Everything You Need to Know About Ball Bearing Components Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ball bearing components
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing high-quality ball bearing components can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The need for reliable, efficient bearings is paramount, as they play a crucial role in reducing friction and enhancing the performance of machinery across various industries. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of ball bearings, their specific applications, and critical considerations for supplier vetting, pricing strategies, and maintenance practices.
By providing a detailed overview of the market, this guide empowers B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—to make informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of ball bearing components not only aids in selecting the right type for specific applications but also helps in negotiating better terms with suppliers, thus optimizing procurement processes.
With insights into the latest trends, best practices for sourcing, and tips for ensuring product quality, this guide is designed to enhance your understanding of the ball bearing market. Equip yourself with the knowledge needed to navigate this critical component landscape effectively, ensuring your operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding ball bearing components Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Groove Ball Bearings | Deep grooves allowing for radial and axial loads | Electric motors, automotive applications | Pros: Versatile, durable; Cons: Limited load capacity compared to specialized bearings. |
| Angular Contact Ball Bearings | Asymmetrical grooves for optimized axial load support | Machine tools, conveyor systems | Pros: High axial load capacity; Cons: Requires precise alignment. |
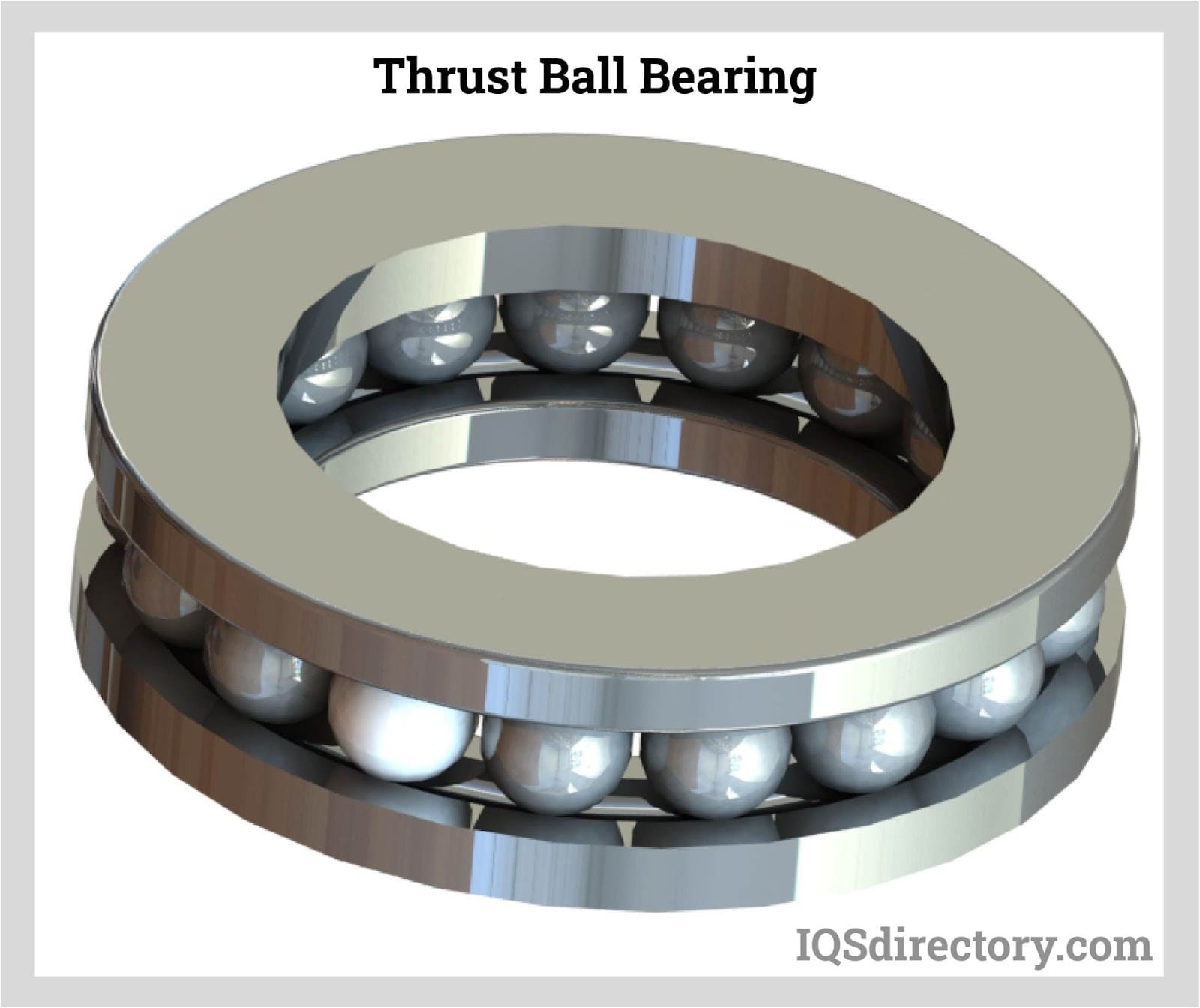
| Thrust Ball Bearings | Designed specifically for axial loads, no radial support | Gearboxes, pumps | Pros: Excellent axial load handling; Cons: Not suitable for radial loads. |
| Self-Aligning Ball Bearings | Dual row design allows for misalignment compensation | Agricultural machinery, textile machinery | Pros: Accommodates misalignment; Cons: More complex installation. |
| Y-Bearings | Extended inner race with screw holes for easy installation | Industrial equipment, conveyors | Pros: Easy to install; Cons: Limited axial load capacity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Deep Groove Ball Bearings?
Deep groove ball bearings are characterized by their deep raceway grooves, which allow them to accommodate both radial and axial loads effectively. This versatility makes them ideal for a wide range of applications, including electric motors and automotive components. When considering deep groove ball bearings, B2B buyers should assess factors like load capacity, speed ratings, and lubrication options to ensure optimal performance in their specific applications.
How Do Angular Contact Ball Bearings Support Axial Loads?
Angular contact ball bearings feature asymmetrical grooves that enable them to support substantial axial loads while also managing radial loads. They are commonly used in machine tools and conveyor systems where precise alignment is crucial. Buyers should consider the load direction and alignment requirements when selecting angular contact bearings, as these factors significantly impact their operational efficiency.
Why Are Thrust Ball Bearings Ideal for Axial Loads?
Thrust ball bearings are specifically designed to handle axial loads and are not suitable for radial loads. Their unique design allows for effective load distribution in applications such as gearboxes and pumps. B2B buyers should evaluate the direction of the axial loads they expect in their applications, as thrust ball bearings can only support loads in one direction unless configured in pairs.
Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
What Advantages Do Self-Aligning Ball Bearings Offer?
Self-aligning ball bearings feature a dual-row design that allows them to compensate for slight misalignments in the shaft. This makes them particularly useful in applications such as agricultural and textile machinery, where alignment may be difficult to achieve. Buyers should be aware of the installation complexity and potential maintenance needs associated with self-aligning bearings to maximize their benefits.
How Do Y-Bearings Simplify Installation?
Y-bearings are distinguished by their extended inner race, which includes screw holes for easy installation. This design is particularly advantageous in industrial equipment and conveyor systems, where quick assembly is essential. However, buyers should keep in mind that while Y-bearings simplify installation, they may have limitations in axial load capacity, which should be considered when making procurement decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of ball bearing components
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ball bearing components | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Wheel hubs and drive shafts | Enhanced performance and durability of vehicles | Quality certifications, load capacity, and compatibility with vehicle models |
| Manufacturing | Conveyor systems | Increased efficiency and reduced downtime | Material specifications, lubrication requirements, and environmental resistance |
| Aerospace | Engine components and landing gear | Improved reliability and safety in critical systems | Compliance with industry standards, weight considerations, and thermal resistance |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine rotor assemblies | Higher energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Corrosion resistance, noise levels, and load ratings for varying wind conditions |
| Heavy Machinery | Excavators and loaders | Enhanced operational reliability and lifespan | Heavy load handling capabilities, maintenance support, and sourcing from local suppliers for timely delivery |
How Are Ball Bearing Components Used in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, ball bearing components are integral to wheel hubs and drive shafts, where they facilitate smooth rotation and reduce friction. This application is crucial for enhancing the performance and durability of vehicles, contributing to better fuel efficiency and driving comfort. Buyers in this sector must consider quality certifications, load capacity, and compatibility with specific vehicle models to ensure optimal functionality and safety.
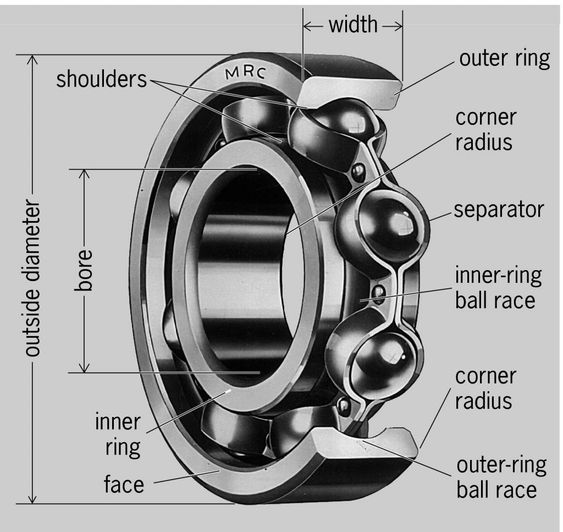
Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
What Role Do Ball Bearings Play in Manufacturing Conveyor Systems?
Ball bearings are essential in conveyor systems within manufacturing settings, enabling smooth and efficient movement of materials. They help reduce friction, which not only increases operational efficiency but also minimizes downtime caused by wear and tear. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing considerations should focus on material specifications, lubrication requirements, and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring longevity and reliability in diverse operational conditions.
How Are Ball Bearing Components Critical in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, ball bearing components are vital for engine components and landing gear. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions while maintaining reliability is critical for safety in flight operations. Buyers must prioritize compliance with stringent industry standards, weight considerations, and thermal resistance to ensure the components can handle high-stress environments effectively.
Why Are Ball Bearings Important in Renewable Energy Applications?
In renewable energy, particularly in wind turbine rotor assemblies, ball bearings play a significant role in enhancing energy efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. These components must endure varying wind conditions, making corrosion resistance and load ratings critical factors for buyers. Sourcing from reputable manufacturers who can guarantee these specifications is essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of wind energy systems.
What Benefits Do Ball Bearings Provide in Heavy Machinery?
In heavy machinery, such as excavators and loaders, ball bearings are crucial for ensuring operational reliability and extending equipment lifespan. They support heavy loads and facilitate smooth movement, which is essential for productivity in construction and mining. Buyers should focus on heavy load handling capabilities, maintenance support, and the availability of local suppliers to ensure timely delivery and service, especially in regions with challenging logistics.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘ball bearing components’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Type of Ball Bearing
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of selecting the appropriate type of ball bearing for their specific applications. With various types available—such as deep groove, angular contact, and self-aligning ball bearings—their differing characteristics can lead to confusion. Buyers may worry about the consequences of choosing the wrong type, such as increased friction, premature wear, or even complete system failure, which can result in costly downtime and repair expenses.
The Solution: To effectively select the right ball bearing, it’s essential to first assess the application’s load requirements—both radial and axial. Buyers should begin by gathering detailed specifications about the machinery and its operational conditions. For instance, if the application involves heavy axial loads in one direction, angular contact ball bearings may be ideal. Conversely, if the application requires accommodating misalignment or varying shaft angles, self-aligning bearings would be more suitable. Engaging with suppliers that offer technical support can also be invaluable. Many manufacturers provide selection guides or online calculators that help in determining the best bearing type based on load specifications, speed, and environmental conditions. Establishing a clear dialogue with suppliers about these factors can lead to better decision-making and product performance.
Scenario 2: High Failure Rates Due to Contamination
The Problem: Another common issue faced by B2B buyers is the premature failure of ball bearing components due to contamination from dust, moisture, or other environmental factors. This is particularly problematic in industries such as manufacturing or agriculture, where equipment is often exposed to harsh conditions. Contaminants can compromise the lubricant and cause excessive wear, leading to frequent replacements and maintenance, thereby increasing operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate contamination-related failures, buyers should prioritize sourcing sealed or shielded ball bearings that provide a barrier against environmental factors. It’s also critical to implement proper installation and maintenance practices. Buyers should ensure that the bearings are installed in clean environments to minimize the risk of introducing contaminants. Additionally, regular inspections and timely lubrication can significantly extend the lifespan of the bearings. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule that includes checking for signs of wear, leakage, and contamination can help identify issues before they escalate into major problems. Furthermore, selecting suppliers that offer high-quality, durable bearings designed for specific environmental conditions can make a significant difference in performance and longevity.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Cost Management and Budgeting
The Problem: Cost management is a significant concern for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to ball bearing components. Buyers often find themselves torn between the need for high-quality products and the pressure to keep costs low. This can lead to decisions that favor cheaper options, which may not meet performance standards, resulting in higher long-term costs due to failures and replacements.
The Solution: To balance quality and cost, buyers should adopt a strategic sourcing approach that evaluates the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront purchase price. This involves considering factors such as the expected lifespan, maintenance requirements, and potential downtime associated with lower-quality bearings. Buyers can work closely with manufacturers to negotiate bulk pricing or explore long-term contracts that provide consistent quality at favorable rates. Additionally, investing in training for maintenance personnel can lead to better care and handling of bearings, thereby enhancing their lifespan and performance. Finally, leveraging case studies or testimonials from other businesses can provide insights into the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality ball bearing components, ultimately supporting more informed budgeting decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ball bearing components
What Are the Key Materials Used in Ball Bearing Components?
When selecting materials for ball bearing components, understanding the properties and performance characteristics is essential. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, ceramic, and plastic. Each material has unique advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact the performance of ball bearings in various applications.
How Does Steel Perform in Ball Bearing Applications?
Steel is the most widely used material for ball bearing components, particularly in high-load applications. It offers excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for high-speed operations. Key properties include high tensile strength, good fatigue resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures, typically up to 200°C. However, steel is prone to corrosion, which can limit its use in environments exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals.
Pros: Steel ball bearings are durable and relatively inexpensive, making them a popular choice for many applications. They can be easily manufactured and machined into precise shapes.
Cons: The primary limitation of steel is its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, which can lead to premature failure in certain environments. Additionally, they may not be suitable for applications requiring extreme temperature resistance.
For international buyers, compliance with standards like ASTM AISI 52100 is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East may also prefer bearings that meet specific quality certifications to ensure reliability.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
What Advantages Do Stainless Steel Ball Bearings Offer?
Stainless steel is an excellent alternative to carbon steel, especially in corrosive environments. It provides similar mechanical properties to steel but with enhanced corrosion resistance due to the presence of chromium. Stainless steel ball bearings can typically operate in temperatures up to 300°C, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, which extends the lifespan of the bearing in challenging environments. They are also easy to clean and maintain.
Cons: However, stainless steel bearings are generally more expensive than their carbon steel counterparts. They can also be less durable under high-load conditions, which may limit their application in heavy machinery.
For B2B buyers, especially in humid regions like Brazil and coastal areas in the Middle East, the corrosion resistance of stainless steel bearings is a significant selling point. Compliance with ASTM A276 standards is often expected.
How Do Ceramic Ball Bearings Compare in Performance?
Ceramic ball bearings are made from materials like silicon nitride, offering unique advantages in specific applications. They are lightweight, non-corrosive, and can withstand extreme temperatures (up to 800°C). Their low thermal expansion coefficient allows for stable performance under varying temperatures.
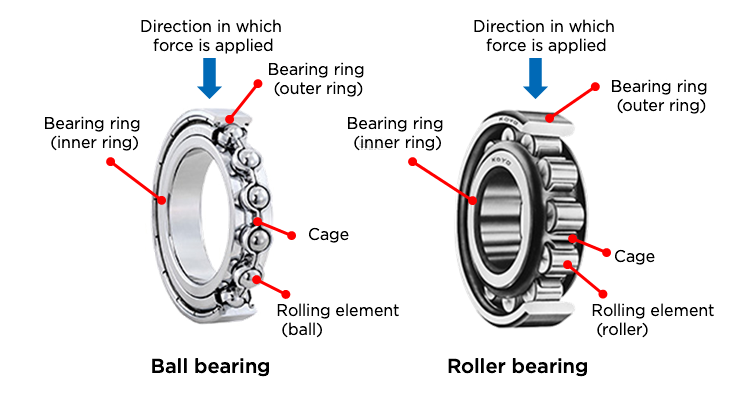
Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
Pros: The primary advantage of ceramic bearings is their ability to operate in extreme conditions without degrading. They also provide lower friction, which can lead to increased efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
Cons: However, ceramic bearings are brittle and can be prone to cracking under shock loads. They are also significantly more expensive than metal bearings, which can be a barrier for some applications.
International buyers should consider the specific application requirements when evaluating ceramic bearings. Compliance with standards like ISO 3290 can enhance confidence in product quality.
What Role Do Plastic Ball Bearings Play in Various Applications?
Plastic ball bearings, often made from materials like nylon or acetal, are becoming increasingly popular for lightweight applications. They are resistant to corrosion and can operate in temperatures up to 80°C. Their non-conductive nature makes them suitable for electrical applications.
Pros: The main advantage of plastic bearings is their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making them ideal for applications in wet or chemical environments. They are also quieter in operation compared to metal bearings.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
Cons: However, plastic bearings typically have lower load capacities and may not perform well under high-speed conditions. Their temperature limitations can also restrict their use in demanding applications.
For B2B buyers, especially in industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, the non-corrosive nature of plastic bearings is appealing. Compliance with FDA regulations may be necessary for certain applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Ball Bearing Components
| Material | Typical Use Case for ball bearing components | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | General industrial applications | High durability and load capacity | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosive environments, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, lower load capacity | High |
| Ceramic | High-speed, high-temperature applications | Lightweight, low friction | Brittle, high cost | High |
| Plastic | Chemical, electrical applications | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower load capacity, temperature limitations | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ball bearing components
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Ball Bearing Components?
The manufacturing of ball bearing components involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality, reliable products. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
How Is Material Prepared for Ball Bearing Production?
Material preparation is the foundational step in ball bearing manufacturing. Typically, high-grade steel is used due to its strength and durability. The steel is subjected to processes such as melting, casting, and forging to achieve the desired properties. Once the raw materials are acquired, they undergo rigorous inspection for purity and quality to meet international standards.
The most commonly used materials include chrome steel (AISI 52100), stainless steel, and ceramics, each chosen based on the application’s specific requirements. For example, chrome steel is preferred for its high load capacity and wear resistance, while stainless steel is favored in corrosive environments.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Ball Bearing Components?
The forming stage encompasses several techniques, including machining, heat treatment, and surface treatment.
-
Machining: This involves processes like turning, grinding, and milling to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes for raceways and balls. The accuracy of machining is critical as it directly impacts the bearing’s performance and longevity.
-
Heat Treatment: Post-machining, components often undergo heat treatment to enhance their hardness and wear resistance. Techniques such as quenching and tempering are common, allowing manufacturers to tailor the mechanical properties of the components according to their intended applications.
-
Surface Treatment: Finally, surface treatments, such as hardening or coating, are applied to improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction. This step is particularly important for ball bearings used in harsh environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
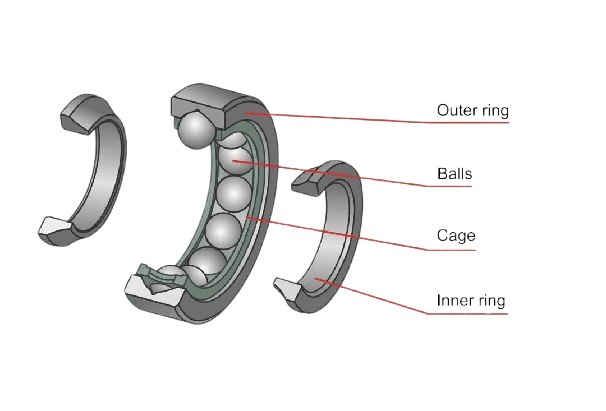
How Are Ball Bearing Components Assembled?
The assembly process is crucial for ensuring that all components fit perfectly and function as intended. During this stage, the inner and outer races are fitted together with the balls, often utilizing a retainer or cage to maintain proper spacing.
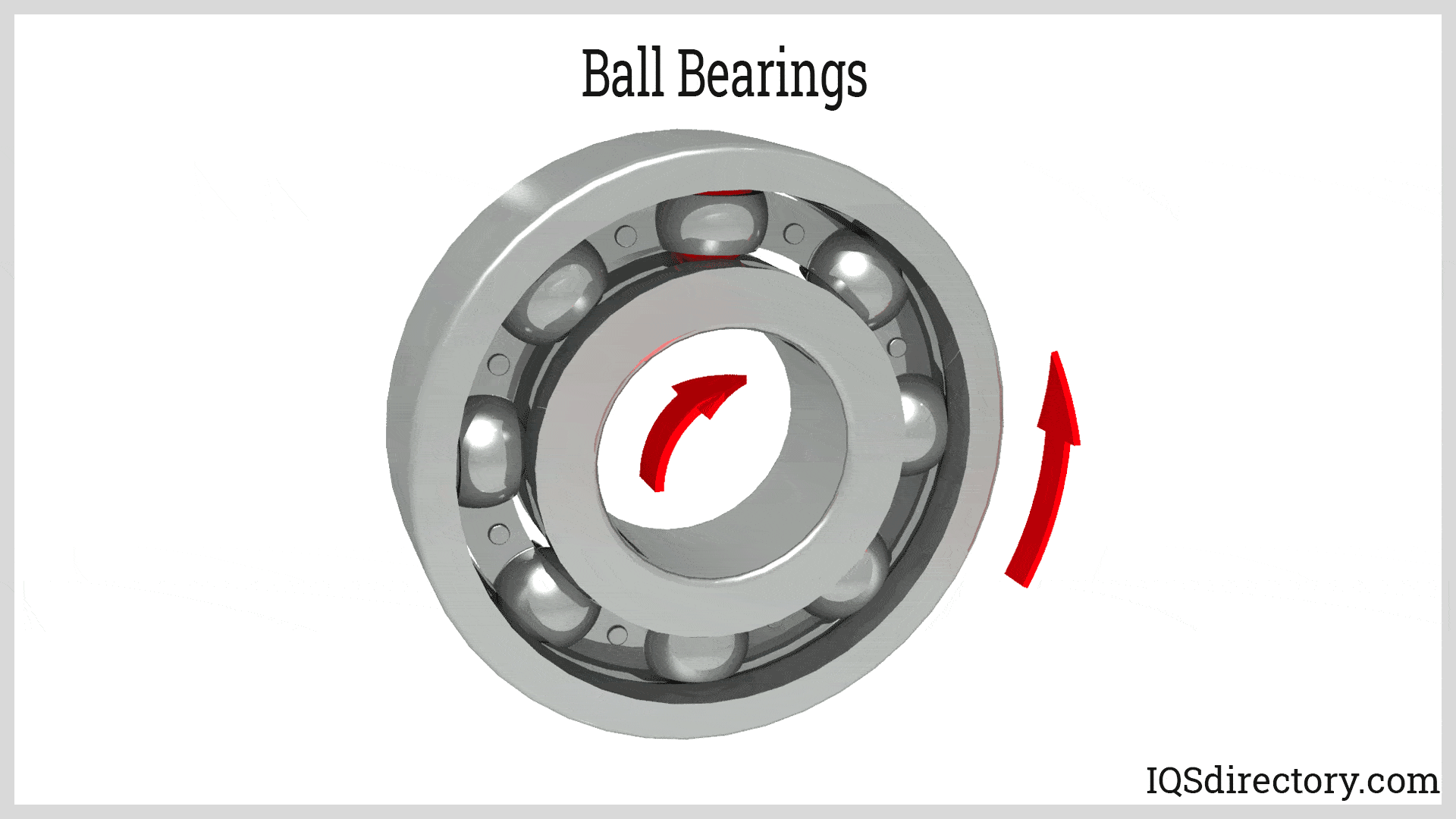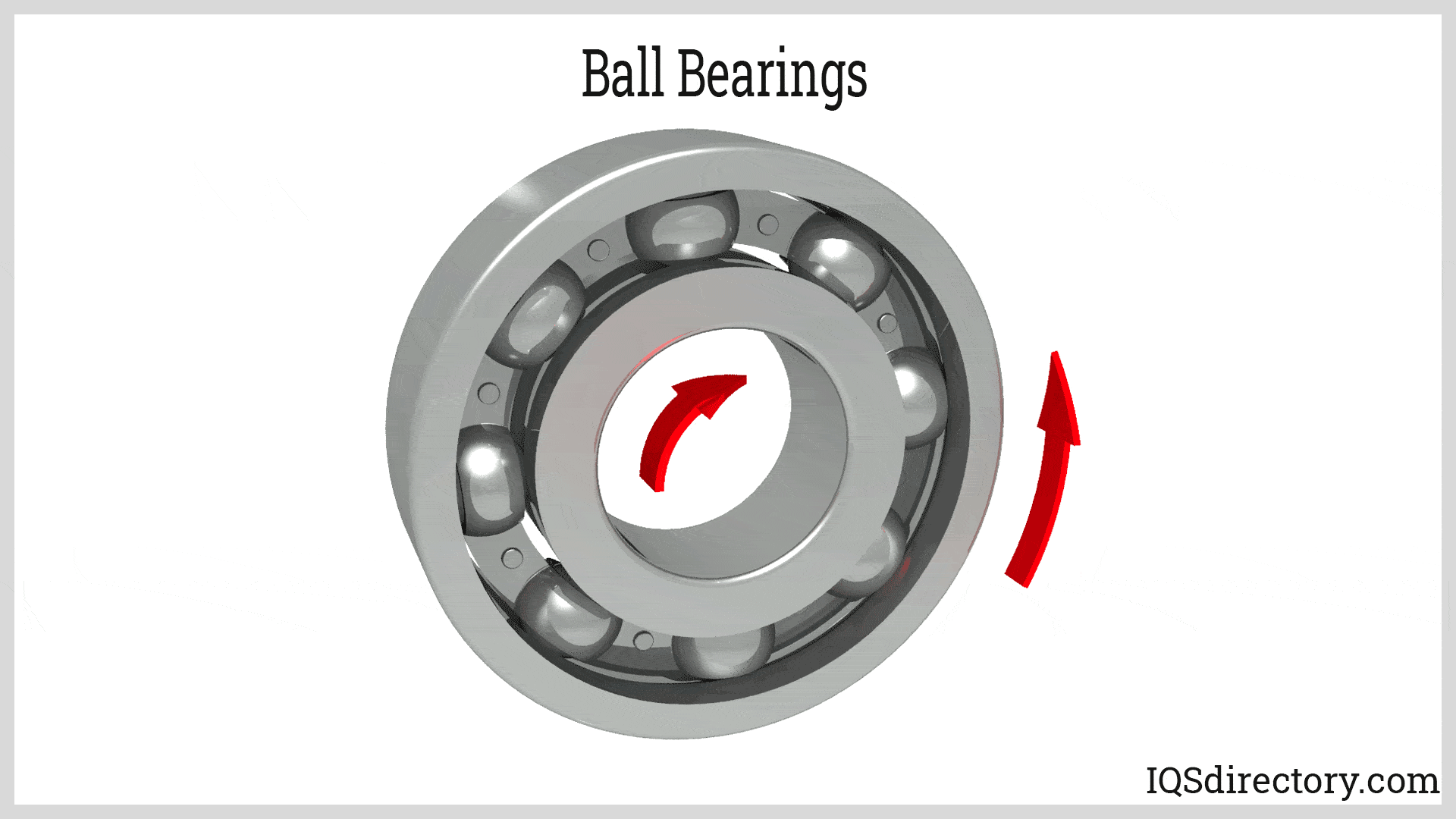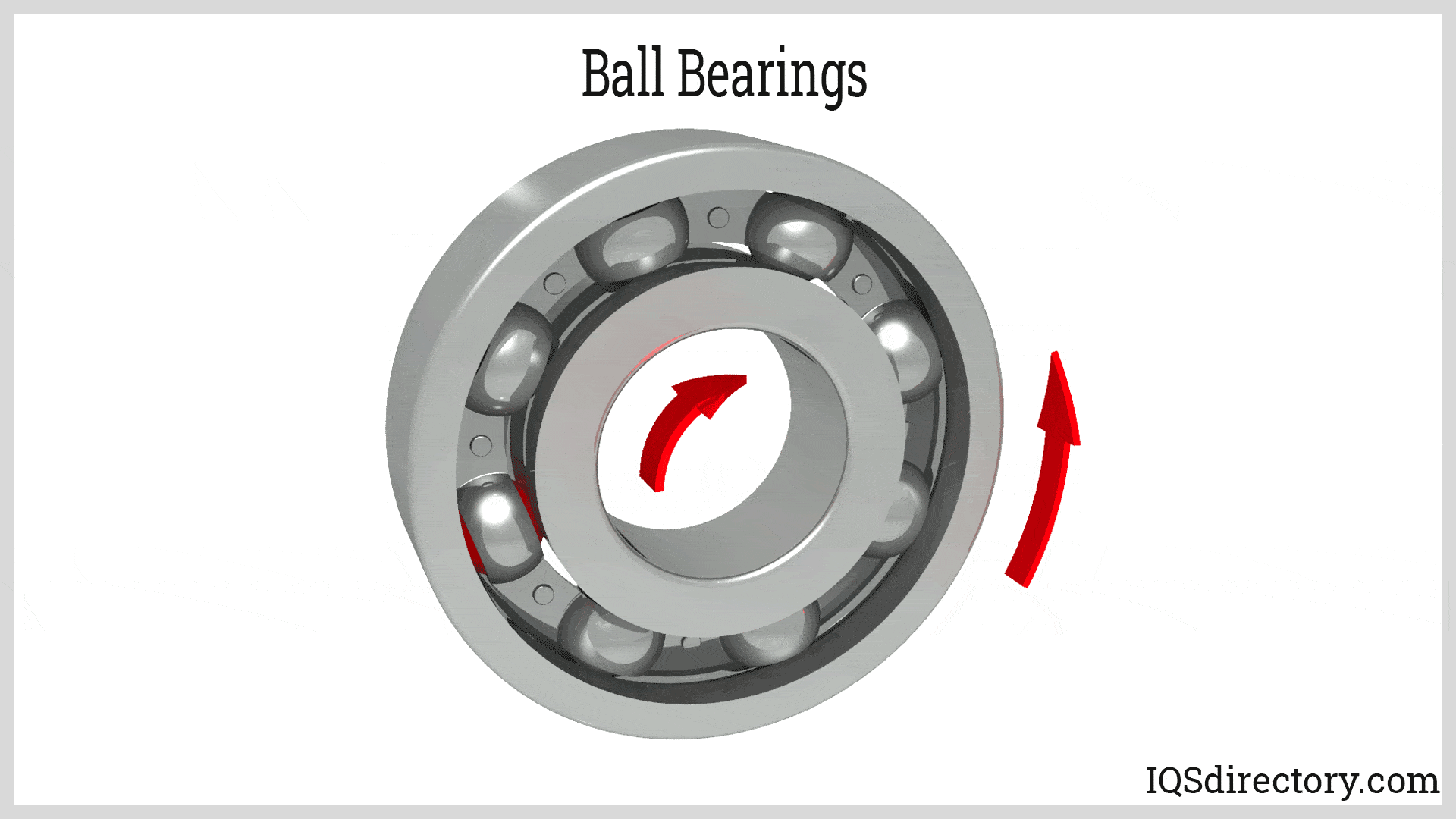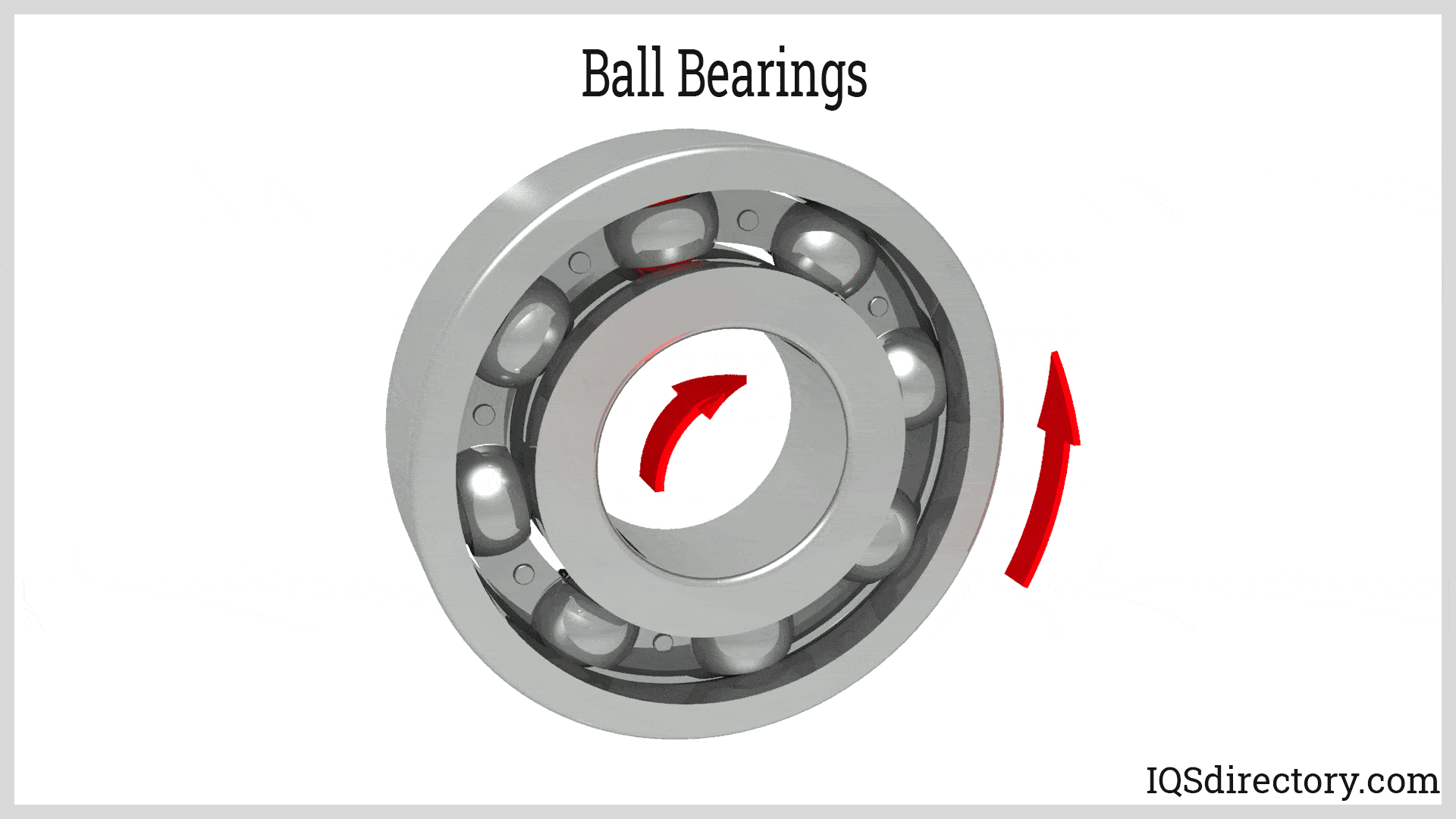
Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
Precision during assembly is vital; even minor misalignments can lead to premature failure. Automated assembly systems are increasingly being used to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Once assembled, the bearings are typically lubricated with grease or oil to reduce friction and wear.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Ball Bearing Components?
Finishing processes involve final inspections and quality checks to ensure that the products meet all specifications. This includes polishing surfaces to achieve a smooth finish and applying protective coatings if necessary.
Additionally, balancing and run-out checks are performed to ensure that the bearings will operate smoothly under load. This final stage is crucial for ensuring that the bearings will perform reliably in their intended applications.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Ball Bearing Components?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Key standards include ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, and industry-specific standards like CE and API.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Quality Assurance?
International standards play a significant role in ensuring product quality and safety. ISO 9001 is one of the most widely recognized standards, focusing on quality management systems and continuous improvement. Compliance with this standard demonstrates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, specific industries may require adherence to standards such as:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Specification: Relevant for bearings used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products meet rigorous safety and performance criteria.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Should Be Considered?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that any deviations from quality standards are identified and corrected promptly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection assesses the finished products against established specifications, ensuring that they meet all functional and performance requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Ball Bearing Components?
Testing methods are crucial for verifying the quality and performance of ball bearing components. Common testing techniques include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using precision measurement tools to ensure components meet specified dimensions.
- Hardness Testing: Assessing the hardness of materials to confirm they meet the required specifications for durability.
- Vibration Testing: Evaluating the performance of bearings under operational conditions to identify any potential failures.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Key methods include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, inspection results, and compliance certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Regulatory requirements may differ significantly between countries, necessitating a thorough understanding of local standards and practices.
Moreover, cultural differences in business practices may influence how quality assurance is perceived and executed. Establishing clear communication and expectations with suppliers is crucial for ensuring that quality standards are consistently met across borders.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for ball bearing components is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and rigorous quality control, buyers can ensure they are sourcing reliable and high-quality components for their applications.
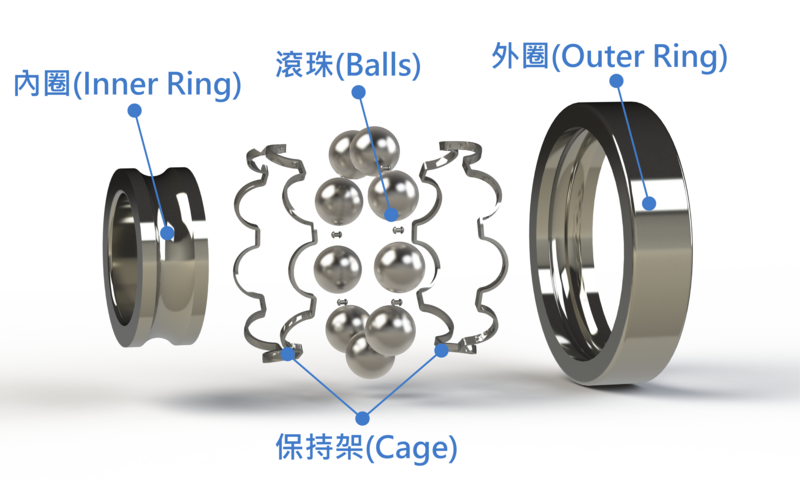
Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘ball bearing components’
To effectively procure ball bearing components, B2B buyers must navigate various technical and logistical considerations. This step-by-step checklist will guide you through the essential actions necessary for successful sourcing, ensuring you select the right products and suppliers for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical for sourcing the right ball bearing components. Consider factors such as load capacity, dimensional requirements, and environmental conditions. This clarity will help you communicate your needs to potential suppliers and ensure you receive appropriate products.
- Load Types: Determine whether you need radial, axial, or a combination of both load-bearing capabilities.
- Material Considerations: Identify materials that can withstand specific temperatures, corrosion, or other environmental factors relevant to your application.
Step 2: Research Different Ball Bearing Types
Understanding the various types of ball bearings is vital for making informed decisions. Each type, such as deep groove, angular contact, or thrust ball bearings, offers distinct advantages based on their design and intended use.
- Application Suitability: Assess which bearing type aligns with your machinery requirements and operational conditions.
- Performance Characteristics: Consider the friction and speed ratings of each type to ensure optimal performance in your application.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vetting potential suppliers is crucial to ensure reliability and quality. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and request documentation such as certifications, case studies, and references.
- Quality Assurance: Confirm that suppliers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications, to ensure product reliability.
- Experience and Reputation: Seek feedback from other businesses in your region or industry to gauge the supplier’s reputation.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the ball bearing components to evaluate their performance. Testing samples in your specific application can reveal potential compatibility or performance issues.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
- Trial Runs: Conduct performance tests under actual working conditions to assess durability and functionality.
- Feedback Loop: Use the results to refine your specifications or supplier selection if necessary.
Step 5: Confirm Pricing and Payment Terms
Understanding the total cost of ownership is essential for budget management. Discuss pricing structures, payment terms, and any potential discounts for bulk orders with your chosen suppliers.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure all costs, including shipping and handling, are clearly outlined to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Negotiation Opportunities: Explore potential discounts for long-term contracts or larger volume orders.
Step 6: Assess Logistics and Delivery Times
Efficient logistics are crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring timely production. Confirm lead times and shipping options with suppliers to align with your project schedules.
- Shipping Methods: Evaluate different shipping options based on urgency and cost-effectiveness.
- Customs and Import Regulations: Be aware of any regulations that may affect delivery times, especially when sourcing internationally.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Building a long-term relationship with reliable suppliers can enhance your procurement process. Regular communication and feedback can lead to better service, tailored solutions, and improved pricing over time.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
- Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews to assess supplier performance and address any issues.
- Collaborative Development: Work together on product improvements or custom solutions that fit your evolving needs.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for ball bearing components, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers for their operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ball bearing components Sourcing
When sourcing ball bearing components, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the key cost components, pricing influencers, and buyer tips to facilitate effective procurement strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Ball Bearing Manufacturing?
The cost structure for ball bearing components is multifaceted, encompassing several critical elements:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. Common materials include high-carbon steel, stainless steel, and ceramics, each with different price points and performance characteristics. Higher-grade materials often lead to increased durability and performance but come at a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the overall pricing of ball bearings. Skilled labor is essential for precision manufacturing, and regions with higher wage standards may see increased costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facilities. Efficient production processes can mitigate overhead costs, while outdated machinery may lead to higher expenses.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and tooling can be substantial, especially for customized or unique bearing designs. Buyers should consider whether these costs are amortized over large production runs or if they will be borne entirely by smaller orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are vital to meet international standards and certifications, which are particularly important for buyers in regulated industries.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can fluctuate significantly based on the distance between supplier and buyer, as well as the chosen shipping method. This is especially relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where logistics may be more complex.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary widely based on competition, market demand, and the supplier’s business strategy.
What Influences Pricing in Ball Bearing Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of ball bearing components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often benefit from economies of scale, resulting in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate for favorable terms that suit their purchasing capabilities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific tolerances can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The grade of materials used and the presence of industry certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can significantly impact pricing. High-quality materials and certifications often justify higher costs due to enhanced performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and quality assurance, while newer entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can influence the total landed cost. Understanding responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Ball Bearings?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Brazil, Saudi Arabia, and Europe, can leverage several strategies to enhance their procurement process:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess the TCO rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, downtime, and replacement costs to make informed decisions.
-
Volume Discounts: Consolidating orders or committing to long-term contracts can provide leverage for negotiating lower prices.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and improved negotiation outcomes.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Explore Alternatives: Consider alternative suppliers or materials that may offer similar performance at a lower cost. However, ensure that any changes do not compromise quality or reliability.
Conclusion
Sourcing ball bearing components requires a nuanced understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics. By comprehensively evaluating the factors influencing costs and employing strategic negotiation tactics, international B2B buyers can secure favorable terms that align with their operational needs. Remember, indicative prices can vary widely based on market conditions, so continuous market analysis is essential for optimal sourcing.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing ball bearing components With Other Solutions
In the realm of mechanical components, ball bearings are widely recognized for their efficiency in reducing friction and facilitating smooth rotation. However, various alternatives exist that can serve similar functions, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. This section explores these alternatives, comparing them to ball bearing components in terms of performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Ball Bearing Components | Magnetic Bearings | Sleeve Bearings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity, low friction | Excellent for high-speed applications, virtually no friction | Moderate load capacity, friction depends on material |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High initial investment, lower long-term costs | Low initial cost, may require replacement |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise fitting and alignment | Complex installation and setup | Simple installation, can be used in various applications |
| Maintenance | Regular lubrication needed, periodic replacement | Minimal maintenance, long lifespan | Regular lubrication needed, prone to wear |
| Best Use Case | Automotive, industrial machinery | Aerospace, high-speed applications | General applications, low-speed machinery |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are Magnetic Bearings and Their Advantages?
Magnetic bearings use magnetic fields to support moving parts without physical contact. This technology offers exceptional performance in high-speed applications where traditional bearings might fail due to friction. They are particularly advantageous in industries such as aerospace and energy, where precision and reliability are critical. However, their high initial cost and complex installation process can be barriers for some businesses.
How Do Sleeve Bearings Compare?
Sleeve bearings, also known as plain bearings, use a sliding motion between the shaft and the bearing surface. They are generally less expensive than ball bearings and can be made from various materials, such as bronze or plastic. While they are suitable for low-speed applications, they can wear out more quickly and require regular lubrication to maintain performance. Their simplicity in installation makes them a popular choice for general applications, but they may not support high loads as effectively as ball bearings.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a bearing solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including load capacity, operating speed, and environmental conditions. Ball bearing components are ideal for applications requiring high load capacities and low friction, while magnetic bearings excel in high-speed contexts. Sleeve bearings may be the best choice for budget-conscious projects with lower performance demands. By thoroughly evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ball bearing components
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Ball Bearing Components?
Understanding the technical specifications of ball bearing components is crucial for B2B buyers, as these properties influence performance, durability, and compatibility with various applications. Here are some essential technical properties:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a ball bearing significantly affects its strength, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. Common materials include high-carbon chrome steel (AISI 52100), stainless steel (AISI 440C), and ceramic materials. High-carbon steel is generally preferred for its toughness and wear resistance, while stainless steel is chosen for environments prone to corrosion. Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring longevity and reliability in specific applications.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. It is critical in ball bearings, as precise tolerances ensure proper fit and function within machinery. Bearings with tighter tolerances can handle higher loads and reduce vibration, which is essential for high-speed applications. Understanding tolerance levels helps in selecting components that meet specific operational requirements, minimizing the risk of premature failure.
3. Load Ratings
Load ratings indicate the maximum load a bearing can support without failing. These ratings are divided into dynamic and static load ratings. Dynamic load ratings apply when the bearing is in motion, while static load ratings are relevant when the bearing is stationary. For B2B buyers, knowing the load ratings helps in selecting bearings that can withstand the operational stresses of their machinery, thereby enhancing efficiency and performance.
4. Lubrication Type
The type of lubrication used in ball bearings—whether grease or oil—affects friction, wear, and heat generation. Grease is typically used for lower-speed applications due to its ability to remain in place, while oil is better for high-speed applications as it reduces friction more effectively. Proper lubrication is essential for extending the lifespan of the bearing and maintaining optimal performance.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
5. Seal Type
Seals protect bearings from contaminants such as dust, dirt, and moisture, which can lead to premature failure. Common seal types include rubber seals, metal shields, and open designs. Each type has its advantages and limitations, affecting factors like friction, heat generation, and maintenance frequency. Choosing the right seal type ensures that the bearing operates efficiently in its intended environment.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Ball Bearing Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication in the ball bearing market. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the ball bearing industry, OEMs often provide components that meet specific design requirements for various applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure that they are sourcing high-quality, compatible parts.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and procurement strategies. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs and avoid excess inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of ball bearings, an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, specifications, and lead times from different manufacturers, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
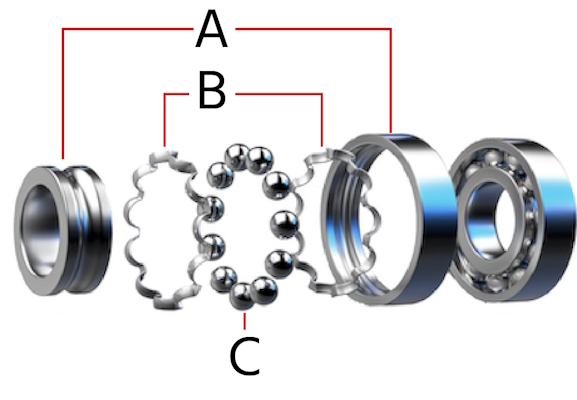
Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. These terms clarify aspects such as shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to navigate global supply chains effectively and minimize risks.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the goods are delivered. In the ball bearing industry, lead times can vary based on factors like manufacturing processes and shipping methods. Awareness of lead times is essential for B2B buyers to plan their production schedules and manage customer expectations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding ball bearing components, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the ball bearing components Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Trends in Ball Bearing Components?
The global ball bearing components market is experiencing notable growth driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. As industries aim for higher efficiency and lower energy consumption, the focus has shifted towards advanced bearing technologies that can support higher loads while minimizing friction. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where infrastructure development and industrialization are accelerating.

Illustrative image related to ball bearing components
Emerging technologies such as IoT and AI are reshaping the sourcing landscape, enabling predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of ball bearing performance. This shift not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces downtime, making it critical for buyers to consider suppliers that integrate these technologies into their offerings. Additionally, suppliers are increasingly adopting digital platforms for streamlined procurement processes, allowing buyers to access a wider range of products and make informed decisions based on comprehensive data analytics.
Moreover, as the market becomes more competitive, there is a growing emphasis on customization. Buyers are seeking suppliers who can offer tailored solutions that meet specific operational needs, from specialized coatings that enhance durability to hybrid materials that balance performance and cost. Understanding these dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their sourcing strategies in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Ball Bearing Components?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal concern in the ball bearing components sector, driven by increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting buyers to prioritize suppliers with sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient production techniques that reduce the carbon footprint associated with ball bearing manufacturing.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitation and adhere to labor standards. This has led to a growing focus on suppliers who can provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices and demonstrate compliance with international labor and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are becoming essential criteria for B2B buyers when evaluating suppliers.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications and materials into sourcing strategies not only enhances corporate social responsibility but also positions companies favorably in a market that increasingly values sustainability. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainability, ensuring that their purchases align with broader environmental and social goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Ball Bearing Components and Their Evolution?
The evolution of ball bearing components can be traced back to the early 18th century when they were first conceptualized as a solution to reduce friction in machinery. Initially, these components were made from wood, but advancements in metallurgy during the Industrial Revolution led to the development of steel ball bearings, significantly enhancing their durability and performance.
Throughout the 20th century, the design and manufacturing processes for ball bearings underwent substantial innovations, including the introduction of precision engineering techniques and the use of advanced materials. The latter half of the century saw the emergence of specialized bearings designed for specific applications, catering to diverse industries from automotive to aerospace.
Today, the continuous evolution of ball bearing technology reflects the need for improved efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. As industries globally strive for innovation and productivity, understanding the historical context of these components provides valuable insights for B2B buyers seeking to make informed sourcing decisions that align with current market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ball bearing components
-
How do I solve issues with ball bearing performance?
To address performance issues with ball bearings, first identify the cause, which may include inadequate lubrication, contamination, or misalignment. Ensure that bearings are properly lubricated with the appropriate grease or oil for the application. Regular maintenance checks can help detect contamination, such as dirt or debris, which can lead to premature failure. If misalignment is suspected, verify the installation angles and adjust as necessary to ensure optimal performance. For persistent issues, consider consulting a technical expert to analyze the application and recommend suitable bearing types. -
What is the best type of ball bearing for high-load applications?
For high-load applications, deep groove ball bearings are often the best choice due to their ability to handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously. They feature deeper grooves, allowing for a greater contact area between the balls and the races, which enhances load distribution. Additionally, angular contact ball bearings are suitable for applications requiring high axial load capacity, especially when arranged in pairs. Evaluating the specific load conditions and operational environment will help determine the most effective bearing type. -
How do I choose the right supplier for ball bearing components?
When selecting a supplier for ball bearing components, consider their industry reputation, experience, and product quality certifications. Check for references from other B2B clients and inquire about their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. It’s also crucial to evaluate their ability to provide customized solutions based on your specific needs. Compare pricing, lead times, and after-sales support to ensure they align with your business requirements. Building a relationship with a reliable supplier can significantly enhance your supply chain efficiency. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for ball bearings?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for ball bearings can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the type of bearing and customization options. Generally, standard bearings may have lower MOQs, while specialized or custom bearings could require larger orders. It’s essential to discuss your needs directly with the supplier to understand their policies. If your requirements are low, consider negotiating terms or exploring suppliers that specialize in smaller orders to avoid excess inventory. -
What payment terms are common for international transactions of ball bearings?
In international transactions, common payment terms include letters of credit, advance payments, and open account terms. Letters of credit offer security for both the buyer and seller, ensuring that payment is made only upon meeting specified conditions. Advance payments may be required for custom or large orders. Open account terms can be beneficial for established relationships but may not be readily available for new clients. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing agreements to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for ball bearing components?
To ensure quality assurance in ball bearing components, request documentation of quality control processes from the supplier, including certificates like ISO 9001. Conduct regular audits of the supplier’s facilities if possible, or consider third-party inspection services to evaluate product quality before shipment. Additionally, establish clear specifications and performance standards in your purchase agreement to hold suppliers accountable for quality. Implementing a robust incoming inspection process will also help catch any issues before the bearings are integrated into your operations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing ball bearings?
When importing ball bearings, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial components to navigate potential challenges effectively. Be aware of import duties, tariffs, and any specific documentation required for customs clearance. Additionally, plan for potential delays by building a buffer into your supply chain timelines. Effective communication with your supplier about shipping schedules and tracking can help mitigate logistical issues. -
Can ball bearings be customized for specific applications?
Yes, ball bearings can often be customized to meet specific application requirements. Customization options may include changes to dimensions, materials, sealing types, and lubrication methods. When seeking customized bearings, communicate your technical specifications clearly to the supplier, including load capacities, environmental conditions, and performance expectations. Many suppliers have the capability to design and manufacture tailored solutions, which can enhance the performance and longevity of the bearings in your application.
Top 8 Ball Bearing Components Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tameson – Ball Bearings
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: A ball bearing is a circular joint that connects a rotating part to a stationary part of a machine, reducing friction during rotation. Key components include two grooved circular tracks (raceways) and a set of balls (ball bearing rollers). Ball bearings can be sealed or open, and lubricants like grease or oil are used to ensure smooth operation. Types of ball bearings include: 1. Deep Groove Ball …
2. Koyo – Bearings Overview
Domain: koyo.jtekt.co.jp
Introduction: The text discusses the structure and components of bearings, which are designed to reduce friction and allow for smooth rotation. Key components include: 1. Bearing rings (races) – ring-shaped components that form the structure of the bearing. 2. Rolling elements – components that roll between the bearing rings, which can be either balls or rollers. 3. Cage – maintains a fixed gap between rolling …
3. NSK – Bearings
Domain: nsk.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Bearings are crucial machine components that increase the efficiency of movement by reducing friction, thereby extending equipment lifespan. There are two main types of bearings: plain (sliding) bearings and rolling (rolling-element) bearings. Rolling bearings have several advantages over plain bearings, including lower friction, standardized dimensions, ease of maintenance, ability to handle vari…
4. Bearing Wizard – Essential Rolling Bearing Components
Domain: bearingwizard.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Main components of rolling bearings include: Inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements, and cage. Optionally, a seal can be installed in a groove on the inner and outer ring. Lubrication with grease or oil reduces friction and wear. Rolling elements can be in ball or roller form, depending on the bearing type. Bearings can be classified as axial or radial based on the direction of the load, with ax…
5. Component Hardware – Bearing Components
Domain: componenthardware.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Bearing Components are part of the Cabinet Hardware and Accessories offered by Component Hardware. The product category includes various components such as bumpers, grommets, catches (both magnetic and mechanical), and drawer assemblies. The offerings are designed for industrial applications and are part of a broader range of cabinet hardware, including drawer components, slides, handles, pulls, h…
6. EZO – Precision Ball Bearings
Domain: ezo-usa.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Ball bearings are mechanical components that reduce friction between rotating elements, consisting of a bearing race, a ball, and a retainer. They are used in various applications including automotive, aerospace, medical, and defense industries. SPB-USA manufactures precision ball bearings in multiple sizes and load capacities, certified in ISO 9000, ISO 9001, and ISO 14001. Types of ball bearings…
7. NMB – Miniature Ball Bearings
Domain: nmbtc.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: NMB specializes in the manufacture of miniature and small-sized ball bearings with an outer diameter of 30mm or less. Ball bearings are used in various applications including small and large motors, car axles, electric fans, and hard disc drives (HDDs). They consist of four major parts: an outer ring, an inner ring, steel balls, and a cage. The primary function is to reduce friction and facilitate…
8. Minebea Mitsumi – Rolling Ball Bearings
Domain: product.minebeamitsumi.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: A rolling ball bearing is composed of an outer and inner ring (raceway rings), balls (rolling elements), and a retainer. Shields, seals, flanges, and snap rings can also be included. Components and Names of Rolling Ball Bearings include: Basic, Shielded, With flange, With snap ring. Engineering Information for Miniature & small ball bearings includes selecting the right part, product catalog, tech…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ball bearing components
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing of ball bearing components is paramount for operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the diverse types of ball bearings—such as deep groove, angular contact, and self-aligning bearings—international B2B buyers can make informed choices that align with their specific application needs. The ability to select the right bearing not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of machinery, ultimately leading to reduced maintenance costs.
As buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate their sourcing strategies, it is crucial to prioritize suppliers who offer quality products, reliable delivery, and competitive pricing. Engaging in strategic partnerships can yield benefits such as access to innovative technologies and tailored solutions that meet unique market demands.
Looking ahead, the global market for ball bearing components is set to expand, driven by advancements in technology and increasing automation. Buyers are encouraged to stay proactive in their sourcing strategies, leveraging data-driven insights to optimize their supply chains. By doing so, they can position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive environment. Embrace the future of manufacturing and ensure your operations are equipped with the best ball bearing solutions available.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.