Everything You Need to Know About Hydraulic Motor Diagram Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic motor diagram
Hydraulic motors play a pivotal role in the efficiency and functionality of hydraulic systems across various industries, yet sourcing the right hydraulic motor diagram can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricate components and workings of hydraulic motors—such as gear, vane, and piston types—can be daunting, especially when navigating global supply chains that vary greatly in quality and availability. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of hydraulic motor diagrams by providing a comprehensive overview that includes detailed breakdowns of motor types, their applications, and essential components.
In addition to outlining the technical aspects, this resource will assist buyers in vetting suppliers, evaluating costs, and ensuring compliance with regional standards, particularly for stakeholders from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Saudi Arabia. By offering actionable insights and expert guidance, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budgets. Whether you are looking to enhance your current hydraulic systems or seeking new suppliers, understanding hydraulic motor diagrams is crucial for maximizing performance and reliability in your applications.
Understanding hydraulic motor diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Motor | Simple design, interlocking gears, high-speed operation | Construction equipment, conveyor systems | Pros: Durable, high-speed performance. Cons: Less efficient at low speeds. |
| Vane Motor | Uses vanes within a rotor, ideal for low-speed torque | Injection molding, material handling | Pros: Compact design, smooth operation. Cons: Limited pressure handling. |
| Piston Motor | High torque and variable displacement options | Heavy machinery, automotive applications | Pros: Versatile, efficient at various speeds. Cons: More complex, higher maintenance. |
| Radial Piston Motor | Piston arrangement in a radial pattern | Agricultural machinery, marine applications | Pros: High torque at low speeds. Cons: Bulkier design may limit installation options. |
| Axial Piston Motor | Piston arrangement along the axis | Industrial applications, robotics | Pros: Compact design, efficient power-to-size ratio. Cons: Sensitive to fluid quality. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Gear Motors in B2B Applications?
Gear motors are characterized by their robust design, featuring interlocking gears that provide high-speed operation. They are well-suited for applications requiring consistent rotational motion, such as construction equipment and conveyor systems. When considering a gear motor, B2B buyers should evaluate factors like durability and speed requirements, as these motors excel in high-speed scenarios but may not perform efficiently at lower speeds.
How Do Vane Motors Function and Where Are They Best Applied?
Vane motors utilize vanes within a rotor to convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical energy, making them ideal for low-speed applications that require high torque, such as injection molding and material handling systems. Their compact design allows for easy integration into various machinery. Buyers should consider the pressure handling capabilities and the smooth operation of vane motors, as they can be limited in high-pressure environments.
What Are the Advantages of Piston Motors for Heavy Machinery?
Piston motors are distinguished by their high torque output and ability to handle variable displacement, making them a preferred choice for heavy machinery and automotive applications. They are versatile and efficient across a range of speeds. However, buyers must account for their complexity and potential maintenance requirements, as these motors can be more intricate than their gear or vane counterparts.
How Do Radial Piston Motors Differ in Design and Use?
Radial piston motors feature pistons arranged in a radial pattern, allowing for high torque generation at low speeds. They are commonly used in agricultural machinery and marine applications. While they provide significant torque, their bulkier design may present challenges in installation. Buyers should assess space constraints and torque needs when considering radial piston motors for their applications.
What Makes Axial Piston Motors a Popular Choice in Industrial Settings?
Axial piston motors arrange pistons along the axis, offering a compact design and efficient power-to-size ratio. They are widely used in industrial applications, including robotics. While they provide excellent performance, buyers should be mindful of the sensitivity of axial piston motors to fluid quality, as contamination can adversely affect their performance.
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic motor diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hydraulic motor diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Hydraulic excavators and loaders | Enhanced operational efficiency and productivity | Compatibility with existing machinery and local suppliers |
| Agriculture | Tractors and tillers | Improved crop yield through efficient soil management | Availability of durable parts and local service support |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling rigs and pumps | Increased safety and reliability in harsh conditions | Compliance with international standards and certifications |
| Manufacturing | Plastic injection molding machines | Higher precision and reduced waste in production | Technical support for integration and maintenance |
| Mining | Conveyor systems and haul trucks | Enhanced material handling and reduced downtime | Source from suppliers with robust after-sales service |
How Is the Hydraulic Motor Diagram Used in Construction Equipment?
In the construction industry, hydraulic motors are integral to the operation of excavators and loaders. The hydraulic motor diagram illustrates how hydraulic pressure is converted into mechanical energy, allowing heavy machinery to perform lifting and digging tasks with precision. By utilizing hydraulic motors, construction companies can achieve greater operational efficiency and productivity, crucial for meeting project deadlines. International buyers should consider sourcing motors that are compatible with their existing equipment and ensure local suppliers can provide timely maintenance services.
What Role Do Hydraulic Motors Play in Agriculture?
Hydraulic motors are pivotal in agricultural machinery, such as tractors and tillers, where they facilitate various functions like tilling soil and planting seeds. The hydraulic motor diagram provides insight into the mechanics of these systems, helping farmers improve crop yield through efficient soil management. For businesses in Africa and South America, sourcing durable hydraulic components is essential, especially in regions where equipment faces harsh conditions. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer robust parts and local service support to minimize downtime during critical planting seasons.
How Are Hydraulic Motors Utilized in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, hydraulic motors are vital for drilling rigs and pumps, where they manage the flow of fluids under high pressure. The hydraulic motor diagram helps engineers understand the system’s design, ensuring safety and reliability in harsh operational environments. For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East, sourcing hydraulic motors that comply with international safety standards is crucial. Additionally, companies should verify that suppliers can provide necessary certifications and support for maintenance in remote locations.
What Benefits Do Hydraulic Motors Provide in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing processes, especially in plastic injection molding, heavily rely on hydraulic motors for their precision and efficiency. The hydraulic motor diagram details how these systems work, allowing manufacturers to reduce waste and improve product quality. For European buyers, sourcing hydraulic motors that meet stringent quality standards is essential. It’s also important to engage with suppliers who can provide technical support for integration and ongoing maintenance, ensuring uninterrupted production processes.
How Do Hydraulic Motors Enhance Operations in Mining?
In the mining industry, hydraulic motors are essential for powering conveyor systems and haul trucks, enhancing material handling capabilities. The hydraulic motor diagram is crucial for understanding the flow of hydraulic fluid and its conversion into mechanical energy, which improves operational efficiency and reduces downtime. Buyers in South America should consider sourcing motors that are specifically designed for rugged environments and ensure they partner with suppliers who offer comprehensive after-sales service to maintain equipment reliability in remote mining locations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘hydraulic motor diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misinterpretation of Hydraulic Motor Diagrams
The Problem: One of the most common challenges B2B buyers face is the misinterpretation of hydraulic motor diagrams. Often, these diagrams contain complex symbols and technical jargon that can lead to confusion, especially for teams that may not have extensive hydraulic system expertise. This can result in incorrect component selection or installation errors, ultimately causing system inefficiencies or even failures. For example, a manufacturer in Brazil may struggle to translate a hydraulic diagram accurately, leading to the installation of a hydraulic motor that doesn’t meet the required specifications for torque and speed.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should invest in training for their teams on reading and interpreting hydraulic diagrams. This can include workshops led by manufacturers or third-party experts. Additionally, it’s beneficial to source diagrams that include detailed legends and simplified explanations of each component’s function. When purchasing hydraulic systems, buyers should request diagrams that are tailored to their specific applications, ensuring clarity in the design and functionality. Furthermore, using software tools that allow for 3D modeling of hydraulic systems can aid in visualizing how components fit and interact, enhancing understanding and accuracy in implementation.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing Compatible Hydraulic Motor Parts
The Problem: Another significant pain point for international B2B buyers is the difficulty in sourcing compatible parts for hydraulic motors as outlined in their diagrams. Given the diversity of hydraulic motor types—gear, vane, and piston—buyers may find it challenging to identify which parts are interchangeable or compatible with their existing systems. For instance, a company in Saudi Arabia may need to replace a specific piston motor component but struggles to find the right part due to limited local suppliers and a lack of clear specifications in the motor diagram.
The Solution: Buyers should establish relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide not only parts but also technical support. When sourcing components, it’s crucial to refer back to the hydraulic motor diagrams and specifications to ensure compatibility. Implementing an inventory management system that tracks the specific parts used in hydraulic systems can also streamline the sourcing process. Buyers should ask suppliers for comprehensive catalogs that include detailed diagrams and compatibility information for each part, ensuring they can quickly identify and order the correct components. Leveraging online platforms that specialize in hydraulic parts can expand sourcing options, providing access to a wider range of suppliers and parts.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Understanding of Hydraulic System Efficiency
The Problem: Many B2B buyers fail to grasp the significance of hydraulic system efficiency as illustrated in hydraulic motor diagrams. This lack of understanding can lead to suboptimal system performance, increased energy costs, and decreased equipment lifespan. For example, a construction company in South America may install hydraulic motors without fully considering the efficiency factors outlined in the diagrams, leading to excessive power consumption and operational delays.
The Solution: To address this challenge, companies should prioritize understanding the efficiency ratings and operational limits specified in hydraulic motor diagrams. Buyers can benefit from consulting with hydraulic system engineers or technical advisors who can explain how to maximize efficiency based on the motor’s design. Additionally, conducting regular system audits and performance assessments can help identify areas for improvement. Investing in advanced monitoring systems that track hydraulic fluid temperature, pressure, and flow rates can provide real-time data that informs operational adjustments, ensuring that the system operates within optimal parameters. This proactive approach not only enhances efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the hydraulic motors and systems in use.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic motor diagram
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Hydraulic Motor Diagrams?
When selecting materials for hydraulic motor diagrams, it is crucial to consider the properties and performance characteristics that will best suit the application. Here, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic motors: cast iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and composite materials. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages that can significantly impact the performance of hydraulic systems.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Hydraulic Motors?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C and can handle pressures exceeding 250 bar.
Pros & Cons: The durability of cast iron makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications; however, its weight can be a disadvantage in mobile equipment. Cast iron is also relatively cost-effective, but manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for precise machining.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with various hydraulic fluids, including mineral oils, making it a versatile choice for many applications. However, it may not be suitable for environments with high corrosion potential unless properly coated.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions can vary, ensuring that cast iron components are treated for corrosion resistance may be necessary.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Hydraulic Motors?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance, with a temperature rating typically around 150°C and pressure limits of about 200 bar.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can improve the efficiency of mobile hydraulic systems. However, it is less durable than cast iron and may be more expensive due to the cost of raw materials and processing.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with hydraulic fluids makes it a good choice for applications where weight is a concern, such as in aerospace or automotive sectors. However, its lower strength may limit its use in high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet local standards and consider the availability of materials in their region. In Europe, for instance, compliance with JIS standards may be a priority.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Hydraulic Motors?
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 400°C) and pressures (over 300 bar).
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, it is generally more expensive than cast iron or aluminum, and its manufacturing processes can be more complex.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for applications involving aggressive fluids, including those found in chemical processing. Its high cost may deter some buyers, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and ISO is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, may find stainless steel particularly beneficial.
How Do Composite Materials Fit into Hydraulic Motor Design?
Key Properties: Composite materials can be engineered for specific applications, providing tailored properties such as lightweight design and high strength. They typically have varying temperature and pressure ratings depending on the formulation.
Pros & Cons: Composites can offer significant weight savings and corrosion resistance, but they may not be as widely accepted or understood in traditional industries. Manufacturing can be complex, leading to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in specialized applications where weight and corrosion resistance are critical. However, their compatibility with hydraulic fluids must be carefully evaluated.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding composite materials, as acceptance may vary by region. In Europe, for example, adherence to specific material standards may be required.
Summary of Material Selection for Hydraulic Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic motor diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty industrial applications | Excellent wear resistance | Heavy and may require precise machining | Medium |
| Aluminum | Mobile hydraulic systems | Lightweight | Less durable under high pressure | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Harsh chemical environments | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Composite | Specialized applications | Tailored properties for weight | Less traditional acceptance | High |
This guide should assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions about material selection for hydraulic motor diagrams, considering both performance and regional compliance factors.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic motor diagram
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Hydraulic Motors?
The manufacturing of hydraulic motors involves a series of well-defined stages, ensuring that each component meets the required specifications for performance and reliability. The main stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Hydraulic Motor Production?
Material preparation is the first crucial step in manufacturing hydraulic motors. High-quality raw materials, such as steel or aluminum, are selected based on the specific requirements of the hydraulic motor type—gear, piston, or vane. These materials are then cut, machined, and treated to achieve the desired properties. For instance, steel components may undergo heat treatment to enhance strength and durability. This stage also involves sourcing components from certified suppliers to ensure compliance with international standards.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Hydraulic Motor Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming process begins. This stage may involve several techniques, including machining, casting, and forging, depending on the design and specifications of the hydraulic motor.
-
Machining: Precision machining is critical for components like shafts, gears, and housings. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for their ability to produce high-tolerance parts efficiently.
-
Casting: For larger components or complex shapes, casting techniques such as sand casting or die casting may be utilized. This allows for intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve through machining alone.
-
Forging: Some components may be forged to enhance strength and structural integrity, especially in high-stress applications.
How Are Hydraulic Motors Assembled?
Assembly is a crucial phase where all individual components come together to form the complete hydraulic motor. This process typically follows a systematic approach:
- Subassembly: Components are first assembled in subgroups, such as gears and vanes, to streamline the final assembly.
- Main Assembly: The subassemblies are then integrated into the motor housing, where meticulous attention is paid to alignment and fitting to ensure optimal performance.
- Sealing: Seals and gaskets are installed to prevent leaks, which is critical for maintaining hydraulic pressure and system efficiency.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Hydraulic Motors?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments and quality checks. Components may undergo processes such as anodizing or painting to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Additionally, this stage often involves final inspections to identify any defects that may have occurred during manufacturing.
What Are the International Standards for Quality Assurance in Hydraulic Motor Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of hydraulic motors, especially for B2B buyers who require reliable performance. Compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001, ensures that manufacturers have established quality management systems in place. This standard focuses on continual improvement and customer satisfaction, critical for maintaining competitive advantage in global markets.
Which Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important for Hydraulic Motors?
In addition to general QA standards, specific industry certifications may apply. For instance:
- CE Marking: Commonly required in Europe, the CE mark indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For hydraulic motors used in oil and gas applications, API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications may be necessary to ensure that products meet rigorous industry standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Hydraulic Motor Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each hydraulic motor meets stringent specifications. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials and components received from suppliers. It ensures that only certified materials enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted at various stages during manufacturing, IPQC involves monitoring processes and components for compliance with specifications. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and performance testing.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final stage involves a thorough inspection of the completed hydraulic motors. It typically includes functionality tests, pressure tests, and performance evaluations to verify that the motor operates correctly under specified conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are actionable steps buyers can take:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards firsthand.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC processes, including any certifications and test results that validate product quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s operations and product quality. This is particularly valuable for buyers unfamiliar with the supplier’s market or practices.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding QC and Certification?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification processes that may vary by region. For example:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. Understanding local regulations, especially in emerging markets, is vital to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
-
Cultural Considerations: Cultural differences may influence communication and expectations regarding quality standards. Buyers should be prepared to navigate these differences to foster effective supplier relationships.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Given the complexities of global supply chains, buyers should prioritize transparency in sourcing and manufacturing processes. This not only helps ensure product quality but also builds trust between buyers and suppliers.
By considering these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for hydraulic motors, ensuring that they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘hydraulic motor diagram’
In this guide, we provide a step-by-step checklist designed for B2B buyers looking to procure hydraulic motor diagrams. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of hydraulic systems, ensuring that you make informed decisions when sourcing these critical components for your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it is essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes understanding the type of hydraulic motor (gear, vane, or piston) suitable for your application. Specify parameters like torque, speed, and displacement to ensure compatibility with your machinery.
- Consider the operational environment and any specific performance criteria you need to meet.
- Document your specifications in detail to facilitate discussions with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Identifying qualified suppliers is crucial for ensuring product quality and reliability. Investigate their certifications, industry experience, and reputation in the market.
- Look for ISO certifications or other relevant industry standards that demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- Check online reviews and testimonials from previous clients, particularly those in your region, to gauge their reliability.
Step 3: Request Detailed Diagrams and Documentation
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed hydraulic motor diagrams and accompanying documentation. This information will provide insights into the motor’s components and operation.
- Ensure that the diagrams include all essential parts, such as the inlet and outlet valves, rotor, and housing.
- Look for explanations on how each component interacts within the system, which can help in troubleshooting and maintenance.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
- Ask for examples of past projects to understand their capabilities and expertise.
- Conduct interviews or meetings to discuss your specific needs and assess their responsiveness and customer service.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Inquire about the after-sales support that suppliers offer, including warranty terms and the availability of replacement parts. This is vital for ensuring long-term operational efficiency.
- Look for suppliers who provide comprehensive support, including installation guidance and maintenance services.
- Understand the warranty coverage for their products, as this can significantly impact your operational costs over time.
Step 6: Consider Localization and Shipping Options
For international buyers, understanding shipping logistics and potential tariffs is essential. Assess the supplier’s ability to deliver to your location efficiently.
- Check if the supplier has local representatives or distribution centers in your region, which can expedite delivery and reduce costs.
- Factor in lead times for shipping and potential customs delays when planning your procurement timeline.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have gathered all necessary information, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. This is a critical step to ensure that you receive the best value for your investment.
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor diagram
- Be prepared to discuss bulk purchase discounts or long-term contracts if you anticipate ongoing needs.
- Ensure that all terms are clearly documented to avoid misunderstandings later on.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for hydraulic motor diagrams, ensuring they select the best suppliers and products for their specific applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic motor diagram Sourcing
When sourcing hydraulic motor diagrams, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis covers the various cost components, price influencers, and tips for maximizing value while negotiating.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Hydraulic Motor Diagram Sourcing?
The cost structure for hydraulic motor diagrams can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost. High-quality metals and polymers used in gears, vanes, and casings can increase costs but also enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the design and manufacturing of hydraulic motor diagrams. Labor costs vary significantly based on the geographic location of the supplier and the complexity of the design.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, facility maintenance, and other operational expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for production, including molds and specialized tools, can be a significant upfront investment. However, these costs can be amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control processes ensures that the hydraulic motors meet required specifications and certifications. While this adds to the cost, it is essential for reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties must be considered.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, demand, and market conditions.
What Factors Influence Pricing for Hydraulic Motor Diagrams?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of hydraulic motor diagrams:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes usually lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can drive up costs. Buyers should assess whether customization is necessary or if standard designs would suffice.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or possess certifications may incur higher costs but offer greater reliability and marketability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Suppliers in regions with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Incoterms: Understanding International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is vital for determining cost responsibilities, including shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Hydraulic Motor Diagrams?
To ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing hydraulic motor diagrams, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the market landscape and average pricing can empower buyers during negotiations. This includes being aware of local suppliers and their pricing structures.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term partnerships often result in more favorable negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of solely considering upfront costs, evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operation, and potential downtime costs. This perspective can justify higher initial expenditures for more reliable products.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ask suppliers for itemized quotes to understand the breakdown of costs. This transparency can reveal areas for potential savings.
-
Be Flexible with Specifications: If possible, consider being flexible with certain specifications that do not compromise the motor’s performance. This can open up options for more cost-effective solutions.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing?
While the pricing of hydraulic motor diagrams may fluctuate based on market conditions and supplier capabilities, buyers should remain cautious of indicative prices. Fluctuations in material costs, labor rates, and logistics can significantly impact final pricing. Always seek updated quotes and engage in thorough discussions to ensure the best possible outcome. By being informed and proactive, international B2B buyers can secure the most advantageous deals in the sourcing of hydraulic motor diagrams.
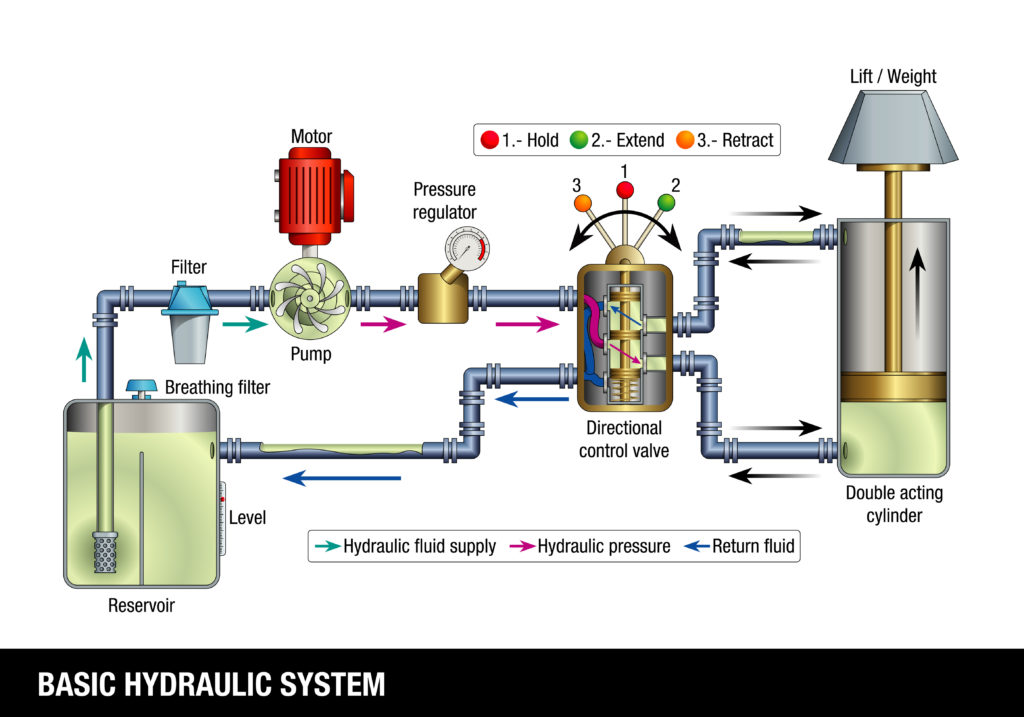
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor diagram
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing hydraulic motor diagram With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Hydraulic Motor Diagrams
In the pursuit of optimizing hydraulic systems, understanding the various components and their configurations is essential. Hydraulic motor diagrams serve as vital tools in visualizing the functionality and assembly of hydraulic motors. However, there are alternative solutions that also aim to achieve similar outcomes in hydraulic applications. This analysis compares hydraulic motor diagrams with other viable options to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Hydraulic Motor Diagram | Electric Motor Diagram | Pneumatic Motor Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, adaptable for various applications | High efficiency, suitable for precise control | Quick response time, ideal for lighter loads |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; maintenance costs can vary | Higher upfront cost, but lower operating costs | Generally lower cost, but can require more maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires hydraulic knowledge; installation can be complex | Generally straightforward installation; needs electrical knowledge | Easier to implement but requires air supply |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular checks needed for seals and fluid | Low; minimal routine maintenance required | Higher due to potential wear and tear from moisture |
| Best Use Case | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Robotics, precision tools | Assembly lines, packaging equipment |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Motor Diagrams
Electric motors are increasingly popular in various applications due to their efficiency and ability to provide precise control. They are often used in robotics and precision tools, where consistent performance is critical. While the initial investment may be higher compared to hydraulic motors, electric motors typically have lower operating costs over time. However, the need for electrical knowledge for installation and potential challenges with power supply can complicate implementation in certain regions.
Pneumatic Motor Diagrams
Pneumatic motors offer a quick response time and are ideal for lighter loads, making them suitable for applications such as assembly lines and packaging equipment. Their installation tends to be easier than hydraulic systems, as they require a compressed air supply rather than hydraulic fluid. However, pneumatic motors can incur higher maintenance costs due to wear and tear from moisture in the air supply, which can affect performance over time.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between hydraulic motor diagrams and alternative solutions like electric and pneumatic motor diagrams, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, ease of implementation, and maintenance capabilities. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses, making it crucial to align the choice with the specific needs of the application. Assessing these aspects will ensure that the selected solution not only meets operational demands but also contributes to overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness in the long run.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic motor diagram
What Are the Key Technical Specifications for Hydraulic Motors?
Hydraulic motors are essential components in various industrial applications, and understanding their technical specifications is critical for B2B buyers. Here are some key specifications that impact performance, reliability, and cost:
-
Material Grade
The choice of material, often steel or aluminum alloys, affects the motor’s durability and resistance to wear and tear. Higher-grade materials can withstand extreme conditions, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Buyers should prioritize materials that offer a balance between strength and weight to optimize performance while minimizing operational costs. -
Torque Rating
Torque rating indicates the rotational force the motor can generate. This specification is crucial for applications requiring precise control over mechanical movements. For B2B buyers, selecting a hydraulic motor with the appropriate torque rating ensures it meets the operational demands of their machinery, preventing premature failure and maintenance issues. -
Displacement Volume
Displacement volume refers to the volume of hydraulic fluid the motor can displace per revolution. It directly influences the speed and power output of the motor. A higher displacement volume typically results in greater power but may require a larger hydraulic pump to match. Buyers must consider their system’s requirements to achieve optimal performance without over-specifying, which can lead to unnecessary costs. -
Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the maximum hydraulic pressure the motor can handle. Understanding the pressure rating is vital for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and avoiding failures due to excessive pressure. B2B buyers should carefully assess their application requirements and select motors that can safely operate within the specified pressure ranges. -
Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings indicate how effectively a hydraulic motor converts hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. Higher efficiency ratings can lead to lower operational costs and energy savings over time. For buyers, understanding efficiency is critical for selecting motors that enhance productivity while minimizing energy consumption. -
Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the conditions under which the hydraulic motor can function effectively. Motors designed for extreme temperatures are essential for applications in harsh environments. Buyers must consider these conditions to avoid performance degradation and ensure longevity.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Hydraulic Motor Procurement?
When engaging in the procurement of hydraulic motors, understanding industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are used in another company’s end product. For buyers, working with OEMs often guarantees compatibility and quality assurance, as these manufacturers adhere to specific industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they are not over-committing financially or operationally. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ allows them to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, fostering competitive pricing and informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and delivery. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations and costs, ensuring smoother logistics and compliance with international trade regulations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to delivery. For buyers, understanding lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management, especially in industries where downtime can result in significant losses. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period indicates the length of time a manufacturer will cover repairs or replacements for defects. Buyers should carefully consider warranty terms as they reflect the manufacturer’s confidence in their product and can significantly impact the total cost of ownership.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting hydraulic motors for their operations, ensuring both performance and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the hydraulic motor diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Driving the Hydraulic Motor Diagram Sector?
The hydraulic motor diagram sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for automation across various industries—such as manufacturing, agriculture, and construction—has led to a surge in hydraulic systems usage. As international B2B buyers seek efficient solutions, the focus has shifted toward high-performance hydraulic motors that can operate under extreme conditions. Key trends include the adoption of advanced materials and technologies that enhance durability and reduce maintenance costs. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is pushing for smart hydraulic systems integrated with IoT capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Emerging markets in Africa and South America present significant opportunities, as industrialization accelerates and infrastructure projects expand. Countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in hydraulic systems for their mining and construction sectors. For buyers in these regions, understanding local regulations and sourcing components that meet international standards is crucial. This landscape requires suppliers to offer not only competitive pricing but also reliable delivery and support services to navigate the complexities of cross-border trade.
How Can B2B Buyers Emphasize Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Hydraulic Motor Diagrams?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern for B2B buyers in the hydraulic motor diagram sector. The environmental impact of hydraulic systems—particularly in terms of fluid leaks and waste—has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials and production processes. This includes sourcing components that are recyclable and have reduced carbon footprints.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is gaining traction, especially in regions with stringent labor laws and environmental regulations. Buyers should seek suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety. These certifications not only assure compliance but also enhance brand reputation. By aligning with suppliers who share these values, B2B buyers can contribute to a more sustainable supply chain, ultimately benefiting their own corporate social responsibility initiatives.
What Are the Historical Developments Influencing Current Hydraulic Motor Technologies?
The evolution of hydraulic motors dates back to the industrial revolution, where the need for more efficient power transmission led to the development of hydraulic systems. Initially, hydraulic motors were simplistic, relying on basic mechanical designs. However, advancements in engineering and materials science have transformed hydraulic motors into sophisticated components capable of handling high pressures and variable loads.
The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools in the late 20th century allowed for more precise engineering of hydraulic motors, leading to improved performance and reliability. Today, the integration of digital technologies—such as IoT and AI—has further revolutionized the sector, enabling predictive analytics and enhanced operational efficiency. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the continuous innovation in hydraulic motor designs and the importance of sourcing the latest technologies for competitive advantage.
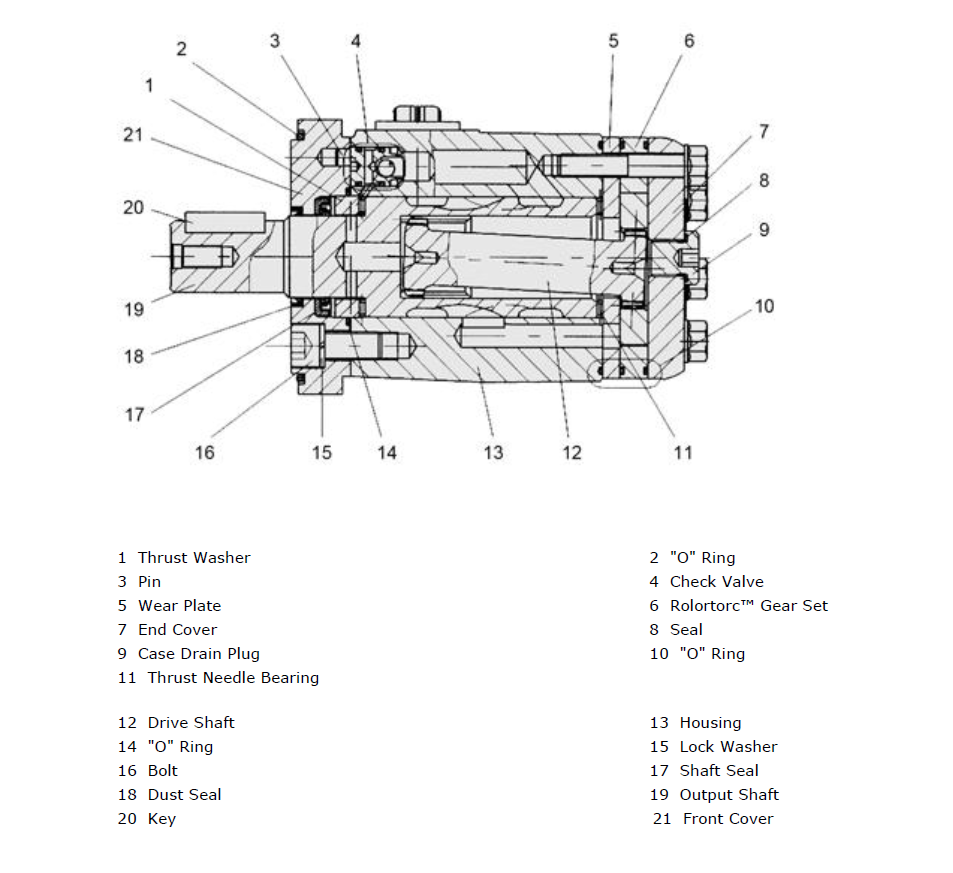
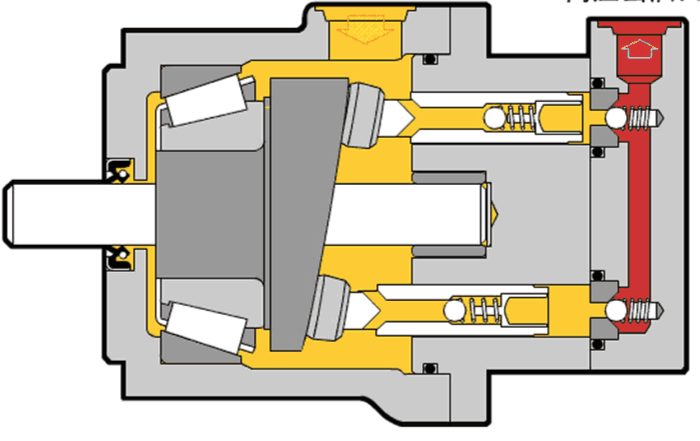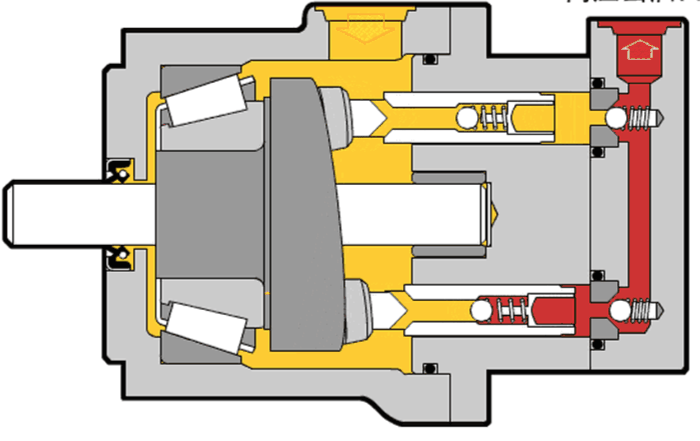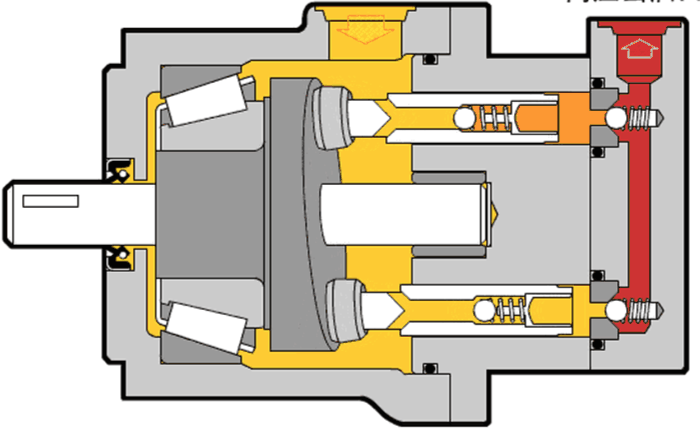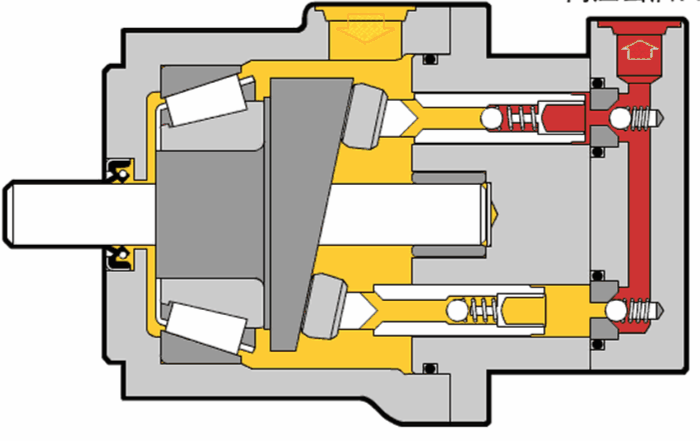
Illustrative image related to hydraulic motor diagram
By staying informed about these market dynamics and trends, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and align with evolving industry standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic motor diagram
-
How do I solve issues with hydraulic motor efficiency?
To enhance hydraulic motor efficiency, first ensure that the motor is appropriately sized for your application. Regular maintenance, including checking for leaks and ensuring fluid cleanliness, is crucial. Additionally, evaluate the hydraulic fluid viscosity, as it should match the operating temperature and conditions. If issues persist, consider consulting with a hydraulic system specialist to analyze the system’s design and operation, potentially leading to adjustments in component specifications or configurations. -
What is the best hydraulic motor type for low-speed, high-torque applications?
For low-speed, high-torque applications, piston hydraulic motors are typically the best choice. They provide superior torque at lower speeds and can handle heavy-duty tasks, making them ideal for industrial machinery and construction equipment. Gear motors can also be suitable, but they generally excel in high-speed applications. It’s essential to assess your specific needs, including load requirements and operating conditions, to select the most appropriate motor type. -
How can I ensure the quality of hydraulic motor components from suppliers?
To ensure quality, establish a robust supplier vetting process that includes reviewing certifications, quality control standards, and industry reputation. Request samples to evaluate the materials and craftsmanship before placing bulk orders. Additionally, consider suppliers who provide detailed documentation and traceability for their components. Regular audits and establishing long-term partnerships can also enhance quality assurance throughout the procurement process. -
What customization options are available for hydraulic motors?
Many suppliers offer customization options for hydraulic motors, including modifications to size, torque ratings, and mounting configurations to suit specific applications. You can also request changes in the material used for specific components to enhance durability or resistance to environmental factors. Communicating your specific requirements with the supplier early in the design phase will help in achieving the desired customization. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for hydraulic motors?
The minimum order quantity for hydraulic motors can vary significantly between suppliers and may depend on factors such as the type of motor, customization options, and production capabilities. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units for standard products to larger quantities for custom orders. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with the supplier to negotiate an MOQ that aligns with your business requirements. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing hydraulic motors internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of hydraulic motors can vary widely but typically include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. Discuss payment terms early in the negotiation process to ensure clarity and establish a mutually beneficial agreement that minimizes financial risk. -
How can logistics impact my procurement of hydraulic motors?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of hydraulic motors. Factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and local infrastructure can affect lead times and costs. It is essential to work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can navigate potential challenges. Additionally, consider local regulations regarding the import of hydraulic components to avoid delays and ensure compliance. -
What should I include in my hydraulic motor specification document?
A comprehensive hydraulic motor specification document should include details such as the desired type (gear, vane, piston), torque requirements, operating speed, mounting dimensions, and environmental conditions. Additionally, specify the required hydraulic fluid compatibility, any necessary certifications, and quality standards. Including this information will facilitate accurate quotes and help suppliers deliver products that meet your specific operational needs.
Top 5 Hydraulic Motor Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Panagon Systems – Hydraulic Motors
Domain: panagonsystems.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
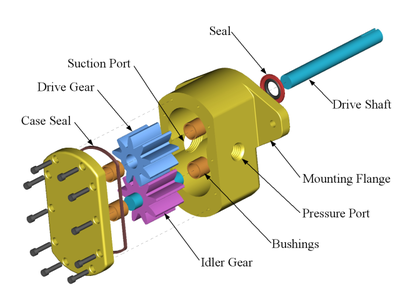
Introduction: Hydraulic motors are critical components of hydraulic systems, converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical energy. Key parts include gears, vanes, pistons, and actuators. Types of hydraulic motors: 1. Gear Motors: Durable, high-speed operation, used in rotating equipment. Main parts: driven gear, idler gear, output shaft. 2. Vane Motors: Suited for low-speed applications, used in industrial equi…
2. Cross Manufacturing – Hydraulic Cylinders & Valves
Domain: crossmfg.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Hydraulics Cylinders, Valves, Gear Pumps & Motors, Accumulators, Filters, Custom Products, Custom Hydraulic Cylinders, Custom Hydraulic Fittings and Manifolds. Applications include Agriculture, Construction, and Mobile/Light Industrial. Key systems include: 1. Front End Loader powered by a PTO driven pump with a 2-spool directional control valve and return line filter. 2. Winch powered by a hydrau…
3. Pinterest – Hydraulic Pumps
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic pumps convert rotary motion of the driving motor into hydraulic pressure.
4. Lunchbox Sessions – Hydraulic Motors
Domain: lunchboxsessions.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic motors convert energy from pressurized hydraulic fluid into motion, functioning as rotary actuators. Common uses include skid steer loaders, where they provide bi-directional movement and allow for stopping without turning off the engine. The schematic symbol for a hydraulic motor is a circle with inward-pointing arrows, similar to a pump symbol. Variations include bi-directional motors …
5. Volvo – Hydraulic Diagram Symbols
Domain: scribd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This document provides explanations for symbols used in a hydraulic diagram for a Volvo A40F vehicle with serial numbers 11001-99999. It includes symbols for lines, reservoirs, filters, heat exchangers, control devices, sources of energy, pumps, motors, cylinders, valves, and their meanings. It notes that the diagram shows hydraulic component connections and functions but not designs, and valve sy…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic motor diagram
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Hydraulic Motors?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of hydraulic technology, strategic sourcing is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring the longevity of machinery. Understanding the intricacies of hydraulic motor components—such as gears, vanes, and pistons—enables B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific applications. Buyers should consider factors like the type of hydraulic motor best suited for their needs—gear, vane, or piston—as well as the importance of reliable suppliers who can provide quality parts and support.
How Can International Buyers Capitalize on Emerging Opportunities?
As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to grow, the demand for efficient hydraulic systems is expected to rise. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, international buyers can not only secure competitive pricing but also ensure access to the latest technological advancements in hydraulic motors. Engaging with reputable manufacturers and distributors can further enhance supply chain resilience.
What’s Next for Your Hydraulic Systems?
Looking ahead, it’s crucial for businesses to stay proactive in evaluating their hydraulic motor needs and to explore partnerships that can provide innovative solutions. Now is the time to invest in the right hydraulic technology to drive your operations forward. Reach out to trusted suppliers to begin your journey toward enhanced efficiency and reliability in your hydraulic systems.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.