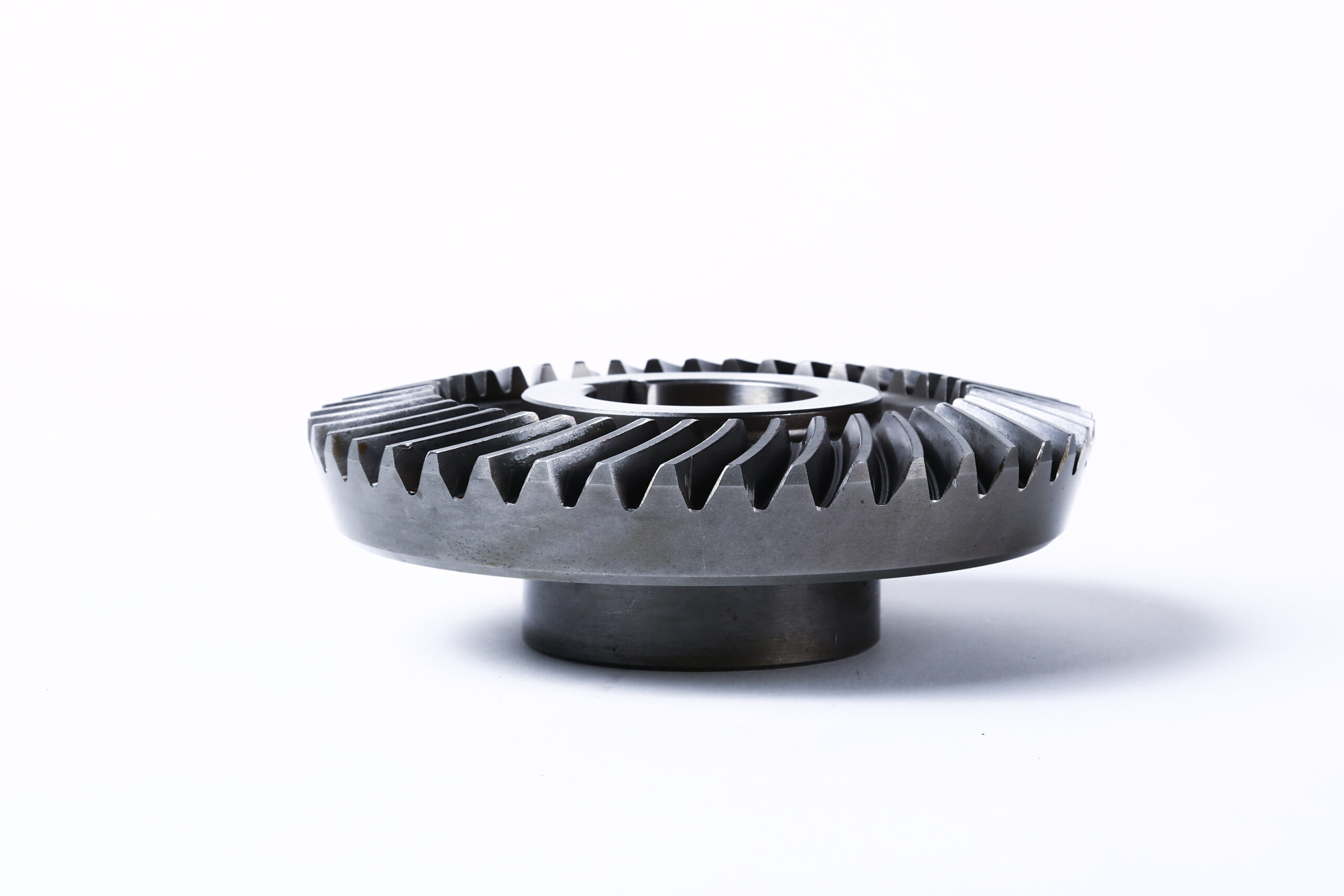
Everything You Need to Know About Face Gears Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for face gears
In an increasingly interconnected global market, sourcing face gears that meet specific engineering requirements can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers. As industries evolve, the demand for efficient and reliable gear systems has surged, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia. This comprehensive guide addresses the complexities of navigating the face gear market, offering insights into the various types of face gears, their applications across multiple sectors, and practical considerations for supplier vetting.
Buyers will find detailed information on the unique advantages of face gears, including their ability to accommodate non-parallel axes and provide axial freedom, which can enhance design flexibility in precision applications. The guide also delves into cost factors, helping businesses understand pricing structures and potential return on investment. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this resource empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right face gear solutions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. With this guide, buyers can confidently approach their sourcing strategies, navigating the complexities of the face gear market with clarity and purpose.
Understanding face gears Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Straight-Toothed Face Gear | Features straight teeth aligned radially; easier to manufacture. | Light-duty applications in robotics, automotive, and industrial machinery. | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited torque capacity. |
| Helical Face Gear | Teeth are angled, allowing for smoother engagement and reduced noise. | Precision machinery, aerospace applications, and high-speed gear systems. | Pros: Higher load capacity, quieter operation. Cons: More complex manufacturing. |
| Involute Face Gear | Uses an involute profile for tooth design, optimizing contact and strength. | High-performance gear systems in automotive and aerospace sectors. | Pros: Improved strength and efficiency. Cons: Higher manufacturing costs. |
| Composite Face Gear | Combines materials or designs for enhanced performance, such as hybrid constructions. | Advanced machinery, robotics, and applications requiring weight reduction. | Pros: Customizable for specific needs, lightweight. Cons: Potentially higher costs and complexity in sourcing. |
| Bevel Face Gear | Integrates features from bevel gears, allowing for angled drive configurations. | Applications requiring direction change in motion, such as in power transmission systems. | Pros: Versatile in design, can handle various load types. Cons: More complex design and potential alignment issues. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Straight-Toothed Face Gears?
Straight-toothed face gears feature teeth that are aligned radially, which simplifies the manufacturing process. They are commonly used in light-duty applications like robotics and automotive systems where low torque is sufficient. When considering straight-toothed face gears, buyers should evaluate the gear’s load capacity against their specific application requirements, as these gears are not suited for high-load scenarios.
How Do Helical Face Gears Enhance Performance?
Helical face gears possess angled teeth that allow for smoother engagement, resulting in quieter operation and increased load capacity. These gears are particularly suitable for precision machinery and high-speed applications, such as in the aerospace sector. Buyers should consider the complexity and cost of manufacturing when selecting helical face gears, as they may require more advanced machining techniques.
Why Choose Involute Face Gears for High-Performance Applications?
Involute face gears utilize a tooth profile that optimizes contact and strength, making them ideal for high-performance systems in automotive and aerospace applications. Their design enhances efficiency and durability, which is crucial for demanding environments. Buyers need to weigh the benefits of improved performance against the higher manufacturing costs associated with these gears.
What Advantages Do Composite Face Gears Offer?
Composite face gears combine various materials or design elements to achieve superior performance, often resulting in lighter and more efficient gear systems. They are increasingly used in advanced machinery and robotics where specific performance characteristics are required. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between customization options and potential increases in costs and sourcing complexity.
How Do Bevel Face Gears Function in Motion Direction Changes?
Bevel face gears incorporate features from traditional bevel gears, enabling them to change the direction of motion effectively. They are often found in power transmission systems where directional changes are necessary. When considering bevel face gears, buyers should be mindful of the potential complexities in design and alignment, which can affect overall system performance.
Key Industrial Applications of face gears
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of face gears | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Helicopter rotor systems | Improved axial freedom allows for design flexibility | Precision manufacturing standards and reliability |
| Automotive | Electric vehicle (EV) drive systems | Efficient power transmission in compact designs | Compatibility with existing systems and material quality |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine gearboxes | Enhanced durability and efficiency under load | Environmental resistance and performance under stress |
| Industrial Machinery | CNC machines | Reduced vibration and noise levels | Tolerance specifications and machining accuracy |
| Marine Engineering | Propulsion systems for ships | Optimized space usage and weight reduction | Corrosion resistance and material strength |
How are Face Gears Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, face gears are primarily utilized in helicopter rotor systems. Their unique design allows for improved axial freedom, which facilitates greater flexibility in the overall design. This is crucial in applications where precision and reliability are paramount, as any failure can lead to catastrophic results. For international buyers, especially from regions like the Middle East and Europe, sourcing face gears requires strict adherence to precision manufacturing standards to ensure that they meet safety regulations and performance expectations.
What Role do Face Gears Play in Electric Vehicle (EV) Drive Systems?
Face gears are increasingly being integrated into electric vehicle (EV) drive systems due to their ability to efficiently transmit power in compact designs. This is particularly valuable in the automotive industry, where space is at a premium. The use of face gears can lead to reduced weight and improved energy efficiency, which are critical factors for EV performance. Buyers from South America and Africa should consider compatibility with existing systems and the quality of materials used to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
How are Face Gears Enhancing Renewable Energy Solutions?
In renewable energy, particularly within wind turbine gearboxes, face gears are favored for their durability and efficiency under load. They can withstand the harsh operating conditions typical in renewable energy applications, thus enhancing the overall reliability of the systems. For businesses in regions with growing renewable energy sectors, such as Africa, sourcing face gears that offer environmental resistance and high performance under stress is essential for long-term success and sustainability.
Why are Face Gears Important in CNC Machines?
Face gears are utilized in CNC machines to reduce vibration and noise levels, which is crucial for maintaining precision in machining operations. This application is particularly relevant for industrial machinery manufacturers who require high accuracy and minimal operational disturbances. International buyers, especially from Europe, need to focus on tolerance specifications and machining accuracy when sourcing these components to ensure they integrate seamlessly into their existing machinery.
How Do Face Gears Benefit Marine Engineering?
In marine engineering, face gears are used in propulsion systems for ships, where their compact design allows for optimized space usage and significant weight reduction. This is especially important in the marine industry, where every kilogram counts towards fuel efficiency and overall performance. Buyers from regions with robust maritime industries, such as the Middle East, should prioritize corrosion resistance and material strength when sourcing face gears to ensure they can withstand the challenging marine environment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘face gears’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Face Gear for Specific Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the appropriate face gear for their specific applications, especially when dealing with complex machinery. Many buyers may not fully understand the implications of different gear configurations, such as the distinction between spur and helical gears, and how these choices affect performance, efficiency, and longevity. This lack of clarity can lead to suboptimal gear selection, resulting in increased wear, inefficiencies, and ultimately higher operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific operational requirements of their applications, including load capacity, speed, and alignment constraints. Collaborating closely with gear manufacturers or suppliers can provide invaluable insights. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s capabilities in producing custom face gears tailored to their specific needs. Additionally, leveraging advanced simulation software can help visualize how different gear types will perform in real-world scenarios. This proactive approach ensures that the selected face gear not only fits the mechanical requirements but also optimizes the overall system performance.
Scenario 2: High Manufacturing Costs and Limited Availability of Face Gears
The Problem: Many international buyers experience frustration with the high costs and limited availability of face gears. This issue is particularly acute in regions with less developed manufacturing infrastructure, where sourcing high-quality face gears can lead to significant delays and inflated costs. Buyers may feel trapped between the need for specialized equipment and the constraints of their budgets, often resulting in compromised operational efficiency.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers can explore partnerships with local manufacturers who have the capability to produce face gears more cost-effectively. Establishing a collaborative relationship can lead to better pricing structures, especially for bulk orders. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in technology that allows for the in-house production of face gears. Techniques such as additive manufacturing can provide flexibility and reduce reliance on external suppliers. Finally, conducting thorough market research to identify alternative suppliers, including those from regions with competitive pricing, can also help alleviate cost burdens.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Reliability and Performance Under Heavy Loads
The Problem: One of the significant concerns for B2B buyers is ensuring that face gears perform reliably under heavy loads. Many industries, such as automotive or aerospace, require components that can withstand extreme conditions without failure. Buyers often worry about the risk of gear failure leading to costly downtimes and safety hazards, which can erode profit margins and damage reputations.
The Solution: To enhance reliability, buyers should prioritize sourcing face gears that have undergone rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. It is crucial to request detailed specifications and performance data from suppliers, including load ratings and fatigue resistance. Engaging in discussions about material selection—such as hardened steel versus plastic—can also yield significant performance benefits. Implementing a robust maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and timely replacements can further mitigate the risks associated with gear failure. Buyers should not hesitate to seek advice from industry experts on best practices for installation and operational management to optimize performance and longevity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for face gears
What Are the Key Materials for Face Gears and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for face gears, it is essential to consider the mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of face gears: steel, aluminum, brass, and polymer composites.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Face Gears?
Steel is the most prevalent material for face gears due to its excellent mechanical properties. It offers high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and deformation under load. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, its susceptibility to corrosion necessitates protective coatings or treatments, particularly in humid or corrosive environments.
Pros: High strength and durability, good wear resistance, suitable for high-load applications.
Cons: Heavier than alternatives, potential for corrosion, higher manufacturing complexity due to machining requirements.
Impact on Application: Steel face gears are ideal for applications involving heavy machinery and automotive systems, where high torque and load-bearing capacity are critical.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN) for mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
What Advantages Do Aluminum Face Gears Offer?
Aluminum is increasingly used for face gears, particularly in applications requiring lightweight components. It offers good corrosion resistance and is easier to machine than steel, resulting in lower manufacturing costs. However, aluminum has a lower strength-to-weight ratio compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-load applications.
Pros: Lightweight, good corrosion resistance, lower manufacturing complexity.
Cons: Lower strength compared to steel, limited suitability for high-load applications.
Impact on Application: Ideal for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries where weight reduction is essential.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should verify that aluminum gears meet specific industry standards for aerospace and automotive applications.
Why Choose Brass for Face Gears?
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications where aesthetic appeal is important, such as decorative machinery components. However, brass has lower tensile strength than steel and aluminum, which may limit its use in high-torque applications.
Pros: Excellent machinability, good corrosion resistance, attractive appearance.
Cons: Lower strength and durability, higher cost compared to aluminum.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in low-load applications such as clock mechanisms and small precision instruments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific alloy grades and compliance with international standards, especially in Europe.
When Are Polymer Composites a Suitable Choice for Face Gears?
Polymer composites are gaining traction in the manufacturing of face gears due to their lightweight nature and inherent corrosion resistance. They are ideal for applications where noise reduction is crucial, as they operate more quietly than metal gears. However, polymer composites may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as metals.
Pros: Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, low noise operation.
Cons: Limited strength and temperature resistance, higher manufacturing costs for specialized composites.
Impact on Application: Suitable for applications in consumer electronics and automotive sectors where weight and noise are critical factors.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers from regions like Nigeria should assess the availability of specific polymer composites and their compliance with relevant standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Face Gears
| Material | Typical Use Case for face gears | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy machinery, automotive systems | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Brass | Decorative machinery, precision tools | Excellent machinability | Lower strength and durability | Medium |
| Polymer Composites | Consumer electronics, automotive | Low noise operation | Limited strength and temperature resistance | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used for face gears, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for face gears
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Face Gears?
The manufacturing of face gears is a complex process that involves multiple stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Face Gear Production?
The first step in manufacturing face gears is material selection and preparation. Common materials used include steel, aluminum, and high-performance polymers, chosen based on the application requirements. The material undergoes several processes, including cutting and shaping, to ensure it meets specific dimensions and tolerances.
Once the material is selected, it is often treated for hardness and strength, which is essential for the longevity and performance of the gear. Heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering are frequently employed to enhance mechanical properties, ensuring the gear can withstand operational stresses.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Face Gear Production?
Forming techniques for face gears can vary based on the design and production volume. The most common methods include:
-
Hobbing and Shaping: While traditional methods like hobbing and shaping are well-known, advanced techniques such as CNC machining are increasingly used for precision and efficiency. These methods allow for the production of complex tooth geometries that are critical for optimal gear performance.
-
Grinding: For high-precision applications, grinding processes are employed post-hobbing to achieve the necessary surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This is particularly important in industries like aerospace and automotive, where tolerances are tight.
-
Alternative Methods: Innovative techniques like plastic molding, sintering, or pressing may be used for specific applications, especially in producing lightweight face gears. These methods can reduce production time and costs while maintaining quality.
How Are Face Gears Assembled for Optimal Performance?
Assembly of face gears is less complex compared to other gear types, primarily due to the axial freedom of the pinion. This feature allows for easier alignment and adjustment during installation. However, proper assembly practices are essential to ensure that the gears mesh correctly and operate efficiently.
During assembly, it is crucial to check the alignment of the face gear with its mating pinion. Misalignment can lead to premature wear or failure. Therefore, using precision tools and fixtures during assembly can enhance the overall performance of the gear system.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Face Gear Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a vital aspect of face gear production, ensuring that the gears meet international standards and specific customer requirements.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. This standard ensures consistency in production and quality assurance processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, like CE marking for safety compliance in Europe or API standards for the oil and gas sector, may also be relevant.
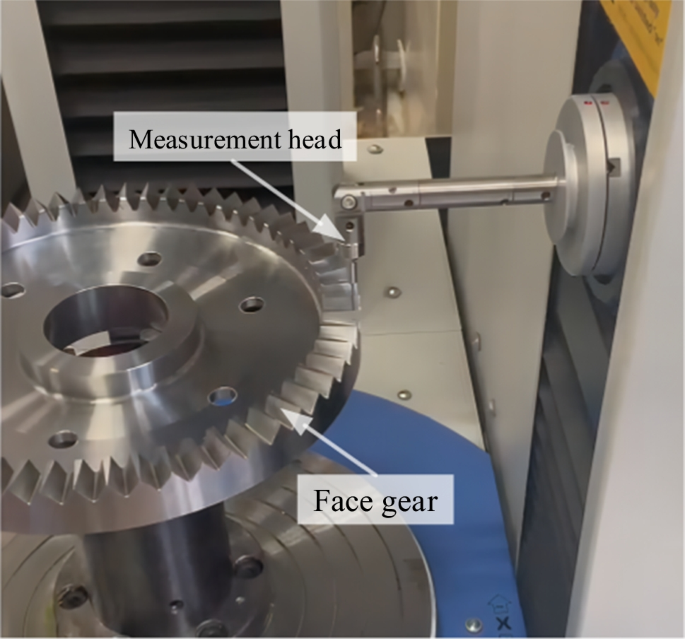
Illustrative image related to face gears
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Face Gear Manufacturing?
Quality control typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for compliance with specified standards before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to monitor dimensions, surface finish, and other critical parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, a comprehensive inspection is performed to ensure the finished gears meet all specifications and quality standards before shipment.
Which Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Face Gears?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the performance and quality of face gears, including:
- Dimensional Inspection: This involves measuring the gear’s dimensions against specified tolerances using calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection can detect internal flaws without damaging the gear.
- Performance Testing: Face gears may undergo operational tests to evaluate their performance under load, ensuring they meet the required torque and speed specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers adhere to robust quality control processes. Here are some effective strategies:
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Requesting audits and quality reports from potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Buyers should specifically look for:
- Certification Documents: Ensure the supplier holds relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 and any industry-specific standards.
- Quality Assurance Reports: These should detail the results of inspections, tests, and any corrective actions taken to address quality issues.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Supplier Reliability?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can conduct audits and inspections, providing unbiased verification of the supplier’s compliance with quality standards.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is crucial. Factors such as local regulations, material availability, and manufacturing capabilities can influence the quality of face gears.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of the varying standards and regulations that suppliers must meet. For instance, European manufacturers may face stricter compliance requirements compared to those in other regions, impacting the overall quality of the products.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Supply Chain Transparency?
In regions with less stringent regulations, buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer transparency in their supply chains. This can include detailed documentation of material sources, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures, ensuring that buyers receive products that meet their specifications and regulatory requirements.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for face gears, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘face gears’
To successfully procure face gears, B2B buyers must navigate a series of essential steps that ensure the selection of high-quality products tailored to their specific needs. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining the technical requirements for your face gears is crucial. Consider factors such as the type of application, load capacity, and required gear dimensions. Providing precise specifications helps suppliers understand your needs and deliver the right products.
- Consider the type of gear: Determine if you need straight-toothed or helical face gears based on your application.
- Assess load and torque requirements: Ensure the gears can handle the expected operational demands.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Identifying reliable suppliers is essential for a successful procurement process. Conduct thorough research to find companies specializing in face gears, particularly those with experience in your industry or region.
- Utilize online platforms: Explore B2B marketplaces, industry directories, and trade shows to compile a list of potential suppliers.
- Check supplier reputation: Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies that demonstrate their reliability and product quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before making a commitment, it’s vital to assess the capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. This includes examining their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and technical expertise.
- Request detailed information: Ask for documentation about their production methods, materials used, and any certifications they hold.
- Inquire about R&D capabilities: Suppliers with strong research and development can offer innovative solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensuring that suppliers adhere to industry standards and quality certifications is a key step in mitigating risks. Certifications such as ISO can indicate a commitment to quality management and continuous improvement.
- Request copies of certifications: Verify that the supplier is compliant with relevant international standards.
- Assess compliance history: Check if the supplier has faced any compliance issues in the past that could affect your partnership.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, it’s advisable to request samples or prototypes of the face gears. This allows you to evaluate the quality and suitability of the gears for your application.
- Conduct performance testing: Evaluate the sample gears under actual working conditions to ensure they meet your specifications.
- Assess compatibility: Ensure that the gears mesh well with your existing equipment.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and pricing. This step is essential to ensure that you receive value for your investment.
- Discuss bulk order discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for larger orders, which can significantly reduce costs.
- Clarify payment and delivery terms: Ensure that payment methods, lead times, and shipping arrangements are clearly defined.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Building a strong, long-term relationship with your supplier can yield ongoing benefits, such as better pricing, priority service, and access to new products.
- Communicate regularly: Maintain open lines of communication to address any issues promptly and foster collaboration.
- Provide feedback: Share your experiences and suggestions to help suppliers improve their products and services.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for face gears, ensuring that they select the right suppliers and products for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for face gears Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for face gears is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. Understanding the various components that contribute to the overall cost and the factors that influence pricing can lead to more effective procurement decisions.
What Are the Main Cost Components in Face Gears Production?
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost of face gears. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and various composites. Higher-quality materials often lead to increased durability and performance but also elevate the initial cost. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in superior materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Skilled labor is essential for precision machining, especially when producing gears with tight tolerances. Countries with lower labor costs may offer attractive pricing, but it’s crucial to balance this with quality assurance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the costs associated with running manufacturing facilities, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can lower these costs, directly affecting the final price of face gears.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom gear specifications. The need for specialized tooling, such as shaping cutters for face gears, can increase initial costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling charges and whether they are included in the pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that face gears meet specific standards involves rigorous QC processes. The cost of quality assurance can vary based on the complexity of the gears and the certifications required. Investing in robust QC processes can prevent costly failures in the field.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are vital components of the total cost structure. International buyers must consider duties, taxes, and freight costs when calculating the landed price of face gears. The choice of shipping methods and routes can also influence overall logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary widely depending on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product. Understanding a supplier’s pricing strategy can help buyers negotiate better terms.
What Factors Influence Face Gears Pricing?
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often decreases with higher order volumes due to economies of scale. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also affect the unit price. Buyers should evaluate their needs and negotiate MOQs that work for both parties.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized face gears tailored to specific applications can significantly alter pricing. Unique specifications may require additional engineering and production time, leading to higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality gears that meet international standards or certifications (like ISO or AS9100) can command premium pricing. Buyers should assess the importance of certifications in their applications and negotiate based on quality needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and production capabilities of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge more but offer better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and risk. Clarity on these terms can prevent misunderstandings and additional costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the overall value rather than just the upfront cost. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and performance when evaluating suppliers.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, more favorable terms, and improved support. Engage in open communication to foster collaboration.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from several suppliers can provide insights into market pricing and help in negotiations. Be transparent about your needs and leverage competitive offers.
-
Consider Long-term Partnerships: Committing to long-term contracts with suppliers can secure better pricing and reliability. Look for suppliers willing to invest in your success.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for face gears can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier factors. The information provided should serve as a guideline, and buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage directly with suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing face gears With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Face Gears for B2B Buyers
When evaluating mechanical solutions for power transmission, particularly in precision applications, face gears present unique advantages. However, there are alternative solutions available that may better suit specific operational needs or constraints. This section compares face gears to bevel gears and worm gears, two widely used alternatives in various industries.
| Comparison Aspect | Face Gears | Bevel Gears | Worm Gears |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate power transmission; ideal for low to medium loads | High torque transmission; suitable for heavy loads | Excellent torque output; high gear reduction ratio |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing costs due to complexity | Moderate; generally lower than face gears | Generally cost-effective for low-speed applications |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise machining; complex setup | Easier to implement; standard designs available | Simple to install; fewer components involved |
| Maintenance | Moderate; requires alignment checks | Low; durable and low wear | Moderate; potential for wear on worm gear teeth |
| Best Use Case | Precision applications with limited space | Heavy machinery and automotive | Applications needing high torque and low speed |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Bevel Gears
Bevel gears are commonly used in right-angle drive applications. They excel in high-torque scenarios, making them suitable for heavy machinery and automotive systems. Their standardized designs facilitate ease of implementation and maintenance, often leading to lower overall costs. However, they require precise alignment to ensure optimal performance, and in some cases, their size may limit their use in compact applications.
Worm Gears
Worm gears offer a unique solution for applications requiring significant torque and a high gear reduction ratio. They are particularly effective in situations where space is limited. Their simple design leads to easier installation compared to face gears, making them a popular choice in conveyor systems and other machinery. However, they may suffer from higher wear rates due to friction between the worm and the gear, necessitating regular maintenance and lubrication.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Gear Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate gear solution involves a careful assessment of performance requirements, cost constraints, and ease of implementation. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific application context is crucial—whether prioritizing high torque, compact design, or cost-effectiveness. Analyzing the operational environment and load conditions will guide the decision-making process, ensuring that the chosen solution aligns with both technical specifications and budgetary considerations. Ultimately, engaging with suppliers and leveraging their expertise can further refine the selection process, leading to an optimal mechanical solution tailored to your unique needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for face gears
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Face Gears?
Understanding the technical properties of face gears is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Face gears are typically made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or plastic. The choice of material directly affects the gear’s strength, weight, and cost. High-grade steel, for instance, offers superior strength and durability, making it suitable for high-load applications. Selecting the right material ensures that the gear can withstand operational demands without premature failure.
2. Tooth Profile and Geometry
The geometry of the teeth—such as pressure angle, tooth height, and width—plays a vital role in how face gears mesh with their mating pinions. A properly designed tooth profile reduces wear and improves efficiency by ensuring optimal contact between gears. For buyers, understanding these parameters can help in selecting gears that minimize noise and maximize performance in their specific applications.
3. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in the dimensions of the gear teeth. Tight tolerances are essential for precision applications, as they ensure proper meshing and reduce the likelihood of mechanical failure. In industries where accuracy is paramount, such as aerospace or automotive, specifying the correct tolerance levels can significantly impact overall equipment reliability.
4. Load Capacity
The load capacity indicates the maximum load a face gear can handle without risk of failure. This property is especially critical in high-torque applications. Buyers should assess the load requirements of their specific applications to ensure the selected gears can operate safely and efficiently under expected conditions.
5. Surface Finish
The surface finish of face gears affects friction, wear resistance, and noise levels. A smoother finish generally leads to lower friction and longer service life. Buyers should consider surface treatment options, such as hardening or coating, to enhance the gear’s performance in demanding environments.
6. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, can significantly enhance the mechanical properties of face gears. This treatment increases hardness and wear resistance, making the gears suitable for more demanding applications. Understanding the heat treatment processes used can guide buyers in selecting gears that will perform reliably over time.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Face Gears?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for B2B buyers to navigate negotiations and procurement effectively. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of face gears, purchasing from an OEM ensures that you receive components specifically designed to meet the original specifications of your machinery.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest order that a supplier is willing to accept. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for small businesses or projects with limited requirements.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specific products, including face gears. It typically outlines the technical specifications and quantities needed, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, risks, and delivery timelines, which is vital for international transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from placing an order to receiving the goods. For face gears, understanding lead times can help buyers plan their production schedules and manage inventory levels effectively.
6. Custom Gears
Custom gears are designed and manufactured to meet specific requirements outside standard offerings. Buyers often opt for custom gears to ensure compatibility with unique applications, which can be critical in specialized industries.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the face gear market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the face gears Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Face Gears Sector?
The global face gears market is experiencing a renaissance, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and an increasing demand for precision engineering across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy. Key trends shaping this market include the adoption of advanced machining techniques like grinding and additive manufacturing, which enhance the performance and efficiency of face gears. Additionally, the trend towards miniaturization in machinery is prompting manufacturers to explore face gears as viable alternatives to traditional bevel gears, due to their compact design and ability to handle complex motion transfer.
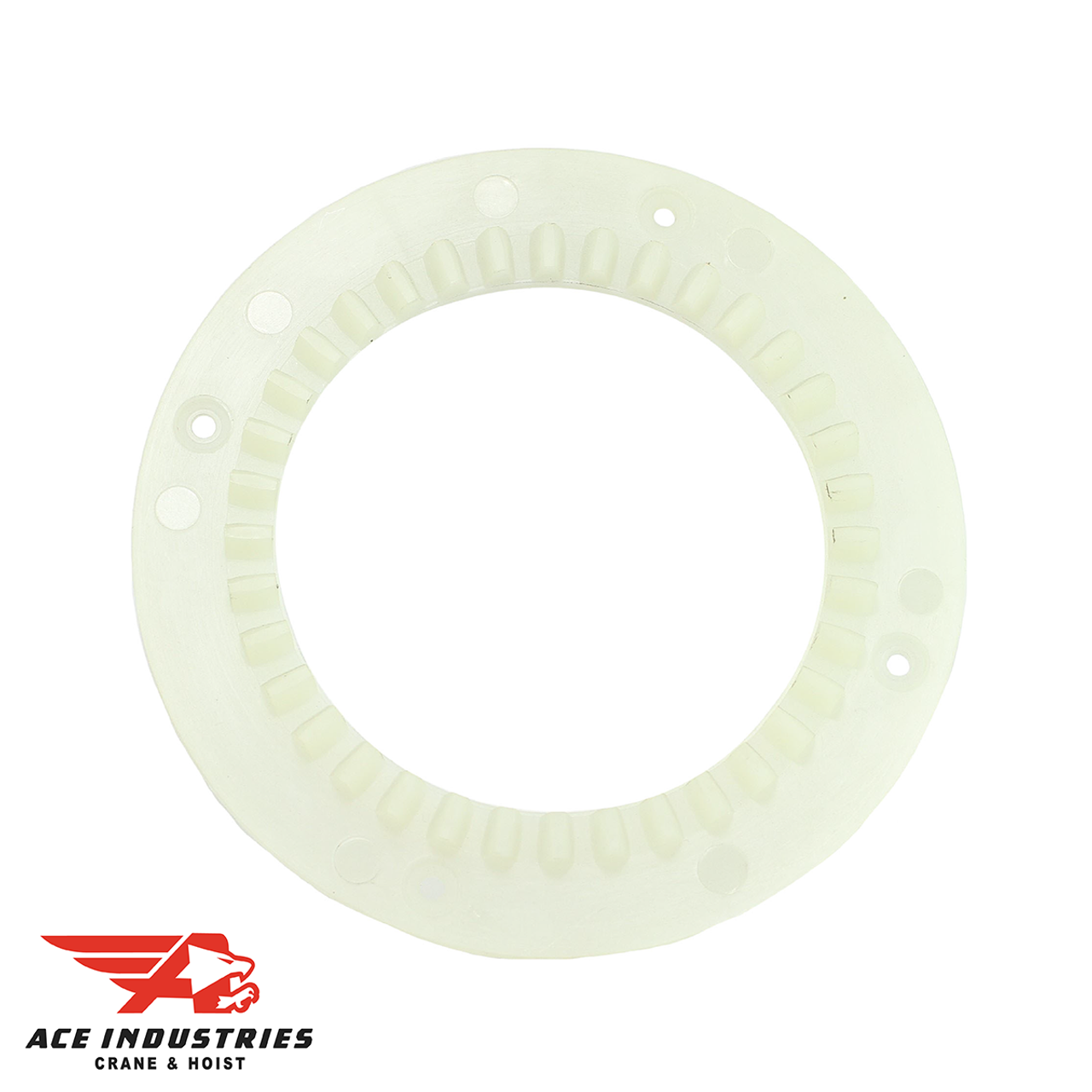

Illustrative image related to face gears
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer customized solutions tailored to specific applications. This demand has catalyzed a shift towards more collaborative sourcing strategies, where manufacturers engage closely with clients to develop bespoke face gear solutions that meet unique operational requirements. Buyers are also placing a premium on suppliers who can demonstrate robust technical expertise and offer comprehensive support throughout the product lifecycle, from design to implementation.
Furthermore, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is revolutionizing the face gears sector. Automation, data analytics, and IoT capabilities are enabling manufacturers to optimize production processes, reduce lead times, and enhance product quality. As a result, B2B buyers can expect more reliable and efficient supply chains, which are crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in their respective markets.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Buyers of Face Gears?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the manufacturing landscape, significantly impacting the sourcing strategies of B2B buyers in the face gears sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting businesses to seek suppliers committed to sustainable practices. This includes the use of renewable energy sources in production, waste minimization techniques, and the adoption of circular economy principles, where materials are reused and recycled.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with buyers increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains for compliance with labor standards and environmental regulations. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Africa and South America, where ethical considerations can influence purchasing decisions significantly. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract international buyers.
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials in the production of face gears, such as biodegradable lubricants and recyclable composites, is on the rise. Buyers who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing can not only enhance their corporate reputation but also align with the growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products. This strategic focus can lead to long-term partnerships with suppliers who share similar values, fostering innovation and ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent regulations.
What is the Historical Context of Face Gears in B2B Applications?
The history of face gears dates back to ancient civilizations, with early implementations observed in Chinese wagons and Roman water mills. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that significant advancements in manufacturing techniques and theoretical understanding of gear geometry spurred renewed interest in face gears. The development of involute face gears and enhanced machining methods allowed for greater precision and performance, positioning face gears as viable alternatives to traditional bevel and worm gears.
In the late 20th century, companies like Crown Gears in the Netherlands began innovating with face gear technology, leading to applications in specialized fields such as aerospace and robotics. The evolution of manufacturing capabilities, particularly in grinding and simulation technologies, has made it feasible to produce high-performance face gears that can withstand the rigors of modern engineering demands. Today, face gears are recognized for their unique advantages, such as axial freedom of pinion positioning, making them an attractive option for precision-driven industries.
The historical context of face gears not only highlights their engineering significance but also underscores the ongoing need for innovation in manufacturing processes to meet the evolving demands of B2B buyers across various sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of face gears
-
How do I select the right face gear for my application?
Selecting the right face gear involves understanding your specific application requirements, including load capacity, speed, and alignment. Face gears are particularly beneficial when you need axial freedom of the pinion, which allows for easier assembly and adjustment. Evaluate the torque requirements and the environment in which the gears will operate. Collaborating with a knowledgeable supplier can provide insights into material selection and design, ensuring that the face gear meets operational demands effectively. -
What are the advantages of using face gears over other gear types?
Face gears offer several advantages, including the ability to handle misalignment and reduced axial load requirements compared to bevel gears. They are easier to manufacture and can be customized to fit specific designs, making them suitable for precision applications. Additionally, face gears can provide a quieter operation due to their unique design, which is beneficial in industries where noise reduction is critical. Their versatility in design can also lead to compact systems, optimizing space in machinery. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for face gears?
The minimum order quantity for face gears can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and customization requirements. Typically, MOQs can range from a few pieces for standard designs to several hundred for custom specifications. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Many manufacturers are willing to accommodate smaller orders, especially if you are a new client or testing a new application. -
How can I ensure the quality of face gears from international suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing face gears internationally, conduct thorough supplier vetting. Look for suppliers with certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Request samples to assess material quality and machining precision. Additionally, establish clear quality assurance processes, including inspection reports and compliance with international standards, to mitigate risks associated with overseas procurement. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing face gears?
Payment terms for face gears typically depend on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, such as net 30 or net 60 days, especially for established clients. It’s essential to discuss and agree upon payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing face gears?
When importing face gears, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Depending on your location, sea freight may be more economical, while air freight offers faster delivery. Ensure you understand the import duties and taxes applicable in your country. Collaborating with a logistics partner familiar with international trade can streamline the process and help navigate any potential challenges. -
Can face gears be customized to fit specific applications?
Yes, face gears can be highly customized to meet specific application requirements. Manufacturers can adjust parameters such as tooth geometry, material selection, and dimensions to align with your operational needs. Customization is particularly useful for specialized machinery or unique operational environments. Engaging in early discussions with your supplier about your needs can lead to optimal designs that enhance performance and longevity. -
What industries commonly use face gears, and what are their applications?
Face gears are utilized across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, robotics, and machine tools. In aerospace, they are often used in helicopter gearboxes where axial freedom is crucial. The automotive industry employs face gears in power steering systems and electric vehicle drivetrains. Robotics applications benefit from the precision and compactness of face gears, enabling efficient motion transfer. Understanding your industry’s specific applications can guide you in sourcing the most suitable face gear solutions.
Top 6 Face Gears Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. KHK Gears – Face Gear Solutions
Domain: khkgears.net
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Face gear is a type of gear where a spur or helical gear acts as a pinion, meshing with a disk-shaped gear that has teeth cut on its end face. The axes of the face gear and the mating gear can be either intersecting or nonparallel and nonintersecting. Face gears are relatively easy to manufacture and can replace bevel or hypoid gears, but they are not suitable for transmitting large amounts of pow…
2. McMaster – Face Gears
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Face Gears, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Gear Technology – Face Gears
Domain: geartechnology.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Face gears are a distinct type of gear used in angle drives, alongside bevel and worm drives. They have historical usage dating back centuries, with significant development in the mid-20th century, particularly in the U.S., Netherlands, and Japan. The main advantage of face gears over bevel gears is the axial freedom of the pinion, allowing for easier installation and operation in precision techno…
4. Gear Solutions – CONIFACE Process
Domain: gearsolutions.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: The CONIFACE process utilizes standard cutting tools and bevel gear machines, resulting in short cutting times comparable to straight CONIFLEX bevel gears. Face gears are defined as plane ring gears with a face angle of 90° that mate with spur or helical pinions, transmitting motion and torque between two shafts intersecting at 90°. The manufacturing complexity arises from the unique generating ge…
5. Yale – Face Gear (9574)
Domain: aceindustries.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Face Gear (9574)”, “SKU”: “Y641012300”, “price”: “$23.85”, “shipping_info”: “Free domestic shipping for online orders over $500 (some restrictions apply)”, “brand”: “Yale”, “description”: “Replacement part for hoists, specifically designed for Yale equipment.”, “availability”: “In stock”, “company_info”: “Established in 1932, Ace Industries has supplied replacement, maintenance, …
6. CNC Cookbook – Face/Hirth Gears
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Face/Hirth gears are used for locking tool turrets and 4th axes in CNC machining. They provide high rigidity and work by meshing two face gears using axial movement. The process involves unlocking the gears, rotating to an approximate position, and then locking the gears to achieve precise positioning. These gears are advantageous for indexing work to fixed positions, commonly used to lock lathe t…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for face gears
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Face Gears?
In summary, strategic sourcing of face gears presents a unique opportunity for businesses operating across various sectors, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With their distinct design advantages—such as axial freedom of the pinion and reduced need for precise axial positioning—face gears can enhance the efficiency of machinery while accommodating specific operational requirements. As the demand for lightweight and high-performance gear systems grows, investing in advanced manufacturing techniques and quality sourcing will be critical.
For international B2B buyers, the importance of establishing relationships with reliable suppliers cannot be overstated. Engaging with manufacturers who specialize in face gears can lead to improved product quality and innovation, ultimately driving competitive advantage in your market. It is essential to assess suppliers not just on cost but also on their ability to provide tailored solutions that meet your unique specifications and operational challenges.
As you look to the future, consider how strategic sourcing of face gears can transform your operations. By prioritizing partnerships that emphasize quality, technology, and customization, you can position your business for long-term success in a rapidly evolving landscape. Take action today to explore the potential of face gears in your applications, and leverage this technology to propel your business forward.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.