Everything You Need to Know About Die Assembly Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for die assembly
In an increasingly competitive global landscape, sourcing die assembly solutions that meet both efficiency and quality demands poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With the complexities of integrating multiple manufacturing processes, businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are seeking innovative solutions to streamline operations while maintaining high standards. This guide delves into the world of die assembly, exploring various techniques, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
From understanding the intricacies of in-die assembly to evaluating cost implications, this comprehensive resource empowers purchasing managers and decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to make informed choices. By examining the latest advancements in die technology and assessing the capabilities of potential suppliers, buyers can optimize their production processes and drive substantial cost savings.
Whether you’re in the automotive, electronics, aerospace, or appliance manufacturing sectors, this guide will equip you with actionable insights tailored to your specific market needs. Explore how to navigate the global market for die assembly and discover strategies to enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and ultimately achieve a competitive edge.
Understanding die assembly Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-Die Assembly | Integrates multiple assembly processes within the die itself. | Automotive, Electronics, Appliances | Pros: Reduces production time and costs. Cons: Requires high initial investment in technology. |
| Progressive Die Assembly | Uses a series of stations to progressively form parts in one stroke. | High-volume manufacturing | Pros: High efficiency for complex parts. Cons: Limited flexibility for small runs. |
| Transfer Die Assembly | Transfers parts between stations using automated mechanisms. | Aerospace, Heavy Machinery | Pros: Excellent for large parts and intricate designs. Cons: Complexity in setup and maintenance. |
| Compound Die Assembly | Combines cutting and forming operations in a single die. | Sheet Metal Fabrication | Pros: Minimizes tooling costs and time. Cons: May lead to higher wear on tools. |
| Custom Die Sets | Tailored die sets designed for specific applications. | Custom Manufacturing, Prototyping | Pros: Meets unique project specifications. Cons: Longer lead times for production. |
What is In-Die Assembly and Its Suitability for B2B Buyers?
In-die assembly is a sophisticated method that integrates multiple assembly operations directly within the stamping process. This technique is particularly suitable for industries like automotive and electronics, where high production volumes and precision are crucial. Buyers should consider the upfront investment in advanced machinery, but the long-term benefits of reduced production time and costs often outweigh initial expenditures.
How Does Progressive Die Assembly Enhance Manufacturing Efficiency?
Progressive die assembly employs a series of stations to progressively shape and form parts within a single press cycle. This method is highly effective for high-volume manufacturing, especially when producing complex components. While it offers remarkable efficiency, buyers should be aware that this approach may limit flexibility, making it less ideal for smaller production runs.
What Are the Benefits of Transfer Die Assembly for Large Parts?
Transfer die assembly utilizes automated mechanisms to move parts between various processing stations. This method is particularly advantageous for industries such as aerospace and heavy machinery, where large and intricate components are common. Though this approach enhances production capabilities, buyers must be prepared for a more complex setup and potential maintenance challenges.

Illustrative image related to die assembly
Why Choose Compound Die Assembly for Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Compound die assembly combines cutting and forming operations within a single die, making it an efficient choice for sheet metal fabrication. This method is well-suited for applications that require a high degree of precision while minimizing tooling costs. However, buyers should consider the potential for increased wear on tools due to the combined operations.
How Do Custom Die Sets Meet Unique Project Needs?
Custom die sets are specifically designed to accommodate unique manufacturing requirements. This approach is beneficial for custom manufacturing and prototyping, allowing companies to create tailored solutions for specialized applications. While the ability to meet specific project needs is a significant advantage, buyers should anticipate longer lead times for production compared to standard die sets.
Key Industrial Applications of die assembly
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of die assembly | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Engineering | Production of complex vehicle components | Enhanced efficiency and reduced production costs | Expertise in high-precision die design and manufacturing |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Assembly of circuit boards and connectors | Improved product quality and reduced assembly time | Access to advanced technology and materials for electronics |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of lightweight structural components | Compliance with stringent safety and weight standards | Experience in aerospace standards and quality assurance |
| Appliance Manufacturing | Production of appliance casings and brackets | Streamlined operations and consistent product quality | Custom die sets tailored to specific appliance designs |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Assembly of critical components like housings | High precision and reliability in production | Certification in medical manufacturing standards |
How is Die Assembly Used in Automotive Engineering?
In the automotive sector, die assembly plays a crucial role in the production of intricate vehicle components such as chassis parts, brackets, and panels. By integrating multiple processes like stamping and welding into one cycle, manufacturers can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce costs. For international buyers, especially those in regions with burgeoning automotive markets like South America and Africa, sourcing partners with specialized expertise in high-precision die design is essential. This ensures compliance with global standards while maximizing production output.
What are the Applications of Die Assembly in Electronics Manufacturing?
Electronics manufacturers utilize die assembly to produce critical components such as circuit boards and connectors with remarkable accuracy and speed. This method minimizes the risk of errors and enhances product quality, which is vital in an industry where reliability is paramount. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should prioritize suppliers equipped with advanced technology and specialized materials to meet the specific demands of electronic components, ensuring they receive products that comply with international quality standards.

Illustrative image related to die assembly
Why is Die Assembly Important in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace manufacturing, die assembly is indispensable for creating lightweight yet durable components that meet stringent safety and performance requirements. Applications include the fabrication of brackets, fasteners, and structural supports that must adhere to rigorous weight reduction and structural integrity standards. For international buyers, particularly in regions with strict aerospace regulations, sourcing suppliers with extensive experience in aerospace manufacturing and proven quality assurance processes is crucial to ensure compliance and reliability.
How Does Die Assembly Enhance Appliance Manufacturing?
Die assembly significantly streamlines the production of appliance casings, brackets, and other essential components. By consolidating multiple manufacturing steps into a single process, it not only improves operational efficiency but also ensures consistent product quality. Buyers from emerging markets should seek suppliers that offer customized die sets tailored to their specific appliance designs, ensuring that the components meet local market requirements while maintaining high standards of durability and performance.
What Role Does Die Assembly Play in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, die assembly is critical for producing high-precision components such as housings and connectors that require stringent quality control. This method ensures that products are manufactured with minimal risk of error, which is essential in an industry where product reliability can impact patient safety. International buyers, particularly those from regions with developing healthcare infrastructures, should prioritize suppliers that are certified in medical manufacturing standards to ensure the highest levels of quality and compliance.

Illustrative image related to die assembly
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘die assembly’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Processes
The Problem: Many manufacturers face the challenge of escalating production costs, particularly in environments that rely heavily on traditional assembly methods. In regions like Africa and South America, where labor and material costs are volatile, inefficiencies can significantly affect the bottom line. A B2B buyer may find themselves wrestling with high machinery upkeep, excessive manual labor, and slow production cycles that lead to missed deadlines and dissatisfied customers. This not only affects profitability but also market competitiveness.
The Solution: Adopting in-die assembly can dramatically reduce production costs by streamlining multiple operations into a single process. To implement this, buyers should first assess their current manufacturing workflows and identify areas where in-die assembly can replace traditional methods. They should seek partnerships with experienced suppliers who specialize in custom die sets that cater to specific production needs. This not only minimizes the number of machines required but also lowers energy consumption and maintenance costs. By investing in modern technology and training staff to operate these integrated systems, companies can achieve significant cost savings while enhancing overall production efficiency.
Scenario 2: Quality Control Issues Leading to Increased Rework
The Problem: Quality control is a persistent issue for B2B buyers engaged in die assembly, especially in industries such as automotive and electronics, where precision is crucial. Inconsistent quality can lead to defects, necessitating costly rework and impacting delivery timelines. Buyers may struggle to maintain stringent quality standards due to variations in raw materials, human error, or outdated machinery, which can erode client trust and damage brand reputation.
The Solution: To address these quality control challenges, companies should leverage the advantages of in-die assembly systems, which often incorporate automated monitoring and control mechanisms. Buyers can collaborate with manufacturers that utilize advanced technology capable of real-time defect detection and reporting. Implementing a robust quality assurance protocol that includes pre-production testing of dies and materials will also mitigate risks. Furthermore, investing in training for personnel on best practices for machine setup and operation can minimize human error. By enhancing quality control measures, companies can ensure that they consistently meet or exceed client expectations, reducing rework and fostering customer loyalty.
Scenario 3: Delays in Production Due to Equipment Downtime
The Problem: Equipment downtime is a significant pain point for B2B buyers in die assembly, often leading to production delays and missed deadlines. In regions such as the Middle East and Europe, where market demands can shift rapidly, unplanned machine failures can cripple production schedules. Buyers may find themselves in a precarious position, struggling to meet orders and maintain strong relationships with clients.
The Solution: Implementing in-die assembly can alleviate some of the pressures associated with equipment downtime. Buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality, durable die sets that are specifically designed for their manufacturing processes. This can involve customizing dies to fit specific applications, which not only improves efficiency but also reduces wear and tear on machinery. Additionally, establishing a preventive maintenance schedule with suppliers can help ensure that machines are regularly serviced, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns. Investing in training for operators to handle routine checks and minor repairs can further enhance production reliability. By taking these proactive steps, companies can maintain smoother operations, minimizing delays and fostering stronger client relationships.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for die assembly
What Are the Key Materials Used in Die Assembly?
When selecting materials for die assembly, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly impact the efficiency, cost, and quality of the final product. Below, we analyze four common materials used in die assembly, focusing on their properties, pros and cons, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Steel Alloys Perform in Die Assembly?
Steel alloys, particularly carbon steel and tool steel, are widely used in die assembly due to their excellent mechanical properties. They typically have high strength, good wear resistance, and can withstand considerable pressure and temperature variations.

Illustrative image related to die assembly
Pros: Steel alloys are durable and can be heat-treated to enhance their hardness, making them suitable for high-volume production. They are also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials.
Cons: However, steel alloys can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated, and their manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for precise machining and heat treatment.
Impact on Application: Steel alloys are compatible with various media, including oils and coolants used in machining processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific grades of steel in their regions.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Die Assembly?
Aluminum is another popular choice for die assembly, especially in industries where weight reduction is critical, such as automotive and aerospace.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. Its lower density compared to steel makes it an attractive option for applications requiring weight savings.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum has lower tensile strength than steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. It can also be more expensive than certain steel alloys.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various environments, including humid and corrosive settings, makes it suitable for diverse applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the aluminum grades meet local standards, such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe, and consider the implications of import tariffs on aluminum products.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Die Assembly?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred material in industries like food processing and medical devices.
Pros: Its durability and ability to withstand harsh environments make stainless steel an excellent choice for die assembly. It also offers good mechanical properties and can be polished for a high-quality finish.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to carbon steel and aluminum. Additionally, machining stainless steel can be more challenging due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including chemicals and food products, making it versatile for various applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with international standards like ISO and ASTM, particularly in industries with stringent hygiene requirements.
What About Composite Materials in Die Assembly?
Composite materials, such as reinforced plastics or metal matrix composites, are increasingly being explored for die assembly applications.
Pros: Composites can offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and can be tailored for specific applications. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be manufactured to precise specifications.
Cons: However, composites can be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes. Their long-term durability under high-stress conditions can also be a concern.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for applications where traditional materials may fail due to weight or corrosion issues.
Considerations for International Buyers: When sourcing composites, buyers should consider the availability of specific formulations and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material safety and performance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Die Assembly
| Material | Typical Use Case for die assembly | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Alloys | Automotive parts, tooling | High strength and durability | Corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium to High |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Composite Materials | Specialized applications | Tailored properties and lightweight | Higher cost and durability concerns | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials used in die assembly, ensuring informed decision-making tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for die assembly
What Are the Main Stages of the Die Assembly Manufacturing Process?
The die assembly manufacturing process is a multi-faceted operation that involves several critical stages. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and efficiency in their supply chains.
How is Material Prepared for Die Assembly?
The initial phase of the die assembly process begins with material preparation. Manufacturers typically select high-quality metals or alloys based on the product specifications. This selection impacts not only the durability of the final product but also the cost-effectiveness of the manufacturing process.
Once the materials are chosen, they undergo cutting, shearing, or blanking to create the necessary shapes and sizes required for assembly. This stage may also involve pre-treatments such as surface cleaning or coating to enhance adhesion and performance during the subsequent forming and assembly processes.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Die Assembly?
Forming is a critical stage in die assembly that shapes the prepared materials into the desired configurations. Techniques such as stamping, bending, and deep drawing are commonly employed. In-die assembly, which integrates stamping with assembly, is gaining traction due to its ability to streamline production while maintaining high precision.
The forming stage requires specialized dies that are tailored to the specific shapes and features of the components being produced. The design of these dies directly influences the efficiency and accuracy of the manufacturing process, making it essential for buyers to partner with manufacturers who specialize in customized die sets.
Illustrative image related to die assembly
How Does the Assembly Process Work in Die Manufacturing?
Once forming is complete, the assembly stage commences. This step may involve welding, riveting, or fastening components together, depending on the complexity of the final product. In-die assembly techniques can significantly reduce the time and labor required in this phase by combining multiple processes into a single operation.
Automation plays a pivotal role here, as computer-controlled systems can execute precise assembly tasks with minimal human intervention. This not only enhances efficiency but also reduces the margin for error, ensuring that the assembled components meet stringent quality standards.
What Finishing Processes Are Critical in Die Assembly?
After assembly, the finishing processes finalize the product for delivery. This may include surface treatments such as polishing, coating, or painting, designed to enhance appearance, corrosion resistance, and durability. Quality control checks are integral at this stage to ensure that the final product adheres to all specifications and standards before it is shipped.
How is Quality Assurance Maintained Throughout the Die Assembly Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in die assembly manufacturing, as even minor defects can lead to significant issues down the line. B2B buyers should be well-versed in the various international and industry-specific standards that govern quality control practices.
What International Quality Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
One of the most widely recognized quality management systems is ISO 9001, which sets the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). It emphasizes customer satisfaction, process efficiency, and continuous improvement, making it relevant for manufacturers across various sectors.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications may be essential for certain applications. For example, the CE mark is crucial for products sold in the European Economic Area, while API standards are vital for products in the oil and gas sector. Buyers from different regions should ensure that their suppliers comply with the relevant standards applicable to their specific industry and market.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Die Assembly?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the die assembly process to monitor and ensure product quality. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage inspects raw materials before they are used in production. It ensures that all materials meet required specifications, reducing the risk of defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and alignment to catch any deviations in real time.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the product is completed, FQC involves a thorough inspection to verify that it meets all specifications and quality standards before shipment.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Die Assembly Quality Control?
Various testing methods can be employed to verify product quality, including:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to ensure that components meet specified dimensions.
-
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or X-ray testing help identify internal defects without damaging the components.
-
Functional Testing: This assesses the performance of the assembled components to ensure they operate as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers is crucial for ensuring product reliability and performance. Here are some actionable steps to consider:
What Steps Can Buyers Take to Audit Supplier QC?
-
Request Documentation: Buyers should ask for copies of quality certifications, audit reports, and quality manuals. This documentation provides insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality practices.
-
Conduct On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe the quality control processes in action and assess the overall production environment.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices and product compliance.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Consider in QC?
International B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several nuances in quality control:
Illustrative image related to die assembly
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality expectations can help in effectively communicating requirements.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that affect product standards and quality assurance processes.
-
Supply Chain Considerations: Buyers should consider the entire supply chain and ensure that quality standards are upheld at every stage, from raw material sourcing to final assembly.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in die assembly is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly processes, finishing touches, and stringent quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions and establish strong partnerships with suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘die assembly’
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, sourcing die assembly services effectively is crucial for ensuring quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure die assembly, emphasizing key considerations throughout the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes details such as the type of materials, dimensions, tolerances, and production volume. Establishing these specifications helps in identifying suppliers that can meet your precise needs and ensures that the final products align with your quality standards.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in die assembly. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry and those that utilize advanced technologies. Key areas to explore include:
– Customer Reviews: Check online platforms for feedback from previous clients.
– Industry Certifications: Verify if they hold relevant certifications that demonstrate adherence to quality standards.
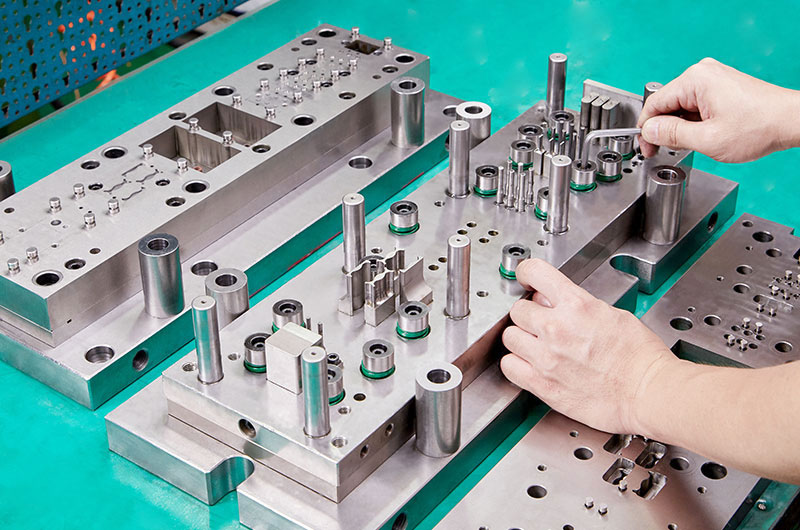
Illustrative image related to die assembly
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Expertise
Before committing, assess the experience and specialization of potential suppliers. Inquire about their history with die assembly and the specific industries they serve. A supplier with extensive experience is more likely to deliver consistent quality and innovative solutions tailored to your requirements.
Step 4: Verify Production Capabilities
It is essential to ensure that the supplier’s production capabilities align with your needs. Investigate their equipment, technology, and processes used in die assembly. Look for:
– In-Dye Assembly Techniques: Suppliers who offer in-die assembly can streamline production and reduce costs.
– Scalability: Ensure they can accommodate future volume increases without compromising quality.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing any agreements, request samples or prototypes of the components. This step allows you to evaluate the quality and precision of their work firsthand. During this phase, assess:
– Material Quality: Ensure that the materials used meet your specifications.
– Dimensional Accuracy: Check if the components adhere to the defined tolerances.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Pricing
Engage in discussions about lead times and pricing structures early in the process. Understanding the supplier’s timelines helps in planning your production schedule effectively. Additionally, clarify:
– Cost Breakdown: Request a detailed breakdown of costs to ensure there are no hidden fees.
– Negotiation Flexibility: Explore options for bulk discounts or long-term contracts.
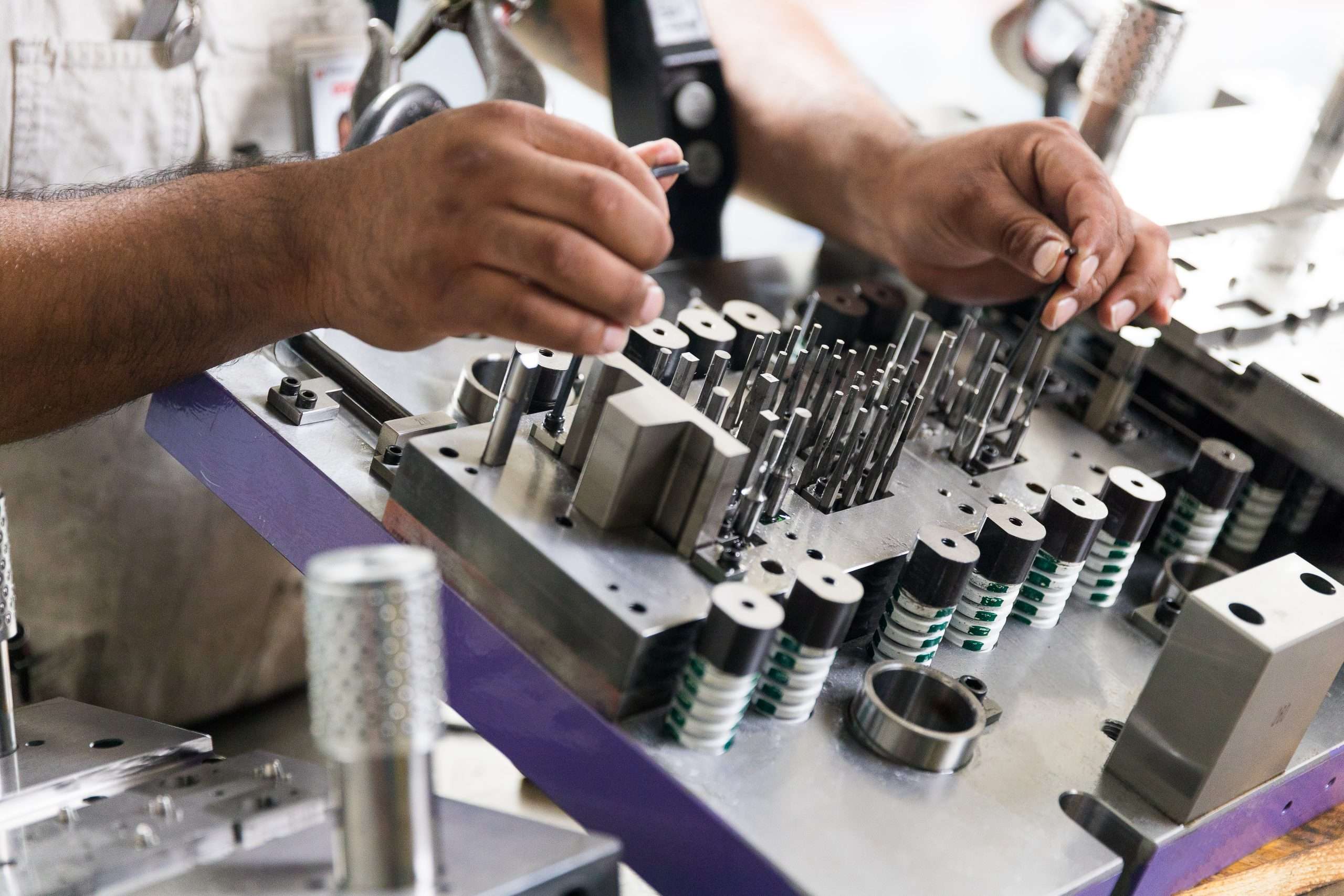

Illustrative image related to die assembly
Step 7: Establish Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance is critical in die assembly. Discuss the supplier’s quality control processes to ensure they meet your standards. Key aspects to consider include:
– Inspection Methods: Inquire about the methods used for quality checks during and after production.
– Defect Handling Procedures: Understand how the supplier addresses defects and manages rework or replacements.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for die assembly services, ensuring they partner with suppliers who meet their technical requirements and contribute to their operational success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for die assembly Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Die Assembly Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with die assembly, it’s essential to consider several key components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used in die assembly significantly impact costs. High-grade metals and specialty materials like stainless steel or aluminum alloys may incur higher prices due to their durability and performance characteristics.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers involved in the die assembly process. This includes machine operators, quality control inspectors, and engineers. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographical location, skill levels, and local labor market conditions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes, like in-die assembly, can help lower overhead by reducing the number of machines and associated operational costs.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling, including the design and creation of custom dies, is a significant expense. Custom tooling may require a higher upfront investment but can lead to cost savings in the long run by improving production efficiency and reducing scrap rates.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust quality control measures is crucial in die assembly to ensure product reliability. QC costs can include testing equipment, inspection processes, and any necessary certifications, which may vary depending on industry standards and regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation and storage costs for raw materials and finished products also play a crucial role in the overall cost structure. International shipping, tariffs, and customs duties can add considerable expenses, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of their services. Understanding the supplier’s margin can provide insight into pricing flexibility during negotiations.
What Influences Pricing in Die Assembly Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of die assembly services, which can vary significantly across regions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their projected volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs and specifications can increase costs. Buyers should balance their need for customization with the potential for higher pricing and longer lead times.
-
Material Choices: The choice of materials can greatly affect pricing. High-quality materials may incur higher initial costs but can offer better performance and longevity, impacting the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers offering certified quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) may charge a premium. However, these certifications often translate into better reliability and reduced risk of defects.
-
Supplier Factors: The experience and reputation of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can significantly affect overall costs. Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for managing logistics costs effectively.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Cost-Efficient Deals in Die Assembly?
To maximize cost-efficiency in die assembly sourcing, buyers should consider the following strategies:
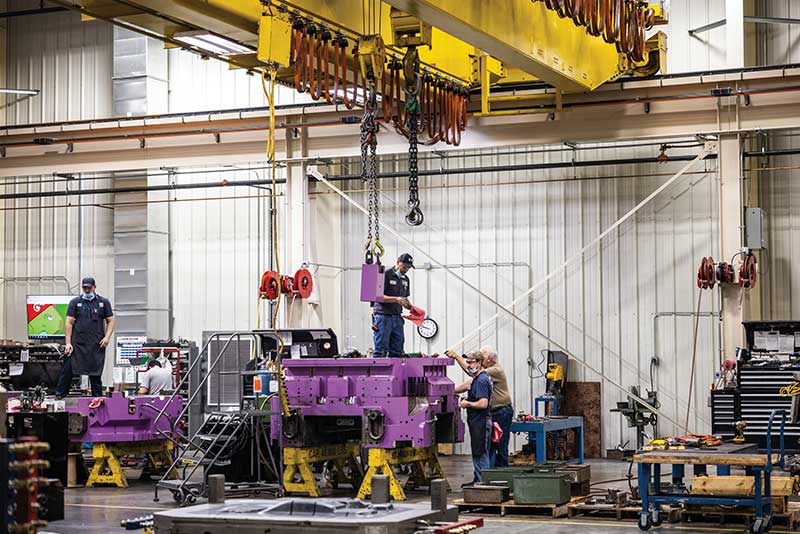

Illustrative image related to die assembly
-
Negotiate Pricing Based on Volume: Leverage projected order volumes to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for larger commitments.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial price but also the long-term implications of quality, durability, and maintenance costs. A slightly higher upfront price may lead to lower overall expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: International buyers must be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and trade regulations that can affect pricing. Engaging local expertise can provide valuable insights.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and increased flexibility in future negotiations.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers in die assembly sourcing can empower international B2B buyers to make informed decisions and secure favorable agreements. It’s essential to evaluate not just the price but the overall value offered by suppliers to optimize manufacturing processes effectively.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing die assembly With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Die Assembly in Manufacturing
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, businesses are continually seeking innovative solutions to enhance production efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. While die assembly has become a prominent method for achieving these goals, alternative solutions also exist that can cater to specific manufacturing needs. This analysis compares die assembly with two viable alternatives: traditional assembly line manufacturing and robotic assembly systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Die Assembly | Traditional Assembly Line | Robotic Assembly Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency with integrated steps | Moderate efficiency, sequential | High efficiency, adaptable |
| Cost | Lower capital and operational costs | Higher costs due to labor | High initial investment, but low operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized tooling and setup | Familiar process for many industries | Complex setup, requires programming expertise |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance due to fewer machines | Higher maintenance due to multiple machines | Moderate maintenance; requires regular software updates |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of complex parts | Low to medium volume production | Flexible production needs across various industries |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Traditional Assembly Line Manufacturing?
Traditional assembly line manufacturing involves a series of workstations where specific tasks are performed sequentially. This method is widely recognized for its simplicity and effectiveness in producing low to medium volumes of products.
Pros:
– Familiarity: Many workers are trained in this method, making implementation straightforward.
– Flexibility: Easily adaptable for various products without needing significant changes to the production line.
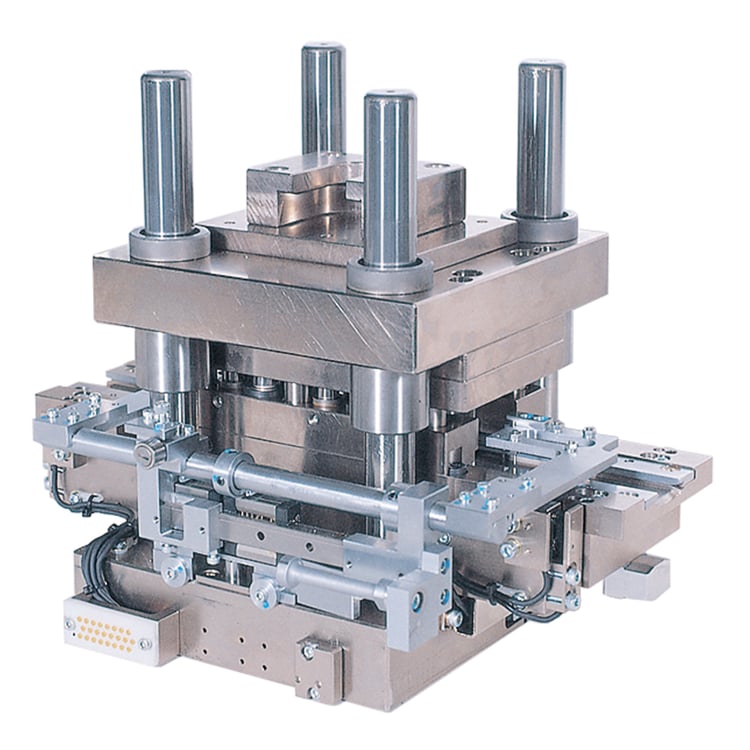
Illustrative image related to die assembly
Cons:
– Labor Costs: Higher operational costs due to the reliance on human labor.
– Production Speed: Slower than die assembly as each step is performed individually, which may affect overall efficiency.
How Do Robotic Assembly Systems Compare?
Robotic assembly systems employ automated robots to perform assembly tasks with precision and speed. These systems are increasingly being adopted across various industries due to their versatility and efficiency.
Pros:
– High Efficiency: Capable of operating continuously, significantly increasing production rates.
– Adaptability: Can be reprogrammed for different tasks, making them suitable for diverse manufacturing needs.
Cons:
– Initial Investment: Requires significant upfront capital for robotic systems and software development.
– Complexity: Implementation can be challenging, requiring skilled personnel for programming and maintenance.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting between die assembly and alternative solutions, B2B buyers must consider their specific manufacturing requirements. Factors such as production volume, product complexity, available budget, and workforce capabilities will influence the decision. Die assembly is an excellent choice for high-volume production of complex parts, while traditional assembly lines may suit businesses with lower volume needs. Robotic assembly systems are ideal for organizations looking for flexibility and high efficiency but should be approached with a readiness to invest in initial setup costs.
In conclusion, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for die assembly
What Are the Key Technical Properties Critical for Die Assembly?
When considering die assembly, understanding the technical properties that influence production efficiency and product quality is essential. Below are critical specifications that B2B buyers should focus on:
Material Grade
The material grade determines the strength, durability, and performance of the dies used in assembly processes. Common materials include A-36 steel for general applications and specialized alloys for high-stress environments. Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring the longevity of dies, which directly impacts production costs and output quality.
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In die assembly, tight tolerances are vital for ensuring that parts fit together correctly, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision is paramount. Understanding tolerance requirements helps manufacturers avoid costly reworks and ensures compliance with industry standards.
Die Set Configuration
The configuration of die sets—including base dimensions and pin lengths—affects how well the die performs during stamping and assembly operations. Custom die sets can be tailored to specific production needs, enhancing efficiency and reducing material waste. Proper configuration is essential for maximizing production output and minimizing downtime.
Press Capacity
The press capacity indicates the maximum force that a stamping press can exert during the die assembly process. It is a critical factor for determining the types of materials and thicknesses that can be processed. Understanding press capacity allows manufacturers to select appropriate machinery that meets production requirements without risking equipment failure.
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to complete one production cycle, including all operations from material feeding to quality control. Shorter cycle times improve overall productivity and reduce operational costs. B2B buyers should analyze cycle time to assess potential suppliers’ efficiency and their ability to meet high-volume demands.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand in Die Assembly?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can significantly enhance communication and negotiation with suppliers. Here are some essential terms:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components that are used in the final products of another company. In die assembly, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted partners who supply high-quality components that meet specific industry standards.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules and budget constraints.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services. In die assembly, issuing an RFQ enables buyers to compare multiple suppliers and ensure they are getting competitive pricing while meeting their technical requirements.
Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocation during the procurement process.
Lead Time
Lead time is the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. In die assembly, shorter lead times can significantly enhance a company’s responsiveness to market demands. Buyers should consider lead times when selecting suppliers to ensure timely project execution.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their manufacturing processes and foster successful partnerships in the die assembly industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the die assembly Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the Die Assembly Sector?
The die assembly sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving consumer demands. One of the primary global drivers is the increasing need for efficiency in manufacturing processes. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to optimize production, in-die assembly techniques are gaining traction. This method reduces the number of machines required, streamlining operations and cutting costs.
Emerging technologies, such as automation and the Internet of Things (IoT), are also reshaping sourcing trends. These innovations facilitate real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, allowing manufacturers to minimize downtime and enhance productivity. Additionally, the rise of Industry 4.0 is prompting companies to adopt smart manufacturing strategies, integrating robotics and AI into die assembly processes. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in competitive markets, where speed and adaptability can make or break a business.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate environmental responsibility, compelling manufacturers to adopt greener practices. This trend reflects a broader shift towards circular economies, where waste reduction and resource efficiency are paramount. As a result, international buyers must stay informed about these dynamics to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both operational goals and ethical standards.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Die Assembly Landscape?
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has prompted a reevaluation of sourcing strategies within the die assembly sector. As businesses face increasing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to adopt sustainable practices, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Suppliers that prioritize sustainability not only reduce their ecological footprint but also appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious buyers.
The use of ‘green’ certifications and materials is gaining importance in the industry. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and LEED for sustainable building practices are becoming key considerations for B2B buyers. These certifications signal a commitment to sustainable practices and can enhance a company’s reputation in the marketplace. Moreover, sourcing materials that are recyclable or made from sustainable resources can significantly reduce waste in die assembly processes.
Additionally, the shift towards ethical sourcing is reshaping supplier relationships. Buyers are increasingly seeking partners who share their values regarding social responsibility, fair labor practices, and community engagement. This focus on ethics not only fosters trust between businesses but also contributes to a more sustainable industry overall.
What Is the Historical Context of Die Assembly and Its Evolution?
Die assembly has evolved significantly over the decades, adapting to the changing landscape of manufacturing and technology. Traditionally, die assembly relied heavily on manual labor and simple machinery, which limited efficiency and scalability. As industries expanded in the mid-20th century, the demand for more complex and precise components grew, driving innovation in die technology.
The introduction of automated systems in the late 20th century marked a pivotal shift, allowing for greater precision and speed in production. In-die assembly techniques emerged as a solution to streamline operations, integrating multiple manufacturing steps into a single process. This evolution has continued into the 21st century, with the rise of smart manufacturing technologies further enhancing efficiency and quality control.
As the die assembly sector continues to evolve, it remains essential for B2B buyers to understand its historical context. This knowledge not only provides insight into current trends but also informs future sourcing strategies that align with technological advancements and market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of die assembly
-
How do I select the right supplier for die assembly?
Choosing the right supplier for die assembly involves evaluating several key factors. First, assess their experience and specialization in your specific industry, as this ensures they understand your unique requirements. Look for suppliers with a track record of high-quality production and modern technology. Additionally, consider their capacity for customization and responsiveness to your needs. Request client references and reviews to gain insight into their reliability and service quality. Lastly, ensure they comply with international quality standards, which is crucial for maintaining product integrity. -
What are the advantages of using in-die assembly in manufacturing?
In-die assembly offers significant advantages, particularly for high-volume production. By integrating multiple assembly processes into a single stamping operation, manufacturers can significantly reduce production time and costs. This method minimizes waste, lowers energy consumption, and requires less floor space due to fewer machines being needed. Moreover, the precision of computer-operated systems reduces the risk of human error, leading to improved product quality. Industries such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace particularly benefit from these efficiencies. -
What customization options are available for die assembly?
Customization in die assembly can vary widely based on the specific needs of your project. Suppliers typically offer tailored die designs to meet particular geometries, dimensions, and material requirements. Custom features may include specific tooling for complex shapes, unique material specifications, or integration with other manufacturing processes. When discussing your project with potential suppliers, clearly outline your requirements to explore all available options. A good supplier should be willing to collaborate with you to achieve the desired outcomes. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for die assembly services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for die assembly services can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as production complexity and material availability. Generally, suppliers may set MOQs to ensure economic viability for their operations. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production goals. Smaller businesses or those with unique requirements may find suppliers willing to accommodate lower MOQs, especially if they can demonstrate long-term potential for collaboration. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing die assembly?
Payment terms for die assembly services can vary by supplier and are often influenced by factors such as order size and the buyer-supplier relationship. Common practices include upfront deposits, progress payments, or full payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider payment methods that offer security, such as letters of credit or escrow services. Always clarify payment terms in advance and ensure they are documented in your contract to avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in die assembly?
To ensure quality assurance in die assembly, it’s essential to partner with suppliers who adhere to recognized quality management systems, such as ISO 9001. Ask about their quality control processes, including in-line inspections and final product testing. Many suppliers use advanced technologies like sensors and real-time monitoring to detect defects during production. Additionally, regular audits and performance reviews can help maintain quality standards. Establishing clear quality expectations in your contract will also support accountability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing die assembly internationally?
When sourcing die assembly services internationally, logistics play a crucial role in the supply chain. Key considerations include transportation methods, shipping times, customs regulations, and tariffs that may apply to your products. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide guidance on documentation and compliance. Additionally, consider the location of the supplier in relation to your operations to minimize lead times and shipping costs. Effective communication about logistics from the outset can streamline the process. -
How do I handle potential delays in the die assembly process?
Delays in the die assembly process can occur due to various factors, such as supply chain disruptions or equipment malfunctions. To manage potential delays, maintain open communication with your supplier to receive regular updates on production timelines. Establishing a buffer in your project schedule can also help accommodate unforeseen issues. Additionally, having contingency plans, such as alternative suppliers or methods, can mitigate the impact of delays. Building strong relationships with your suppliers can facilitate quicker resolutions when challenges arise.
Top 5 Die Assembly Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Metal Stamper – In-Die Assembly Solutions
Domain: metalstamper.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: In-die assembly integrates multiple assembly operations directly into the stamping process, streamlining production and reducing costs. It combines metal stamping, forming, and assembly in a single workflow, enhancing efficiency and minimizing waste. Key benefits include enhanced efficiency, cost reduction, and improved product quality. Industries that benefit from in-die assembly include automoti…
2. DMC Tools – WA23 Die Assembly
Domain: dmctools.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “WA23-2”, “description”: “WA23 Die Assembly – Gage 8, Go .130 & No-Go .136”, “price”: “$346.35”, “qualification”: “Mil-Spec/AS Qualified”, “crimp_applications”: “Machined Contacts”, “applicable_gage”: “G693”, “crimp_tool_type”: “Dies”, “NSN_associated_numbers”: [“5130001173889”, “5130011173889”, “414DA-8N”], “shipping_weight”: “1.25 lbs”}
3. Moeller Punch – Key Components of Metal Stamping Dies
Domain: moellerpunch.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Key components of metal stamping dies include: 1. Die Plates (Shoes, Sets) – Foundation for mounting other components, made from steel or aluminum. 2. Die Guide Pins and Bushings – Align upper and lower die plates, available as friction pins or ball-bearing pins. 3. Die Punches – Tools that press into metal sheets, available in various nose shapes and shank diameters. 4. Die Buttons – Counterparts…
4. Semi Engineering – Chiplet Solutions
Domain: semiengineering.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Multi-die assemblies, chiplet-based products, varying die dimensions (x, y, z), bump pitch challenges, need for standardized component handling and interfaces, interposers, bonding methods, packaging approaches, warpage management, thermal dissipation, mechanical stability, different foundries, manufacturing inconsistencies, new materials and process recipes, increased manufacturing steps, cost im…
5. Header – Complete Die Assembly Packages
Domain: header.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Complete die assembly packages include casings, inserts, fillers, sleeves, nuts, and more. Benefits include streamlined production, elimination of insert variances, extended tool life through seamless finishes, simplified purchasing with one vendor, and reduced costs over the tool’s life. Reloading dies reduces delivery times and is on average 30% less expensive than new dies.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for die assembly
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in Die Assembly?
In the competitive landscape of die assembly, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for success. By adopting in-die assembly techniques, manufacturers can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. This approach not only streamlines production but also minimizes waste, making it an essential consideration for companies aiming to meet high-volume demands across diverse industries such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace.

Illustrative image related to die assembly
How Can International Buyers Leverage Strategic Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of die assembly is crucial. Sourcing from experienced partners who specialize in modern technology and custom die sets can lead to superior quality and performance. As markets evolve, leveraging these strategic partnerships will be vital for maintaining a competitive edge.
What Should Buyers Do Next?
As you explore your sourcing options, prioritize companies with a proven track record in in-die assembly and advanced manufacturing capabilities. Engage with suppliers that align with your specific needs and can adapt to the dynamic requirements of your industry. The future of die assembly is bright, and those who invest in strategic sourcing today will be well-positioned to thrive in tomorrow’s market. Take the next step in enhancing your supply chain by identifying the right partners to drive innovation and efficiency in your production processes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.