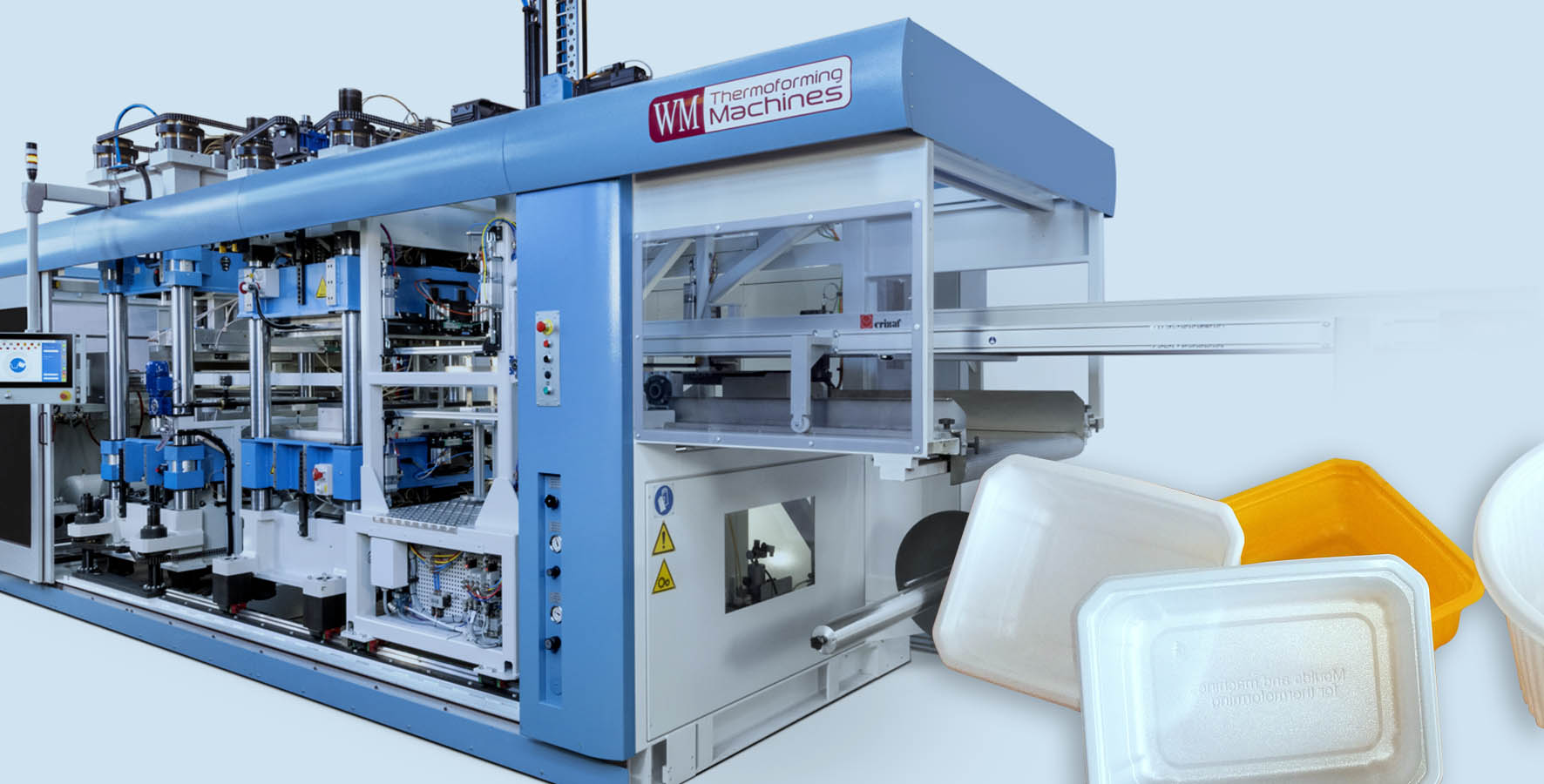
Everything You Need to Know About Thermoforming Machine Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thermoforming machine
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, sourcing the right thermoforming machine can be a daunting task for B2B buyers across the globe. The challenge lies not only in identifying the most suitable machine for specific applications, such as packaging or automotive components, but also in navigating a market filled with diverse options and varying supplier capabilities. This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Brazil and Germany.
We delve into the various types of thermoforming machines, including desktop, floor-standing, and fully automatic models, highlighting their distinct applications and advantages. Furthermore, we provide insights into supplier vetting processes, enabling buyers to assess reliability and quality effectively. Cost considerations are also meticulously outlined, ensuring that buyers can make informed financial decisions that align with their operational needs.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and a detailed understanding of the thermoforming machine market, this guide empowers them to streamline their procurement processes. Ultimately, our goal is to facilitate smarter purchasing decisions that lead to enhanced productivity and innovation in their respective industries.
Understanding thermoforming machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop Thermoforming Machines | Compact design, ideal for small-scale production, easy to use | Prototyping, arts & crafts, small product lines | Pros: Affordable, space-efficient; Cons: Limited production capacity. |
| Floor-Standing Thermoforming Machines | Larger forming areas, auto-level features, semi-automatic options | Prototyping, small-scale production | Pros: Greater control, versatile; Cons: Higher investment than desktop models. |
| Large Format Thermoforming Machines | High-capacity, semi-automatic, touchscreen controls | Industrial applications, large-scale production | Pros: Efficient for large projects; Cons: Higher operational costs. |
| Semi/Fully Automatic Machines | Fully automated processes, advanced specifications | High-volume production, complex applications | Pros: High efficiency, reduced labor costs; Cons: Significant initial investment. |
| Reel-Fed Thermoforming Machines | Designed for continuous feed, ideal for packaging | Food packaging, clamshells, trays | Pros: High-speed production; Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
What are the Characteristics of Desktop Thermoforming Machines?
Desktop thermoforming machines are designed for users who need a compact and economical solution for small-scale production. These machines are perfect for prototyping and creative projects, offering features like built-in vacuum pumps and energy-efficient heating. They are suitable for businesses in sectors such as arts and crafts, small product lines, or culinary applications. Buyers should consider their production volume needs and workspace constraints when choosing this type, as the capacity is limited compared to larger models.
How Do Floor-Standing Thermoforming Machines Enhance Production?
Floor-standing thermoforming machines represent a step up from desktop models, providing greater control and versatility for small to medium-scale production. With features like auto-leveling and pre-stretch capabilities, these machines are excellent for proofing design concepts and small batch runs. Industries such as packaging and automotive benefit from their enhanced functionality. Buyers should evaluate the balance between cost and required production capabilities, as these machines require a larger investment but offer improved efficiency.
What Makes Large Format Thermoforming Machines Suitable for Industrial Applications?
Large format thermoforming machines are built for high-capacity production, making them ideal for industrial applications. They combine semi-automatic operations with advanced controls, allowing for real-time adjustments during the forming process. These machines are commonly used in manufacturing sectors that require large components, such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers must weigh the benefits of high productivity against the higher operational costs, ensuring their investment aligns with long-term production goals.

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
Why Choose Semi/Fully Automatic Thermoforming Machines for High-Volume Production?
Semi and fully automatic thermoforming machines are engineered for demanding industrial applications, providing high efficiency and reduced labor costs. They are particularly beneficial for businesses that require consistent and high-volume output, such as packaging and complex manufacturing processes. While these machines offer significant advantages in terms of speed and efficiency, the initial investment can be substantial. Buyers should consider their production requirements and budget constraints when evaluating these machines.
What Advantages Do Reel-Fed Thermoforming Machines Offer in Packaging?
Reel-fed thermoforming machines are specialized for continuous feed applications, making them a popular choice for food packaging and clamshell production. Their design allows for high-speed operations and efficient material usage, which is crucial in competitive markets. These machines are especially effective for businesses focused on packaging solutions, such as food and consumer goods. However, potential buyers should assess whether their production needs align with the specific applications these machines excel in, as they may not be suitable for all thermoforming projects.
Key Industrial Applications of thermoforming machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of thermoforming machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Packaging | Production of clamshell packaging for fresh produce | Enhances product visibility and extends shelf life | Material compatibility (e.g., PET, PP), machine speed, automation capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of custom trays for surgical instruments | Ensures safety and sterility of medical products | Compliance with health regulations, precision in forming, customization options |
| Consumer Goods | Creation of drink cups and containers | Offers versatility in design and reduces production costs | Variety of designs, material strength, and environmental sustainability |
| Automotive Components | Production of interior trim and protective covers | Reduces weight and enhances aesthetic appeal | Material durability, design flexibility, and heat resistance |
| Electronics Packaging | Forming protective cases for electronic devices | Provides shock resistance and enhances product integrity | Customization for size and shape, cost-effectiveness, and production speed |
How is Thermoforming Used in Food Packaging?
In the food packaging sector, thermoforming machines are essential for producing clamshells that protect and showcase fresh produce. These packages are designed to be visually appealing while ensuring product freshness and extending shelf life. For international buyers, especially those in Africa and South America, sourcing machines that can handle various materials like PET and PP is crucial. Additionally, considerations regarding automation and production speed can significantly impact overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
What Role Does Thermoforming Play in Medical Devices?
Thermoforming technology is pivotal in the medical industry for creating custom trays that safely house surgical instruments. These trays are designed to ensure sterility and safety during transportation and storage. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing machines that comply with stringent health regulations is non-negotiable. Precision in forming is also a critical requirement, as any deviation can lead to compromised instrument safety.

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
How is Thermoforming Beneficial for Consumer Goods?
In the consumer goods industry, thermoforming machines facilitate the production of various drink cups and containers. This process allows for a wide range of designs, catering to consumer preferences while also reducing production costs. For buyers in regions like Germany, the ability to source versatile machines that can accommodate different designs and materials is essential. Additionally, sustainability is becoming increasingly important, prompting businesses to consider eco-friendly materials in their sourcing decisions.
How is Thermoforming Applied in Automotive Components?
Thermoforming is utilized in the automotive sector for producing lightweight interior trims and protective covers. This technology not only helps in reducing the overall weight of vehicles but also enhances their aesthetic appeal. B2B buyers must consider the durability and heat resistance of the materials used, as well as the design flexibility offered by the machines. In regions with strict automotive regulations, compliance with safety standards is also a critical factor.
What is the Importance of Thermoforming in Electronics Packaging?
In the electronics packaging domain, thermoforming machines are crucial for creating protective cases for devices. These cases provide shock resistance, ensuring the integrity of sensitive electronic components during transportation. Buyers should prioritize customization capabilities to fit specific device dimensions, as well as cost-effectiveness and production speed. In markets like Europe, where competition is fierce, the ability to quickly adapt to changing designs can provide a significant advantage.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘thermoforming machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Production Times Impacting Profitability
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as packaging or food production find that their existing thermoforming machines operate at suboptimal speeds. This inefficiency can stem from outdated technology, lack of automation, or improper machine calibration. As a result, companies experience longer lead times, increased labor costs, and ultimately reduced profitability. Buyers often face pressure from clients for quicker turnaround times, making it imperative to address these production bottlenecks.
The Solution: To enhance production efficiency, B2B buyers should consider investing in semi-automatic or fully automatic thermoforming machines that are specifically designed for high-speed applications. These modern machines often come equipped with advanced features such as real-time monitoring, automated sheet feeding, and integrated quality control systems. When selecting a new machine, buyers should prioritize models with a compact footprint but robust capabilities, allowing for rapid changeovers and minimal downtime. Additionally, conducting a thorough assessment of current production processes can help identify specific areas for improvement. Collaborating with suppliers who offer custom solutions tailored to unique production needs can further streamline operations and boost output.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Product Quality Leading to Customer Complaints
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter issues with inconsistent product quality due to variations in the thermoforming process. Problems such as uneven wall thickness, poor sealing, or defective molds can lead to customer dissatisfaction and increased returns. This is particularly problematic in industries like food packaging, where maintaining product integrity and compliance with safety standards is crucial. Buyers may feel overwhelmed trying to pinpoint the root cause of these quality issues, leading to costly production delays.
The Solution: To combat quality inconsistencies, buyers should invest in high-precision thermoforming machines that offer advanced control features. Look for machines equipped with temperature control systems, pressure sensors, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to ensure consistent performance. Additionally, implementing a robust quality assurance process that includes regular machine maintenance, mold inspection, and calibration checks can significantly reduce defects. Training operators on best practices for setup and operation is equally important, as skilled personnel can better monitor the thermoforming process and quickly address any deviations from quality standards. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive support, including training and troubleshooting, can further enhance product quality.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Energy Inefficiency
The Problem: Many companies using thermoforming machines face escalating operational costs primarily due to energy inefficiencies. Outdated machines often consume more power, resulting in higher utility bills that can eat into profit margins. This issue is particularly pressing for manufacturers looking to maintain competitive pricing while adhering to sustainability goals. Buyers may feel trapped between the need to minimize costs and the desire to invest in greener technologies.
Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
The Solution: B2B buyers should explore energy-efficient thermoforming machines that utilize advanced heating technologies, such as infrared or quartz heating elements, which can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional systems. It’s essential to conduct a cost-benefit analysis to compare the upfront investment of a new machine against long-term savings on energy bills. Additionally, incorporating automation features can optimize the heating and cooling cycles, further enhancing energy efficiency. Buyers should also consider implementing a comprehensive energy management strategy that includes monitoring energy usage and identifying peak consumption times. Collaborating with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability in their equipment design can also align with corporate social responsibility goals while contributing to cost savings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thermoforming machine
What Are the Key Properties of Common Thermoforming Materials?
When selecting materials for thermoforming, it is essential to consider their properties, as these directly influence product performance and application suitability. Here, we analyze four common materials used in thermoforming: Polypropylene (PP), Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Polystyrene (PS), and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS).
How Does Polypropylene (PP) Perform in Thermoforming Applications?
Polypropylene (PP) is known for its excellent chemical resistance and relatively high melting point, typically around 160°C (320°F). This makes it suitable for applications requiring durability and resistance to various chemicals, including acids and bases.
Pros: PP is lightweight, flexible, and has a good strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for packaging applications such as food containers and medical supplies. It is also cost-effective and easy to process.
Cons: However, PP has lower impact resistance compared to other materials and can become brittle at lower temperatures. Its transparency is limited, which may not be suitable for applications requiring visibility of the product.
Impact on Application: PP is commonly used in food packaging and medical applications due to its safety and compliance with health regulations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local food safety standards, while those in Europe may need to adhere to EU regulations regarding plastic use.
What Are the Advantages and Limitations of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)?
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is renowned for its excellent clarity and strength, with a melting point around 250°C (482°F). It is highly resistant to impact and moisture, making it a popular choice for packaging applications.
Pros: PET is recyclable, which aligns with global sustainability trends. Its high tensile strength and barrier properties make it suitable for beverages and food packaging.
Cons: The main limitation of PET is its higher cost compared to PP and PS. Additionally, while it is resistant to many chemicals, it can be affected by strong acids.
Impact on Application: PET is widely used in the beverage industry and for food containers, where product visibility and safety are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM and DIN standards is crucial for buyers in Europe, while South American markets may have different regulations regarding recyclability and food safety.

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
How Does Polystyrene (PS) Compare in Thermoforming?
Polystyrene (PS) is a cost-effective material with good thermal stability, with a melting point of around 100°C (212°F). It is often used for disposable products like cups and plates.
Pros: PS is easy to mold and offers good clarity, making it suitable for applications requiring visibility. It is also lightweight and inexpensive.
Cons: However, PS has lower impact resistance and is not as chemically resistant as PP or PET. It can also be less durable, making it unsuitable for long-term applications.
Impact on Application: PS is commonly used in food service products and packaging, where cost efficiency is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of environmental regulations, as PS is often scrutinized for its environmental impact, particularly in Europe, where there are increasing restrictions on single-use plastics.
What Role Does Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Play in Thermoforming?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a robust thermoplastic with a melting point around 105°C (221°F). It is known for its excellent impact resistance and toughness.
Pros: ABS is highly durable and can withstand rough handling, making it suitable for applications requiring high strength. It also offers good aesthetic qualities, with the ability to be easily painted or finished.
Cons: The primary drawback of ABS is its relatively high cost compared to other materials like PP and PS. It also has limited chemical resistance, which may restrict its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: ABS is often used in automotive parts and consumer products, where durability and appearance are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with industry standards for automotive components, particularly in Europe, where regulations are stringent.
Summary Table of Thermoforming Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for thermoforming machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Food packaging, medical supplies | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited transparency and brittleness | Low |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Beverage and food containers | Excellent clarity and recyclability | Higher cost and sensitivity to strong acids | High |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Disposable cups and plates | Easy to mold and inexpensive | Lower impact resistance and durability | Low |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Automotive parts, consumer products | High durability and aesthetic quality | Higher cost and limited chemical resistance | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on material properties, applications, and regulatory considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thermoforming machine
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Thermoforming Machines?
The manufacturing of thermoforming machines involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and customer specifications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess supplier capabilities effectively.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Prepared?
The process begins with the selection and preparation of materials. Typically, thermoforming machines are constructed using high-quality metals such as steel and aluminum, which provide durability and resistance to wear. The materials are sourced from reputable suppliers and undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet specified standards.
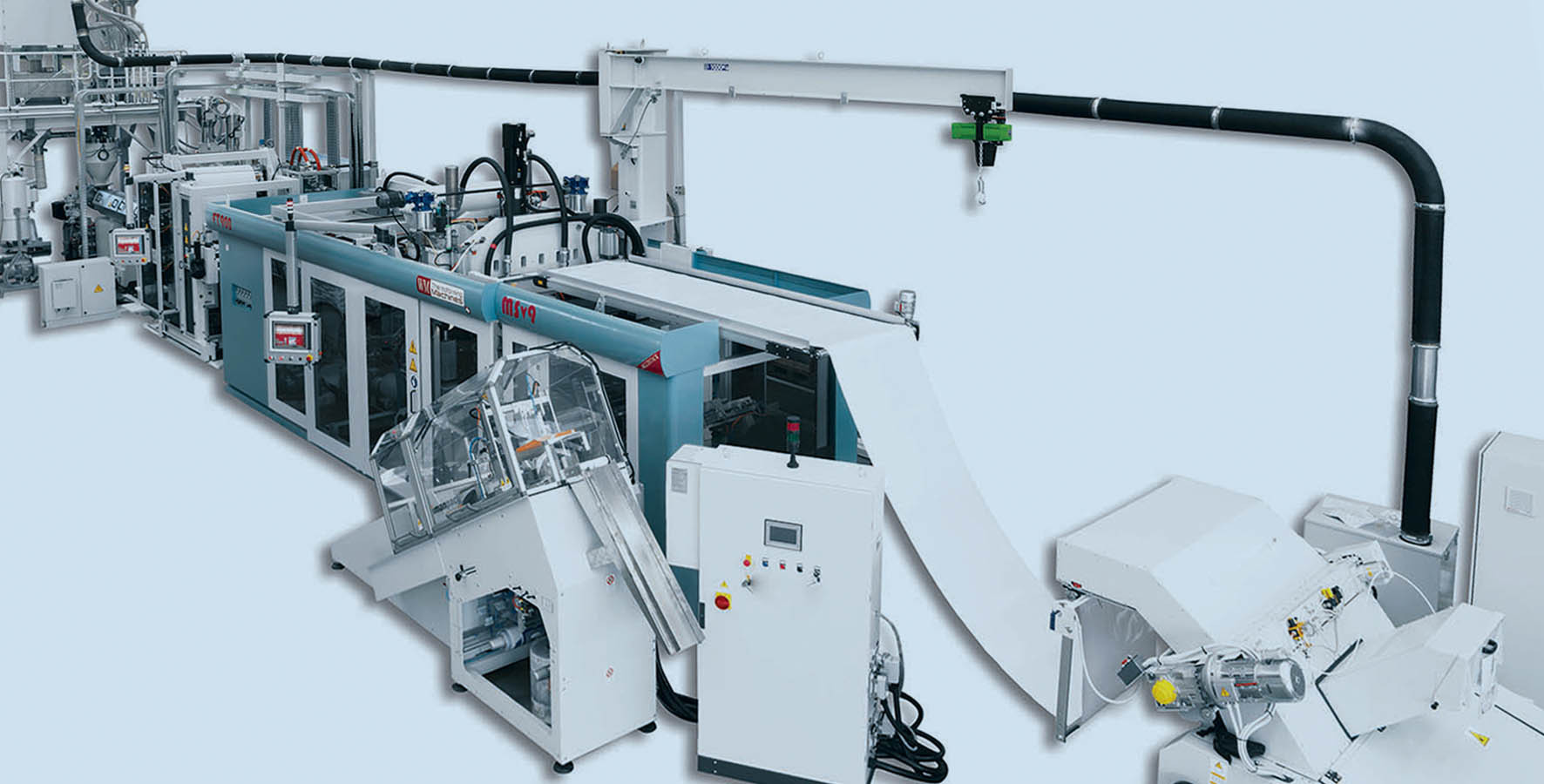

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
Before manufacturing, raw materials are cut to size and treated to improve their properties. For instance, surface treatments may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance. This preparatory phase is crucial, as the quality of materials directly affects the machine’s performance and longevity.
2. Forming: How Is the Thermoforming Process Executed?
The forming stage involves heating plastic sheets until they become pliable and then shaping them into desired forms using molds. This is typically achieved through vacuum forming or pressure forming techniques.
-
Vacuum Forming: Involves placing a heated plastic sheet over a mold and using vacuum pressure to pull the sheet into the mold. This method is highly effective for creating intricate shapes and is commonly used in sectors such as packaging and automotive.
-
Pressure Forming: Utilizes air pressure to push the heated sheet into the mold. This technique is beneficial for producing high-quality parts with precise details and is favored in high-volume production settings.
The forming process is carefully monitored to ensure consistent results, with parameters such as temperature and pressure being adjusted based on the material and design requirements.
3. Assembly: How Are Thermoforming Machines Assembled?
Post-forming, the components of the thermoforming machine are assembled. This stage requires precision, as the alignment and integration of parts are critical to the machine’s overall functionality.
Assembly typically includes:
- Integration of Heating Elements: Ensuring that heating systems are correctly positioned for uniform heating of the plastic sheets.
- Installation of Pneumatics: Incorporating pneumatic systems that control the movement of molds and clamping mechanisms.
- Electrical Connections: Wiring the control systems and ensuring all electronic components are functional and compliant with safety standards.
Quality assurance during this stage involves meticulous checks for alignment and functionality, as any discrepancies can lead to operational inefficiencies.
4. Finishing: What Steps Are Taken to Ensure Quality and Aesthetics?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments, painting, and the application of any necessary coatings. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the machine but also contributes to its durability.
Quality checks during finishing may involve visual inspections and tests to ensure that the machine meets the required specifications for appearance and function. Additionally, protective packaging is used to prevent damage during shipping.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of thermoforming machines. B2B buyers should be familiar with both international and industry-specific standards that ensure product reliability and safety.
1. What Are the Relevant International Standards?
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems that can significantly enhance the reliability of a supplier. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer follows systematic processes to ensure consistent quality in their products.
Additionally, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For B2B buyers in Africa and South America, understanding these certifications can be pivotal when evaluating suppliers.
2. What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important?
Certain industries may have additional certifications that are relevant, such as API for oil and gas or FDA approvals for food-related applications. These certifications ensure that the thermoforming machines meet specific regulatory requirements, which can be crucial for end-users in regulated markets.
Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
What Are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is embedded throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for quality before they enter the production line. This step is crucial for preventing defects from the outset.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous checks are performed to monitor critical parameters such as temperature and pressure. This ensures that any deviations are promptly addressed.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished product undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure it meets all specifications and standards. This includes functional tests and visual inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers maintain robust quality control practices:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality systems directly. This can provide insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the frequency and results of quality checks performed during the manufacturing process.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and ensure compliance with relevant standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is essential. Buyers should be aware of the following:
-
Regional Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. Familiarity with local standards can help buyers ensure that the machines will be compliant upon arrival.
-
Documentation: Ensuring that all certificates and quality reports are available in a language that is understandable is crucial for effective communication and verification.
-
Logistics and Shipping Considerations: Understanding how quality assurance practices may be affected by shipping and logistics is also vital. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have protocols in place to protect the integrity of the machines during transit.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with thermoforming machines, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘thermoforming machine’
When sourcing a thermoforming machine, it’s essential to approach the process methodically to ensure you select the right equipment for your needs. This guide provides a checklist to help B2B buyers navigate through the complexities of procurement, ensuring that every critical aspect is considered.
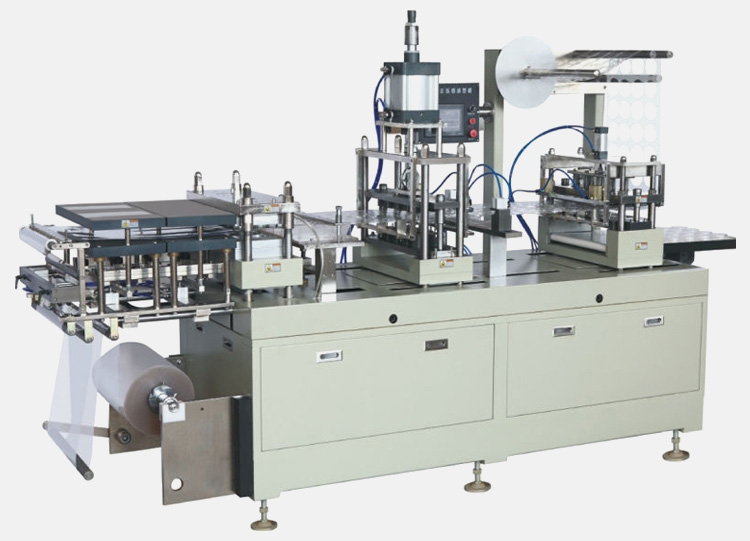

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the size of the forming area, depth of draw, and the materials you intend to use. Understanding these specifications helps narrow down your options and ensures the machine can handle your production needs.
- Consider production volume: Determine whether you need a desktop model for prototyping or a fully automatic machine for high-volume production.
- Identify material types: Different machines are optimized for various materials such as PET, PP, or PVC.
Step 2: Research Available Models
Explore the different types of thermoforming machines available in the market. Familiarize yourself with key features, such as automation levels, temperature control, and energy efficiency. This knowledge will aid you in selecting a model that aligns with your operational goals.
- Compare machine types: Evaluate desktop, floor-standing, and large-format machines based on your production requirements.
- Look for automation options: Fully automatic machines may save labor costs and increase efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from existing clients, particularly those in your industry. This step ensures that you are dealing with reputable manufacturers who can meet your needs.
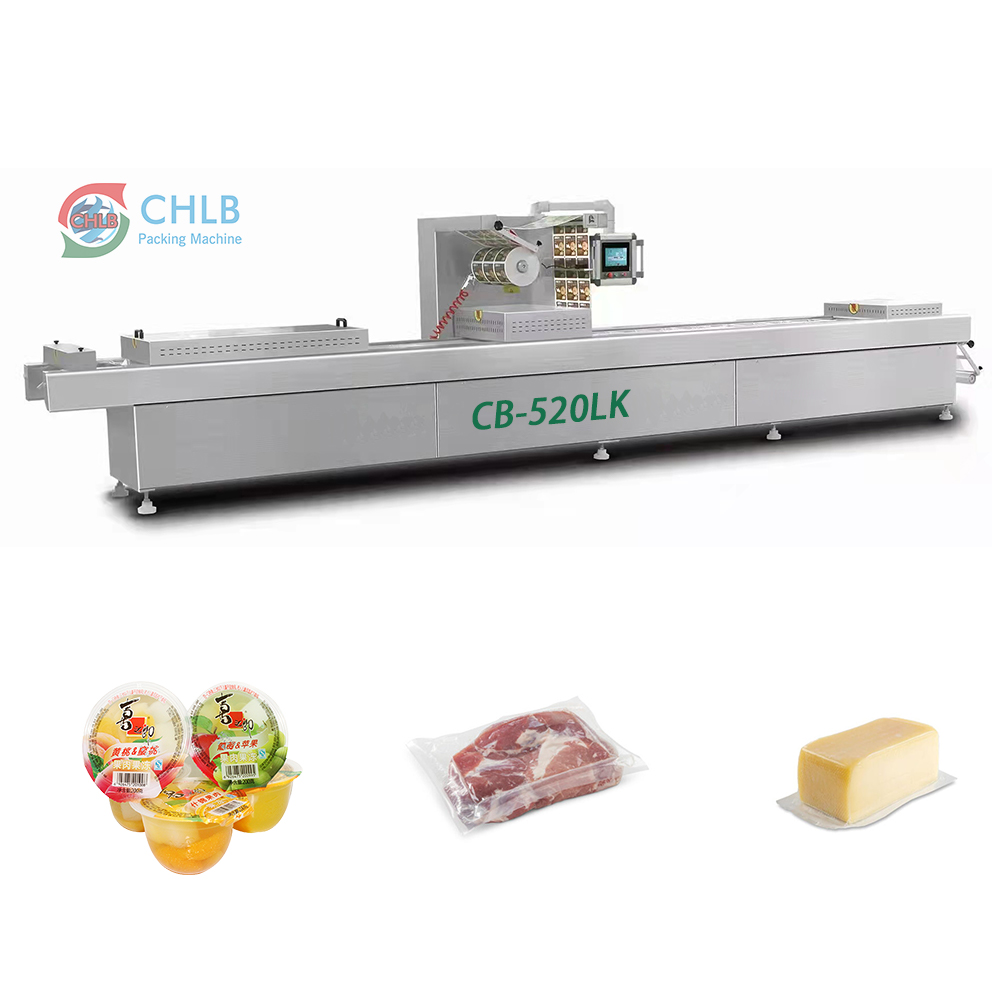

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
- Check for industry experience: Suppliers with a solid track record in thermoforming machinery are more likely to provide reliable products.
- Ask for case studies: This can provide insights into how their machines have performed in similar applications.
Step 4: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Consider the level of after-sales support offered by the supplier. Good customer service is critical for ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting, which can significantly impact your production efficiency.
- Inquire about training: Ensure that the supplier offers training for your staff to operate the machine effectively.
- Evaluate warranty and service agreements: A robust warranty can save costs on repairs and maintenance.
Step 5: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the thermoforming machines meet international standards and regulations relevant to your industry. Compliance with safety and quality certifications is crucial for ensuring the machine’s reliability and your company’s reputation.
- Look for ISO certifications: These indicate adherence to quality management standards.
- Check for CE marking: This is particularly important in Europe, indicating conformity with health and safety standards.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations or Samples
Where possible, request a demonstration of the machine or samples of products produced. This hands-on experience can provide valuable insights into the machine’s performance and capabilities.
- Test for ease of use: Ensure that the machine operates intuitively and fits well within your production workflow.
- Evaluate the output quality: Assess whether the products meet your quality standards.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Purchase
Once you’ve selected a supplier and machine, it’s time to negotiate purchase terms. Discuss pricing, delivery timelines, and payment options to ensure a mutually beneficial agreement.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Look beyond the purchase price to include maintenance, energy consumption, and operational costs.
- Clarify delivery and installation timelines: Ensure that you have a clear understanding of when the machine will be delivered and installed.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring a thermoforming machine, ensuring that their investment aligns with their operational needs and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thermoforming machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Thermoforming Machine Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing a thermoforming machine, it’s essential to understand the various components that contribute to the total expenditure. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in the construction of the machine significantly impact the cost. High-grade materials that enhance durability and performance will typically incur a higher price.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct labor involved in the manufacturing process and indirect labor for design, engineering, and assembly. Skilled labor may drive costs up, particularly in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can vary widely based on geographic location and operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often necessary for specific machine configurations or unique production requirements. The complexity of tooling can add substantially to the overall cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that machines meet industry standards and buyer specifications. The associated costs for testing and certification can be significant but are crucial for reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling, especially for international buyers, can vary dramatically based on distance and shipping methods. Duties and tariffs may also apply, affecting the final landed cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin, which can be influenced by market demand, competition, and perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Thermoforming Machine Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of thermoforming machines, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals:
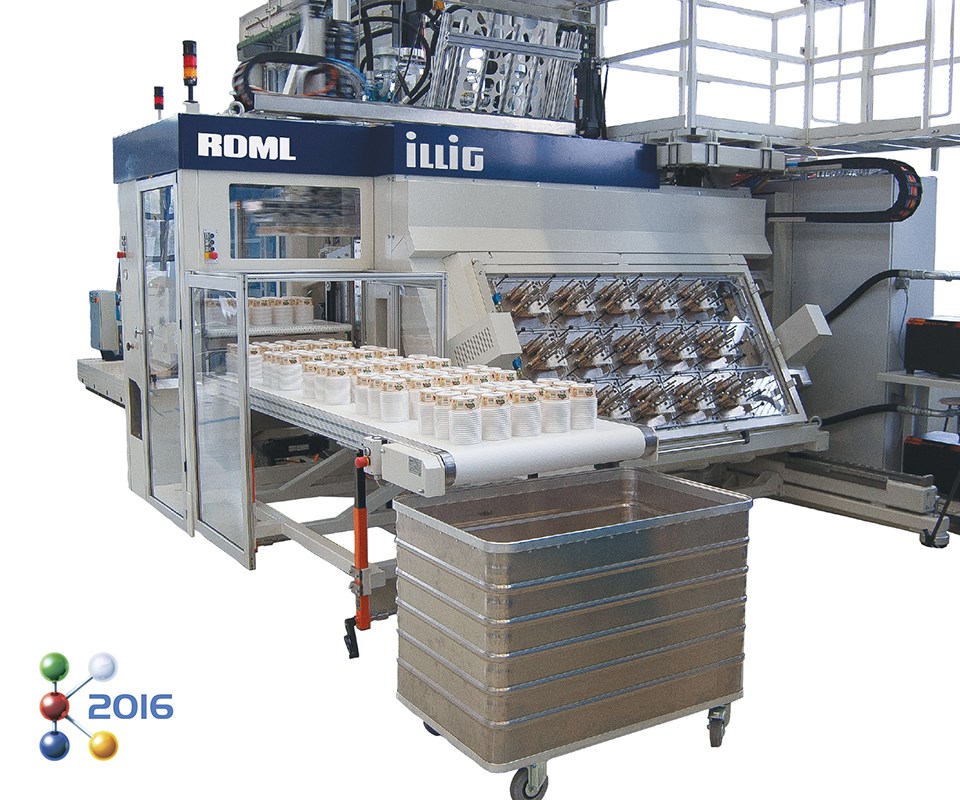

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to reduced per-unit costs. Manufacturers may offer better pricing for bulk orders, making it advantageous for businesses planning long-term production runs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom machines tailored to specific needs can drive up costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects pricing, with more specialized materials (such as those that offer enhanced barrier properties) typically being more expensive.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines that meet higher quality standards or possess relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may command higher prices due to the assurance of performance and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium but offer better support and warranty options.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is critical for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost Insurance Freight) can significantly affect the total cost, as they dictate who bears the responsibility for shipping expenses and risks.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Thermoforming Machine Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing thermoforming machines, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially if purchasing in bulk. Demonstrating a willingness to commit to larger orders can leverage better terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime costs when evaluating machine options.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of the economic conditions in the supplier’s country, as fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact final costs. Additionally, consider the logistical challenges specific to shipping to regions in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices and features across different suppliers. This can provide insights into what constitutes a fair price and help identify the best value.
-
Seek Local Partnerships: If feasible, consider local suppliers to minimize shipping costs and potential tariffs. Local partnerships can also facilitate faster service and support.
In summary, understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers is essential for B2B buyers in the thermoforming machine market. By leveraging these insights, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing thermoforming machine With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Thermoforming Machines?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing and packaging, businesses are constantly seeking efficient solutions to meet their production needs. Thermoforming machines are a popular choice for creating plastic products, but they are not the only option available. B2B buyers should consider alternative technologies that can achieve similar outcomes while potentially offering unique advantages. This section compares thermoforming machines with other viable methods, including injection molding and blow molding, to help businesses make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Thermoforming Machine | Injection Molding | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High, versatile for various shapes and sizes | Excellent for complex shapes and high precision | Best for hollow objects with uniform thickness |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; lower for low volumes | High initial costs, but lower per unit for high volumes | Moderate initial investment with lower costs for large runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized skills; relatively easy setup | Complex setup with longer lead times for molds | Simpler setup than injection molding, but requires specific machinery |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular checks needed | High; complex machinery requires skilled technicians | Low; fewer moving parts lead to less frequent maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for custom shapes, packaging, and prototyping | Best for high-volume production of detailed parts | Perfect for producing bottles, containers, and hollow products |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Injection Molding: Pros and Cons
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create a specific shape. One of the main advantages of injection molding is its ability to produce high-precision, complex shapes with a smooth finish. This makes it an excellent choice for industries requiring intricate designs, such as automotive and electronics. However, the high initial setup costs and longer lead times for mold production can be a barrier for companies looking to start small-scale production. Moreover, the need for skilled technicians for maintenance adds to the operational costs.
Blow Molding: Advantages and Disadvantages
Blow molding is a process primarily used for creating hollow plastic products, such as bottles and containers. The method is generally more cost-effective than injection molding for producing large volumes of uniform items. One significant advantage is the relatively simple setup, which reduces time to market for new products. However, blow molding is limited to specific shapes and materials, and achieving consistent wall thickness can be challenging. For businesses focused on high-volume production of hollow items, blow molding could be a practical alternative to thermoforming.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between thermoforming machines and alternative solutions like injection and blow molding, B2B buyers should assess their specific production needs, budget, and product requirements. Thermoforming machines offer versatility and are particularly advantageous for custom shapes and low to moderate production volumes. In contrast, injection molding excels in precision for high-volume runs, while blow molding is ideal for hollow products. By carefully evaluating each method’s performance, cost, and ease of implementation, businesses can select the solution that best aligns with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thermoforming machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Thermoforming Machines?
When evaluating thermoforming machines for your business, understanding critical specifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key technical properties to consider:

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
1. Material Compatibility
Thermoforming machines are designed to process a variety of materials, including thermoplastics such as PET, PS, PVC, and PP. Each material has unique properties affecting its suitability for specific applications, such as strength, flexibility, and barrier characteristics. Understanding the compatibility of the machine with your intended materials ensures optimal production quality and efficiency.
2. Forming Area
The forming area, often measured in millimeters or inches, indicates the maximum size of the sheet that can be processed. This specification is crucial for businesses that require large or custom-sized products. A larger forming area allows for the creation of diverse product shapes, accommodating various market needs without the need for multiple machines.
3. Depth of Draw
Depth of draw refers to the maximum depth achievable during the forming process. This property directly impacts the design complexity of the final product. For example, products with intricate designs or deeper profiles may require machines capable of greater draw depths, ensuring quality and structural integrity.
4. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the duration required to complete one full thermoforming process, from heating the sheet to cooling and removal. A shorter cycle time can significantly enhance productivity, making it a vital consideration for businesses focused on high-volume production. Efficient machines reduce downtime and increase throughput, ultimately impacting profitability.
5. Control Features
Advanced control features, such as touchscreen interfaces and programmable settings, allow operators to adjust parameters easily for various applications. Machines equipped with such technology enable consistent quality control and adaptability in production processes, which can be vital for meeting diverse customer demands.

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
6. Energy Efficiency
Energy consumption is an important factor in operational costs. Machines designed with energy-efficient heating systems and insulation can lead to significant savings over time. This aspect is particularly relevant in regions where energy costs are high, making energy-efficient machines a wise investment.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in the Thermoforming Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation. Here are several important trade terms relevant to thermoforming machines:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of thermoforming machines, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality of components used in their machines.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is essential when budgeting for machine purchases or spare parts, as it affects inventory levels and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their production needs and financial constraints.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request issued to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ for thermoforming machines helps buyers compare offers, assess supplier capabilities, and make cost-effective purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing logistics and ensuring that both parties are clear on their obligations throughout the transaction process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from the placement of an order until its delivery. In the context of thermoforming machines, shorter lead times can enhance production planning and responsiveness to market demands. Buyers should consider lead times when selecting suppliers to ensure timely project execution.
6. Customization
Customization refers to the ability to modify standard machine configurations to meet specific requirements. This capability is particularly valuable for businesses with unique product needs, as it can lead to enhanced efficiency and reduced waste. Understanding the extent of customization options available can help buyers make strategic decisions aligned with their operational goals.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms, you can enhance your procurement strategy and ensure that your investments in thermoforming machines align with your business objectives.

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the thermoforming machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Thermoforming Machine Sector?
The thermoforming machine sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by several global factors. The demand for lightweight and flexible packaging solutions, particularly in the food and beverage industry, is a significant market driver. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, the focus is shifting toward advanced thermoforming technologies that offer automation, speed, and efficiency. For instance, the rise of semi-automated and fully automated machines is enabling manufacturers to optimize production lines and reduce operational costs.
Emerging technologies, such as Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT), are revolutionizing how thermoforming machines operate. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, thereby minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity. Furthermore, buyers are increasingly prioritizing machines that support diverse material types, including biodegradable options, reflecting a broader trend towards versatile and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Additionally, the global supply chain dynamics are evolving, influenced by geopolitical factors and economic shifts. Manufacturers are adapting to these changes by diversifying their sourcing strategies and exploring partnerships that ensure reliability and cost-effectiveness. International buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and leverage local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with long-distance logistics.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Being Integrated into the Thermoforming Machine Sector?
As environmental concerns continue to gain prominence, sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the thermoforming machine sector. The production processes involved in thermoforming can have a significant environmental impact, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation. As a response, many manufacturers are innovating their operations to reduce carbon footprints and improve resource efficiency.

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially as consumers and businesses alike demand transparency and responsibility from manufacturers. Buyers are increasingly looking for thermoforming machines that utilize sustainable materials and eco-friendly production processes. For example, machines designed to work with recycled plastics or those that support the development of biodegradable packaging solutions are gaining traction.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and compliance with regional regulations on sustainability are becoming essential for manufacturers aiming to attract international buyers. Additionally, companies that can demonstrate a commitment to green practices through certifications and sustainable sourcing strategies are more likely to build trust and long-term relationships with their B2B partners.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Thermoforming Technology Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of thermoforming technology has been marked by significant advancements since its inception. Initially developed in the mid-20th century, thermoforming offered a cost-effective way to produce plastic products by heating sheets and forming them into desired shapes using molds. Over the decades, this technology has evolved from manual processes to highly automated systems that enhance precision and reduce cycle times.

Illustrative image related to thermoforming machine
The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) has further transformed thermoforming, allowing manufacturers to create complex shapes with minimal material waste. As a result, the sector has become increasingly competitive, pushing companies to innovate continually. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers who must understand the technological advancements that can impact their purchasing decisions and operational efficiencies.
In conclusion, the thermoforming machine sector is adapting to changing market dynamics, with sustainability and technology leading the charge. International buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business goals and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thermoforming machine
-
How do I choose the right thermoforming machine for my business needs?
Selecting the right thermoforming machine involves evaluating your production volume, material types, and product specifications. Start by assessing the size and complexity of the items you plan to produce, as this will influence the machine’s forming area and depth of draw. Consider whether you need a desktop, floor-standing, or large-format model based on your workspace and production capacity. Additionally, consult with suppliers to understand customization options and request a demo or trial, if possible, to ensure the machine meets your operational requirements. -
What factors should I consider when assessing suppliers of thermoforming machines?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Verify their ability to provide after-sales support, including installation, maintenance, and training services. Evaluate the range of machines they offer to ensure they can meet your specific needs. It’s also important to inquire about their compliance with international quality standards, warranty terms, and the availability of spare parts. Engaging in direct communication with previous clients can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability and service quality. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing thermoforming machines?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers, but common practices include a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery or installation. Some suppliers may offer flexible financing options or installment plans to accommodate your budget. Ensure that you clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers or letters of credit, particularly for international transactions. Always review the terms in detail before committing to avoid any hidden fees or unfavorable conditions. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for thermoforming machines?
MOQs for thermoforming machines can vary based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the machine. Generally, suppliers may set a MOQ to cover production costs and ensure profitability. For standard machines, the MOQ might be one unit, while custom or specialized machines may require a larger order. It’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront with potential suppliers to align your purchasing plans with their production capabilities. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for thermoforming machines?
To ensure quality assurance, inquire about the supplier’s QA processes, including testing procedures and certifications. Request documentation that demonstrates compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications. Consider visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facility to observe their quality control measures in action. Additionally, ask for references from other clients regarding their experience with the machine’s performance and reliability to gauge long-term quality assurance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing thermoforming machines?
When importing thermoforming machines, consider the shipping method, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties that may apply to your region. Choose a reliable freight forwarder with experience in handling industrial machinery to facilitate the logistics process. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, to prevent delays. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping when planning your production schedule. -
What customization options are available for thermoforming machines?
Many suppliers offer customization options to tailor machines to specific production needs. This may include modifications to the forming area, adjustments for different material types, or specialized tooling for unique product shapes. Discuss your requirements with the supplier to understand what modifications are feasible. Custom solutions can enhance efficiency and output, but be aware that they may increase lead times and costs, so plan accordingly. -
How do I handle technical support and maintenance for thermoforming machines?
Securing reliable technical support is crucial for the smooth operation of thermoforming machines. Before purchasing, inquire about the supplier’s support services, including response times for troubleshooting and availability of spare parts. Ensure that they provide comprehensive training for your staff on machine operation and maintenance procedures. Establish a preventive maintenance schedule to minimize downtime and extend the machine’s lifespan. Consider contracts for ongoing support or service agreements to ensure consistent assistance as needed.
Top 5 Thermoforming Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Formech – Desktop Vacuum Forming Machines
Domain: formech.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“Desktop Models”: [{“Model”: “Formech 300DT”, “Price”: “$3,090.00”, “Forming Area”: “280 x 230 mm”, “Depth of Draw”: “136 mm”, “Sheet Size”: “300 x 250 mm”}, {“Model”: “Formech 450DT”, “Price”: “$5,900.00”, “Forming Area”: “430 x 280 mm”, “Depth of Draw”: “160 mm”, “Sheet Size”: “450 x 300 mm”}, {“Model”: “Formech 508DT”, “Price”: “$8,285.00”, “Forming Area”: “482 x 432 mm”, “Depth of Draw”: “185…
2. WM Thermoforming – Key Product Series
Domain: wm-thermoforming.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: WM Thermoforming Machines offers a variety of thermoforming solutions tailored for different industries. Key product series include:
1. **FX/FC Series**: Designed for medium-high productivity multilayer sheet forming, ideal for dairy products, trays, and medical applications. Features include precise cutting, automated systems, and compatibility with various materials.
2. **FT Series**: Suitab…
3. OneBMG – Thermoforming Solutions
Domain: onebmg.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Thermoforming Machine – Precision in Thermoforming, Engineered for Success. Offers entry-level and turnkey thermoforming systems for custom applications. Applications include plastic thermoforming for food packaging, medical devices, and industrial components; paper thermoforming for sustainable products; and consumer packaged goods (CPG) for retail packaging. Supports various forming methods: pre…
4. Ulma Packaging – Thermoforming Machines
Domain: ulmapackaging.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Thermoformers – Thermoforming machines are horizontal automatic packing machines characterized by package formation within the machine using two film coils, typically made of different materials. These machines can produce flexible or rigid packages depending on the materials used and are designed for both food and non-food markets. Models include TFE 500, TFE 700, TFS 80, TFS 200, TFS 200 MSV, TF…
5. Cannon – High-Performance Thermoforming Machines
Domain: cannon.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: High-performance thermoforming machines designed for modern industry. Tailored solutions for various applications including pressure forming, thermocovering, and twin sheet thermoforming. CREA thermoforming machines custom-designed for a range of thermoplastic materials with features like automatic size adjustment, servo-electric drive, and optimized cycle times for medium to large parts productio…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thermoforming machine
As the demand for efficient and versatile packaging solutions continues to rise across various industries, strategic sourcing of thermoforming machines has never been more critical. By investing in the right thermoforming technology, businesses can enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and maintain superior product quality. Whether for the automotive, food packaging, or medical sectors, selecting the appropriate machine—from desktop models for prototyping to fully automated systems for high-volume production—can provide a competitive edge.
Global buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider not only the technical specifications of these machines but also the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and support services. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer customizable solutions and comprehensive after-sales support will ensure that your investment aligns with long-term business goals.
Looking ahead, the thermoforming landscape is poised for innovation, driven by advancements in materials and automation. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and leverage the latest technologies to meet evolving market demands. By making informed decisions, you can position your business for success in an increasingly competitive global environment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.