Everything You Need to Know About Pvc Structure Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pvc structure
Navigating the complexities of the global market for PVC structures presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers. Sourcing high-quality, durable, and cost-effective PVC products is essential, yet navigating supplier options and understanding material specifications can be daunting. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of PVC structures, covering various types, applications, and the critical aspects of supplier vetting and cost analysis.
PVC, known for its remarkable durability, chemical resistance, and versatility, has become a staple in sectors ranging from construction to electrical insulation. Understanding the properties and applications of PVC can empower buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring that they select the right products for their specific needs. This guide is tailored for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Brazil, providing actionable insights that facilitate successful procurement strategies.
By equipping buyers with in-depth knowledge of PVC’s physical characteristics and market trends, this guide not only streamlines the sourcing process but also enhances the overall purchasing experience. Whether you are seeking to enhance your supply chain efficiency or to diversify your product offerings, the insights presented here will help you navigate the global PVC landscape with confidence.
Understanding pvc structure Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid PVC (uPVC) | Stiff structure, high chemical resistance, low thermal expansion | Pipes, window frames, doors | Pros: Durable, low maintenance; Cons: Limited flexibility, can be brittle in cold conditions. |
| Flexible PVC | Contains plasticizers, high flexibility, and elasticity | Flooring, electrical insulation, automotive | Pros: Versatile, easy to mold; Cons: Less durable than rigid PVC, can degrade over time. |
| CPVC (Chlorinated PVC) | Enhanced thermal resistance, higher chlorine content | Hot and cold water pipes, industrial applications | Pros: Superior temperature resistance; Cons: More expensive than standard PVC. |
| PVC Foam Board | Lightweight, easy to fabricate, and resistant to moisture | Signage, displays, interior construction | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to work with; Cons: Less structural strength compared to rigid PVC. |
| PVC Coated Fabrics | Flexible PVC layer over fabric, weather-resistant | Tarpaulins, tents, upholstery | Pros: Durable and weatherproof; Cons: Can be heavier and less breathable than other materials. |
What Are the Characteristics of Rigid PVC (uPVC)?
Rigid PVC, commonly referred to as uPVC, is known for its robust structure and high resistance to chemicals and moisture. Its low thermal expansion makes it suitable for various applications, particularly in construction. B2B buyers seeking durable solutions for window frames and plumbing systems will find uPVC advantageous due to its longevity and low maintenance needs. However, its rigidity can pose challenges in applications requiring flexibility, making it essential to evaluate specific project requirements.
How Does Flexible PVC Differ from Other Types?
Flexible PVC is enhanced with plasticizers, giving it excellent flexibility and elasticity. This type of PVC is widely used in applications such as flooring and electrical insulation, where adaptability is crucial. B2B purchasers should consider the trade-offs between flexibility and durability; while flexible PVC offers ease of use and moldability, it may not withstand harsh conditions as well as its rigid counterpart. Buyers should assess their specific needs for durability versus flexibility when selecting this material.
Why Choose CPVC for High-Temperature Applications?
Chlorinated PVC (CPVC) is a variant that boasts superior thermal resistance due to its higher chlorine content. This makes CPVC ideal for transporting hot and cold water in plumbing systems and industrial applications. For B2B buyers, CPVC presents a reliable option for projects requiring materials that can withstand elevated temperatures. However, the higher cost associated with CPVC compared to standard PVC might necessitate a thorough cost-benefit analysis based on long-term usage.
What Are the Advantages of PVC Foam Boards?
PVC foam boards are lightweight and moisture-resistant, making them an excellent choice for signage and interior construction. Their ease of fabrication and cost-effectiveness appeal to businesses looking for versatile materials. However, while they are easy to work with, they lack the structural strength of rigid PVC. B2B buyers should consider the specific application to ensure that PVC foam boards meet their performance and durability requirements.
How Do PVC Coated Fabrics Enhance Durability?
PVC coated fabrics combine the flexibility of PVC with the durability of fabric, resulting in a weather-resistant material ideal for tarpaulins and upholstery. This combination offers businesses a robust solution for outdoor applications. While PVC coated fabrics provide excellent protection against the elements, they can be heavier and less breathable than alternative materials. B2B buyers should weigh these factors based on the intended use to maximize product performance and lifespan.
Key Industrial Applications of pvc structure
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of PVC Structure | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | PVC Pipes for Plumbing | High durability, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance costs | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards |
| Electrical | Electrical Insulation and Cable Sheathing | Excellent insulating properties and fire resistance | Verify certifications for safety standards and compliance |
| Automotive | Automotive Interior Components | Lightweight, flexible, and durable materials | Consider the impact of temperature and chemical exposure |
| Agriculture | PVC Films for Greenhouses | UV resistance and long lifespan, promoting sustainable farming | Assess thickness and UV protection ratings |
| Packaging | PVC Packaging Solutions | Cost-effective, versatile, and recyclable options | Evaluate material safety for food contact and recyclability |
How is PVC Structure Used in Construction and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the construction industry, PVC pipes are widely utilized for plumbing due to their high durability and resistance to corrosion. These pipes maintain structural integrity even in harsh environments, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing maintenance costs. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing PVC pipes that comply with local building codes is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of various diameters and lengths to suit specific project requirements.
What Role Does PVC Structure Play in Electrical Applications?
PVC is extensively used in electrical applications, particularly for insulation and cable sheathing. Its excellent electrical insulating properties and inherent fire-retardant characteristics make it a preferred choice for safeguarding electrical systems. For B2B buyers, especially in Europe and South America, it is essential to ensure that the PVC used in electrical applications meets international safety standards and certifications. Factors such as temperature tolerance and resistance to environmental factors should also be assessed to ensure longevity and reliability.
How is PVC Structure Beneficial in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, PVC is employed for interior components such as dashboards, door panels, and seat covers. Its lightweight nature combined with flexibility and durability contributes to fuel efficiency and passenger comfort. International buyers, particularly in emerging markets, should prioritize sourcing PVC materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and exposure to automotive fluids. Additionally, compliance with automotive industry standards is critical to ensure product reliability and safety.
How Does PVC Structure Enhance Agricultural Practices?
Agriculture benefits from PVC through the use of films for greenhouses. These films provide UV resistance and durability, promoting sustainable farming practices by extending the growing season and protecting crops from adverse weather conditions. Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should focus on the thickness and UV protection ratings of PVC films to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, sourcing from manufacturers with sustainable practices can align with eco-friendly initiatives.
What Advantages Does PVC Structure Offer in Packaging Solutions?
PVC packaging solutions are recognized for their versatility and cost-effectiveness. They are widely used in various sectors, including food and consumer goods, due to their recyclability and ability to preserve product integrity. For B2B buyers, especially in Europe, evaluating the safety of PVC materials for food contact is crucial. Additionally, understanding the recyclability options available can enhance brand sustainability efforts and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pvc structure’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Ensuring Durability and Longevity of PVC Structures
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges when it comes to ensuring that the PVC structures they procure will stand the test of time, particularly in harsh environmental conditions. Factors like extreme temperatures, exposure to chemicals, and UV radiation can lead to deterioration, affecting the reliability of products such as pipes, siding, and electrical insulation. For instance, a construction firm may invest significantly in PVC for a project, only to discover that the materials degrade faster than expected, leading to costly repairs and project delays.
The Solution:
To mitigate durability concerns, buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality, specifically engineered PVC products designed for their intended use. When purchasing, inquire about the manufacturer’s testing standards and certifications that guarantee longevity under specific conditions. Additionally, consider using products that incorporate additives or modifiers to enhance resistance to UV radiation and oxidation. For instance, selecting PVC with UV stabilizers can significantly extend the lifespan of outdoor applications. Regular maintenance and inspections can also help identify early signs of wear, allowing for timely interventions before more severe issues arise.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Compliance with International Standards
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers involves navigating the complex landscape of international standards and regulations governing PVC products. For companies operating in multiple regions, such as those in Africa, South America, and Europe, ensuring compliance with varying local regulations can be overwhelming. Non-compliance can lead to legal repercussions, project delays, and financial losses, which are particularly burdensome for smaller businesses with limited resources.
The Solution:
To address compliance issues, buyers should conduct thorough research on the regulatory requirements specific to their target markets. Engaging with local experts or compliance consultants can provide valuable insights into the necessary certifications and documentation needed for PVC products. Furthermore, establishing partnerships with manufacturers who are familiar with these regulations can streamline the sourcing process. Buyers should also consider requesting product certifications from suppliers that comply with international standards, such as ISO or ASTM, to ensure that their PVC structures meet safety and performance benchmarks.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Customization and Adaptability of PVC Products
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently encounter issues related to the customization of PVC structures to meet specific project requirements. For example, a manufacturer may need PVC components that can withstand unique stressors or environmental conditions, but standard products often do not meet these needs. This lack of adaptability can lead to delays in production and increased costs, as buyers may have to resort to custom solutions that are not readily available.

Illustrative image related to pvc structure
The Solution:
To overcome customization challenges, buyers should seek suppliers that offer a range of PVC formulations and processing options. Engaging with manufacturers who specialize in tailored solutions can lead to the development of products that meet specific performance criteria, such as enhanced flexibility or increased chemical resistance. When discussing project needs, provide detailed specifications and potential application scenarios to help manufacturers recommend the most suitable PVC variants. Additionally, exploring collaborative opportunities for R&D with suppliers can yield innovative solutions that not only meet current requirements but also anticipate future needs, ensuring a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pvc structure
When selecting materials for PVC structures, it is essential for international B2B buyers to understand the various types of PVC and their unique properties. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in PVC structures, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from diverse regions.
What are the Key Properties of Rigid PVC (uPVC)?
Rigid PVC, or unplasticized PVC (uPVC), is characterized by its high strength and rigidity. It has a melting point of approximately 212°C (414°F) and offers excellent resistance to chemicals, making it suitable for various applications, including construction and plumbing. Its durability is a significant advantage, as it can withstand harsh environmental conditions without degrading.
Illustrative image related to pvc structure
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of uPVC is its long lifespan and low maintenance requirements. However, its rigidity can be a limitation in applications requiring flexibility. Additionally, while uPVC is cost-effective, the initial manufacturing processes can be complex, which may affect overall pricing.
Impact on Application: Rigid PVC is particularly effective in applications involving water and sewage systems due to its corrosion resistance. It is also commonly used in window frames and doors, where structural integrity is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, where building regulations are stringent, adhering to these standards is critical.
How Does Flexible PVC Compare in Terms of Performance?
Flexible PVC is known for its elasticity and versatility, making it ideal for applications requiring bending and shaping. Its properties can be modified through the addition of plasticizers, allowing it to maintain flexibility at lower temperatures. The melting point is similar to rigid PVC, but its flexibility allows for different manufacturing processes.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility of PVC makes it suitable for various applications, including flooring, electrical insulation, and automotive parts. However, it may not have the same durability as rigid PVC and can be more susceptible to environmental degradation over time. Additionally, while the initial costs are low, the need for additives can increase overall expenses.

Illustrative image related to pvc structure
Impact on Application: Flexible PVC is widely used in applications where movement is necessary, such as in hoses and cables. Its ability to withstand bending without breaking is a significant advantage in these scenarios.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the environmental regulations regarding plasticizers, especially in regions like Europe, where there are strict guidelines on chemical additives.
What are the Benefits of PVC Composites?
PVC composites combine PVC with other materials, such as fiberglass or mineral fillers, to enhance specific properties. These composites can improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to impact and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of PVC composites is their enhanced performance characteristics, making them suitable for demanding applications. However, the complexity of manufacturing and the higher costs associated with these materials can be a drawback.
Impact on Application: PVC composites are often used in applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as in the construction of lightweight structures or automotive parts.

Illustrative image related to pvc structure
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the local market’s acceptance of composite materials and ensure compliance with relevant standards, as specifications can vary significantly between regions.
How Does PVC Foam Compare in Terms of Versatility?
PVC foam is a lightweight material that offers excellent insulation properties and is often used in signage, display boards, and interior applications. It has a lower density than solid PVC, making it easier to handle and install.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of PVC foam is a significant advantage for applications requiring ease of installation. However, it may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications due to its lower mechanical strength compared to solid PVC options.
Impact on Application: PVC foam is ideal for indoor applications where insulation and ease of installation are priorities. Its versatility allows for a wide range of finishes and colors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of PVC foam in their local markets and ensure that the products meet local fire safety standards, especially in regions with strict building codes.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for pvc structure | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid PVC (uPVC) | Plumbing and construction | Long lifespan and low maintenance | Limited flexibility | Medium |
| Flexible PVC | Electrical insulation and hoses | High flexibility | Less durable than rigid PVC | Low |
| PVC Composites | Lightweight structures and automotive parts | Enhanced performance characteristics | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| PVC Foam | Signage and interior applications | Lightweight and easy to install | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the properties, advantages, and considerations of various PVC materials, enabling informed decision-making for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pvc structure
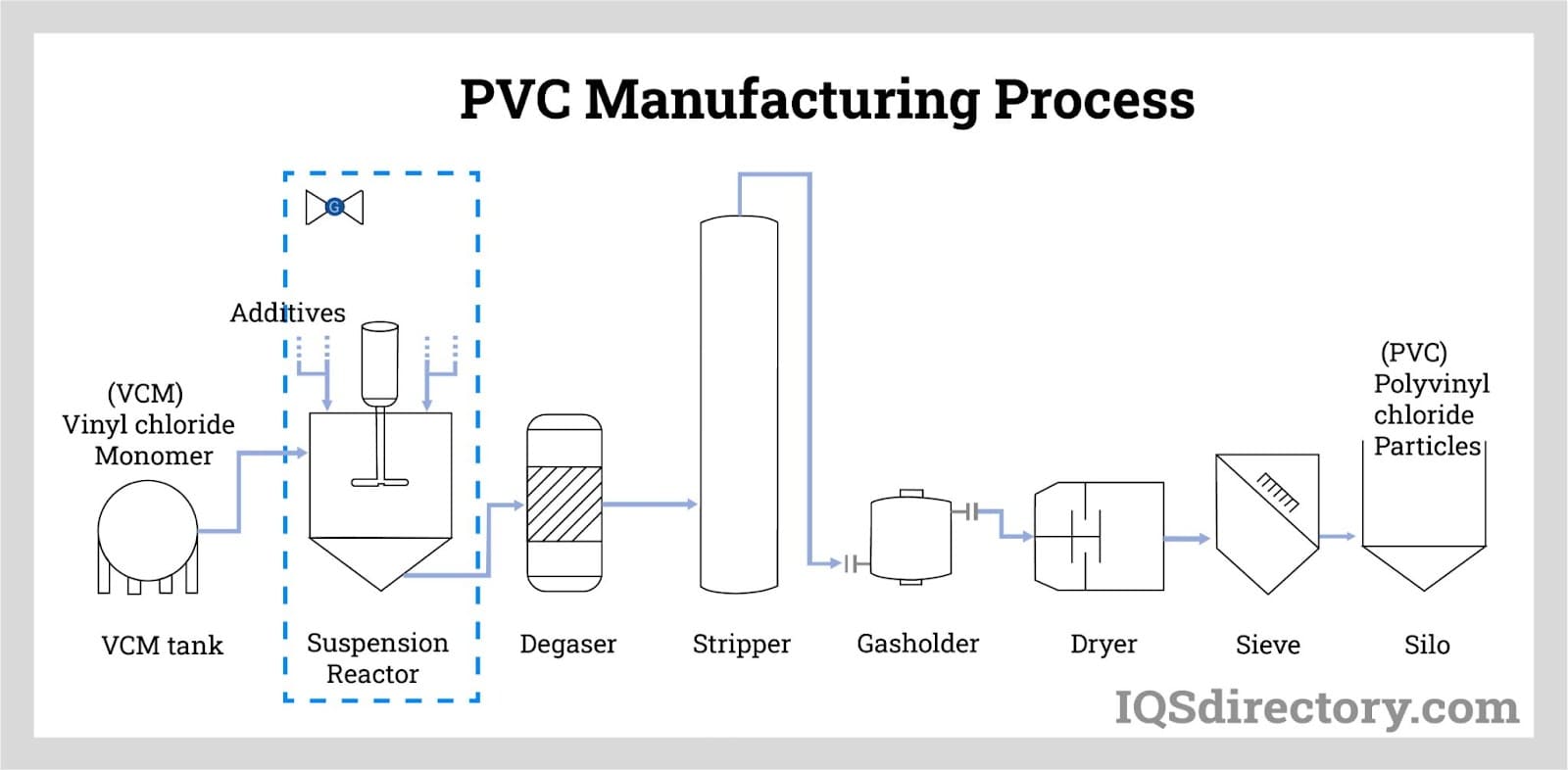
What Are the Main Stages of the PVC Structure Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing of PVC structures involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both functional and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to pvc structure
Material Preparation
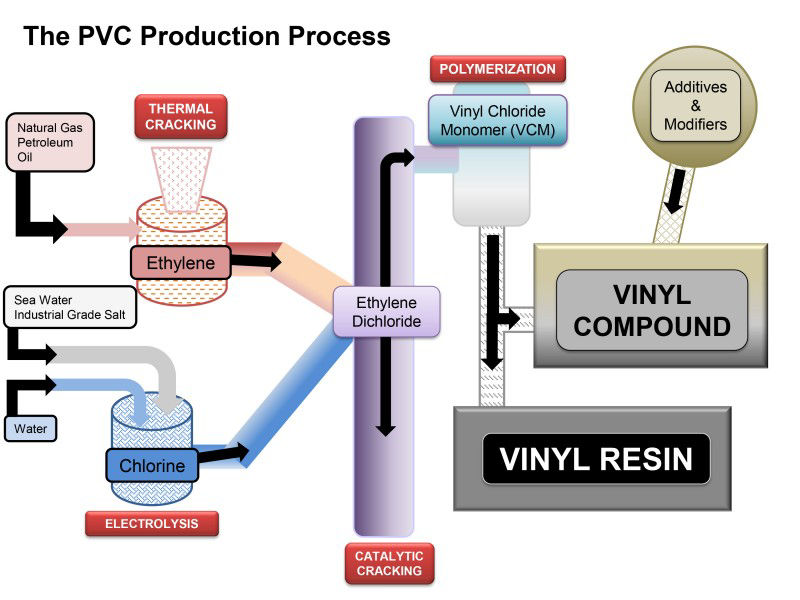
The first step in manufacturing PVC structures is the preparation of the raw materials. This typically begins with the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers (VCM) to create PVC resin. The polymerization process is usually conducted through methods such as suspension or emulsion polymerization, depending on the desired properties of the final product. After polymerization, the resin is purified and compounded with various additives, including plasticizers, stabilizers, and colorants, to enhance specific characteristics such as flexibility, durability, and UV resistance.
Forming Techniques
Once the PVC resin is prepared, it undergoes forming, which can be accomplished through several techniques, including extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding.
- Extrusion is often used for producing pipes, sheets, and profiles. In this process, the compounded PVC is heated until it becomes malleable and then forced through a die to create the desired shape.
- Injection Molding is suitable for creating complex shapes and parts with high precision, commonly used for fittings and connectors.
- Blow Molding is utilized for hollow products, such as bottles and tanks.
Each of these techniques requires careful control of temperature and pressure to ensure optimal product characteristics.
Assembly and Finishing
After forming, the components may require assembly, particularly for complex structures that include multiple parts. This stage may involve welding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening.
Illustrative image related to pvc structure
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the product’s aesthetics and functionality. Techniques such as surface treatments, coatings, and embossing can be applied to improve appearance and performance. For instance, PVC can be treated to enhance its resistance to UV light or to improve its anti-fouling properties.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into PVC Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the PVC manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with this standard indicates a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking (for European markets) and API standards (for products used in the oil and gas industry) are crucial for ensuring that products meet specific regulatory requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically implemented throughout the manufacturing process. These typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. It ensures that only materials that meet predefined specifications are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring and testing are performed to detect any deviations from standards. This can include monitoring temperature and pressure during forming processes, as well as visual inspections for defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are completed, a final inspection is conducted to ensure that they meet all specifications and standards before shipping. This may involve dimensional checks, mechanical property testing, and visual inspections for surface defects.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in PVC Quality Control?
To ensure the integrity and performance of PVC structures, various testing methods are employed throughout the manufacturing process.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tests such as tensile strength, elongation, and impact resistance are conducted to assess the mechanical properties of the final product. These tests ensure that the PVC structure can withstand the stresses it will encounter during use.
-
Chemical Resistance Testing: Given PVC’s use in a variety of environments, it’s crucial to test its resistance to various chemicals. This includes exposure to acids, bases, and solvents to ensure that the material maintains its integrity.
-
Thermal Testing: Assessing the thermal properties of PVC is vital, especially for applications that may involve exposure to heat. Tests for heat distortion temperature and flammability are common.
-
Environmental Testing: This includes UV resistance testing and weathering tests to ensure that the PVC structure can withstand environmental factors over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability.
Supplier Audits and Certifications
Buyers should request documentation of quality certifications and consider conducting supplier audits. This involves evaluating the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. A thorough audit can reveal the supplier’s commitment to quality and their capability to meet specific requirements.
Quality Control Reports
Requesting regular QC reports from suppliers can provide insights into their quality performance over time. These reports should detail the results of various tests conducted throughout the manufacturing process, including any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent organizations can conduct audits and testing to verify compliance with international standards and the supplier’s quality control procedures. This is particularly important for buyers operating in highly regulated markets.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers should be aware of potential nuances in quality control that can vary by region.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries may have varying regulations regarding the use of PVC products, particularly in construction and plumbing. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local regulations and standards.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can also play a role in quality control. For instance, the approach to quality assurance may differ between regions, which can impact the consistency of product quality.
-
Supply Chain Logistics: The logistics of sourcing PVC structures can also affect quality. Longer supply chains may introduce risks related to handling and transportation, which can impact the final product’s quality.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing PVC structures, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pvc structure’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides a systematic checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure PVC structures. It covers essential steps to ensure that your sourcing process is efficient, effective, and aligned with your specific needs. By following this guide, you can make informed decisions and secure high-quality PVC products that meet your project requirements.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for ensuring that the PVC structure meets your project needs. Consider factors such as the type of PVC (rigid or flexible), dimensions, load-bearing capacity, and environmental resistance. Documenting these requirements will streamline communication with potential suppliers and help avoid misunderstandings.
Illustrative image related to pvc structure
2. Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in the PVC industry. Look for companies that specialize in the type of PVC structures you require and have experience in your region, such as Africa or South America. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online reviews to compile a list of potential suppliers.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Pay attention to their history of fulfilling orders on time, their quality assurance processes, and their customer service responsiveness.
4. Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers possess relevant certifications and compliance with international standards. Look for ISO certifications, environmental management certifications, and adherence to industry-specific regulations. This step helps mitigate risks associated with product quality and reliability.
5. Request Product Samples
Before placing a bulk order, request samples of the PVC structures you intend to purchase. Testing samples will allow you to assess the material’s quality, durability, and suitability for your applications. Evaluate the samples under conditions that mimic your intended use to ensure they meet performance expectations.
6. Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes shipping, tariffs, and potential maintenance costs. Establishing clear terms will help prevent disputes and ensure a smooth procurement process.
7. Plan for Logistics and Delivery
Coordinate with your supplier to establish a reliable logistics plan for delivery. Ensure that the supplier can meet your timelines and that you have a strategy for receiving and inspecting the products upon arrival. Proper logistics planning can minimize delays and ensure that your project stays on schedule.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for PVC structures with confidence, ensuring that they select the right products and partners for their business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pvc structure Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in PVC Structure Sourcing?
When sourcing PVC structures, understanding the cost components is essential for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw PVC resin is a significant portion of total expenses. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand, availability of vinyl chloride monomers, and global oil prices, which affect production costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct labor for manufacturing and indirect labor for support functions. Skilled labor may command higher wages, particularly in regions where technical expertise is scarce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses such as factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, making it crucial to assess the supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery can be substantial, especially for custom PVC products. Tooling costs are amortized over production runs, impacting pricing based on order volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality involves systematic inspections and testing, contributing to overall costs. Certifications for quality standards can also add to expenses but are vital for maintaining market trust.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling of finished products can vary based on distance, method of shipping, and import/export duties. Understanding logistics costs is crucial for accurate pricing.
-
Margin: Finally, the supplier’s profit margin will influence the final price. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market positioning, competition, and perceived value of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect PVC Structure Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of PVC structures, especially in international markets:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often result in lower per-unit costs. Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements can significantly increase costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. Clearly defining specifications can help mitigate unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. High-quality, certified materials may come at a premium but can enhance product durability and performance.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards may have higher prices but are often more reliable and accepted in diverse markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of the supplier play a role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide greater assurance of product quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen shipping terms can affect total costs. Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively and clarify responsibilities.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in PVC Structure Sourcing?
To optimize the procurement process for PVC structures, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in proactive negotiations with suppliers. Leveraging volume commitments or long-term contracts can yield better pricing and terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, operational costs, and disposal expenses. A lower initial price may not always result in overall savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and regional market conditions that could impact pricing. Conduct market research to ensure competitive pricing.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, focusing on their production capabilities, financial stability, and customer service history. This can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
-
Understanding Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding PVC products, as compliance costs can affect overall pricing.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost estimates provided are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, order specifications, and supplier negotiations. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations before making procurement decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pvc structure With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to PVC Structures in B2B Applications
In the quest for effective and efficient solutions for various industrial applications, PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) structures are frequently considered due to their unique properties. However, alternatives do exist, each with distinct advantages and limitations. This analysis aims to provide a clear comparison between PVC structures and two viable alternatives: Polypropylene (PP) and Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP). By evaluating these options across multiple performance metrics, B2B buyers can make informed decisions based on their specific project requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | PVC Structure | Polypropylene (PP) | Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High chemical resistance; durable; fire-retardant | Good chemical resistance; less durable under UV; lower heat resistance | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio; good chemical resistance; non-corrosive |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective; low maintenance costs | Lower initial cost; less expensive to produce | Higher upfront cost; long-term savings due to durability |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to process and fabricate; suitable for various applications | Simple to mold and shape; less complex manufacturing | Requires specialized skills for installation; complex manufacturing process |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; long lifespan (up to 100 years) | Moderate maintenance; susceptible to UV degradation | Low maintenance; resistant to corrosion but can be damaged by impact |
| Best Use Case | Plumbing, construction, and electrical insulation | Packaging, automotive parts, and textiles | Structural applications, marine environments, and chemical processing |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer that is commonly used in various applications, including packaging and automotive parts. One of its main advantages is its lower initial cost compared to PVC, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. However, while PP exhibits good chemical resistance, it is less durable when exposed to UV radiation and has lower heat resistance. This can lead to degradation over time, particularly in outdoor applications. Despite its limitations, the ease of molding and shaping PP makes it a practical choice for many applications.
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
FRP is a composite material made from a polymer matrix reinforced with fiberglass. It offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and is highly resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for use in harsh environments, such as marine and chemical processing applications. However, the initial cost of FRP is typically higher than both PVC and PP, which can be a barrier for some buyers. Additionally, the installation of FRP requires specialized skills and techniques, adding complexity to the implementation process. Despite these challenges, the long-term durability and low maintenance of FRP can lead to significant cost savings over time, particularly in demanding conditions.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting a structural material for a specific application, B2B buyers should consider various factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance expectations. PVC structures offer a compelling combination of durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of implementation, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, in scenarios where extreme strength or corrosion resistance is critical, alternatives like FRP may provide superior performance despite their higher initial costs. Ultimately, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each material will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and project goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pvc structure
What Are the Key Technical Properties of PVC Structures?
When evaluating PVC structures, several critical specifications must be understood to ensure the right material is selected for specific applications. These properties not only influence the material’s performance but also affect cost, longevity, and safety.
1. Chemical Resistance
PVC is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and inorganic substances. This resistance is crucial for industries such as plumbing and chemical processing, where materials are frequently exposed to corrosive substances. For B2B buyers, understanding the chemical compatibility of PVC can prevent costly failures and maintenance issues.
2. Fire Retardancy
One of the standout features of PVC is its inherent fire-retardant properties due to its chlorine content. With an ignition temperature around 455°C, PVC poses a lower risk of fire spread compared to other plastics. For businesses in construction and manufacturing, this property is vital for meeting safety standards and ensuring long-term durability of products used in high-risk environments.
3. Mechanical Stability and Creep Resistance
PVC exhibits excellent mechanical stability, with minimal deformation under stress. Its low creep deformation makes it suitable for applications requiring long-term load-bearing capabilities, such as pipes and structural components. B2B buyers should consider these properties when sourcing materials for projects where durability and long service life are essential.
4. Thermal Properties
The thermal characteristics of PVC, including a melting point of approximately 212°C, influence its processing methods and applications. Understanding these properties helps in selecting the right PVC type for manufacturing processes like extrusion and molding. Buyers should ensure that the thermal stability aligns with the operational temperatures of their specific applications.
5. Density and Weight
PVC typically has a density ranging from 1.3 to 1.45 g/cm³, making it a lightweight option compared to other materials. This property is beneficial for reducing shipping costs and improving handling efficiency. Buyers should assess density when considering transportation logistics and application requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to PVC Structures?
In the PVC industry, understanding trade terminology is crucial for effective communication and transaction execution. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of PVC, an OEM might provide custom PVC components tailored to specific applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate sourcing strategies effectively.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For PVC products, MOQs can vary significantly based on the complexity and customization of the order. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to ensure they can meet their project requirements without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for price estimates on specific products or services. In the PVC industry, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. For PVC procurement, understanding Incoterms is essential for clarifying who bears the cost and risk during shipping and delivery, which can impact overall project budgeting.
Illustrative image related to pvc structure
5. Plasticizer
Plasticizers are additives used to increase the flexibility and workability of PVC. Different types of plasticizers can significantly alter the physical properties of the final product. Buyers should understand the implications of plasticizers on performance and compliance with safety regulations.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project needs and business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pvc structure Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the PVC Structure Sector?
The global PVC structure market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors such as construction, automotive, and electrical industries. Key trends influencing this market include the rise of smart building technologies, which integrate PVC materials for their durability and insulating properties. Additionally, the growing emphasis on lightweight materials in construction and automotive applications is propelling the demand for PVC due to its advantageous strength-to-weight ratio.
In emerging markets like Africa and South America, infrastructure development is a critical driver. Governments and private sectors are investing heavily in construction projects, creating a robust demand for PVC pipes, sheets, and other structural components. In the Middle East, particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia, the push for sustainable urban development is further catalyzing the need for high-performance PVC products. European buyers are increasingly focusing on the recyclability of PVC and its lower environmental impact compared to other plastics, which is shaping procurement strategies.
Moreover, advancements in manufacturing technology, including automation and additive manufacturing, are enhancing the efficiency and customization of PVC products. International B2B buyers must stay abreast of these technological trends to optimize their sourcing strategies and ensure competitive advantage.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the PVC Structure Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of sourcing PVC materials in the B2B landscape. The environmental impact of PVC production, primarily linked to its chemical processes, has led to a heightened focus on ethical sourcing. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing supply chains to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and corporate social responsibility standards.
The demand for ‘green’ certifications is on the rise, with many buyers seeking materials that are produced with minimal environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) for sustainable building practices are becoming critical criteria in procurement decisions. Additionally, the development of bio-based PVC and the incorporation of recycled materials are gaining traction, allowing buyers to meet sustainability goals while maintaining product performance.
In this context, international buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East are leading the charge towards ethical sourcing, often preferring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation and marketability.
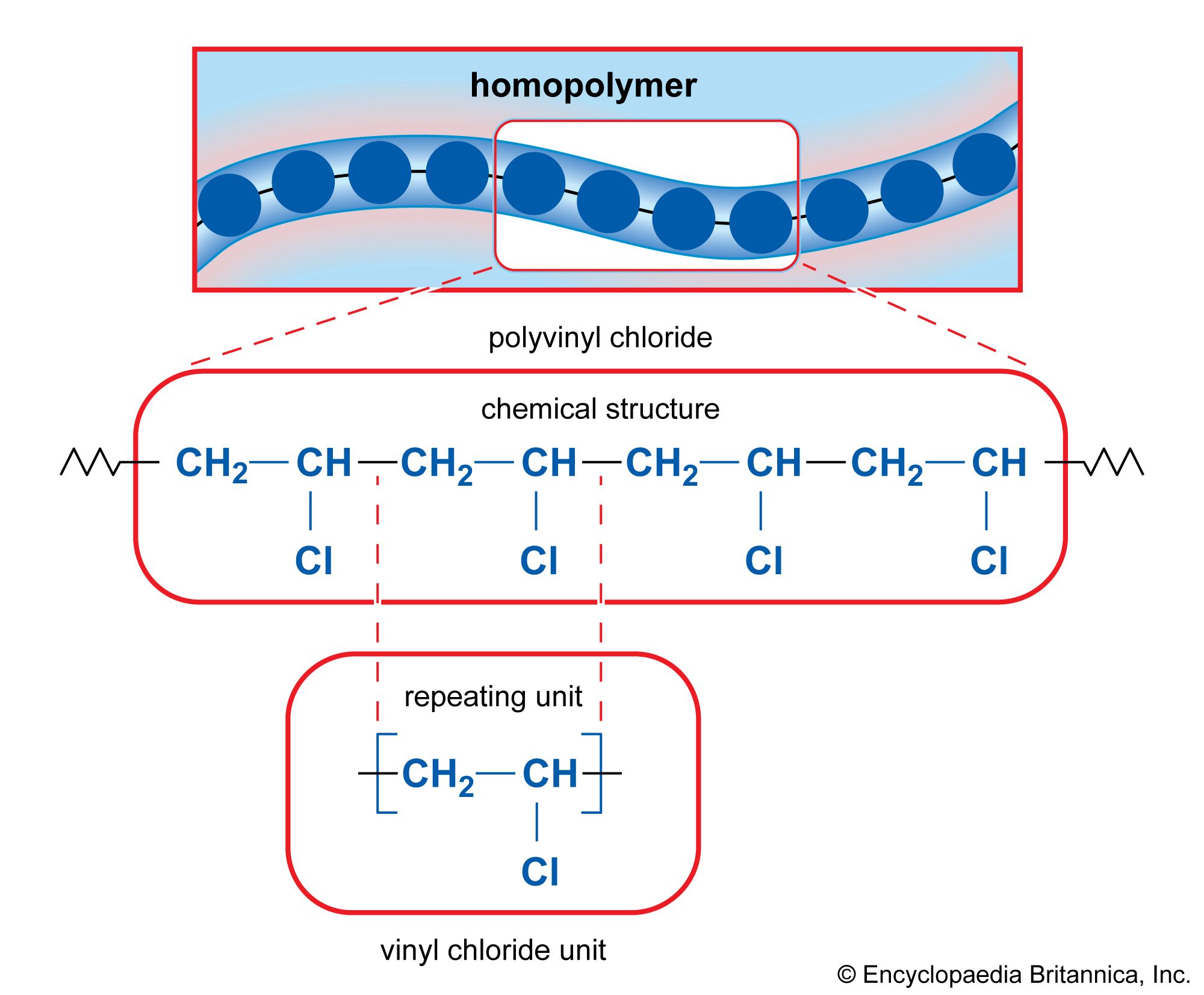
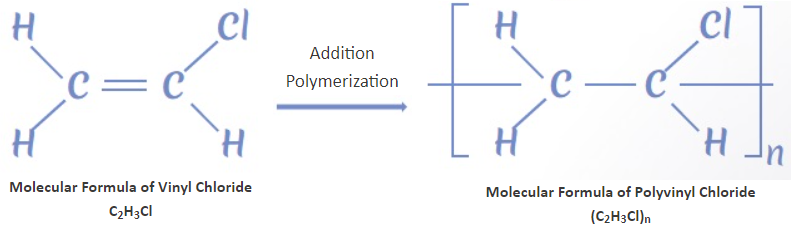
What is the Brief Evolution of PVC in the B2B Context?
The evolution of PVC can be traced back to its discovery in the 19th century, but its commercial viability surged in the mid-20th century, particularly during the post-war construction boom. Initially used for electrical insulation and plumbing, PVC quickly expanded into diverse applications due to its unique properties, such as chemical resistance, durability, and low cost.
In recent decades, the PVC industry has adapted to changing market demands, focusing on innovation and sustainability. The introduction of flexible PVC and advancements in processing technologies have broadened its applications, making it a staple in construction, automotive, and medical industries. Today, as businesses face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, the PVC sector is evolving once more, integrating recycling and ethical sourcing into its operational frameworks to meet the demands of environmentally conscious consumers and regulatory bodies.
This evolution underscores the importance of understanding PVC’s historical context for B2B buyers, as it informs current sourcing trends and market dynamics that are crucial for making informed procurement decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pvc structure
-
How do I ensure the quality of PVC structures from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of PVC structures, start by requesting certifications such as ISO 9001 or other relevant industry standards. Conduct factory visits or audits to evaluate production practices and material sourcing. Request samples for testing to assess durability, chemical resistance, and compliance with your specifications. Establish a clear quality assurance process that includes periodic inspections and testing throughout the production cycle. Additionally, consider third-party inspections to validate the quality claims of your suppliers. -
What are the advantages of using PVC structures in construction?
PVC structures offer a range of advantages in construction, including durability, chemical resistance, and lightweight properties. They are inherently fire-retardant, reducing the risk of fire hazards. PVC is also resistant to corrosion and weathering, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. Furthermore, its versatility allows for various forms, such as pipes, sheets, and profiles, which can be customized to meet specific project requirements. This adaptability can lead to cost savings in both material and labor. -
What factors should I consider when selecting a PVC supplier?
When selecting a PVC supplier, consider their reputation, experience, and specialization in PVC products. Evaluate their production capacity, lead times, and ability to meet your specific requirements. Check for compliance with international standards and regulations in your target market. Assess their customer service and communication responsiveness. Additionally, inquire about their supply chain management practices, including sourcing of raw materials and logistics capabilities to ensure timely delivery. -
What customization options are available for PVC products?
Customization options for PVC products include variations in thickness, color, flexibility, and surface texture. Suppliers can incorporate additives to enhance properties such as UV resistance, fire retardancy, or impact resistance. Custom shapes and sizes can also be produced through various manufacturing techniques like extrusion or molding. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to determine the extent of customization they can provide and any associated costs or minimum order quantities. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for PVC structures?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for PVC structures vary by supplier and the type of product being ordered. Typically, MOQs can range from a few hundred to several thousand units, depending on production capabilities and cost-effectiveness. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify their MOQ requirements and explore options for bulk purchasing or combined orders to meet your needs. Some suppliers may also offer flexibility in MOQs for first-time buyers or ongoing partnerships. -
What payment terms are common in international PVC trade?
Common payment terms in international PVC trade include letters of credit (LC), advance payments, or payment on delivery. The choice of payment method often depends on the buyer-supplier relationship, the order size, and the country of origin. It’s essential to negotiate clear payment terms upfront, including deposit amounts, payment schedules, and any applicable penalties for late payments. Using secure payment platforms can also help mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How does logistics impact the sourcing of PVC structures?
Logistics plays a crucial role in sourcing PVC structures, influencing costs, delivery times, and overall supply chain efficiency. Consider factors such as shipping methods, freight costs, and customs regulations in your target market. Work with suppliers who have reliable logistics partners to ensure timely delivery. Additionally, plan for potential delays due to international shipping complexities, and incorporate buffer times in your project timelines to accommodate any unforeseen issues. -
What are the best practices for importing PVC structures from overseas?
To successfully import PVC structures, conduct thorough research on the target market’s regulations, tariffs, and import duties. Ensure that your supplier complies with all relevant standards and certifications required in your country. Prepare all necessary documentation, including bills of lading, invoices, and customs declarations. Engage a customs broker to navigate the complexities of international trade and facilitate smooth clearance. Finally, maintain open communication with your supplier throughout the process to address any issues that may arise.
Top 5 Pvc Structure Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Pinterest – PVC Structures & DIY Projects
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: PVC Structures, DIY projects, outdoor canopies, greenhouse frames, patio covers, privacy screens, tarps, and various PVC pipe crafts and structures.
2. Study – Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Domain: study.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a man-made thermoplastic material with the chemical formula C2H3Cl. It is composed of long chains of vinyl chloride molecules, which consist of carbon, hydrogen, and chlorine. PVC can be designed in flexible or rigid states, making it versatile for various applications. Common uses of PVC include water and drainage pipes, flexible tubing, transparent storage bags, and b…
3. Seepvcforum – Key Properties of PVC
Domain: seepvcforum.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: PVC has an amorphous structure with polar chlorine atoms, providing unique features compared to other plastics. Key physical properties include: 1. Fire Retarding Properties: High ignition temperature (455°C), less risk of ignition, and lower heat release when burning. 2. Durability: Highly resistant to oxidation, maintaining performance over long periods; 35-year-old PVC pipes showed no deteriora…
4. FORMUFIT – PVC Fittings
Domain: formufit.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: FORMUFIT offers a variety of PVC products including:
1. **PVC Fittings**:
– Furniture Grade PVC Fittings
– Specialty PVC fittings for structural use:
– 3-Way Elbow PVC Fitting
– 4-Way Tee PVC Fitting
– 5-Way Cross PVC Fitting
– Slip Sling Tee PVC Fitting
– Cross PVC Fitting
– Tee PVC Fitting
– 90° Elbow PVC Fitting
– 45° Elbow PVC Fitting
– Adju…
5. Fabritecture – PVC Coated Polyester Solutions
Domain: fabritecture.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) coated polyester is a commonly selected material for tensile membrane structures due to its excellent strength, waterproof properties, flexibility, transparency, and durability. It is cost-effective and versatile, meeting a wide range of color and application needs for both permanent and temporary structures. PVC is treated to be stain, fire, and UV resistant. The approxim…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pvc structure
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your PVC Structure Procurement?
As the global demand for PVC continues to rise, particularly in construction, plumbing, and electrical applications, strategic sourcing becomes imperative for international B2B buyers. Key takeaways from this guide highlight the remarkable physical properties of PVC, including its durability, chemical resistance, and fire-retardant characteristics. These attributes not only enhance product lifespan but also ensure safety and reliability in various applications, making PVC an invaluable material for diverse industries.
Investing in strategic sourcing allows businesses to optimize procurement processes, reduce costs, and ensure a consistent supply of high-quality PVC products. By fostering partnerships with reputable manufacturers, buyers can gain access to the latest innovations and tailored solutions that meet specific market needs.

Illustrative image related to pvc structure
Looking ahead, it is crucial for B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to stay informed about advancements in PVC technologies and market trends. By leveraging strategic sourcing strategies, companies can position themselves for success in an evolving landscape. Embrace the potential of PVC and enhance your supply chain today—your future growth hinges on it.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.