Everything You Need to Know About Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications Sourcing in…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for industrial rubber shredding applications
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing efficient industrial rubber shredding solutions presents a significant challenge for businesses across various sectors. As industries seek to enhance sustainability and reduce waste, understanding the intricacies of rubber shredding applications becomes crucial. This guide offers an in-depth exploration of the types of rubber shredders available, their diverse applications—from tire recycling to the processing of rubber waste in manufacturing—and the importance of selecting the right supplier.
International B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Nigeria and Vietnam—will benefit from actionable insights into supplier vetting processes and cost considerations. With a focus on empowering informed purchasing decisions, this guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing key factors that influence the effectiveness and efficiency of rubber shredding operations.
By delving into the latest technologies, best practices, and market trends, you can navigate the complexities of the industrial rubber shredding landscape confidently. This knowledge not only aids in optimizing waste management strategies but also enhances your competitive edge in a market that increasingly values sustainability and resource recovery. Embrace this opportunity to transform your rubber waste into valuable materials while ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
Understanding industrial rubber shredding applications Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tire Shredding | Specialized for whole tires; high torque; multi-stage | Tire recycling, rubber powder production | Pros: Reduces waste, recycles materials. Cons: High initial investment. |
| Industrial Rubber Scrap | Versatile; handles various rubber forms; customizable | Manufacturing, construction, automotive | Pros: Adaptable to different materials. Cons: Maintenance complexity. |
| E-Waste Rubber Components | Focused on rubber parts in electronic devices; safe disposal | Electronics recycling, component recovery | Pros: Environmentally friendly, compliant with regulations. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Hazardous Rubber Waste | Designed for safe handling of toxic materials; robust safety features | Chemical processing, industrial waste management | Pros: Ensures regulatory compliance. Cons: Requires specialized training. |
| Green Waste Rubber Recycling | Combines organic and rubber waste; eco-friendly design | Landscaping, compost production | Pros: Supports sustainability initiatives. Cons: Lower processing speed. |
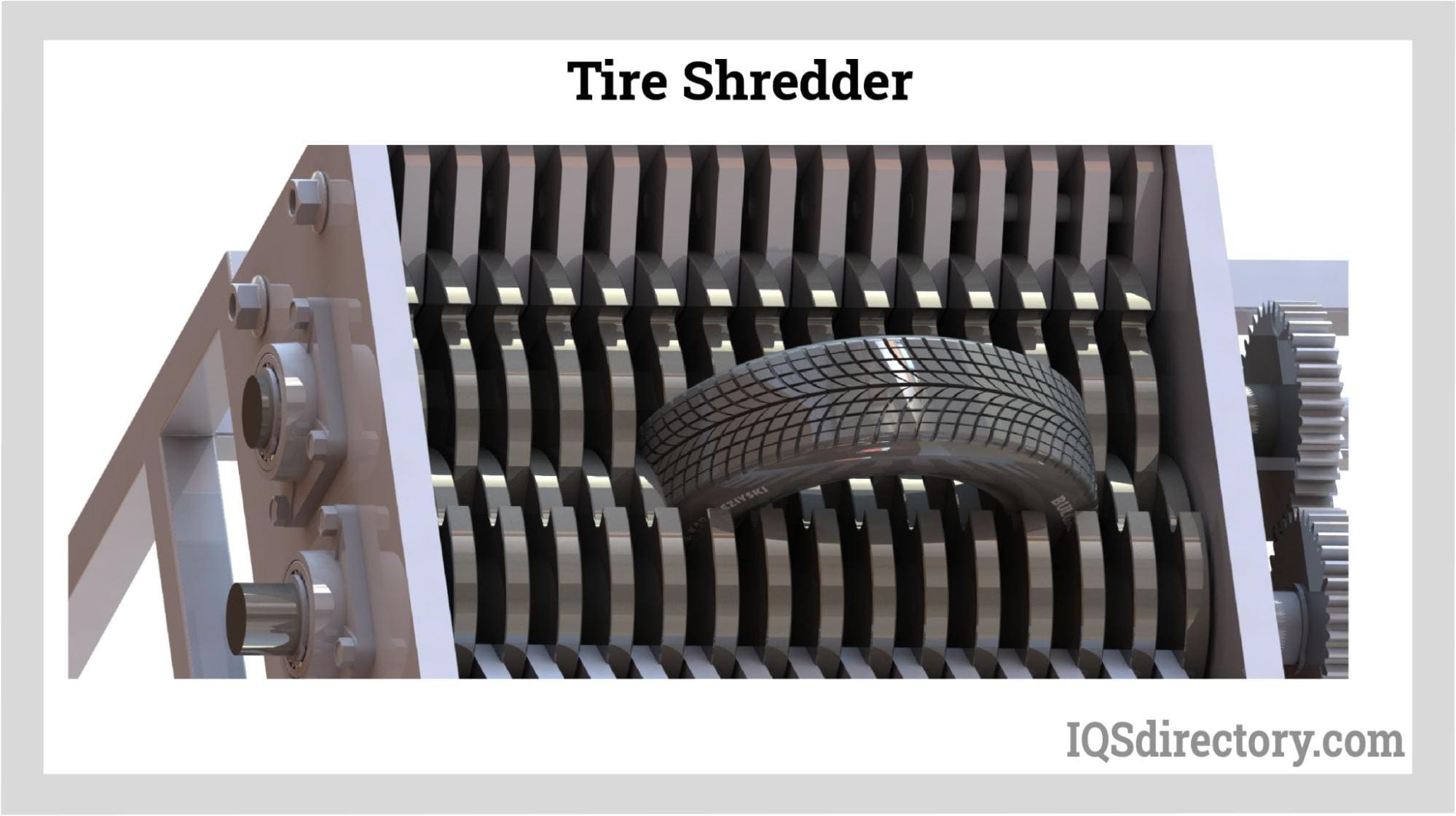
What are the Key Characteristics of Tire Shredding Applications?
Tire shredding is a specialized application designed for processing whole tires into smaller, manageable pieces. These machines employ high torque and multi-stage shredding techniques to efficiently reduce tire size. Commonly used in tire recycling facilities, the shredded rubber can be repurposed for various applications, including rubber powder production for new tires or other rubber products. Buyers should consider the initial investment and energy consumption when selecting tire shredding equipment, as these factors can significantly impact operational costs.
How Does Industrial Rubber Scrap Shredding Work?
Industrial rubber scrap shredding involves the processing of various forms of rubber waste, including off-cuts, rejects, and end-of-life products. These shredders are highly versatile and can be customized to meet the specific needs of different industries, such as manufacturing and construction. The ability to handle diverse rubber materials makes this option attractive for businesses looking to optimize waste management. However, potential buyers should be aware of the maintenance requirements and the complexity of the machinery involved.
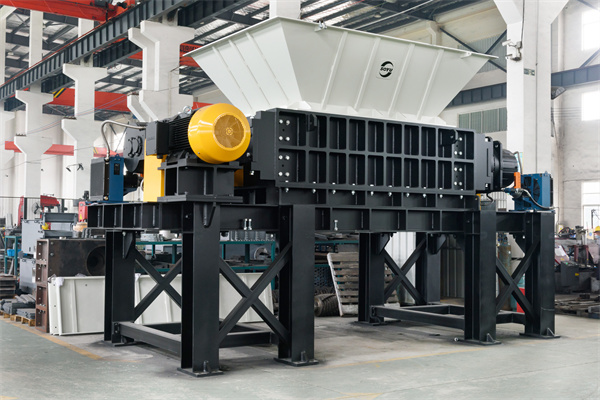

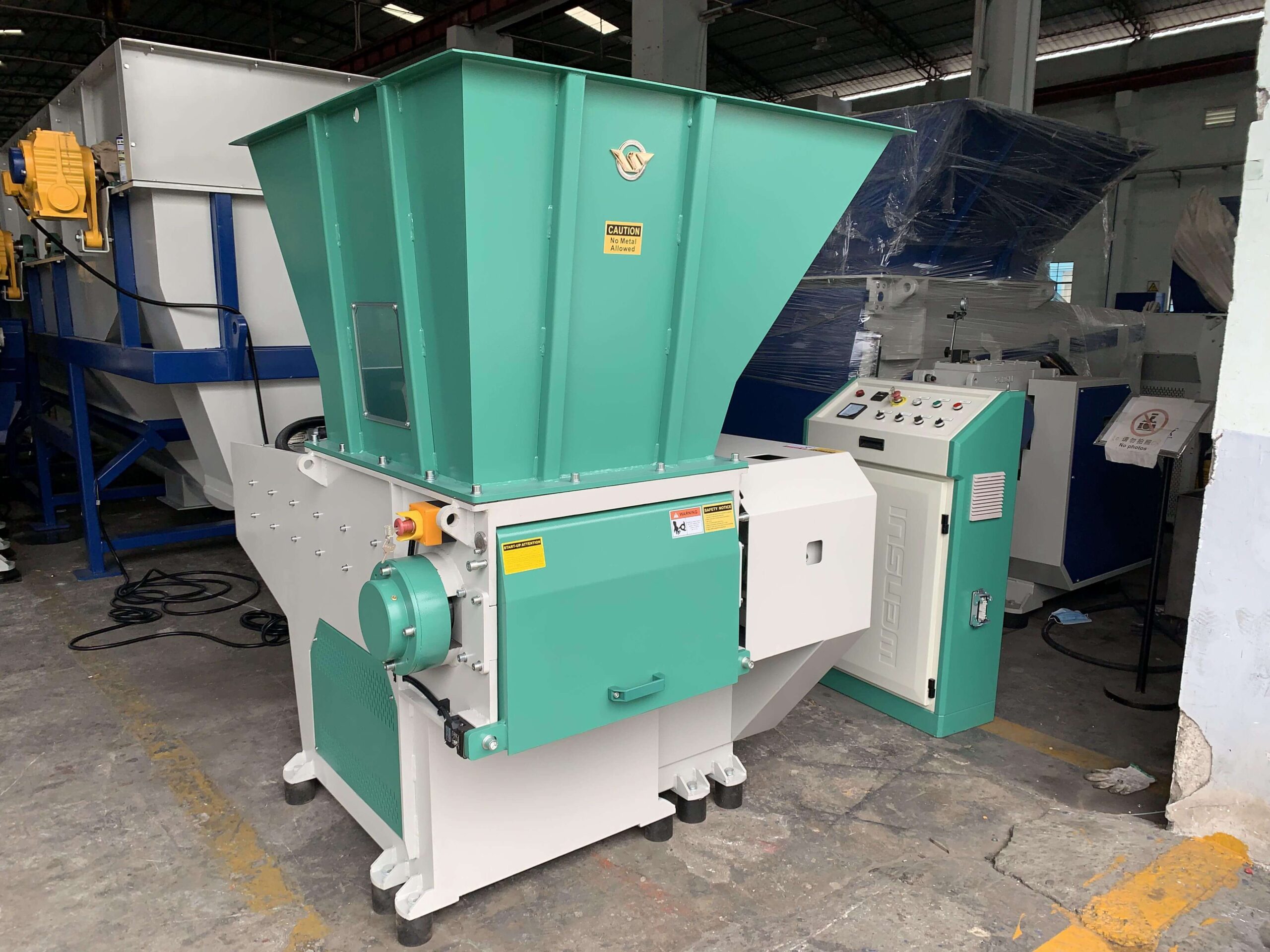
Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
What are E-Waste Rubber Components and Their Applications?
E-waste rubber component shredding focuses on the safe disposal and recycling of rubber parts found in electronic devices. With growing concerns over electronic waste, these shredders offer an environmentally friendly solution by recovering valuable materials while ensuring compliance with disposal regulations. This application is particularly relevant for electronics recycling companies looking to enhance their sustainability efforts. Buyers should consider the specific regulatory requirements in their regions, as well as the potential for recovering valuable materials.
What are the Benefits of Hazardous Rubber Waste Shredding?
Hazardous rubber waste shredding is essential for industries that deal with toxic materials, ensuring safe handling and disposal. These shredders are equipped with robust safety features to comply with environmental regulations and protect workers. Commonly used in chemical processing and industrial waste management, they play a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact. However, the need for specialized training and compliance with strict regulations can pose challenges for potential buyers.
How Does Green Waste Rubber Recycling Contribute to Sustainability?
Green waste rubber recycling combines the processing of organic materials with rubber waste, promoting sustainable practices in landscaping and compost production. This eco-friendly approach helps reduce landfill waste and supports composting initiatives. While the technology is beneficial for companies aiming to enhance their sustainability credentials, buyers should be mindful of the potentially lower processing speeds compared to traditional rubber shredding methods, which may affect productivity.
Key Industrial Applications of industrial rubber shredding applications
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of industrial rubber shredding applications | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tire Recycling | Shredding of used tires for material recovery and recycling | Reduces landfill waste, recovers valuable materials like rubber and steel | Compliance with environmental regulations, machine durability, and capacity for high volume processing |
| Manufacturing | Processing rubber waste from production lines | Enhances sustainability, reduces raw material costs, and minimizes waste disposal fees | Equipment efficiency, maintenance support, and adaptability to various rubber types |
| Construction | Recycling rubber for use in construction materials | Produces eco-friendly building materials, reduces costs associated with new materials | Quality of shredded material, processing speed, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Automotive Repair | Shredding rubber parts and components from decommissioned vehicles | Facilitates recycling of rubber, contributing to circular economy initiatives | Safety features, ability to handle diverse rubber types, and ease of operation |
| Sports and Recreation | Shredding rubber for use in playground surfaces and sports fields | Provides safe, durable, and sustainable surfaces, enhancing user experience | Material quality, compliance with safety standards, and sourcing of appropriate machinery |
How is Industrial Rubber Shredding Used in Tire Recycling?
In the tire recycling industry, industrial rubber shredding plays a crucial role in converting end-of-life tires into reusable materials. The shredding process breaks down tires into smaller pieces, enabling the recovery of valuable components such as rubber, steel, and fiber. This not only reduces the environmental impact of tire waste but also provides raw materials for new products, such as asphalt, playground surfaces, and molded rubber goods. Buyers in this sector should consider machinery that meets regulatory standards for safety and efficiency, as well as the capability to process large volumes of tires.
What are the Benefits of Rubber Shredding in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often generate significant amounts of rubber waste during production. Industrial rubber shredding allows companies to efficiently recycle this waste, transforming it into reusable material for new products. This process not only enhances sustainability efforts but also reduces costs associated with raw materials and waste disposal. For international buyers, particularly in developing regions, sourcing shredders that are durable and require minimal maintenance can be critical to maintaining production efficiency and profitability.

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
How is Rubber Shredding Applied in Construction?
In the construction sector, shredded rubber is increasingly used as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials. It can be incorporated into asphalt mixtures, providing enhanced durability and flexibility. Additionally, rubberized surfaces are utilized in playgrounds and sports fields for safety and shock absorption. Buyers must ensure that the shredding equipment can produce high-quality, consistent rubber granules that meet industry standards, as well as consider the machine’s processing capabilities for various rubber types.
Why is Rubber Shredding Important for Automotive Repair?
The automotive repair industry often deals with decommissioned vehicles that contain various rubber components. Industrial rubber shredding allows for the efficient disposal and recycling of these parts, helping to reduce the environmental footprint of automotive waste. By converting rubber into reusable materials, businesses can contribute to a circular economy while also minimizing disposal costs. Buyers should prioritize shredders that offer versatility in handling different types of rubber and ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
What Role Does Rubber Shredding Play in Sports and Recreation?
Rubber shredding is essential in the sports and recreation sector, where shredded rubber is used to create safe and durable surfaces for playgrounds and athletic fields. This application enhances user safety by providing shock absorption and reducing injuries. Buyers in this industry should focus on sourcing shredders that can produce high-quality rubber granules, ensuring compliance with safety standards. Additionally, understanding the local market’s demand for recycled materials can help businesses capitalize on this growing trend.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘industrial rubber shredding applications’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Challenge of Inefficient Material Processing
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in the rubber recycling industry encounter inefficiencies in their shredding processes. For instance, a company handling large volumes of scrap rubber may find that their current shredding equipment cannot keep up with production demands. This can lead to bottlenecks, resulting in delayed operations, increased labor costs, and wasted resources. Additionally, inadequate shredding can produce inconsistent material sizes, complicating downstream processing and reducing the quality of recycled rubber products.
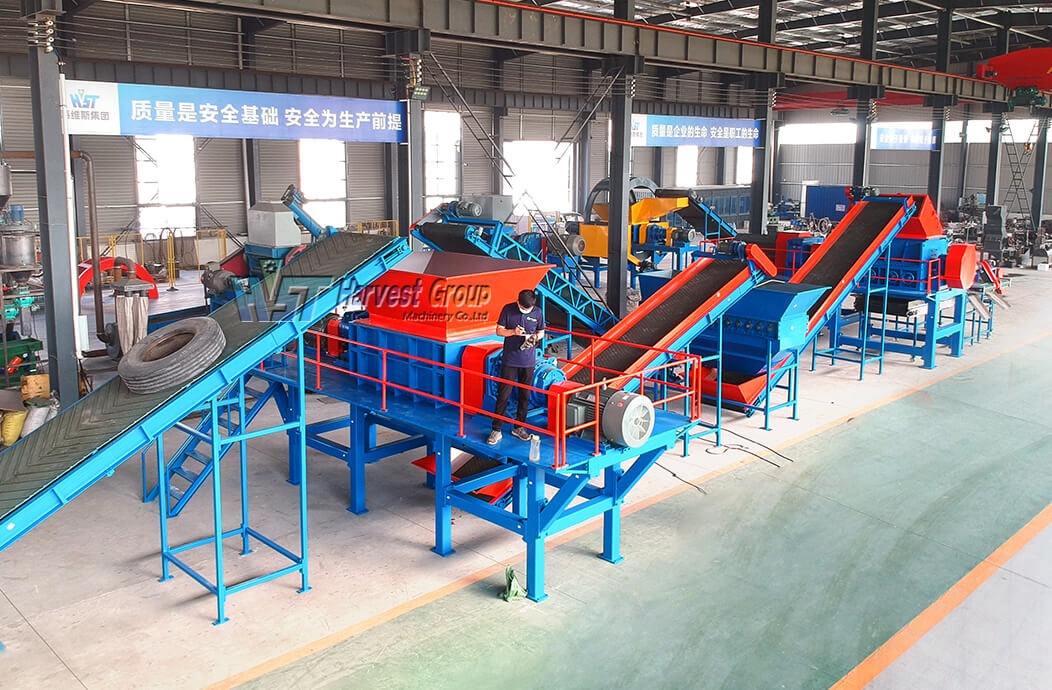

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
The Solution: To address this issue, businesses should invest in high-capacity, variable-speed industrial rubber shredders designed to handle large volumes efficiently. When sourcing equipment, buyers should prioritize features such as adjustable cutting speeds and customizable configurations that can be tailored to specific rubber types. It’s also beneficial to collaborate with manufacturers who offer comprehensive testing services, allowing potential buyers to assess how different shredders perform with their materials before making a purchase. Regular maintenance and operator training can further enhance the efficiency of the shredding process, ensuring that equipment operates at optimal capacity.
Scenario 2: Compliance with Environmental Regulations
The Problem: Compliance with environmental regulations is a significant pain point for companies involved in industrial rubber shredding. Regulatory standards often require that businesses manage waste responsibly and minimize their environmental impact. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines, operational disruptions, and damage to the company’s reputation. For example, a facility that improperly disposes of rubber waste may face scrutiny from regulatory bodies, leading to costly penalties and potential shutdowns.
The Solution: To ensure compliance, businesses should invest in shredding systems equipped with advanced dust and emissions control technologies. When selecting shredders, buyers should consult with manufacturers about the latest environmental regulations and inquire about how their equipment can help meet compliance standards. Additionally, implementing a robust waste management strategy, including regular audits and employee training programs on best practices for waste disposal, can bolster compliance efforts. By proactively addressing environmental concerns, companies can not only avoid penalties but also enhance their brand image as environmentally responsible enterprises.
Scenario 3: High Operating Costs and Downtime
The Problem: A common concern for B2B buyers in the rubber shredding industry is the high operating costs associated with machinery maintenance and downtime. Aging equipment often requires frequent repairs, which can lead to extended periods of inactivity and disrupt production schedules. This not only affects profitability but can also impact customer satisfaction due to delays in order fulfillment. For example, a manufacturer may struggle to meet deadlines if their shredding equipment is constantly breaking down.
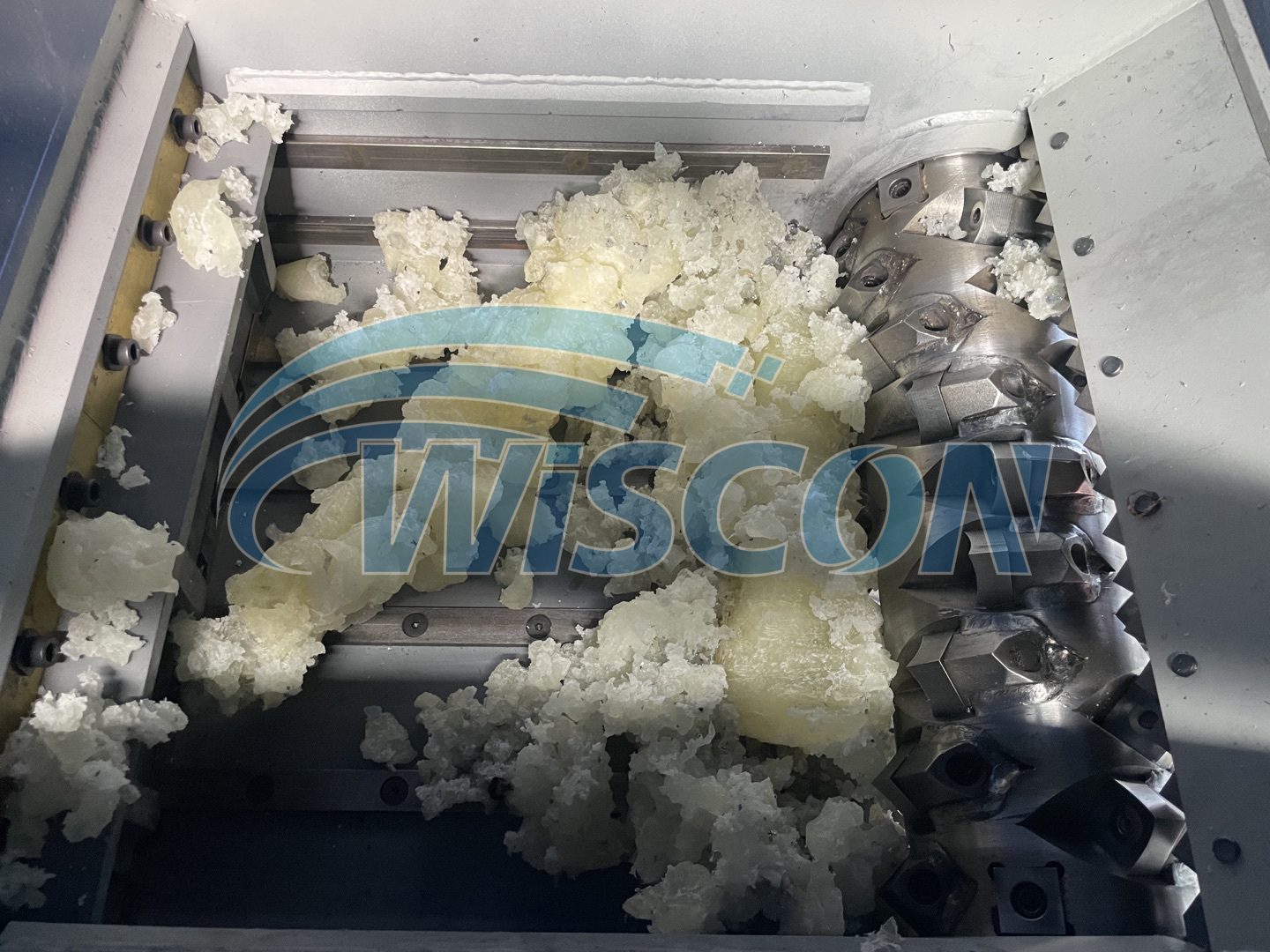

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
The Solution: To mitigate high operating costs and reduce downtime, businesses should consider investing in newer, more reliable shredding technologies that come with warranties and service agreements. These advanced machines often feature self-diagnostic tools that can predict maintenance needs before a failure occurs. Buyers should look for suppliers who offer comprehensive after-sales support, including training on proper machine operation and regular maintenance schedules. Additionally, exploring options for leasing equipment can provide flexibility and reduce upfront costs, enabling companies to allocate resources more effectively while still maintaining high production standards. By prioritizing reliability and support, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and minimize disruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for industrial rubber shredding applications
What Are the Key Materials for Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications?
In the realm of industrial rubber shredding, selecting the right materials is crucial for optimizing machine performance and ensuring compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in rubber shredding applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Natural Rubber
Key Properties: Natural rubber exhibits excellent elasticity, tensile strength, and resilience. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically from -50°C to 100°C, making it suitable for various industrial environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of natural rubber is its superior flexibility and durability, which enhances the shredding process. However, it is vulnerable to degradation from UV light and ozone exposure, which can limit its lifespan. Additionally, natural rubber tends to be more expensive than synthetic alternatives.
Impact on Application: Natural rubber is compatible with a range of shredding media, allowing for effective processing of tires and other rubber products. Its unique properties make it suitable for applications requiring high elasticity.
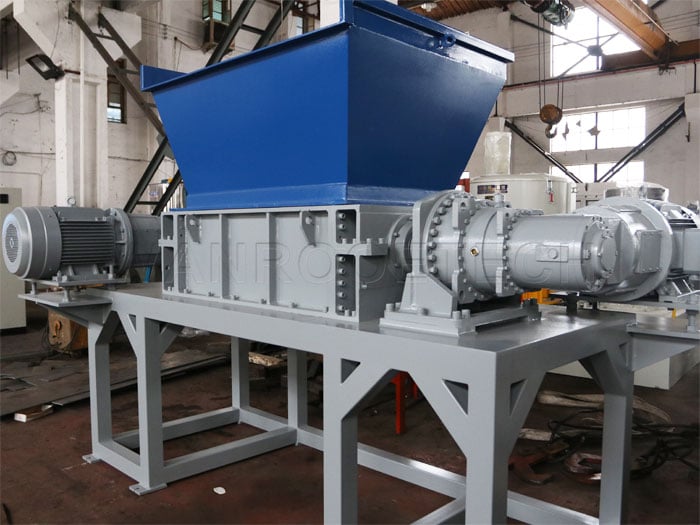

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is essential for natural rubber applications. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local sourcing to reduce costs and ensure material quality.
2. Synthetic Rubber (SBR – Styrene-Butadiene Rubber)
Key Properties: SBR offers good abrasion resistance and aging stability, with a temperature range of -40°C to 100°C. It is less elastic than natural rubber but provides better wear resistance.
Pros & Cons: The cost-effectiveness of SBR makes it a popular choice for industrial applications. Its durability against wear and tear is advantageous for shredding operations. However, SBR has a lower tensile strength compared to natural rubber, which may affect performance in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: SBR is widely used in tire manufacturing and can be effectively shredded for recycling. Its compatibility with various shredding techniques enhances operational efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local and international standards, such as ISO and DIN. In regions like Europe, adherence to environmental regulations regarding synthetic materials is critical.
3. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Key Properties: EPDM is known for its excellent weather resistance, UV stability, and temperature tolerance, typically ranging from -50°C to 150°C. It is also resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of EPDM is its longevity and performance in harsh environments, making it ideal for outdoor applications. However, its higher manufacturing complexity can lead to increased costs.
Impact on Application: EPDM’s chemical resistance allows it to be used in applications where exposure to oils and solvents is common. This makes it suitable for shredding rubber products used in automotive and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with ASTM and JIS standards, particularly in the automotive sector. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are prevalent, EPDM’s performance can be a significant selling point.
4. Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Key Properties: Nitrile rubber is characterized by its excellent oil and fuel resistance, with a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C. It also exhibits good abrasion resistance.
Pros & Cons: NBR’s resistance to oils makes it ideal for applications where rubber products are exposed to hydrocarbons. However, it is less flexible than natural rubber, which may limit its use in certain shredding applications.
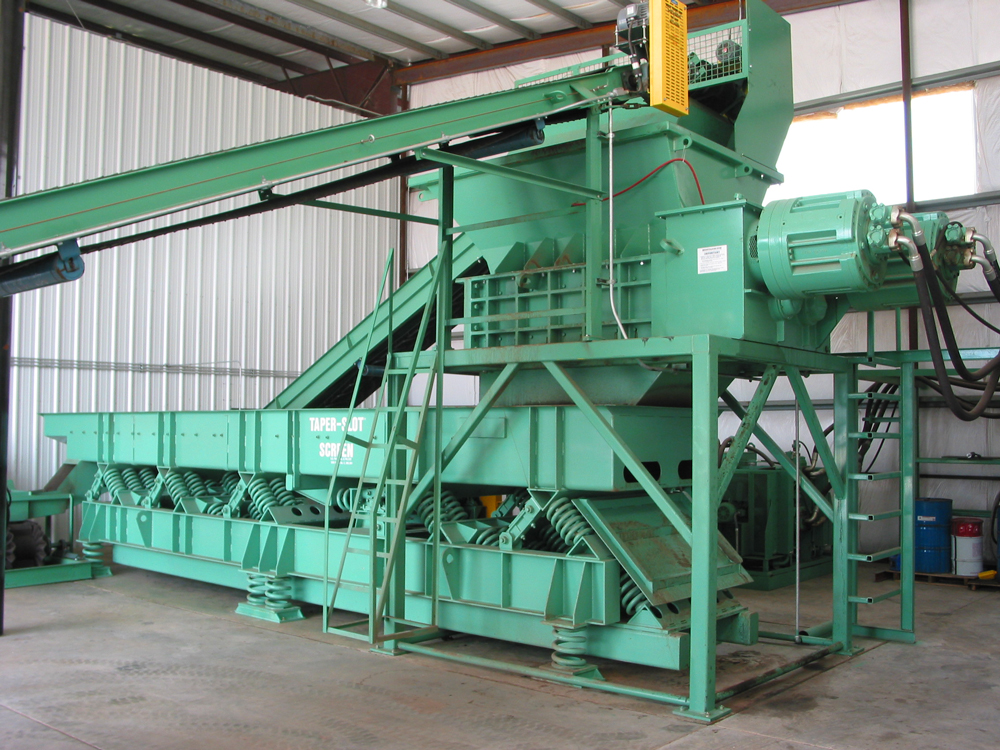

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
Impact on Application: NBR is commonly used in automotive seals and hoses, making it suitable for shredding applications in the automotive industry. Its compatibility with various shredding methods enhances the recovery of valuable materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM and ISO standards is crucial, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations like Europe. Buyers should also consider the availability of NBR in local markets to minimize logistics costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications
| Material | Typical Use Case for industrial rubber shredding applications | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Rubber | Tire recycling and general rubber products | High elasticity and durability | UV and ozone degradation | High |
| Synthetic Rubber (SBR) | Tire manufacturing and recycling | Cost-effective and durable | Lower tensile strength compared to natural rubber | Medium |
| EPDM | Outdoor applications and automotive products | Excellent weather and UV resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Automotive seals and hoses | Excellent oil and fuel resistance | Less flexibility than natural rubber | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for industrial rubber shredding applications
What Are the Key Stages in Manufacturing Industrial Rubber Shredding Equipment?
The manufacturing process for industrial rubber shredding equipment involves several critical stages that ensure the end product meets the required performance and durability standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The process begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, such as high-strength steel for blades and frames. Suppliers should provide certifications to ensure that materials comply with industry standards. Rigorous inspections are performed to verify material integrity before proceeding to the next stage.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the necessary components using various techniques, including laser cutting, CNC machining, and forging. These methods allow for precise dimensions and ensure that components can withstand the stresses encountered during shredding operations.
-
Assembly: After forming, components are assembled into complete shredding machines. This stage involves meticulous attention to detail, ensuring that all parts fit together correctly and function seamlessly. The assembly process may also include the integration of automation systems for improved efficiency.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatments such as powder coating or galvanizing to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Quality control checks are implemented throughout the finishing process to ensure that the aesthetic and functional aspects of the equipment meet specifications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Industrial Rubber Shredding Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is vital in the manufacturing of industrial rubber shredding equipment. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the quality assurance process, ensuring that equipment is safe, efficient, and reliable.
-
International Standards: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, a globally recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for quality management systems. Compliance with this standard ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the market, additional certifications such as CE marking (for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards) or API (American Petroleum Institute) specifications may be required. These certifications provide an added layer of assurance regarding the quality and safety of the equipment.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, several quality control checkpoints are established, including:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they are used in production. Any non-conforming materials are rejected.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that each component meets specified tolerances and standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection assesses the completed equipment for functionality, safety, and compliance with specifications before it is shipped to customers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance for Rubber Shredders?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the performance and durability of industrial rubber shredders. These methods ensure that the equipment can handle the intended workload and operate efficiently.
-
Performance Testing: This includes operational tests where the shredders are run under typical conditions to evaluate their efficiency, throughput, and effectiveness in shredding rubber materials. Parameters such as noise levels, vibration, and energy consumption are also monitored.
-
Durability Testing: Components are subjected to stress tests to simulate long-term usage. This may involve running the machine continuously for extended periods to identify any potential failure points.
-
Safety Testing: Safety features, such as emergency stop functions and protective guards, are tested to ensure compliance with safety regulations. This is crucial for preventing workplace accidents and ensuring user safety.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring the reliability of industrial rubber shredding equipment.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should assess the factory’s capabilities, quality management systems, and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers can request detailed quality reports that outline the results of performance and safety tests, as well as compliance with relevant certifications. These documents should be transparent and accessible.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can be conducted at various stages of production, providing an additional layer of assurance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges when it comes to quality control in the procurement of industrial rubber shredders. Understanding these nuances can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
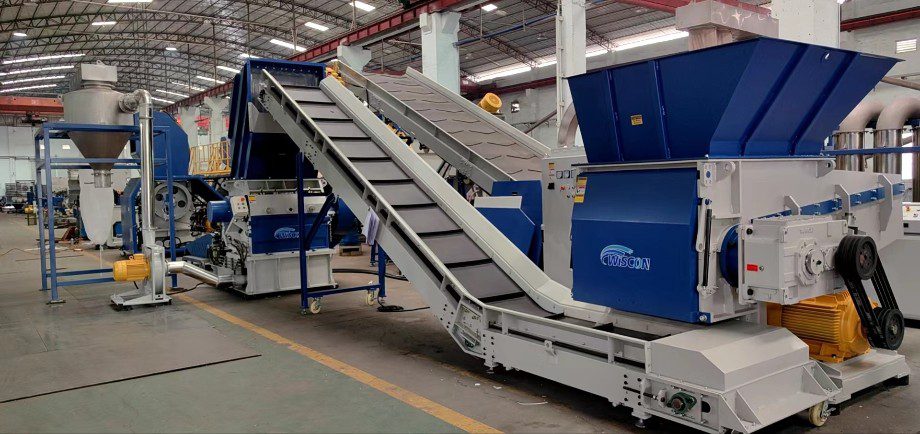

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulations regarding industrial equipment. Buyers must ensure that the equipment meets local standards and certifications, which may differ from those in the supplier’s country.
-
Cultural Considerations: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across regions. Buyers should be aware of these differences and adapt their approaches accordingly to facilitate effective collaboration with suppliers.
-
Logistical Challenges: Shipping and handling equipment across international borders can introduce risks of damage or non-compliance with local regulations. Buyers should work with suppliers who have experience in international logistics and can navigate these complexities efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for industrial rubber shredding applications is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages of manufacturing, implementing robust quality control measures, and ensuring compliance with international standards, buyers can secure reliable and efficient equipment that meets their operational needs. Engaging in thorough supplier verification processes will further enhance the likelihood of successful procurement in the global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘industrial rubber shredding applications’
This guide serves as a practical resource for B2B buyers looking to procure solutions for industrial rubber shredding applications. By following these steps, you can ensure that your sourcing process is thorough, efficient, and tailored to your specific business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for ensuring that the shredders you consider meet your operational requirements. Consider factors such as the type of rubber materials you’ll be processing, the desired output size, and throughput capacity. This clarity will guide your discussions with suppliers and help you avoid costly mismatches.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct extensive research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in industrial rubber shredding. Look for companies that specialize in this field and have a history of successful installations. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online reviews to compile a list of potential partners.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it is crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Analyze their experience with rubber shredding applications and assess the range of solutions they offer, ensuring they align with your specifications.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of suppliers, request detailed proposals that include pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty information. This will allow you to compare offerings effectively. Look for transparency in pricing and any additional costs that may arise, such as installation or maintenance services.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. This includes safety certifications and environmental compliance, which are particularly crucial in the rubber recycling sector. Suppliers should provide documentation of their certifications and any quality control processes they follow.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Reliable after-sales support is essential for the longevity of your shredding equipment. Inquire about the availability of technical support, spare parts, and maintenance services. A supplier that offers comprehensive support can minimize downtime and enhance the overall efficiency of your operations.
Step 7: Conduct Site Visits and Demonstrations
If possible, arrange site visits or demonstrations of the shredders in action. Observing the equipment firsthand can provide invaluable insights into its performance and suitability for your needs. Pay attention to the ease of operation, maintenance requirements, and the quality of the shredded material.
By following these steps, you can make informed decisions when sourcing industrial rubber shredding solutions, ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency and sustainability efforts.
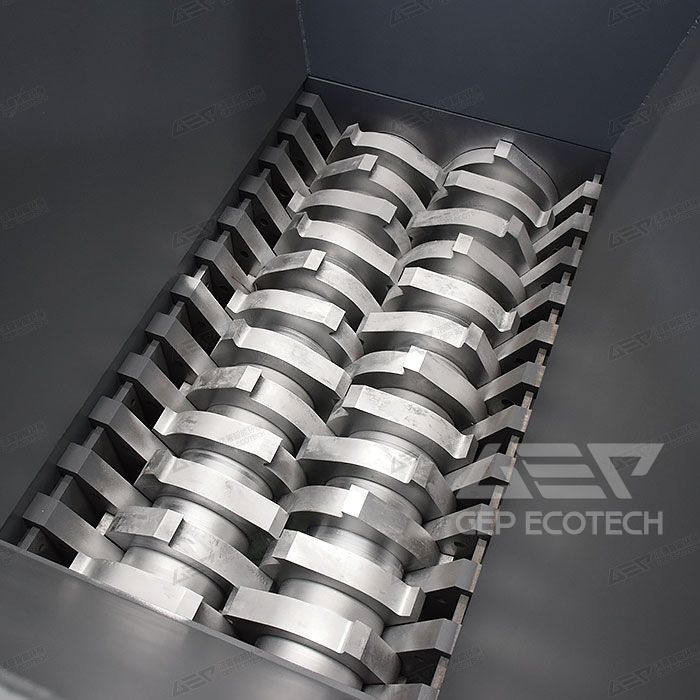

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for industrial rubber shredding applications Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Industrial Rubber Shredding?
When sourcing industrial rubber shredding equipment, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing shredders significantly influence costs. High-quality steel, specialized cutting blades, and wear-resistant components tend to come at a premium but offer better durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled technicians involved in the design, assembly, and testing of shredding machines. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, the overall price may reflect this.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and maintenance of machinery. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, thus lowering prices for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific rubber shredding applications can add to initial costs. However, investing in tailored solutions often results in better performance and efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality assurance processes ensure that the equipment meets industry standards. This aspect can increase costs but is vital for long-term reliability and compliance with regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary based on the origin of the equipment, destination, and chosen Incoterms. International buyers must consider potential tariffs, customs duties, and freight charges.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the equipment. Buyers should be aware of this when negotiating prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Industrial Rubber Shredding Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of industrial rubber shredders:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to bulk discounts, reducing the unit price significantly. Buyers should assess their needs and consider placing larger orders if possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. However, these customizations can enhance operational efficiency and longevity, potentially justifying the higher price.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Equipment made from superior materials and those that come with industry certifications typically command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced performance and reliability against the initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can also play a role in pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more but often provide better support, warranties, and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of sale is crucial. Options such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total cost significantly, especially for international buyers.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs in Industrial Rubber Shredding?
To ensure cost-effectiveness when sourcing shredding equipment, consider these buyer tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts or incentives to secure a deal.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Analyze not just the purchase price but also the operational costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A lower initial price might result in higher long-term costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local market conditions, shipping costs, and tariffs. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should conduct thorough research to understand these dynamics.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Whenever possible, evaluate local suppliers who may offer lower shipping costs and faster delivery times, which can enhance overall cost efficiency.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends and technological advancements can provide leverage in negotiations and decision-making, ensuring that your investment aligns with future needs.
Disclaimer
The prices and insights provided in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on specific circumstances and market conditions. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information tailored to your unique requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing industrial rubber shredding applications With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications
In the realm of waste management and recycling, industrial rubber shredding applications serve a crucial role in converting rubber waste into reusable materials. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can also achieve similar objectives. By evaluating these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
| Comparison Aspect | Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications | Alternative 1: Granulation | Alternative 2: Incineration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly efficient in size reduction and material recovery | Excellent for producing fine rubber particles | Reduces waste volume but does not recover materials |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment with ongoing operational costs | Lower initial investment, variable operational costs | Lower capital costs but potential regulatory fees |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and space | Easier to implement with less space required | Simple setup but requires regulatory compliance |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optimal performance | Lower maintenance needs | Minimal maintenance but requires monitoring systems |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for recycling tires and industrial rubber products | Best for producing rubber granules for further processing | Suitable for waste-to-energy applications with no recycling focus |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: Granulation
Granulation is a process where rubber is reduced to small granules, often through mechanical means. This method is particularly advantageous for producing fine rubber particles that can be used in various applications, such as rubber flooring or new tires. Granulation requires less capital investment compared to shredding machines and can be implemented in smaller facilities. However, it may not be as effective in recovering larger, reusable rubber pieces, limiting its applicability in certain contexts.
Alternative 2: Incineration
Incineration involves burning rubber waste to convert it into energy, significantly reducing the volume of waste. This method can be cost-effective in terms of initial investment and is often simpler to implement than shredding. However, incineration does not allow for the recovery of materials, which can be a significant drawback for businesses aiming to maintain sustainability practices. Additionally, regulatory compliance can be stringent, requiring ongoing monitoring and reporting, which may increase operational complexity and costs.
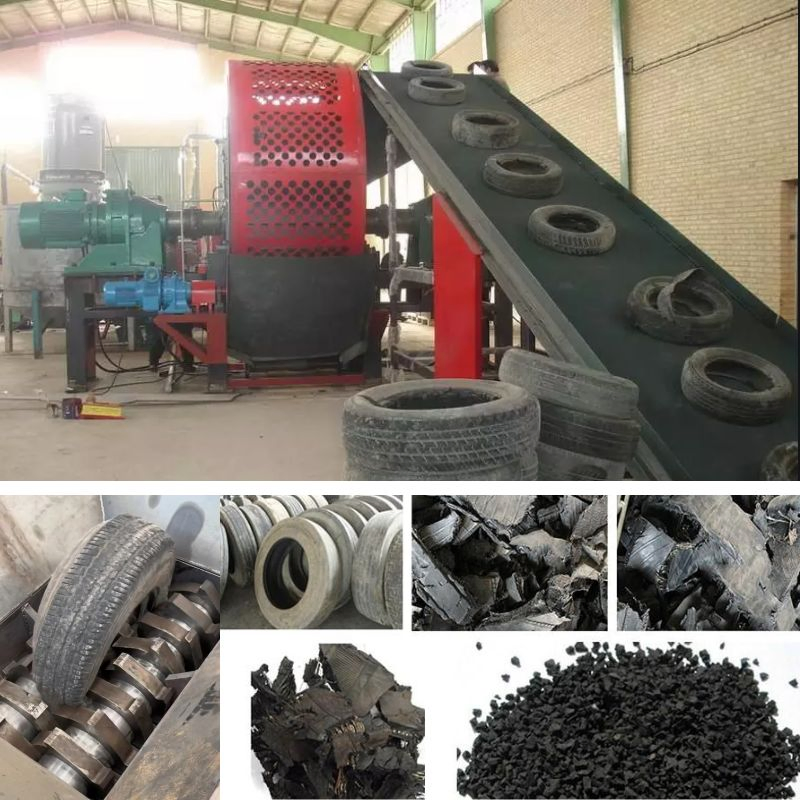

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating industrial rubber shredding applications against alternative solutions, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider their specific operational goals, budget constraints, and sustainability objectives. While shredding offers robust material recovery capabilities, granulation may suit smaller operations or those focused on producing fine rubber products. Conversely, incineration presents an efficient waste disposal method but lacks the material recovery benefits that many businesses prioritize. By thoroughly assessing these factors, buyers can select the most appropriate solution that aligns with their strategic vision and operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for industrial rubber shredding applications
What Are the Key Technical Properties Relevant to Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications?
In the industrial rubber shredding sector, understanding specific technical properties is vital for selecting the right machinery and ensuring effective processing. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of rubber influences its durability and shreddability. Different grades, such as natural rubber or synthetic rubber, require distinct shredding techniques. For B2B buyers, selecting the right machine based on material grade can optimize processing efficiency and reduce wear on equipment. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during the shredding process. In rubber shredding, maintaining tight tolerances ensures consistent particle sizes, which is crucial for subsequent recycling processes. This is particularly important for manufacturers who require specific particle dimensions for downstream applications. -
Throughput Capacity
This specification indicates the volume of material that can be processed within a specific timeframe, often measured in tons per hour. A higher throughput capacity is essential for large-scale operations, allowing businesses to maximize productivity and meet demand effectively. Understanding throughput helps buyers evaluate whether a machine meets their operational requirements. -
Motor Power Rating
The motor power rating determines the machine’s efficiency and ability to handle tough materials. Higher power ratings typically mean better shredding performance, particularly for heavy-duty rubber applications. For B2B buyers, this translates into considerations of energy consumption and operational costs, which can impact the overall profitability of rubber processing. -
Cutting Mechanism
The type of cutting mechanism—whether single shaft, dual shaft, or granulator—affects shredding performance and the final material size. Different mechanisms cater to varying material types and desired outcomes. Buyers must understand these distinctions to select the appropriate machine for their specific application. -
Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance specifications dictate how often and what type of upkeep is needed for optimal machine performance. Lower maintenance requirements are preferable for reducing downtime and operational costs. B2B buyers should assess maintenance needs to ensure long-term reliability and efficiency of their shredding equipment.
What Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Industrial Rubber Shredding?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the rubber shredding sector. Here are some key terms:
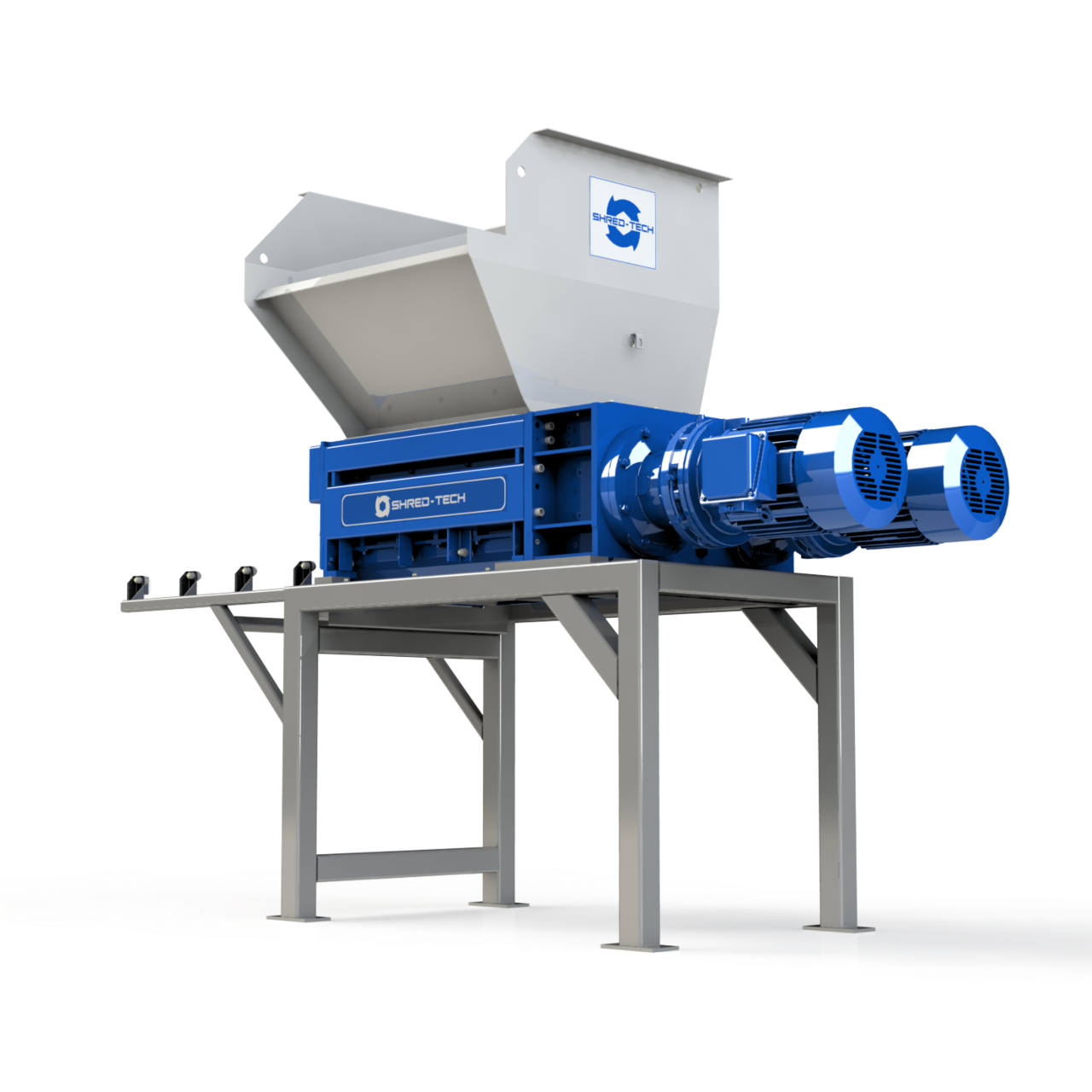

Illustrative image related to industrial rubber shredding applications
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is important for buyers looking for quality machinery and components that meet industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and manage inventory effectively, especially in bulk operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure they receive competitive pricing for their shredding equipment. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with their purchases. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In the rubber shredding industry, understanding lead times is critical for project planning and ensuring timely operations. -
Warranty and Service Agreements
These are contracts that outline the manufacturer’s commitment to repair or replace faulty equipment. Buyers should carefully review warranty terms to ensure they receive adequate protection and support for their investment.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right machinery and negotiate effectively in the industrial rubber shredding market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the industrial rubber shredding applications Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications?
The industrial rubber shredding applications sector is experiencing notable growth driven by increasing environmental regulations and the demand for sustainable waste management solutions. Global initiatives aimed at reducing landfill waste and promoting recycling have led to heightened interest in rubber recycling, particularly from used tires and industrial rubber products. As countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to implement circular economy principles, international B2B buyers are presented with lucrative opportunities to source advanced shredding technologies that facilitate the efficient processing of rubber waste.
Emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are transforming the landscape of industrial shredding applications. Smart shredders equipped with sensors can monitor performance and maintenance needs in real-time, optimizing operational efficiency. Furthermore, automation in sorting and processing is reducing labor costs and increasing throughput, making it essential for buyers to consider suppliers who integrate these technologies into their shredding solutions. Additionally, the growth of electric vehicles is generating a significant increase in rubber waste, further stimulating demand for effective shredding and recycling solutions.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing in the Industrial Rubber Shredding Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of decision-making for B2B buyers in the industrial rubber shredding sector. The environmental impact of rubber waste is significant, with improper disposal leading to pollution and resource wastage. Ethical sourcing practices are increasingly important as buyers look for suppliers who prioritize sustainability in their operations. This includes the use of energy-efficient machinery and processes that minimize emissions during shredding.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to local and international environmental regulations are crucial indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers should also consider sourcing materials from companies that offer ‘green’ certifications, which can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. By prioritizing suppliers with sustainable practices, companies can not only improve their operational efficiencies but also contribute positively to the environment and their communities.
What is the Evolution of Industrial Rubber Shredding Technology?
The evolution of industrial rubber shredding technology can be traced back to the increasing need for efficient waste management solutions in the late 20th century. Initially, rubber shredding was a manual and labor-intensive process, often resulting in inconsistent output and high operational costs. However, advancements in machinery design and engineering have transformed the sector, leading to the development of powerful, automated shredders capable of processing large volumes of rubber waste efficiently.
Over the past few decades, the introduction of multi-shaft shredders and granulators has allowed for more precise size reduction and enhanced material recovery. This evolution has been driven by both regulatory pressures and the rising demand for recycled rubber in various industries, including automotive and construction. As technology continues to advance, the focus on integrating smart features and sustainable practices is likely to shape the future of industrial rubber shredding applications, making it imperative for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest innovations and trends in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of industrial rubber shredding applications
-
How do I choose the right industrial rubber shredder for my needs?
Selecting the ideal industrial rubber shredder involves assessing several factors, including the type of rubber materials you intend to process, your desired output size, and the volume of material to be shredded. Consideration of the machine’s capacity, power requirements, and operational efficiency is crucial. Additionally, you may want to consult with manufacturers for tailored solutions, especially if you deal with specific rubber products, like tires or industrial scraps. Always request performance data and case studies to understand how the shredder performs in real-world applications. -
What are the key features to look for in a rubber shredding machine?
When evaluating rubber shredding machines, prioritize features such as cutting efficiency, durability, and ease of maintenance. Look for machines with robust construction, high-torque motors, and versatile blade configurations. Advanced features like noise reduction technologies, energy efficiency, and automated controls can enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, inquire about the machine’s ability to handle diverse rubber types and its adaptability for future processing needs, ensuring it meets both current and long-term business requirements. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing industrial shredders?
Payment terms for industrial shredders can vary significantly based on the supplier and the size of the order. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%), with the balance due prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger purchases. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront and consider factors such as currency exchange rates and any additional fees associated with international transactions, particularly when sourcing from different regions. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for industrial rubber shredders?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can differ widely among manufacturers. Some suppliers may have no MOQ for standard models, while custom machines may require a higher minimum. If you are sourcing for a specific project, it’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your operational capabilities. Understanding MOQs is crucial, especially for international buyers who may face shipping and logistics challenges when ordering large quantities. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing shredders internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing industrial shredders, start by vetting suppliers thoroughly. Look for manufacturers with certifications (such as ISO 9001) that indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request samples or visit production facilities if possible. Additionally, consider third-party quality inspections before shipment to verify that the machines meet your specifications. Establishing clear quality control agreements and performance metrics in your contracts can further safeguard your investment. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing shredders to my country?
Logistics considerations for importing shredders include understanding shipping regulations, customs duties, and potential tariffs in your country. It’s vital to work with logistics partners familiar with international shipping to ensure compliance with all necessary documentation. Assess the most cost-effective shipping methods and delivery timelines, factoring in the weight and size of the machinery. Additionally, consider the final destination’s infrastructure to ensure smooth transportation from the port to your facility. -
Can I customize my rubber shredding solution?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific processing needs. Customization can include modifications to the shredder’s size, capacity, blade design, and additional features such as integrated sorting systems or dust collection units. When discussing customization, be clear about your operational requirements and any unique challenges you face. Collaborating with engineers during the design phase can lead to a more efficient solution tailored to your business processes. -
What industries benefit most from rubber shredding applications?
Rubber shredding applications are beneficial across various industries, including tire recycling, automotive manufacturing, and construction. Companies involved in waste management and recycling also leverage rubber shredding to reduce landfill waste and recover valuable materials. Additionally, industries focused on sustainable practices can utilize shredded rubber in products like playground surfaces, rubberized asphalt, and composite materials. Understanding which industries align with your capabilities can help target your marketing efforts and expand your customer base effectively.
Top 5 Industrial Rubber Shredding Applications Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CM Shredders – Industrial Shredding Equipment
Domain: cmshredders.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: CM Shredders offers a range of industrial shredding and recycling equipment including: 1. CM Tire Shredders – Designed for tire processing and recycling. 2. CM Liberators – Used for rubber mulch and crumb rubber production. 3. CM Disc Screens – For material separation. 4. CM Granulators – Utilize V-Force knife technology for size reduction and fiber liberation. 5. CM Crackermill – For fine grindin…
2. JWCE – Industrial Shredders
Domain: jwce.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Industrial shredders are high-powered machines designed to cut through and destroy tough debris in various environments, primarily used in waste processing applications to reduce waste size and protect pumps and equipment. There are different types of industrial shredders: 1. Single-Shafted Shredders: Feature a single solid shaft with rotary blades, suitable for processing a variety of materials l…
3. 3R-Machinery – Slow-Speed Shredders
Domain: 3rmachinery.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: 3R-Machinery’s slow-speed shredders are heavy-duty machines designed for a wide range of applications including bulky waste recycling, green waste disposal, biomass shredding, hazardous waste disposal, industrial waste recycling, landfill shredding, metal recycling, municipal solid waste (MSW) shredding, and pallet recycling. These shredders can reduce waste volume by up to 75%, handle tough mater…
4. IQS Directory – Shredding Machines
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Shredding machines are designed to slice or shred various materials into smaller fragments. They are used for document destruction, plastic reclamation, scrap metal recovery, electronic waste management, wood recycling, and tire shredding. Key components include feed shafts, crushing gears or slicing blades, a motor, and a chute. Shredding machines can be customized based on target material, volum…
5. AISHRED – Rubber Shredder
Domain: aishred.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Rubber Shredder can handle all rubber products such as conveyor belts and scrap tires. The shredded items can be used for recycling, producing other products, or as fuel for cement kilns. Features include: Shredder Type: Twin-Shaft Shredder, Production Capacity: 1 – 30 Ton/h, Discharge Size: 50 – 300mm. Optional equipment includes wire separator, electromagnetic separator, granulator, and pulveriz…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for industrial rubber shredding applications
In the evolving landscape of industrial rubber shredding applications, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and environmental responsibility. By investing in high-quality shredding equipment, businesses can not only optimize their recycling processes but also contribute to the circular economy, reducing waste and reclaiming valuable materials. The demand for sustainable practices is growing, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory frameworks increasingly favor eco-friendly solutions.
International buyers should prioritize partnerships with established manufacturers that offer tailored solutions for specific rubber shredding needs, ensuring compliance with local regulations and maximizing throughput. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive support—from equipment selection to after-sales service—will empower companies to navigate the complexities of the recycling landscape effectively.
As we look to the future, the integration of advanced technologies in shredding equipment will further enhance efficiency and profitability. B2B buyers are encouraged to seize the opportunity to invest in innovative shredding solutions that not only meet current market demands but also position their businesses for long-term success. Embrace this transformative journey towards sustainable industrial practices and explore the potential of strategic sourcing today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.