Everything You Need to Know About Components Of A Conveyor System Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for components of a conveyor system
In the fast-paced world of global commerce, sourcing reliable components of a conveyor system can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The complexity of selecting the right parts—from belts and pulleys to motors and sensors—requires a comprehensive understanding of their functions, applications, and compatibility within various operational environments. This guide serves as an indispensable resource, equipping buyers with crucial insights into the types of components available, their specific applications across industries, and best practices for supplier vetting and cost management.
With a focus on diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key players like Germany and Vietnam, this guide aims to empower decision-makers by providing actionable strategies to navigate the competitive landscape of conveyor system components. Whether you’re looking to enhance efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, or ensure compliance with local standards, understanding the intricacies of conveyor systems is vital for maximizing operational effectiveness.
By delving into each component’s role and offering practical tips for procurement, this guide not only facilitates informed purchasing decisions but also enhances your ability to implement continuous improvement initiatives within your operations. Equip your organization with the knowledge necessary to thrive in the global market and make informed choices that drive success.
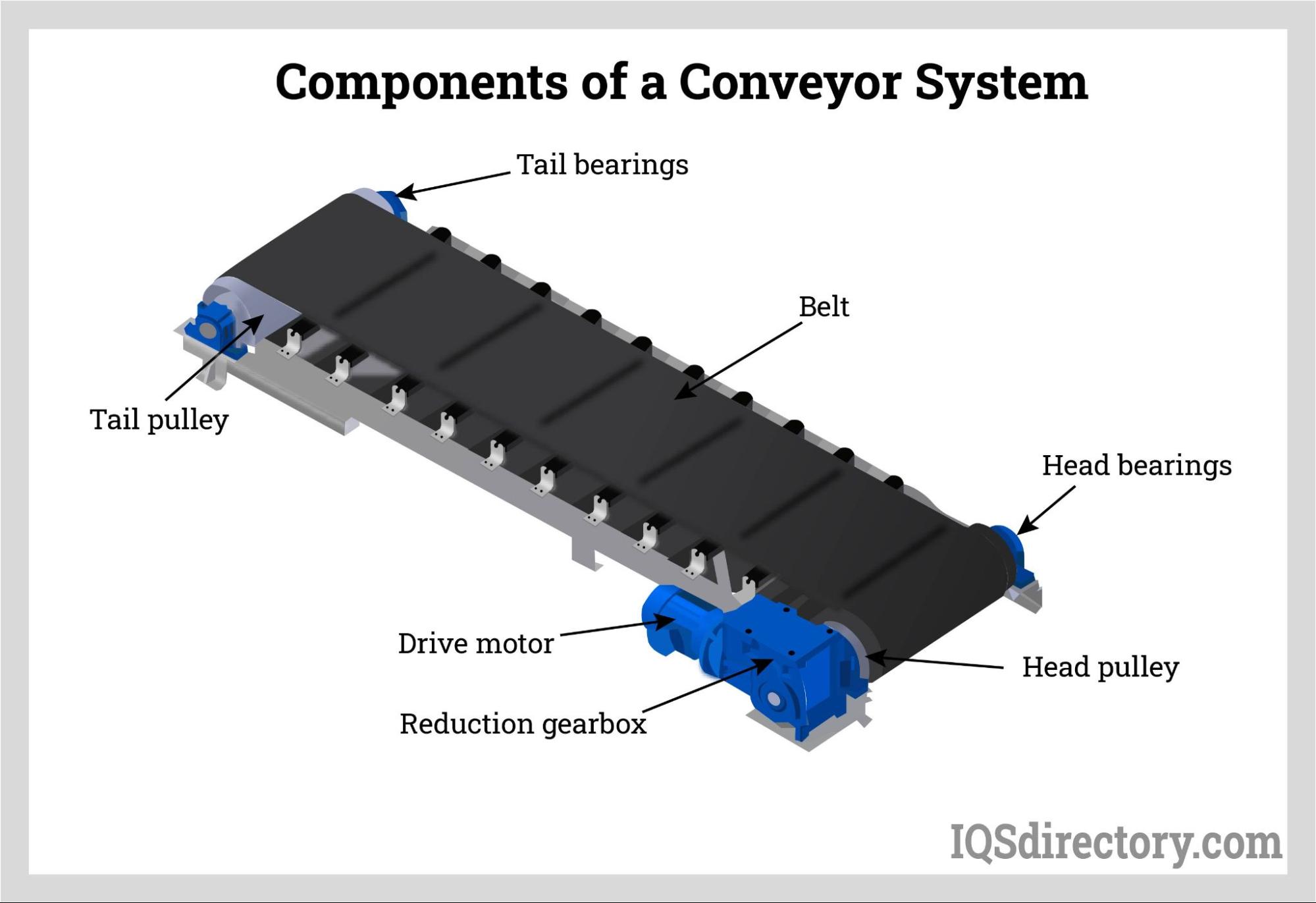
Understanding components of a conveyor system Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belt Conveyors | Continuous loop of flexible material; various materials available | Packaging, manufacturing, distribution | Pros: Versatile; suitable for diverse materials. Cons: Potential wear and tear on belts. |
| Roller Conveyors | Uses rollers to transport goods; gravity or powered | Warehousing, assembly lines | Pros: Low maintenance; efficient for heavy loads. Cons: Requires more space for installation. |
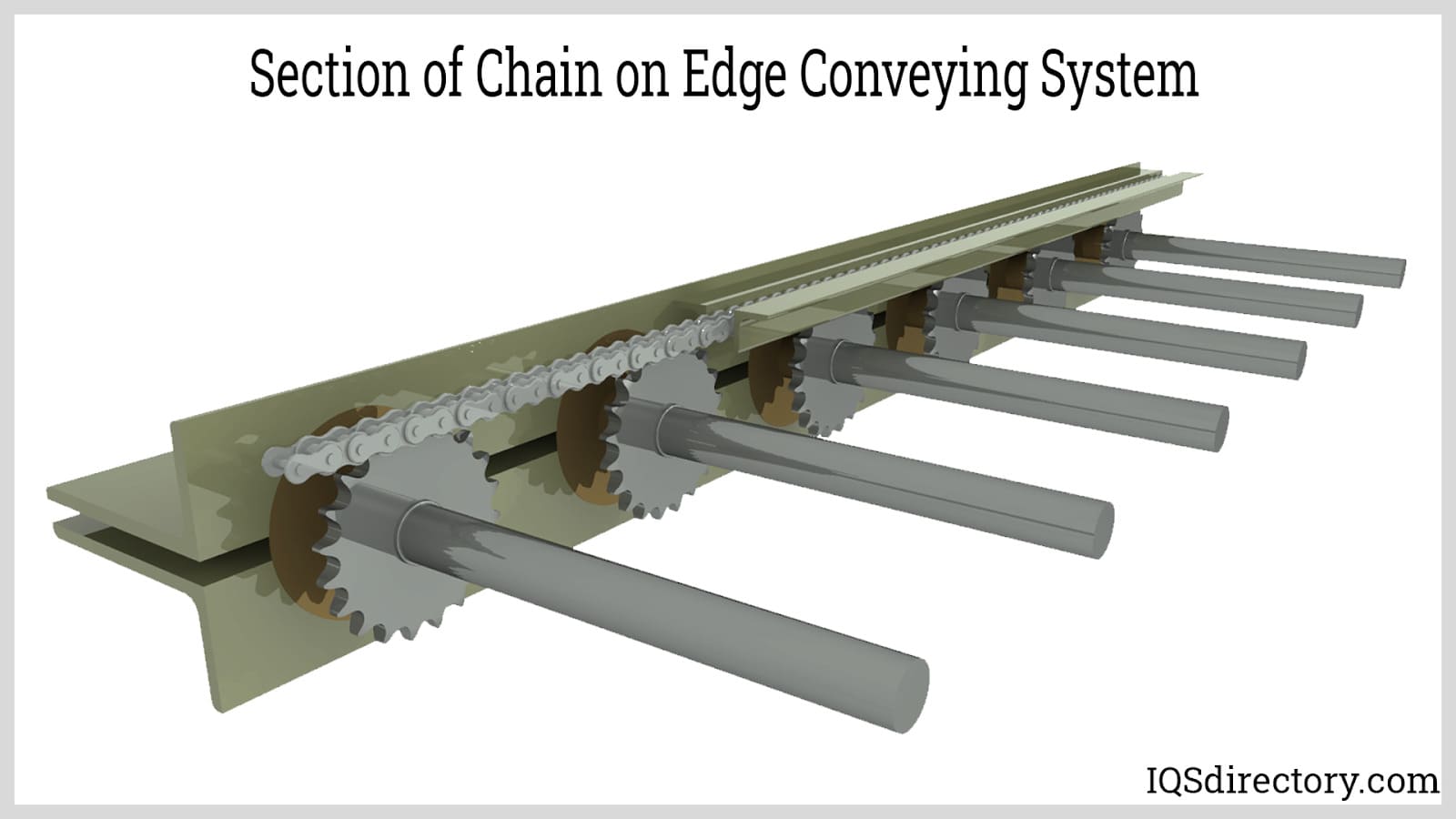
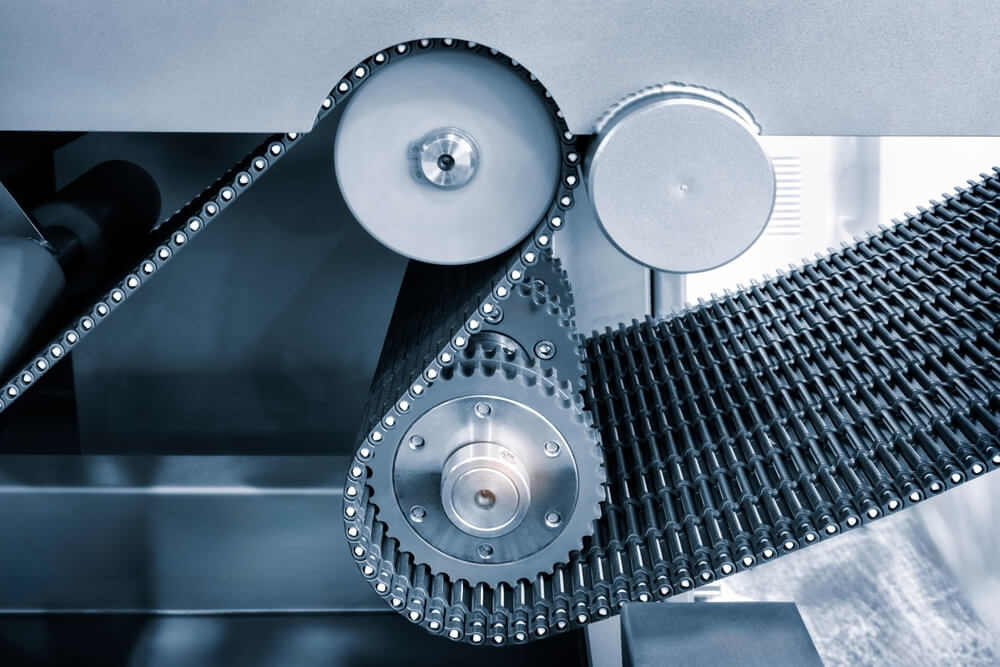
| Chain Conveyors | Utilizes chains for moving products; robust design | Heavy-duty applications, automotive | Pros: High durability; ideal for heavy items. Cons: Higher initial cost; limited flexibility. |
| Screw Conveyors | Helical screw mechanism for bulk materials | Agriculture, food processing | Pros: Effective for bulk handling; minimal spillage. Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
| Magnetic Conveyors | Incorporates magnets to move ferrous materials | Recycling, manufacturing | Pros: Secure handling of metal items; reduces slippage. Cons: Limited to magnetic materials only. |
What are the Characteristics of Belt Conveyors and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
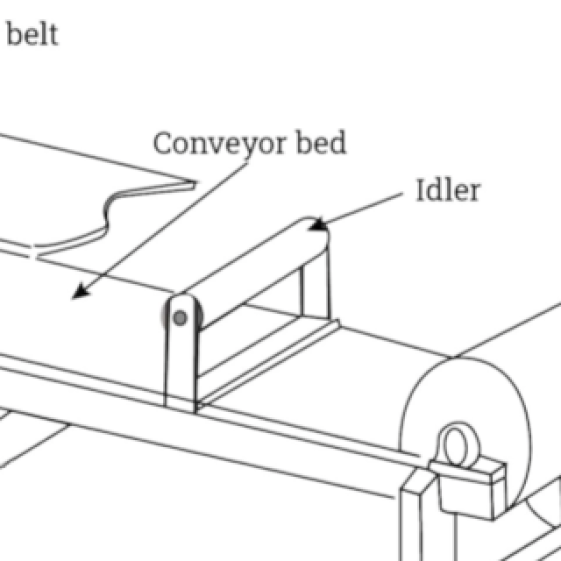
Belt conveyors are characterized by their continuous loop of flexible material, typically made from rubber or fabric, which is driven by pulleys. They are highly versatile, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from packaging to manufacturing. B2B buyers should consider the specific material handling requirements, such as weight, size, and environmental conditions, when selecting a belt conveyor. Additionally, understanding the maintenance needs and potential wear of belts is crucial for long-term operational efficiency.
How Do Roller Conveyors Function and What Are Their Key Benefits?
Roller conveyors transport goods by utilizing a series of rotating rollers, either powered or gravity-driven. They are particularly effective in warehousing and assembly line environments, where they facilitate the easy movement of heavy items. Buyers should evaluate the load capacity and space requirements of roller conveyors, as they may require more installation space compared to other conveyor types. Their low maintenance needs and efficiency in handling heavy loads are significant advantages for businesses looking to optimize their material flow.
What Makes Chain Conveyors Ideal for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Chain conveyors are designed with robust chains that provide the necessary strength for transporting heavy products. They are commonly used in heavy-duty applications such as automotive manufacturing and bulk material handling. When considering chain conveyors, B2B buyers should assess the specific load requirements and the environment in which the conveyor will operate. While they offer exceptional durability, the higher initial costs and limited flexibility for lighter items may be drawbacks for some buyers.
Why Choose Screw Conveyors for Bulk Material Handling?
Screw conveyors utilize a helical screw mechanism to efficiently transport bulk materials, making them ideal for industries like agriculture and food processing. Their design minimizes spillage and is highly effective for handling granular or powdery materials. Buyers should consider the types of materials being transported and the specific application requirements when selecting a screw conveyor. While they are excellent for bulk handling, their application may be limited to specific material types.
What Are the Advantages of Magnetic Conveyors in Material Handling?
Magnetic conveyors utilize magnets to securely transport ferrous materials, making them particularly useful in recycling and manufacturing settings. Their ability to reduce slippage and ensure secure handling of metal items is a key benefit. B2B buyers should evaluate whether their material types are compatible with magnetic conveyors, as this system is limited to magnetic materials. The enhanced safety and efficiency in handling metal products can significantly improve operational workflows for businesses that rely on such materials.
Key Industrial Applications of components of a conveyor system
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of components of a conveyor system | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Automated packaging lines using conveyor belts | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs in packaging | Ensure compliance with food safety standards; select durable materials that resist contamination. |
| Manufacturing | Assembly line conveyor systems | Streamlines production processes and minimizes bottlenecks | Focus on modular designs for flexibility; evaluate motor power for specific load requirements. |
| Mining and Minerals | Bulk material handling with heavy-duty conveyors | Enhances material transport efficiency and reduces manual labor | Consider the environmental conditions; choose robust components to withstand harsh environments. |
| Warehousing and Logistics | Order fulfillment systems with roller conveyors | Improves order accuracy and speeds up shipping processes | Assess space constraints and scalability; prioritize ease of maintenance and component availability. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Conveyor systems for drug packaging and distribution | Ensures precision in handling sensitive materials and compliance | Look for high-quality sensors and controls; focus on systems that support traceability and validation. |
How Are Components of a Conveyor System Used in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, conveyor systems are vital for automating packaging lines. These systems utilize durable conveyor belts and rollers to transport products from production to packaging. This automation reduces labor costs and improves efficiency while ensuring compliance with stringent food safety regulations. Buyers should prioritize sourcing components that are made from food-grade materials and are easy to clean, as hygiene is paramount in this industry.
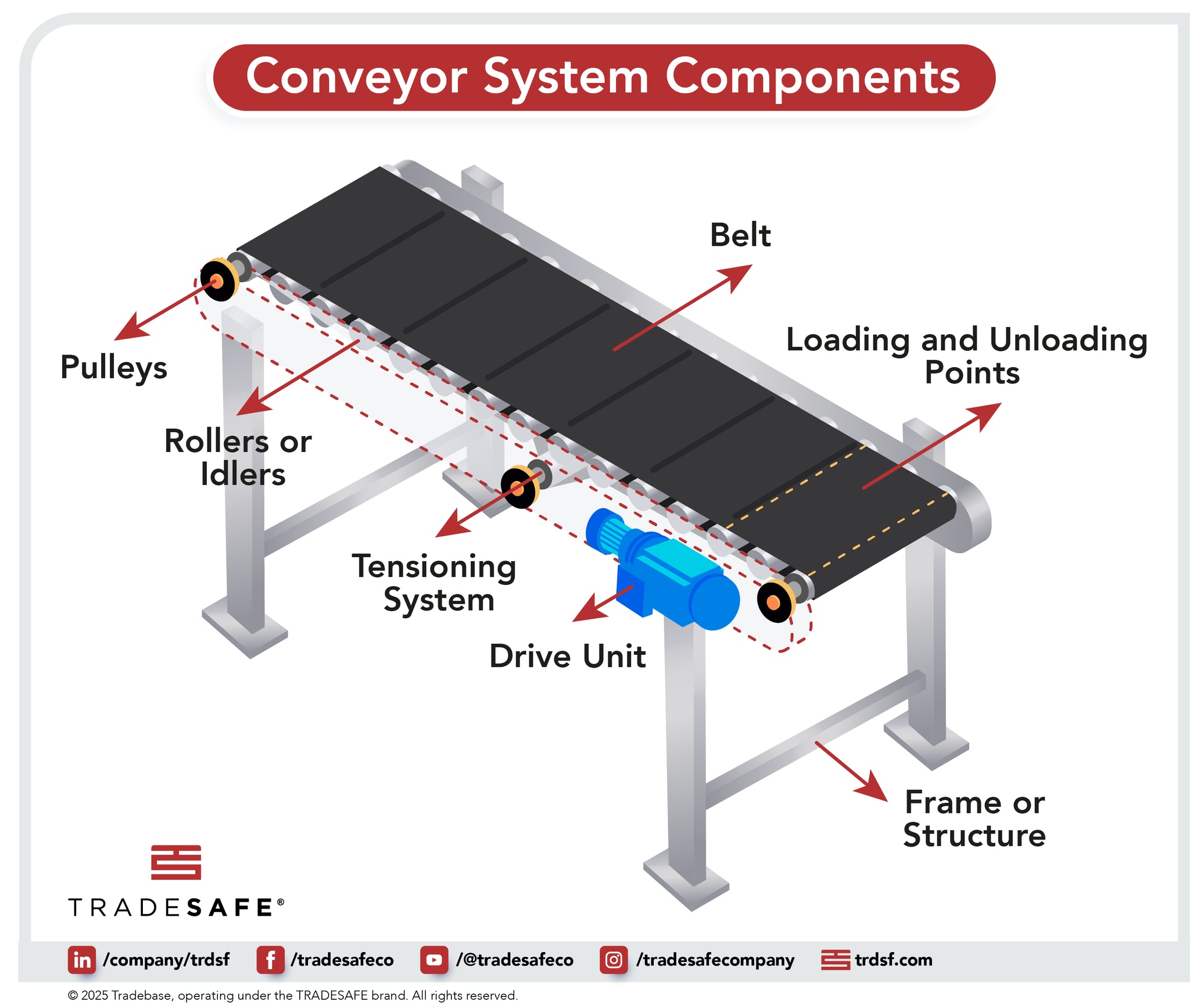
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
What Role Do Conveyor Systems Play in Manufacturing?
Manufacturing industries leverage conveyor systems to create streamlined assembly lines. These systems facilitate the smooth flow of materials, minimizing bottlenecks and enhancing overall productivity. Buyers in this sector should focus on modular conveyor designs that can be easily adjusted to accommodate different production needs. Additionally, the selection of motors must align with the specific load requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Why Are Conveyor Systems Critical for Mining and Minerals?
In the mining and minerals sector, conveyor systems are essential for transporting bulk materials efficiently. Heavy-duty conveyors are designed to handle large volumes of material, reducing the need for manual labor and enhancing operational efficiency. International buyers should consider the environmental conditions—such as dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures—when sourcing components. Robust materials and designs are crucial to ensure long-lasting performance in harsh mining environments.
How Do Conveyor Systems Enhance Warehousing and Logistics?
In warehousing and logistics, conveyor systems, particularly roller conveyors, are utilized for order fulfillment. These systems automate the movement of products, improving order accuracy and expediting shipping processes. Buyers should assess their specific space constraints and scalability needs when sourcing conveyor systems. Emphasis should be placed on components that allow for easy maintenance and quick repairs to minimize downtime.
What Are the Benefits of Conveyor Systems in Pharmaceuticals?
Conveyor systems in the pharmaceutical industry are crucial for the packaging and distribution of drugs. These systems ensure precise handling of sensitive materials while maintaining compliance with industry regulations. Buyers should look for high-quality sensors and control systems that enhance traceability and validation processes. Additionally, components must be made from materials that can withstand sterilization processes to ensure product safety and integrity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘components of a conveyor system’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Frequent Downtime Due to Conveyor Belt Failures
The Problem: A common issue faced by B2B buyers is the frequent downtime caused by conveyor belt failures. These failures can stem from various factors, including wear and tear, improper installation, or inadequate maintenance. For companies relying on conveyors for material handling, such interruptions can lead to significant productivity losses and increased operational costs. Additionally, the complexity of diagnosing the root cause of belt issues can lead to prolonged downtimes, affecting the entire supply chain.
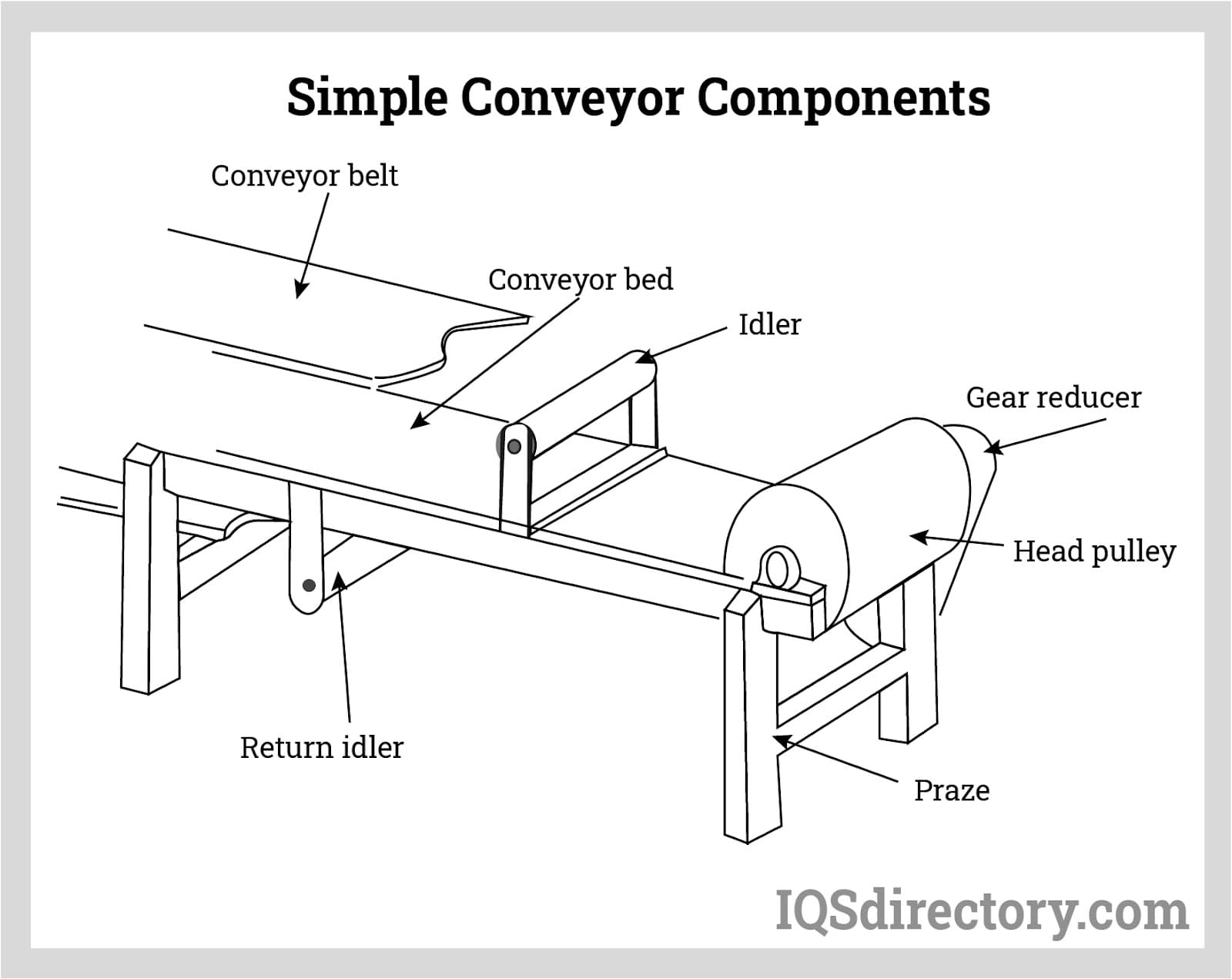
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
The Solution: To mitigate belt failures, buyers should prioritize selecting high-quality conveyor belts tailored to their specific operational needs. When sourcing belts, it’s essential to consider factors such as load capacity, material compatibility, and environmental conditions (e.g., moisture, temperature). Implementing a regular maintenance schedule is crucial; this includes routine inspections for signs of wear, splicing repairs, and tension adjustments. Buyers should also invest in training for their maintenance teams to ensure they can effectively identify and address potential issues before they lead to significant failures. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive warranties and support can also provide peace of mind, as they may assist in troubleshooting and replacement.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Material Flow Due to Poor Roller Functionality
The Problem: Another prevalent pain point is inefficient material flow resulting from malfunctioning rollers. Rollers can become jammed or fail to rotate, disrupting the continuous movement of products and leading to bottlenecks. This scenario not only hampers operational efficiency but can also increase labor costs as employees are pulled away from their primary tasks to address these disruptions. Moreover, an inefficient conveyor system can lead to misaligned products and increased waste.
The Solution: To enhance roller functionality, buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality rollers designed for their specific application. It’s essential to choose the correct type of roller (e.g., motorized drive rollers, gravity rollers) based on the materials being transported and the overall conveyor design. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for debris accumulation, damaged O-rings, or misalignment that can hinder roller performance. Implementing predictive maintenance strategies, such as vibration analysis and temperature monitoring, can help identify potential roller issues before they escalate. Establishing a relationship with a reliable supplier who can provide timely replacement parts and technical support can also aid in maintaining optimal conveyor performance.
Scenario 3: Safety Hazards from Inadequate Guardrails and Supports
The Problem: Safety hazards due to inadequate guardrails and supports present a significant challenge for many organizations. In environments where heavy materials are being transported, the absence of proper guardrails can lead to accidents, causing injuries to personnel and damage to equipment. Additionally, insufficient supports can compromise the structural integrity of the conveyor system, leading to potential failures and costly repairs. These risks not only threaten the well-being of employees but can also result in legal liabilities and increased insurance costs.
The Solution: To address safety concerns, it’s critical for buyers to invest in robust guardrails and supports that meet industry safety standards. When selecting guardrails, it’s important to consider the height, material, and configuration that best suits the operational environment. Regular audits should be conducted to ensure that guardrails are properly installed and maintained, with any damaged sections promptly replaced. For supports, buyers should assess load capacities and ensure they are appropriately designed to handle the weight of both the conveyor system and the materials being transported. Furthermore, implementing safety training programs for employees on the importance of using guardrails and adhering to safety protocols can foster a culture of safety and awareness within the organization.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for components of a conveyor system
When selecting materials for components of a conveyor system, it is essential to consider the specific properties and applications of each material. This analysis focuses on four common materials: steel, plastic, rubber, and aluminum. Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and longevity of conveyor systems.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Conveyor Components?
Steel is a widely used material in conveyor systems due to its strength and durability. It offers high tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel components can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for environments where heavy loads are transported. Additionally, steel has good corrosion resistance when treated or coated, which is crucial for applications in humid or corrosive environments.
Pros: Steel components are extremely durable and can handle significant wear and tear. They are also relatively cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing.
Cons: However, steel is heavier than other materials, which can increase transportation costs. It may also require additional maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, especially in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used for structural components like frames and supports, where strength is paramount.
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial, especially for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. Buyers should also consider local regulations regarding material treatment and corrosion protection.
How Does Plastic Compare for Conveyor System Components?
Plastic is increasingly popular in conveyor systems due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. Common types include polyethylene and polypropylene, which can handle a variety of temperatures and are resistant to many chemicals. Plastic components are also quieter in operation and can be molded into complex shapes, providing flexibility in design.
Pros: The primary advantages of plastic include its low weight, resistance to corrosion, and ease of manufacturing.
Cons: However, plastics may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can be less durable than metals, leading to potential wear issues over time.
Impact on Application: Plastic is commonly used for rollers and modular belt systems, where flexibility and ease of installation are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic materials meet relevant standards, such as ISO or JIS, particularly in regions like Asia and Europe, where compliance is strictly monitored.
What Role Does Rubber Play in Conveyor Systems?
Rubber is a versatile material commonly used for conveyor belts and other components due to its excellent elasticity and grip. It can withstand a range of temperatures and is resistant to abrasion, making it suitable for various material handling applications. Rubber can also be formulated to enhance specific properties, such as oil resistance or anti-static capabilities.
Pros: The key advantages of rubber include its durability, flexibility, and ability to absorb shock, which helps in reducing wear on other components.
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
Cons: However, rubber can degrade over time when exposed to UV light and certain chemicals, necessitating regular inspections and replacements.
Impact on Application: Rubber is primarily used in conveyor belts and as a lining material for components that come into contact with abrasive materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that rubber materials comply with international standards for safety and performance, particularly in industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals.

Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
Why Is Aluminum a Preferred Material for Some Conveyor Components?
Aluminum is known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making it an excellent choice for conveyor frames and supports. It is easy to machine and can be anodized for additional protection against corrosion. Aluminum also has a good strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for efficient designs that do not compromise structural integrity.
Pros: The primary benefits of aluminum include its lightweight nature, resistance to corrosion, and ease of fabrication.
Cons: On the downside, aluminum is generally more expensive than steel, and its strength is lower, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as portable conveyor systems or in environments where corrosion is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN is essential, particularly for buyers in Europe, where material specifications are strictly enforced.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for components of a conveyor system | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, frames, and supports | High strength and durability | Heavier, potential for corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Rollers and modular belt systems | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable at high temperatures | Low |
| Rubber | Conveyor belts and lining materials | Excellent elasticity and grip | Degrades under UV and certain chemicals | Medium |
| Aluminum | Frames and supports in lightweight applications | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, lower strength | High |
This guide aims to provide B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for conveyor system components, ensuring that they make informed choices that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for components of a conveyor system
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Conveyor System Components?
The manufacturing of conveyor system components involves a systematic approach that ensures the final products meet industry standards for durability and performance. The process can be broken down into four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Conveyor Components?
Material preparation is the foundational stage where raw materials are sourced and prepped for production. Common materials used in conveyor systems include various grades of steel, rubber, and plastics. The quality of these materials directly affects the performance and longevity of the components.
In this stage, manufacturers conduct thorough inspections of incoming materials to ensure compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001. This includes verifying certifications and material specifications to avoid defects that could lead to failures in the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Conveyor Components?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves shaping the materials into their required forms through various techniques such as:
- Machining: Precision machining is used to create components like pulleys and gearboxes, ensuring tight tolerances and surface finishes.
- Injection Molding: For plastic components, this method allows for efficient mass production while maintaining consistency.
- Welding: Steel parts are often welded together to form the structural components of conveyor systems, ensuring strength and stability.
Each technique must adhere to specific parameters to ensure that the formed components are fit for purpose and can withstand operational stresses.
How Are Conveyor Components Assembled?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form a complete unit. This process typically involves:
- Integration of Sub-Assemblies: Components such as motors, belts, and rollers are assembled into the main conveyor framework.
- Alignment and Calibration: Proper alignment is crucial to prevent operational issues. This may involve adjusting the tension in belts and ensuring that rollers rotate freely.
- Installation of Safety Features: Components like guardrails and brakes are added to enhance the safety and reliability of the conveyor system.
Efficient assembly processes are critical, as they directly impact the speed of production and the overall quality of the finished product.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Quality Conveyor Components?
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the durability and aesthetics of the components. This may include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as powder coating or galvanization protect metal parts from corrosion and wear.
- Quality Inspections: Before final products are packaged, they undergo inspections to ensure they meet specified quality standards and customer requirements.
Finishing processes not only improve the lifespan of components but also enhance their visual appeal, which can be crucial for client satisfaction.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Conveyor Components?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for B2B buyers who rely on the reliability of conveyor systems in their operations. Key international standards and industry-specific certifications include:
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
- ISO 9001: This globally recognized standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Particularly important for European markets, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API (American Petroleum Institute): Relevant for components used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring that products meet stringent safety and performance criteria.
Understanding these standards is essential for B2B buyers to ensure they are partnering with reputable manufacturers.
What Are the QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks at various stages of production to identify defects early and ensure product integrity. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch issues in real-time. This could involve checking tolerances during machining or ensuring proper assembly techniques are followed.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the completed products before they are shipped. This may include functional testing, dimensional checks, and visual inspections to ensure all components meet quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality assurance practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into a manufacturer’s processes, quality control measures, and adherence to standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers assess a supplier’s performance over time, including defect rates and compliance with standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer unbiased evaluations of the manufacturer’s quality control processes and final products.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances when dealing with QC and certification. Different countries may have varying standards for quality and safety, which can affect the import and use of conveyor components.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the products meet local regulations in the destination country, which may differ from the manufacturer’s home country.
- Documentation: Buyers should ensure that all necessary documentation, including certifications and test results, is provided and is up to date.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the business culture of suppliers can also play a role in ensuring compliance with quality standards, as expectations may vary significantly across regions.
By being informed about the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices relevant to conveyor system components, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable partners that meet their operational needs.
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘components of a conveyor system’
In the competitive landscape of material handling, procuring the right components for a conveyor system is vital for operational efficiency and productivity. This guide provides a practical checklist for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Follow these steps to ensure a successful procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes identifying the types of materials to be handled, load capacities, and specific environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity). Understanding your needs will help streamline your search for components that meet your operational demands.
- Consider the conveyor type: Is it belt-driven, roller-based, or modular?
- Specify dimensions and weight limits: Ensure the components can support your operational flow.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on suppliers who specialize in conveyor components. Look for companies with a solid track record and experience in your industry. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for future negotiations and partnerships.
- Utilize online directories and industry forums: Engage with communities that discuss best practices and supplier recommendations.
- Check for reviews and testimonials: Seek feedback from existing customers to gauge reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant industry certifications and quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management, which is essential for ensuring the reliability of conveyor components.
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of certifications and compliance reports.
- Inquire about manufacturing processes: Understanding their production methods can give insights into quality control.
Step 4: Assess Product Compatibility
Ensure that the components you are considering are compatible with your existing systems. This involves checking specifications such as size, material type, and operational capabilities. Mismatched components can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs.
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
- Request technical datasheets: These documents provide detailed information about dimensions and performance.
- Consult with engineers: Involve technical staff to validate compatibility.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure the best pricing and terms. Be transparent about your budget and seek flexibility in payment options or bulk discounts. Effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings.
- Consider total cost of ownership: Evaluate not just the initial price but also maintenance and operational costs over time.
- Discuss warranty and service agreements: Ensure that you understand the terms for support and replacements.
Step 6: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before finalizing any purchase, ask for samples or prototypes of the components. Testing these products in your operational environment can reveal critical performance insights and highlight any potential issues.
- Conduct a pilot test: Assess how well the components integrate with your system.
- Gather feedback from operators: Their insights can be invaluable in identifying usability or functionality issues.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Monitor Delivery
Once satisfied with the product and terms, place your order. It’s essential to establish clear communication regarding delivery timelines and logistics. Monitoring this process can help mitigate any unexpected delays.
- Confirm shipping arrangements: Ensure that the delivery method aligns with your operational schedule.
- Set up a tracking system: This can help you stay informed about the shipment status and any potential issues.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing conveyor system components, ensuring they select the right products that enhance productivity and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for components of a conveyor system Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of conveyor system components is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will provide insights into the various cost components, price influencers, and strategic tips for effective sourcing.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Conveyor System Components?
The cost structure for conveyor system components typically includes several key elements:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Common materials such as rubber, steel, and plastic vary in price based on quality and sourcing location. For instance, high-quality rubber for conveyor belts may be more expensive but offers longer durability, reducing long-term costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the region and local wage standards. Countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but quality may vary. It’s essential to evaluate the trade-off between labor costs and the quality of workmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, thereby impacting the overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specific tooling, which can add to upfront costs. However, investing in appropriate tooling can enhance production efficiency and lead to better quality products.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability but can also contribute to higher costs. Buyers should weigh the importance of quality against potential savings.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary dramatically based on distance, mode of transport, and the complexity of delivery. Understanding logistics costs is essential, especially for international buyers who may face customs duties and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and perceived value of their offerings.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Conveyor Component Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of conveyor system components:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom components tailored to specific applications typically carry a premium. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Components that meet international quality standards or possess certifications may be priced higher. While this can increase upfront costs, it often leads to lower total costs of ownership due to reduced failures and maintenance needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants might offer lower prices to penetrate the market.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect total landed costs and should be negotiated upfront.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Conveyor Component Costs?
To maximize value and minimize costs when sourcing conveyor system components, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or better payment terms to secure a deal.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, energy consumption, and lifespan to make informed decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand regional pricing variations and be aware of any additional costs that may arise from customs or import duties. Collaborate with local experts to navigate these complexities effectively.
-
Supplier Audits: Regularly evaluate suppliers to ensure they meet quality and performance standards. This proactive approach can prevent costly disruptions in the supply chain.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics of conveyor system components empowers international buyers to make informed decisions. By considering these insights and strategies, businesses can enhance their sourcing efficiency and optimize their operational costs. Always remember that prices may vary significantly based on specific circumstances, and it’s advisable to seek multiple quotes for accurate comparisons.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing components of a conveyor system With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Conveyor System Components
In the realm of material handling, conveyor systems are pivotal for efficient transport and processing of goods. However, businesses often seek alternative solutions that may offer unique benefits or align better with specific operational needs. This analysis compares the traditional components of a conveyor system with two viable alternatives: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Overhead Conveyor Systems. Each option presents distinct advantages and disadvantages that can significantly influence a buyer’s decision.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Components of a Conveyor System | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Overhead Conveyor Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High throughput; reliable for continuous flow | Flexible routing; adaptable to various layouts | Efficient for high-density areas; minimizes floor space |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Higher upfront investment; lower operational costs over time | Initial costs can be high; long-term savings on labor |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires careful planning and installation | Quick deployment; less structural modification needed | Complex installation; needs infrastructure adjustments |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required; parts can wear out | Low maintenance; automated diagnostics available | Moderate maintenance; can be labor-intensive |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for high-volume, linear transport | Suited for dynamic environments with variable paths | Best for assembly lines and areas with limited floor space |
Analyzing Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) offer a flexible alternative to traditional conveyor systems. They are equipped with sensors and navigation technology, allowing them to transport materials autonomously throughout a facility. One of the primary advantages of AGVs is their adaptability; they can easily navigate around obstacles and change routes as needed, making them suitable for environments with frequent layout changes. However, the initial investment for AGVs is typically higher than that of conveyor systems, although they can reduce labor costs over time. Maintenance is generally low, as many AGVs come with self-diagnostic features, but they may require periodic software updates and battery replacements.
Exploring Overhead Conveyor Systems
Overhead conveyor systems utilize a network of tracks suspended from the ceiling to transport goods. This method is particularly advantageous in facilities where floor space is limited, as it keeps pathways clear and maximizes the use of vertical space. Overhead systems can handle a variety of items and are often used in manufacturing and assembly applications. However, they usually entail a complex installation process that may require significant modifications to existing infrastructure. While the initial costs can be substantial, these systems can lead to long-term savings by reducing labor needs and increasing efficiency. Maintenance can be moderate, as components may require regular inspection to ensure smooth operation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the best solution for material handling, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the specific operational needs, facility layout, and budget constraints. Conveyor systems are ideal for high-volume, linear processes, while AGVs provide flexibility for dynamic environments. Overhead conveyor systems excel in space-limited facilities but may require significant upfront investment. By evaluating performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and the best use case for each option, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance overall efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for components of a conveyor system
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Conveyor System Components?
Understanding the essential technical properties of conveyor system components is crucial for B2B buyers. These specifications not only influence the performance and reliability of the conveyor systems but also affect maintenance costs and operational efficiency. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of conveyor components, such as belts, rollers, and pulleys, determines their strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. Common materials include rubber, steel, and plastic. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring that the conveyor can handle the specific loads and conditions of the operating environment, such as temperature extremes or exposure to chemicals.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions and manufacturing processes of conveyor components. For instance, the tolerance in roller diameter can impact how smoothly the belt runs. Tight tolerances are essential for high-speed applications where precision is key, while looser tolerances may suffice for less demanding tasks. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers ensure compatibility and performance stability.
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
3. Load Capacity
Load capacity specifies the maximum weight a conveyor can handle at any given time. This property is critical for applications in industries such as mining, food processing, and logistics, where heavy materials are common. B2B buyers must assess their operational requirements to select components that can accommodate peak loads without compromising safety or efficiency.
4. Speed Rating
Speed rating indicates the maximum operational speed of conveyor belts and rollers. Different applications may require varying speeds; for example, sorting systems might need faster speeds compared to bulk material handling. Knowing the speed rating is essential for optimizing throughput and ensuring that the system aligns with production schedules.
5. Power Rating
The power rating of motors used in conveyor systems defines the amount of energy they consume and their efficiency. Motors can vary in horsepower and voltage, affecting their ability to drive the conveyor under different load conditions. Buyers should evaluate power ratings to ensure that the motor meets the operational demands while minimizing energy consumption.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Conveyor Systems?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and decision-making in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms used in the conveyor system industry:
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the conveyor industry, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure they are sourcing quality components that meet specific standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their procurement strategies to avoid overstocking or stockouts.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the context of conveyor systems, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping agreements. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs clearance. Proper knowledge of Incoterms helps prevent disputes and ensures smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the products. In the conveyor system industry, lead times can vary significantly based on the complexity of the components and the supplier’s production capabilities. Awareness of lead times allows buyers to plan their projects effectively and avoid delays in operations.

Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency and reliability of their conveyor systems, ultimately leading to improved operational performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the components of a conveyor system Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Impacting the Components of a Conveyor System?
The conveyor system components market is experiencing significant evolution driven by globalization, technological advancements, and changing consumer demands. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are navigating a landscape shaped by the need for automation and efficiency. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is revolutionizing how conveyor systems are designed and operated. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced operational efficiency, which are essential for meeting the demands of modern supply chains.
Emerging trends include a shift towards modular conveyor systems that offer flexibility and scalability. These systems allow businesses to adapt quickly to changing production needs without significant capital investment. Additionally, there is a growing focus on energy-efficient components, which not only reduce operational costs but also align with global sustainability goals. As more companies prioritize automation and efficiency, the demand for advanced components such as smart motors and automated control systems is likely to rise.
Moreover, the market is witnessing a surge in e-commerce and logistics operations, particularly in developing regions. This trend is driving investments in conveyor systems that can handle diverse materials and complex workflows. For international buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions and securing competitive advantages in their respective markets.
Illustrative image related to components of a conveyor system
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Conveyor System Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor in the sourcing of conveyor system components. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and disposing of these components. As a result, companies are prioritizing ethical sourcing practices that minimize ecological footprints and promote social responsibility.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are looking for suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and ensuring fair labor conditions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are becoming critical benchmarks for assessing supplier sustainability credentials.
Additionally, the use of eco-friendly materials in conveyor components, such as biodegradable plastics and energy-efficient motors, is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce the environmental impact but also enhance the overall efficiency of conveyor systems. As regulations surrounding environmental impact tighten globally, B2B buyers must consider sustainability as a key criterion in their sourcing strategies, ensuring that their supply chains are resilient and compliant with emerging standards.
What Is the Historical Context of Conveyor System Components in B2B Markets?
The evolution of conveyor system components can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, which laid the groundwork for mechanized material handling. Initially, conveyor systems were simple, consisting of rudimentary belts and pulleys. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of more sophisticated components, such as motorized drive rollers and automated sensors.
The introduction of electric motors in the early 20th century significantly enhanced the efficiency and reliability of conveyor systems. This shift enabled manufacturers to automate processes, reduce labor costs, and improve productivity. As industries evolved, so did the complexity of conveyor systems, incorporating advanced technologies to meet the demands of diverse sectors, from manufacturing to logistics.
Today, the conveyor system components market is marked by continuous innovation, driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers as they navigate the current market landscape and make strategic sourcing decisions that align with future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of components of a conveyor system
-
How do I solve conveyor belt alignment issues?
To address conveyor belt alignment problems, first, inspect the pulleys and rollers for wear or damage. Misalignment can often be resolved by adjusting the positioning of the pulleys or using alignment tools. Regular maintenance, including checking the tension and ensuring the belt is properly seated on the pulleys, can prevent future issues. If problems persist, consider consulting with a conveyor specialist for a thorough evaluation and potential upgrades to your system. -
What is the best motor type for a conveyor system in heavy-duty applications?
For heavy-duty conveyor systems, a three-phase AC motor is typically the best choice. These motors offer higher efficiency, durability, and better torque compared to single-phase options. Additionally, they can be paired with variable frequency drives (VFDs) to optimize speed control and energy consumption. Ensure the motor’s horsepower rating aligns with the load requirements of your application to prevent underperformance or mechanical failures. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing conveyor components internationally?
When sourcing conveyor components internationally, consider factors such as supplier reputation, product quality certifications, lead times, and shipping costs. It’s also crucial to understand local regulations and compliance standards. Evaluating suppliers through quality assurance processes, customer reviews, and previous project references can help mitigate risks. Establish clear communication regarding specifications and expectations to ensure a successful procurement process. -
What are common payment terms for international B2B transactions in conveyor systems?
Common payment terms in international B2B transactions often include options such as letters of credit, advance payment, or net 30/60/90 days. Letters of credit provide security for both parties, ensuring payment is released only upon meeting specified conditions. Advance payments can be advantageous for suppliers, while net terms offer buyers flexibility. It’s essential to negotiate terms that reflect the trust level and transaction size between the parties involved. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for conveyor components purchased internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced conveyor components, request certifications such as ISO 9001, which signifies adherence to quality management systems. Conducting factory audits, if feasible, can provide insights into the manufacturing processes. Additionally, consider implementing quality control checks upon arrival, such as inspection of materials and performance tests. Collaborating closely with suppliers to establish quality standards can foster long-term reliability. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) typically required for conveyor components?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for conveyor components can vary widely based on the supplier and component type. Generally, MOQs may range from a few units for standard components to larger quantities for specialized items. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your project requirements. Some suppliers may offer flexibility, especially for repeat orders or long-term contracts. -
How can I customize conveyor components to fit my specific application?
Customization of conveyor components can often be achieved by discussing your requirements directly with manufacturers or suppliers. Key areas for customization include belt materials, sizes, and configurations, as well as motor specifications and control systems. Many suppliers offer design services or support to help tailor solutions to your operational needs. Providing detailed specifications and examples of your application can help facilitate the customization process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing conveyor components?
When importing conveyor components, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with your destination country to navigate the complexities of international shipping. Ensure all documentation is complete and accurate to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping when planning your project timelines, as these can significantly impact your operations.
Top 5 Components Of A Conveyor System Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Conveyor Rollers – Standard and Heavy-Duty Solutions
Domain: conveyorrollers.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Conveyor Rollers: 1. Standard Rollers – Made of steel, used in medium load capacity systems for general material handling in packaging and warehousing. 2. Heavy-Duty Rollers – Steel construction, designed for high load capacities, suitable for industrial settings like mining and construction. 3. Coated Rollers – Made of plastic with a rubber layer for extra grip, medium load capacity, used in food…
2. Ocado Intelligent Automation – Conveyor Systems
Domain: ocadointelligentautomation.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: A conveyor system is a mechanical handling apparatus designed for automatically transporting loads and materials within an area. It minimizes human error, lowers workplace risks, and reduces labor costs. Conveyor systems can use belts, wheels, rollers, or chains for transportation. They consist of a belt stretched across pulleys, with a drive pulley that powers the belt. Common types include belt,…
3. BBC Arizona – Bearings and Belting Solutions
Domain: bbcarizona.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: {“Bearings”: {“Type”: “Pillow Blocks / Take Ups”, “Description”: “A pedestal made of cast iron or steel that provides support for the conveyor. Take up bearings align conveyor tracks.”}, “Belting”: {“Type”: “Heavy Duty / Light Duty”, “Description”: “Material that helps move objects along the conveyor and supports the load, chosen based on application.”}, “Chain Drives”: {“Type”: “Roller Chain / En…
4. DPH Engineering – Belt Conveyors
Domain: dphengg.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Belt Conveyors are systems that move materials, goods, and people using a flexible belt stretched between rollers powered by an electric motor. Key components include: 1. Head Pulley – Drives the belt and is located at the discharge end, often with a rough jacket for grip. 2. Tail Pulley – Located at the loading end, provides tension and guides the belt back. 3. Idler Rollers – Support the belt an…
5. Belt Power – Conveyor Components & Belting
Domain: beltpower.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Conveyor Components: Segmented Transfer Plates, Roller Chain Sprockets, Belt Scrapers / Brushes, Belt Trackers, Take-Ups, Clean-In-Place, Wear Strips, Guide Rails, Hose Guarding, Bearing Covers, Hoppers. Conveyor Belting: Lightweight Conveyor Belting, Food Conveyor Belting (FDA, USDA, AAA Dairy), General Conveyor Belting, Incline Conveyor Belting, Machine Tapes / Power Transmission, Airport / Dist…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for components of a conveyor system
In summary, understanding the critical components of a conveyor system is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring long-term reliability. Each element, from belts and pulleys to motors and sensors, plays a pivotal role in the seamless movement of materials. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of these components can significantly impact the overall performance of your material handling systems.
Investing in high-quality components not only enhances productivity but also minimizes downtime and maintenance costs. Prioritizing suppliers that offer durable, energy-efficient, and easily replaceable parts can lead to improved operational agility and reduced total cost of ownership.
As you look to the future, consider how emerging technologies and innovations in conveyor systems can further enhance your supply chain efficiency. Engage with reputable manufacturers and distributors who can provide tailored solutions that meet your unique operational needs. By leveraging strategic sourcing, you position your business for success in an increasingly competitive global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.