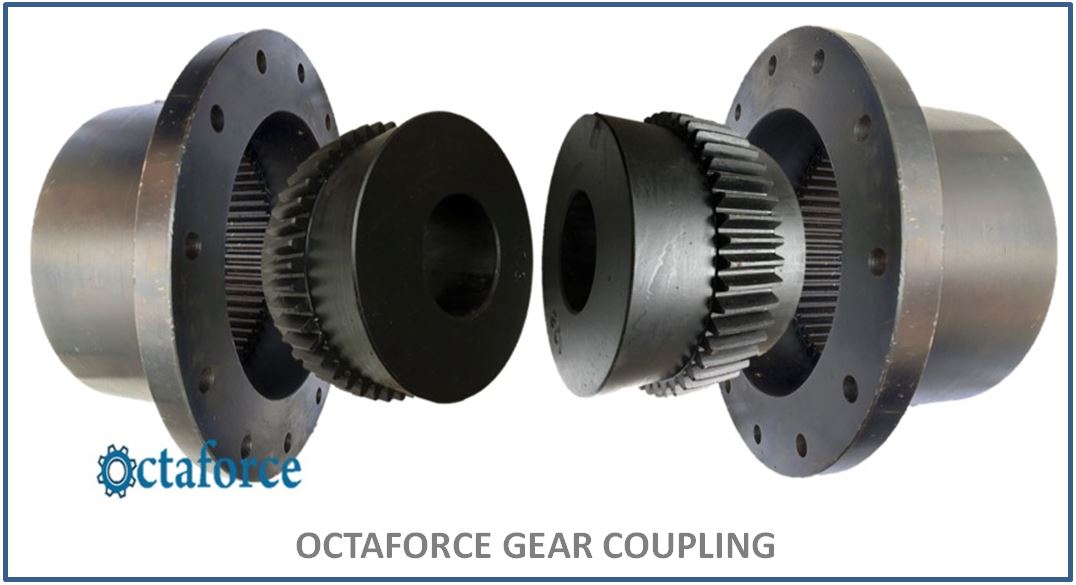
Everything You Need to Know About Gear Shaft Coupling Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gear shaft coupling
In the complex landscape of industrial machinery, sourcing the right gear shaft coupling can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. These critical components are essential for transmitting torque between shafts that may not be perfectly aligned, making their selection crucial for operational efficiency. Understanding the myriad types, applications, and specifications of gear couplings is vital for businesses looking to enhance performance while minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse world of gear shaft couplings, exploring various styles, such as flexible and rigid couplings, and their specific applications across multiple industries. We will also address critical considerations for supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can confidently select reliable partners. Additionally, insights into cost factors, installation procedures, and maintenance best practices will be provided to empower informed purchasing decisions.
Designed specifically for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets such as Saudi Arabia and Germany—this guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate the global market effectively. By leveraging the insights within, you can make strategic sourcing decisions that align with your business needs, ultimately driving productivity and enhancing your competitive edge in the marketplace.
Understanding gear shaft coupling Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible Gear Coupling | Allows for angular, radial, and axial misalignment; uses crowned gear teeth. | Heavy machinery, pumps, and compressors | Pros: High torque capacity; compensates for misalignment. Cons: Requires regular lubrication; potential wear over time. |
| Rigid Gear Coupling | Fixed connection with no flexibility; designed for precise alignment. | Applications requiring precise power transmission | Pros: Robust design; minimal backlash. Cons: Not suitable for misalignment; limited installation flexibility. |
| Floating Shaft Coupling | Utilizes a central floating shaft; connects two shafts without rigid attachment. | Long-distance power transmission in large setups | Pros: Reduces stress on shafts; adaptable to various setups. Cons: Requires careful alignment; complex installation. |
| Split Gear Coupling | Features a split design for easier installation and maintenance. | Industries with frequent coupling replacements | Pros: Simplifies maintenance; reduces downtime. Cons: May have slightly lower torque capacity compared to solid designs. |
| Tapered Bore Gear Coupling | Designed for interference fit; allows for secure attachment. | High-performance applications in industrial settings | Pros: Strong connection; suitable for high torque. Cons: Installation complexity; requires precision machining. |
What are the characteristics of Flexible Gear Couplings?
Flexible gear couplings are engineered to accommodate misalignment between connected shafts, making them ideal for heavy machinery and applications such as pumps and compressors. Their design incorporates crowned gear teeth, allowing for smooth torque transmission while compensating for angular, radial, and axial misalignment. B2B buyers should consider the need for regular lubrication to maintain performance and mitigate wear, as neglecting this can lead to premature failure.
Why choose Rigid Gear Couplings for precise applications?
Rigid gear couplings provide a solid connection without the flexibility to accommodate misalignment. This makes them suitable for applications where precise alignment is crucial, such as in high-precision manufacturing or robotics. While they offer a robust design with minimal backlash, B2B buyers must ensure that their installation environments are free from misalignment to avoid operational issues.
How does Floating Shaft Coupling enhance power transmission?
Floating shaft couplings utilize a central shaft that connects two other shafts without a rigid attachment, allowing for flexibility in long-distance power transmission setups. This design reduces stress on individual shafts and can be advantageous in large industrial applications. However, buyers should be aware that careful alignment is necessary to prevent operational inefficiencies, and installation may be more complex compared to traditional couplings.
What benefits does a Split Gear Coupling provide?
Split gear couplings are designed for easier installation and maintenance, making them a popular choice in industries where couplings are frequently replaced. Their split design allows for quick access during maintenance, reducing downtime significantly. However, buyers should note that while they simplify maintenance, they may have slightly lower torque capacity compared to solid designs, so it’s essential to assess the torque requirements of the application.
When to consider Tapered Bore Gear Couplings?
Tapered bore gear couplings are engineered for secure attachment through an interference fit, making them particularly suitable for high-performance applications where strong connections are necessary. This design enhances torque transmission capabilities, which is crucial in demanding industrial environments. However, installation complexity and the need for precision machining are important considerations for buyers to ensure proper function and longevity.
Key Industrial Applications of gear shaft coupling
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gear shaft coupling | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Connecting drilling rigs and pumps | Enhances reliability and efficiency in high-torque environments | Ensure compatibility with high torque ratings and environmental conditions. |
| Manufacturing | Power transmission in conveyor systems | Increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Look for couplings that accommodate misalignment and are easy to maintain. |
| Mining | Linkage between crushers and grinding mills | Maximizes uptime and performance in harsh conditions | Select robust materials that withstand heavy loads and abrasive environments. |
| Water Treatment | Integration in pump systems for water distribution | Improves flow control and system reliability | Consider couplings that offer corrosion resistance and are easy to install. |
| Renewable Energy | Connecting turbines to generators | Enhances energy efficiency and system durability | Focus on couplings designed for variable loads and high-speed applications. |
How Are Gear Shaft Couplings Used in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, gear shaft couplings are essential for connecting drilling rigs and pumps, where they transmit high torque efficiently. These couplings are designed to handle significant misalignment, which is common due to the dynamic nature of drilling operations. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Saudi Arabia, it’s crucial to source couplings that meet stringent quality standards and can withstand harsh environments, including extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions.
What Role Do Gear Shaft Couplings Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, gear shaft couplings are integral to the operation of conveyor systems, where they facilitate the transfer of power from motors to conveyor belts. This application is critical for maintaining a steady flow of materials, thereby increasing overall operational efficiency. Buyers should prioritize couplings that allow for easy maintenance and have the flexibility to accommodate misalignment, which can occur due to wear and tear over time.
How Are Gear Shaft Couplings Applied in Mining Operations?
Mining operations utilize gear shaft couplings to link crushers and grinding mills, ensuring the effective transmission of power in challenging environments. These couplings must withstand heavy loads and abrasive materials, making durability a key consideration for buyers. When sourcing, it’s important to select couplings made from robust materials that can endure the demanding conditions often found in mining, particularly in regions like South America and Africa.
Why Are Gear Shaft Couplings Important in Water Treatment?
In water treatment facilities, gear shaft couplings are used to integrate pump systems essential for water distribution. They help improve flow control and ensure the reliability of the entire system, which is vital for maintaining water quality and availability. Buyers should seek couplings that offer corrosion resistance and are designed for easy installation and maintenance, particularly in regions with varying water quality challenges.
How Do Gear Shaft Couplings Enhance Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy applications, such as wind turbines, gear shaft couplings connect turbines to generators, playing a crucial role in energy efficiency and system durability. These couplings must be capable of handling variable loads and high-speed operations. For international buyers, it is essential to focus on sourcing couplings that meet specific industry standards and can adapt to different environmental conditions, ensuring optimal performance in diverse climates across Europe and the Middle East.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘gear shaft coupling’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misalignment Causing Equipment Downtime
The Problem: One of the most prevalent issues faced by B2B buyers is the misalignment of gear shaft couplings, which can lead to excessive wear, increased vibrations, and ultimately, equipment failure. This is particularly concerning for industries that rely on continuous operation, such as manufacturing and energy. Misalignment can stem from various factors, including installation errors, thermal expansion, or wear and tear over time. When misalignment occurs, it not only affects the performance of the machinery but can also result in costly downtime and repairs.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of misalignment, it’s crucial to implement a robust installation and maintenance protocol. Begin by ensuring precise alignment during installation, utilizing tools such as laser alignment systems for accuracy. Regularly scheduled maintenance checks should include alignment verification, as even minor shifts can lead to significant issues. Additionally, consider opting for gear couplings designed to accommodate some degree of misalignment. These couplings can absorb angular and radial misalignment, thus enhancing the longevity of your equipment. Finally, investing in training for your maintenance team on alignment techniques and the importance of monitoring can yield substantial long-term savings.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Lubrication Leading to Gear Wear
The Problem: Another common pain point is the inadequate lubrication of gear shaft couplings, which can significantly shorten their lifespan and lead to premature failure. Many buyers underestimate the importance of proper lubrication intervals and the type of lubricant used. Insufficient lubrication can result in increased friction, overheating, and wear, ultimately compromising the coupling’s ability to transmit torque effectively. This is especially critical in high-speed and high-torque applications where the demands on the coupling are greatest.
The Solution: To address lubrication challenges, develop a comprehensive lubrication strategy tailored to the specific operational conditions of your gear couplings. Start by selecting the appropriate lubricant; high-performance grease that resists separation and retains its viscosity under high temperatures is advisable. Implement a regular lubrication schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and your operational environment. Additionally, consider using automatic lubrication systems to ensure consistent application. Regular inspections should also be conducted to check for signs of lubricant degradation or contamination, enabling timely maintenance actions that can prevent costly failures.
Scenario 3: Difficulty Sourcing the Right Gear Coupling for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges in sourcing the right gear shaft coupling that meets their specific application requirements. With the vast array of options available, including variations in size, torque capacity, and material, it can be overwhelming to determine which coupling is the best fit for their machinery. This issue is exacerbated in global markets where different suppliers may have varying standards, potentially leading to miscommunication and the procurement of subpar components.
The Solution: To streamline the sourcing process, begin by conducting a thorough needs assessment that outlines the specific requirements of your application, including torque requirements, shaft dimensions, and environmental conditions. Use this information to create a detailed specification sheet. When evaluating suppliers, look for those who can provide comprehensive technical support and customization options. Engaging with suppliers that offer a wide range of inventory and the ability to rebore couplings can also enhance flexibility. Consider leveraging online platforms and industry forums to gather reviews and insights from other users, helping you make more informed decisions. Establishing relationships with trusted suppliers can also facilitate quicker access to the right gear couplings in the future.
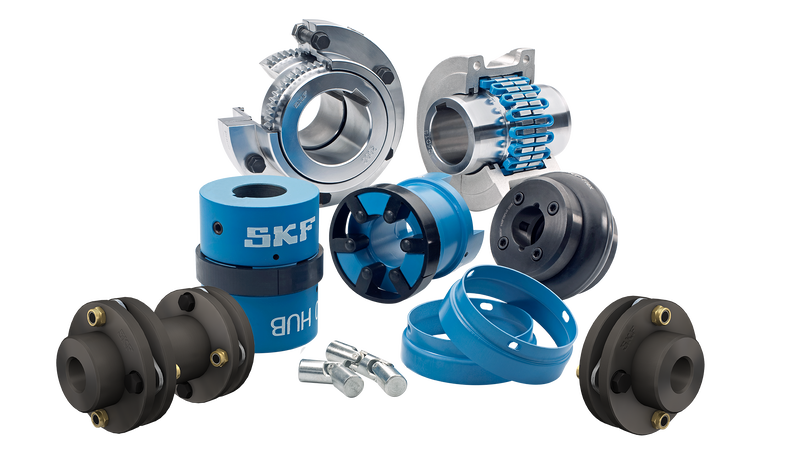
Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gear shaft coupling
When selecting materials for gear shaft couplings, B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in gear shaft couplings, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international applications.
What are the Key Properties of Steel in Gear Shaft Couplings?
Steel is the most prevalent material for gear shaft couplings due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high tensile strength, good fatigue resistance, and the ability to withstand high torque loads. Steel couplings can operate effectively at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 200°C, making them suitable for various industrial applications. Additionally, steel has a moderate corrosion resistance, which can be enhanced through surface treatments like galvanization or coating.
Pros of steel include its high durability and strength, which translate to longer service life and reliability in heavy-duty applications. However, its cons include susceptibility to corrosion if not properly treated, and higher manufacturing complexity due to the need for machining and finishing processes.
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Steel couplings must meet specific quality certifications to ensure performance in demanding environments.

Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Gear Shaft Couplings?
Aluminum is another material option, known for its lightweight properties and good corrosion resistance. It typically operates effectively at lower temperatures, generally up to 150°C. While aluminum gear couplings can handle moderate torque loads, they are not as strong as steel counterparts.
The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which reduces the overall mass of machinery and can improve energy efficiency. However, its key disadvantage is lower strength, which may limit its use in high-torque applications. Additionally, aluminum is more expensive than steel, which can impact project budgets.
For international buyers, aluminum couplings must comply with specific standards, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations. Buyers should ensure that the aluminum used is of high quality to avoid issues with fatigue and wear.
What are the Benefits of Using Nylon in Gear Shaft Couplings?
Nylon is often used for gear couplings that require flexibility and low weight. It provides excellent resistance to wear and has good shock-absorbing properties, making it suitable for applications with misalignment. Nylon couplings can operate effectively at temperatures up to 80°C and are resistant to many chemicals, which is beneficial in various industrial environments.
Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
The advantage of nylon is its ability to dampen vibrations and reduce backlash, enhancing the performance of precision machinery. However, the disadvantage is that nylon has a lower load-bearing capacity compared to metals, limiting its application in high-torque environments. Additionally, its susceptibility to UV degradation and moisture absorption can affect longevity.
International buyers should consider the specific chemical environment of their applications when selecting nylon couplings. Compliance with standards such as JIS may also be necessary, depending on the region.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Gear Shaft Couplings?
Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It can withstand high temperatures, typically up to 300°C, and offers good corrosion resistance when treated. Cast iron couplings are robust and can handle significant torque loads.
Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
The key advantage of cast iron is its durability and ability to operate under extreme conditions. However, the key disadvantage is its brittleness, which can lead to failure under shock loads. Additionally, cast iron is heavier than other materials, which may not be suitable for applications where weight is a concern.
For international buyers, cast iron couplings must meet specific industry standards, such as ASTM, to ensure reliability and performance in demanding environments. Buyers should also consider the weight implications in their machinery design.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Gear Shaft Couplings
| Material | Typical Use Case for gear shaft coupling | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight machinery and transport | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Lower strength than steel | High |
| Nylon | Precision machinery with misalignment | Vibration dampening and flexibility | Lower load-bearing capacity | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Heavy machinery in extreme conditions | Excellent durability and wear resistance | Brittle under shock loads | Medium |
This material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in various international markets, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gear shaft coupling
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Gear Shaft Couplings?
The manufacturing process of gear shaft couplings involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential for ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications for performance and durability.
How is Material Prepared for Gear Shaft Couplings?
Material selection is the first step in manufacturing gear shaft couplings. High-strength steel alloys are commonly used due to their excellent tensile strength and fatigue resistance. The selected raw materials undergo a thorough inspection to ensure they meet quality standards. This includes checking for material defects, dimensions, and chemical composition.
Once the materials are approved, they are cut into appropriate sizes using precision cutting techniques, such as laser cutting or water jet cutting. This ensures minimal waste and precise dimensions, which are crucial for the subsequent forming processes.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Gear Shaft Couplings?
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into the desired forms. Common techniques include forging and machining.
-
Forging: This process involves shaping the metal using compressive forces. Hot or cold forging can be employed, depending on the required strength and ductility of the final product. Forging enhances the material’s grain structure, resulting in improved mechanical properties.
-
Machining: After forging, the components are machined to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are typically used for this purpose, allowing for high accuracy in the production of complex shapes and features, such as gear teeth.
What Steps Are Involved in the Assembly of Gear Shaft Couplings?
Once individual components are formed, they move on to the assembly stage. This process typically involves the following steps:
-
Component Inspection: Before assembly, each component is inspected for dimensional accuracy and surface integrity. This ensures that any defects are identified early in the process.
-
Assembly: The components are assembled according to predefined specifications. This may involve aligning the gear teeth, applying lubricants, and securing components with set screws or bolts.
-
Alignment Checks: Proper alignment is critical for the performance of gear couplings. During assembly, alignment checks are performed to ensure that the shafts and couplings are correctly positioned, minimizing wear and maximizing efficiency.
How is the Finishing Process Conducted for Gear Shaft Couplings?
The finishing stage includes several processes aimed at enhancing the performance and aesthetic of the couplings.
-
Surface Treatment: This can involve processes such as shot blasting, coating, or heat treatment. These treatments improve wear resistance, reduce friction, and enhance corrosion resistance.
-
Final Inspection: After finishing, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure that all specifications have been met. This includes visual inspections and dimensional checks to confirm compliance with design tolerances.
-
Packaging: Finally, the couplings are packaged for shipment, ensuring they are protected from damage during transit.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Gear Shaft Couplings?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for gear shaft couplings, ensuring that products meet both international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards, such as ISO 9001, are essential for manufacturers to follow. This standard focuses on quality management systems and helps organizations ensure they meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently. Other relevant certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for gear couplings used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products meet specific safety and performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify their quality and conformity to specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, periodic checks are performed to monitor critical dimensions and tolerances. This proactive approach helps identify issues early, reducing waste and rework.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, a final inspection ensures that the couplings meet all specifications and performance criteria before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Gear Shaft Couplings?
Testing methods for gear shaft couplings include:
- Torque Testing: Measures the coupling’s ability to transmit torque under various conditions.
- Vibration Analysis: Assesses the coupling’s performance in operational conditions, identifying potential misalignment or imbalance issues.
- Load Testing: Evaluates the coupling’s performance under specified load conditions to ensure it can withstand operational stresses.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance Practices?
B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should implement several strategies to verify the quality assurance practices of potential suppliers.
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Supplier Verification?
Conducting supplier audits is crucial for assessing a manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards. Buyers can request:
- Quality Assurance Reports: These documents outline the quality processes and results from various testing stages.
- Certification Documentation: Verification of compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001 or CE, provides assurance of a supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Important is Third-Party Inspection for Ensuring Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can enhance confidence in product quality. These independent entities conduct thorough evaluations of the manufacturing processes and final products, ensuring compliance with international standards. This extra layer of verification is particularly valuable for buyers concerned about quality discrepancies that may arise from different manufacturing practices in various regions.

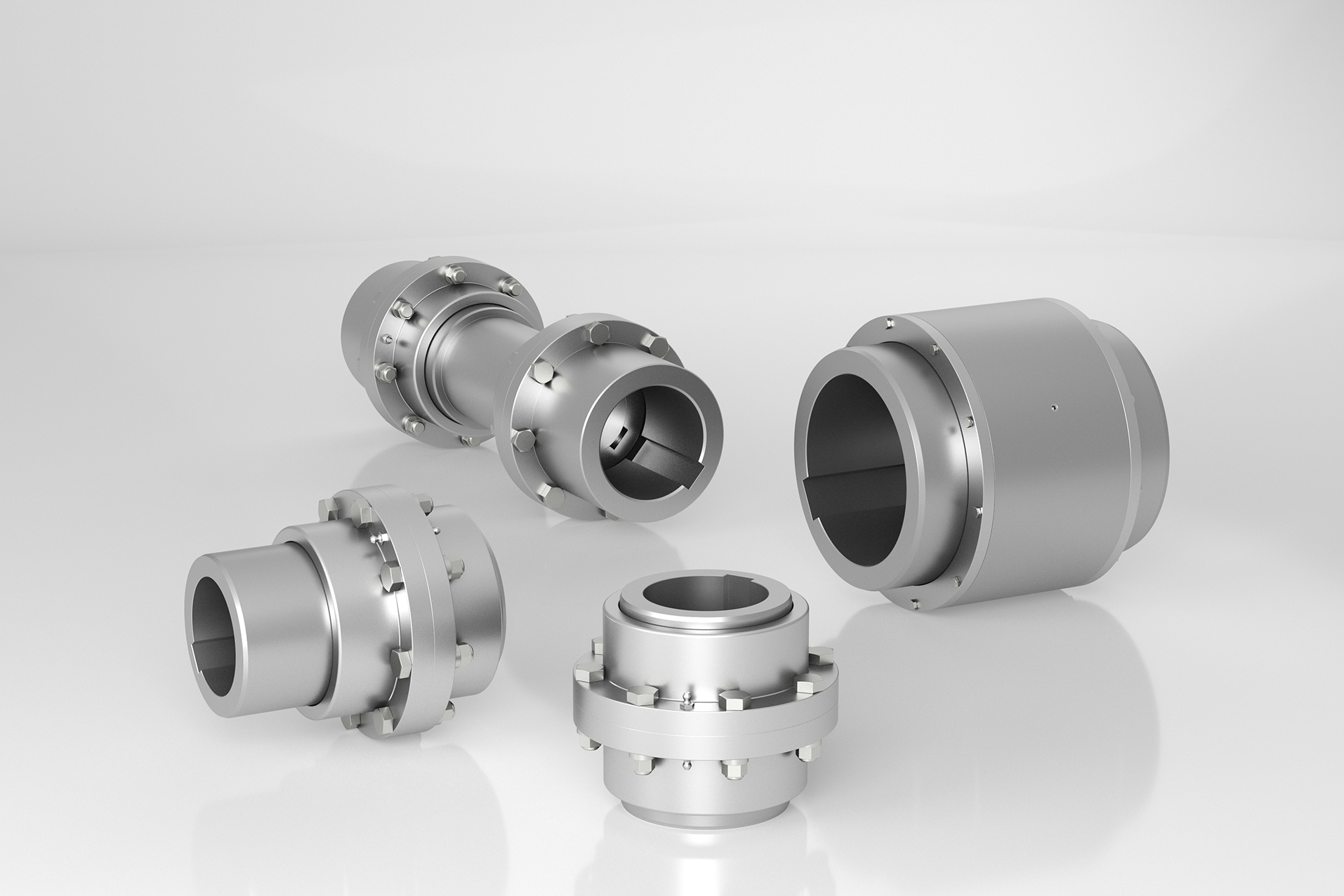
Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International buyers should be aware of regional differences in quality standards and regulations. For instance, while European standards may emphasize stringent environmental regulations, manufacturers in other regions may have different compliance requirements. Understanding these nuances can aid buyers in making informed decisions and ensuring that the gear shaft couplings they procure meet their operational needs effectively.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for gear shaft couplings enables B2B buyers to make informed procurement decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that adhere to international quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘gear shaft coupling’
To assist B2B buyers in effectively sourcing gear shaft couplings, this practical guide provides a structured checklist. Following these steps will ensure that you select the right product for your operational needs while working with reliable suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility with your existing equipment. Consider factors such as torque capacity, shaft size, and misalignment tolerance. Providing detailed specifications will streamline the sourcing process and help suppliers provide the most suitable options.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their credentials and industry experience. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, check for industry-specific certifications that may be relevant in your region, as they can assure compliance with local regulations.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
It’s essential to conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers to ensure reliability and quality. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from clients within your industry. This can provide insights into their performance, product quality, and customer service track record.
Step 4: Compare Product Offerings
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare their product offerings based on your specifications. Look for variations in design, material, and additional features such as lubrication types and maintenance requirements. Understanding the differences can help you identify the best fit for your applications.
Step 5: Inquire About Customization Options
Many applications may require custom solutions. Ask suppliers about their capabilities to modify products to meet specific requirements, such as bespoke sizes or unique material compositions. Customization can enhance the performance of gear couplings in specialized environments.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Availability
Understanding lead times and product availability is vital for project planning. Confirm the suppliers’ stock levels and typical delivery times for your desired products. This ensures that you can meet project deadlines and avoid potential delays in your operations.
Step 7: Review Warranty and Support Policies
Finally, examine the warranty and post-purchase support offered by suppliers. A robust warranty indicates confidence in product quality and performance, while comprehensive support can be invaluable in addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase. Clarifying these terms can save costs and ensure smooth operations in the long term.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing gear shaft couplings, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reliability in their mechanical systems.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gear shaft coupling Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of gear shaft couplings is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section provides a detailed analysis of the key cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic tips for effective sourcing.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Gear Shaft Coupling Manufacturing?
The cost structure for gear shaft couplings can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in gear couplings include high-strength steel and, in some cases, nylon for sleeves. The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost, with higher-grade materials commanding a premium.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the precise machining and assembly of gear couplings. Labor costs can vary significantly by region, with developed countries typically facing higher wage structures compared to emerging markets.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Manufacturers with advanced machinery may have lower per-unit overhead costs due to increased efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often required for specific designs or large diameter couplings. Tooling costs can be substantial, especially if the coupling specifications are unique or non-standard.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that couplings meet industry standards. Costs associated with testing and inspection should be factored into the pricing structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the location of the supplier and buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. These costs are crucial for buyers to consider, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market competition and demand.
What Influences the Pricing of Gear Shaft Couplings?
Several factors can influence the pricing of gear shaft couplings:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs while maximizing cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific torque ratings can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials: The choice between standard and premium materials can significantly affect pricing. High-performance couplings made from specialty alloys will be priced higher.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards or have specific certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should assess whether the additional cost aligns with their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can affect the total landed cost, as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers in Negotiating Gear Shaft Coupling Prices?
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, durability, and potential downtime costs. A higher upfront investment in a quality coupling may lead to lower long-term costs.
-
Leverage Volume for Negotiation: If your business has significant purchasing power, use this to negotiate better pricing or terms. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for bulk purchases.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Comparing quotes from different suppliers can reveal pricing discrepancies and provide leverage during negotiations. Ensure that you are comparing similar specifications.
-
Assess Local vs. International Sourcing: While international suppliers may offer competitive prices, consider additional logistics and customs costs. Local suppliers might provide advantages in terms of speed and ease of communication.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and regulatory impacts. Stay informed about these factors to avoid surprises.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for gear shaft couplings can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to obtain detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions. Always consider obtaining a sample or prototype to assess quality before committing to a large order.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing gear shaft coupling With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Gear Shaft Coupling
When evaluating mechanical connections for power transmission in industrial applications, understanding the various alternatives to gear shaft couplings is crucial. Each solution presents unique strengths and weaknesses, making it essential for B2B buyers to assess their specific needs in terms of performance, cost, and application requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Gear Shaft Coupling | Disc Coupling | Jaw Coupling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque capacity, accommodates misalignment | Excellent for high-speed applications, minimal backlash | Good for moderate torque, compensates for angular misalignment |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on size and specifications | Generally lower cost, but varies by design | Cost-effective for low to medium torque applications |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise alignment and regular lubrication | Easier installation with less maintenance | Simple installation with fewer components |
| Maintenance | Requires regular lubrication and alignment checks | Low maintenance, minimal wear | Limited maintenance, but replacement of elastomers may be needed |
| Best Use Case | Heavy industrial machinery, pumps, compressors | High-speed applications, precision machinery | General-purpose applications, light to moderate loads |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Disc Coupling
Disc couplings are designed to transmit torque while accommodating angular and axial misalignments through flexible discs. Their construction allows for minimal backlash and high-speed operation, making them ideal for applications requiring precision, such as robotics and CNC machinery. However, while they are generally more affordable than gear couplings, their torque capacity may not match that of gear couplings for heavy-duty applications.
Jaw Coupling
Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with a flexible element in between, typically made of rubber or polyurethane. This design provides a simple and effective means of coupling shafts while absorbing shock loads and accommodating some misalignment. Jaw couplings are particularly cost-effective and easy to install, making them suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in light to moderate torque scenarios. However, their performance diminishes under high torque conditions, limiting their use in heavy industrial settings.
Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
For B2B buyers, selecting the right coupling solution involves weighing the performance requirements against cost and maintenance considerations. Gear shaft couplings are ideal for high-torque, heavy-duty applications but may require more intricate installation and regular maintenance. In contrast, disc couplings offer a balance of performance and ease of maintenance, making them suitable for precision-driven environments. Jaw couplings are a great choice for general-purpose applications where cost-effectiveness is paramount.
Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific operational demands of the machinery and the overall cost-effectiveness of the solution in the long term. Consideration of factors such as torque requirements, operational speed, and maintenance capacity will guide buyers towards the most appropriate coupling solution for their business needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gear shaft coupling
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Gear Shaft Couplings?
Understanding the essential technical properties of gear shaft couplings is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed decisions. Here are some critical specifications and their importance in various applications:

Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
1. Material Grade
Gear couplings are typically made from high-strength steel or alloy materials, which contribute to their durability and load-bearing capacity. The choice of material affects the coupling’s resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures reliability and longevity in harsh industrial environments, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
2. Torque Rating
The torque rating of a gear coupling defines the maximum torque it can transmit without failure. Common ratings can range from 10,000 to over 70 million lbs-in, depending on the size and design. Knowing the appropriate torque rating is vital for applications where high power transmission is required, ensuring that the coupling can handle operational demands without risk of breakdown.
3. Bore Size
Bore size refers to the internal diameter of the coupling where it fits onto the shaft. Gear couplings come in various bore sizes, accommodating shafts typically ranging from 1/2” to 28”. A precise bore size is critical for achieving a proper fit, which minimizes vibration and misalignment, leading to improved performance and reduced wear on both the coupling and connected equipment.
4. Misalignment Tolerance
Gear couplings are designed to accommodate angular, radial, and axial misalignment. The ability to tolerate a certain degree of misalignment is essential in applications where perfect alignment is impractical. For B2B buyers, understanding misalignment tolerance ensures that the selected coupling can maintain efficiency and extend the life of the connected machinery.
5. Lubrication Requirements
Most gear couplings require regular lubrication to function optimally, as this reduces friction and wear between the meshing teeth. The type of lubricant—grease or oil—can significantly influence the coupling’s performance and maintenance schedule. Buyers should consider lubrication needs when selecting couplings to ensure compliance with operational protocols and maintenance capabilities.

Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
6. Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
Proper installation and maintenance are critical for the longevity of gear couplings. This includes alignment procedures and periodic inspections for wear and lubrication levels. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive installation guides and maintenance recommendations, which can lead to smoother operations and lower overall costs.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry terminology can greatly enhance communication and negotiations in the procurement process. Here are several key terms to be aware of:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for buyers to ensure compatibility and quality in replacement parts or new machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management, especially when sourcing specialized gear couplings.
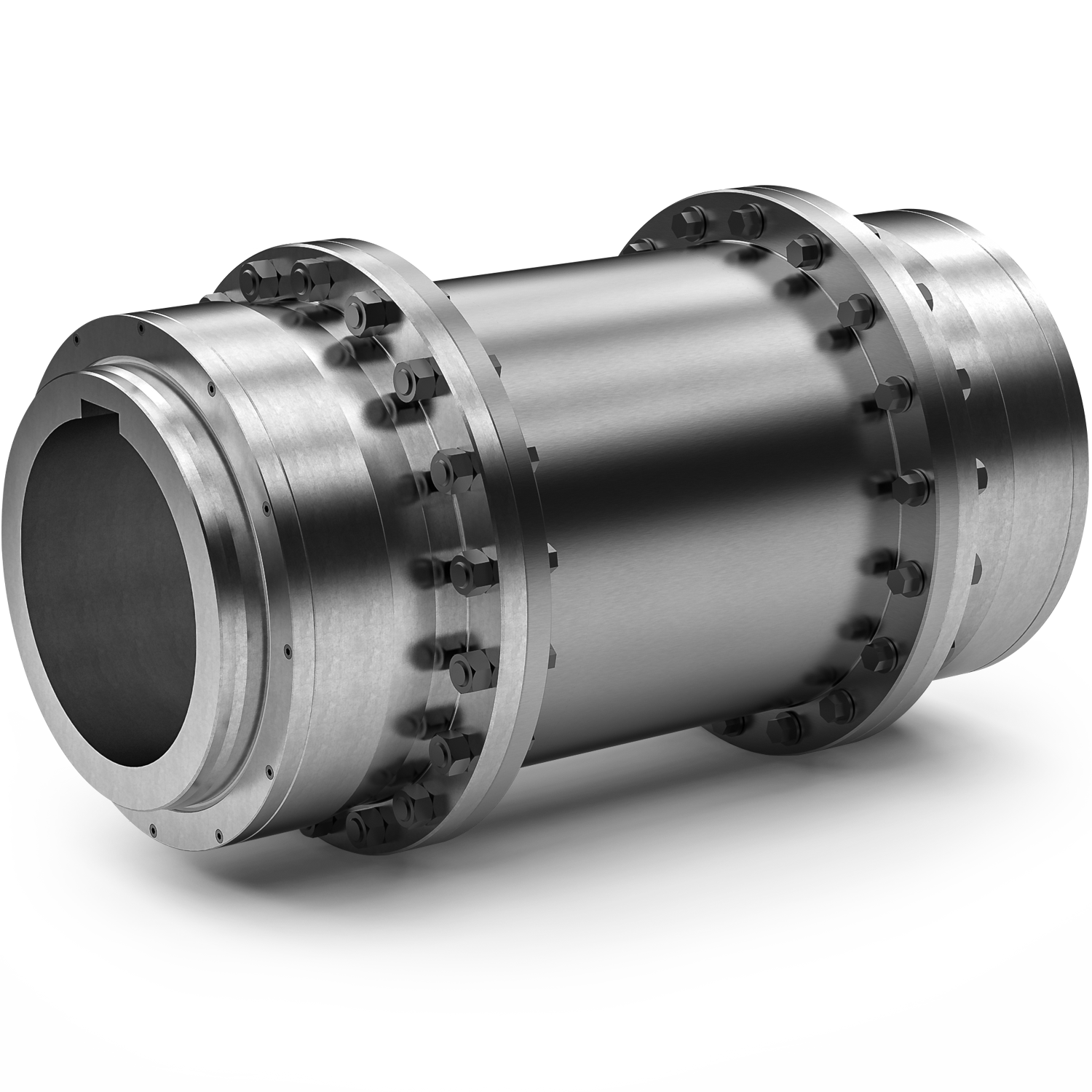

Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive the best value for their purchases.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risk management.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for B2B buyers to plan their projects and manage inventory effectively.
Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
6. Custom Solutions
This term refers to products tailored to meet specific customer requirements. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that offer custom solutions for gear couplings to ensure they receive products that meet unique operational needs.
By understanding these properties and terms, B2B buyers can navigate the gear shaft coupling market more effectively, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational requirements and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the gear shaft coupling Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting Gear Shaft Couplings?
The gear shaft coupling market is experiencing a robust growth trajectory, driven by the increasing demand for efficient power transmission across various industries, such as manufacturing, energy, and construction. The global push for automation and the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies are significant market drivers, as businesses seek to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. In regions like Africa and South America, infrastructural development is fueling demand, while in Europe and the Middle East, the focus is on upgrading aging machinery to meet modern performance standards.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the utilization of advanced materials that enhance the durability and performance of gear couplings. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as predictive maintenance tools and IoT connectivity, are becoming integral, allowing for real-time monitoring of coupling performance and early detection of issues. This trend is especially relevant for international buyers, as it not only optimizes operational efficiencies but also reduces long-term costs.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing an increase in customization options. Suppliers are now offering tailored solutions that meet specific torque requirements and shaft dimensions, thus catering to the diverse needs of various industries. As the competition intensifies, buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Germany are advised to leverage these trends for strategic sourcing, ensuring they select suppliers who can provide both standard and bespoke coupling solutions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Decisions in the Gear Shaft Coupling Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of sourcing decisions in the gear shaft coupling sector. With the growing awareness of environmental impacts, international buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to ethical practices and sustainable manufacturing processes. The environmental footprint of producing gear couplings, which often involves significant energy consumption and material waste, is prompting companies to adopt greener alternatives.
Buyers should look for suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, which indicates adherence to effective environmental management systems. Additionally, the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly lubricants in manufacturing gear couplings is gaining traction. This not only minimizes environmental impact but also enhances the overall sustainability profile of the product.

Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
Moreover, companies that implement transparent supply chains and ethical sourcing practices are likely to gain a competitive edge. This is particularly relevant in regions where consumers and regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing corporate responsibility. By prioritizing sustainability in their procurement strategies, international buyers can align with global trends, enhance their brand reputation, and meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Historical Context of Gear Shaft Couplings?
The evolution of gear shaft couplings dates back to the early 20th century when the need for effective torque transmission solutions in industrial machinery became apparent. Initially, couplings were simple mechanical devices, primarily made of metal, designed to connect rotating shafts with minimal misalignment. Over time, advancements in materials science and engineering led to the development of more sophisticated designs, including flexible gear couplings that accommodate angular, radial, and axial misalignment.
The introduction of standardized designs and manufacturing practices in the mid-20th century further revolutionized the industry, allowing for mass production and greater accessibility. Today, gear couplings are integral components in various applications, ranging from heavy machinery to high-speed industrial equipment. As technology continues to advance, the focus on enhancing performance, durability, and sustainability remains at the forefront of innovation in the gear shaft coupling sector. This historical context informs current trends, emphasizing the importance of understanding both the technical evolution and the market dynamics shaping today’s sourcing landscape.

Illustrative image related to gear shaft coupling
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gear shaft coupling
-
How do I select the right gear shaft coupling for my application?
To choose the right gear shaft coupling, first assess the torque requirements and shaft sizes of your machinery. Consider the type of misalignment your application experiences—angular, parallel, or axial—as gear couplings are designed to accommodate these issues. Additionally, evaluate the operating environment, such as temperature and humidity, which may affect material selection. Finally, consult with suppliers about their inventory and customization options, ensuring the coupling meets industry standards and specifications relevant to your region. -
What factors should I consider when sourcing gear shaft couplings internationally?
When sourcing gear shaft couplings internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, quality assurance processes, and compliance with international standards. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, including customization options, and inquire about lead times and delivery logistics. Additionally, understand the payment terms, including any currency exchange implications. Research local regulations in your country regarding imports and tariffs, and consider the supplier’s ability to provide after-sales support and warranty options for the couplings. -
What is the typical lead time for custom gear shaft couplings?
Lead times for custom gear shaft couplings can vary significantly based on the complexity of the design, the manufacturer’s production capacity, and the supply chain logistics involved. Generally, expect a timeframe of 4 to 12 weeks for custom orders. It’s crucial to communicate your specific requirements early in the process and confirm timelines with the supplier to ensure they align with your project deadlines. Always factor in additional time for shipping, especially for international orders. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for gear shaft couplings?
Minimum order quantities for gear shaft couplings typically depend on the manufacturer’s policies and the specific coupling type. Standard MOQs can range from as low as 10 units to several hundred for custom designs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you are a smaller buyer or require a specialized product. Additionally, consider the potential cost benefits of ordering in bulk to meet your operational requirements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for gear shaft couplings?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing gear shaft couplings, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Inquire about their quality control processes, including testing methods for durability, tolerance, and performance under load. Consider suppliers who provide third-party testing reports or ISO certifications. Establish clear communication regarding your quality expectations and consider visiting the manufacturing facility if possible to observe their processes firsthand. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing gear shaft couplings?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common arrangements include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and the balance upon delivery. For international transactions, be aware of additional costs such as tariffs, taxes, and shipping fees. It’s advisable to use secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties. Always clarify the payment terms in writing to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing gear shaft couplings?
When importing gear shaft couplings, consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), delivery times, and costs associated with each. Be aware of customs regulations in your country, including any necessary documentation and duties that may apply. Work with reliable logistics partners who can provide end-to-end solutions, including customs clearance. Additionally, ensure that the couplings are properly packaged to avoid damage during transit, and confirm insurance coverage for high-value orders. -
How do I handle installation and maintenance of gear shaft couplings?
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for the longevity of gear shaft couplings. Follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines, ensuring correct alignment and securing all fasteners to the specified torque. Regular maintenance should include checking alignment, inspecting lubrication levels, and replacing any worn seals. Schedule periodic inspections based on operational hours to preemptively address wear and tear. Document maintenance activities to track performance and ensure compliance with operational standards.
Top 7 Gear Shaft Coupling Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. McMaster – Gear Couplings
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Gear Couplings, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Drive Components – Gear Couplings
Domain: drivecomponentsllc.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Gear Couplings are available in stock at Drive Components’ Cleveland, OH facility. They come in various styles including G20 Flexible Gear Couplings (sizes 10FF – 70FF) and G52 Rigid Gear Couplings (sizes 10 – 50). The couplings accommodate shaft sizes ranging from 1/2″ to 11″ and are rated for torque from 10,000 to 1,100,000 lbs-in. Custom rebore capabilities are offered for fitting specific shaf…
3. Guardian – Gear Grip Flexible Shaft Coupling
Domain: guardiancouplings.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Gear Grip Flexible Shaft Coupling is a general use coupling designed for applications with a large degree of misalignment, accommodating up to 50 HP. It features a three-piece highly flexible design with two hubs and a flexible sleeve. Available sleeve materials include neoprene, urethane, and reinforced neoprene, while hubs are typically made of zinc or sintered steel. Key features include:
– By…
4. BJ-Gear – Gear Couplings
Domain: bj-gear.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: BJ-Gear A/S supplies AXO gear couplings and couplings from leading manufacturers worldwide. Key types of gear couplings include: 1. Gear Tooth Couplings: Transmit torque and accommodate misalignment, ideal for high torque and balance applications. 2. Claw and Servo Couplings: Optimal for positioning applications with high torque transmission. 3. Metal Bellow Couplings: Suitable for precise positio…
5. Rowland Company – Amerigear Gear Coupling
Domain: rowlandcompany.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Gear couplings use gear teeth to accommodate misalignment and have large torque capacity in a small envelope. They can be mounted horizontally or vertically and feature minimum backlash. Key products include:
1. **Amerigear Gear Coupling**:
– Special fully-crowned tooth design for maximum torque capacity with minimum size.
– Torque range: 158 to 86,083 lb-ft (214 to 116,712 Nm).
– Ty…
6. Boston Gear – FC Series Coupling Half
7. Huading Machine – Gear Couplings
Domain: huadingmachine.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Gear couplings are designed to transmit torque between non-collinear shafts, consisting of two flexible joints connected by a spindle. They connect drive motors to gearboxes and can also connect gearboxes to smaller wire rope drums. Gear couplings feature hubs with crowned gear teeth in permanent mesh with straight gear teeth of sleeves, providing high torque transmission in a compact size. They a…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gear shaft coupling
As the demand for reliable and efficient power transmission solutions continues to grow globally, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the strategic sourcing of gear shaft couplings emerges as a critical component for industrial operations. Buyers must recognize the importance of selecting high-quality gear couplings that can accommodate varying torque capacities and shaft sizes while ensuring durability and minimal maintenance requirements.
Strategic sourcing not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who can provide tailored solutions, ensuring that businesses remain competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace. By considering factors such as material quality, design specifications, and adaptability to specific applications, international buyers can optimize their supply chains and reduce operational risks.
Looking ahead, it is imperative for B2B buyers to stay informed about advancements in gear coupling technology and market trends. Engaging with reputable suppliers and leveraging their expertise will facilitate informed decision-making, ultimately leading to improved productivity and cost-effectiveness. Take the next step in enhancing your operational capabilities by exploring strategic sourcing opportunities for gear shaft couplings that align with your business objectives.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.