Everything You Need to Know About Different Types Of Heaters Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for different types of heaters
In an increasingly interconnected world, sourcing the right heating solutions can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The market for different types of heaters is vast and diverse, encompassing a range of technologies such as forced air systems, radiant heating, and traditional boiler setups. Each type presents unique advantages, costs, and applications that can significantly impact operational efficiency and comfort.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the heating market. We delve into various heater types, discussing their specifications, fuel sources, and suitability for different environments—from residential buildings in Europe to industrial facilities in Saudi Arabia and Brazil. Additionally, we provide actionable insights on supplier vetting, pricing structures, and maintenance considerations, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
By understanding the nuances of each heating solution and its market dynamics, B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the most effective and efficient heating systems for their specific needs. This guide serves as your go-to resource, transforming a potentially overwhelming process into a streamlined approach to finding the perfect heating solution tailored to your operational requirements.
Understanding different types of heaters Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forced Air Heating Systems | Utilizes ducts and a blower to distribute heated air | Warehouses, commercial buildings | Pros: Quick temperature adjustments, high efficiency. Cons: Requires ductwork, can create dry air. |
| In-Floor Radiant Heating | Heats objects directly, often using water or electric | Retail spaces, residential developments | Pros: Even heat distribution, energy-efficient. Cons: Slower to heat, installation can be costly. |
| Traditional Boiler and Radiator | Central boiler system with radiators for heat | Apartment buildings, older commercial | Pros: Less dry air, energy-efficient with modern boilers. Cons: Bulky radiators, limited cooling integration. |
| Hot Water Baseboard Radiator | Low-profile units using hot water for heating | Office spaces, schools | Pros: Efficient heat distribution, quieter operation. Cons: Requires boiler maintenance, space for units. |
| Electric Heaters | Portable units, often plug-in, using electrical energy | Small offices, temporary spaces | Pros: Easy to install and use, no ductwork needed. Cons: Higher operating costs, less efficient for large areas. |
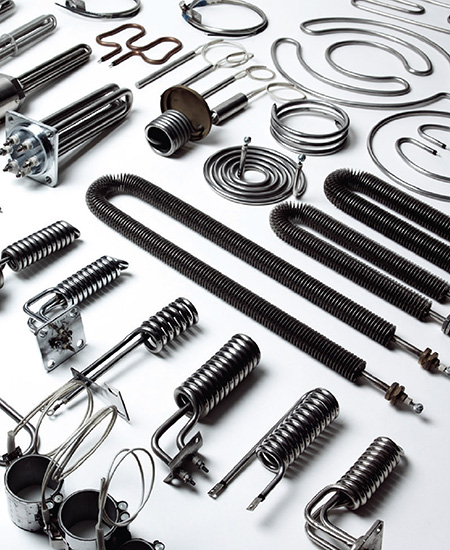
What Are the Key Characteristics of Forced Air Heating Systems?
Forced air heating systems are prevalent in commercial settings due to their ability to quickly adjust temperatures across large spaces. They utilize a furnace connected to a network of ducts, allowing for efficient heating and cooling. B2B buyers should consider the installation costs, which can range from $5,000 to $10,000, and the need for regular maintenance of the ductwork. These systems are ideal for environments requiring rapid temperature changes but may necessitate additional air quality controls to manage dryness.

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
Why Choose In-Floor Radiant Heating for Commercial Spaces?
In-floor radiant heating systems provide a modern approach to heating by warming objects and surfaces rather than just air. This method is particularly suitable for retail spaces and residential developments where comfort and energy efficiency are paramount. While installation costs can be high (between $1,800 and $6,000), the long-term energy savings and consistent heat distribution can justify the investment. Buyers should also consider the difficulty of maintaining hidden piping, which can complicate repairs.
What Makes Traditional Boiler and Radiator Systems Still Relevant?
Despite being an older technology, traditional boiler and radiator systems remain common in apartment buildings and older commercial properties. These systems use a centralized boiler to circulate steam or hot water through radiators, offering a reliable heating solution. While they provide a more humid environment compared to forced air systems, buyers should be aware of the space required for radiators and the potential for aesthetic issues. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure longevity, typically every 10 to 15 years.
How Do Hot Water Baseboard Radiators Function in Office Environments?
Hot water baseboard radiators are a modern evolution of traditional radiator systems, designed to provide efficient heating in office spaces and schools. These low-profile units use a centralized boiler to circulate hot water, facilitating effective heat distribution without the noise of forced air systems. Installation costs range from $450 to $1,200 per unit, making them a cost-effective solution for many businesses. However, buyers must account for the need for boiler maintenance and the physical space these units occupy.
Are Electric Heaters a Practical Option for Temporary Spaces?
Electric heaters offer a flexible and portable heating solution, making them ideal for small offices and temporary spaces. These plug-in units are easy to install and operate, with no need for ductwork or complex installations. However, B2B buyers should consider the higher operating costs associated with electricity compared to other heating methods, particularly in larger areas. While convenient, electric heaters are best suited for supplemental heating rather than primary heating solutions in expansive environments.
Key Industrial Applications of different types of heaters
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of different types of heaters | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Process heating for refining and petrochemical operations | Enhances efficiency and safety in processing units | Compliance with international safety standards |
| Food & Beverage | Industrial ovens and dryers for food processing | Improves product quality and reduces spoilage | Energy efficiency and local regulations on emissions |
| Pharmaceuticals | Controlled heating in drug manufacturing | Ensures product consistency and regulatory compliance | Precision in temperature control and reliability |
| Construction | Temporary heating for curing concrete | Accelerates construction timelines | Portability and adaptability to site conditions |
| Textile Manufacturing | Heat setting and drying processes | Increases production capacity and quality | Material compatibility and energy consumption |
How Are Different Types of Heaters Used in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, heaters are critical for process heating in refining and petrochemical operations. These heaters ensure that crude oil is heated to the necessary temperatures for effective separation and conversion into valuable products. By maintaining optimal temperatures, companies can enhance efficiency and safety, reducing the risk of accidents. International buyers must consider compliance with safety standards and the specific heating requirements of their processing units, especially in regions with strict regulations.

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
What Role Do Heaters Play in Food & Beverage Processing?
In the food and beverage industry, industrial ovens and dryers are essential for processing various products, from baked goods to dried fruits. These heaters improve product quality by ensuring even cooking and drying, thus reducing spoilage and waste. Additionally, they help maintain food safety standards by achieving the required temperatures for pasteurization. Buyers should focus on energy efficiency and local regulations regarding emissions when sourcing these heating solutions, particularly in developing regions where sustainability is becoming increasingly important.
Why Are Heaters Important in Pharmaceuticals?
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, controlled heating is crucial for ensuring the consistency and quality of drug products. Heaters are used in various stages, from mixing to drying, where precise temperature control is vital for compliance with regulatory standards. This ensures that products are effective and safe for consumer use. Buyers in this sector should prioritize precision in temperature control and the reliability of heating systems to prevent production delays and maintain compliance with stringent regulations.
How Do Heaters Benefit Construction Projects?
Heaters are often employed in construction to provide temporary heating for curing concrete, especially in colder climates. This application accelerates the curing process, allowing construction projects to stay on schedule. By maintaining optimal curing temperatures, businesses can enhance the strength and durability of concrete. Buyers should look for portable heating solutions that can adapt to various site conditions, ensuring that projects are completed efficiently and effectively.

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
What Is the Role of Heaters in Textile Manufacturing?
In textile manufacturing, heaters are vital for processes such as heat setting and drying, which enhance the quality and durability of fabrics. By applying consistent heat, manufacturers can improve production capacity and reduce defects in the final products. When sourcing heating solutions, businesses should consider material compatibility and energy consumption, as these factors can significantly impact operational costs and sustainability efforts, especially in regions focusing on eco-friendly practices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘different types of heaters’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing High Energy Costs with Inefficient Heating Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those in regions with extreme climates, face skyrocketing energy costs due to outdated or inefficient heating systems. For instance, a manufacturing facility in Brazil might rely on an old forced air heating system that consumes excessive amounts of energy while failing to maintain a consistent temperature. This inefficiency not only inflates operational costs but can also impact productivity and employee comfort.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should conduct an energy audit to assess the current heating system’s efficiency. Investing in modern, high-efficiency heating solutions—such as condensing boilers or variable refrigerant flow (VRF) systems—can significantly reduce energy consumption. When selecting a new heating system, consider options with high Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) ratings and those that utilize renewable energy sources like biomass or solar heating. Additionally, implementing smart thermostats and automation can optimize energy use based on real-time occupancy and operational needs, leading to substantial cost savings.
Scenario 2: Dealing with Uneven Heating in Large Commercial Spaces
The Problem: In large commercial spaces, such as warehouses or shopping centers, B2B buyers often encounter the issue of uneven heating. For example, a retail store in Saudi Arabia might have sections that are uncomfortably cold while others become excessively warm. This inconsistency not only affects customer experience but can also lead to increased wear on the heating system, driving up maintenance costs.
The Solution: To overcome uneven heating, buyers should consider zoned heating solutions that allow for tailored temperature control in different areas of the building. Implementing ductless mini-split systems or radiant floor heating can provide more even distribution of heat. Additionally, integrating a building management system (BMS) can help monitor and adjust heating levels based on real-time data, ensuring optimal comfort across all zones. Regular maintenance and inspections are also crucial to ensure that all components are functioning effectively and to prevent hot or cold spots.
Scenario 3: Navigating Space Constraints and Installation Challenges
The Problem: Many businesses, particularly in urban environments across Europe, face challenges when it comes to installing new heating systems due to space constraints. For instance, a small café might not have the physical space to accommodate traditional radiators or ductwork for a forced air system, limiting their options for effective heating.
The Solution: In such scenarios, B2B buyers should explore compact and innovative heating solutions. Options like wall-mounted electric heaters or infrared heating panels can provide effective warmth without requiring extensive installation space. Additionally, consider using underfloor heating systems, which can be installed without taking up wall space and can be effective in smaller areas. When specifying these systems, it is crucial to work with experienced HVAC professionals who can design a layout that maximizes efficiency while minimizing the impact on the café’s aesthetics and available space. Exploring modular heating solutions can also allow for scalable options that adapt as the business grows.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for different types of heaters
When selecting materials for different types of heaters, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to consider various factors such as performance characteristics, cost implications, and regional compliance standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in heating systems, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Heating Systems?
Steel is a widely used material in heating systems, particularly for boilers and radiators. It boasts high tensile strength and can withstand elevated temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various heating applications. Its corrosion resistance can be enhanced through galvanization or the use of stainless steel grades, which are particularly beneficial in humid or corrosive environments.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s durability is a significant advantage, allowing for long service life and minimal maintenance. However, its weight can complicate installation, and it may require additional support structures. The cost of steel can vary, with carbon steel being more economical than stainless steel, which is more expensive but offers superior corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various heating media, including water and steam, making it versatile for different heating systems. However, care must be taken to ensure that the steel is adequately protected from corrosion, especially in regions with high humidity or saline environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards such as ASTM A106 for carbon steel pipes and ASTM A312 for stainless steel. In regions like Europe, adherence to EN standards is crucial, while buyers in the Middle East may need to consider local regulations regarding material specifications.
How Does Copper Perform in Heating Applications?
Copper is another popular choice for heating applications, especially in piping and heat exchangers. It is known for its excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer. Copper also has natural antimicrobial properties, which can be beneficial in certain applications.
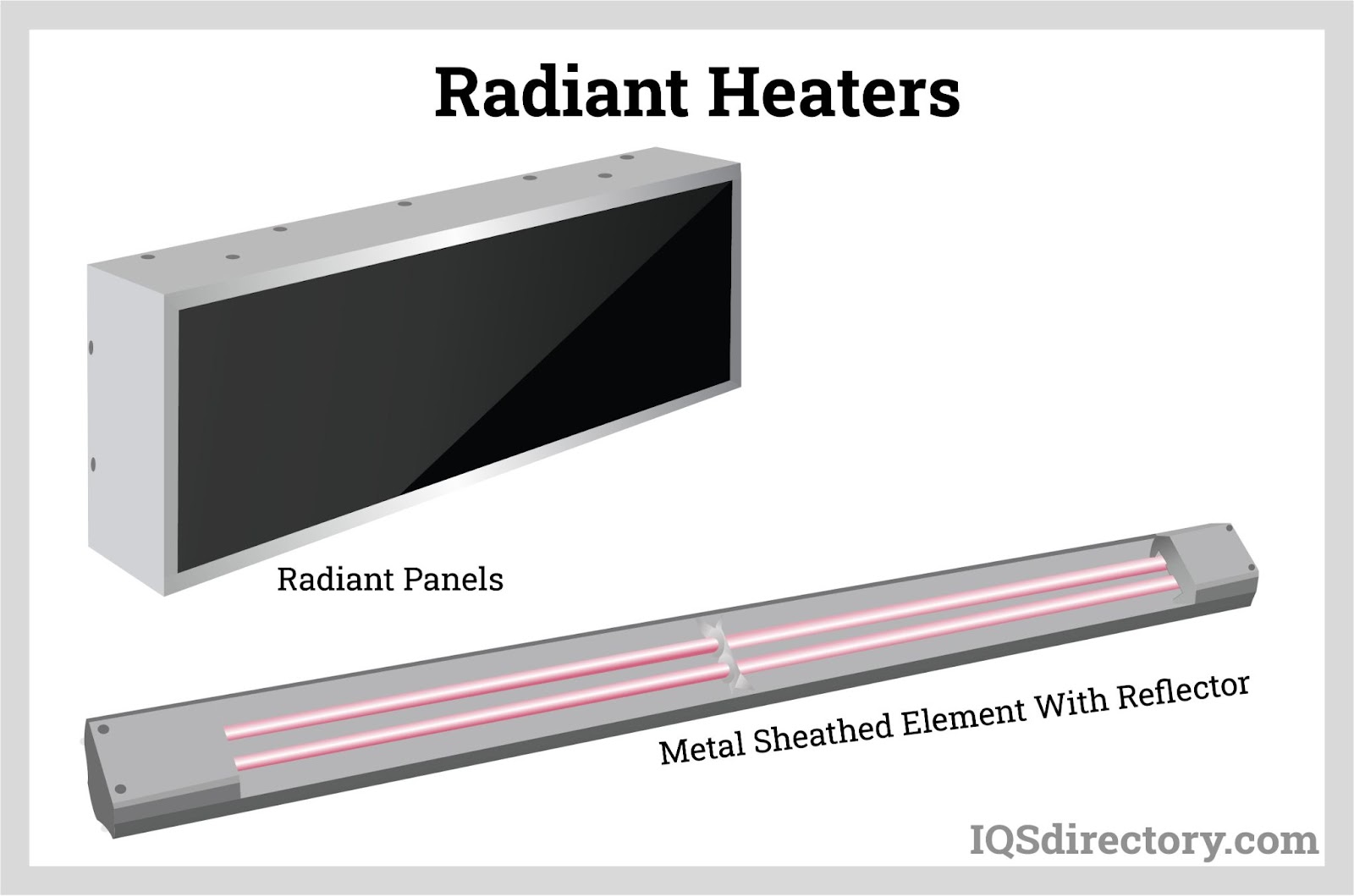
Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its high thermal efficiency and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for hot water systems. However, copper is more expensive than steel and can be prone to thermal expansion, which may lead to installation challenges. Additionally, its softness can make it susceptible to damage during installation.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with water and various heating fluids, providing reliable performance in both residential and industrial applications. Its superior heat transfer capabilities make it ideal for systems requiring rapid heating.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B88 for copper water tubes. In regions like South America, where copper theft can be an issue, securing the supply chain is essential.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Heating Systems?
Aluminum is increasingly being used in heating applications due to its lightweight and good thermal conductivity. It is often found in radiators and heat exchangers, where its properties can enhance overall efficiency.
Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
Pros & Cons: Aluminum’s lightweight nature simplifies installation and reduces structural load requirements. However, it is less durable than steel and can be prone to corrosion if not properly coated. The cost of aluminum is generally moderate, making it an attractive option for many applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various heating media is beneficial, but it is essential to ensure that the heating system is designed to prevent galvanic corrosion when used with other metals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions with high temperatures, such as the Middle East, the thermal expansion properties of aluminum need to be considered during design.
Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
How Does Plastic Fit into Heating Solutions?
Plastic materials, particularly cross-linked polyethylene (PEX), are gaining popularity in heating systems, especially for radiant floor heating applications. They are lightweight, flexible, and resistant to corrosion and scale buildup.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility of plastic allows for easier installation and less labor, reducing overall project costs. However, plastics generally have lower temperature and pressure ratings compared to metals, which may limit their application in high-temperature systems. The cost of plastic materials is typically lower than that of metals.
Impact on Application: Plastic is suitable for low to moderate temperature heating applications and is often used in hydronic heating systems. Care must be taken to ensure compatibility with the heating media to prevent degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM F876 for PEX is essential. In regions with varying climate conditions, such as Africa and South America, buyers should consider the impact of UV exposure on plastic materials.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for different types of heaters | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Boilers, radiators | High durability and strength | Heavy, potential for corrosion | Medium |
| Copper | Piping, heat exchangers | Excellent thermal conductivity | Expensive, prone to thermal expansion | High |
| Aluminum | Radiators, heat exchangers | Lightweight, good thermal efficiency | Less durable, corrosion risk | Medium |
| Plastic | Radiant floor heating | Flexible, easy installation | Lower temperature ratings | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of key materials used in heating systems, emphasizing their properties, advantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific regional needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for different types of heaters
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heaters?
The manufacturing of heaters encompasses several stages, each critical to ensuring the final product’s efficiency, safety, and reliability. The process typically involves material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Depending on the heater type, manufacturers select materials such as metals (e.g., steel, aluminum), plastics, and insulation materials. Quality of materials is paramount, as they directly influence the heater’s performance and longevity. Suppliers should be vetted for compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001, which ensures a systematic approach to quality management.
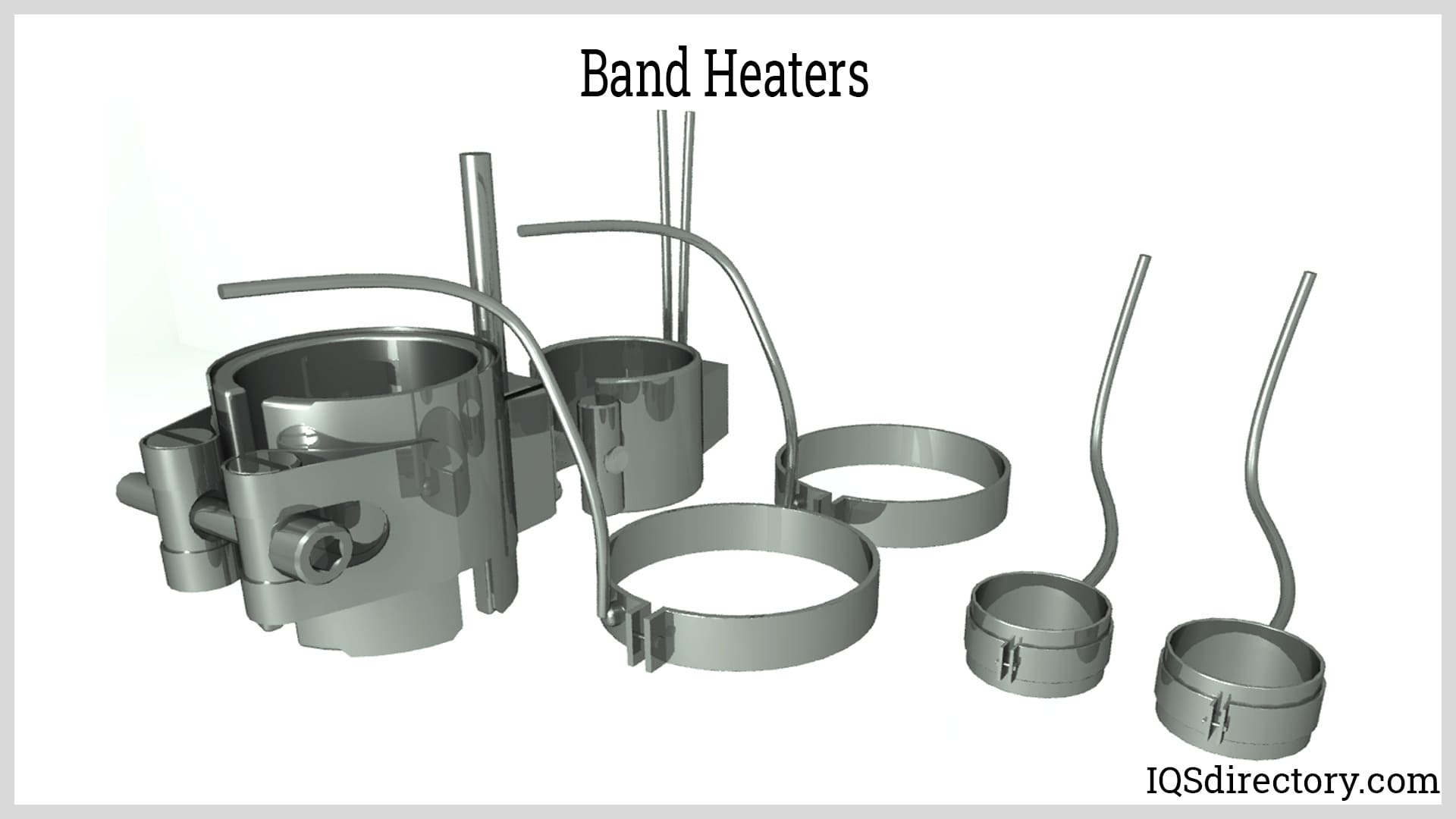
Forming Techniques
Once materials are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques. For metal components, techniques such as stamping, welding, and machining are common. For instance, forced air systems often involve intricate ductwork that requires precision forming techniques to ensure efficient airflow. In contrast, radiant heating systems may utilize plastic tubing that is bent and shaped through thermal forming methods. Each technique must adhere to strict tolerances to prevent leaks or inefficiencies in the final product.

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
Assembly Process
The assembly stage combines all the components into a functional unit. This can involve manual labor or automated assembly lines, depending on the scale of production. For example, in forced air systems, the furnace, blower, and ducting must be carefully aligned to maximize heating efficiency. Quality control is critical at this stage, as any misalignment can lead to performance issues.
Finishing Touches
Finally, the finishing process includes painting, insulation, and packaging. This stage not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the heater but also ensures compliance with safety standards. For example, heaters must be insulated to prevent heat loss and protect users from burns. The finishing stage is often where manufacturers apply certifications, ensuring products meet specific international and regional standards.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in Heater Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is essential in the heater manufacturing process to ensure that products meet safety and performance standards. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these QC processes.

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
Relevant International Standards
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that many heater manufacturers adopt. Compliance with this standard indicates a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, heaters may need to comply with CE marking in Europe, which ensures products meet health, safety, and environmental protection standards. In regions like the Middle East and Africa, local certifications may also apply, such as the Saudi Arabian Standards Organization (SASO) standards.
QC Checkpoints: What to Look For
Quality control is typically divided into three main checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards is crucial for the subsequent manufacturing stages.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to monitor production quality. This includes checking tolerances on formed parts and verifying assembly accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the heater is fully assembled, it undergoes final inspections and testing to ensure it meets performance specifications. This may include pressure testing for leaks, electrical safety tests, and efficiency evaluations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Heaters?
Testing methods vary depending on the type of heater but generally include:
- Thermal Efficiency Testing: This assesses how effectively the heater converts energy into heat.
- Electrical Safety Testing: Ensures that electrical components are safe and compliant with standards.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term usage to identify potential failures over time.
- Noise Level Testing: Particularly important for forced air systems to ensure they operate within acceptable noise thresholds.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must conduct due diligence to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are several actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes, QC checkpoints, and adherence to international standards. Audits help identify any potential risks in the supply chain.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation of their QC processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC reports. This information can provide insights into their commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to assess the manufacturing facility and the quality of finished products. This adds an additional layer of verification.
-
Certifications Review: Ensure that the supplier holds relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or CE marking. This provides assurance that the supplier adheres to recognized quality management practices.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in QC and certification processes:
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Different regions may have varying certification requirements. Understanding local regulations is critical for compliance and market entry.
-
Documentation Requirements: Ensure that suppliers provide all necessary documentation for customs clearance and regulatory compliance in your region. This includes certificates of conformity and test reports.
-
Cultural and Language Considerations: Engage with suppliers who understand the cultural and language nuances of your region. Effective communication can facilitate smoother negotiations and ensure that quality expectations are met.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance collaboration on quality initiatives and lead to better overall product performance.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing heaters, ensuring that they receive products that meet their specific needs and compliance requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘different types of heaters’
Introduction
In the competitive landscape of international B2B procurement, sourcing the right heating solutions is essential for operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This checklist serves as a comprehensive guide for buyers looking to procure various types of heaters, ensuring a strategic approach to evaluating options and suppliers tailored to your specific needs.

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
Step 1: Define Your Heating Requirements
Understanding your heating needs is the first critical step in the procurement process. Consider factors such as the size of the space, local climate conditions, and the specific applications of the heating system.
– Types of Heat: Determine whether you need forced air, radiant, or hydronic heating.
– Efficiency Standards: Evaluate the efficiency ratings required for your location, especially in regions where energy costs are significant.
Step 2: Research Available Heater Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of heaters available in the market. Each type has distinct advantages and disadvantages based on fuel sources, installation costs, and maintenance requirements.
– Fuel Sources: Understand the implications of different fuel types (e.g., natural gas, electricity, solar) on operational costs and environmental impact.
– System Longevity: Investigate the typical lifespan of each heating system to assess long-term value.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region.
– Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold necessary industry certifications and comply with local regulations.
– Reputation: Look for reviews or testimonials that highlight the supplier’s reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that outline the specifications of the heating systems they offer. This will allow you to make informed comparisons.
– Cost Breakdown: Ensure proposals include installation costs, operational expenses, and any potential savings from energy efficiency.
– Warranty Information: Review warranty terms to understand the level of support and protection offered.
Step 5: Conduct Site Assessments
Where applicable, arrange for site assessments by your shortlisted suppliers. This step is crucial for understanding how each system would perform in your specific environment.
– Customization Needs: Discuss any customization that may be required based on your facility’s layout or unique heating demands.
– Installation Considerations: Ensure that potential installation challenges are identified and addressed.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Effective negotiation can significantly impact your overall costs and service levels.
– Payment Terms: Discuss flexible payment options that align with your budget cycles.
– Service Agreements: Negotiate service and maintenance agreements to ensure ongoing support post-installation.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Place Orders
After selecting a supplier, finalize contracts that clearly outline all agreed-upon terms, specifications, and timelines. This is a crucial step to protect your interests and ensure accountability.
– Review Legal Terms: Ensure all legal aspects are clear and satisfactory to both parties.
– Order Confirmation: Obtain written confirmation of your order, including expected delivery and installation dates.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing different types of heaters, ensuring they make informed, strategic decisions that align with their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for different types of heaters Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Heater Sourcing?
When sourcing heaters, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. Key cost components include:

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly impacts the overall cost. For instance, high-grade metals and advanced insulation materials may increase the price but enhance efficiency and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the heater design. Skilled labor is essential for assembly and quality assurance, impacting the total cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes factory costs, utilities, and equipment depreciation. A manufacturer with high overhead might pass these costs onto buyers, affecting pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized heaters. These costs are often amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investment in QC processes ensures product reliability and adherence to certifications, which can influence the pricing structure. Stringent QC can lead to higher upfront costs but lower failure rates and maintenance costs.
-
Logistics: Transporting heaters can be costly, especially for bulk orders. Shipping methods, distance, and customs duties play critical roles in the final price.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary widely based on brand reputation, exclusivity, and market demand. Understanding a supplier’s margin can provide insights into their pricing flexibility.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Heater Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of heaters, particularly for B2B transactions:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often results in lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, so negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized heaters with specific features or design alterations typically incur higher costs due to increased material and labor requirements. Clearly defining specifications upfront can mitigate unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly alter the price. For instance, heaters made with advanced materials for energy efficiency may cost more but provide long-term savings through reduced energy consumption.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with international standards and certifications can influence costs. Buyers should consider whether the added expense of certified products aligns with their market requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: A supplier’s reputation, reliability, and service capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their brand, but this often translates into better support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for pricing transparency. They dictate who bears the costs and risks associated with shipping, impacting the overall purchase price.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Heater Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing and terms upfront. Discuss volume discounts, payment terms, and delivery schedules to secure better deals.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the total cost, including installation, maintenance, and energy consumption, rather than just the upfront price. This can lead to better long-term investment decisions.
-
Research Market Rates: Understand the market landscape and pricing trends for heaters in your region. This knowledge empowers you during negotiations and ensures you receive competitive offers.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Local suppliers may offer lower shipping costs and faster delivery times, which can significantly impact the TCO. Establishing relationships with local manufacturers can also enhance supply chain reliability.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variances due to tariffs, duties, and local economic conditions. This knowledge can help you anticipate price fluctuations and plan accordingly.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices discussed herein are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage in direct negotiations with suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing different types of heaters With Other Solutions
Understanding the available alternatives to traditional heating systems is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize energy efficiency and operational costs. In diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, selecting the right heating solution can significantly impact both the bottom line and environmental footprint. This section evaluates various heater types against alternative heating technologies, providing insights into their respective advantages and disadvantages.
| Comparison Aspect | Different Types of Heaters | Solar Heating Systems | Heat Pumps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, quick heating | Moderate, dependent on sunlight | High efficiency, consistent year-round |
| Cost | Installation: $1,800 – $10,000; Operating costs vary | Installation: $5,000 – $30,000; low operating costs | Installation: $3,000 – $8,000; moderate operating costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires professional installation and ductwork for some types | Requires significant space and structural adjustments | Flexible installation, can be retrofitted into existing systems |
| Maintenance | Moderate; filters and ducts need regular cleaning | Low; minimal moving parts | Moderate; requires regular servicing |
| Best Use Case | Residential and commercial buildings needing rapid heating | Regions with high solar exposure; eco-conscious businesses | Diverse climates; both heating and cooling needs |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Heating Systems?
Solar heating systems harness energy from the sun to provide heating, either for domestic hot water or for space heating. Their primary advantage is the significant reduction in operating costs after initial installation, as they utilize a renewable energy source. Additionally, they contribute positively to sustainability goals. However, they are dependent on sunlight availability, which can be inconsistent in certain regions. The installation can also be expensive and may require structural modifications to buildings.
What are the Key Features of Heat Pumps?
Heat pumps are versatile systems that can provide both heating and cooling. They are recognized for their high energy efficiency, as they transfer heat rather than generate it. This makes them a cost-effective solution in the long run. Heat pumps can be installed in various settings, including residential and commercial spaces. However, they may require more maintenance compared to traditional heaters, and their efficiency can drop in extremely cold climates, necessitating a supplemental heating source.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Heating Solution?
When selecting a heating solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific needs, including the operational environment, budget constraints, and long-term sustainability goals. Understanding the trade-offs between initial costs and ongoing energy expenses is vital. For instance, while traditional heaters may provide immediate warmth, alternatives like solar heating or heat pumps offer energy efficiency and lower operational costs in the long run. Ultimately, the right choice will align with the organization’s values, operational demands, and geographical considerations, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for different types of heaters
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Different Types of Heaters?
Understanding the essential technical properties of heaters is vital for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating options for commercial or industrial applications. Here are some critical specifications that can significantly impact purchasing decisions:
Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a heater, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum, influences its durability, resistance to corrosion, and overall performance. Higher-grade materials often offer better longevity and efficiency, which are crucial for long-term investments. Buyers should prioritize material grades that align with the specific environmental conditions they will face, such as humidity or exposure to chemicals. -
Heating Capacity (BTU/H)
The British Thermal Unit per hour (BTU/H) rating indicates the heating capacity of a unit. This specification helps buyers determine whether a heater can adequately warm a given space. Understanding the BTU requirements for specific applications ensures that the chosen heater can meet operational demands without excessive energy consumption, thereby optimizing costs. -
Efficiency Rating (AFUE)
The Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating measures how effectively a heater converts fuel into heat over a year. A higher AFUE percentage signifies better efficiency, which can lead to significant cost savings on energy bills. B2B buyers should evaluate efficiency ratings to enhance sustainability and reduce operational expenses. -
Power Source Compatibility
Different heaters can be powered by natural gas, propane, electricity, or renewable energy sources like solar. Compatibility with local energy supplies is crucial for operational feasibility and cost-effectiveness. Buyers should consider the availability and pricing of these energy sources in their regions to make informed decisions. -
Temperature Control Features
Advanced temperature control features, such as programmable thermostats and smart technology integration, enhance user convenience and energy efficiency. These features allow for better management of heating schedules, ultimately leading to cost savings. B2B buyers should assess the technology used for temperature control to ensure it aligns with their operational needs. -
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Understanding the installation complexity and ongoing maintenance needs of different heater types is essential for budget planning. Some systems may require extensive ductwork or specialized installation, while others might be more straightforward. B2B buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance, when selecting a heater.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Heater Purchases?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the heating sector, understanding OEM relationships is essential for sourcing quality components and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better deals and manage inventory effectively, particularly for bulk purchases. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate quotes that meet their specifications and budget constraints. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and delivery obligations, minimizing risks in cross-border purchases. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Awareness of lead times can assist buyers in planning their procurement strategies and managing project timelines effectively. -
Warranty
A warranty is a guarantee from the manufacturer regarding the quality and longevity of a product. Understanding warranty terms is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they are protected against defects and can plan for potential future costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing heaters, ensuring they meet their operational needs while optimizing costs and efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the different types of heaters Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Heater Sector?
The global heating market is shaped by several driving forces, including energy efficiency regulations, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. The increasing emphasis on energy efficiency is particularly relevant in regions like Europe and North America, where regulations mandate higher efficiency standards for heating systems. In contrast, emerging markets in Africa and South America are witnessing a rising demand for affordable, reliable heating solutions due to expanding urbanization and economic growth. International B2B buyers should pay attention to the growing trend of integrating smart technology into heating systems, enabling remote monitoring and control, which enhances energy management and reduces operational costs.
Additionally, the market is seeing a shift towards versatile heating systems that can serve both residential and commercial needs. Multi-functional units, such as heat pumps that provide both heating and cooling, are gaining traction, particularly in regions with varying climates like the Middle East. The demand for renewable energy solutions, including solar-assisted heating systems, is also on the rise, driven by sustainability goals and government incentives. As a result, suppliers are increasingly focusing on offering hybrid systems that combine traditional heating methods with renewable sources, presenting opportunities for B2B buyers to invest in innovative solutions.
How Is Sustainability Shaping B2B Sourcing Trends in the Heater Market?
Environmental impact is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of heating systems. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices and offer products with lower carbon footprints. This shift is not only about compliance with environmental regulations but also about meeting the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers. The use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient technologies is crucial for reducing the overall environmental impact of heating systems.
Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
Ethical sourcing is another important aspect, with buyers seeking suppliers who maintain transparent supply chains and ensure fair labor practices. Certifications such as Energy Star, LEED, and other green building certifications are becoming essential indicators of a product’s environmental performance. These certifications not only assure buyers of the sustainability of the heating solutions but also enhance their marketability in a competitive landscape. By aligning with suppliers committed to sustainability, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with regulatory changes and enhance their brand reputation.
What Is the Historical Context of Heating Systems and Their Evolution?
The evolution of heating systems has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing energy sources. Initially, heating methods relied heavily on coal and wood, but as urbanization progressed in the 20th century, more efficient and cleaner options emerged, including natural gas and electricity. The introduction of centralized heating systems, such as boilers and forced air systems, revolutionized the way heat was distributed in homes and commercial buildings.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, leading to the development of advanced heating technologies like heat pumps and solar thermal systems. These innovations not only improve energy consumption but also provide consumers with a wider range of options tailored to their specific needs. Understanding this historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it provides insights into market evolution and helps identify future trends in heating solutions that can drive business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of different types of heaters
-
How do I solve heating inefficiencies in my facility?
To address heating inefficiencies, first assess your current heating system’s performance. Look for issues such as inadequate insulation, outdated equipment, or improper sizing of heaters. Conduct a thorough energy audit to identify heat loss areas and consider upgrading to more efficient systems, like in-floor radiant heating or high-efficiency boilers. Consulting with a heating specialist can help tailor a solution that meets your facility’s specific needs and enhances overall energy efficiency. -
What is the best type of heater for large industrial spaces?
For large industrial spaces, forced air heating systems are often the best choice due to their ability to quickly distribute heat. However, radiant heating systems, such as in-floor or overhead infrared heaters, can provide consistent warmth and comfort while minimizing energy costs. The decision should consider factors like the space’s insulation, heating requirements, and energy sources available, ensuring a system that optimally balances efficiency and cost. -
How can I vet suppliers for heating systems?
When vetting suppliers for heating systems, assess their experience and reputation in the industry. Look for certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Request client references and case studies to evaluate their reliability and service history. Additionally, inquire about their ability to provide ongoing support, spare parts, and warranties, which are crucial for long-term partnerships, especially in regions with unique heating requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for heating systems?
MOQs for heating systems can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of heater. Generally, commercial suppliers may require MOQs ranging from 10 to 50 units, while manufacturers may have higher thresholds. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers, as some may offer flexibility for smaller orders or trial runs, especially for new or emerging markets. -
What payment terms are standard for international heating system purchases?
Standard payment terms for international purchases of heating systems typically include options like Letter of Credit (LC), advance payment, or net terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). Many suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for custom orders. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that ensure security for both parties, considering currency fluctuations and international transaction fees that could impact the final cost. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in heater procurement?
To ensure quality assurance in heater procurement, establish clear specifications and standards that the products must meet. Request certifications such as ISO or CE marks, which demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards. Conduct pre-shipment inspections and request samples before full-scale orders. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties and after-sales service, as these can be indicators of their commitment to quality. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing heaters?
When importing heaters, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, including certificates of origin and compliance. Planning for lead times is crucial, as heating equipment can be bulky and may require special handling. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in international shipping can help streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
How do seasonal demands affect heater pricing and availability?
Seasonal demands can significantly impact heater pricing and availability, particularly in regions with distinct heating seasons. Prices may rise during peak demand periods, such as pre-winter months, due to increased orders and limited stock. To mitigate this, plan your purchases ahead of the heating season and consider bulk ordering during off-peak times. Engaging with suppliers early can also secure better pricing and ensure availability, especially for customized solutions.
Top 5 Different Types Of Heaters Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Spruce – Forced Air Heating/Cooling Systems
Domain: thespruce.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. Forced Air Heating/Cooling Systems:
– Best for: Multipurpose HVAC that heats and cools quickly.
– Cost: $5,000 – $10,000 based on square footage.
– Lifespan: Up to 25 years.
– Fuel sources: Natural gas, liquid propane (LP), fuel oil, electricity.
– Distribution: Ductwork delivers warmed air to rooms.
– Pros: Can add air filters and humidifiers, high AFUE ratings, combine…
2. Reddit – Heaters Explained
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Heaters convert electricity or gas into heat energy to increase room temperature. Efficiency varies based on how heat is generated and transferred. Electric heaters are theoretically 100% efficient, producing 3.412 BTU per watt. Natural gas heaters have a calorific value of 1000 BTU per cubic foot but can be less efficient due to heat loss in exhaust gases. Heat pumps can be significantly more eff…
3. Sylvane – Heaters
Domain: sylvane.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: This company, Sylvane – Heaters, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Hyett Refrigeration – Heaters & Heating Systems
Domain: hyettrefrigeration.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Types of Heaters: Electric Heaters (Convection Heaters, Infrared Heaters, Oil-Filled Heaters, Fan Heaters, Ceramic Heaters); Gas and Fuel-Based Heaters (Natural Gas Heaters, Propane Heaters, Kerosene Heaters); Central Heating Systems (Furnaces, Boilers, Heat Pumps); Portable Heaters (Space Heaters, Garage Heaters, Patio Heaters).
5. Save On Energy – Space Heaters
Domain: saveonenergy.ca
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Space heaters are electric devices used to heat specific rooms in a home, particularly during cold weather. They can save energy if used correctly by lowering the overall home thermostat and heating only occupied spaces. Key considerations include:
1. **Energy Efficiency**: All electric space heaters are 100% efficient at converting electricity to heat, but wattage varies. Lower wattage models sa…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for different types of heaters
In navigating the diverse landscape of heating solutions, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the various types of heaters—from forced air systems to radiant heating—enables companies to align their choices with specific regional needs, energy availability, and budget constraints. By analyzing the pros and cons of each system, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency while maintaining comfort.
Illustrative image related to different types of heaters
The value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated, particularly in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where climate conditions and energy resources vary significantly. Buyers should consider local suppliers that offer products tailored to the unique demands of their environments, ensuring compliance with regional regulations and standards.
Looking ahead, the heating market is poised for innovation, with advancements in energy efficiency and sustainability at the forefront. Companies are encouraged to stay abreast of emerging technologies and renewable energy options that can lead to long-term savings and environmental benefits. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore new heating solutions, and position your business for success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

Illustrative image related to different types of heaters