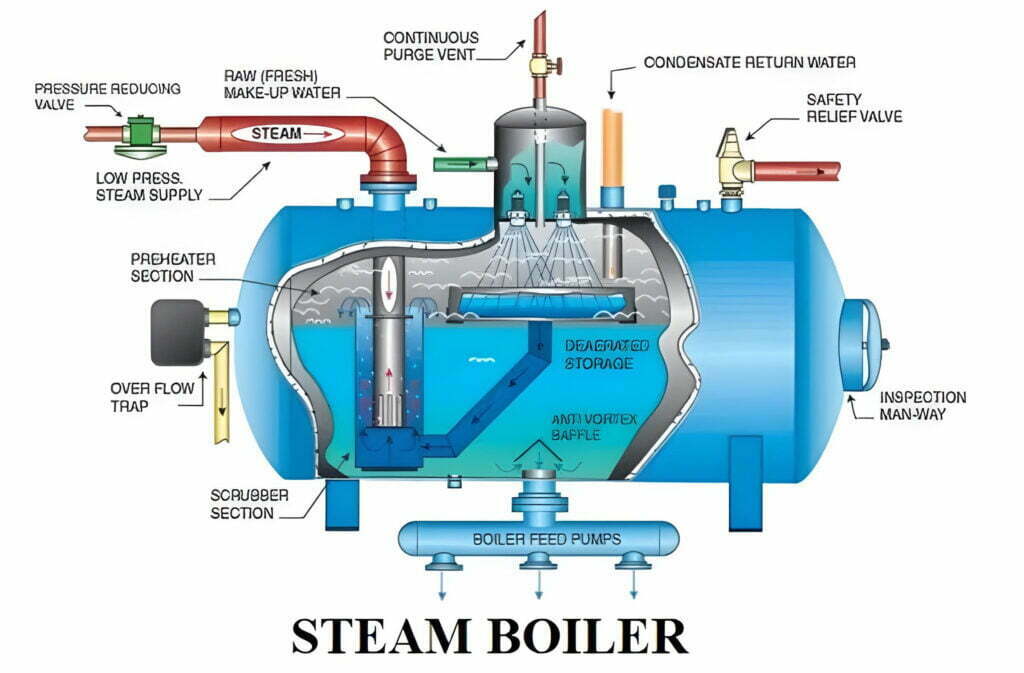
Everything You Need to Know About Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for simple steam boiler diagram
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, sourcing a simple steam boiler diagram can often present a significant challenge for B2B buyers. With a myriad of options available across various markets—especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the intricacies of steam boiler systems is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential elements of steam boiler diagrams, including the various types, their applications, and critical factors to consider during the supplier vetting process.
From low-pressure to high-pressure steam boilers, and from electric to gas-fired options, this guide elucidates the operational mechanics and efficiencies associated with each type. We will also cover the cost implications and the factors that can influence pricing, ensuring that buyers can navigate the financial aspects with clarity. Additionally, insights into selecting reputable suppliers will empower international buyers to make choices that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
By equipping B2B buyers with in-depth knowledge and actionable insights, this guide aims to streamline the process of sourcing steam boilers, fostering confidence in decision-making. Whether you are in Germany, Nigeria, or any other global market, understanding the fundamentals of steam boiler diagrams will be instrumental in enhancing efficiency and achieving long-term operational success.
Understanding simple steam boiler diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fire Tube Boiler | Water flows around heated tubes; simpler design. | Food processing, textile manufacturing | Pros: Lower initial cost, easier maintenance. Cons: Limited pressure capabilities. |
| Water Tube Boiler | Water flows through tubes surrounded by combustion gas. | Power generation, chemical processing | Pros: High efficiency, suitable for high pressures. Cons: Higher complexity and cost. |
| Electric Boiler | Uses electric elements for heating; no combustion. | Hospitals, hotels, and small industries | Pros: Clean operation, low maintenance. Cons: Higher energy costs, limited capacity. |
| Oil-Fired Boiler | Burns oil for heat; efficient heat transfer. | Heavy industry, commercial heating | Pros: High efficiency, long lifespan. Cons: Requires regular fuel supply, higher upfront costs. |
| Low Pressure Boiler | Operates at lower pressure levels (10-15 psi). | Heating applications, steam cleaning | Pros: Quick steam production, safer operation. Cons: Limited for high-demand applications. |
What Are the Characteristics of Fire Tube Boilers?
Fire tube boilers are characterized by their relatively simple design, where water surrounds tubes heated by combustion gases. This design is particularly suitable for applications in industries such as food processing and textiles, where lower pressure steam is adequate. Buyers appreciate the lower initial investment and ease of maintenance; however, they should consider that fire tube boilers may not be suitable for high-pressure requirements, limiting their use in certain industrial settings.
How Do Water Tube Boilers Differ from Other Types?
Water tube boilers feature a design where water circulates through tubes that are heated externally by combustion gases. This configuration allows for higher efficiency and the ability to generate steam at much higher pressures, making them ideal for power generation and chemical processing. While they offer significant advantages in terms of performance, potential buyers should weigh the higher complexity and initial costs against the long-term operational benefits.
Why Choose Electric Boilers for Specific Applications?
Electric boilers utilize electric heating elements instead of combustion, making them an environmentally friendly choice. They are particularly suitable for applications in hospitals, hotels, and smaller industries where steam demand is moderate. The advantages of electric boilers include cleaner operation and reduced maintenance needs. However, buyers must consider the higher energy costs associated with electric heating and the limited capacity for larger-scale operations.
What Are the Advantages of Oil-Fired Boilers?
Oil-fired boilers are known for their efficient heat transfer and ability to produce high-pressure steam. They are commonly used in heavy industry and commercial heating applications. While they can achieve efficiencies above 90%, buyers should be aware of the need for a consistent oil supply and the higher upfront costs associated with installation. The longevity of oil-fired boilers can be a significant advantage in terms of return on investment.
What Makes Low Pressure Boilers Suitable for Certain Applications?
Low pressure boilers operate within a pressure range of 10-15 psi, making them ideal for applications that require quick steam production, such as heating and steam cleaning. They are favored for their safety and simplicity of operation. However, potential buyers should note their limitations regarding high-demand applications and the potential need for larger systems as operational needs grow.
Key Industrial Applications of simple steam boiler diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of simple steam boiler diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Steam sterilization and cooking processes | Ensures food safety and quality through effective sterilization. | Compliance with health standards, energy efficiency, and scalability. |
| Textile Manufacturing | Dyeing and finishing processes | Enhances fabric quality and color consistency. | Material compatibility, pressure requirements, and maintenance support. |
| Chemical Processing | Reaction heating and distillation | Facilitates precise temperature control for chemical reactions. | Safety certifications, fuel type, and operational efficiency. |
| Power Generation | Steam turbines for electricity production | Provides a reliable energy source with high efficiency. | Regulatory compliance, fuel availability, and boiler capacity. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Sterilization and formulation processes | Ensures product safety and efficacy through controlled environments. | Material certifications, energy consumption, and system integration. |
How Is the Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Utilized in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, the simple steam boiler diagram is instrumental in processes such as steam sterilization and cooking. Steam boilers provide the necessary heat to sterilize equipment and ingredients, ensuring food safety and extending shelf life. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing boilers that comply with local health regulations is essential. Additionally, energy efficiency and scalability are critical factors, as companies aim to reduce operational costs while meeting increasing production demands.
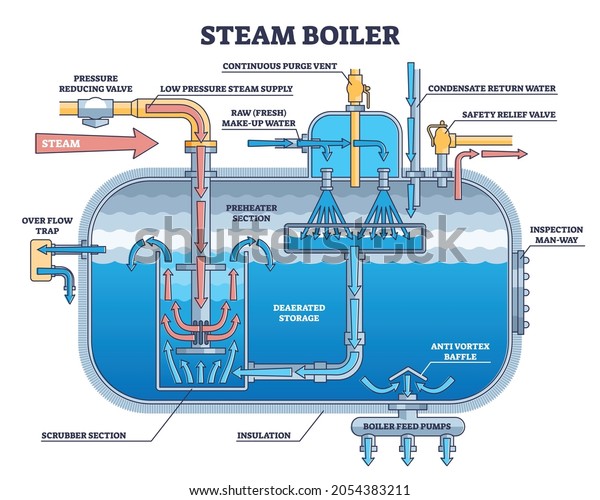
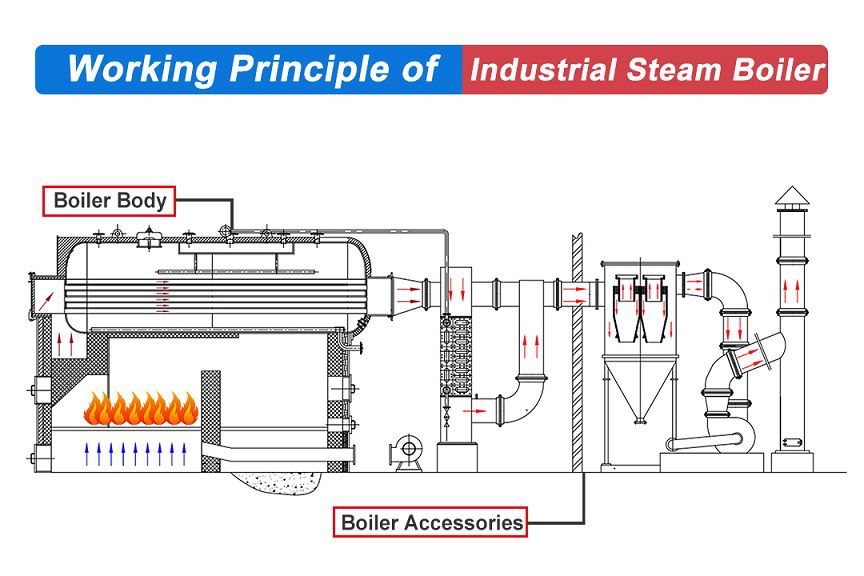
Illustrative image related to simple steam boiler diagram
What Role Does the Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Play in Textile Manufacturing?
Textile manufacturers utilize the simple steam boiler diagram for dyeing and finishing processes, where precise temperature control is crucial. The steam generated helps in achieving uniform dye application and improves the overall quality of fabrics. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the compatibility of the boiler materials with various dye chemicals and the specific pressure requirements of their processes. Maintenance support and the availability of spare parts are also key considerations to ensure uninterrupted production.
How Is the Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Essential in Chemical Processing?
In the chemical processing sector, the simple steam boiler diagram is vital for providing heat during reactions and distillation processes. The ability to maintain precise temperature control directly impacts the efficiency and safety of chemical reactions. For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Germany and Nigeria, sourcing steam boilers with appropriate safety certifications and high operational efficiency is paramount. Additionally, the type of fuel used can influence both cost and environmental impact, making it an important factor in procurement decisions.
In What Ways Does the Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Contribute to Power Generation?
In power generation, the simple steam boiler diagram is fundamental in driving steam turbines that produce electricity. The efficiency of steam generation directly correlates with the overall energy output of the facility. International buyers should prioritize regulatory compliance and assess the availability of the chosen fuel type to ensure consistent operation. Furthermore, the boiler’s capacity must align with the energy demands of the facility, making it a crucial aspect of sourcing decisions.
How Is the Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Used in Pharmaceuticals?
Pharmaceutical companies leverage the simple steam boiler diagram for sterilization and formulation processes, where maintaining a controlled environment is critical for product safety. The steam generated is used to sterilize equipment and raw materials, ensuring that the final products meet stringent safety standards. Buyers in the pharmaceutical sector must focus on sourcing boilers that meet material certifications and energy consumption standards, as well as those that can be integrated seamlessly into existing production lines.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘simple steam boiler diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Boiler Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when trying to interpret the specifications and diagrams associated with simple steam boilers. This can lead to confusion about which boiler type suits their industrial needs, especially when multiple diagrams present varying configurations and capabilities. For instance, a buyer in Nigeria looking to purchase a boiler for a food processing plant may find it overwhelming to choose between firetube and watertube designs, leading to potential misinvestment and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should seek comprehensive resources that break down the specifications in user-friendly terms. When sourcing a simple steam boiler diagram, prioritize vendors that provide detailed explanations of the diagram components, such as pressure ratings, fuel types, and efficiency levels. Additionally, consider engaging with technical support or consultants who can clarify boiler specifications and their implications for your specific application. This proactive approach ensures that you select the right boiler type, minimizing the risk of costly mistakes and optimizing operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Maintenance Knowledge
The Problem: Another common pain point is the lack of understanding regarding the maintenance needs of steam boilers. For companies in South America, where operational downtimes can significantly impact production, failing to grasp the maintenance requirements illustrated in simple steam boiler diagrams can lead to unexpected breakdowns. This is especially critical for industries relying on continuous steam supply, such as textiles and pharmaceuticals, where even minor disruptions can halt operations.
The Solution: To address maintenance-related issues, buyers should seek out diagrams that not only illustrate the boiler’s operation but also include maintenance schedules and checklists. These diagrams should highlight key components that require regular inspection, such as safety valves, water level indicators, and blow-off valves. Furthermore, investing in training for personnel on how to interpret these diagrams can enhance the team’s ability to conduct preventive maintenance. Partnering with boiler manufacturers who offer maintenance training or resources can also be invaluable in ensuring that your team is well-equipped to handle boiler upkeep effectively.
Illustrative image related to simple steam boiler diagram
Scenario 3: Compliance with Safety Standards
The Problem: Compliance with safety standards is a crucial concern for B2B buyers, particularly in the Middle East and Europe, where regulations can be stringent. Buyers may struggle to understand how the simple steam boiler diagram relates to local safety regulations and codes. This is particularly relevant for those in industries like oil and gas, where non-compliance can lead to severe penalties and operational risks.
The Solution: To navigate compliance challenges, buyers should ensure that the steam boiler diagrams they are using are aligned with relevant local and international standards. This involves researching the specific safety regulations applicable to their industry and geographical location. Seek out diagrams that are certified or endorsed by recognized safety organizations, as these will typically provide information on safety features such as pressure relief systems and emergency shut-off mechanisms. Additionally, engaging legal or compliance experts during the purchasing process can help ensure that your boiler installation meets all safety requirements, thereby safeguarding your operations and reputation in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for simple steam boiler diagram
What Are the Key Materials for Simple Steam Boiler Diagrams?
When selecting materials for steam boilers, understanding their properties, advantages, and limitations is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in steam boiler construction: carbon steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and copper.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Steam Boiler Applications?
Carbon steel is one of the most widely used materials for steam boilers due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and cost-effectiveness. Key properties include high tensile strength and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, especially in high-moisture environments, which can lead to premature failure.
Pros: Carbon steel is durable and relatively inexpensive, making it an attractive option for many manufacturers. Its ease of fabrication allows for complex designs, which is beneficial for custom applications.
Cons: The primary limitation is its susceptibility to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings or regular maintenance. International buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with standards such as ASTM A106 for high-temperature applications.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Steam Boilers?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making it ideal for steam boilers that may encounter aggressive media. Key properties include a high melting point and excellent mechanical strength. This material is particularly suitable for applications requiring hygiene, such as food processing or pharmaceuticals.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and reduced maintenance costs due to its corrosion-resistant properties. It also offers aesthetic benefits, making it suitable for visible installations.
Cons: The main drawback is its higher cost compared to carbon steel. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to weld, which may complicate manufacturing processes.
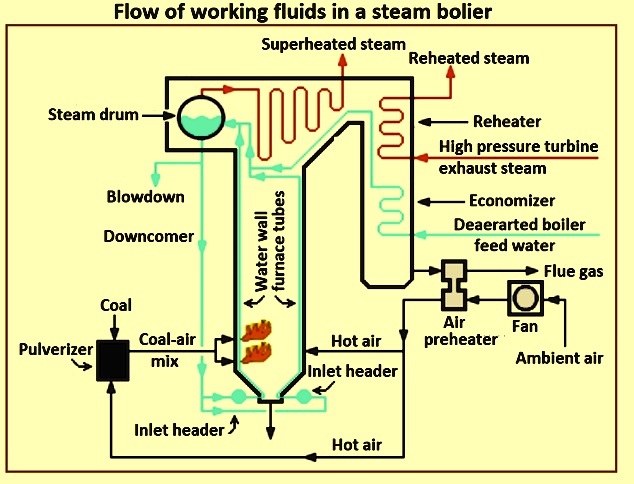
Illustrative image related to simple steam boiler diagram
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Steam Boiler Design?
Cast iron is another traditional choice for steam boilers, particularly in residential and small industrial applications. It is known for its excellent thermal conductivity and ability to retain heat. Key properties include high compressive strength and good resistance to thermal shock.
Pros: Cast iron is durable and provides excellent heat retention, which can lead to energy savings. Its ability to withstand high pressures makes it suitable for low-pressure steam applications.
Cons: However, cast iron is brittle and can crack under extreme stress or thermal shock. International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM A48 for cast iron products, especially in regions with varying temperature conditions.
How Does Copper Compare as a Boiler Material?
Copper is less commonly used in large steam boilers but is prevalent in smaller applications such as residential hot water systems. Its key properties include excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Copper’s ability to transfer heat efficiently makes it a preferred choice for heat exchangers.
Pros: The primary advantage of copper is its high thermal efficiency, leading to faster heating times. It is also resistant to corrosion, which enhances its longevity.
Cons: The main limitation is its relatively high cost and lower strength compared to steel options. Additionally, copper may not be suitable for high-pressure applications, which could limit its use in certain industrial settings.
Summary of Material Selection for Steam Boiler Applications
| Material | Typical Use Case for simple steam boiler diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General industrial applications | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Corrosion-resistant and durable | Higher cost and complex welding | High |
| Cast Iron | Residential and low-pressure applications | Excellent heat retention | Brittle and can crack | Medium |
| Copper | Residential hot water systems | High thermal efficiency | High cost and lower strength | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these materials’ properties and compliance requirements can significantly impact the efficiency, durability, and overall performance of steam boiler systems.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for simple steam boiler diagram
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Simple Steam Boiler?
The manufacturing process of a simple steam boiler involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets rigorous standards of efficiency and safety. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages:
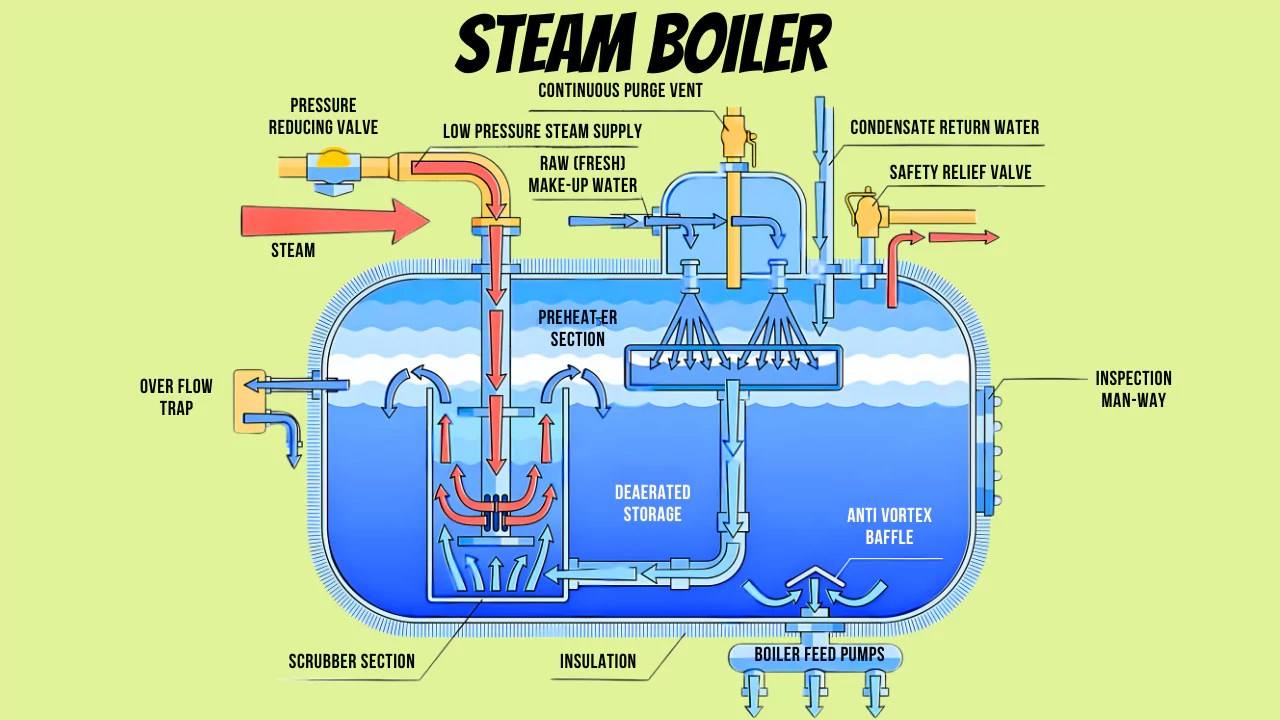
Illustrative image related to simple steam boiler diagram
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing a steam boiler is material preparation. High-quality materials are essential for durability and performance. Common materials include:
- Steel: Typically used for the boiler shell and tubes due to its strength and ability to withstand high pressure and temperature.
- Insulation Materials: Used to minimize heat loss and improve efficiency.
- Fittings and Valves: Made from various materials, including brass and stainless steel, to ensure longevity and resistance to corrosion.
Before production, materials undergo thorough inspections to check for defects or inconsistencies, ensuring only the best materials are used.
2. Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, they are subjected to forming processes, which may include:
- Cutting: Steel sheets are cut into precise dimensions using laser cutting or plasma cutting technologies.
- Bending: Sheets are bent into the required shapes for the boiler body and tubes using hydraulic presses.
- Welding: Various welding techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) are employed to join parts together, ensuring strong, leak-proof seams.
These forming techniques are critical in achieving the exact specifications required for the steam boiler’s operation.
3. Assembly Procedures
In the assembly phase, the formed components are brought together. This stage typically involves:
- Sub-Assembly: Components like burners, heat exchangers, and control systems are pre-assembled for efficiency.
- Main Assembly: The sub-assemblies are integrated into the main boiler framework. This includes installing piping, valves, and safety devices.
- Quality Checks: Each assembly stage includes quality checks to ensure proper fit and alignment, critical for safety and efficiency.
4. Finishing Processes
The final stage involves finishing touches that enhance both functionality and appearance:
- Surface Treatment: Components may undergo processes such as sandblasting or coating to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Insulation Installation: Insulation is applied to retain heat and improve efficiency.
- Painting: A protective coating may be applied to prevent rust and enhance the boiler’s aesthetic.
These finishing processes contribute to the boiler’s longevity and performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Steam Boiler Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of steam boilers to ensure compliance with international standards and customer expectations. Here’s how QA is typically structured:
Relevant International Standards for Steam Boiler Manufacturing
Compliance with international standards is vital for manufacturers aiming to compete in the global market. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking confirms that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers focusing on oil and gas applications, adhering to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential for safety and performance.
Understanding these standards can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers’ commitment to quality.
What Are the QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control is typically integrated at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various parameters such as dimensions, weld integrity, and pressure testing are monitored.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the entire boiler undergoes rigorous testing, including pressure tests and safety checks, to ensure it operates safely and efficiently.
These checkpoints help identify any issues early in the production process, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Testing methods play a significant role in ensuring that steam boilers meet required standards. Common testing methods include:
- Hydrostatic Testing: This test checks for leaks by filling the boiler with water and pressurizing it beyond its operational limits.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiography are used to identify internal flaws without damaging the components.
- Performance Testing: The boiler’s efficiency and output are tested under simulated operational conditions to ensure it meets performance specifications.
These testing methods provide B2B buyers with assurance regarding the reliability and safety of the steam boilers they purchase.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and adherence to standards firsthand.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports, including test results and compliance certifications, to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices and product reliability.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations that must be adhered to. Buyers should ensure suppliers are compliant with both local and international standards.
- Cultural and Communication Differences: Effective communication is critical. Buyers should be aware of potential language barriers and cultural differences that may affect business negotiations and quality assurance processes.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Understanding the logistics involved in transporting steam boilers internationally is crucial, as delays or damage during transit can impact quality and delivery timelines.
By being proactive in these areas, B2B buyers can mitigate risks and ensure they receive high-quality steam boilers that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘simple steam boiler diagram’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring a simple steam boiler diagram, this checklist offers a structured approach to ensure that all essential aspects are considered. By following these steps, you can streamline your sourcing process and make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s vital to clarify your technical requirements. Consider the specific steam generation needs of your operation, including the desired pressure and temperature outputs. Clearly defined specifications will guide your search and help you communicate effectively with suppliers.
- Capacity Needs: Determine the volume of steam required for your applications.
- Fuel Type: Identify the fuel source (e.g., gas, oil, biomass) that aligns with your operational practices and environmental standards.
Step 2: Research Available Designs
Understanding the various designs of steam boilers is essential. Familiarize yourself with different types, such as fire tube and water tube boilers, to identify which design best suits your needs.
- Efficiency Ratings: Look for designs with high thermal efficiency to minimize operational costs.
- Compliance Standards: Ensure the designs meet local and international safety and environmental regulations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; engage in discussions to understand their capabilities.
- Experience in Your Market: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your geographical area, as they are more likely to understand local regulations and customer needs.
- After-Sales Support: Ensure the supplier offers robust support services, including maintenance and spare parts availability.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have identified potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline pricing, terms, and conditions. This step is essential for comparing offers effectively.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure that the quotations include a clear breakdown of costs, including installation and delivery.
- Warranty Terms: Pay attention to warranty offerings, which can significantly impact long-term operational costs.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
It is essential to confirm that your chosen supplier holds relevant certifications. These certifications demonstrate compliance with industry standards and regulations, ensuring product safety and reliability.
- Quality Assurance: Look for ISO certifications or other relevant quality assurance certifications that indicate a commitment to manufacturing excellence.
- Safety Certifications: Ensure the supplier complies with safety regulations pertinent to your region and industry.
Step 6: Assess Delivery and Installation Capabilities
Understanding the supplier’s logistics and installation capabilities is crucial for timely project execution. Delays in delivery can impact your operations significantly.
- Lead Times: Inquire about lead times for delivery and installation, and ensure they align with your project timeline.
- Installation Expertise: Verify that the supplier has qualified personnel to handle installation, ensuring it meets safety and operational standards.
Step 7: Finalize Contract Terms
Before finalizing your order, carefully review all contract terms. This is a critical step to protect your interests and ensure clarity in the transaction.
- Payment Terms: Negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow requirements.
- Liabilities and Responsibilities: Ensure that the contract clearly outlines the responsibilities of both parties, particularly regarding warranties and service obligations.
By following this practical checklist, you can navigate the procurement process for a simple steam boiler diagram with confidence, ensuring that you choose a solution that meets your operational needs and contributes to your overall efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for simple steam boiler diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Simple Steam Boilers?
When sourcing a simple steam boiler diagram, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials for steam boilers include steel, stainless steel, and various alloys, which can vary in price based on market conditions and quality. High-quality materials typically result in better durability and efficiency but come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses related to skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. This includes assembly, welding, and installation. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the geographic location of the manufacturer and prevailing wage rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturers often have lower overhead costs, which can translate to better pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom designs. These costs are amortized over the production volume, making them a critical factor for buyers considering larger orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control processes ensures that the steam boilers meet safety and performance standards. While QC adds to the upfront cost, it can reduce long-term operational risks and maintenance costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the size and weight of the boiler, as well as the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer. Understanding logistics costs is crucial, especially for international buyers who may face additional tariffs and fees.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market competition and the uniqueness of the product. Buyers should be aware of typical margins in their specific market to gauge fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Steam Boiler Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of steam boilers, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Many suppliers offer tiered pricing structures based on order size, incentivizing larger purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-designed boilers can incur additional costs due to unique specifications. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential for increased pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or ASME) can increase costs but are essential for compliance and safety, particularly in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reputation, but they often provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international transactions. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly influence the total landed cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Steam Boiler Prices?
To achieve the best value in sourcing steam boilers, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation Skills: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Buyers should be prepared to discuss volume discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the boiler, including maintenance, energy consumption, and operational efficiency. A lower initial price may not always equate to better value over the lifecycle of the product.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of regional pricing dynamics. Fluctuations in currency exchange rates and local market conditions can affect overall costs.
-
Request for Proposals (RFPs): Issuing RFPs to multiple suppliers can create competitive pressure, leading to better pricing and service offers. Clearly outline specifications and expectations to receive accurate quotes.
-
Due Diligence on Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Assess their financial stability, track record, and customer reviews to ensure reliability and quality.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for simple steam boilers can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct their own market research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate, up-to-date pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing simple steam boiler diagram With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Simple Steam Boiler Diagram
In the quest for efficient energy generation and management, businesses often evaluate various technologies that can provide similar functionalities to a simple steam boiler. While steam boilers have been a staple in industrial applications, alternatives such as electric boilers and hot water boilers are gaining traction. This section will compare the simple steam boiler diagram with two viable alternative solutions, providing insights for B2B buyers on which technology may best suit their specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Simple Steam Boiler Diagram | Electric Boiler | Hot Water Boiler |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-pressure steam generation suitable for various applications | Quick heating, ideal for smaller applications | Consistent hot water supply for heating |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing fuel costs can be high | Higher upfront cost but lower operating costs | Moderate cost, variable based on system size |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires considerable space and infrastructure | Compact design, easy to install in smaller spaces | Requires space for water tanks and piping |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed to ensure safety and efficiency | Lower maintenance; minimal moving parts | Regular maintenance required for tank and heating elements |
| Best Use Case | Heavy industrial applications needing high steam output | Residential or light commercial use | Industrial heating and domestic hot water needs |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Boilers?
Electric boilers are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficient and clean operation. They utilize electric components to generate heat, which makes them an environmentally friendly option as they do not rely on fuel combustion. The primary advantage of electric boilers is their lower maintenance requirements, as they have fewer moving parts and do not require regular fuel deliveries. However, they may have higher upfront costs and are less suitable for large-scale industrial applications where high steam output is necessary.
How Do Hot Water Boilers Compare to Steam Boilers?
Hot water boilers offer a versatile solution for heating applications, circulating heated water through a system rather than producing steam. They are particularly effective in scenarios where a constant supply of hot water is essential, such as in large buildings or industrial facilities. While they generally require similar maintenance to steam boilers, they can be more cost-effective in terms of fuel usage, especially in regions where gas or electricity prices are lower. However, they may not achieve the same level of thermal efficiency or steam pressure that a steam boiler can provide.
Conclusion: Which Solution is Right for Your Business?
When evaluating the right heating solution, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, including performance needs, budget constraints, and space availability. The simple steam boiler diagram remains an excellent choice for high-demand industrial applications, while electric and hot water boilers provide alternative solutions for smaller-scale operations or specific heating needs. By carefully assessing the pros and cons of each option, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for simple steam boiler diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Simple Steam Boiler?
Understanding the technical properties of a simple steam boiler is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating options that meet specific operational and safety standards. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The material used for constructing steam boilers typically includes carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel. The grade of the material affects the boiler’s strength, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. For example, stainless steel is preferred in environments prone to corrosion, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs. -
Pressure Rating
– Pressure ratings indicate the maximum pressure a boiler can safely handle. This is critical in industrial applications where high-pressure steam is necessary. Selecting a boiler with an appropriate pressure rating ensures safety compliance and operational efficiency. A high-pressure boiler may be necessary for applications like power generation, while low-pressure options suffice for heating. -
Heat Transfer Efficiency
– This property measures how effectively a boiler converts fuel into steam. Higher efficiency translates to lower fuel costs and reduced emissions, making it an essential consideration for environmentally-conscious businesses. Efficiency ratings can be influenced by design features such as economizers and heat exchangers. -
Capacity
– The capacity of a steam boiler is usually expressed in terms of output in pounds per hour (lb/hr) or tons per hour (TPH). This specification is vital for determining whether the boiler can meet the steam demand of a facility. Inadequate capacity may lead to operational inefficiencies and production downtimes. -
Tolerance Levels
– Tolerance levels refer to the acceptable variations in dimensions and specifications of boiler components. Tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring proper fit and function, particularly in high-pressure systems. Understanding tolerance levels can help buyers avoid issues related to performance and safety.
What Trade Terminology Is Important for Understanding Simple Steam Boilers?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and decision-making. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of steam boilers, understanding the OEM can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the components used in the boiler. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers who need to manage inventory and cost. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases effectively and avoid excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. In the context of steam boilers, an RFQ helps buyers gather information on pricing, delivery times, and specifications from multiple suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when importing or exporting steam boilers, as they clarify shipping costs, risk, and liability. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the steam boiler industry, lead times can vary significantly based on manufacturing processes and supplier capabilities. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring timely installations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting simple steam boilers that align with their operational needs and business objectives.
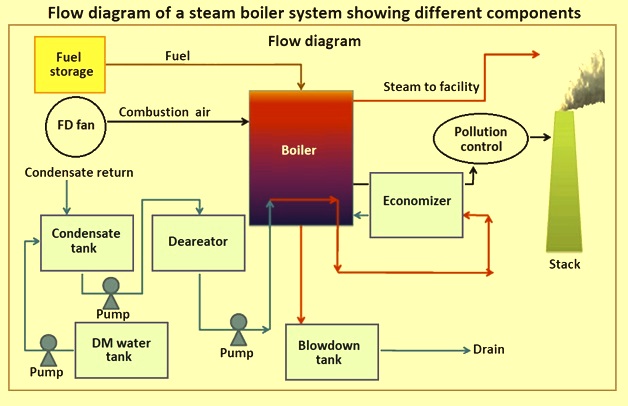
Illustrative image related to simple steam boiler diagram
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the simple steam boiler diagram Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Market?
The simple steam boiler diagram market is significantly influenced by several global drivers. One of the primary factors is the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions across various industries. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive to meet regulatory requirements and reduce operational costs, there is a growing preference for advanced steam boilers that offer better thermal efficiency and lower emissions. Moreover, the rapid industrialization in emerging markets, particularly in Nigeria and Brazil, is leading to a heightened need for reliable steam generation systems.
Current B2B technology trends also play a crucial role. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in steam boiler systems is enhancing operational efficiency through real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This trend is particularly beneficial for international buyers looking to minimize downtime and maximize productivity. Additionally, automation technologies are streamlining sourcing processes, enabling buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and products with ease.
Emerging sourcing trends, such as direct procurement from manufacturers, are gaining traction. This approach allows businesses to cut out middlemen, thus reducing costs and ensuring a more transparent supply chain. International buyers are increasingly focusing on suppliers that can provide comprehensive technical support and after-sales service, ensuring that they can effectively implement and maintain their steam boiler systems.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Simple Steam Boilers?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the simple steam boiler sector. The environmental impact of traditional steam boilers, particularly those relying on fossil fuels, has prompted a shift towards greener alternatives. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that offer steam boilers using sustainable fuels, such as biomass or natural gas, which significantly reduce carbon emissions.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly interested in sourcing from manufacturers that adhere to environmental regulations and demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or energy efficiency certifications can provide buyers with the assurance that they are partnering with responsible suppliers.
The market is also witnessing a rise in the availability of “green” materials used in the production of steam boilers. These materials not only enhance the efficiency of the boilers but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the supply chain. By choosing suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, international buyers can align their purchasing decisions with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Simple Steam Boilers in B2B?
The evolution of steam boilers dates back to the early 18th century, marking a significant advancement in industrial technology. Initially, steam boilers were rudimentary and often unsafe, with limited efficiency. However, as industries grew and the demand for reliable energy sources surged, technological innovations led to the development of more sophisticated designs.
By the late 19th century, the introduction of fire-tube and water-tube boilers revolutionized the steam generation process, allowing for higher pressures and greater efficiency. This evolution continued into the 20th century, with advancements in materials and control systems enhancing safety and performance.
Today, the simple steam boiler diagram represents a culmination of historical innovations, tailored to meet modern industrial needs. This historical perspective is essential for B2B buyers, as it underscores the importance of selecting reliable, efficient boiler systems that have been proven over time, ensuring a sound investment in energy generation technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of simple steam boiler diagram
-
How do I select the right steam boiler for my industrial needs?
Selecting the right steam boiler involves assessing your specific operational requirements, including pressure, temperature, and steam capacity. Consider the type of fuel available, as this will influence the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the boiler. Additionally, evaluate the installation space and maintenance capabilities. It’s beneficial to consult with manufacturers or suppliers who can provide detailed diagrams and specifications tailored to your application, ensuring that the boiler meets both your current and future needs. -
What are the key components of a simple steam boiler diagram?
A simple steam boiler diagram typically includes key components such as the combustion chamber, heat exchanger, steam drum, and safety valves. The combustion chamber is where fuel is burned to generate heat, while the heat exchanger transfers this heat to the water. The steam drum collects steam produced from the heated water. Understanding these components helps in identifying potential areas for efficiency improvements and maintenance needs. -
What are the advantages of different types of steam boilers?
Different types of steam boilers offer various advantages. For instance, gas boilers are known for their efficiency and lower emissions, making them environmentally friendly. Oil boilers, while generally more expensive, provide high efficiency and durability. Electric boilers offer quick heating with minimal maintenance. Understanding the specific benefits of each type can aid in selecting the best option for your operational needs and environmental goals. -
How can I ensure the quality and safety of steam boilers from suppliers?
To ensure quality and safety, conduct thorough vetting of potential suppliers by checking their certifications, industry reputation, and customer reviews. Request documentation of compliance with international safety standards. Additionally, consider visiting manufacturing facilities or requesting samples to assess build quality. Establishing a clear communication channel for quality assurance processes will also ensure that your specifications are met throughout the manufacturing and delivery phases. -
What are the typical payment terms in international steam boiler transactions?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on supplier policies and the nature of the transaction. Common practices include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify terms early in the negotiation process to avoid misunderstandings. Consider using escrow services for larger transactions to protect both parties. Always review the supplier’s payment policies in relation to your country’s regulations and currency stability. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for steam boilers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for steam boilers often depends on the supplier and the specific model of the boiler. Some manufacturers may have flexible MOQs for custom orders, while others may require a higher MOQ for standard models due to production costs. Discussing your needs with suppliers can help negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are considering long-term partnerships or bulk purchases. -
How does logistics and shipping work for steam boilers internationally?
International shipping of steam boilers typically involves coordination between manufacturers, freight forwarders, and customs agents. It’s crucial to understand shipping logistics, including container sizes, weight restrictions, and import regulations in your country. Suppliers should provide detailed shipping plans, including estimated delivery times and costs. Ensure that all necessary documentation for customs clearance is prepared to avoid delays and additional charges. -
What are the customization options available for steam boilers?
Customization options for steam boilers can include modifications to size, fuel type, pressure output, and additional features like automated controls or safety systems. Discussing your specific operational requirements with suppliers allows them to provide tailored solutions that enhance efficiency and performance. Be sure to inquire about the implications of customization on delivery times and costs, as bespoke designs may require longer lead times and additional investments.
Top 4 Simple Steam Boiler Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CN Control Valve – Steam Boilers
Domain: cncontrolvalve.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Steam boilers are heating systems that generate steam by boiling water. They convert thermal energy from various fuels, including gas, coal, biomass, and fuel oil, into steam for industrial and domestic purposes. Key types include electric boilers, hot water boilers, gas boilers, oil boilers, low pressure boilers, high pressure boilers, watertube boilers, firetube boilers, and shell boilers. Elect…
2. Steam Boiler – Free Diagram Resources
Domain: in.pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: This company, Steam Boiler – Free Diagram Resources, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Steamax Energy – Key Steam Boilers
Domain: steamaxenergyindia.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Steam Boiler Diagram | Steamax Energy India
Key Products:
1. Vertical Wood Fired Steam Boiler
2. Coal Fired Steam Boiler
3. LDO Oil Fired Steam Boiler
4. Steam Boiler Plant
5. Briquettes Fired Steam Boiler
6. Non-IBR Wood Fired Steam Boiler
7. Natural Gas Steam Boiler
8. Industrial Boiler Tank
9. Industrial Horizontal Steam Boilers
10. Electric Steam Boiler
11. Boiler for Pharmaceuticals Industry…
4. Cleaver-Brooks – Steam Boilers
Domain: cleaverbrooks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Steam Boilers: A Comprehensive Guide – Advanced steam boiler solutions designed for industrial and commercial operations with efficiency and reliability. Types of Steam Boilers: Firetube Boilers (used in commercial and small industrial applications), Watertube Boilers (ideal for high pressures in demanding industrial processes), Electric and Electrode Boilers (efficient, emission-free alternatives…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for simple steam boiler diagram
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of simple steam boilers is essential for maximizing operational efficiency and ensuring sustainability in various industries. Understanding the diverse types of steam boilers, their operational principles, and applicable fuel sources allows international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. As demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions grows, sourcing partners that offer innovative technologies and robust support will be invaluable.
Moreover, investing in a well-designed steam boiler system can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced productivity. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Nigeria, should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to quality, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
As we look ahead, the integration of advanced technologies, such as IoT and automation, will redefine the steam boiler landscape, presenting new opportunities for efficiency and performance. We encourage B2B buyers to actively engage with suppliers, participate in industry discussions, and explore innovative solutions that align with their strategic objectives. Embrace the future of steam generation—your operational success depends on it.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.