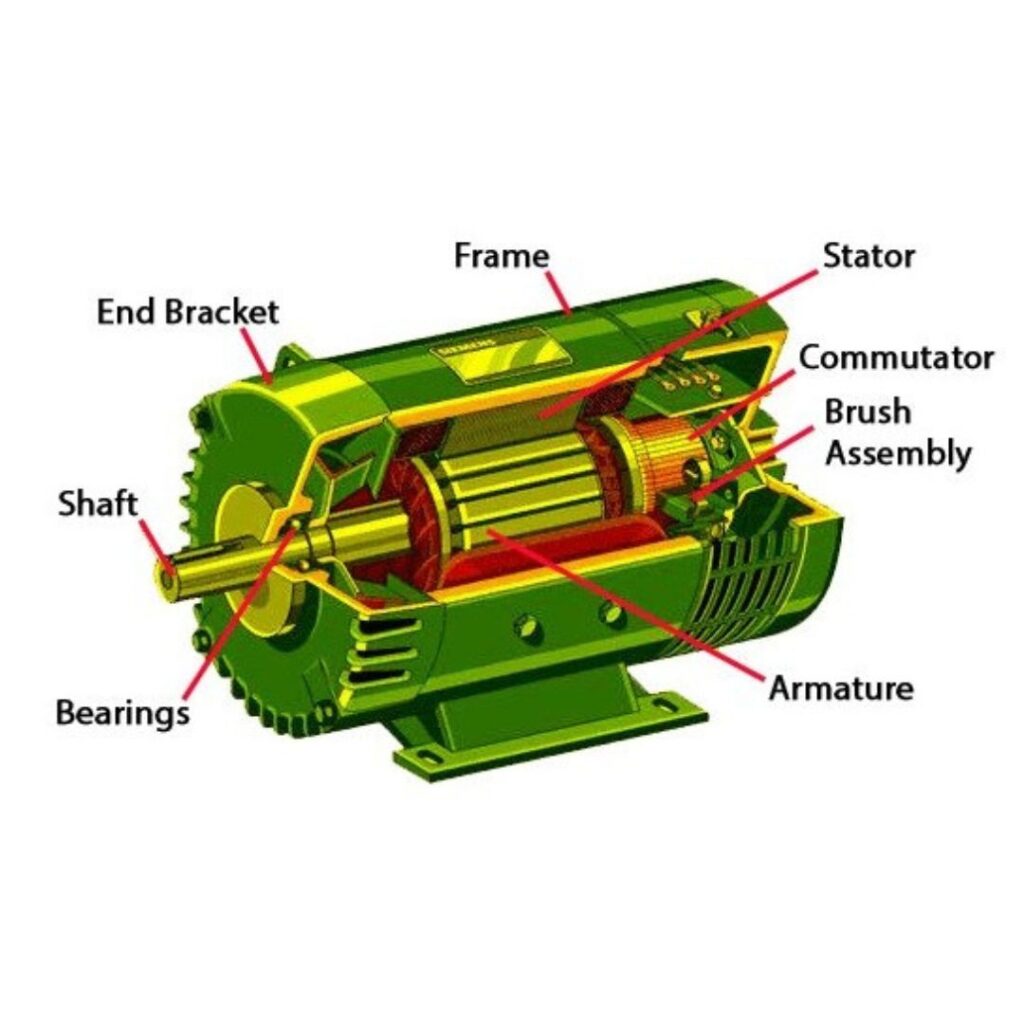
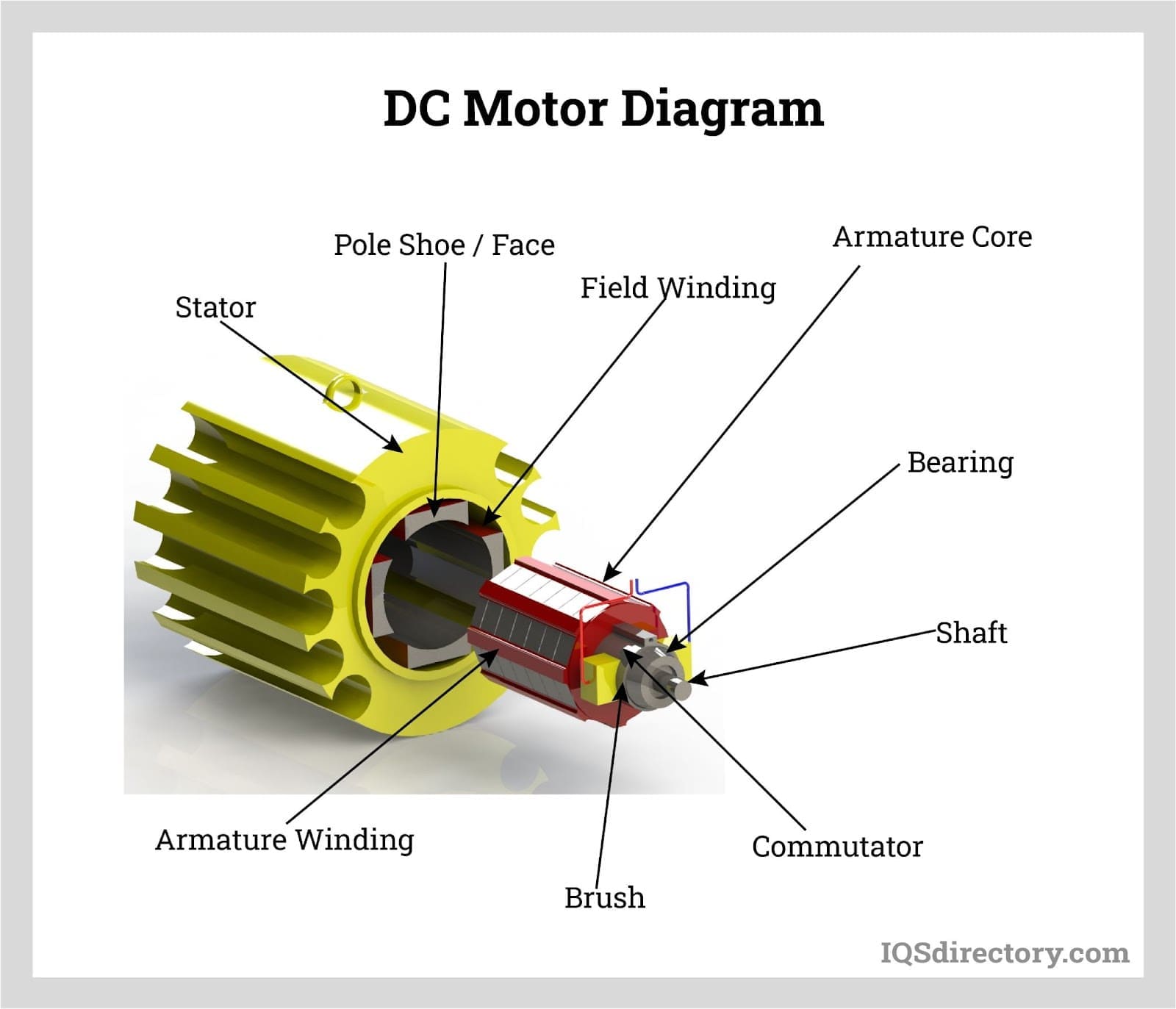
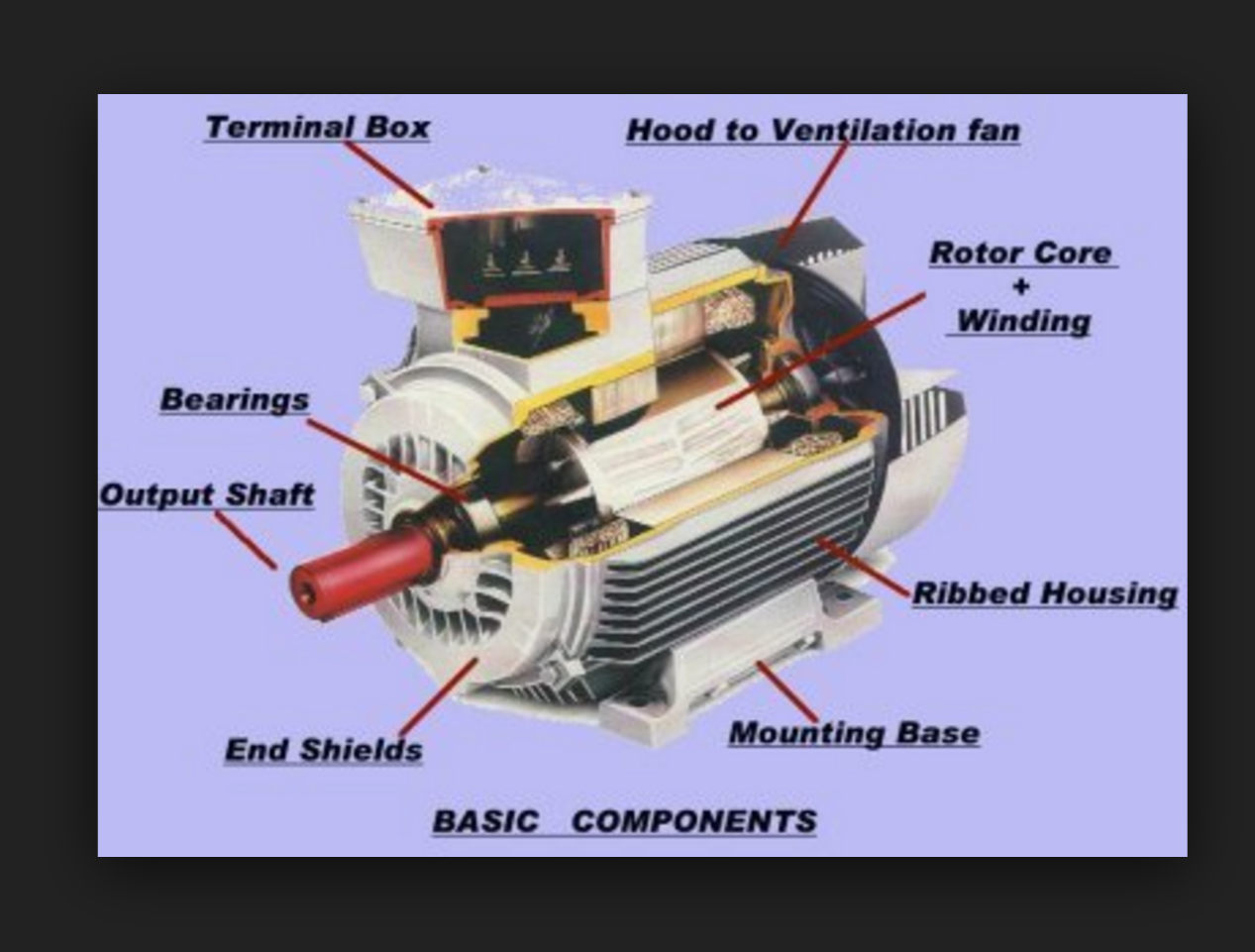
Everything You Need to Know About Electric Motor Components Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric motor components
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global commerce, sourcing high-quality electric motor components presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets like Brazil, Nigeria, and across the Middle East and Europe. As industries increasingly rely on electric motors for automation and energy efficiency, understanding the intricacies of component selection—ranging from stators and rotors to bearings and lead wires—becomes crucial. This guide delves into the various types of electric motor components, their applications in diverse sectors, and the critical factors influencing procurement decisions.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, international buyers will gain insights into evaluating suppliers, assessing costs, and identifying the best practices for integrating these components into their operations. By addressing key considerations such as performance specifications, material quality, and manufacturing standards, this guide empowers B2B purchasers to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce long-term costs.
Whether you are a manufacturer seeking to optimize production or an engineer tasked with ensuring reliability, navigating the complexities of the electric motor components market will be simplified with the actionable insights provided here. This guide aims to bridge the knowledge gap, enabling stakeholders from Africa to Europe to effectively source and leverage electric motor components for competitive advantage in their respective markets.
Understanding electric motor components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squirrel-Cage Rotor | Simple construction, robust design, and high efficiency. | HVAC systems, industrial fans, pumps. | Pros: Low maintenance, cost-effective. Cons: Limited speed control. |
| Permanent Magnet Stator | Utilizes permanent magnets for enhanced efficiency. | Electric vehicles, robotics, consumer electronics. | Pros: High torque, compact design. Cons: Higher initial cost, sensitivity to temperature. |
| Induction Stator | Relies on electromagnetic induction for operation. | Manufacturing machinery, compressors. | Pros: Durable, widely used. Cons: Lower efficiency compared to PM stators. |
| Brushless DC Motor | Features electronic commutation, reducing wear. | Electric bikes, drones, automation systems. | Pros: Longer lifespan, quieter operation. Cons: More complex control systems. |
| Laminated Core Rotor | Made from thin sheets to reduce energy losses. | Generators, transformers, high-speed applications. | Pros: Improved efficiency, reduced eddy current losses. Cons: Higher manufacturing costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Squirrel-Cage Rotors?
Squirrel-cage rotors are characterized by their simple construction, which consists of conductive bars shorted at both ends. This design enhances their efficiency and robustness, making them ideal for applications such as HVAC systems and industrial fans. For B2B buyers, the low maintenance requirements and cost-effectiveness are significant advantages. However, the limited speed control may be a drawback in applications requiring precise motor speed adjustments.
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
Why Choose Permanent Magnet Stators for Your Applications?
Permanent magnet stators leverage permanent magnets to create a magnetic field, resulting in high efficiency and compact designs. They are particularly suitable for electric vehicles, robotics, and consumer electronics. For B2B purchasers, the high torque output is a major benefit, enabling powerful performance in smaller packages. Nevertheless, the higher initial cost and sensitivity to temperature fluctuations should be carefully considered when evaluating long-term investments.
How Do Induction Stators Operate and Where Are They Used?
Induction stators operate based on electromagnetic induction principles, making them a reliable choice for many industrial applications, including manufacturing machinery and compressors. Their durability and widespread use are attractive to B2B buyers seeking proven technology. While they tend to be less efficient than permanent magnet alternatives, their robustness and lower cost make them a solid option for various applications.
What Are the Advantages of Brushless DC Motors?
Brushless DC motors utilize electronic commutation instead of mechanical brushes, leading to reduced wear and longer lifespan. These motors are ideal for applications such as electric bikes, drones, and automation systems. B2B buyers appreciate their quieter operation and extended service life, although the complexity of control systems can be a drawback for some applications, requiring more specialized knowledge for implementation.
Why Are Laminated Core Rotors Important in Electric Motors?
Laminated core rotors are constructed from thin sheets of metal to minimize energy losses due to eddy currents, enhancing overall efficiency. They are commonly used in generators, transformers, and high-speed applications. B2B buyers benefit from the improved performance and energy savings these rotors provide. However, the higher manufacturing costs associated with laminated cores can be a consideration when budgeting for motor components.
Key Industrial Applications of electric motor components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electric Motor Components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automation Equipment | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Focus on durability and compatibility with existing systems |
| Agriculture | Electric Pumps for Irrigation | Enhances crop yield through efficient water management | Ensure energy efficiency and suitability for local conditions |
| Transportation | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Reduces operational costs and carbon footprint | Evaluate battery compatibility and motor performance under load |
| HVAC Systems | Electric Motors for Compressors and Fans | Improves energy efficiency and indoor air quality | Consider noise levels and energy ratings for compliance |
| Mining and Construction | Heavy-Duty Electric Motors for Machinery | Increases productivity and equipment reliability | Assess ruggedness and resistance to harsh environmental conditions |
How Are Electric Motor Components Utilized in Manufacturing Automation?
In manufacturing, electric motor components are integral to automation equipment, driving conveyors, robotic arms, and assembly lines. By utilizing efficient stators and rotors, businesses can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce labor costs. For international buyers, especially in developing regions like Africa and South America, sourcing motors that meet local voltage and frequency standards is crucial. Additionally, durability in high-cycle operations is essential to minimize downtime and maintenance costs.
What Role Do Electric Motor Components Play in Agriculture?
Electric motor components are vital in agricultural applications, particularly in electric pumps used for irrigation. These motors help optimize water usage, directly impacting crop yields and resource management. For B2B buyers in regions like Brazil and Nigeria, it’s important to consider the motor’s energy efficiency to align with local sustainability goals. Additionally, motors must be robust enough to handle varying water conditions and ensure longevity in outdoor environments.
How Are Electric Motor Components Transforming Transportation?
In the transportation sector, electric motor components are crucial for electric vehicles (EVs), where they convert electrical energy into mechanical energy for propulsion. This application not only reduces operational costs but also lowers carbon emissions, aligning with global sustainability trends. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing motors that offer high torque and efficiency to enhance vehicle performance, while also ensuring compatibility with existing battery technologies.
What Are the Applications of Electric Motor Components in HVAC Systems?
Electric motors in HVAC systems power compressors and fans, playing a key role in regulating indoor climates and improving air quality. By employing high-efficiency motors, businesses can achieve significant energy savings, leading to lower operational costs. For international B2B buyers, especially in Europe, understanding local regulations regarding energy efficiency ratings is essential. Additionally, noise levels must be considered to ensure compliance with residential standards.
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
How Are Electric Motor Components Critical in Mining and Construction?
In the mining and construction industries, heavy-duty electric motors are essential for powering machinery such as drills, excavators, and conveyors. These motors enhance productivity and ensure reliable operation under demanding conditions. Buyers in these sectors must prioritize sourcing motors that are rugged and capable of withstanding harsh environments, including dust and moisture. Additionally, evaluating the motors’ thermal management capabilities is vital for maintaining performance during extended operation periods.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric motor components’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Component Compatibility and Sourcing
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges when it comes to sourcing electric motor components that are compatible with their existing systems. This issue is particularly prevalent in regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains can be less robust. Buyers often encounter situations where they purchase components that do not fit their specific motor designs or fail to meet performance standards. This can lead to significant downtime, increased costs due to returns or replacements, and frustration over the inability to find reliable suppliers.
The Solution: To overcome compatibility and sourcing issues, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their existing motor systems before making purchases. This includes documenting specifications such as dimensions, material requirements, and performance characteristics of current components. Engaging with multiple suppliers to obtain detailed product catalogs and compatibility charts can also be beneficial. Additionally, buyers should consider establishing partnerships with manufacturers that offer customization services, ensuring components are tailored to their exact needs. Utilizing digital platforms to connect with manufacturers can streamline this process, allowing for better communication and faster resolution of compatibility concerns.
Scenario 2: Addressing Quality and Reliability Concerns
The Problem: Quality and reliability of electric motor components are paramount for businesses that rely on consistent performance. However, many buyers struggle with the inconsistency of product quality, especially when sourcing from multiple vendors. This issue can lead to premature failures, increased maintenance costs, and compromised operational efficiency. In regions with limited access to high-quality components, this pain point becomes even more pronounced as buyers may feel compelled to settle for subpar options.
The Solution: To mitigate quality concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing components from reputable manufacturers known for their rigorous quality assurance processes. Implementing a vendor evaluation system that includes criteria such as certifications (e.g., ISO standards), customer reviews, and historical performance data can help in selecting reliable suppliers. Furthermore, buyers can request samples or conduct small-scale trials before committing to larger orders. Establishing long-term relationships with a select few trusted suppliers can also enhance quality assurance, as these vendors are more likely to prioritize the needs of repeat customers. Additionally, investing in training for maintenance personnel can ensure that components are installed and maintained correctly, further enhancing reliability.
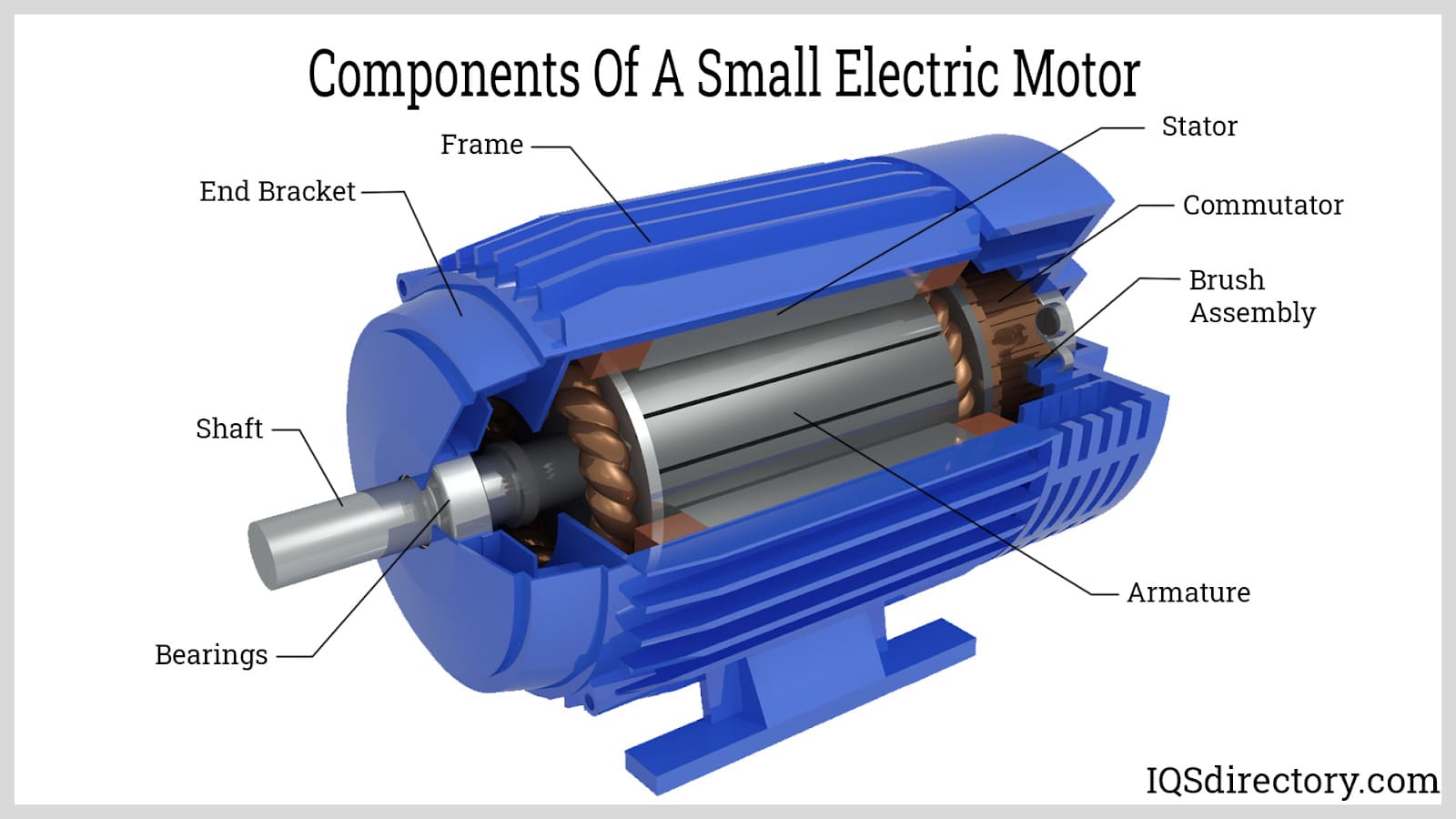
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
Scenario 3: Navigating Complex Technical Specifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often find themselves overwhelmed by the complex technical specifications associated with electric motor components. This is particularly true for businesses in emerging markets where technical knowledge may be limited. The difficulty in understanding specifications such as torque ratings, winding types, and thermal limits can lead to poor purchasing decisions, resulting in inefficient motors that do not meet operational demands.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of technical specifications, buyers should invest in training and development for their purchasing and engineering teams. This can include workshops, webinars, or online courses focusing on electric motor technology and component specifications. Additionally, creating a resource library that includes technical documentation, product datasheets, and comparison charts can provide quick reference points when evaluating different components. Engaging with technical sales representatives from suppliers can also provide valuable insights, as they can explain specifications in practical terms and offer tailored recommendations based on specific applications. Finally, leveraging software tools that facilitate the modeling and simulation of motor performance can help buyers visualize how different components will perform in their systems, leading to more informed purchasing decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric motor components
What are the Key Materials Used in Electric Motor Components?
When selecting materials for electric motor components, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials: copper, silicon steel, aluminum, and permanent magnets.
How Does Copper Influence Electric Motor Performance?
Copper is the primary conductor used in electric motor windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and can withstand significant thermal stress, making it suitable for high-performance applications. Its corrosion resistance is moderate, but protective coatings can enhance longevity.
Pros: Copper’s high conductivity allows for efficient energy transfer, reducing energy losses and improving overall motor efficiency. It is also readily available and widely accepted in the industry.
Cons: The main drawback is its cost, which is higher than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper is heavier, which can impact the weight of the motor assembly.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with various media, including oils and coolants used in motor applications. However, care should be taken regarding the potential for galvanic corrosion when paired with dissimilar metals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable suppliers who meet these standards is essential to avoid quality issues.
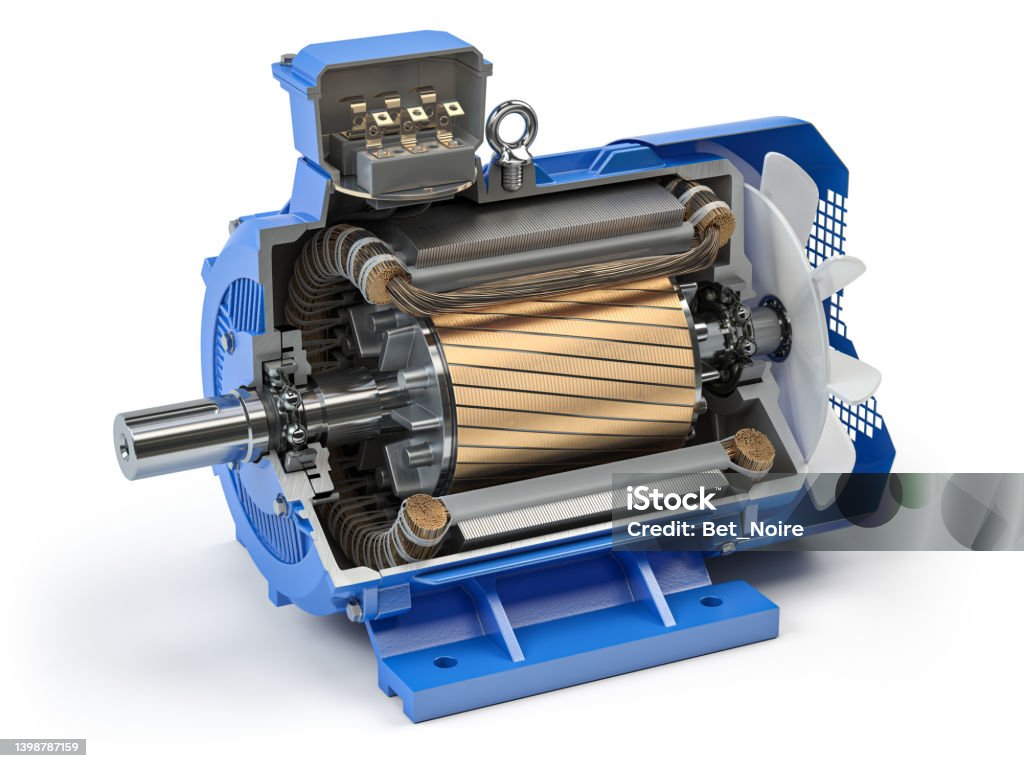
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
What Role Does Silicon Steel Play in Electric Motor Efficiency?
Silicon steel is commonly used for the cores of stators and rotors due to its magnetic properties. It has a high permeability and low core loss, which enhances the efficiency of electric motors. Silicon steel typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 500°F (260°C).
Pros: The primary advantage of silicon steel is its ability to reduce energy losses in the magnetic circuit, leading to improved motor efficiency. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other magnetic materials.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex, requiring precise lamination to minimize eddy current losses. Additionally, silicon steel is susceptible to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings.
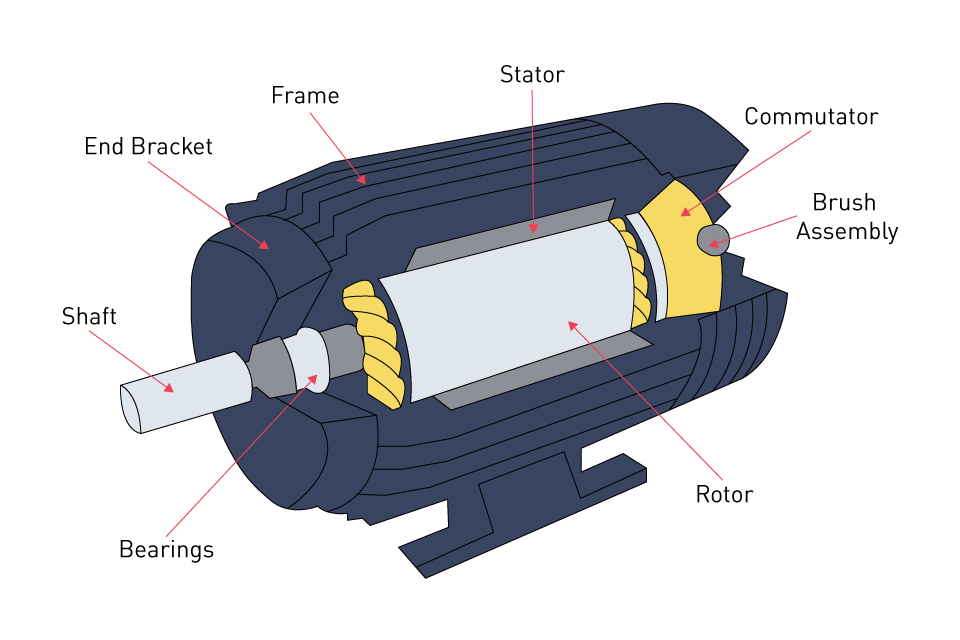
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
Impact on Application: Silicon steel is suitable for applications involving alternating current (AC) motors, where its magnetic properties can be fully utilized.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN EN 10106 is important for ensuring quality. Buyers in Europe may prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate adherence to these standards.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Electric Motor Components?
Aluminum is often used as an alternative to copper in windings and for structural components due to its lightweight and good conductivity. It has a lower melting point (1,221°F or 660°C) compared to copper, which can limit its use in high-temperature applications.
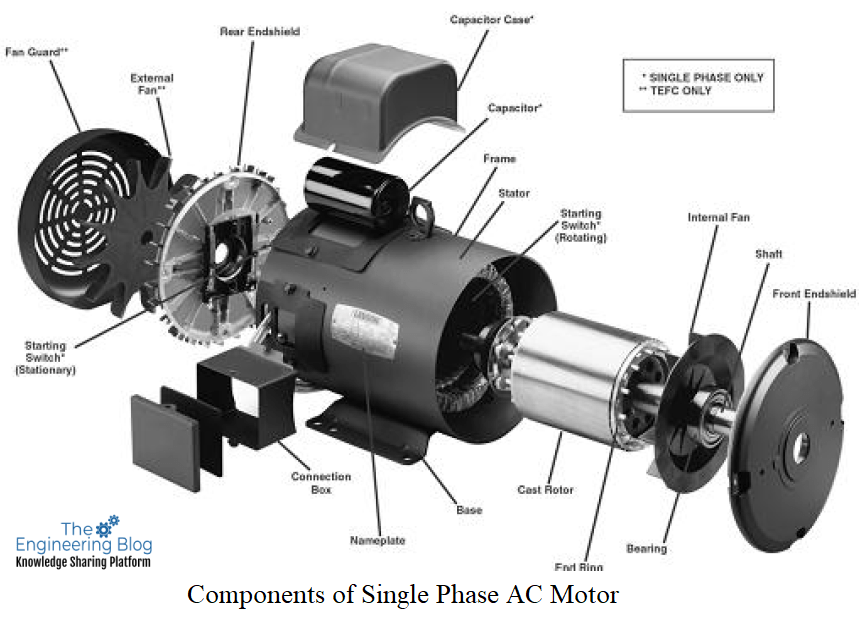
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and weight, making it an attractive option for applications where weight savings are critical. It is also resistant to corrosion, especially when anodized.
Cons: Aluminum has lower electrical conductivity than copper, which can lead to higher resistive losses. Additionally, its mechanical strength is lower, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media but may require careful consideration regarding thermal management due to its lower thermal conductivity.
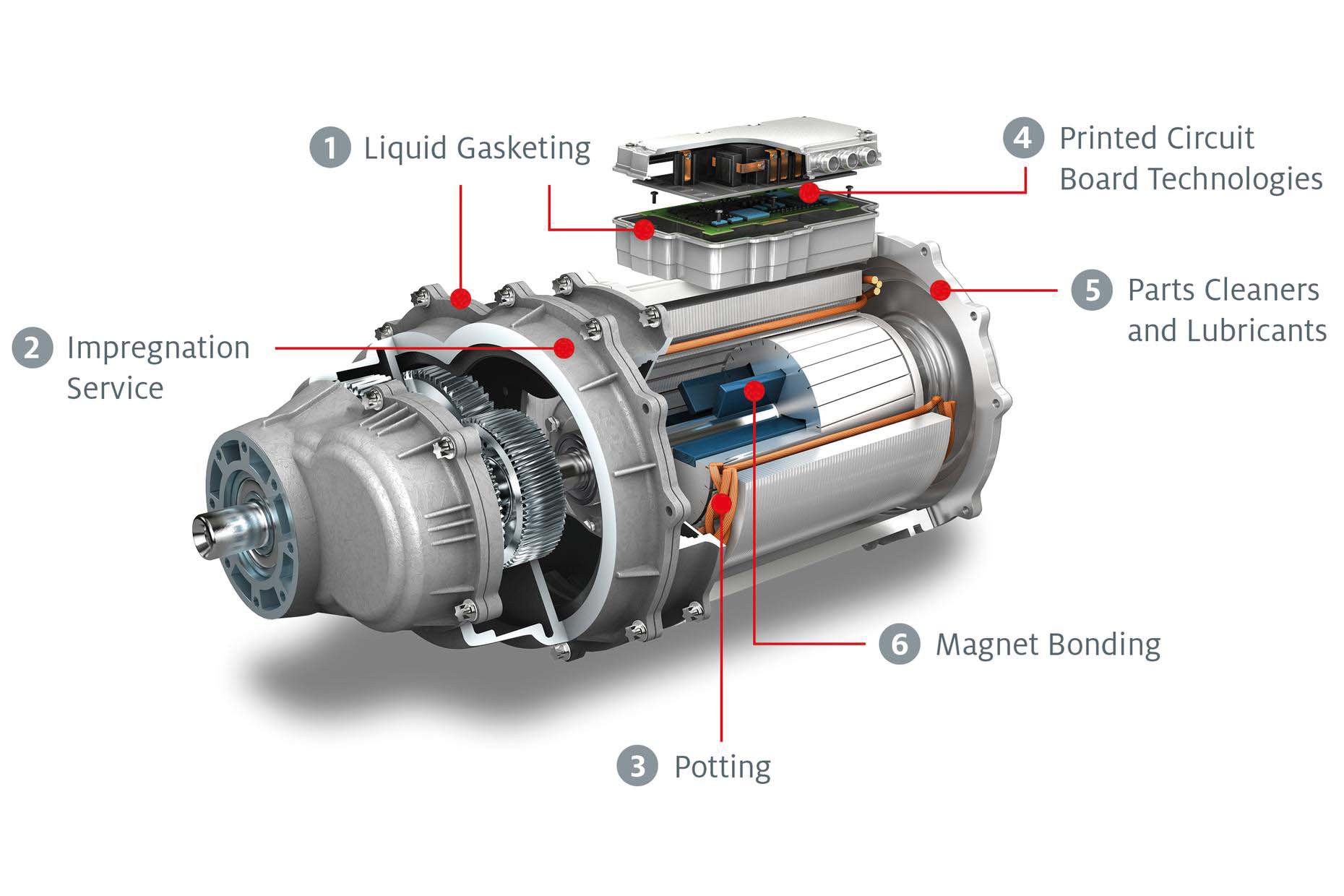
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum products. In regions like the Middle East, understanding local sourcing capabilities is crucial for maintaining quality.
What is the Importance of Permanent Magnets in Electric Motors?
Permanent magnets are critical for specific types of motors, such as brushless DC motors. They generate a consistent magnetic field, enhancing efficiency and performance. Common materials include neodymium and ferrite, with neodymium offering superior magnetic strength.
Pros: Permanent magnets improve motor efficiency and reduce the size and weight of the motor. They are also reliable over time, requiring minimal maintenance.
Cons: The main limitation is the cost, particularly for high-performance neodymium magnets, which can be significantly more expensive than other materials. Additionally, they can be sensitive to temperature changes, affecting performance.
Impact on Application: Permanent magnets are essential for applications requiring high torque and compact designs, such as electric vehicles and robotics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ISO 9001 for quality management is critical. Buyers should also consider the geopolitical factors affecting the supply chain of rare earth materials, particularly in regions like Africa.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Motor Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric motor components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | High conductivity and thermal resistance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Silicon Steel | Stator and rotor cores | Reduces energy losses | Susceptible to corrosion, complex mfg | Medium |
| Aluminum | Structural components and windings | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity and strength | Low |
| Permanent Magnets | Brushless DC motors | High efficiency and compact design | High cost and temperature sensitivity | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric motor components
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Motor Components?
The manufacturing of electric motor components involves several critical stages to ensure precision, efficiency, and quality. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Selected and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This stage involves selecting the appropriate materials, such as silicon steel for cores, copper for windings, and various insulating materials. Suppliers often source these materials from reputable vendors to ensure quality. Once selected, materials undergo processes like cutting, shaping, and annealing to achieve desired specifications. For instance, steel sheets are cut into specific dimensions and laminated to improve magnetic performance.
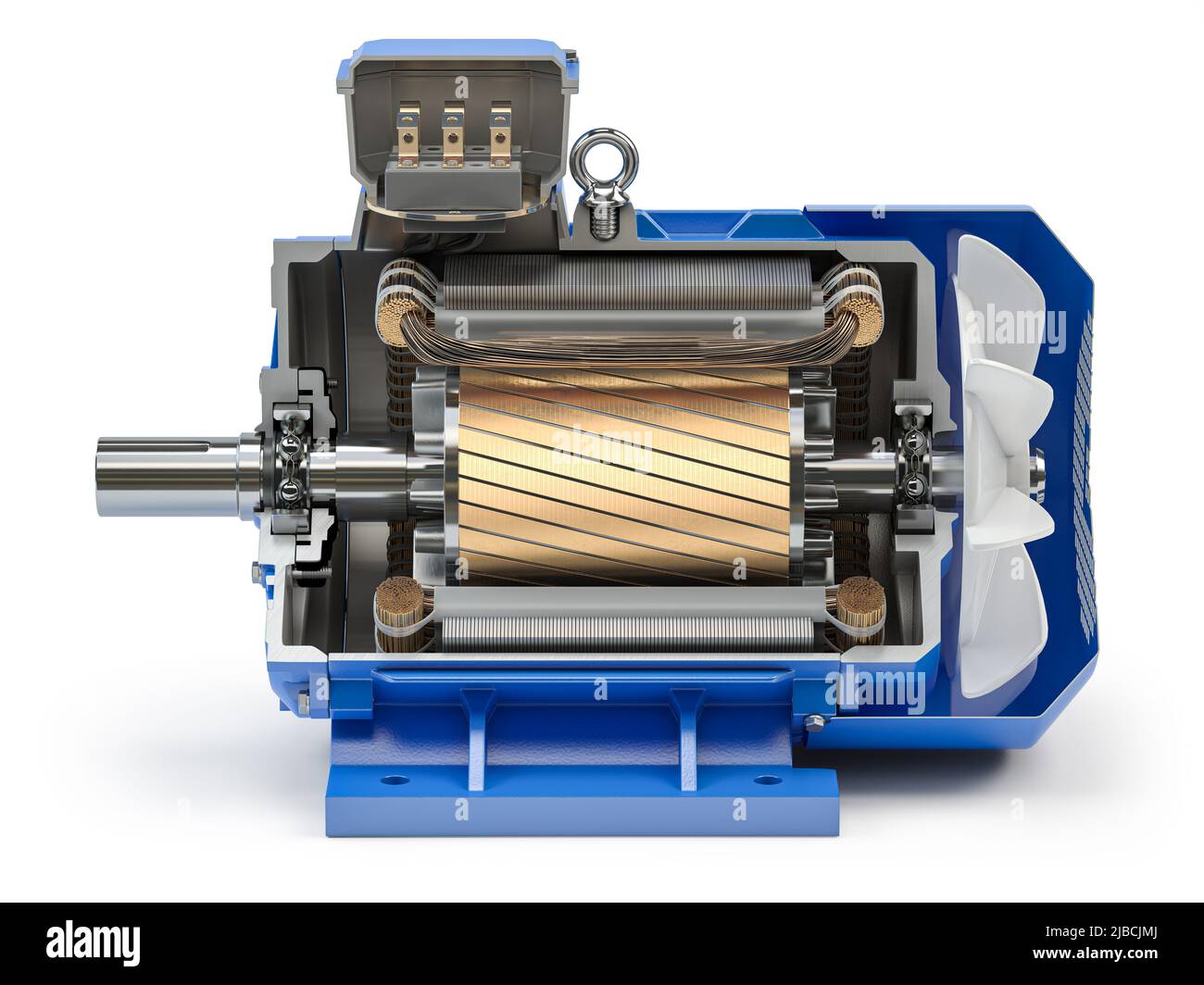
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
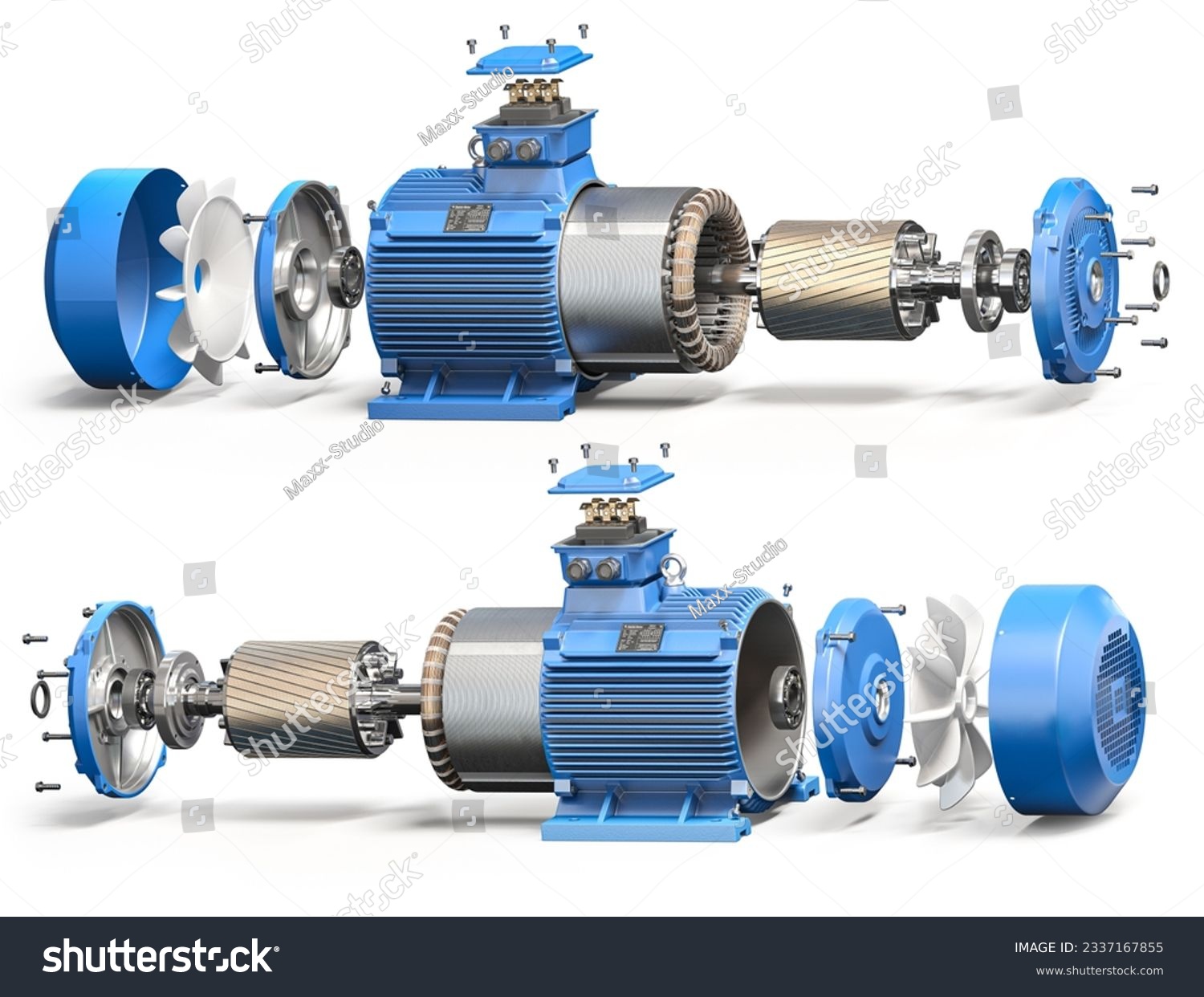
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Motor Components?
Forming is the stage where raw materials are transformed into usable motor components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and machining are commonly employed. Stamping is frequently used for producing stator and rotor laminations, as it allows for high-volume production with consistent accuracy. For components requiring intricate designs or tighter tolerances, machining methods such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling are utilized. This precision is particularly vital for components like bearings and end plates, which must fit perfectly to minimize friction and wear.
Assembly: How Are Different Components Brought Together?
The assembly phase is where the individual components come together to form the complete motor unit. This process typically involves several steps:
-
Winding the Stator and Rotor: Copper wires are wound around the stator and rotor cores to create electromagnetic fields. The winding process is often automated to ensure uniformity and precision.
-
Press-Fitting and Joining: Components such as bearings, end plates, and lead wires are press-fitted or joined using techniques like welding or adhesive bonding. Each connection point is critical for the overall performance of the motor.
-
Final Assembly: The final assembly includes integrating all components, followed by a thorough inspection to ensure everything is correctly positioned and secured.
What Are the Finishing Processes Applied to Electric Motor Components?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic quality of motor components. Common techniques include:
-
Coating: Components are often coated with protective layers to prevent corrosion and wear. This is especially important for motors operating in harsh environments, such as those found in industrial applications.
-
Balancing: Rotors are dynamically balanced to minimize vibrations during operation. This process is crucial for ensuring the longevity of the motor and reducing noise levels.
-
Testing and Quality Checks: Before leaving the manufacturing facility, components undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specified performance standards.
What Quality Control Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of manufacturing electric motor components. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with relevant international and industry-specific standards to ensure they are sourcing from compliant suppliers.
International Standards: How Do ISO Certifications Affect Quality?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Suppliers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to consistently providing products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. This certification is particularly important for international buyers, as it assures them of the supplier’s adherence to quality protocols.
Industry-Specific Standards: What Additional Certifications Are Necessary?
In addition to ISO certifications, various industry-specific standards may apply, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, API standards for motors used in the oil and gas industry, and UL certification for electrical safety. Understanding these certifications can help buyers ensure that the motor components they procure are compliant with local regulations and safety standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
To maintain high-quality standards, manufacturers implement several checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection ensures that raw materials meet specified criteria before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checkpoints allow for real-time monitoring of processes and component specifications. This helps in identifying defects early in the production cycle.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the entire motor undergoes final inspections and testing to verify that it meets performance specifications before shipping.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Component Quality?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to validate the quality of electric motor components, including:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes insulation resistance testing, which checks for electrical leaks, and continuity testing to ensure proper connections.
-
Mechanical Testing: Components are subjected to stress tests to evaluate their mechanical integrity. This may involve vibration tests or thermal cycling to simulate real-world operating conditions.
-
Performance Testing: Motors are tested for efficiency, speed, and torque to ensure they meet the specified performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should take the following actions:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can assess a supplier’s adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This can be done internally or by hiring third-party inspection agencies.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and production capabilities.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating quality control can be complex. Buyers should consider:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the local manufacturing culture can help in establishing effective communication and expectations regarding quality standards.
-
Logistical Challenges: International shipping and customs can introduce risks to product quality. It’s advisable to establish clear agreements regarding packaging and handling during transit.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding electric motor components. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with local laws and standards to avoid issues at customs or during usage.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms in place, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric motor components, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric motor components’
Introduction
Sourcing electric motor components can be a complex process, especially for international B2B buyers. This guide serves as a practical checklist to streamline your procurement process, ensuring you acquire high-quality components that meet your technical requirements and operational standards.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical specifications is the first crucial step in sourcing electric motor components. These specifications will guide your supplier selection process and ensure that the components meet your operational needs. Consider factors such as power requirements, size constraints, and material preferences, which can significantly impact performance and compatibility.
2. Research Market Trends and Standards
Understanding the current market trends and industry standards is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Research the latest advancements in electric motor technology, such as energy efficiency and sustainability practices, to stay competitive. Additionally, familiarize yourself with relevant international standards (e.g., IEC, ISO) to ensure compliance and quality.

Illustrative image related to electric motor components
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conducting thorough evaluations is imperative. Assess suppliers based on their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar industries or regions to gauge their reliability and performance history.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that suppliers hold necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards.
- Assess Technical Capabilities: Determine if the supplier has the technical expertise to meet your specific requirements.
4. Request Samples and Prototypes
Obtaining samples or prototypes is vital for assessing the quality and compatibility of the components with your existing systems. This step allows you to conduct hands-on testing to evaluate performance, durability, and fit. Make sure to provide feedback and communicate any necessary adjustments to the supplier.
5. Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified suitable suppliers and evaluated their components, it’s time to negotiate pricing and terms. Discuss bulk purchasing discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules to ensure a mutually beneficial agreement. Be clear about your expectations to avoid misunderstandings later on.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Assess not only the upfront costs but also the long-term operational costs associated with the components, such as maintenance and energy efficiency.
6. Verify Supply Chain Logistics
Understanding the supply chain logistics is critical to ensure timely delivery and inventory management. Inquire about the supplier’s lead times, shipping methods, and return policies. Make sure they can accommodate your delivery schedules and have contingency plans for potential disruptions.
7. Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Building a long-term partnership with your suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into future product developments. Maintain open communication and provide feedback on their products and services. This relationship can enhance your procurement process and ensure consistent quality in the components you source.
By following this checklist, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing electric motor components and make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric motor components Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Motor Components?
When sourcing electric motor components, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. For instance, copper is commonly used for windings due to its excellent conductivity, but it is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, the use of high-quality steel for cores can increase costs, but it also enhances performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the location of manufacturing. Regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but this may come at the expense of quality or lead times. Automation in manufacturing can also affect labor costs, potentially lowering them while increasing initial investment in technology.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, allowing suppliers to offer better pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment, especially for specialized components. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of such investments against initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to costs. Certifications like ISO can enhance credibility but may also increase the price.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer and the chosen shipping method. International buyers should account for tariffs and taxes that may apply during import.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their pricing, which can vary depending on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electric Motor Component Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric motor components, and understanding these can aid in negotiations.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can lead to significant savings. Higher volume orders often attract bulk pricing discounts, making it economically viable for businesses to stock larger inventories.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom components require additional design and manufacturing efforts, which can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials impacts pricing. Premium materials can enhance performance but also come at a higher cost.
-
Quality/Certifications: Components that meet higher quality standards or certifications generally command higher prices. Buyers should evaluate whether these standards align with their performance requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and reliability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipment can affect overall costs. Understanding the responsibilities of the buyer and seller in logistics can help manage unexpected expenses.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Electric Motor Components?
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: When negotiating, consider consolidating orders to meet MOQs, which can reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Instead of solely comparing initial prices, consider the long-term savings associated with quality, reliability, and efficiency of the components.
-
Research Market Prices: Familiarize yourself with market trends and average pricing to strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms over time.
-
Be Open to Alternative Materials or Designs: Discussing alternative options can lead to cost savings without compromising performance.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers may reduce shipping costs and lead times, providing a competitive advantage.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Sourcing Electric Motor Components?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific pricing nuances:

Illustrative image related to electric motor components
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact pricing, so it’s advisable to lock in prices when possible.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Different countries have varying import regulations and taxes that can significantly affect total costs.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local business practices and negotiation styles can facilitate smoother transactions.
-
Logistical Challenges: Be mindful of potential delays and additional costs related to international shipping.
In conclusion, navigating the cost and pricing landscape for electric motor components requires a thorough understanding of various cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies. By leveraging this knowledge, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that optimize both cost and performance.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric motor components With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Electric Motor Components
In the evolving landscape of industrial solutions, electric motor components stand as a staple for converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. However, as technology advances, several alternative solutions have emerged that can achieve similar objectives. This analysis aims to compare electric motor components with viable alternatives, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Motor Components | Hydraulic Systems | Pneumatic Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency (up to 95%) and precise control of speed and torque. | Excellent for high force applications but less precise in speed control. | Good for quick operations; however, less efficient in energy usage. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, but low operational costs due to energy efficiency. | Higher initial costs due to installation and equipment. | Generally lower upfront costs but higher long-term operational costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor for installation and maintenance. | Complex installation; requires hydraulic expertise. | Easier to implement but may require frequent maintenance. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks on windings and insulation; low downtime when maintained. | Regular fluid checks and potential leaks; maintenance can be costly. | Requires regular maintenance of compressors and hoses; can lead to downtime. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for applications needing precision and energy efficiency, such as in manufacturing and robotics. | Best for heavy machinery and lifting applications in construction and mining. | Suitable for packaging, assembly lines, and applications needing quick bursts of power. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydraulic Systems?
Hydraulic systems utilize fluid pressure to generate movement and are often favored in applications requiring high force, such as construction equipment. The primary advantage is their ability to exert significant force with relatively compact components. However, they have a higher initial setup cost and require expertise for installation and maintenance. Additionally, hydraulic systems can suffer from leaks and fluid degradation over time, leading to increased operational costs and potential downtime.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Pneumatic Systems?
Pneumatic systems harness compressed air to create motion, making them ideal for applications that require rapid actuation, such as in packaging and assembly lines. They are generally easier to implement than hydraulic systems and can be less expensive upfront. However, they tend to have lower energy efficiency and higher operational costs due to the energy required to compress air. Furthermore, pneumatic systems may require frequent maintenance of compressors and hoses, which can lead to operational downtime.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between electric motor components, hydraulic systems, and pneumatic systems, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Electric motors offer superior efficiency and precision, making them suitable for high-tech applications. Hydraulic systems excel in heavy-duty applications, while pneumatic systems are beneficial for quick, repetitive tasks. By evaluating these factors, businesses can choose the solution that best aligns with their operational goals and financial considerations, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in their applications.
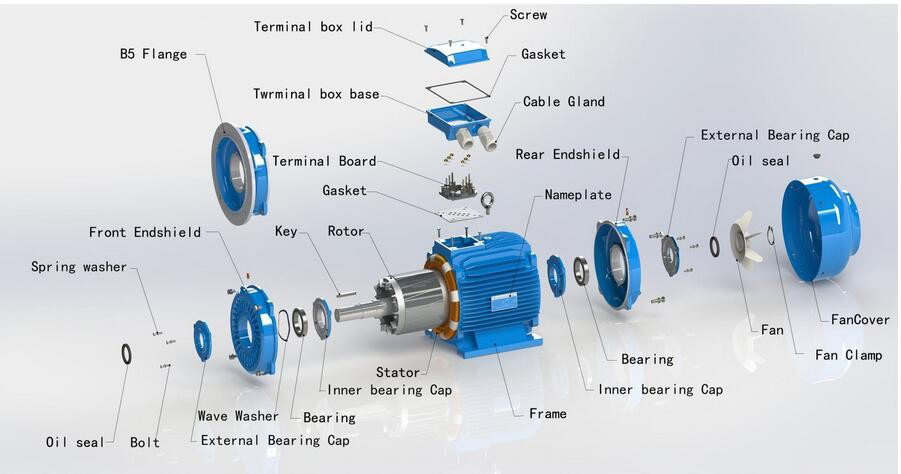
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric motor components
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Motor Components?
Understanding the technical properties of electric motor components is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when making procurement decisions. Here are several essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of metal used in the construction of motor components, such as copper for windings or silicon steel for cores. The grade affects conductivity, magnetic properties, and overall durability. High-grade materials enhance performance and longevity, which is vital for reducing operational costs in industrial applications.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance denotes the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In electric motors, precise tolerances ensure that components fit together correctly, minimizing wear and maximizing efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications is critical to ensure compatibility and reliability in motor assembly, especially when sourcing parts from different manufacturers.
3. Thermal Rating
Thermal rating indicates the maximum temperature at which a component can operate effectively. Components like windings and insulation materials must withstand high temperatures without degrading. Buyers should prioritize components with appropriate thermal ratings to avoid failures and ensure optimal performance, particularly in high-demand environments.
4. Insulation Class
Insulation class categorizes the thermal properties of the insulation materials used in motors. Classes range from A (maximum temperature of 105°C) to H (maximum temperature of 180°C). Selecting the right insulation class is essential for ensuring safety and preventing electrical failures, which can lead to costly downtime in operations.
5. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency rating measures how effectively an electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Higher efficiency ratings (e.g., IE3 or IE4) indicate lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs. For international buyers, understanding efficiency ratings is important for compliance with energy regulations and for maximizing return on investment.
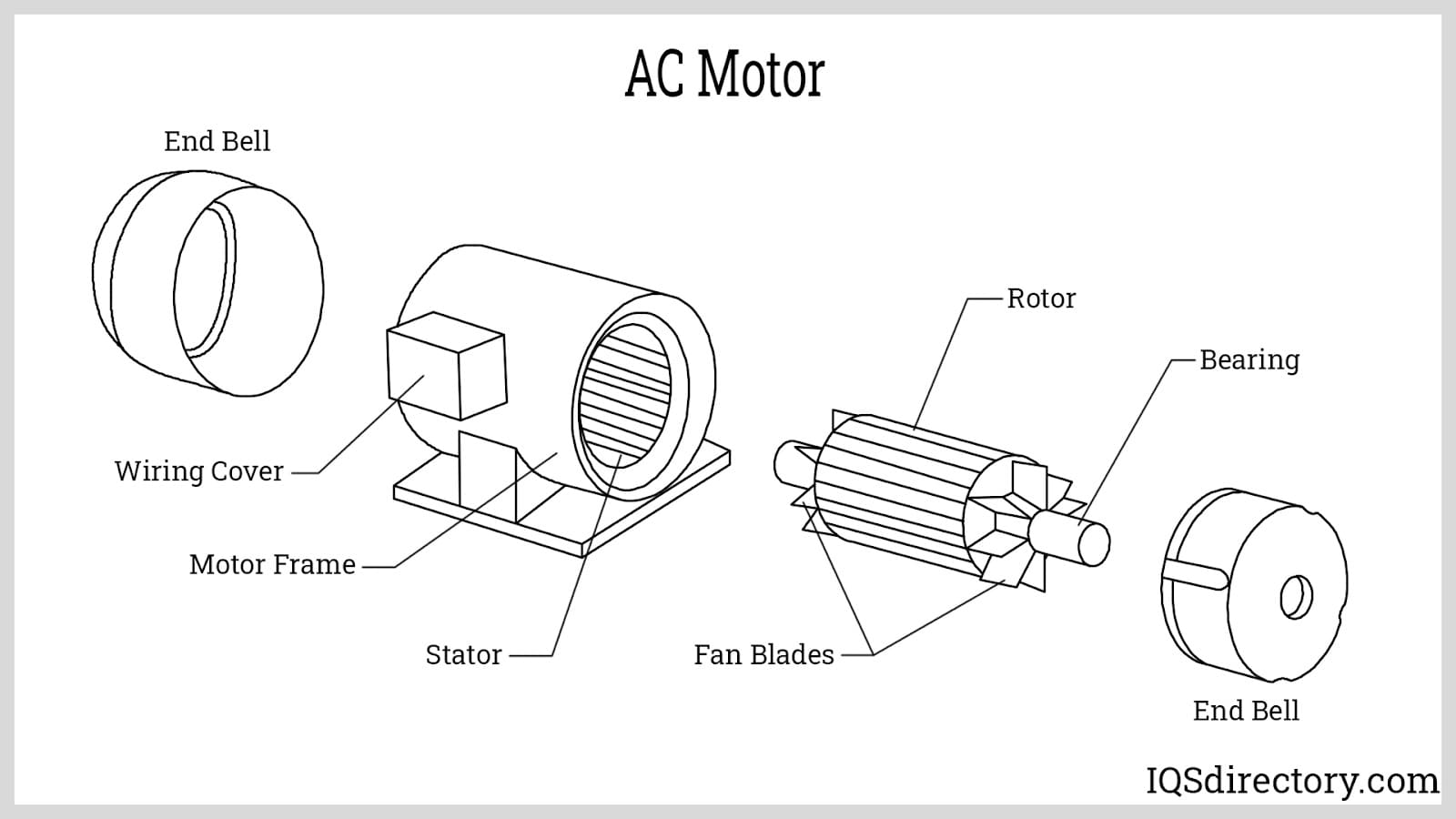
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Electric Motor Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the electric motor sector. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape is crucial for B2B buyers as it helps identify reliable suppliers and ensures the quality of components sourced for assembly.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to assess whether a supplier’s terms align with their purchasing needs, particularly when dealing with international suppliers where shipping costs can be significant.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. This process is critical for B2B buyers to gather competitive pricing and assess supplier capabilities, helping them make informed purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smooth logistics and compliance with international trade regulations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. For electric motor components, understanding lead times is critical for supply chain management, allowing buyers to plan production schedules and meet customer demands effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, optimize supplier relationships, and ensure the successful integration of electric motor components into their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric motor components Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing Electric Motor Components?
The electric motor components market is experiencing dynamic growth, driven primarily by the global shift towards renewable energy and electrification of transportation. International B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focusing on sourcing high-efficiency electric motors to meet the growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and sustainable industrial applications. A significant trend is the advancement in manufacturing technologies such as additive manufacturing and automation, which enhance production efficiency and reduce lead times.

Illustrative image related to electric motor components
Additionally, the integration of smart technology in motor components is gaining traction. Innovations in IoT and AI are enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which can significantly lower operational costs. For buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, where infrastructure development is crucial, sourcing components that support these technologies can lead to enhanced performance and reliability in their applications.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape is shifting towards stricter energy efficiency standards. This is prompting manufacturers to invest in R&D for next-generation components that not only meet these regulations but also offer enhanced performance. Understanding these trends allows international buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both market demands and regulatory requirements.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Motor Components Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the electric motor components sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Companies are increasingly expected to adopt ethical sourcing practices that prioritize the use of sustainable materials and minimize ecological footprints.
Buyers should look for suppliers who are committed to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other green certifications that validate the use of eco-friendly materials. For example, sourcing components made from recycled metals or those that utilize bio-based insulation materials can significantly reduce the overall environmental impact.
Furthermore, the shift towards electric vehicles and renewable energy systems necessitates the use of components that support energy efficiency. By focusing on suppliers who prioritize sustainability, international buyers not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile but also align with consumer demand for greener products. This approach can ultimately lead to cost savings and improved brand loyalty in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
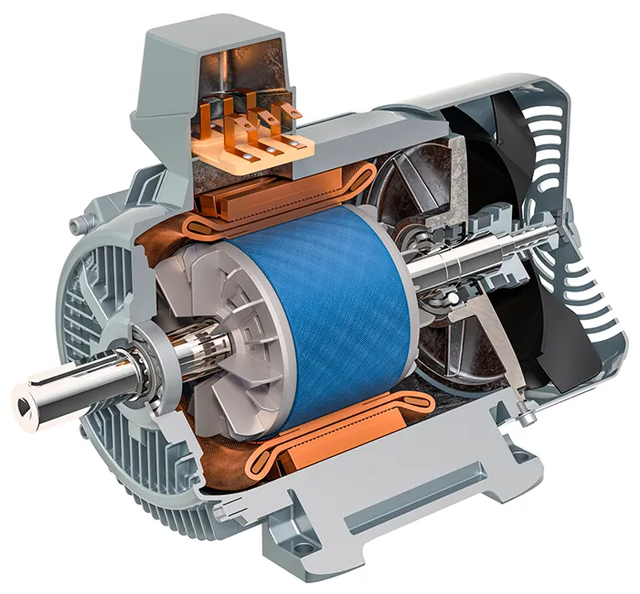
Illustrative image related to electric motor components
How Has the Electric Motor Components Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the electric motor components sector has been marked by significant technological advancements and changes in market demands. Initially, electric motors were primarily used in industrial applications, with limited focus on efficiency and sustainability. However, as global energy concerns emerged and electrification trends gained momentum, manufacturers began to innovate, leading to the development of more efficient motors and components.
The introduction of permanent magnet technology and advancements in materials science have drastically improved the performance of motor components. Moreover, the rise of digital technologies has transformed how electric motors are designed and manufactured, allowing for greater customization and efficiency.
Today, the market is not only shaped by technological innovations but also by changing consumer preferences and regulatory pressures towards sustainability. This evolution presents B2B buyers with new opportunities to source high-performance electric motor components that meet modern standards of efficiency and environmental responsibility. Understanding this historical context can help buyers appreciate the complexity of sourcing decisions in the current landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric motor components
-
How do I solve compatibility issues when sourcing electric motor components?
Compatibility issues often arise due to variations in specifications, materials, and manufacturing processes. To mitigate this, ensure that you have a clear understanding of your motor’s requirements, including voltage, frequency, and torque specifications. Collaborate closely with suppliers to discuss your needs and verify that the components they offer meet industry standards. Request samples for testing in your applications before making bulk purchases to confirm compatibility. -
What is the best type of rotor for high-efficiency electric motors?
For high-efficiency electric motors, a permanent magnet rotor is often the best choice. This type of rotor provides superior torque production and energy efficiency by utilizing permanent magnets to create a strong magnetic field. When sourcing, consider factors such as the rotor’s design, material quality, and the specific application it will serve. Discuss your performance goals with suppliers to ensure you select a rotor that aligns with your operational needs. -
How can I vet suppliers for electric motor components effectively?
Vetting suppliers involves thorough research and assessment. Start by checking their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials. Evaluate their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their experience with product reliability and after-sales support. Conducting a factory visit, if feasible, can also provide insight into their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric motor components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric motor components can vary widely based on the supplier and the specific component. Typically, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units for standard components. However, custom components may have higher MOQs due to setup costs. Always communicate your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production scale and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric motor components internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly based on the supplier and the buyer’s relationship. Common terms include a 30% upfront payment with the balance due before shipment, or net 30 days post-delivery. For new suppliers, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risk. Always clarify terms in your contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure both parties are aligned. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in electric motor components?
When sourcing electric motor components, prioritize suppliers with robust quality assurance (QA) measures. Look for manufacturers that implement ISO standards and have quality control processes in place, such as incoming material inspections, in-process monitoring, and final product testing. Request documentation of QA processes and product certifications to ensure that components meet specified performance and safety standards. -
How do logistics and shipping impact sourcing electric motor components?
Logistics and shipping can significantly affect lead times and overall sourcing costs. Evaluate suppliers based on their shipping capabilities, delivery timelines, and costs associated with international shipping. Consider factors such as customs clearance, tariffs, and local regulations in your target market. Collaborating with suppliers who have experience in international logistics can help streamline the process and minimize delays. -
What customization options are available for electric motor components?
Many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific application requirements. Customization may include adjustments in size, materials, winding configurations, or component designs. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and performance criteria to ensure the final product meets your needs. Be aware that customized components may have longer lead times and higher costs, so plan your sourcing strategy accordingly.
Top 10 Electric Motor Components Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Nidec – Motor Components
Domain: nidec.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
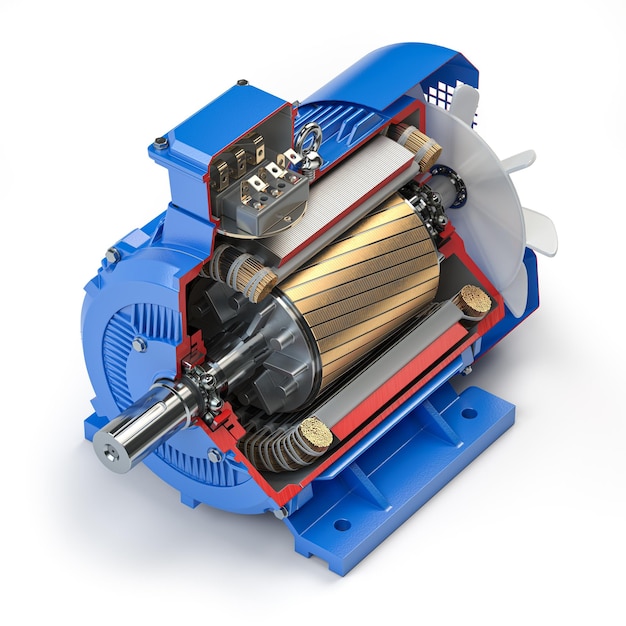
Introduction: Motor components are classified into five main portions: (1) Rotor – Rotating part; (2) Bearing – Supporting part of the rotating shaft of the rotor; (3) Stator – Part generating force used to rotate the rotor; (4) Bracket or end plate – Bearing supporting part integral for the stator; (5) Lead wire – Wire connected to the drive circuit supplying power to the motor or wire connected to the power s…
2. Thomson Lamination Company – High-Precision Motor Laminations
Domain: tlclam.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Thomson Lamination Company specializes in producing high-precision, thin metal sheets called laminations for electric motors. They manufacture both rotor and stator laminations to meet application requirements, offering standard and custom motor laminations. The company works with high-conductivity metals and adheres to tight tolerances, accommodating production runs from prototype to high-volume….
3. Fukuta – High-Performance Motors
Domain: fukuta-motor.com.tw
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Fukuta provides a versatile range of high-performance motors tailored to meet various industry needs: IEC Motors: Available in both cast iron and aluminum housings, designed for a wide range of applications including woodworking machines, ventilation equipment, pumps, compressors, textile machinery, agricultural machinery, food processing equipment, rubber and plastics, elevators, cranes, and trea…
4. Electric Motor Repairs – Key Components
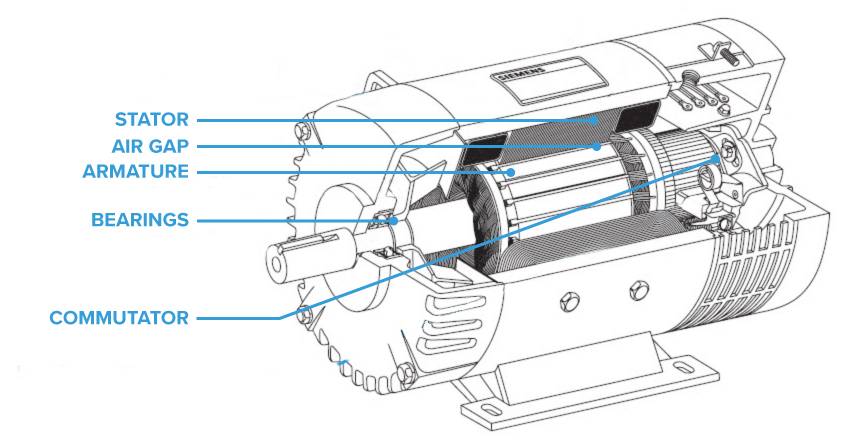
Domain: electricmotorrepairsales.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Electric motors operate by turning electrical energy into mechanical energy. Key components include: 1. Rotor – the main moving part that turns a shaft to direct power. 2. Stator – generates the magnetic field necessary for propulsion, typically made with metal linings. 3. Air Gap – located between the stator and rotor, ensuring efficient magnetic field interaction. 4. Commutator – reverses curren…
5. IQS Directory – Electric Motors
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy by generating a magnetic field through electric current in wire coils, creating torque on the motor shaft. They can be powered by DC sources (like batteries) or AC sources (like power grids). Types include DC or AC motors, brushless or brushed, and can operate on single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase power. They are used in industr…
6. Byju’s – Electric Motor Components
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: An electric motor is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Key components include: 1. Power Supply – usually DC for simple motors. 2. Field Magnet – can be a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. 3. Armature or Rotor – helps the motor to run. 4. Commutator – the rotating interface of the armature coil with a stationary circuit. 5. Brushes – conduct current between stationary wi…
7. ISL Products – Electromagnetic Components
Domain: shop.islproducts.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, ISL Products – Electromagnetic Components, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. KMM Components – Key Offerings
Domain: kmmp.de
Introduction: Components for electric motors include die-cast aluminum and cast iron parts, stator-rotor packs, ventilation fans, fan cowls, machine tool pumps, and various accessories. Key offerings include:
1. **Die-cast Aluminum Components**:
– Stator housings (IEC sizes 56 to 180)
– End shields, flange bearing shields, terminal boxes
– Available unmachined or standard machined in smaller batches
…
9. LN Electric – Electric Motors
Domain: lnelectric.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Electric motors consist of three basic parts: a stator, a commutator, and a rotor. The stator remains stationary and typically contains a row of magnets within a drum-like casing. The rotor, made of copper wire coiled around a spinning axle, is inserted into the stator. The commutator, a metal ring at the end of the coil, reverses the current between the rotor and the battery to maintain continuou…
10. ScienceDirect – Electric Motors Overview
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Electric motors are electromechanical devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy and vice versa. They are categorized into two major types: DC motors and AC motors, each with several subcategories. Key components of an electric motor include the rotor, stator, bearings, and control electronics, which together influence the motor’s efficiency and performance. Electric motors can …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric motor components
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Electric Motor Components?
In the dynamic landscape of electric motor components, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricate roles of major components—such as stators and rotors—enables procurement professionals to make informed decisions that enhance performance and efficiency. By prioritizing high-quality materials and advanced technologies, businesses can reduce operational costs, minimize downtime, and ensure superior product reliability.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Competitive Advantage?
Investing in strategic sourcing not only fosters partnerships with reputable suppliers but also streamlines supply chains across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging localized knowledge and global best practices, buyers can adapt to market demands and sustainability goals, ultimately positioning themselves for long-term success.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
Looking forward, it is essential for buyers to stay informed about emerging trends and technologies in electric motor components. By adopting a proactive sourcing strategy, businesses can harness innovation to drive efficiency and sustainability. Engage with suppliers who share your vision for quality and performance, and take the next step in optimizing your supply chain for a more competitive future.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.