Everything You Need to Know About Die For Cutting Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for die for cutting
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right die for cutting can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With a myriad of options available, navigating through various types of dies—ranging from metal cutting dies to multimedia dies capable of handling thicker materials—requires a strategic approach. This guide aims to demystify the complexities associated with die-cutting products, offering insights into the different types, their applications across industries, and crucial factors for vetting suppliers.
Understanding the nuances of die for cutting is essential not only for enhancing product quality but also for optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive resource will explore the intricacies of supplier selection, including criteria for evaluating reliability, quality assurance, and pricing strategies. By addressing these critical components, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their unique business needs.
Whether you are a manufacturer in Vietnam looking to streamline production or a craft supplier in Brazil seeking innovative solutions, this guide is tailored to equip you with the knowledge necessary to successfully navigate the global market for die cutting. By leveraging the insights provided, you can enhance your sourcing strategy and ultimately gain a competitive edge in your respective industry.
Understanding die for cutting Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thin Dies | Thin metal blades for intricate designs | Paper crafting, scrapbooking, card making | Pros: Precision cutting; Cons: Limited material types |
| Steel Rule Dies | Flexible steel blades for various thicknesses | Packaging, labels, textiles | Pros: Versatile; Cons: Durability varies with use |
| Rotary Dies | Circular blades for continuous cutting | Mass production of labels, stickers | Pros: High-speed operation; Cons: Higher initial cost |
| Embossing Dies | Creates raised designs on materials | Crafting, packaging, branding | Pros: Adds texture; Cons: Requires specific machines |
| Multi-Media Dies | Cuts through various materials like fabric and foam | Apparel, home décor, crafts | Pros: Multi-functional; Cons: May need additional equipment |
What are Thin Dies and Their B2B Suitability?
Thin dies are characterized by their lightweight metal construction, allowing for intricate designs and detailed cuts. They are primarily used in paper crafting, scrapbooking, and card making. B2B buyers should consider the compatibility of these dies with their existing cutting machines, as well as the types of materials they plan to use. While thin dies offer precision, they may be limited to lighter materials, which could restrict their application in heavier industrial settings.
How Do Steel Rule Dies Stand Out in the Market?
Steel rule dies feature flexible blades that can be customized for various thicknesses, making them highly versatile. These dies are commonly used in packaging, labels, and textiles, appealing to businesses that require adaptability in their cutting solutions. When purchasing steel rule dies, buyers should evaluate the die’s durability and the specific thickness required for their production processes. While these dies offer versatility, their longevity can vary based on usage, making it essential for buyers to assess their operational needs.
What are the Advantages of Rotary Dies for High-Volume Production?
Rotary dies utilize circular blades for continuous cutting, making them ideal for high-speed operations in mass production environments, such as labels and stickers. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and operational costs when integrating rotary dies into their production lines. While they provide efficient cutting, the upfront cost may be higher compared to other die types. Businesses that prioritize speed and efficiency will find rotary dies advantageous for scaling operations.
How Can Embossing Dies Enhance Product Presentation?
Embossing dies are specifically designed to create raised designs on various materials, adding a tactile and aesthetic dimension to products. They are widely used in crafting, packaging, and branding to enhance visual appeal. B2B buyers should consider the compatibility of embossing dies with their existing machinery and the types of materials they will be working with. While they add texture and sophistication to products, embossing dies often require specialized equipment, which may represent an additional investment.
What Makes Multi-Media Dies a Versatile Choice for Various Industries?
Multi-media dies are capable of cutting through a range of materials, including fabric, foam, and thicker papers, making them suitable for applications in apparel, home décor, and crafts. B2B buyers should assess their production needs and the types of materials they will utilize when considering multi-media dies. While these dies offer significant flexibility and functionality, they may require additional equipment to handle thicker materials effectively, which could impact overall costs.
Key Industrial Applications of die for cutting
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of die for cutting | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Custom packaging solutions for food and consumer goods | Enhances product presentation and shelf appeal | Material compatibility, precision of cuts, lead times |
| Automotive | Production of interior components and gaskets | Reduces waste and ensures high-quality parts | Durability, material selection, compliance with standards |
| Textile and Fashion | Fabric cutting for garments and accessories | Increases production efficiency and design versatility | Accuracy, variety of designs, machine compatibility |
| Electronics | Die-cutting of insulation materials and circuit boards | Ensures optimal performance and safety in devices | Precision cutting, material specifications, supply chain |
| Construction | Custom shapes for insulation and drywall applications | Improves energy efficiency and reduces installation time | Material durability, customization capabilities, cost |
How is die for cutting applied in the packaging industry, and what benefits does it provide?
In the packaging industry, die for cutting is essential for creating custom packaging solutions tailored to specific products, such as food and consumer goods. It allows manufacturers to produce boxes, labels, and inserts with precise shapes and dimensions, enhancing product presentation and shelf appeal. This customization can significantly impact brand recognition and consumer choice. For international buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, sourcing dies that accommodate local materials and production capabilities is crucial to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
What role does die cutting play in the automotive sector, and how does it improve production processes?
In the automotive sector, die cutting is utilized for producing various interior components, such as upholstery and gaskets. The precision of die-cutting reduces material waste and ensures that parts fit perfectly, which is vital for vehicle safety and aesthetics. For buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe, understanding the durability and material specifications is essential, as these components must withstand varying environmental conditions while maintaining quality standards.
Illustrative image related to die for cutting
How does die cutting enhance efficiency in the textile and fashion industries?
Die cutting in the textile and fashion industries enables the rapid and accurate cutting of fabrics for garments and accessories. This process not only increases production efficiency but also allows for intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve with traditional cutting methods. For buyers from diverse markets, including Vietnam and Brazil, the ability to source dies that cater to various fabric types and thicknesses can significantly impact production timelines and costs.
In what ways is die cutting used in electronics, and what are the key benefits for manufacturers?
Die cutting is crucial in the electronics industry for fabricating insulation materials and circuit boards, where precision is paramount. This technique ensures that components are cut to exact specifications, enhancing the performance and safety of electronic devices. For B2B buyers, especially in regions with stringent safety regulations, sourcing high-quality dies that comply with international standards is vital to maintain product integrity and reliability.
How does die cutting contribute to construction applications, and what should buyers consider?
In construction, die cutting is used to create custom shapes for insulation and drywall applications, which can improve energy efficiency in buildings. The ability to produce tailored solutions quickly can significantly reduce installation time and labor costs. Buyers should consider the durability of materials and the customization capabilities of the dies to ensure they meet specific project requirements, especially in diverse climates found across Africa and South America.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘die for cutting’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Material Compatibility in Die Cutting
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face difficulties when sourcing die-cutting solutions that effectively handle various materials. This is particularly evident in sectors like packaging, textiles, and crafts, where companies require dies that can cut through materials ranging from thick cardboard to delicate fabrics. A lack of material compatibility can lead to increased production costs, wasted materials, and delays in project timelines. Buyers often find themselves frustrated when the dies they purchase fail to perform adequately on the intended substrates, leading to inconsistent product quality.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, buyers should thoroughly assess the material properties before selecting die-cutting dies. When sourcing dies, look for suppliers that offer detailed specifications on the types of materials their dies can handle. Consider investing in multi-media dies, which are designed for versatility and can cut through a range of materials. Additionally, engage with manufacturers who provide samples or demonstrations, allowing you to test the dies with your specific materials before making a bulk purchase. Establishing a relationship with a knowledgeable supplier can also facilitate ongoing support and advice tailored to your material needs.
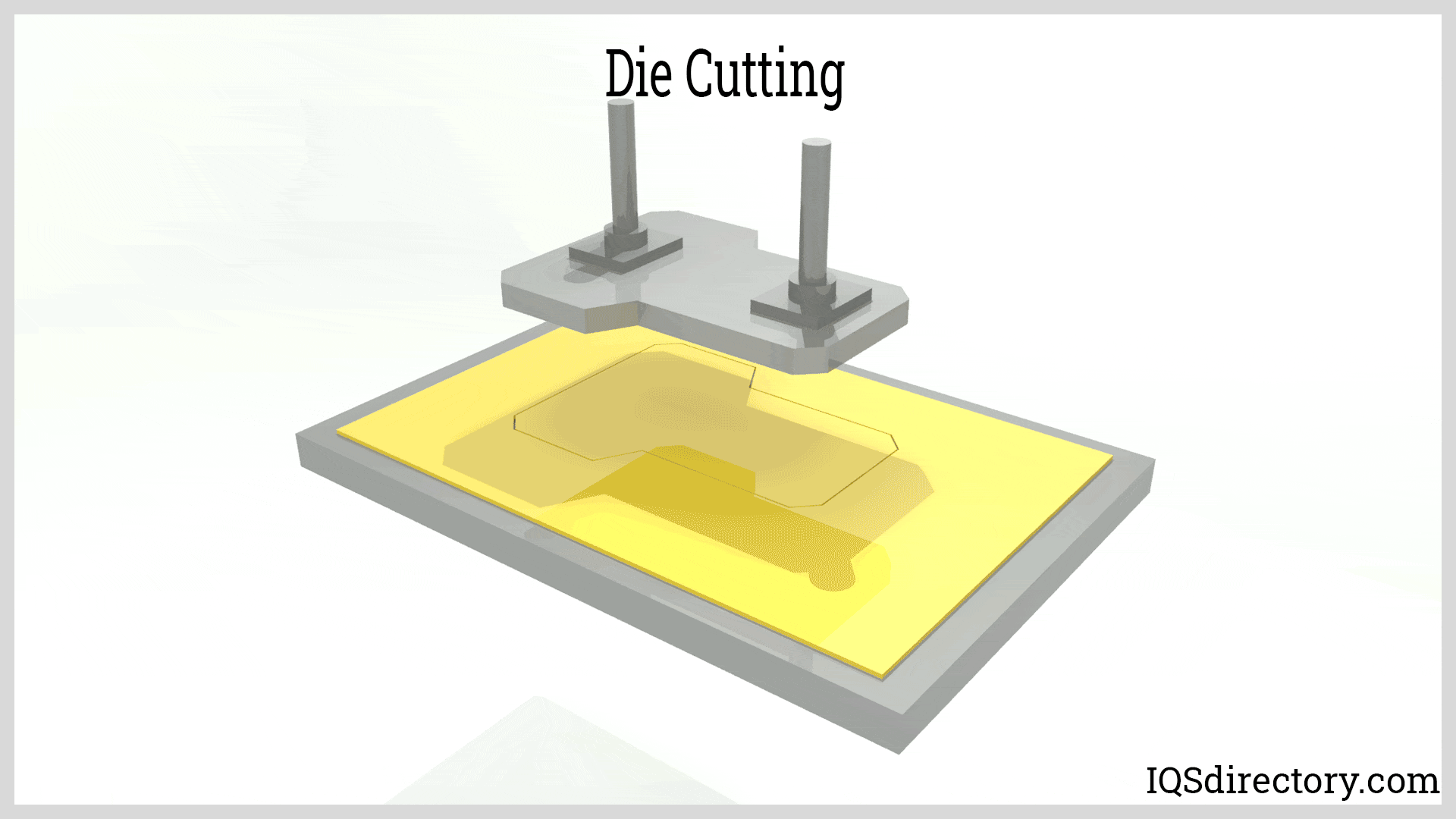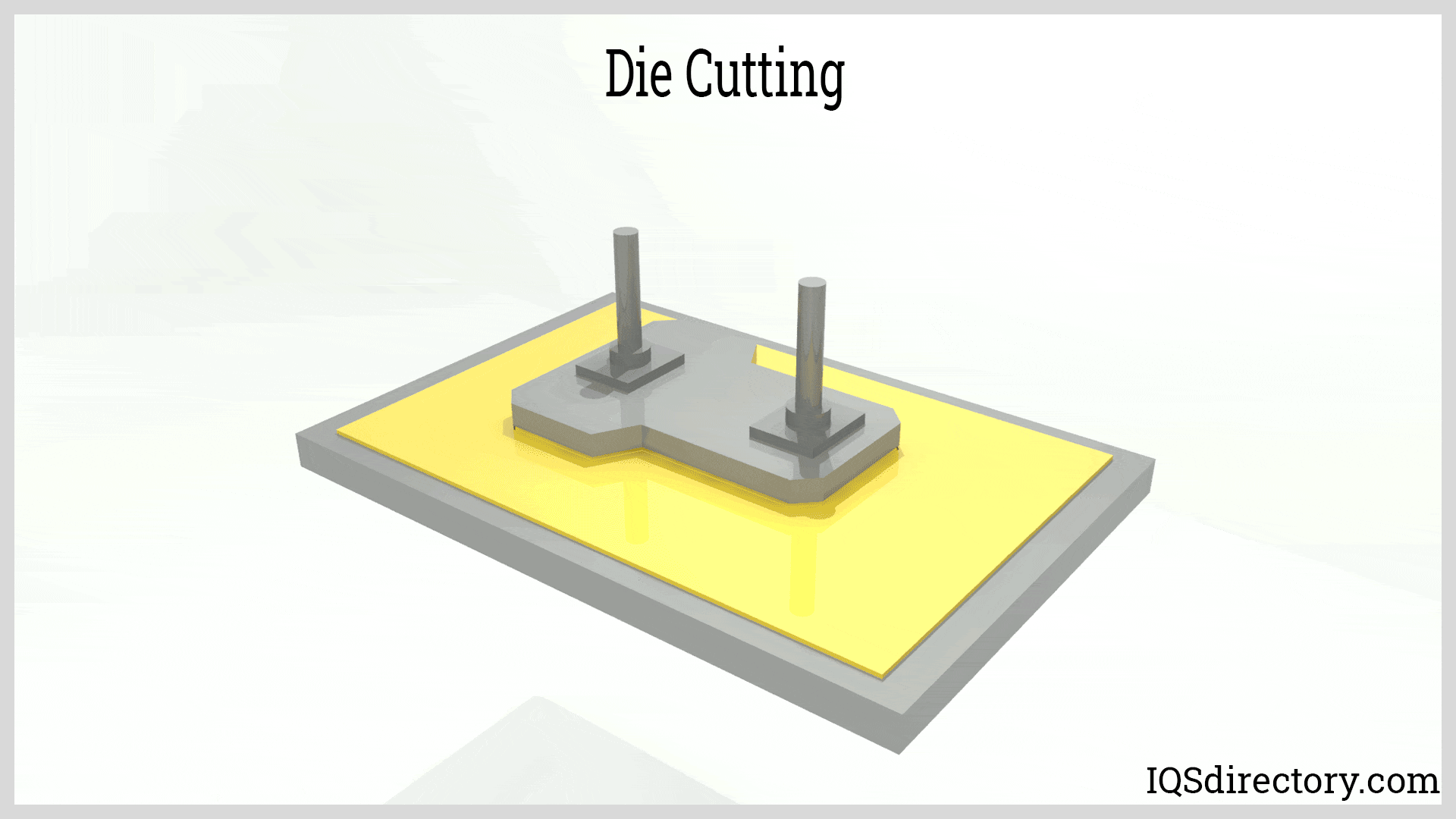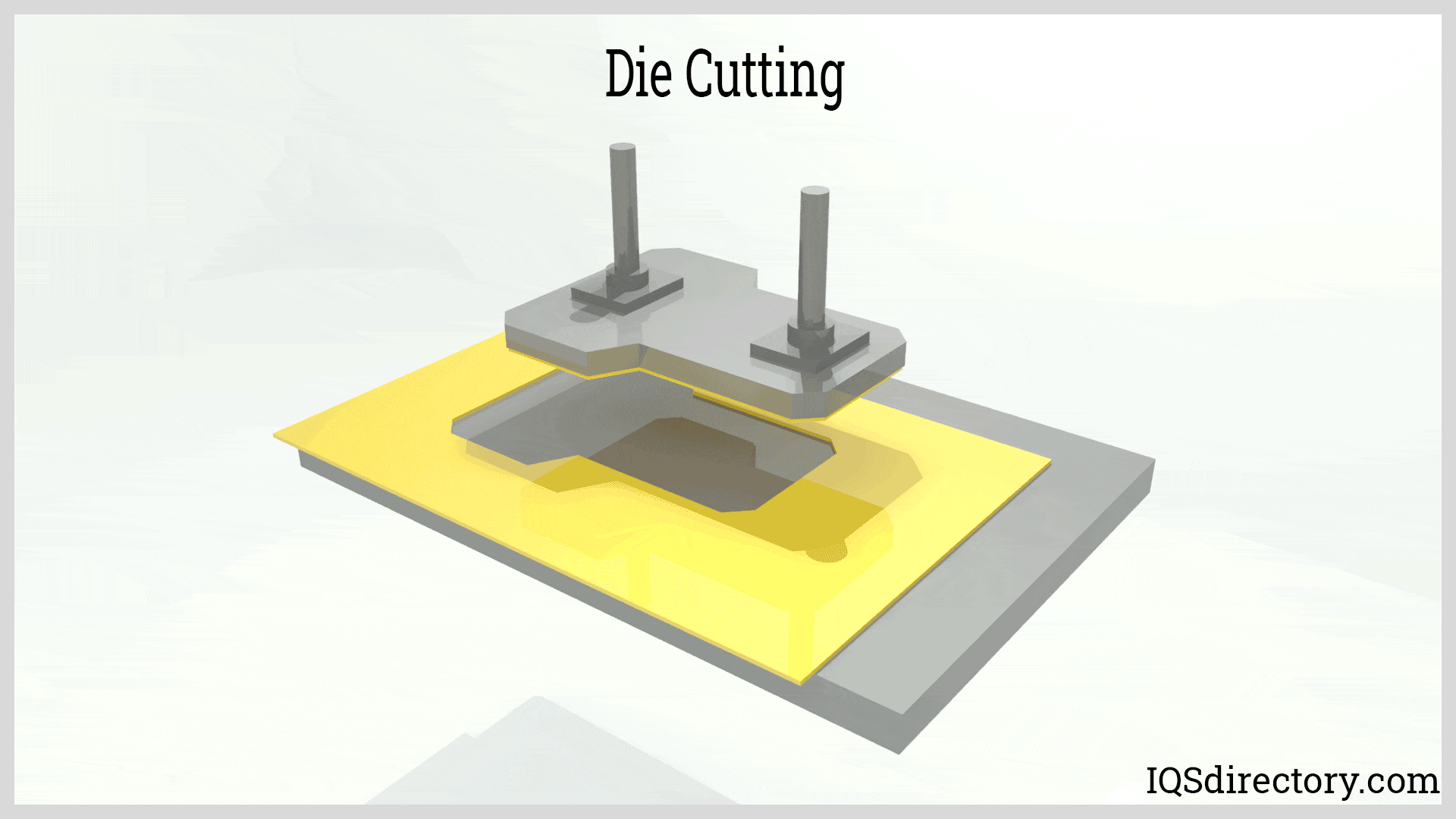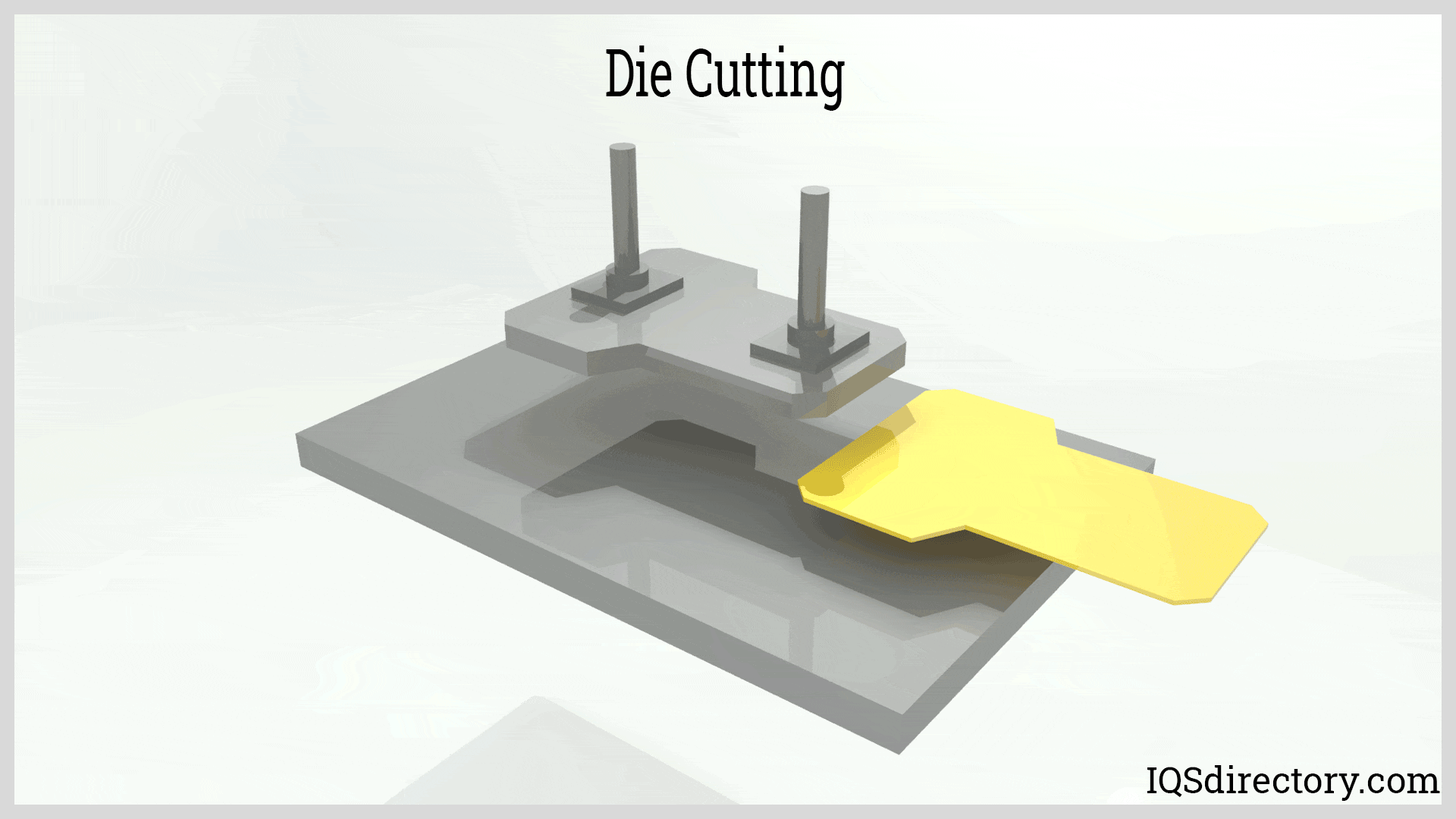
Illustrative image related to die for cutting
Scenario 2: High Tooling Costs and Budget Constraints
The Problem: A common issue for B2B buyers in the die-cutting industry is the high upfront cost associated with custom tooling and dies. Companies aiming to scale production may hesitate to invest significantly due to tight budgets, especially in developing markets. This financial pressure can lead to compromises in quality, with businesses opting for lower-cost dies that may not meet their production demands or longevity expectations. The result is often a cycle of increased expenses from frequent replacements and repairs, further straining budgets.
The Solution: To address high tooling costs, buyers should explore options for bulk purchasing or supplier partnerships that offer discounts on larger orders. Additionally, consider investing in high-quality, durable dies that, while initially more expensive, can provide long-term savings through reduced wear and lower replacement rates. Another strategic approach is to utilize die-sharing or leasing arrangements with other companies within your industry, allowing for shared costs and access to a wider range of die options without the full financial burden. Regular maintenance and proper storage of dies can also extend their lifespan, offering further cost savings over time.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Achieving Precision and Consistency
The Problem: In industries that rely heavily on die-cutting, such as packaging and manufacturing, achieving precision and consistency in cuts is paramount. B2B buyers often encounter issues with dies that produce inconsistent results, leading to product rejection, customer dissatisfaction, and increased rework. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including poor die design, inadequate machine calibration, or improper usage. For businesses focused on quality control, these challenges can significantly impact their reputation and bottom line.
The Solution: To enhance precision and consistency, it is essential for buyers to prioritize the quality of the dies and the machines they use. Opt for dies made from high-quality materials and those that are engineered for specific applications. Investing in advanced die-cutting machines that offer adjustable settings and precise calibration can also help achieve more consistent results. Furthermore, implementing a robust training program for staff on the proper use and maintenance of die-cutting equipment can minimize human error. Regular quality checks and feedback loops can help identify issues early, allowing for timely adjustments and improvements to the cutting process. By focusing on these areas, businesses can enhance their product quality and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for die for cutting
When selecting materials for die cutting, it is crucial for B2B buyers to understand the properties and implications of each material type. This guide analyzes four common materials used in die cutting, providing insights into their performance, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international markets.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Die Cutting Applications?
Steel, particularly high-carbon steel, is a prevalent choice for die cutting due to its exceptional hardness and durability. It typically has a high-temperature rating, allowing it to withstand the pressures involved in cutting various materials without deforming. Steel also exhibits good corrosion resistance when properly treated, which is essential for maintaining tool longevity.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of steel is its durability, making it suitable for high-volume production runs. However, its manufacturing complexity can be a drawback, as it often requires specialized equipment and processes. Additionally, the initial cost of steel dies can be high, although they tend to offer better long-term value due to their lifespan.
Impact on Application:
Steel dies are compatible with a wide range of materials, including paper, cardboard, and certain plastics. This versatility makes them ideal for industries like packaging and textiles.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for steel quality. Additionally, the availability of steel can vary, affecting lead times and costs.
How Does Aluminum Compare to Steel for Die Cutting?
Aluminum is another popular material for die cutting, particularly in applications where weight is a concern. It has a lower density than steel, making it easier to handle and transport. Aluminum also has good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
Pros and Cons:
The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can reduce shipping costs and improve handling efficiency. However, it is less durable than steel and may not withstand the same level of pressure, which can limit its use in high-volume applications. The cost of aluminum can be moderate, making it a cost-effective alternative for certain projects.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum dies are often used for softer materials like foam and thin plastics, making them suitable for industries such as automotive and consumer goods.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it’s important to consider the availability of aluminum and its compliance with international standards. Quality certifications may vary, impacting the choice of suppliers.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Die Cutting?
Plastic dies, particularly those made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polycarbonate, are increasingly used in die cutting applications. They are lightweight and can be manufactured quickly, making them suitable for prototyping and low-volume production runs.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of plastic dies is their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications, as they can wear down more quickly than metal dies. The relative cost of plastic dies is generally low, appealing to budget-conscious buyers.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
Impact on Application:
Plastic dies are ideal for cutting softer materials like paper and thin films, making them popular in the craft and packaging industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that plastic dies comply with relevant safety and environmental standards, especially in regions with strict regulations. Understanding local preferences for materials can also influence purchasing decisions.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Die Cutting Performance?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, are gaining traction in die cutting due to their unique properties. They combine the lightweight nature of plastics with the strength of fibers, offering a balance of durability and flexibility.
Pros and Cons:
The main advantage of composite materials is their ability to withstand high pressures while remaining lightweight. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized equipment for production. The relative cost of composite dies is typically medium to high.
Impact on Application:
Composite dies are suitable for cutting a variety of materials, including textiles and advanced composites, making them valuable in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific compliance requirements for composite materials in their regions, as standards can differ significantly. Additionally, sourcing composite materials may be more challenging in emerging markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Die Cutting
| Material | Typical Use Case for die for cutting | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-volume production runs | Exceptional durability | High initial cost | High |
| Aluminum | Soft materials (foams, plastics) | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Prototyping, low-volume runs | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited pressure tolerance | Low |
| Composite | Advanced materials (textiles, etc.) | Lightweight and strong | Higher manufacturing costs | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights to make informed decisions when sourcing die cutting materials, ensuring compatibility with their specific applications and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for die for cutting
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Die Cutting?
The manufacturing of die for cutting involves several critical stages that ensure precision, durability, and effectiveness. Understanding these stages will help B2B buyers select the right suppliers capable of meeting their specific requirements.
How is Material Prepared in Die Cutting Manufacturing?
The first step in the die manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality steel is commonly used for die cutting due to its strength and resistance to wear. Suppliers typically source raw materials that meet international standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications. The materials are then subjected to processes like annealing, which involves heating and cooling to relieve stress and improve machinability.
What Forming Techniques Are Employed in Die Manufacturing?
Once the material is prepared, it undergoes forming processes. The most common technique is CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, which allows for precise shaping of the die components. Laser cutting and waterjet cutting are also employed for intricate designs, ensuring that the dies can produce detailed cuts. These techniques not only enhance precision but also allow for complex geometries that cater to various industries, including packaging, textiles, and automotive.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
How is the Assembly of Die Cutting Tools Conducted?
After forming, the next stage is assembly. This involves aligning and fastening the die components, which may include various parts like blades, frames, and guides. Proper assembly is crucial for maintaining the die’s integrity and performance. During this phase, manufacturers often employ jigs and fixtures to ensure accurate alignment and reduce the risk of errors.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential in Die Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are critical in enhancing the performance and longevity of die cutting tools. These may include surface treatments such as coating, polishing, or heat treating to improve hardness and resistance to corrosion. The final finishing touches often determine the die’s effectiveness in various applications. Manufacturers may also employ inspection techniques to ensure that the finishing meets specified standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Die Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the die manufacturing process, ensuring that the final product meets or exceeds customer expectations. For B2B buyers, understanding these QA measures is essential when selecting suppliers.
Which International Standards Are Relevant to Die Cutting Quality Control?
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which specifies requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a supplier’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may apply, depending on the application of the die.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Die Manufacturing?
Quality control in die manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process. Suppliers often conduct tests to verify that materials meet specified standards and are free from defects.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the production stages. This may involve measuring dimensions, checking for proper alignment, and ensuring that machining processes are within tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the die is fully assembled, a final inspection is performed to ensure it meets all specifications. This may include functional testing, where the die is tested under actual working conditions to verify its performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Here are several strategies to ensure quality assurance:
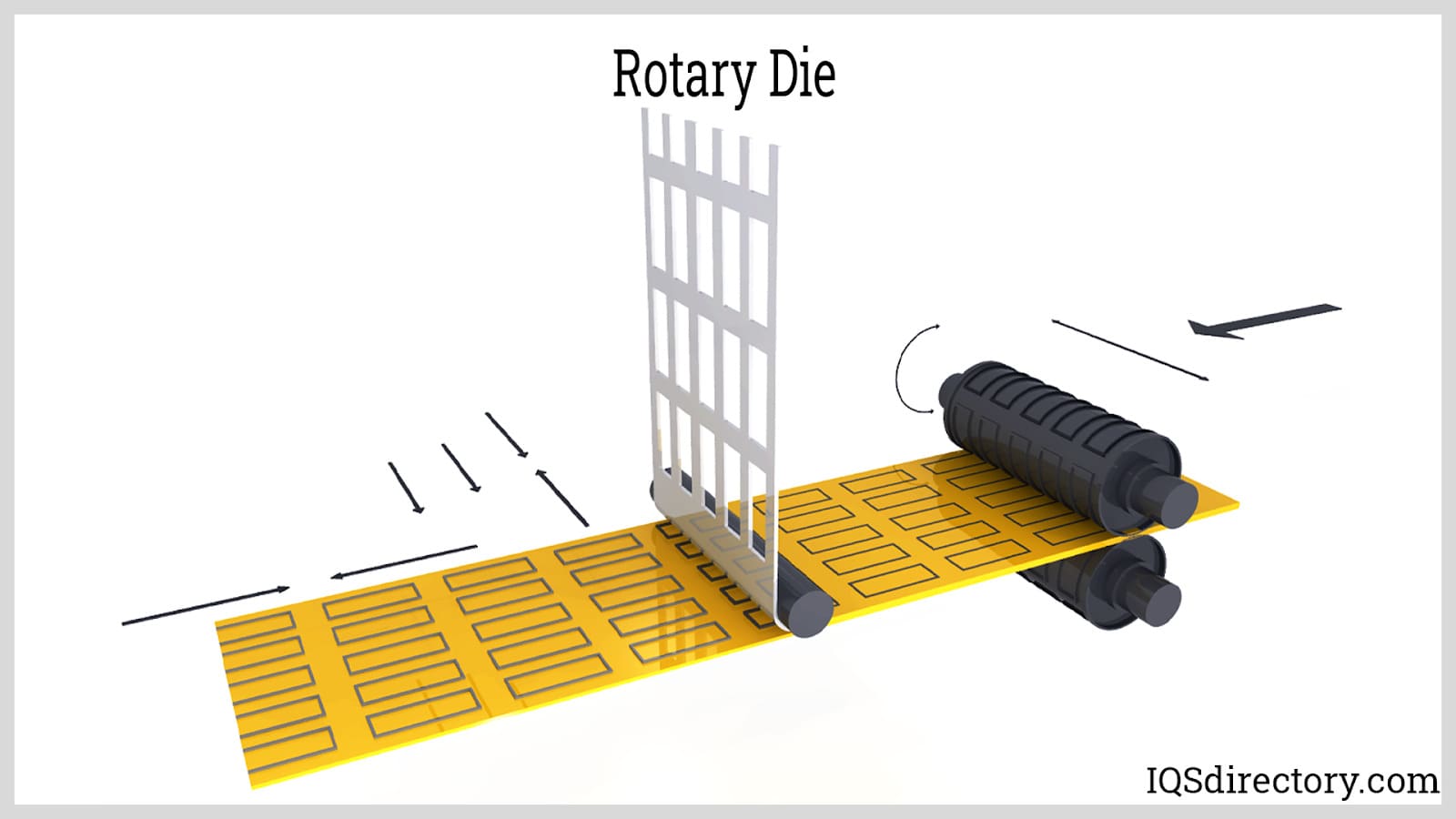
Illustrative image related to die for cutting
What Methods Can Be Used for Supplier Audits and Reports?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers should request access to quality management system documentation, including internal audit reports and corrective action records. This transparency can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to maintaining high standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be scheduled at various stages of production, providing additional assurance that the die meets required specifications. Buyers should inquire about the inspector’s credentials and experience in the industry to ensure reliability.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider in Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Different countries may have varying standards and regulations that affect the manufacturing and testing of die cutting tools.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Die Manufacturing?
Buyers should be aware of regional standards that may apply to their specific markets. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while buyers in the Middle East may look for compliance with local regulations. Understanding these differences can help buyers make informed decisions when sourcing from international suppliers.
What Should Buyers Know About Language and Communication Barriers?
Language and communication can pose challenges in quality assurance. Buyers should ensure that they can clearly communicate their requirements to suppliers. It may be beneficial to have documentation translated into the supplier’s language to avoid misunderstandings regarding quality expectations and specifications.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in die for cutting, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. This comprehensive approach not only enhances product quality but also fosters long-term partnerships in the competitive global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘die for cutting’
Introduction
Sourcing die-cutting tools effectively is essential for businesses looking to enhance their production capabilities. This guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers to ensure they procure the right die for cutting, tailored to their specific needs and operational requirements. By following these steps, you can minimize risks and maximize the value of your investment.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you start reaching out to suppliers, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your technical requirements. Consider the materials you will be cutting (e.g., paper, fabric, metal) and the thickness of these materials. This information will help you choose the appropriate die type and ensure compatibility with your existing machinery.
- Material Compatibility: Verify that the dies can handle the types of materials you plan to use.
- Cutting Precision: Specify the level of detail required for your projects, as some dies offer intricate designs while others are more basic.
Step 2: Identify Reputable Suppliers
Finding reliable suppliers is key to ensuring quality and service. Conduct thorough research to identify vendors with a strong reputation in the die-cutting industry. Look for suppliers with positive reviews and testimonials from previous customers.
- Industry Experience: Prefer suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry or application.
- Local vs. International: Consider the benefits of sourcing locally (e.g., faster shipping) versus internationally (potentially lower costs).
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and safety standards. Check for relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, which demonstrates a quality management system, or any industry-specific certifications that may apply.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure that the supplier adheres to local and international regulations related to die production.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about the supplier’s quality control measures to mitigate defects.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the dies you’re considering. This step allows you to assess the quality, durability, and performance of the products firsthand.
- Testing with Your Materials: Use the samples with your intended materials to evaluate their effectiveness and compatibility.
- Performance Feedback: Gather feedback from your production team regarding the usability and efficiency of the dies.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, compare their pricing structures and terms of sale. Remember that the cheapest option may not always be the best; consider the overall value, including quality and service.
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing for larger orders, as many suppliers offer significant discounts.
- Payment Terms: Understand the payment options and terms of credit available, as these can impact your cash flow.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order with Clear Agreements
Once you’ve selected a supplier, ensure that all agreements are documented clearly. This should include details on delivery timelines, warranties, and after-sales support.
Illustrative image related to die for cutting
- Delivery Expectations: Specify the expected delivery dates and any penalties for delays.
- Support and Maintenance: Discuss the level of support available post-purchase, including troubleshooting and replacement parts.
Step 7: Evaluate After Purchase
After your initial order, take the time to evaluate the supplier’s performance. Monitor the quality of the dies and the efficiency of their service.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a system for providing feedback to the supplier about the products and services received.
- Long-term Relationships: Consider building long-term partnerships with suppliers that consistently meet your needs, which can lead to better pricing and service in the future.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing die-cutting tools more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for die for cutting Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Die Cutting Manufacturing?
When sourcing dies for cutting, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
- Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. High-quality steel or specialized alloys can raise the initial investment but may lead to better durability and performance over time.
- Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the precise manufacturing of dies. Labor costs can vary greatly depending on the region and the complexity of the die design.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient operations can minimize overhead expenses, impacting overall pricing.
- Tooling: Tooling costs involve the initial setup for die production. Custom tooling can be expensive but may be necessary for specialized applications.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the dies meet industry standards requires investment in quality assurance processes. This can include both material testing and performance evaluations.
- Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on distance, weight, and the chosen Incoterms. These should be factored into the total cost of ownership.
- Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. This can vary based on market demand and supplier reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Die Cutting Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of die cutting products, making it essential for buyers to consider these elements when negotiating.
- Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to cost reductions. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help in negotiating better pricing.
- Specifications and Customization: Customized dies may incur additional costs for design and manufacturing. Clearly defining specifications can help mitigate unexpected expenses.
- Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and compliance with international standards can lead to increased costs. However, they often provide better longevity and performance, justifying the investment.
- Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and experience can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but can offer better reliability and service.
- Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery can significantly affect costs. Buyers should be clear on who bears the risks and costs at each stage of transportation.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Their Die Cutting Sourcing Costs?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing dies for cutting, buyers should consider several strategic approaches.
- Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume discounts and express your willingness to establish a long-term partnership. Suppliers may offer better pricing for committed buyers.
- Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. A lower initial price may not always result in overall savings.
- Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local economic conditions and currency fluctuations, which can impact pricing.
- Conduct Market Research: Familiarize yourself with market rates and competitor pricing. This knowledge can empower negotiations and help identify fair pricing.
- Build Relationships with Multiple Suppliers: Establishing connections with various suppliers can provide leverage and alternative options in case of supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion
In the competitive landscape of die cutting sourcing, understanding the intricate cost structure and price influencers is essential for B2B buyers. By leveraging effective negotiation strategies and considering total ownership costs, businesses can optimize their sourcing decisions, ensuring both quality and cost-efficiency in their procurement processes. While prices may vary, thorough research and strategic planning can lead to better deals and long-term supplier relationships.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing die for cutting With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Die for Cutting in B2B Applications
When evaluating solutions for cutting materials, it’s crucial to understand the range of available options. While die cutting is a popular method, several alternative technologies can achieve similar outcomes. This analysis compares die cutting with laser cutting and rotary cutting, providing insights into their respective advantages and disadvantages.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Die For Cutting | Laser Cutting | Rotary Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for intricate designs | Excellent precision, capable of cutting complex shapes | Fast for continuous cuts but less intricate |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; dies can be expensive | Higher initial costs due to equipment | Lower operational costs, but requires significant setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific machines and dies | Requires skilled operators and safety measures | Easier to implement for ongoing projects |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of dies and machines | Requires calibration and lens maintenance | Minimal maintenance if properly set up |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for bulk production of detailed designs | Best for versatile materials and complex shapes | Suitable for continuous cutting of simpler designs |
Analyzing Laser Cutting: Pros and Cons
Laser cutting is a highly precise method that uses focused light to cut through various materials, including metals, plastics, and fabrics. One of its primary advantages is its versatility; it can handle complex designs and a variety of material types without needing specialized dies. However, the initial investment for laser cutting machines can be substantial, and they require skilled operators who are trained in safety protocols. Maintenance can also be more intensive, as lenses need regular cleaning and calibration to ensure optimal performance.
Exploring Rotary Cutting: Benefits and Drawbacks
Rotary cutting employs a rotating blade to cut materials and is often used in textile and paper industries for its speed and efficiency. This method excels in high-volume production, making it ideal for projects that require continuous cuts, such as rolls of fabric or paper. The setup is relatively straightforward, allowing for quick adjustments. However, rotary cutting may not achieve the same level of precision as die or laser cutting, particularly for intricate designs, limiting its use for detailed work.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate cutting technology depends on various factors, including the specific application, budget, and production volume. Die cutting is ideal for high-precision, bulk production of detailed designs, making it suitable for industries like packaging and crafts. Laser cutting offers versatility and precision but comes with higher costs and maintenance requirements. Rotary cutting stands out for its efficiency in continuous production but may fall short in precision for complex designs. By assessing these factors, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for die for cutting
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Die for Cutting?
When considering dies for cutting, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Below are several key properties that B2B buyers should be familiar with:

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
1. Material Grade
The material used in the construction of cutting dies significantly affects their durability and cutting precision. Common materials include high-carbon steel, tungsten carbide, and tool steel. Each material offers different levels of hardness, wear resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Selecting the appropriate material grade can lead to improved production efficiency and reduced downtime due to tool wear.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the die’s design. In die cutting, precise tolerances are essential for ensuring that the finished product meets quality standards. Tighter tolerances typically result in a higher manufacturing cost but are critical in applications requiring high precision, such as electronics or medical devices. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers avoid costly errors and rework.
3. Die Thickness
The thickness of a cutting die influences its strength and the types of materials it can effectively cut. Thicker dies can withstand greater pressure and are suitable for cutting tougher materials, while thinner dies are often used for lighter materials. Knowing the appropriate die thickness for specific applications ensures that buyers do not compromise on quality or efficiency.
4. Cutting Edge Geometry
The geometry of the cutting edge, including angle and profile, plays a vital role in the cutting process. Different shapes and angles can affect the quality of the cut and the speed of operation. Buyers should consider the intended application and material type when evaluating cutting edge geometry to achieve optimal performance.
5. Coating
Coatings can enhance the performance of cutting dies by providing additional wear resistance, reducing friction, and preventing corrosion. Common coatings include titanium nitride (TiN) and diamond-like carbon (DLC). Understanding the benefits of different coatings can help buyers select dies that offer better performance and longer life spans, ultimately reducing overall costs.
6. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, are used to enhance the hardness and toughness of cutting dies. These processes improve the die’s ability to maintain its cutting edge under high-pressure conditions. Buyers should inquire about the heat treatment methods used in die production to ensure they are investing in high-quality tools that will withstand rigorous use.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Die for Cutting?
Navigating the world of die cutting also involves understanding specific industry terminology. Here are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the die-cutting industry, OEMs provide dies that are compatible with specific machines. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure compatibility and quality in their die purchases.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory effectively and avoid overcommitting resources. It’s essential for negotiating pricing and understanding the scalability of a supplier’s offerings.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This formal process allows buyers to compare options and make informed purchasing decisions. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Familiarity with these terms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for B2B transactions, as they clarify costs and responsibilities during the shipping process.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is vital for inventory management and production scheduling. Buyers should always confirm lead times with suppliers to avoid production delays.
6. TQM (Total Quality Management)
TQM is a management approach focused on long-term success through customer satisfaction. In the die-cutting industry, implementing TQM practices can lead to improved product quality and operational efficiency. Buyers should consider suppliers that prioritize TQM to ensure they receive high-quality dies consistently.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing dies for cutting, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the die for cutting Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Die Cutting Sector?
The die cutting industry is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors, including the rise of personalized consumer goods and increased demand for efficient manufacturing processes. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking high-quality, versatile die cutting solutions that cater to diverse applications—from packaging to crafting and industrial design. The advent of advanced technologies, such as computer numerical control (CNC) and automation, is reshaping the landscape, allowing for faster production times and enhanced precision.

Illustrative image related to die for cutting
Emerging trends indicate a shift toward digital die cutting solutions, enabling businesses to streamline operations and reduce waste. The integration of software-driven design tools is gaining traction, allowing for customization at scale and reducing lead times. B2B buyers are also focusing on sourcing from suppliers who can provide a range of materials, including metal, plastic, and eco-friendly options. This trend is particularly pronounced in markets like Brazil and Vietnam, where local manufacturers are capitalizing on global sourcing strategies to meet evolving customer demands.
How is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Die Cutting Products?
As environmental concerns continue to rise, sustainability has become a pivotal factor in sourcing decisions for die cutting products. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing practices and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their environmental impact. This includes the use of sustainable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and waste reduction strategies.
Certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for paper products and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are becoming essential for companies looking to enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Furthermore, the demand for biodegradable and recyclable materials in die cutting is on the rise, prompting suppliers to innovate and develop eco-friendly alternatives. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also helps businesses in regions like Africa and the Middle East to tap into new market opportunities.
How Has the Die Cutting Industry Evolved Over Time?
The die cutting industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from manual processes to sophisticated automated systems. Initially, die cutting was primarily used in textile and paper industries; however, advancements in technology have broadened its applications across various sectors, including packaging, automotive, and electronics.
Today, the integration of digital technologies and software-driven solutions has transformed die cutting into a more precise and efficient process. This evolution has enabled manufacturers to cater to diverse market needs, allowing for rapid prototyping and customization. As B2B buyers continue to seek innovative and sustainable solutions, the die cutting industry is poised for further growth and transformation in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of die for cutting
-
How do I solve issues with die compatibility for my cutting machine?
To resolve compatibility issues between dies and cutting machines, first, verify the specifications of both the die and the machine. Check for the die’s thickness and material type, ensuring it aligns with your machine’s cutting capacity. If the die is too thick or made from incompatible materials, it may not work properly. Consider reaching out to the supplier for recommendations on compatible dies or explore adjustable settings on your machine to accommodate various dies. -
What is the best type of die for cutting different materials?
The best type of die depends on the materials you intend to cut. For paper and lightweight materials, thin metal dies like Thinlits are ideal. For thicker materials such as fabric or chipboard, consider using Bigz dies or multi-media dies designed for heavy-duty cutting. Always consult the supplier’s guidelines for each die type to ensure optimal results based on your specific project requirements. -
How can I customize dies to meet specific project requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for dies, allowing you to design unique shapes or sizes that fit your projects. To initiate this process, contact your supplier with detailed specifications, including dimensions, material preferences, and any design elements you wish to incorporate. Be prepared to discuss minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times, as custom dies may require longer production times. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for die purchases?
MOQs for die purchases can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of die. Standard production dies may have MOQs ranging from 50 to 100 units, while custom designs often require higher quantities, sometimes exceeding 200 units. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their specific requirements and negotiate favorable terms based on your purchasing capacity. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing dies internationally?
Payment terms can vary among suppliers, but common practices include a 30% deposit upfront with the remaining balance due before shipping. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, such as net 30 or net 60 days, depending on your business relationship. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, credit card) and ensure that you have a clear understanding of the total costs, including shipping and customs duties. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing dies?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing dies, begin by vetting suppliers through reviews, testimonials, and certifications. Request samples to evaluate the die’s performance and precision before committing to larger orders. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s QA processes, including material sourcing, production techniques, and post-production inspections. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations can also help mitigate any issues down the line. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing dies?
When importing dies, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping to handle documentation and customs clearance. Additionally, factor in potential delays due to customs inspections or restrictions in your country. It’s wise to plan for extra time in your project timeline to accommodate unforeseen logistics challenges. -
How do I compare different suppliers for die cutting?
To effectively compare different suppliers for die cutting, evaluate them based on key criteria such as product quality, pricing, customization capabilities, and customer service. Request quotes and samples from multiple suppliers to assess their offerings. Furthermore, consider their delivery times, payment terms, and reputation in the market. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your specific needs.
Top 4 Die For Cutting Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Anna Griffin – Premium Die Cuts
Domain: annagriffin.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Die Cuts | Shop Premium Dies for Crafting – Anna Griffin Inc. offers a variety of crafting products including Cut & Emboss Dies (174), Embossing Folders (14), and seasonal crafting supplies for Christmas (32), Easter (3), Fall (9), Summer (4), Valentine’s (3), and St. Patrick’s Day (2). The collection features tools for creating intricate die cuts and adding depth with embossing dies, making the c…
2. Altenew – Die Cutting Dies
Domain: altenew.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Best Craft Die Cuts and Die Cutting Dies from Altenew. Free U.S. shipping on orders over £75.00. $10 OFF international shipping on orders over £151.00 with code SHIP10OFF. Product types include 451 dies and 4 tools. Die types include Key-Hole (39), Layering (130), Matching (8), Zero-Waste (6). Die themes include Cover (42), Edible (3), Elements & Borders (1), Floral (168), Frames & Labels (1), Nat…
3. Tonic Studios – Die Cutting Sets
Domain: tonic-studios.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Die Cutting Sets | Die Cuts for Card Making, Tonic Studios USA, Tangerine machine, high-quality die-cutting sets, precise and intricate shapes, durable materials, compatible with most die-cutting machines, versatile and long-lasting addition to craft supplies.
4. Best Cutting Die – Precision Cutting Dies
Domain: bestcuttingdie.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Best Cutting Die specializes in precision cutting dies and modules, offering a wide range of products including:
– Envelope Converting Dies
– Flexible Dies
– Magnetic Cylinders and Shells
– High Cutting Dies (Blank Cutters)
– Side Knives & Accessories
– Segment (Panel) Dies & Gummers
– Embossing Cylinders and Units
– High-Quality AMC Dies for Envelope Converting
– Resharpen, Repair, and R…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for die for cutting
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers in the Die Cutting Industry?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in the die cutting sector presents immense opportunities for international buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse range of die cutting options—from precision metal dies to versatile multi-media solutions—enables businesses to enhance their production capabilities and streamline operations. By prioritizing quality and innovation, companies can not only meet their project requirements but also foster long-term relationships with suppliers who can support their growth.
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond mere cost savings; it encompasses the ability to adapt to market trends, leverage technological advancements, and ensure sustainability in sourcing practices. As the demand for customized and efficient die cutting solutions continues to rise, international buyers should remain proactive in exploring new suppliers and innovative products.
How Can International Buyers Prepare for Future Trends in Die Cutting?
Looking ahead, it is crucial for B2B buyers to embrace a forward-thinking mindset. Engaging in continuous market research, attending trade shows, and collaborating with industry experts will position companies to capitalize on emerging trends. By taking these steps, businesses can not only secure competitive advantages but also contribute to the evolving landscape of the die cutting industry. Now is the time to act—evaluate your sourcing strategies, invest in quality solutions, and position your business for success in the global marketplace.
Illustrative image related to die for cutting
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.