Everything You Need to Know About Automated Screw Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for automated screw
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, sourcing automated screw solutions can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. The need for efficient, reliable, and adaptable fastening systems is critical, particularly for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Brazil and Vietnam. This guide is designed to navigate the complexities of the automated screw market, offering insights into various types of systems, their applications across multiple industries, and best practices for supplier vetting.
We will delve into the mechanics of automated screwdriving technology, exploring both handheld and fixtured systems, as well as the latest innovations in screw feeding and dispensing. Additionally, we will provide a comprehensive overview of cost considerations, enabling buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational budgets and production needs.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge of industry leaders and emerging trends, this guide empowers them to streamline their procurement processes and enhance their manufacturing capabilities. Whether you are seeking to optimize production lines in automotive, aerospace, or general manufacturing, understanding the nuances of automated screw systems is essential for driving efficiency and reducing downtime. With actionable insights and expert advice, this guide serves as your roadmap to successfully sourcing automated screw solutions that meet your specific business requirements.
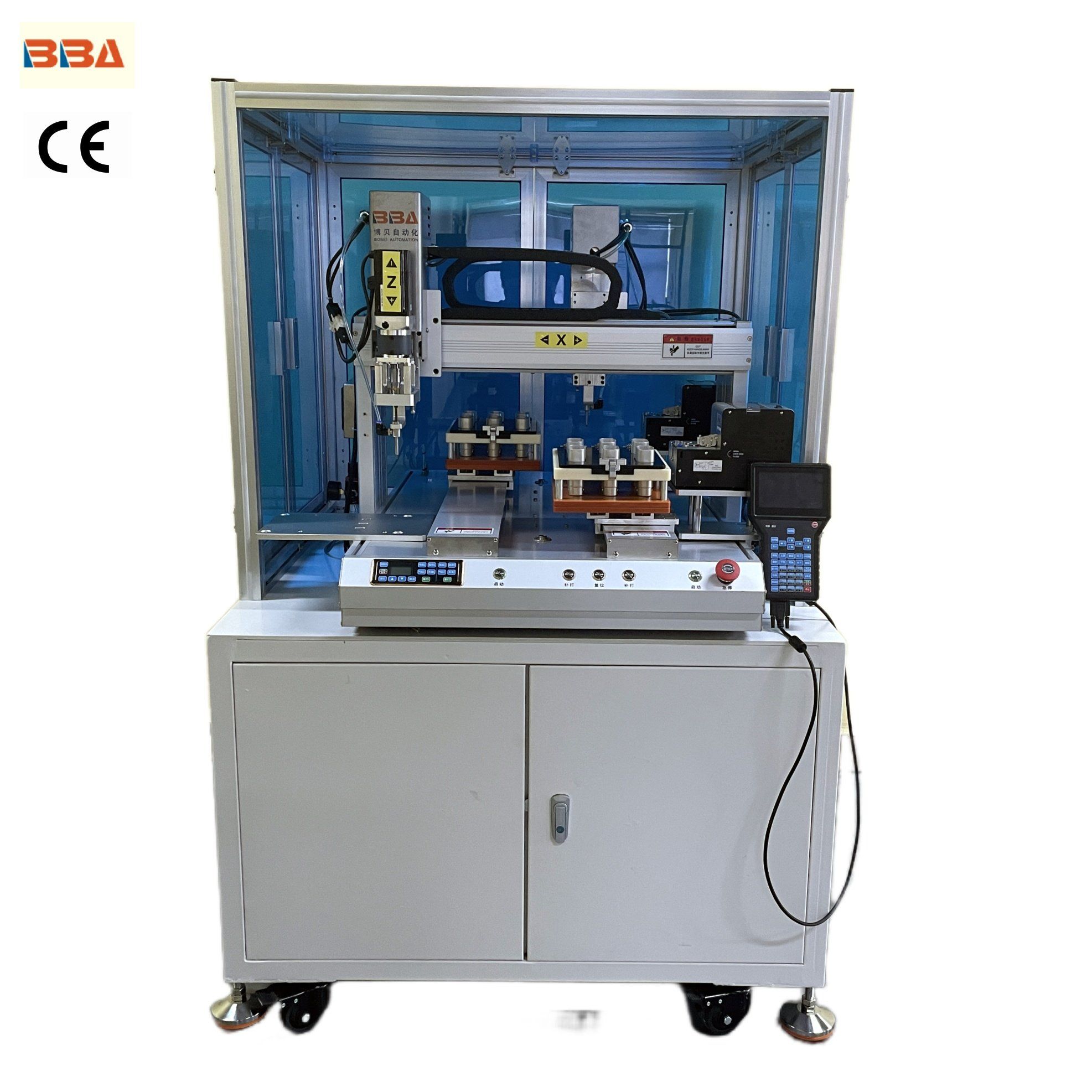
Understanding automated screw Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixtured Drive Heads | Integrated with robotic systems; high torque capabilities | Automotive assembly, electronics manufacturing | Pros: High precision, efficient for repetitive tasks. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Handheld Drive Heads | Portable and flexible; suitable for various fasteners | Small-scale assembly, maintenance operations | Pros: Versatile, easy to use. Cons: Less power for heavy-duty applications. |
| Multi-Spindle Screwdrivers | Multiple screws driven simultaneously; ideal for high-volume tasks | Mass production environments | Pros: Increased productivity, reduced cycle time. Cons: Complexity in setup and maintenance. |
| Vibratory Screw Feeders | Automated feeding system; reduces downtime between screw placements | General manufacturing, assembly lines | Pros: Streamlined operation, minimizes manual handling. Cons: Requires space and setup time. |
| CoBot Integrated Systems | Collaborative robots (CoBots) for enhanced safety and efficiency | Flexible manufacturing environments | Pros: Safe human-robot interaction, adaptable. Cons: May have limitations in payload capacity. |
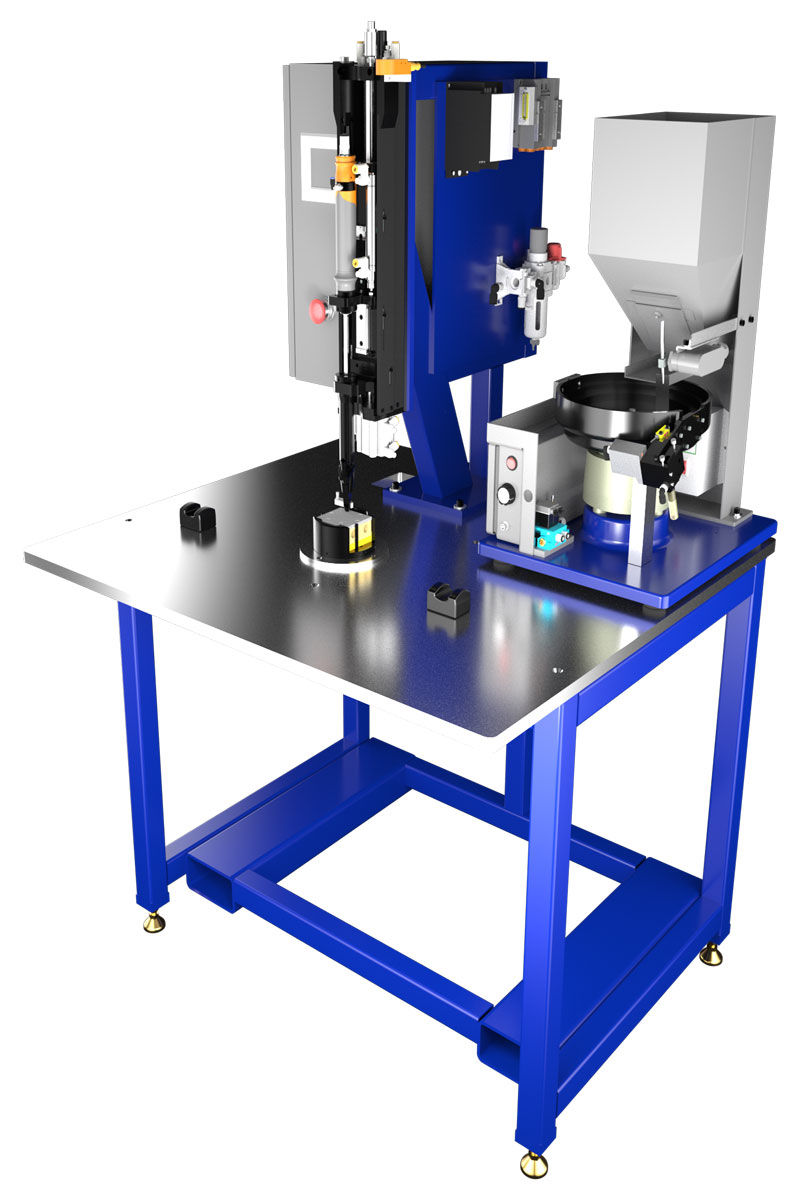
What are the characteristics and suitability of Fixtured Drive Heads?
Fixtured drive heads are highly specialized automated screwdriving systems designed to integrate seamlessly with robotic positioning systems. These devices are characterized by their ability to deliver high torque in a compact design, making them suitable for industries such as automotive and electronics manufacturing. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate their production volume needs and the compatibility of these systems with existing robotic frameworks.
How do Handheld Drive Heads differ in application?
Handheld drive heads offer flexibility and portability, making them ideal for varied applications, including small-scale assembly tasks and maintenance operations. These systems are user-friendly and can adapt to different fastener types, providing an excellent solution for businesses requiring versatility. Buyers should consider the specific use cases and whether the power output meets their operational demands, particularly for heavier applications.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
What advantages do Multi-Spindle Screwdrivers provide for high-volume production?
Multi-spindle screwdrivers are designed to drive multiple screws simultaneously, significantly enhancing productivity in mass production environments. This type of automated screwdriving system reduces cycle times, making it an attractive option for manufacturers focused on efficiency. However, potential buyers should be aware of the complexity involved in setup and maintenance, which may require specialized training or support.
Why are Vibratory Screw Feeders essential in manufacturing?
Vibratory screw feeders automate the feeding process, allowing for continuous operation and minimizing downtime between screw placements. This system is particularly beneficial in general manufacturing and assembly lines, where efficiency is paramount. B2B buyers should assess the space requirements and the initial setup time, as these systems can require a significant investment in infrastructure.
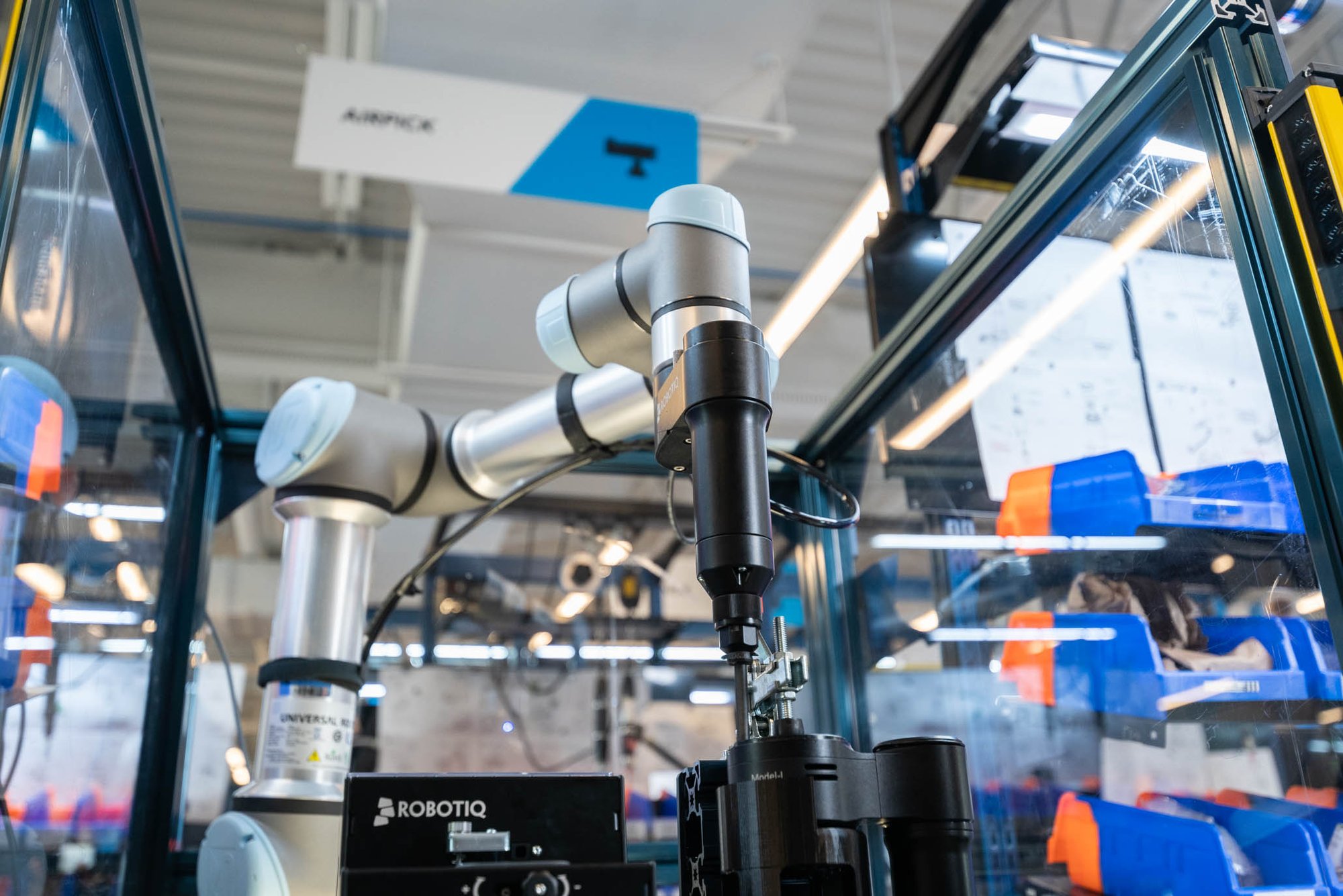
What role do CoBot Integrated Systems play in modern manufacturing?
CoBot integrated systems utilize collaborative robots to enhance safety and efficiency in manufacturing environments. These systems are designed for flexible applications, allowing for safe human-robot interactions while automating screwdriving tasks. Buyers should consider the payload capacity and the specific applications for which they intend to use CoBots, as these systems may not be suitable for all production scenarios.
Key Industrial Applications of automated screw
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of automated screw | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Assembly of vehicle components | Increased assembly speed and accuracy | Compatibility with various fasteners and torque settings |
| Electronics | Installation of circuit boards | Enhanced precision and reduced assembly time | Customization options for different board sizes |
| Aerospace & Defense | Fastening of structural components in aircraft | Improved safety and reliability in critical assemblies | Compliance with industry regulations and standards |
| Medical Devices | Assembly of surgical instruments and devices | Ensured sterility and precision in manufacturing | Ability to handle delicate components with care |
| General Manufacturing | Integration into production lines for various products | Streamlined operations and reduced labor costs | Flexibility to adapt to different manufacturing setups |
How is Automated Screw Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, automated screw systems are crucial for the assembly of various vehicle components, such as engines, chassis, and interior fittings. These systems enhance production efficiency by significantly speeding up the fastening process while maintaining high accuracy, which is vital for safety and quality control. International buyers should consider sourcing solutions that offer compatibility with different fasteners and adjustable torque settings to accommodate the diverse range of automotive applications.
What Role Does Automated Screw Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
Automated screwdriving technology is extensively used in the electronics industry, particularly for the installation of screws in circuit boards and other electronic assemblies. This application not only speeds up the production process but also ensures high precision, reducing the risk of errors that could lead to product failures. Buyers in this sector should seek customizable solutions that can be tailored to various board sizes and configurations, ensuring compatibility with their specific manufacturing processes.
How is Automated Screw Technology Applied in Aerospace & Defense?
In aerospace and defense, automated screw systems are employed for fastening structural components in aircraft and military vehicles. These applications demand the highest levels of safety and reliability, as any failure can have catastrophic consequences. Therefore, sourcing solutions that comply with strict industry regulations and standards is paramount. Buyers should prioritize systems that can deliver consistent performance under rigorous conditions, ensuring that all components are securely fastened.
What Benefits Does Automated Screw Provide in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Automated screw technology plays a vital role in the assembly of medical devices and surgical instruments, where precision and sterility are critical. These systems help manufacturers maintain stringent quality control while speeding up production times. For international buyers in this sector, it is essential to select automated screw solutions capable of handling delicate components with care, ensuring that the integrity of the devices is preserved throughout the assembly process.
How Can Automated Screw Systems Enhance General Manufacturing Operations?
In general manufacturing, automated screw systems are integrated into production lines to streamline the assembly of various products, from appliances to furniture. This technology reduces labor costs and increases operational efficiency by automating repetitive fastening tasks. Buyers should look for flexible systems that can easily adapt to different manufacturing setups, allowing for quick changes in production lines to meet varying demands.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘automated screw’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Integrating Automated Screw Systems into Existing Workflows
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant challenges when trying to integrate automated screw systems into their existing manufacturing workflows. They often encounter compatibility issues with current machinery or processes, leading to delays and increased costs. For example, a buyer in the automotive industry may find that their existing assembly line cannot accommodate a new automated screwdriving system due to size constraints or differing operational speeds. This lack of compatibility can result in frustration and a reluctance to invest in automation, as the perceived complexity and costs outweigh the potential benefits.
The Solution: To overcome these integration challenges, buyers should first conduct a comprehensive assessment of their existing workflows. This involves mapping out current processes, identifying bottlenecks, and understanding the specific requirements of the automated screw systems they are considering. Engaging with suppliers who offer customized solutions can also be beneficial. For instance, suppliers like Carlson Engineering provide tailored systems that can be adjusted to fit unique operational environments. Additionally, buyers should seek systems with modular designs, allowing for easier integration without requiring a complete overhaul of existing machinery. Finally, investing in training for staff can ensure that the transition to automated systems is smooth and that employees are equipped to maximize the benefits of new technology.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance Costs of Automated Screw Systems
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the ongoing maintenance costs associated with automated screwdriving systems. Many organizations find that while these systems initially improve efficiency, they often require expensive repairs and part replacements over time, which can erode their return on investment. For example, a manufacturer in the medical device sector may invest heavily in a high-tech screwdriving solution only to face unexpected downtime due to mechanical failures, leading to lost production hours and revenue.
The Solution: To mitigate high maintenance costs, buyers should prioritize sourcing equipment known for its reliability and low maintenance requirements. Suppliers like WEBER emphasize durability and long-term performance in their automated systems, which can be a crucial selling point. Buyers should also consider investing in preventive maintenance programs that include regular inspections and servicing to catch potential issues before they escalate. Implementing a tracking system for maintenance schedules can further help in minimizing unexpected downtime. Lastly, opting for equipment with readily available spare parts and strong supplier support can significantly reduce the cost and complexity of repairs, ensuring that operations remain uninterrupted.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Consistent Quality in Automated Screw Applications
The Problem: Quality control is a major concern for B2B buyers utilizing automated screw systems. Inconsistent screw placement or fastening can lead to product defects, which not only affects customer satisfaction but can also result in costly recalls. For instance, a manufacturer producing electronic devices may find that automated screw applications are not providing the precision required, leading to product failures and warranty claims. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including equipment misalignment, incorrect torque settings, or the use of low-quality fasteners.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should focus on selecting automated screwdriving systems that offer advanced control features, such as torque monitoring and feedback mechanisms. Systems that integrate with quality control processes can help ensure that every screw is placed correctly and securely. Additionally, investing in high-quality fasteners that are compatible with the automated systems can further enhance product integrity. Regular training and calibration of the automated systems are essential to maintain precision. Collaborating with suppliers who provide comprehensive training and support can ensure that teams are skilled in operating the equipment effectively and addressing any quality concerns proactively. By prioritizing quality in both equipment selection and operational practices, manufacturers can significantly reduce defects and enhance their product reliability.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for automated screw
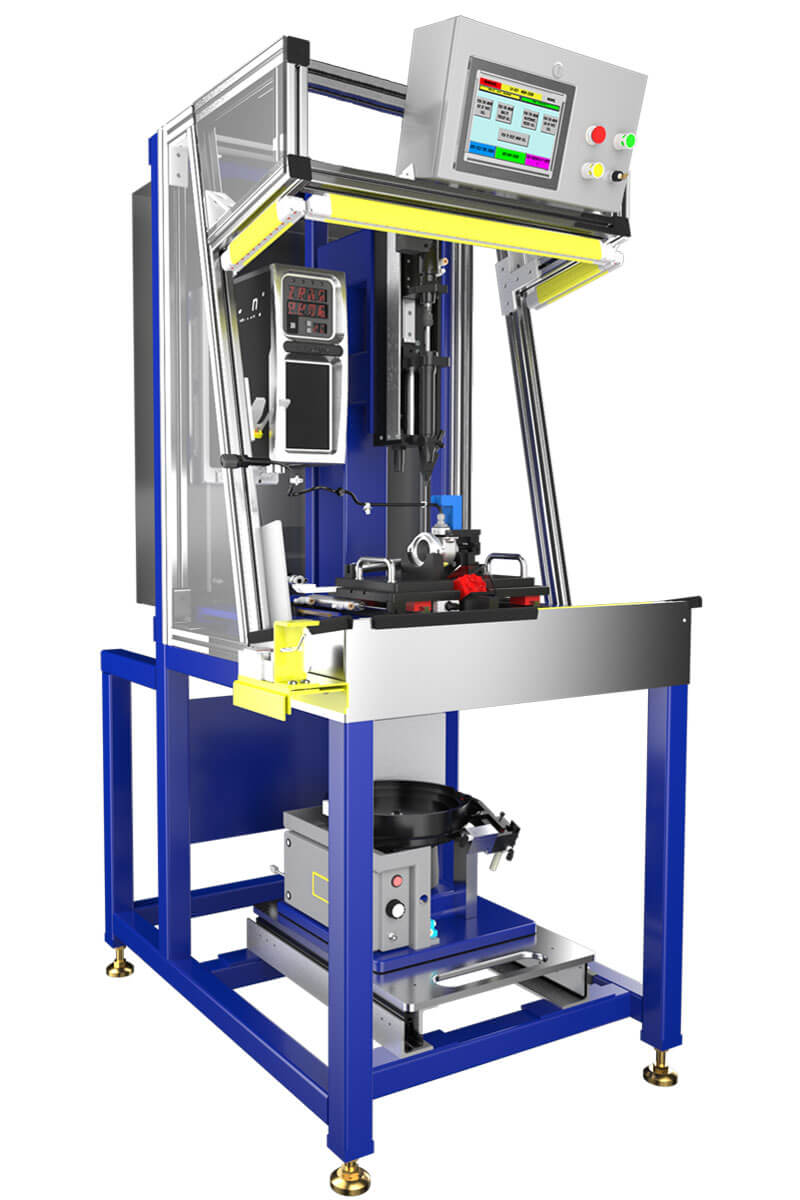
What Are the Key Materials Used for Automated Screws?
Automated screws are essential components in various industries, and the selection of the right material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used for automated screws: stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and plastic. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact application suitability, particularly for international B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
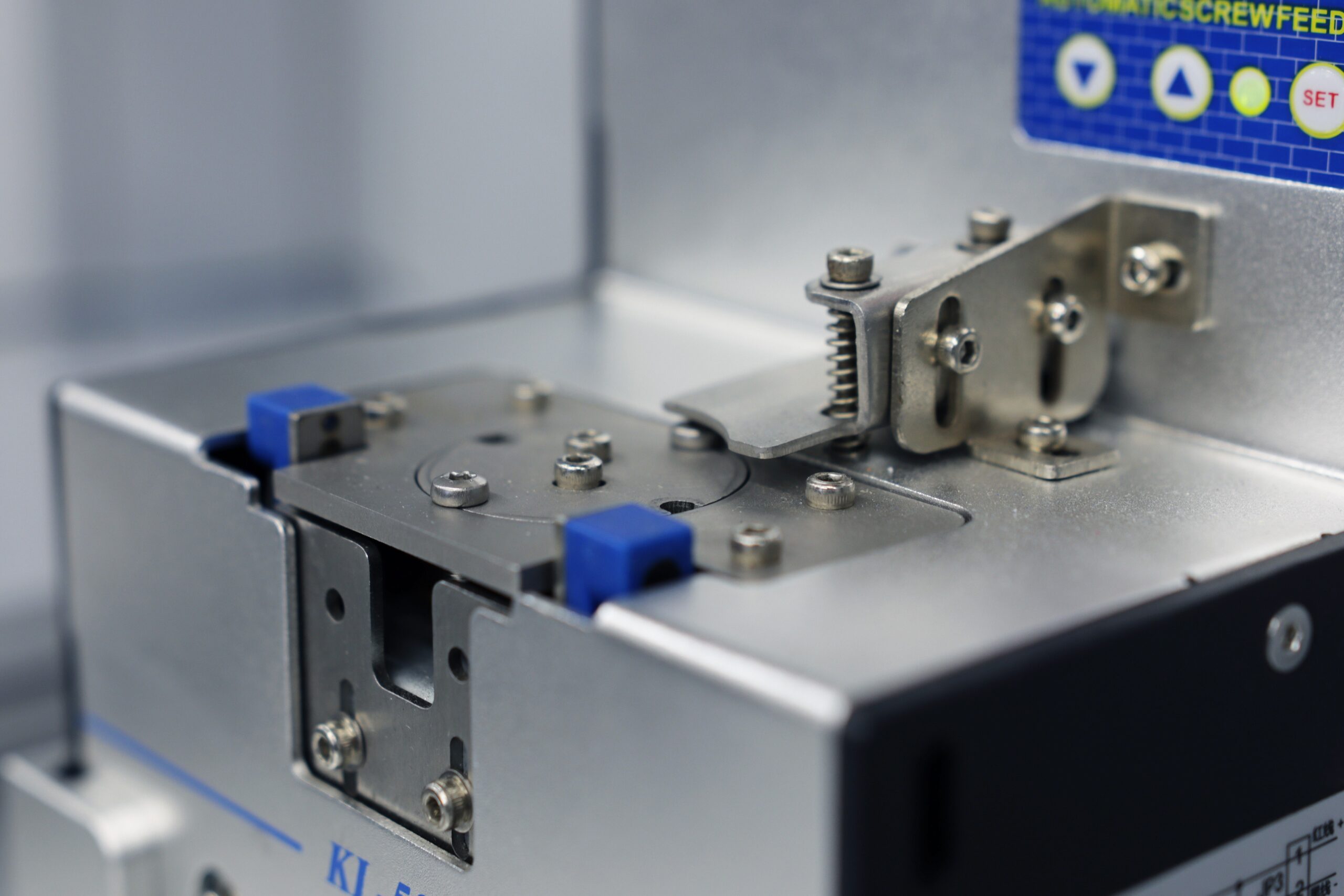
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Automated Screws?
Stainless steel is widely used in automated screw applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength. It typically withstands high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for harsh environments. The key properties include a temperature rating of up to 800°F (427°C) and significant resistance to oxidation and rust.
Pros: Stainless steel screws are durable and can last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements. They are also compliant with various international standards, making them suitable for global markets.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to other materials. Manufacturing stainless steel screws can also be more complex, requiring specialized equipment.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
Impact on Application: Stainless steel screws are ideal for applications in the automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors, where reliability and safety are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM and DIN standards is essential, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where quality regulations are stringent.
What Advantages Does Carbon Steel Offer for Automated Screws?
Carbon steel is another popular choice for automated screws, known for its strength and affordability. It typically has a high tensile strength and can be heat-treated to enhance its properties.
Pros: The main advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, making it a preferred choice for mass production. It also offers good mechanical properties, suitable for various applications.
Cons: However, carbon steel is prone to rust and corrosion if not properly coated or treated. This makes it less suitable for environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel screws are commonly used in general manufacturing and construction, where cost savings are critical, but the environment is less aggressive.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid regions such as parts of Africa and South America.
How Does Brass Compare as a Material for Automated Screws?
Brass is often utilized for specialized applications in automated screws, particularly in electrical and plumbing systems. Its key properties include good conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Brass screws are non-magnetic and have excellent machinability, making them easy to work with during manufacturing. They also provide good aesthetic appeal due to their golden color.
Cons: The main limitation of brass is its relatively lower strength compared to steel, making it unsuitable for high-stress applications. Additionally, brass can be more expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application: Brass screws are ideal for electrical connections and plumbing fixtures, where conductivity and corrosion resistance are crucial.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with JIS standards is essential for buyers in Asia, while European buyers may prefer screws that meet EN standards.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Automated Screws?
Plastic screws are increasingly being used in applications where weight reduction and corrosion resistance are priorities. They are lightweight and can be manufactured in various colors and shapes.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastic screws is their resistance to corrosion and chemicals, making them suitable for outdoor applications. They are also non-conductive, which is beneficial in electrical applications.
Cons: However, plastic screws generally have lower strength and durability compared to metal options. They may not perform well under high temperatures or heavy loads.
Impact on Application: Plastic screws are commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive interiors, where lightweight and corrosion resistance are more critical than strength.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic materials used comply with relevant safety and environmental regulations, particularly in Europe and North America.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Automated Screws
| Material | Typical Use Case for automated screw | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Aerospace, automotive, medical | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Steel | General manufacturing, construction | Cost-effective, strong | Prone to rust, requires coatings | Low |
| Brass | Electrical, plumbing applications | Good conductivity, aesthetic appeal | Lower strength, higher cost than steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics, automotive interiors | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower strength, temperature limitations | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions about automated screw materials, ensuring compliance and suitability for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for automated screw
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Automated Screws?
The manufacturing process for automated screws is a complex sequence that involves several critical stages to ensure precision and reliability. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages involved:
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing of automated screws is material preparation. High-quality steel or other alloys are typically chosen based on the application requirements, such as tensile strength, corrosion resistance, or weight. The raw materials undergo several preparatory processes, including:
- Cutting: Raw metal is cut into manageable lengths for further processing.
- Heat Treatment: This process enhances the material properties, improving hardness and strength.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as coating or plating are applied to prevent corrosion and improve durability.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. Automated screws are shaped using techniques like:
- Cold Heading: This process involves deforming the metal at room temperature, which preserves its structural integrity while shaping it into a screw form.
- Thread Rolling: Threads are formed through a rolling process, which is more efficient and produces a stronger thread than cutting.
- Machining: For precision applications, screws may undergo machining to achieve exact dimensions and tolerances.
Assembly
During the assembly stage, various components of the automated screw systems are integrated. This can include the installation of:
- Drive Mechanisms: These include electric or pneumatic systems that ensure the screws can be driven into materials effectively.
- Feeding Systems: Automated feeders are integrated to supply screws in a continuous manner, enhancing production efficiency.
Finishing
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing. This includes:
- Quality Inspections: Rigorous checks are performed to ensure that all products meet specified tolerances.
- Packaging: Finished products are packaged in a manner that prevents damage during transport, especially crucial for international shipping.
- Documentation: Accompanying documentation is prepared to certify compliance with international standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Implemented?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of automated screws is vital to ensure that products meet international standards and customer specifications. Here are some key aspects of QA that buyers should consider:

Illustrative image related to automated screw
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, understanding international quality standards is essential. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable to organizations looking to enhance customer satisfaction and ensure consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: This indicates that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for screws used in the oil and gas industry, the American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards that ensure the reliability of products used in critical applications.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established?
Quality control (QC) is typically structured around several key checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the first checkpoint where raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure that the processes are in control and that product specifications are being met.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, finished products undergo rigorous testing to verify that they meet quality standards. This may include functional tests, dimensional inspections, and surface quality assessments.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
The following testing methods are frequently employed to ensure the quality and performance of automated screws:
- Tensile Testing: This evaluates the strength and ductility of the screws under tension.
- Hardness Testing: Ensures that the screws have the required hardness for their intended applications.
- Torque Testing: Measures the ability of the screw to withstand torque without failure.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Essential for screws intended for use in harsh environments, this testing evaluates the material’s ability to resist corrosion over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is critical to ensure that products will meet their operational requirements. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities can provide insight into their quality control processes, equipment, and compliance with international standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for documentation detailing the results of quality inspections and tests performed on the products.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality management practices.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing automated screws from international suppliers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers must navigate several nuances:
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding local regulations and how they align with international standards is crucial. Different regions may have varying requirements that affect product acceptance.
- Cultural Differences: Variations in business practices and communication styles can impact the negotiation and quality assurance processes.
- Logistical Challenges: Shipping and handling can introduce risks to product integrity. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping protocols in place.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for automated screws, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they select reliable suppliers who meet their quality expectations and operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘automated screw’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers looking to procure automated screw systems. The automated screwdriving technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing manufacturing efficiency, reducing labor costs, and ensuring precision in assembly processes. By following this step-by-step checklist, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as the types of screws you’ll be using, the torque specifications needed, and the speed of operation required for your assembly line.
– Types of Fasteners: Identify whether you need systems for screws, bolts, nuts, or other fasteners.
– Automation Level: Determine if you require fully automated systems or semi-automated solutions based on your production scale.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in automated screwdriving systems. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry, as their experience can significantly impact the reliability of the equipment.
– Industry Experience: Focus on suppliers that have worked with similar industries, such as automotive, aerospace, or medical.
– Client Testimonials: Seek out reviews and case studies from previous clients to gauge customer satisfaction.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
It is crucial to ensure that potential suppliers meet industry standards and regulations. Certifications can serve as a benchmark for quality and reliability.
– ISO Certifications: Check for ISO 9001 or other relevant certifications that indicate a commitment to quality management systems.
– Compliance with Local Regulations: Ensure that the equipment adheres to regional safety and operational standards, especially if you’re sourcing from international suppliers.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals outlining their solutions. This will allow you to compare offerings effectively.
– Technical Specifications: Ensure that proposals include information on the types of systems offered, customization options, and integration capabilities.
– Pricing Structure: Look for transparency in pricing, including potential hidden costs such as installation, training, and maintenance.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
After-sales support is a critical factor in the longevity and efficiency of your automated screwdriving systems. Evaluate the level of service each supplier offers post-purchase.
– Training Programs: Confirm whether the supplier provides comprehensive training for your staff on operating and maintaining the equipment.
– Technical Support: Assess the availability of technical support, including response times and service agreements.
Step 6: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Demos
If possible, arrange site visits to see the automated screwdriving systems in action. Alternatively, request virtual demonstrations to evaluate the technology firsthand.
– Real-World Performance: Observing the equipment in use can provide insights into its operational efficiency and ease of use.
– User Experience: Engage with current users to gather feedback about their experience with the system and the supplier’s support.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Terms
Once you’ve made your choice, carefully review and negotiate the terms of the contract. Ensure all agreed specifications, delivery timelines, and support services are clearly outlined.
– Warranty and Maintenance: Confirm the warranty period and any maintenance packages available.
– Payment Terms: Discuss payment schedules and conditions to avoid any future misunderstandings.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing automated screw systems, ensuring they select the right solution for their manufacturing needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for automated screw Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Automated Screw Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of automated screw sourcing is vital for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement processes. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as metals (steel, aluminum) and plastics significantly impacts pricing. High-quality materials that meet industry standards can elevate costs but also enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region, skill level required, and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but buyers should also consider the skill level and training of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, impacting the overall cost of automated screws.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling investments can be substantial, especially for custom designs. These costs are often amortized over large production runs, making it essential for buyers to consider the minimum order quantities (MOQ).
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure that products meet specifications and standards. While these processes can add to costs, they are essential for maintaining product integrity and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the distance, mode of transport, and volume of the order. International buyers must factor in customs duties and potential delays.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on brand reputation, product quality, and competitive landscape. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can provide insight into pricing strategies.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Automated Screw Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of automated screws, which can vary significantly across different regions and markets:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically reduce the per-unit cost due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQ to ensure they receive favorable pricing without overcommitting.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom solutions often incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define specifications upfront to avoid unexpected expenses later in the process.
-
Material Selection: The choice of materials can dramatically affect pricing. High-performance materials may be more expensive but can lead to lower long-term costs due to enhanced reliability.
-
Quality Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certified products against cost.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and service levels can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices due to their proven track record, which can be worth the investment.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can affect total costs. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears the cost of shipping and insurance, impacting the final price.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Costs in Automated Screw Procurement?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the complexities of automated screw sourcing requires strategic planning:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage your purchasing power, particularly if you can commit to larger volumes.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes all costs associated with the product over its lifecycle, not just the purchase price. This approach helps in assessing the long-term value of a supplier’s offering.
-
Research Local Suppliers: Local suppliers may offer competitive pricing due to reduced logistics costs. Understanding the local market can provide significant savings.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different markets may have varying pricing structures due to economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and import tariffs. Stay informed about these factors to make educated purchasing decisions.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: When seeking quotes, ask for a breakdown of costs. This transparency can help identify potential areas for negotiation or cost savings.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for automated screws can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The information provided is indicative and should be validated through direct quotes from suppliers. Always conduct thorough research and due diligence before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing automated screw With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Automated Screw Solutions
In the quest for efficient assembly processes, businesses often consider various fastening solutions. While automated screw systems have gained significant traction due to their precision and speed, it is essential to explore other viable alternatives that might better suit specific operational needs. This analysis will compare automated screw solutions with two alternative fastening methods: manual fastening and adhesive bonding.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Automated Screw | Manual Fastening | Adhesive Bonding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-speed, precise | Slower, variable accuracy | Strong bond, time-dependent curing |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower long-term costs | Low initial cost, higher labor costs | Moderate initial cost, variable long-term costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training and integration | Simple to implement | Requires surface preparation and curing time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; regular checks needed | High maintenance; human error prevalent | Low maintenance; depends on application |
| Best Use Case | High-volume, repetitive tasks | Low-volume, diverse tasks | Applications requiring permanent bonds |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Manual Fastening
Manual fastening involves the use of handheld tools to drive screws into materials. This method is often favored in low-volume production environments where the flexibility to adapt to various tasks is required.
Pros: The initial investment is minimal, making it accessible for small businesses. Additionally, manual fastening allows for greater operator control, which can be beneficial for intricate assembly tasks.
Cons: However, this method is time-consuming and can lead to inconsistencies in screw placement and torque, resulting in potential quality issues. The reliance on human labor also introduces variability in performance and increases the risk of fatigue-related errors over time.
Adhesive Bonding
Adhesive bonding uses various types of adhesives to create a bond between components. This method is particularly advantageous in applications where traditional mechanical fastening methods may not suffice, such as in the automotive or aerospace industries.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
Pros: Adhesives can provide a strong, permanent bond that is often more resistant to environmental factors. This method is ideal for joining dissimilar materials and can reduce the weight of assemblies compared to mechanical fasteners.
Cons: The downsides include the need for careful surface preparation, which can complicate the assembly process. Additionally, adhesive curing times can slow production rates, making it less suitable for high-speed assembly lines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When deciding on the best fastening solution for your business, it is crucial to evaluate the specific requirements of your production processes. For high-volume manufacturing where speed and precision are paramount, automated screw systems offer clear advantages. However, if your operations are more varied and require flexibility, manual fastening may be more appropriate. Adhesive bonding is an excellent choice for applications demanding strong, permanent connections but may not be suitable for environments that prioritize speed.
Ultimately, the right choice will depend on your operational goals, budget constraints, and the nature of the products you are assembling. By carefully analyzing these factors, you can select a fastening solution that enhances efficiency and meets your production needs.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for automated screw
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Automated Screws?
In the realm of automated screw systems, understanding the technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties that buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of screws significantly affects their strength and durability. Common materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel, each offering different levels of corrosion resistance, tensile strength, and weight. For example, stainless steel screws are ideal for environments exposed to moisture, while carbon steel offers better tensile strength for heavy-duty applications. Selecting the right material grade is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of the automated screw system.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. High tolerance levels in screw dimensions ensure that parts fit together seamlessly, minimizing the risk of assembly errors. In automated environments, precise tolerances are critical for maintaining production efficiency and reducing waste. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers ensure that the automated screw systems will work effectively with their existing machinery.
3. Torque Rating
The torque rating indicates the maximum rotational force that a screw can withstand during installation. This property is particularly important in automated systems where screws must be driven with precision. A higher torque rating allows for the use of screws in demanding applications, such as automotive assembly, where securing components is crucial. Buyers should consider the torque requirements of their specific applications to ensure optimal performance.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
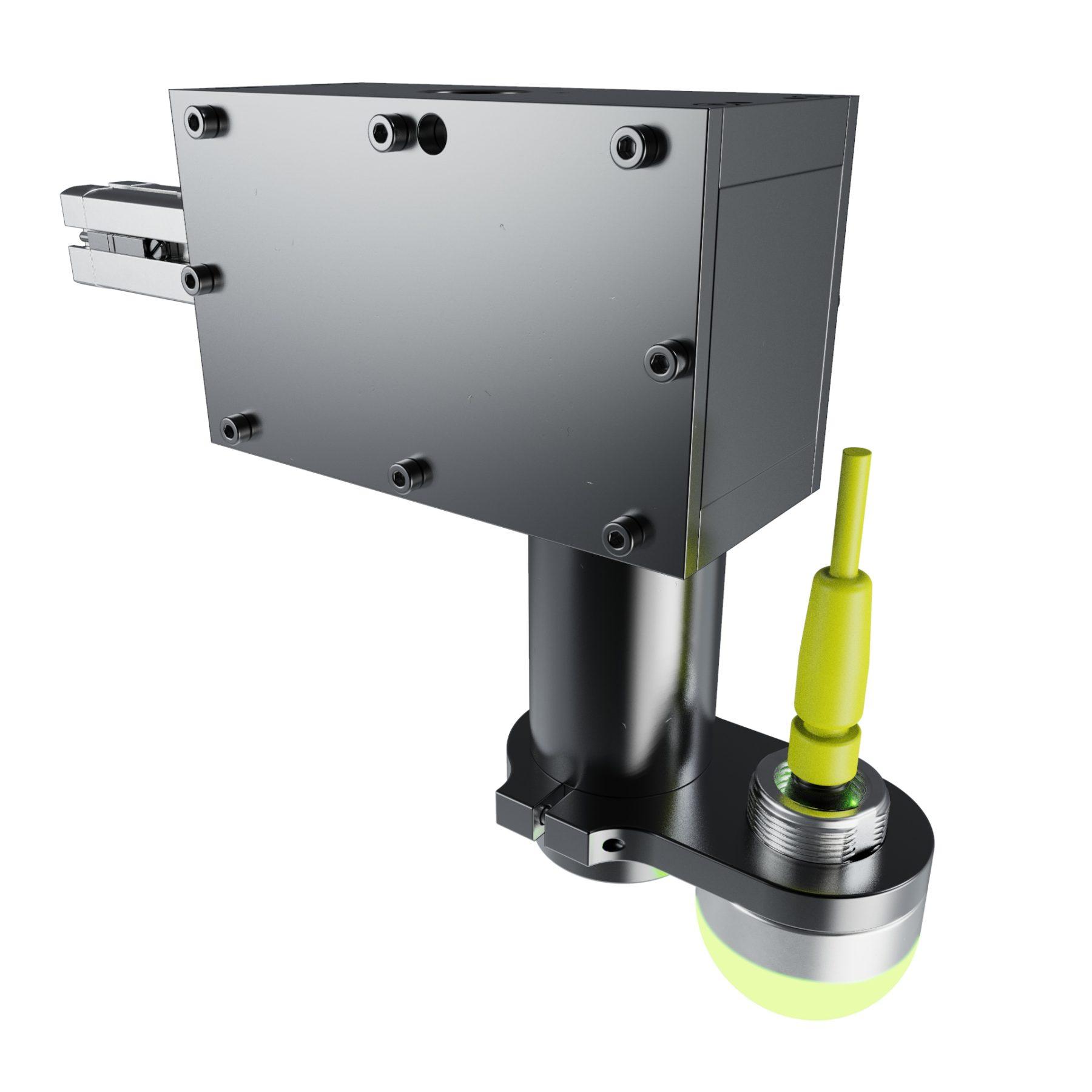
4. Drive Type
The drive type defines how the screw is installed, with common options including Phillips, Torx, and hex drives. Each type offers different advantages in terms of grip, ease of use, and resistance to stripping. Understanding the drive type is vital for selecting the appropriate automated screwdriver system that matches the screws being used, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
5. Coating and Finish
The coating or finish applied to screws can enhance their resistance to corrosion, wear, and friction. Popular finishes include zinc plating, black oxide, and nylon coatings. These coatings are important for specific applications, especially in harsh environments where exposure to chemicals or moisture is a concern. Buyers should evaluate the environmental conditions of their manufacturing processes to select screws with the appropriate coating.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Automated Screw Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in the manufacturing of another company’s products. In the context of automated screws, an OEM may provide screws that are integral to the assembly of machinery or consumer goods. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who meet their specific requirements.

Illustrative image related to automated screw
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand, as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses gauge whether a supplier’s offerings align with their production needs and budget constraints.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the context of automated screws, an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and specifications across multiple vendors, aiding in informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized international shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the transportation of goods. Understanding Incoterms is essential for buyers engaged in international trade, as they clarify shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the automated screw industry, understanding lead times is critical for production planning and ensuring that assembly lines remain operational without delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of automated screw purchasing with confidence, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the automated screw Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Automated Screw Sector?
The automated screw sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by technological advancements and evolving market needs. A significant global driver is the increasing demand for efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics are pushing for automation solutions that not only enhance production speed but also reduce labor costs. In regions like Africa and South America, where manufacturing is expanding rapidly, the adoption of automated screwdriving systems is becoming essential to compete on a global scale.
Emerging technologies, such as collaborative robots (CoBots) and advanced screw feeding systems, are reshaping sourcing strategies. These innovations allow for seamless integration into existing workflows, enhancing flexibility and scalability. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Europe and the Middle East, the focus is on sourcing equipment that is not only reliable but also adaptable to various manufacturing environments. This adaptability is crucial as companies increasingly seek to tailor solutions to specific production challenges.
Additionally, sustainability is becoming a pivotal trend in the sourcing of automated screw solutions. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices and materials, aligning with global sustainability goals. As the market evolves, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Automated Screw Industry?
The importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly pronounced in the automated screw industry. Manufacturers are under pressure to minimize their environmental impact, leading to a greater emphasis on sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This includes the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and waste reduction strategies. B2B buyers are encouraged to consider suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, as this can enhance their own brand reputation and compliance with regulatory standards.
Moreover, ethical sourcing has emerged as a critical factor in supplier selection. Buyers are scrutinizing the supply chain to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly, with a focus on fair labor practices and minimizing environmental degradation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and those related to sustainable sourcing are becoming increasingly relevant in supplier evaluations.
In the automated screw sector, manufacturers that adopt “green” certifications and materials not only contribute to a healthier planet but also position themselves as leaders in an increasingly eco-conscious market. For international B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers that prioritize sustainability and ethical practices can lead to long-term partnerships and enhanced corporate responsibility.
What Is the Historical Context of the Automated Screw Industry?
The automated screw industry has evolved significantly since its inception, with its roots tracing back to the early 20th century when manual fastening methods were prevalent. As manufacturing processes began to industrialize, the need for efficient fastening solutions emerged, leading to the development of early automated screwdriving systems. These systems laid the foundation for the advanced technology we see today.
Over the decades, innovations in materials, design, and automation technology have transformed automated screwdriving into a highly specialized field. The integration of robotics and artificial intelligence has further accelerated this evolution, enabling manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of speed and precision. Today, the automated screw industry stands at the forefront of manufacturing technology, offering solutions that cater to a diverse range of applications across various sectors.
Understanding this historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the industry’s resilience and adaptability in meeting the evolving demands of global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of automated screw
-
How do I solve issues with inconsistent screw feeding?
Inconsistent screw feeding can disrupt production lines and lead to inefficiencies. To address this, ensure that you are using a high-quality vibratory feeder or screw presenter designed for the specific fasteners you are using. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the feeding system can also prevent jams and misfeeds. If problems persist, consider consulting with your supplier for customization options tailored to your assembly line’s requirements. They may provide advanced solutions, such as integrated control systems, to enhance feeding reliability. -
What is the best automated screwdriving system for my industry?
The best automated screwdriving system depends on your specific industry needs. For example, automotive and aerospace sectors often require robust, high-speed systems capable of handling various fastener sizes. In contrast, medical device manufacturers might prioritize precision and cleanliness. Assess your production environment, the types of fasteners used, and the required speed and torque specifications. Collaborating with a supplier experienced in your industry can help you select a system that enhances productivity and meets compliance standards. -
How can I customize my automated screwdriving solution?
Customization options for automated screwdriving solutions can include specialized drive heads, unique feeding mechanisms, and tailored control systems. Discuss your specific assembly challenges with potential suppliers, as many offer bespoke services to adapt their systems to your needs. This could involve integrating robotic automation or modifying the software for specific applications. Be sure to communicate your requirements clearly, including any limitations in workspace or production volume, to find a solution that fits seamlessly into your operations. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for automated screwdriving systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, established manufacturers may have a higher MOQ due to production costs, while smaller companies might offer lower quantities. It’s crucial to inquire directly with the supplier about their MOQ policies, especially if you are testing a new product or solution. In some cases, suppliers may be open to negotiating MOQs based on your potential for future orders, particularly in international markets where demand may be variable. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing automated screwdriving systems?
Payment terms can differ widely depending on the supplier and your location. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days after invoice, but some suppliers may require partial upfront payments, especially for custom orders. Always clarify payment methods accepted, including bank transfers, letters of credit, or credit terms. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also lead to more favorable payment terms as you demonstrate reliability in business transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in automated screwdriving systems?
To ensure quality assurance, start by selecting suppliers with established reputations and certifications, such as ISO 9001. Request documentation of quality control processes, including testing methods for their automated systems. Many manufacturers provide warranties and after-sales support, which are crucial for maintaining system performance. Regular maintenance and inspections of the equipment will also help ensure it operates reliably, thus avoiding production downtime. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing automated screwdriving systems?
Logistics plays a critical role when importing automated screwdriving systems, particularly regarding shipping costs, customs duties, and lead times. Ensure your supplier can provide detailed shipping options and estimated delivery timelines. Familiarize yourself with the import regulations in your country, as well as any specific certifications required for industrial equipment. Engaging with a freight forwarder can also streamline the process, ensuring compliance and efficiency in transporting your systems to their final destination. -
How can I vet suppliers for automated screwdriving systems?
Vetting suppliers involves assessing their industry experience, customer reviews, and certifications. Start by researching their history and reputation in the automated screwdriving market. Request references from other clients and inquire about their after-sales support and service capabilities. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facility if feasible or attending trade shows to see their products in action. Building a relationship based on trust and transparency with your supplier is essential for long-term collaboration.
Top 6 Automated Screw Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carlson Engineering – Automatic Screwdriving Solutions
Domain: carlsoneng.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Carlson Engineering offers a range of automatic screwdriving and screw feeding products, including:
1. **Single-Spindle Drive Heads**: Designed for driving screws into parts, available in multiple types (Type 1 to Type 6).
2. **Multi-Spindle Drive Heads**: Custom heavy-duty drive heads that can drive 2+ fasteners simultaneously, including models like MultiDrive, MidDrive, and TwinSlim.
3. **…
2. Design Tool Inc – Hand Held Automatic Screwdrivers
Domain: designtoolinc.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Hand Held Automatic Screwdrivers: DTI 5000 systems with pneumatic or electric options, various rpm’s and torque. Multiple Spindle Fixtured Systems and Robotics: Custom designed multi-spindle screwdriver systems and X-Y-Z Point-to-Point systems. Fixture Components: Custom design for screwdriver platens, multi-exit feeder bowls, and supply hoppers. Automatic Fastener Dispensing: Nail, Screw, Pin, Nu…
3. Robotiq – Screwdriving Solution
Domain: robotiq.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Robotiq Screwdriving Solution is an all-in-one system designed for automating small assemblies. Key features include:
– **Screwdriver SD-100**:
– Torque range: 0.3 Nm to 4 Nm (2.66 in-lb to 35 in-lb)
– Screw diameter: M2.5 (#3) to M5 (#10)
– Speed: 1 to 600 RPM
– Air consumption: 65 l/min
– Weight: 1.5 kg (3.3 lb)
– Dimensions: 272 mm x 143.5 mm x 75 mm (10 3/4 in. x 5 5/8 in. x…
4. HowToRobot – Automated Screwdriving Solutions
Domain: howtorobot.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Automated screwdriving involves machinery or robots performing screw picking and screwdriving processes. Key components include a screwdriving machine, which holds an automatic screwdriver tool, and a screw feeder that supplies screws one at a time. Benefits include increased precision, faster screwdriving, and improved product quality. Automated solutions can be either machines, which are cheaper…
5. Sumake – Automatic Screw Feeder M1.0 – M5.0
Domain: sumake.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Automatic Screw Feeder for Screw M1.0 – M5.0
6. OPTIMO Robotics – OPTIMO Screwdriving System
Domain: universal-robots.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “OPTIMO Screwdriving System with automatic feeding”, “manufacturer”: “OPTIMO Robotics”, “components”: [“screwdriver”, “screw feeder”, “screwdriver controller”], “suitable_industries”: [“telecommunications”, “electronics”, “automotive”, “plastic part producers”, “wood industry”, “furniture producers”], “programming_interface”: “graphical user interface”, “user_experience”: “No prev…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for automated screw
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Automated Screw Sourcing?
In the evolving landscape of automated screw technology, strategic sourcing remains paramount for maximizing efficiency and reducing operational costs. By partnering with reputable manufacturers that offer tailored solutions—such as Carlson Engineering’s versatile screwdriver systems or WEBER’s innovative feeding technologies—businesses can significantly enhance their assembly line productivity. Ensuring equipment reliability and durability is essential, as these factors directly influence maintenance costs and downtime.
How Can International Buyers Leverage Automated Screw Solutions?
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional market dynamics and technological capabilities is crucial. Engaging with industry leaders who provide comprehensive support and customization options can lead to more effective supply chains. Prioritizing local suppliers with a strong service network can also facilitate quicker responses to operational challenges.
What’s Next for Your Business in Automated Screw Sourcing?
As the demand for automation continues to rise, now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies. Consider investing in advanced automated screwdriving systems that align with your production goals. By doing so, you can not only streamline your operations but also position your business for future growth in an increasingly competitive global market. Embrace innovation and take the first step toward a more efficient assembly process today.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.