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of plug in cords
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing the right types of plug-in cords can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying electrical standards and plug configurations, ensuring compatibility and safety while selecting power cords for your devices is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad types of plug-in cords available, their specific applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting and cost analysis.
By exploring various power cord types—including NEMA, IEC, and CEE standards—this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance operational efficiency. You’ll gain insights into the unique features and functionalities of each cord type, helping you choose solutions tailored to your specific needs. Moreover, understanding the regional variations in plug types will assist in navigating the complexities of international procurement and logistics.
Ultimately, this resource aims to equip B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to confidently select the right power cords, ensuring both functionality and safety for their electronic devices. Whether you are setting up a new facility or upgrading existing equipment, our guide serves as an invaluable tool for optimizing your sourcing strategy in a global marketplace.
Understanding types of plug in cords Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA Power Cords | Flat blade connectors; various amperage ratings | Home appliances, HVAC systems, industrial equipment | Pros: Wide availability; reliable performance; Cons: Limited to North America. |
| IEC Power Cords | Standardized connectors (e.g., C13, C19); versatile | Computers, servers, telecommunications | Pros: Global compatibility; safe design; Cons: Can be less robust for heavy-duty applications. |
| CEE Power Cords | Robust design; higher voltage ratings; waterproof options | Industrial machinery, commercial equipment | Pros: Durable; suitable for harsh environments; Cons: Bulkier and may require specific installations. |
| Schuko Plugs | Round pins; grounding feature; high safety standards | European appliances, power tools | Pros: High safety; widely used in Europe; Cons: May need adapters for non-European devices. |
| BS 1363 Plugs | Three rectangular pins; fused for safety | UK appliances, consumer electronics | Pros: Enhanced safety features; standardized in the UK; Cons: Limited to UK and some former colonies. |
What Are NEMA Power Cords and Their B2B Relevance?
NEMA power cords are designed primarily for North American usage, featuring flat blade connectors that come in various configurations based on amperage and voltage requirements. They are commonly found in home appliances, HVAC systems, and industrial equipment. When purchasing NEMA cords, businesses should consider the specific amperage ratings and ensure compatibility with their devices. Their widespread availability makes them a reliable choice, but they may not be suitable for international applications due to their regional limitations.
How Do IEC Power Cords Function in Global Markets?
IEC power cords adhere to international standards, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, particularly in electronics like computers and servers. These cords feature standardized connectors such as C13 and C19, allowing for easy compatibility across different devices and regions. B2B buyers should prioritize IEC cords for their versatility and safety features, especially when dealing with international clients. However, businesses should note that while IEC cords are safe, they may not be robust enough for high-power industrial applications.
What Makes CEE Power Cords Ideal for Industrial Use?
CEE power cords are specifically designed for high-voltage and high-amperage applications, making them ideal for industrial machinery and commercial equipment. They often feature robust designs that include waterproof and dustproof capabilities, ensuring performance in harsh environments. When sourcing CEE cords, businesses should evaluate the specific voltage and amperage requirements of their equipment. While these cords are durable, they are bulkier and may require specialized installation, which could increase overall costs.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
Why Are Schuko Plugs Essential for European Operations?
Schuko plugs are characterized by their round pins and grounding features, providing enhanced safety for electrical connections. They are widely used across Europe for appliances and power tools, making them essential for businesses operating in this region. B2B buyers should consider Schuko plugs for their high safety standards and compatibility with a variety of devices. However, companies outside of Europe may need to invest in adapters to accommodate these plugs, potentially complicating logistics.
How Do BS 1363 Plugs Enhance Safety in the UK Market?
BS 1363 plugs, known for their three rectangular pins and built-in fuse, are the standard in the UK and provide enhanced safety for electrical devices. They are commonly used for consumer electronics and household appliances. For businesses operating in the UK or supplying products to this market, understanding the specifications and safety features of BS 1363 plugs is crucial. While they offer significant safety benefits, their use is largely restricted to the UK and some former colonies, which may limit their applicability in global markets.
Key Industrial Applications of types of plug in cords
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of plug in cords | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering machinery and equipment | Ensures operational efficiency and minimizes downtime | Voltage ratings, durability, and compatibility with equipment |
| Information Technology | Connecting servers and data center equipment | Enhances data reliability and performance | IEC compliance, cord length, and heat resistance |
| Construction | Powering tools and temporary lighting setups | Increases productivity and safety on job sites | Weatherproofing, length, and amperage ratings |
| Healthcare | Connecting medical devices and diagnostic equipment | Ensures patient safety and equipment reliability | Compliance with safety standards and cord flexibility |
| Hospitality | Powering appliances and entertainment systems in hotels | Improves guest experience and operational reliability | Aesthetic design, cord length, and electrical capacity |
How Are Types of Plug-in Cords Utilized in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, types of plug-in cords are crucial for powering various machinery and equipment, ranging from assembly lines to heavy-duty tools. These cords must meet specific voltage ratings and durability standards to ensure that they can withstand the rigorous demands of industrial environments. International buyers, especially those in Africa and South America, need to consider the compatibility of these cords with local electrical standards to avoid operational disruptions. Additionally, durability against wear and tear is vital to minimize downtime and maintenance costs.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
What Role Do Plug-in Cords Play in Information Technology?
In the information technology sector, plug-in cords are essential for connecting servers and various data center equipment. The reliability of these connections directly impacts data integrity and system performance. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize IEC-compliant cords to ensure compatibility with global standards. Furthermore, factors such as cord length and heat resistance are critical, especially in high-density server environments, where overheating can lead to equipment failure and data loss.
How Are Plug-in Cords Used on Construction Sites?
In the construction industry, plug-in cords power tools and provide temporary lighting setups. These cords must be robust and weatherproof to withstand the challenging conditions often found on job sites. For international buyers, especially those in regions with extreme weather, sourcing cords that meet local safety regulations and have appropriate amperage ratings is essential. The use of high-quality cords not only enhances productivity but also ensures the safety of workers by reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
Why Are Plug-in Cords Important in Healthcare?
In healthcare settings, plug-in cords are vital for connecting medical devices and diagnostic equipment. The reliability of these cords is paramount, as any failure can jeopardize patient safety. Buyers in the healthcare sector must ensure that cords comply with stringent safety standards and are flexible enough to accommodate various medical setups. Additionally, sourcing cords that can withstand sterilization processes and have a minimal risk of electrical interference is crucial for maintaining the integrity of medical equipment.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
How Do Plug-in Cords Enhance Hospitality Services?
In the hospitality industry, plug-in cords are used to power appliances and entertainment systems, significantly enhancing the guest experience. Hotels and resorts must consider both functionality and aesthetics when sourcing these cords. International buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, should focus on cord length and electrical capacity to accommodate diverse room layouts and guest needs. Ensuring that these cords are reliable and visually appealing can lead to improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘types of plug in cords’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Incompatibility Issues with Power Cords
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the electronics manufacturing sector faces significant challenges when dealing with various power cords for their products. They often find that the power cords they source do not match the specifications of their devices, leading to compatibility issues. This situation not only causes production delays but also increases costs as they have to reorder the correct cords. Additionally, in international markets, differing standards for plugs and sockets can complicate the sourcing process, causing frustration and potential loss of sales opportunities.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of the power cord specifications required for their products. This involves understanding the type of plugs and sockets that will be used in their target markets. A detailed analysis should include voltage ratings, amperage requirements, and regional plug standards such as NEMA for North America or IEC for Europe. Once the specifications are clear, buyers should partner with reputable suppliers who specialize in international standards and can provide a range of compatible power cords. Utilizing tools like compatibility charts can streamline the selection process and ensure that the correct cords are sourced, thus avoiding costly reorders and delays.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns with Electrical Equipment
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the industrial equipment sector is concerned about the safety of their machinery and electronic devices that rely on power cords. They recognize that using cords that do not meet safety standards can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or even equipment damage. This concern is particularly pronounced when working in regions with varying electrical regulations, such as in parts of Africa and South America, where standards may not be well enforced.
The Solution: To address safety concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing power cords that are UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certified or equivalent, ensuring that the cords have passed rigorous safety tests. Additionally, it’s essential to implement a regular inspection and maintenance program for all power cords used in their equipment. This program should include checks for wear and tear, frayed wires, and proper installation. Buyers can also invest in training for their staff on the importance of using the right cords and following safety protocols, which can further mitigate risks associated with electrical equipment.
Scenario 3: Durability Challenges in Harsh Environments
The Problem: A B2B buyer in the construction industry often encounters power cords that fail prematurely due to harsh working conditions, such as exposure to moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. This durability issue leads to frequent replacements, resulting in increased operational costs and downtime, which can significantly impact project timelines and budgets.
The Solution: To combat durability challenges, buyers should consider investing in heavy-duty power cords specifically designed for tough environments. These cords often feature reinforced insulation, weatherproofing, and robust connectors that can withstand extreme conditions. When sourcing these cords, buyers should look for products that meet industry standards for durability and environmental resistance, such as those rated for outdoor use or those with IP (Ingress Protection) ratings. Additionally, creating a procurement strategy that includes a variety of cord types tailored to different environmental conditions will ensure that the right products are available when needed, minimizing downtime and replacement costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of plug in cords
When selecting materials for plug-in cords, B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Here’s an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of power cords, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international markets.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
What Are the Key Properties of PVC in Plug-In Cords?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used materials in power cord insulation and sheathing. It offers excellent electrical insulation properties and is resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and moisture. PVC can typically withstand temperatures ranging from -10°C to 70°C, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, leading to lower production costs. However, it has a lower thermal resistance compared to other materials, which can limit its use in high-temperature applications. Additionally, PVC can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light, which may affect its longevity.
Impact on Application: PVC is compatible with a wide range of devices, including household appliances and consumer electronics. However, its limitations in high-temperature environments may restrict its use in industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that PVC cords comply with local safety standards, such as ASTM in the U.S. and IEC in Europe.
How Does Rubber Compare for Power Cord Applications?
Rubber is another common material for power cords, particularly in environments where flexibility and durability are paramount. It offers excellent resistance to heat, moisture, and abrasion, with temperature ratings typically between -40°C to 90°C.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
Pros & Cons: The flexibility of rubber makes it ideal for applications requiring frequent movement, such as tools and outdoor equipment. However, rubber can be more expensive than PVC and may complicate manufacturing processes due to its varying properties.
Impact on Application: Rubber is particularly suitable for heavy-duty applications and environments where cords are exposed to harsh conditions, such as construction sites. Its resistance to environmental factors enhances the longevity of the cords.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like EN 50525 in Europe and JIS in Japan. The higher cost may be justified in applications requiring increased durability.
What Are the Advantages of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) in Power Cords?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) combine the properties of rubber and plastic, offering flexibility, durability, and excellent resistance to extreme temperatures (-50°C to 105°C). TPE is also lightweight, making it easier to handle and install.
Pros & Cons: TPE provides superior performance in terms of flexibility and resistance to environmental stressors. However, it is generally more expensive than PVC and rubber, which may deter cost-sensitive buyers.
Impact on Application: TPE is ideal for applications requiring high flexibility and durability, such as medical devices and high-performance electronics. Its versatility allows for a wide range of uses across different sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should ensure that TPE products meet relevant safety and environmental regulations, such as REACH in Europe.
Why Is Polyethylene (PE) a Viable Option for Power Cords?
Polyethylene (PE) is often used as an insulating material for power cords due to its excellent electrical properties and resistance to moisture. It can typically handle temperatures from -40°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons: PE is lightweight and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for low-voltage applications. However, it is less flexible than rubber and may not perform well in extreme temperature conditions.
Impact on Application: PE is suitable for applications such as low-voltage lighting and consumer electronics. Its moisture resistance makes it ideal for indoor use but may limit its effectiveness outdoors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that PE cords comply with local standards, such as DIN in Germany and other relevant regional certifications.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
Summary Table of Material Selection for Plug-In Cords
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of plug in cords | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Household appliances, consumer electronics | Cost-effective and good insulation | Lower thermal resistance, UV sensitivity | Low |
| Rubber | Heavy-duty tools, outdoor equipment | Excellent flexibility and durability | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Med |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Medical devices, high-performance electronics | Superior flexibility and environmental resistance | Higher cost compared to PVC and rubber | High |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Low-voltage lighting, indoor electronics | Lightweight and moisture-resistant | Less flexibility, limited outdoor use | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in plug-in cords, equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of plug in cords
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Plug-In Cords?
The manufacturing of plug-in cords is a meticulous process that involves several stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets safety and performance standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the quality and reliability of their suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing plug-in cords is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality raw materials such as copper for conductors, PVC or thermoplastic rubber for insulation, and various types of plastics for plugs. Suppliers must ensure that these materials meet international standards for electrical safety and environmental regulations.
Conducting tests on raw materials, such as electrical conductivity and thermal resistance, is essential before they enter the production line. B2B buyers should inquire about the suppliers’ material sourcing practices and whether they adhere to sustainability standards.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This typically includes:
- Wire Drawing: Copper wires are drawn to the required gauge, ensuring they can handle the necessary electrical load without overheating.
- Insulation: The wires are coated with insulating materials to prevent electrical leakage and short circuits. This process often uses extrusion techniques to apply a uniform layer of insulation.
- Plug Manufacturing: The plastic components of the plugs are molded using injection molding techniques. This step is crucial, as the quality of the plug affects the overall safety and functionality of the cord.
In this stage, B2B buyers should verify that suppliers utilize advanced machinery and techniques to ensure consistency and precision in forming.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves connecting the insulated wires to the plug and socket components. This process can include:
- Crimping: For secure connections, wires are crimped into the plug terminals, ensuring a robust electrical connection.
- Soldering: In some cases, soldering may be used to connect wires to terminals, particularly in high-performance applications.
- Testing Connections: After assembly, electrical testing is often performed to ensure that connections are secure and functioning correctly.
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that have automated assembly lines equipped with quality control systems to minimize human error.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes such as:
- Visual Inspection: Cords are inspected for any physical defects, such as fraying or improper insulation.
- Marking and Labeling: Cords are labeled according to international standards, indicating voltage ratings, certifications, and safety warnings.
- Packaging: Proper packaging is essential for protecting cords during transportation and storage.
Buyers should inquire about the finishing processes to ensure that all safety and branding requirements are met.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
What Are the International Standards and Quality Assurance Practices for Plug-In Cords?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of plug-in cords, ensuring that products are safe, reliable, and compliant with international standards. Here are some key aspects of quality assurance relevant to B2B buyers.
ISO 9001: What Does It Mean for Quality Management?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems (QMS). Manufacturers of plug-in cords that adhere to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to quality through consistent processes, effective management, and continuous improvement. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification, as it provides assurance of their commitment to quality.
CE Marking and Other Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to ISO 9001, many plug-in cords require compliance with specific regional standards, such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
Other certifications to consider include:
- UL Certification: In the U.S., Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification signifies that the product has been tested for safety and performance.
- RoHS Compliance: Ensures that electrical products are free from hazardous substances, which is crucial for environmental safety.
Understanding these certifications helps B2B buyers assess the compliance and safety of their suppliers’ products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Plug-In Cord Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, involving several checkpoints to ensure that products meet specified standards.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC focuses on the inspection of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers should perform tests on materials, including:
- Electrical Conductivity Tests: Ensuring materials meet required conductivity standards.
- Material Integrity Tests: Checking for any physical defects in raw materials.
B2B buyers can request documentation of IQC results to verify material quality.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring production stages to catch defects early. Key activities include:
- Routine Inspections: Regular checks of assembly lines to ensure processes are followed correctly.
- Testing Equipment Calibration: Regular checks to ensure all testing equipment is calibrated and functioning accurately.
B2B buyers should ask about the IPQC practices of their suppliers to ensure that they maintain high-quality standards throughout production.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC occurs at the end of the manufacturing process. This stage typically includes:
- Functional Testing: Each cord is tested for electrical performance, ensuring it meets voltage and amperage specifications.
- Visual Inspections: Final inspections for physical defects, ensuring that products are free from flaws.
Buyers should request FQC reports from suppliers to confirm that the products meet quality and safety standards before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control practices, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to share detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several nuances to consider regarding quality control and certification:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have unique safety and quality requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to avoid compliance issues.
- Cultural Differences: Communication and expectations regarding quality may vary by region. Buyers should establish clear guidelines and expectations with suppliers to ensure alignment.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Importing products may involve additional certifications or inspections. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to navigate these complexities effectively.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for plug-in cords, ensuring that they receive high-quality, reliable products that meet their needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘types of plug in cords’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers focused on sourcing various types of plug-in cords. Understanding the specifications and requirements for power cords is essential to ensure safety, compatibility, and optimal performance in your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search for plug-in cords, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your applications. This includes voltage ratings, amperage, and the type of connectors needed. Ensure you understand the environmental conditions, such as temperature or moisture levels, that the cords must withstand.
- Voltage and Amperage Requirements: Identify the maximum voltage and current that your devices will use to prevent overheating or electrical failures.
- Connector Types: Determine whether you need NEMA, IEC, or CEE connectors based on your equipment and regional requirements.
Step 2: Research Regional Standards and Compliance
Different regions have unique electrical standards that must be adhered to when sourcing power cords. Familiarize yourself with the regulations in the countries where your products will be used.
- Safety Certifications: Look for cords that meet international safety standards, such as UL or CE certifications, to ensure they comply with local regulations.
- Plug Types: Understand the plug types prevalent in your target markets to avoid compatibility issues.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specific needs. Request comprehensive company profiles, product catalogs, and customer references.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
- Supplier Background: Investigate their experience in the industry and their reputation among other B2B buyers.
- Product Quality: Ask for samples to assess the quality of their cords, including durability and insulation.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Be sure to understand their payment terms, including any potential discounts for bulk orders.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure there are no hidden costs that could affect your overall budget.
- Bulk Order Discounts: Inquire about pricing tiers for large orders, which can significantly reduce costs.
Step 5: Assess Lead Times and Delivery Options
Understanding lead times is crucial for planning your inventory and project timelines. Confirm how long it will take for the supplier to fulfill your order and what shipping options are available.
- Production Time: Ask for the average production time based on your order size and specifications.
- Shipping Methods: Evaluate shipping options to ensure timely delivery, particularly if you have tight deadlines.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Warranty
After securing a supplier, ensure they offer robust after-sales support and warranty options. This will protect your investment and provide peace of mind.
- Support Channels: Confirm the availability of support through various channels such as email, phone, or chat.
- Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty coverage for defects or issues, which can save costs in the long run.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Maintain Communication
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize your order while maintaining open communication throughout the process. This helps in addressing any last-minute changes or questions.
- Order Confirmation: Request a written confirmation detailing your order, including specifications and delivery dates.
- Regular Updates: Stay in touch with the supplier to receive updates on production and shipping status, ensuring a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing plug-in cords, ensuring compatibility, safety, and reliability for their operations.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of plug in cords Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of plug-in cords is essential for international B2B buyers looking to source these products effectively. The cost components involved in manufacturing plug-in cords include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins. Each of these components significantly impacts the final pricing of the cords.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Plug-in Cords?
-
Materials: The primary materials used in plug-in cords include copper for conductors, PVC or rubber for insulation, and various plastics for the casing. The choice of materials can vary based on specifications like voltage and environmental resistance, affecting the overall cost. For example, cords designed for high-temperature environments will use more expensive materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and Southeast Asia, manufacturing may be cheaper. However, labor costs can increase in regions with higher wages, impacting pricing for buyers in Europe and North America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses such as factory rent, utilities, and administrative salaries. These costs are typically distributed across all products manufactured, influencing the per-unit cost of plug-in cords.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for molds and production setups can be substantial, particularly for customized or specialized cords. Buyers seeking unique designs or specifications may face higher upfront costs that are amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring safety and compliance with international standards (such as UL, CE, or IEC certifications) requires rigorous testing and inspection, adding to the overall cost. Buyers should consider the impact of quality assurance on long-term reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, particularly for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and import duties can significantly affect the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market conditions. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the uniqueness of the product.
What Influences the Pricing of Plug-in Cords?
Several factors influence the pricing of plug-in cords, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer better pricing for larger orders. Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary, and negotiating these terms can lead to cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed cords or those with specific technical requirements (like increased amperage or unique plug types) will generally incur higher costs. Standardized products typically offer better pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can lead to increased prices. However, investing in certified products often results in better safety and reliability, ultimately reducing the total cost of ownership.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for calculating total costs. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact the final price and risk associated with shipping.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs?
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if you are ordering in bulk. Leverage your position as a potential long-term customer to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Cheaper cords may save money upfront but could lead to higher costs due to failures or replacements.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Buyers from different regions may face varying costs due to local economic conditions and supply chain logistics. Researching local market conditions can provide insights into competitive pricing.
-
Evaluate Quality vs. Cost: While lower-priced options may be tempting, prioritize quality to ensure safety and compliance with standards. Investing in higher-quality cords can prevent costly issues down the line.
-
Stay Informed About Global Trends: Market fluctuations in materials, labor, and shipping can impact pricing. Keeping abreast of these trends can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
By understanding the complex cost structure and pricing dynamics associated with plug-in cords, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that balance quality, safety, and cost-efficiency. As international trade continues to evolve, adapting to these factors will be essential for successful procurement strategies.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing types of plug in cords With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Types of Plug-In Cords
In the realm of electrical connectivity, plug-in cords are a standard solution for powering devices. However, as technology evolves, various alternatives have emerged that may better suit specific applications or environments. This analysis provides a comparative look at traditional plug-in cords and alternative solutions, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Types of Plug-In Cords | Wireless Power Transfer | Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable and stable for electrical devices | Limited by distance and interference | Effective for low-power devices |
| Cost | Variable based on type and quality | High initial setup cost | Moderate installation costs, lower than wireless |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple plug-and-play installation | Complex setup requiring specialized equipment | Requires compatible devices and infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Minimal upkeep; replace damaged cords | Minimal, but technology may require updates | Low; mainly network management |
| Best Use Case | Household appliances, industrial equipment | Charging mobile devices, powering wearables | IP cameras, VoIP phones, and network devices |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Wireless Power Transfer
Wireless power transfer (WPT) technology allows devices to receive power without physical connections. This method is particularly useful for charging mobile devices and powering small electronics.
Pros: WPT eliminates cord clutter and enhances mobility, making it ideal for consumer electronics and environments where physical connections are impractical. It also reduces wear and tear on connectors.
Cons: The technology can be limited by distance and may suffer from efficiency losses due to interference from physical objects or electronic devices. Additionally, the initial setup cost can be significant, as it requires specialized transmitters and receivers.
2. Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology enables electrical power and data to be transmitted simultaneously over standard Ethernet cables. This solution is commonly utilized in network devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points.
Pros: PoE simplifies installations by reducing the need for separate power cables, making it cost-effective for businesses that require numerous devices in a single location. It also facilitates easy reconfiguration of network setups.
Cons: While PoE is efficient for low-power devices, it may not be suitable for high-energy appliances. Additionally, the need for compatible devices and infrastructure can be a limiting factor for some organizations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the most appropriate solution for powering devices, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific operational requirements. Plug-in cords remain a reliable choice for a wide range of applications, especially in environments requiring high power and stability. However, alternatives like wireless power transfer and Power over Ethernet can provide innovative solutions for specific use cases, such as mobility and integrated network systems. By assessing performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance needs, buyers can make informed decisions that best align with their organizational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of plug in cords
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Plug-In Cords?
Understanding the technical properties of plug-in cords is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility, safety, and performance. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material of the cord insulation and conductors plays a significant role in durability and safety. Common materials include PVC, rubber, and silicone. High-grade materials resist heat, moisture, and abrasion, making them suitable for various environments. This is particularly important for businesses operating in harsh conditions, as inferior materials can lead to failures and safety hazards.
2. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the cord can safely handle. For instance, cords rated for 125V are suitable for North American appliances, while those rated for 250V are more common in Europe and Asia. Ensuring that the voltage rating matches the application is critical to prevent overheating and electrical fires.
3. Amperage Rating
The amperage rating reflects the maximum current the cord can carry without overheating. This is essential for ensuring that the power supply meets the demands of the connected device. Using cords with inadequate amperage ratings can lead to circuit failures or damage to equipment, impacting operational efficiency.
4. Cord Length and Thickness
Cord length affects the placement of devices and the potential for voltage drop, while thickness (gauge) influences the amount of current the cord can safely carry. Thicker cords are generally more durable and can handle higher loads. Buyers should assess their specific needs to select the appropriate cord length and thickness for their applications.
5. Temperature Rating
The temperature rating indicates the maximum environment temperature the cord can withstand. This is particularly relevant for industrial applications where cords may be exposed to extreme heat or cold. Choosing cords with appropriate temperature ratings ensures that they function safely and effectively under varying conditions.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Plug-In Cords?
Familiarity with industry terminology helps streamline communication and negotiation processes. Here are several key terms relevant to plug-in cords:

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that can be rebranded and sold by other companies. In the context of power cords, buyers may source cords from OEMs who provide customized solutions tailored to specific needs, ensuring compatibility with their devices.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers, as it can impact inventory management and cost efficiency. Negotiating lower MOQs can be beneficial for smaller companies or those testing new products.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple vendors, thereby facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs associated with importing power cords from various regions.
5. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne), indicate that a product meets specific safety and performance criteria. For B2B buyers, sourcing certified power cords ensures compliance with regulations and enhances product reliability.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring the selection of appropriate plug-in cords that meet their operational needs while maintaining safety and efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the types of plug in cords Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Types of Plug-In Cords Sector?
The global market for plug-in cords is shaped by several dynamic factors, particularly relevant for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One primary driver is the increasing demand for consumer electronics and smart devices, necessitating a diverse range of power cords. As technology advances, the trend towards higher power requirements and compatibility across various devices is evident, leading to innovations in cord designs that accommodate multiple voltages and amperages.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on interoperability among international plug types due to globalization and cross-border trade. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking products that comply with international standards, such as NEMA and IEC, to ensure compatibility across different markets. This trend is particularly significant for buyers in emerging markets who are looking to import technology that meets regional electrical regulations.
Another emerging trend is the rise of smart power solutions, including cords with integrated smart technology for energy efficiency and monitoring capabilities. The proliferation of renewable energy sources is also influencing the types of cords in demand, as industries pivot towards sustainable energy solutions.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Plug-In Cords?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers in the plug-in cords sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including the use of toxic materials and non-biodegradable components, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint, which includes using recyclable materials and minimizing waste during production.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are gaining traction as consumers demand greater transparency. Businesses that source plug-in cords from suppliers with fair labor practices and responsible sourcing are likely to build stronger reputations and customer loyalty. Certifications such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) are increasingly important, as they signal compliance with environmental standards and commitments to sustainability.

Illustrative image related to types of plug in cords
In addition, the industry is seeing a rise in eco-friendly materials such as bio-based plastics and recycled metals, which not only reduce environmental impact but also appeal to eco-conscious buyers. As these trends continue to evolve, B2B buyers must remain vigilant in selecting partners that align with their sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Plug-In Cords in the B2B Sector?
The evolution of plug-in cords has been significantly influenced by technological advancements and regulatory changes over the years. Initially, the development of power cords was driven by the need for basic electrical connectivity, primarily for household appliances. As the demand for electronics surged in the latter half of the 20th century, the industry responded with a wider variety of plug types and standards.
The standardization of power cords began in earnest with organizations like the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) establishing guidelines to ensure safety and compatibility. This led to the creation of various plug types that catered to specific regional needs, facilitating international trade and the growth of the electronics market.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing safety and efficiency, with innovations aimed at reducing energy consumption and improving user experience. The historical trajectory of plug-in cords highlights a continuous adaptation to changing market demands, regulatory requirements, and technological advancements, underscoring the importance of understanding these dynamics for today’s B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of plug in cords
-
How do I choose the right power cord for my devices?
To choose the right power cord, consider the device’s voltage and amperage requirements. Review the specifications to ensure compatibility with regional standards, like NEMA in North America or IEC globally. Assess the cord length and thickness, which affect its durability and suitability for your environment. For high-demand applications, opt for cords with reinforced insulation to prevent wear and overheating. Consulting product datasheets and working with reliable suppliers can further ensure you select the appropriate cords. -
What is the best power cord type for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, CEE power cords are often the best choice due to their robustness and ability to handle higher voltages (up to 400 volts). They are designed for heavy-duty use in harsh environments, making them ideal for machinery and equipment in manufacturing settings. Additionally, IEC power cords can be suitable for various industrial devices, particularly in IT and telecommunications. When selecting a cord, consider the specific power requirements and environmental conditions of your operations. -
How can I ensure the quality of the power cords I am sourcing?
To ensure the quality of power cords, request certifications such as UL or CE, which indicate compliance with safety standards. Conduct thorough supplier vetting by checking their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Request samples for testing before bulk orders, and consider visiting the supplier’s facility if feasible. Engaging third-party inspection services can provide additional assurance of product quality, especially for large orders. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing power cords?
When sourcing power cords, consider customization options such as length, connector types, and insulation materials. Different industries may require specific connectors or cord configurations to ensure compatibility with their equipment. Additionally, inquire about branding options, such as adding your logo or specific color coding for identification. Discussing these options with suppliers can help meet your specific operational needs and enhance your brand visibility. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power cords in international trade?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power cords can vary significantly depending on the supplier and cord specifications. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units. It’s essential to communicate your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are testing a new product line. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for customized products, while others might require larger orders for standard items to maintain cost-effectiveness. -
What payment terms are common for B2B transactions involving power cords?
Common payment terms in B2B transactions for power cords often include options like a 30% deposit upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 payment terms, allowing businesses to manage cash flow more effectively. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your financial capabilities and establish trust with the supplier. Using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit, can also mitigate risks. -
How do logistics impact the sourcing of power cords internationally?
Logistics play a crucial role in the international sourcing of power cords. Factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations can significantly affect delivery schedules and costs. Working with suppliers who have experience in international shipping can help streamline the process. Additionally, consider the location of your supplier and their ability to provide reliable shipping options to your region, which can minimize delays and ensure timely product availability. -
What are the key safety standards I should look for in power cords?
When sourcing power cords, look for compliance with international safety standards such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) for North America and CE (Conformité Européenne) for Europe. These certifications ensure that the cords have been tested for safety and performance. Additionally, consider cords that meet IEC standards for global compatibility. Understanding the specific regulations in your target market can help ensure that the products you import are safe and compliant, reducing liability risks.
Top 5 Types Of Plug In Cords Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Volex – Electrical Plug Types
Domain: volex.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Volex offers a range of electrical plug types including A, B, C, D, E, F, F/G, G, H, I, J, K, L, and N. These plugs are designed for compatibility with various country sockets and meet specific current and voltage ratings. Each plug type has unique designations such as NEMA 1-15P, NEMA 5-15P, Class 1, Class 2, and others. Volex plugs are used in a variety of applications including business IT peri…
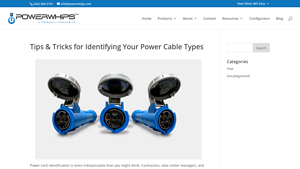
2. PowerWhips – Essential Power Cord Types
Domain: powerwhips.com
Introduction: Power cord types include NEMA 1-15P (two-pronged plugs), NEMA 5-15P (three-prong plugs), NEMA 1-15R (two-hole receptacles), and NEMA 5-15R (three-prong receptacles). Tips for identification include inspecting the number of prongs, checking receptacles, and labeling cords for organization.
3. IQS Directory – Power Cords
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Power cords, also known as line cords or power cables, are used to connect electronic devices to power sources, facilitating electricity transmission. They typically consist of copper wires insulated and protected by non-conductive materials. Power cords can be categorized into basic power cords (plug at one end, bare wires at the other) and connector power cords (connector at one end, wires at th…
4. IEC – Global Plug Guide
Domain: iec.ch
Introduction: World plugs provide information on various plug and socket types used globally. Users can explore by selecting a location, electric potential, or frequency to discover the corresponding plug types, voltage, and frequency utilized in that area. The resource is aimed at seasoned travelers and those needing practical information about electrical standards worldwide.
5. World Standards – Electrical Plug Types
Domain: worldstandards.eu
Introduction: [{‘type’: ‘A’, ‘usage’: ‘USA, Canada, Mexico, Japan’, ‘pins’: ‘2’, ‘grounded’: ‘not grounded’, ‘current’: ’15 A’, ‘voltage’: ‘100 – 127 V’}, {‘type’: ‘B’, ‘usage’: ‘USA, Canada, Mexico’, ‘pins’: ‘3’, ‘grounded’: ‘grounded’, ‘current’: ’15 A’, ‘voltage’: ‘100 – 127 V’}, {‘type’: ‘C’, ‘usage’: ‘Europe, Africa, South America, Asia’, ‘pins’: ‘2’, ‘grounded’: ‘not grounded’, ‘current’: ‘2.5 A, 10 A & 1…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of plug in cords
In the evolving landscape of global commerce, understanding the diverse types of plug-in cords is essential for effective strategic sourcing. By familiarizing yourself with NEMA, IEC, and CEE standards, you can ensure compatibility and safety for your electrical devices, minimizing risks and enhancing functionality. Moreover, recognizing regional variations in plug types enables you to make informed purchasing decisions that can optimize supply chains and reduce costs.
As B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, prioritizing the right power cord types is not just about compliance; it’s a strategic move to ensure operational efficiency and reliability. Emphasizing quality and durability in your sourcing strategies can lead to long-term partnerships with suppliers who understand your unique regional needs.
Looking ahead, the demand for safe, efficient, and versatile power solutions will only increase as technology advances. We encourage you to leverage this guide to refine your sourcing approach and explore high-quality options that align with your business goals. Together, let’s power the future of your enterprise with confidence.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.