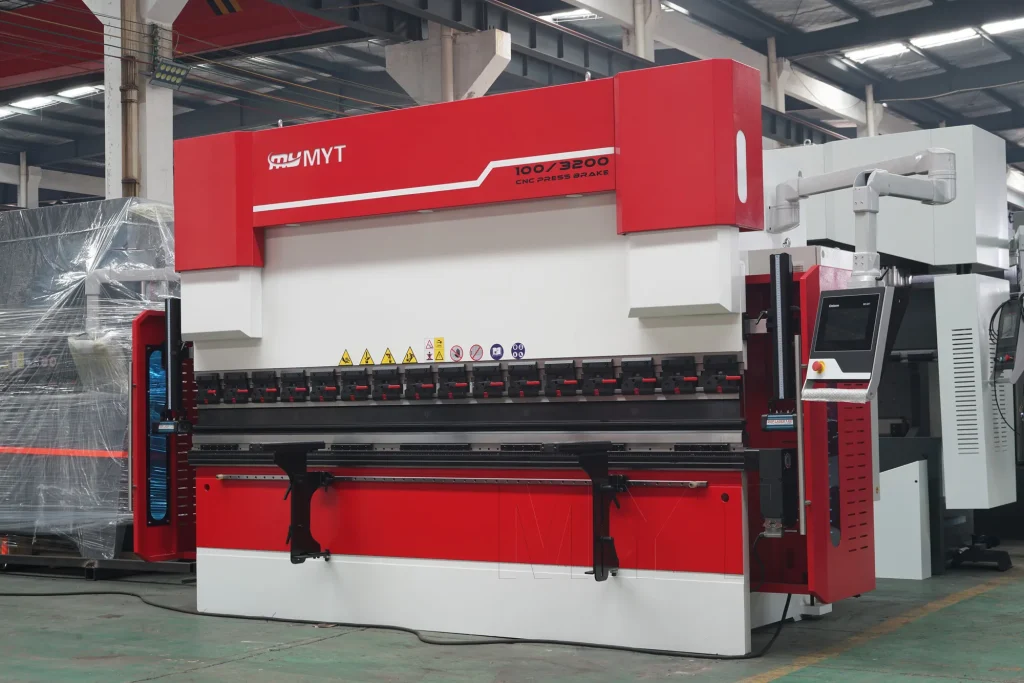
Everything You Need to Know About Bending Machine Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bending machine
The global market for bending machines presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing machinery that meets specific production needs while balancing quality and cost. As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, understanding the intricacies of bending machine technology becomes essential. This comprehensive guide will delve into various types of bending machines, including die, panel, and roll benders, each tailored for distinct applications ranging from metal fabrication to complex industrial projects.
In addition to exploring machine specifications and capabilities, this guide will provide actionable insights on supplier vetting processes, ensuring that international buyers can identify reputable manufacturers and distributors. We will also address cost considerations, maintenance requirements, and the latest innovations in bending technology that can drive efficiency in production. By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide serves as a vital resource for navigating the complexities of the bending machine market. Whether you are based in bustling manufacturing hubs like Vietnam or established industries in Germany, this guide aims to empower your sourcing strategy, helping you secure the right bending solutions for your operational needs.
Understanding bending machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Bending Machines | Uses a press beam to bend sheet metal into a V-shape. | Manufacturing of simple and complex parts. | Pros: High precision, suitable for various materials. Cons: Requires skilled operators for setup. |
| Panel Bending Machines | Features a C-profile frame for bending complex shapes. | Automotive and aerospace component production. | Pros: Excellent for intricate designs, flexible. Cons: Higher investment cost compared to simpler machines. |
| Roll Benders | Utilizes three rollers for bending tubes and pipes. | HVAC, furniture, and automotive industries. | Pros: Capable of creating large radius bends. Cons: Limited to round shapes; may require additional tooling for different profiles. |
| Automated Bending Cells | Fully automated systems for high-volume production. | Mass production of metal components. | Pros: Increased efficiency, consistent quality. Cons: High initial investment; may require technical support. |
| Manual Bending Machines | Operated manually, suitable for small-scale tasks. | Prototyping and small batch productions. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to operate. Cons: Slower production speed, less precision for complex shapes. |
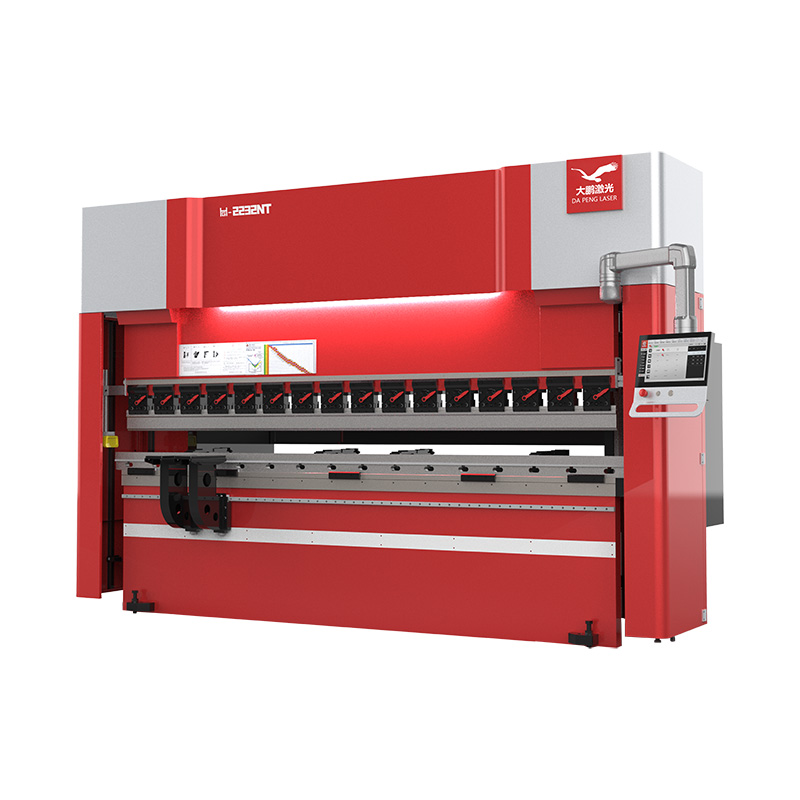
What Are the Key Characteristics of Die Bending Machines?
Die bending machines are designed for bending sheet metal using a press beam that forces the material into a V-shaped die. This method is particularly effective for producing both simple and complex parts with high precision. B2B buyers should consider the machine’s tonnage and bending length to ensure it meets their production requirements. While die bending machines can deliver exceptional accuracy, they often require skilled operators for setup and operation, which can impact labor costs.
How Do Panel Bending Machines Stand Out?
Panel bending machines utilize a C-profile frame to achieve complex bends, making them ideal for applications in the automotive and aerospace sectors where precision and versatility are paramount. These machines can handle intricate designs that would be challenging for other types of bending equipment. Buyers should evaluate the machine’s adaptability to different materials and thicknesses, as well as the initial investment required, which tends to be higher due to the advanced technology involved.
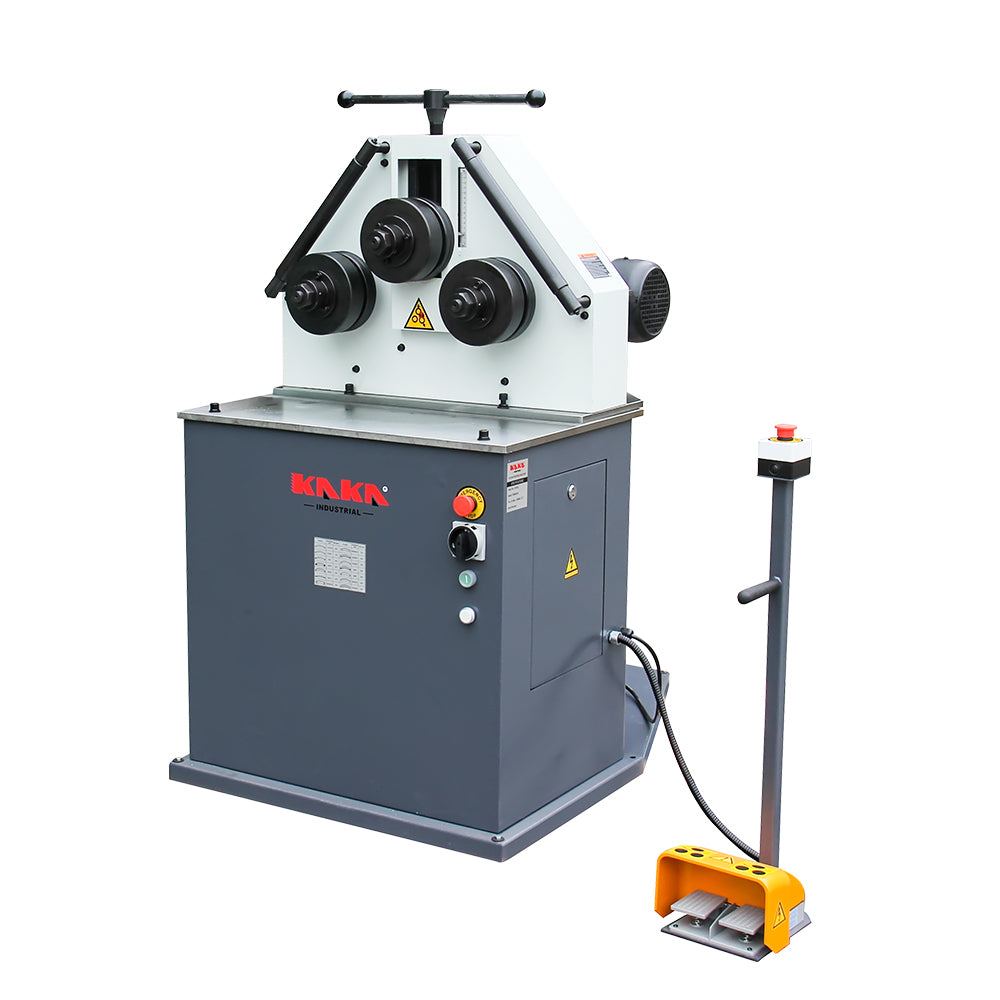
What Are the Advantages of Roll Benders?
Roll benders employ three rollers to create bends in tubes and pipes, making them suitable for industries such as HVAC, furniture manufacturing, and automotive. They excel at producing large radius bends, which can be crucial for specific applications. However, buyers should note that roll benders are typically limited to round shapes and may require additional tooling for different profiles. Understanding the machine’s capacity and the types of materials it can handle is essential for making an informed purchase.
Why Choose Automated Bending Cells?
Automated bending cells represent the cutting edge of bending technology, designed for high-volume production environments. These systems offer increased efficiency and consistent quality, making them ideal for mass production of metal components. However, the initial investment is significant, and businesses may need to factor in ongoing technical support and maintenance costs. Buyers should assess their production volume and the potential return on investment when considering these advanced machines.
What Are the Benefits of Manual Bending Machines?
Manual bending machines are straightforward devices that allow operators to bend materials by hand. They are particularly useful for prototyping and small batch productions where flexibility and cost-effectiveness are priorities. While these machines are easier to operate and require a lower initial investment, they typically offer slower production speeds and less precision for complex shapes. Buyers should consider their production needs and whether the trade-off in speed and precision aligns with their business goals.
Key Industrial Applications of bending machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Bending Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Manufacturing vehicle frames | Enhanced structural integrity and weight reduction. | Ensure compatibility with various materials and designs. |
| Construction | Fabricating metal structures | Improved precision and reduced waste in materials. | Look for machines that handle large sheets and complex bends. |
| HVAC | Ductwork fabrication | Increased efficiency in airflow and reduced installation time. | Consider automation features for higher production rates. |
| Furniture | Creating custom metal furniture | Unique designs that enhance market competitiveness. | Evaluate the machine’s versatility for different styles and finishes. |
| Shipbuilding | Forming hull and structural components | Enhanced durability and resistance to marine conditions. | Assess the machine’s ability to handle large and heavy materials. |
How Are Bending Machines Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, bending machines are essential for manufacturing vehicle frames and components. These machines enable the precise bending of metal sheets to create strong, lightweight structures that improve fuel efficiency and safety. For international buyers, especially in developing regions, sourcing machines that can accommodate various metal types and thicknesses is crucial. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding automotive safety standards is necessary to ensure compliance.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
What Role Do Bending Machines Play in Construction?
In construction, bending machines are pivotal for fabricating metal structures such as beams, columns, and supports. They enhance precision in bending metal sheets, which reduces material waste and ensures that components fit together seamlessly. Buyers in Africa and South America should focus on machines that can handle large dimensions and complex profiles, as construction projects often require custom solutions. Moreover, investing in machines that offer quick setup times can significantly enhance project timelines.
How Are Bending Machines Utilized in HVAC Systems?
Bending machines are vital in the HVAC industry for fabricating ductwork. They allow for the efficient production of bends that optimize airflow and fit within existing structures. This precision leads to improved energy efficiency and reduced installation times. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider sourcing machines with automation capabilities to boost production efficiency, especially in regions where HVAC installations are rapidly increasing.
Why Are Bending Machines Important for Furniture Manufacturing?
In the furniture industry, bending machines are used to create unique metal furniture designs, offering a competitive edge in the market. These machines allow for intricate bends that can transform basic metal into stylish pieces. For international buyers, particularly from Europe, it’s important to evaluate the machine’s versatility in handling different materials and finishes, ensuring that they can produce a wide range of styles to meet consumer demands.
How Do Bending Machines Contribute to Shipbuilding?
In shipbuilding, bending machines are crucial for forming hulls and structural components that withstand harsh marine environments. The ability to bend heavy metal sheets accurately ensures the durability and strength of vessels. Buyers in regions with significant maritime industries, such as South America and the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing machines that can handle large and thick materials, as well as those that offer high precision to meet stringent industry standards.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bending machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Precision in Complex Bending Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges when it comes to achieving precision in complex bending applications. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction often require intricate designs that demand high accuracy. Buyers may encounter issues with their current machines not delivering the necessary precision, leading to increased waste, rework, and ultimately higher costs. This lack of precision can stem from inadequate tooling, poor machine calibration, or insufficient operator training.
The Solution: To overcome precision challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing bending machines that come equipped with advanced automation features and intelligent software solutions. Machines like the TruBend Series 3000 or 5000 offer sophisticated control systems that ensure consistent bending accuracy. Investing in high-quality, application-specific tooling can also significantly enhance precision. Furthermore, providing comprehensive training for operators on the specific capabilities and features of the bending machine can help minimize errors. Regular maintenance checks and calibration routines should be established to keep the machines operating optimally, ensuring that every bend meets the required specifications.
Scenario 2: Long Setup Times Affecting Production Efficiency
The Problem: Long setup times can be a significant pain point for B2B buyers, especially in fast-paced environments where time is money. When switching between different bending projects, the need for extensive tool changes and machine adjustments can lead to production bottlenecks. This inefficiency can hinder a company’s ability to meet customer deadlines and reduce overall profitability.
The Solution: To mitigate long setup times, buyers should consider investing in bending machines that feature quick-change tooling systems and intuitive programming software. Machines like the TruBend Center Series 7000 allow for semi-automatic or fully automatic setups, drastically reducing downtime between projects. Additionally, implementing a Tool Setup Optimizer can streamline the process by identifying compatible tools for multiple parts, thus minimizing the need for frequent adjustments. Establishing a lean manufacturing approach can also help identify inefficiencies in the setup process, allowing teams to implement best practices that enhance productivity.
Scenario 3: Lack of Support for Diverse Material Types
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with bending machines that are not versatile enough to handle different material types and thicknesses. This limitation can restrict their operations, forcing them to invest in multiple machines for varied tasks, which can be cost-prohibitive. In regions where material availability may vary, the inability to adapt to different materials can also lead to delays and lost business opportunities.
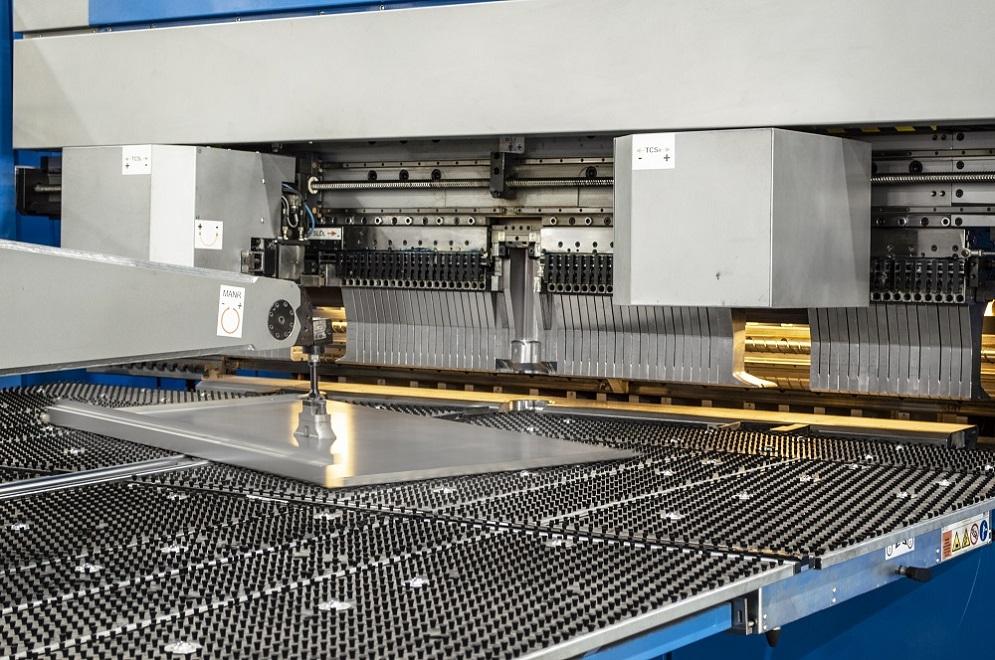

Illustrative image related to bending machine
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should seek out bending machines designed for versatility and compatibility with a range of materials, including aluminum, steel, and composite materials. The TruBend Series 8000, for instance, is engineered to accommodate large format parts while maintaining the flexibility needed for different materials. Additionally, buyers should evaluate machine specifications carefully to ensure they meet the requirements for the thickness and type of materials they plan to work with. Investing in modular tooling options can also provide the flexibility needed to adapt to diverse bending tasks without requiring additional machinery. Finally, partnering with suppliers that offer robust customer support and training can help buyers optimize their machine’s performance across various material types, ultimately leading to greater operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bending machine
What Are the Key Materials Used in Bending Machines?
When selecting materials for bending machines, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they fit into specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in bending machines: Steel, Aluminum, Polyamide, and Stainless Steel.
How Does Steel Perform in Bending Machines?
Steel is the most commonly used material in the construction of bending machines due to its excellent strength and durability. It has a high-temperature rating and can withstand significant pressure, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its robustness, which translates to long-lasting performance and reliability. However, steel is heavier than other materials, which can complicate transport and installation. Additionally, it is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which can affect its longevity.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media makes it versatile for different bending applications. It is particularly effective for bending thicker metals, which is essential in industries like automotive and aerospace.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should consider local availability and compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN. In Europe, particularly Germany, the emphasis on quality and adherence to safety standards is paramount.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Bending Machines?
Aluminum is another popular choice for bending machines, particularly in applications requiring lightweight materials. It has a lower density compared to steel, making it easier to handle and transport.
Pros and Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its corrosion resistance, which is beneficial in humid environments. However, aluminum is not as strong as steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Its cost can also be higher than steel, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the aerospace industry. It is also suitable for bending thinner sheets, making it versatile for various manufacturing processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards like JIS for quality assurance. The demand for aluminum may vary by region, influencing pricing and availability.
Why Is Polyamide a Suitable Material for Bending Machines?
Polyamide, often referred to as nylon, is increasingly being used in the manufacturing of bending machines due to its unique properties. It is lightweight, flexible, and resistant to wear.
Pros and Cons: The key advantage of polyamide is its ability to absorb shocks and vibrations, which can enhance the performance of bending machines. However, it has a lower temperature tolerance compared to metals, limiting its use in high-heat applications. Additionally, polyamide may not be suitable for heavy-duty bending tasks.
Impact on Application: Polyamide is particularly effective in applications requiring precision and flexibility, such as in the production of custom parts. Its compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice for different manufacturing settings.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of polyamide available and their compliance with local regulations. In regions like the Middle East, where temperature fluctuations can be significant, selecting the right grade is crucial.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Bending Machines?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a preferred material in various industries, including food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust, which is essential in environments exposed to moisture. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to work with due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring high hygiene standards, such as in food and medical equipment manufacturing. Its strength and resistance to corrosion make it suitable for bending thin to medium-gauge materials.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe often prefer stainless steel due to stringent hygiene regulations. Compliance with standards such as EN and ISO is critical for ensuring product quality and safety.
Summary of Material Selection for Bending Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for bending machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications | Corrosion resistance | Lower strength than steel | High |
| Polyamide | Precision and flexible applications | Shock absorption and flexibility | Lower temperature tolerance | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Hygiene-critical applications | Corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide serves as a strategic reference for international B2B buyers, aiding in the selection of the most suitable materials for bending machines based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bending machine
What are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Bending Machines?
The manufacturing process of bending machines involves several critical stages that ensure precision, durability, and operational efficiency. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers and their capabilities.
1. Material Preparation: Selecting Quality Raw Materials
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of high-quality raw materials. Typically, bending machines utilize steel, aluminum, or other alloys that provide the necessary strength and flexibility. Suppliers often source materials that meet international standards to ensure consistency and reliability.
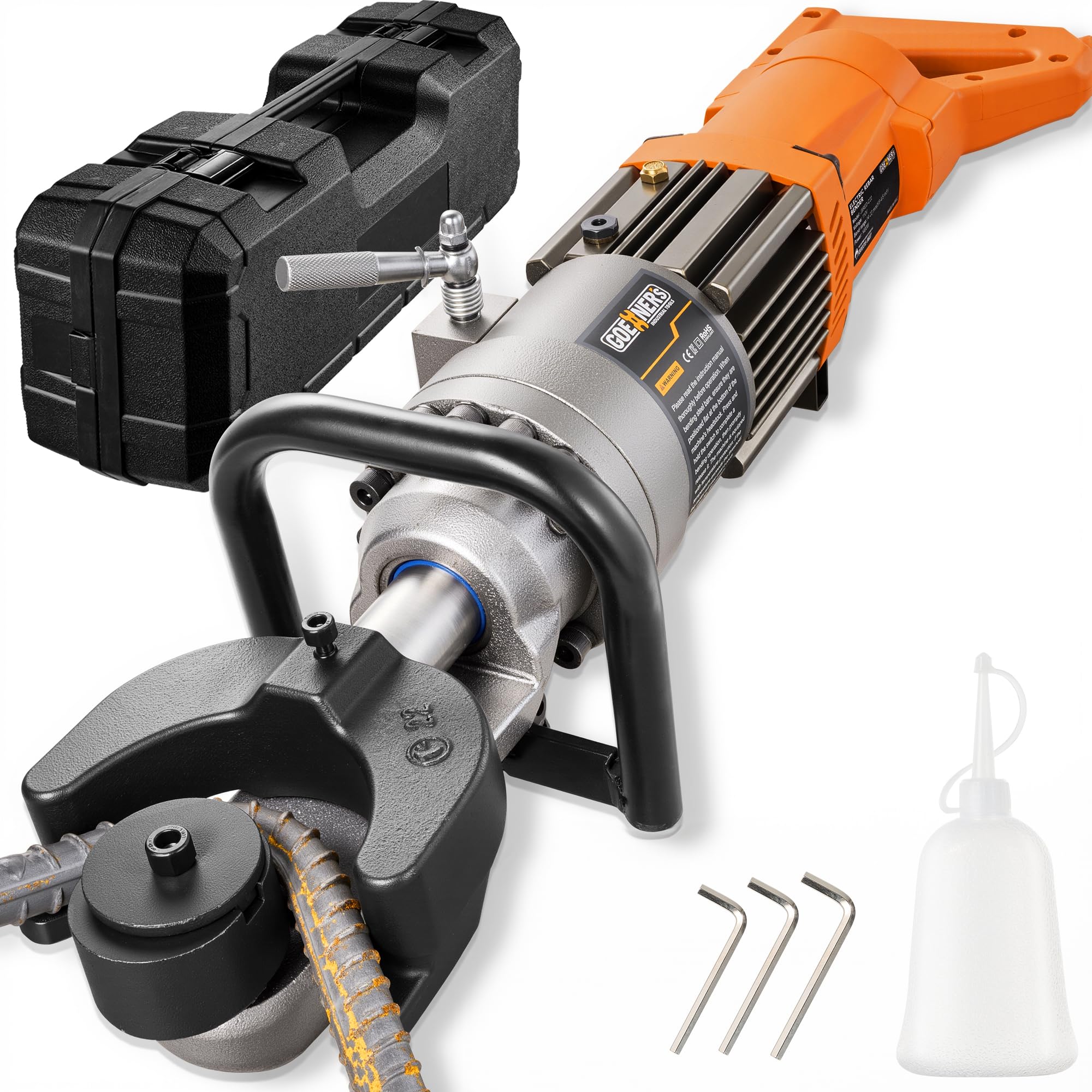

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Once selected, materials undergo cutting and machining to prepare them for the bending process. This might involve laser cutting or CNC machining, which allows for precise dimensions and shapes. The quality of the raw materials and their preparation directly impacts the machine’s performance and longevity.
2. Forming: Utilizing Advanced Techniques for Bending
Forming is the heart of the manufacturing process for bending machines. This stage can vary significantly based on the type of bending machine being produced, such as press brakes or roll benders.
-
Press Brake Bending: In this method, sheets of metal are bent using a press brake that applies force through a punch and die setup. The process allows for both simple and complex bends, and the machines can be equipped with advanced software for programming and automation.
-
Roll Bending: This technique involves passing metal sheets through a series of rollers to achieve the desired curvature. Roll bending is particularly useful for creating large arcs or circular forms.
Automation plays a crucial role here, with many manufacturers integrating robotic systems for enhanced precision and efficiency. This not only speeds up production but also reduces human error.
3. Assembly: Ensuring Precision and Functionality
Following the forming process, the next stage is assembly. This involves the careful integration of various components, including hydraulic systems, electronic controls, and safety features. Quality control is vital during assembly, as even minor misalignments can lead to significant operational issues.
Manufacturers often use jigs and fixtures to maintain accuracy during assembly. Moreover, this stage may involve the installation of additional features such as automated tool changers or programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that enhance the machine’s versatility and user-friendliness.
4. Finishing: Enhancing Durability and Aesthetics
The finishing stage involves applying protective coatings and performing surface treatments to enhance durability and aesthetics. This may include powder coating, painting, or galvanizing to prevent rust and wear.
Finishing also extends to quality checks where the machine undergoes final inspections to ensure all components meet required specifications. This is particularly important for B2B buyers who demand high-quality standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Should B2B Buyers Look For?
Quality assurance (QA) is essential in the production of bending machines to ensure that they meet both international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should be well-versed in the various QA practices that manufacturers employ.
International Standards: Why are They Important?
Manufacturers often adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards indicates that the manufacturer has a robust process for ensuring product quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets or API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may also be relevant. These certifications provide further assurance that the bending machines meet stringent safety and operational standards.
What are the Key QC Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are critical in ensuring the consistency and reliability of bending machines. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage focuses on inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements. Any subpar materials are rejected before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to verify that components are being produced to the required specifications. This may involve dimensional checks and performance tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before machines are shipped, a final inspection is performed to ensure that all systems function correctly and meet quality standards. This includes operational tests and safety checks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to assess the production environment, quality control processes, and overall operational efficiency. Audits can help identify any potential red flags.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality assurance processes, including test results and compliance certificates. This transparency can help build trust between buyers and suppliers.
-
Engage Third-party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can verify compliance with international standards and industry-specific requirements.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
When sourcing bending machines from international suppliers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should consider several nuances:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural differences in business practices and negotiation styles can enhance communication and foster better supplier relationships.
-
Regulatory Requirements: Different countries have varying regulations regarding machinery safety and environmental impact. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations to avoid potential legal issues.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: International logistics can be complex. B2B buyers should evaluate a supplier’s logistics capabilities, including shipping methods, lead times, and potential customs challenges.
By focusing on these critical aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing bending machines, ensuring that they invest in high-quality, reliable equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bending machine’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring bending machines, which are essential for various industrial applications. By following this step-by-step checklist, you will ensure that your selection process is thorough, efficient, and aligned with your operational requirements.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital to ensure that the bending machine you procure meets your production needs. Consider factors such as bending capacity, material types, and specific bending processes (e.g., die bending or panel bending). This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and avoid costly mismatches.
Step 2: Assess Your Production Volume Needs
Understanding your production volume is crucial for selecting the right machine. Evaluate both current and anticipated future needs to determine whether you require a manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated bending machine. This assessment will guide you in choosing a machine that balances efficiency with your budget constraints.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Investigate their reputation, including customer service quality, machine reliability, and after-sales support.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that suppliers have relevant industry certifications, which often indicate adherence to quality and safety standards.
- Review Product Range: A supplier with a diverse product range may better accommodate your future needs.
Step 4: Request Machine Demonstrations
Whenever possible, arrange for live demonstrations of the bending machines you are considering. This allows you to observe the machine in action and evaluate its performance against your specifications. Pay attention to the ease of use, setup time, and any automation features that can enhance productivity.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Step 5: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Inquire about warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and the supplier’s support for maintenance services. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower operating expenses over time.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, negotiate terms that protect your interests. Discuss payment terms, delivery schedules, and installation support. Ensure that the agreement includes provisions for training operators on using the machine effectively, which can significantly impact productivity.
Step 7: Plan for Future Needs
Finally, consider your long-term operational strategy. Choose a bending machine that not only meets your current requirements but also has the capability to adapt to future production demands. This foresight can save you from needing additional purchases or upgrades down the line, ensuring sustained competitiveness in your market.
By following these steps, you can make an informed decision when sourcing bending machines, ultimately enhancing your production capabilities and contributing to your business’s success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bending machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Bending Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing bending machines, international B2B buyers must consider a multifaceted cost structure that includes various components. The primary cost factors include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as high-grade steel and specialized alloys, can significantly influence the overall pricing. Quality materials enhance the durability and performance of the machines, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both manufacturing and assembly processes. Labor costs can vary depending on the geographical location of the supplier, with regions like Europe and North America typically having higher wage standards compared to countries in Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these overheads, allowing suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling required for specific bending applications adds to the initial setup costs. Buyers should evaluate whether standard tooling can meet their needs or if customization is necessary.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that machines meet international standards and certifications, which may influence pricing. Machines with higher quality assurance typically command higher prices but reduce the risk of operational failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors like distance, shipping method, and Incoterms can affect the total logistics costs, impacting the overall price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the competitive landscape, brand reputation, and perceived value of the machines.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Bending Machine Costs?
Several key influencers can impact the pricing of bending machines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses while ensuring the machine meets operational needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines built with premium materials and certified for international standards tend to be more expensive. Buyers must balance the need for quality with their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Well-established brands may command higher prices due to perceived quality and service support.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage costs effectively.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Bending Machine Prices?
When negotiating prices for bending machines, especially in international markets, consider the following tips:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the market landscape and average prices can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge helps in assessing whether a supplier’s pricing is competitive.
-
Emphasize Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Highlight the importance of TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A higher initial investment in a reliable machine may yield lower overall costs.
-
Explore Financing Options: Many suppliers offer financing plans or leasing options, which can alleviate upfront costs. Discussing these options during negotiations may lead to more favorable terms.
-
Leverage Long-term Relationships: Building relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms in the long run. Consistent purchasing can often be rewarded with discounts or preferential treatment.
-
Be Aware of Regional Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have distinct pricing strategies based on local market conditions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of these differences to make informed decisions.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on the specific requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Buyers should seek detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they obtain the best possible pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bending machine With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Bending Machines
In the realm of metal fabrication, bending machines are crucial for shaping materials with precision and efficiency. However, several alternative solutions can also achieve similar outcomes, each with unique benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational needs, budget, and project requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Bending Machine | Roll Bender | Manual Bending Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for complex bends | Good for large radius bends, less precise | Basic functionality, limited precision |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate cost, more affordable options | Low cost, but limited capabilities |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training and setup | Simple to operate, minimal training needed | Very easy to use, no setup required |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Low maintenance, durable design | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Complex, high-volume production | Large radius bends, structural applications | Small-scale projects, DIY applications |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Roll Benders?
Roll benders, such as those offered by Pro-Tools, are designed for bending materials into arcs and circles. They are particularly effective for creating large radius bends and can be a cost-effective alternative for businesses focusing on structural applications like piping and framing. However, while they excel in simplicity and affordability, they may not provide the precision required for intricate designs, making them less suitable for high-end fabrication tasks.
How Do Manual Bending Tools Compare?
Manual bending tools are the most straightforward option, offering low-cost solutions for basic bending tasks. Ideal for small-scale projects or DIY applications, these tools require no training or complex setup. However, their limitations in precision and capacity make them unsuitable for high-volume or intricate projects. Businesses relying heavily on precision and efficiency may find these tools lacking when compared to more advanced options like bending machines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Bending Needs
When considering which bending solution to adopt, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, including the complexity of the bends, production volume, and budget constraints. Bending machines provide unmatched precision and efficiency for high-volume production, while roll benders offer a balance of cost and capability for simpler applications. Manual tools serve well for smaller projects but may fall short in precision and productivity. By evaluating these alternatives against their unique needs, buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their operations and drive profitability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bending machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Bending Machines?
Understanding the essential technical properties of bending machines is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those in manufacturing and metal fabrication. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of metal or alloy that can be processed by the bending machine. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel. The choice of material affects the machine’s durability and performance. For international buyers, knowing the material grade is vital for ensuring compatibility with local manufacturing standards and practices.
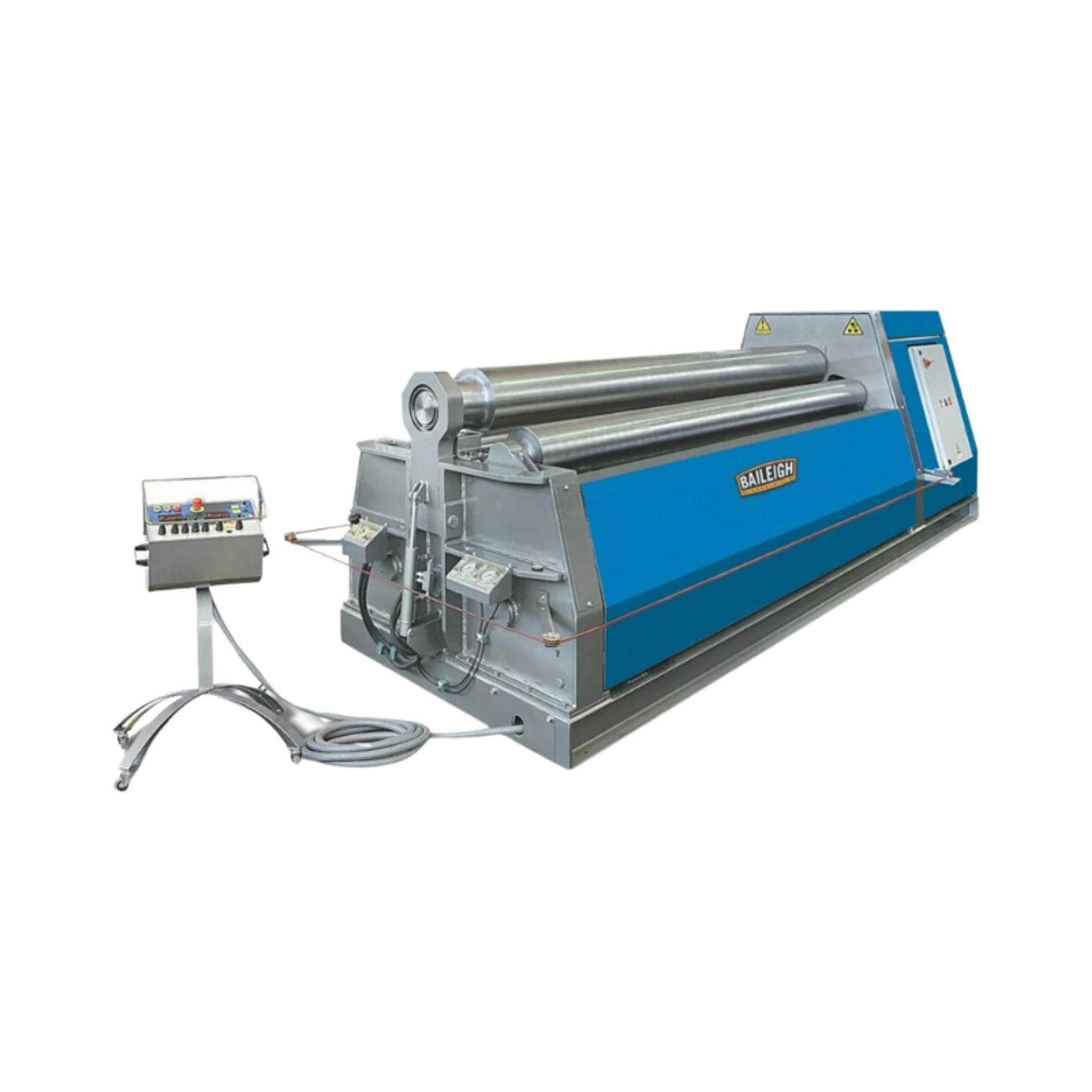

Illustrative image related to bending machine
2. Bending Capacity
Bending capacity is defined by the maximum thickness and width of the material that the machine can handle. This specification is often measured in tons or millimeters. Understanding bending capacity is essential for buyers to ensure that the machine meets their production needs. Overestimating capacity can lead to increased costs, while underestimating it can result in operational inefficiencies.
3. Precision and Tolerance
Precision refers to the machine’s ability to produce consistent and accurate bends, while tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from the desired specifications. High precision and tight tolerances are critical for industries requiring intricate designs, such as automotive or aerospace. Buyers should assess the precision capabilities of a bending machine to avoid costly rework and waste.
4. Automation Level
Bending machines can vary significantly in automation, ranging from manual operation to fully automated systems. Automation enhances productivity and reduces labor costs, making it a key consideration for businesses looking to scale operations. Buyers should evaluate their production workflow to determine the appropriate level of automation required.
5. Control System
The control system encompasses the software and interface used to operate the machine. Advanced systems offer programmable features, enabling users to store multiple bending profiles and optimize setups. A user-friendly control system can reduce training time and improve operational efficiency, making it a significant factor for decision-makers.
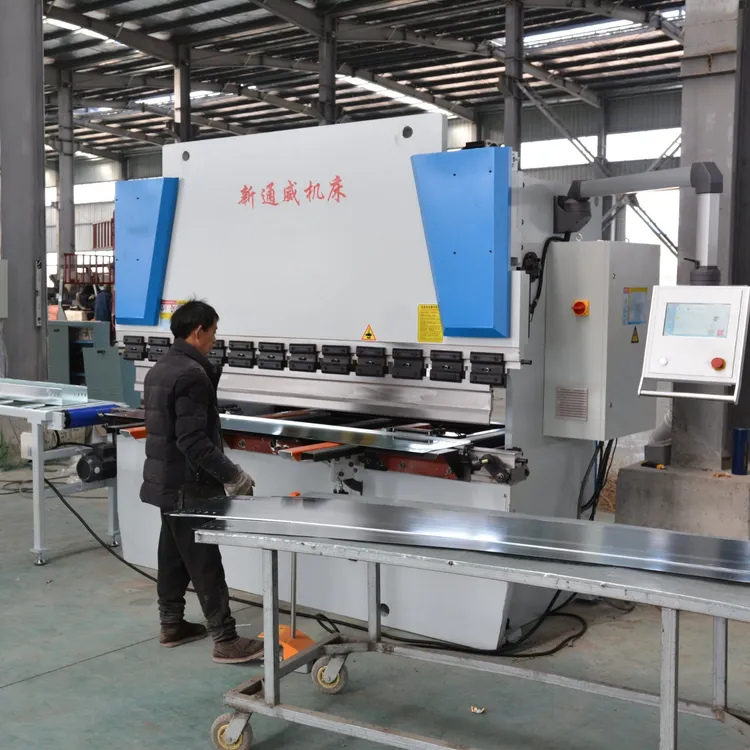

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Which Trade Terms Are Commonly Used in Bending Machine Transactions?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline negotiations and enhance communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some key trade terms relevant to bending machines:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of bending machines, buyers often look for OEMs to ensure they are getting high-quality, reliable equipment backed by the manufacturer’s reputation.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to align their purchasing strategies with supplier requirements, especially in regions where bulk purchasing can lead to cost savings.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. Crafting a clear and detailed RFQ can significantly impact the negotiation process and final pricing.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify shipping obligations, risk transfer, and cost responsibilities. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate global shipping complexities, ensuring smoother transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing inventory levels. Buyers should consider lead time when evaluating suppliers to ensure that they meet their operational timelines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in bending machines, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bending machine Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Bending Machine Market?
The bending machine sector is witnessing transformative growth driven by several global trends. One significant driver is the increasing demand for customization across manufacturing processes, which necessitates flexible and versatile bending solutions. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction are emphasizing precision and efficiency, leading to a preference for advanced bending machines equipped with automation and intelligent software. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including countries like Vietnam and Germany) explore options, they should consider solutions that offer not just functionality but also adaptability to diverse production requirements.
Emerging technologies, such as Industry 4.0, are reshaping the landscape by integrating IoT and machine learning into bending operations. This integration allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has facilitated easier access to suppliers, enabling buyers to compare products and services effectively, thus driving competition and innovation within the sector.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming increasingly important, with manufacturers focusing on energy-efficient machines and processes that minimize waste. Buyers should be aware of suppliers that prioritize environmentally friendly practices, as this trend is likely to influence purchasing decisions moving forward. Overall, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Bending Machine Procurement?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are pivotal considerations for B2B buyers in the bending machine market. The manufacturing process of bending machines can have significant environmental impacts, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation. As industries globally shift towards sustainable practices, buyers should seek suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. This includes utilizing energy-efficient technologies, recycling materials, and minimizing hazardous waste.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is essential to ensure that the materials and components used in bending machines are obtained responsibly. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their adherence to fair labor practices and their environmental stewardship. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
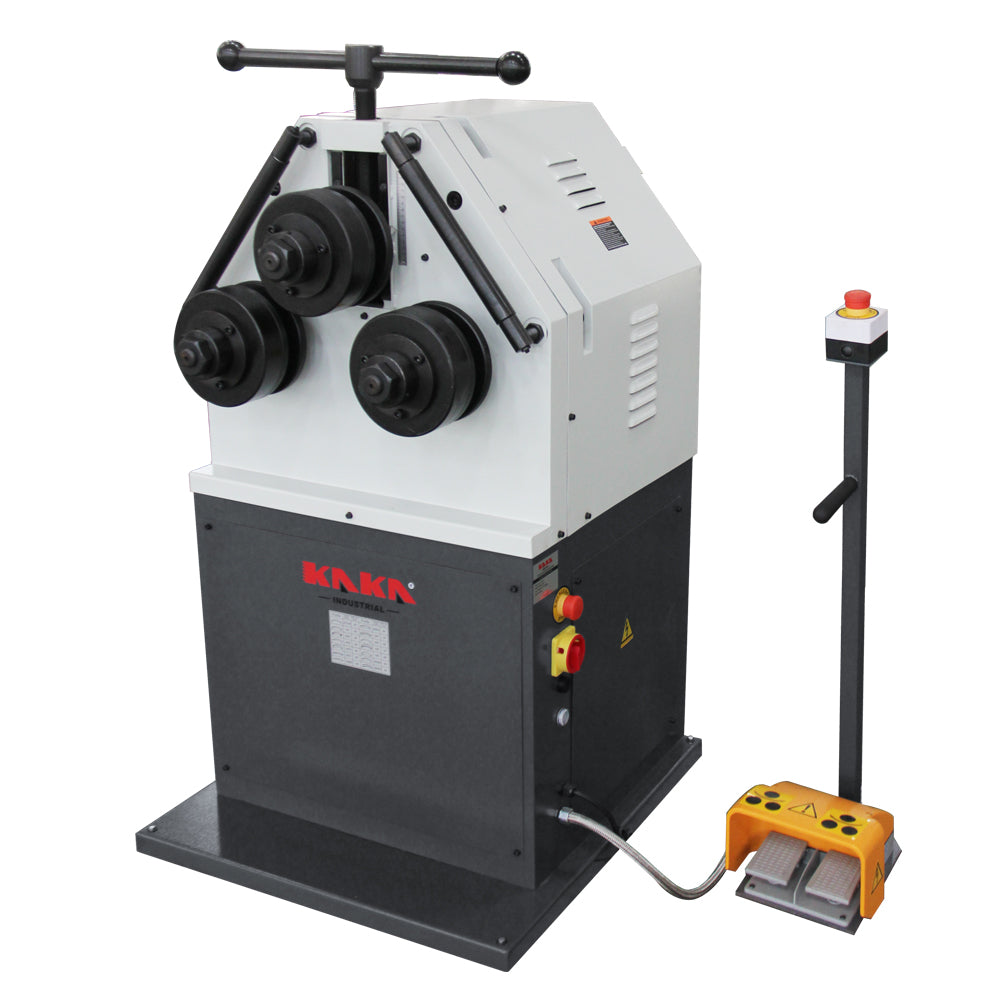

Illustrative image related to bending machine
In addition to compliance with regulations, opting for ‘green’ materials and technologies can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also differentiate themselves in a competitive marketplace, ultimately leading to long-term business success.
How Has the Bending Machine Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the bending machine sector reflects broader technological advancements and changing market needs. Initially, bending machines were simple manual devices primarily used for basic bending tasks. Over the decades, the industry has transitioned towards automation and precision engineering, driven by the demands of increasingly complex manufacturing processes.
The introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology revolutionized bending operations, allowing for higher accuracy and repeatability. As industries sought to optimize production efficiency, manufacturers began to develop advanced bending solutions that incorporate automation, such as robotic arms and intelligent software for process management.
Today, the focus has shifted towards integrating IoT capabilities and smart technologies, enabling real-time data analysis and machine learning for predictive maintenance. This evolution signifies not only the technological advancements within the sector but also the changing expectations of B2B buyers who now prioritize flexibility, efficiency, and sustainability in their sourcing decisions. Understanding this historical context can help buyers appreciate the value of investing in modern bending technologies that align with their strategic objectives.
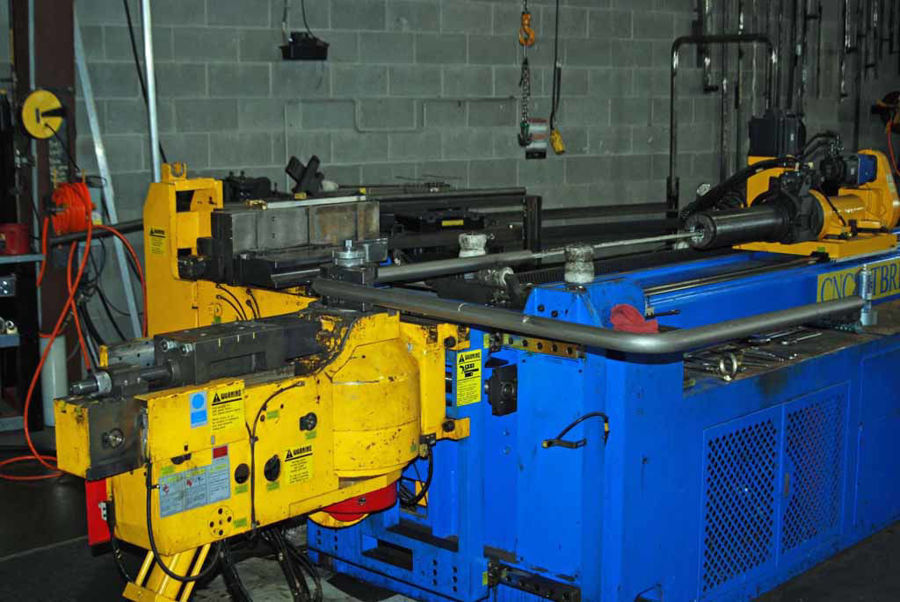

Illustrative image related to bending machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bending machine
-
How do I choose the right bending machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right bending machine involves assessing your specific production requirements, including the type of materials you’ll be bending, the complexity of the shapes needed, and your production volume. Consider factors such as machine capacity, bending technology (like die or panel bending), automation options, and the types of tools available. It’s also crucial to evaluate the after-sales support offered by the supplier and the availability of spare parts to ensure long-term operational efficiency. -
What are the advantages of automated bending machines versus manual ones?
Automated bending machines offer several advantages over manual machines, including increased precision, reduced labor costs, and higher production rates. They can handle complex shapes with greater consistency and often come with advanced software for optimized programming and setup. While manual machines may have lower initial costs, the long-term benefits of automation, such as decreased waste and improved throughput, can lead to better ROI for businesses with high production demands. -
What customization options are available for bending machines?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor bending machines to your specific needs. This could include modifications to machine size, tooling, and software capabilities to accommodate unique bending requirements. When discussing options with suppliers, be clear about your application needs, such as material thickness and bending angles, to ensure the machine is capable of meeting your production goals. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for bending machines?
The minimum order quantity for bending machines can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the machine. Generally, for larger, more complex machines, the MOQ may be one unit, while for simpler models or accessories, manufacturers may require orders of multiple units. It’s essential to discuss MOQ with potential suppliers to understand their policies and ensure they align with your purchasing strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bending machines internationally?
Payment terms for international orders typically vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include full payment upfront, a deposit followed by balance upon delivery, or payment terms extending to 30, 60, or 90 days post-delivery. It’s important to negotiate these terms before finalizing your order and to consider using secure payment methods, such as letters of credit or escrow services, to mitigate risk. -
How can I ensure the quality of bending machines before purchase?
To ensure quality, request detailed specifications and certifications from the manufacturer, including compliance with international standards. Conducting a factory visit or third-party inspection can also provide insights into the manufacturing process and quality control measures. Additionally, seek references or testimonials from other customers to gauge their satisfaction with the machine’s performance and the supplier’s reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing bending machines?
Logistics for importing bending machines involve several key considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Work with a logistics provider experienced in heavy machinery to ensure proper handling and transport. Understand the import regulations and tariffs in your country to avoid unexpected costs. Also, confirm with the supplier about packaging and documentation to facilitate a smooth shipping process. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing bending machines from different regions?
Vetting suppliers requires thorough research and due diligence. Start by checking the supplier’s reputation through online reviews, industry forums, and references from previous customers. Verify their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider visiting their facility if possible, and engage in direct communication to assess their responsiveness and customer service quality. Using third-party verification services can also add an extra layer of assurance.
Top 6 Bending Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. TRUMPF – Bending Machines
Domain: trumpf.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: TRUMPF bending machines offer a diverse portfolio including die and panel bending technologies, large format bending machines, and fully automated solutions. Key models include: TruBend 2100 (10′ bending length, 110 US tons pressing force), TruBend Series 1000 (easy to operate, highly precise), TruBend Series 3000 (addresses rising costs and fluctuating quality), TruBend Series 5000 (most successf…
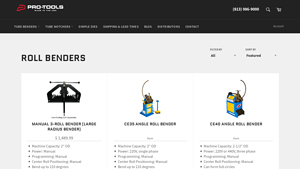
2. Pro Tools – Manual 3-Roll Bender
Domain: pro-tools.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Manual 3-Roll Bender (Large Radius Bender)’, ‘price’: ‘$1,489.99’, ‘machine_capacity’: ‘2″ OD’, ‘power’: ‘Manual’, ‘programming’: ‘Manual’, ‘center_roll_positioning’: ‘Manual’, ‘bend_capacity’: ‘up to 210 degrees’}, {‘name’: ‘CE35 Angle Roll Bender’, ‘price’: ‘$2,139.99’, ‘machine_capacity’: ‘2″ OD’, ‘power’: ‘220V, single phase’, ‘programming’: ‘Manual’, ‘center_roll_positioning’: ‘Man…
3. Küberit – Bendable Profiles
Domain: kuberitusa.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Bending Machine”, “price”: “$496.00”, “material”: “high grade, wear resistant polyamide and glass-fiber”, “description”: “Küberit Bendable Profiles are designed with a unique perforation for creating curved edge protection. These profiles can easily be bent on site to project specifications using the Küberit Bending Machine. Design your own unique curved connection for carpet, resilient,…
4. Prima Power – Advanced Bending Technologies
Domain: primapower.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Prima Power offers advanced bending technologies that include a range of press brakes and automation solutions. The key features include high precision, flexibility, and efficiency in bending operations. The product line is designed to accommodate various materials and thicknesses, ensuring optimal performance for different applications. Additionally, the integration of automation enhances product…
5. Trick-Tools – Sheet Metal Bending Machines
Domain: trick-tools.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Bending Machines at Trick-Tools include a variety of tools and equipment for metal shaping and forming. Related items include angle finders, levels, bend protractors, tube rotation gauges, radius and contour gauges, and layout tools. Other categories include bead rolling and rotary forming machines, brakes, shears, slip rolls, grinding and polishing tools, ironworkers, presses, machini…
6. Schnell – Rebar Fabrication Equipment
Domain: schnellgroup.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Schnell is a leading company in rebar fabrication equipment, offering a wide range of cutting and bending machines and plants for reinforcement processing. Key products include: 1. Stirrup benders and bar shaping machines for bending, shaping, and cutting wire in rolls and bars. 2. Multi-rotor straightening and shaping machines for producing cut-to-size straight bars. 3. Bar cutting machines, bar …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bending machine
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Bending Machine Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of bending machine procurement, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital approach for international B2B buyers. By focusing on understanding specific needs—whether for die bending, panel bending, or automated solutions—businesses can optimize their purchasing decisions. This not only ensures the acquisition of high-quality machines but also maximizes operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Investing in advanced bending technology, like those offered by leading manufacturers, allows companies to benefit from superior precision and flexibility. Solutions that integrate automation and user-friendly interfaces can significantly enhance productivity, which is crucial for businesses aiming to stay ahead in fast-evolving markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As global demand for innovative bending solutions continues to rise, now is the opportune time to align your sourcing strategies with technological advancements. Engage with trusted suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet your unique operational challenges. By making informed decisions today, you position your business for sustained growth and success in the future. Take the next step in enhancing your manufacturing capabilities—explore the latest bending machine offerings and elevate your production processes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to bending machine
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.