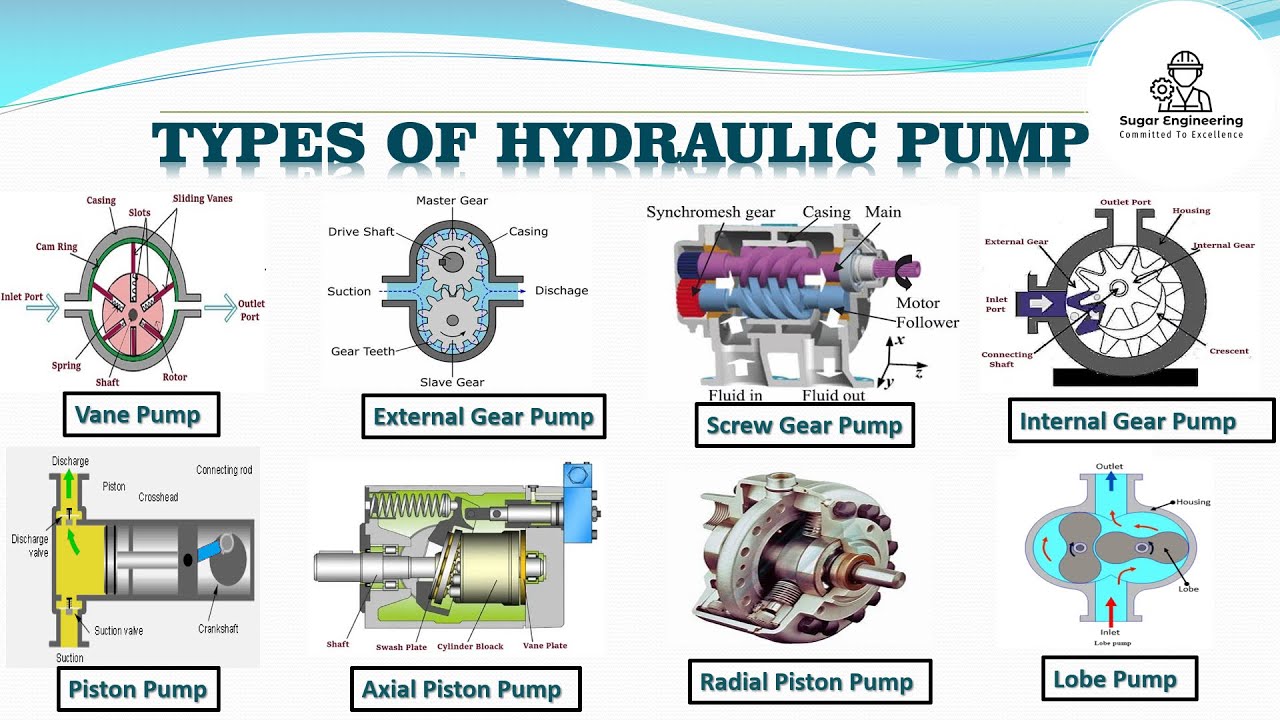
Everything You Need to Know About 2 Classifications Of Hydraulic Pumps Sourcing in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
In an increasingly competitive landscape, sourcing the right hydraulic pumps is a critical challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide delves into two primary classifications of hydraulic pumps—gear pumps and piston pumps—offering a comprehensive overview that addresses key factors such as operational efficiency, maintenance requirements, and application suitability. Understanding these classifications is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific operational needs.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the unique characteristics, advantages, and typical applications of each pump type, enabling buyers to identify the most suitable options for their machinery and projects. Additionally, we will cover crucial aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for integrating hydraulic systems within various industrial frameworks. By arming B2B buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of hydraulic pump technologies, this guide aims to empower strategic purchasing decisions that enhance productivity and operational reliability.
Whether you’re in Brazil, Nigeria, or anywhere in between, navigating the complexities of hydraulic pump procurement doesn’t have to be daunting. With the right knowledge, you can streamline your sourcing process and ensure that your investments yield optimal returns.
Understanding 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gear Pumps | Fewer moving parts, fixed displacement, cost-effective | Truck-mounted hydraulic systems | Pros: Simple design, easy maintenance. Cons: Limited in high-pressure applications. |
| Piston Pumps | Higher pressure tolerance, variable displacement options | Truck-mounted cranes, industrial machines | Pros: Efficient under high pressure. Cons: Higher initial cost, complex maintenance. |
| Vane Pumps | Rotating vanes, moderate efficiency, compact design | Utility vehicles | Pros: Good for low to medium pressures. Cons: Less common, lower efficiency than gear pumps. |
| Clutch Pumps | Electromagnetic clutch, small displacement | Aerial bucket trucks, wreckers | Pros: Engages on demand, compact. Cons: Limited to low flow applications (up to 15 GPM). |
| Dump Pumps | Integrated pressure relief, designed for dumping applications | Dump trailers, tandem axle dump trucks | Pros: Purpose-built for dumping, reliable. Cons: Not versatile for other applications. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Gear Pumps for B2B Buyers?
Gear pumps are characterized by their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them a popular choice for truck-mounted hydraulic systems. They operate using fixed displacement, meaning they deliver a consistent volume of fluid with each rotation. This design is particularly advantageous in applications where reliability and ease of maintenance are crucial. However, their limitation lies in their pressure capabilities, as they may not perform efficiently in high-pressure scenarios. B2B buyers should consider the specific pressure requirements of their applications when opting for gear pumps.
Why Choose Piston Pumps for High-Pressure Applications?
Piston pumps are renowned for their ability to handle higher operating pressures compared to gear pumps. They come in both fixed and variable displacement designs, allowing for flexibility in flow rates. This makes them ideal for applications such as truck-mounted cranes and industrial machinery where pressure and flow need to be adjusted based on operational demands. While they provide excellent performance under high pressure, B2B buyers should be aware of the higher initial costs and the need for stricter maintenance protocols due to their complexity.
How Do Vane Pumps Compare in Efficiency and Use Cases?
Vane pumps utilize rotating vanes to create fluid movement, offering a compact design suitable for utility vehicles. They are effective in low to medium pressure applications and can be advantageous in scenarios where space is limited. However, their lower efficiency compared to gear pumps has led to a decline in popularity. Buyers in the B2B sector should evaluate the specific requirements of their utility applications and consider whether the efficiency trade-offs of vane pumps align with their operational goals.
What Benefits Do Clutch Pumps Offer for Specialized Applications?
Clutch pumps are unique due to their electromagnetic clutch feature, allowing them to engage only when needed. This design is particularly beneficial for applications like aerial bucket trucks and wreckers, where space and power efficiency are vital. However, they are limited to lower flow applications, typically not exceeding 15 GPM. B2B buyers should assess the operational demands of their equipment to ensure that the clutch pump’s capabilities align with their needs.
When Should Dump Pumps Be Considered for Specific Applications?
Dump pumps are specifically designed for applications involving the unloading of materials, such as in dump trailers and tandem axle dump trucks. They feature integrated pressure relief systems and are built for reliability in dumping operations. While they excel in their niche, their lack of versatility for other hydraulic applications could be a drawback for some buyers. Companies should consider their operational needs and whether a dedicated dump pump provides the best return on investment for their specific use cases.
Key Industrial Applications of 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Hydraulic cranes utilizing piston pumps | High lifting capacity and precision in material handling | Reliability, pressure ratings, and service support |
| Agriculture | Gear pumps in tractors for hydraulic attachments | Efficient power transfer for various farming implements | Compatibility with existing equipment and durability |
| Waste Management | Dump pumps in refuse collection vehicles | Quick and efficient waste disposal | Pump design suited for specific waste types and pressures |
| Mining | Hydraulic systems in excavators using gear and piston pumps | Enhanced operational efficiency and safety | Resistance to contamination and maintenance requirements |
| Oil and Gas | Hydraulic fracturing using high-pressure piston pumps | Increased extraction efficiency and reduced downtime | Compliance with industry standards and pressure capabilities |
How Are Hydraulic Pumps Used in Construction Equipment?
In the construction industry, hydraulic cranes often employ piston pumps due to their ability to handle high operating pressures. These pumps enable precise control when lifting heavy materials, which is crucial for safety and efficiency on job sites. Buyers must consider the pump’s reliability and pressure ratings, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where equipment must withstand challenging environments and operational demands.
Illustrative image related to 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
What Role Do Hydraulic Pumps Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, gear pumps are commonly integrated into tractors for hydraulic attachments such as plows and seeders. These pumps provide efficient power transfer, allowing farmers to operate multiple implements simultaneously. When sourcing these pumps, buyers should ensure compatibility with their existing machinery and assess the durability of the pumps, particularly in regions with varying soil conditions and climates, such as Brazil and Nigeria.
How Are Hydraulic Pumps Essential in Waste Management?
Dump pumps are integral to refuse collection vehicles, facilitating the rapid unloading of waste materials. These pumps are designed for efficiency, ensuring that waste can be disposed of quickly and effectively, which is vital for maintaining sanitation in urban areas. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should focus on pump designs that can handle specific waste types and pressures, ensuring compliance with local environmental regulations.
What Advantages Do Hydraulic Pumps Offer in Mining Operations?
In mining, hydraulic systems powered by gear and piston pumps are critical for excavators and other heavy machinery. These pumps enhance operational efficiency by providing the necessary force for digging and transporting materials. For international B2B buyers, particularly in developing regions, sourcing pumps that resist contamination and require minimal maintenance is essential to minimize downtime and operational costs.

Illustrative image related to 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
How Are Hydraulic Pumps Used in Oil and Gas Extraction?
In the oil and gas sector, high-pressure piston pumps are employed in hydraulic fracturing processes to extract resources efficiently. These pumps increase extraction rates while reducing downtime, making them invaluable for maximizing production. Buyers must ensure that their pumps comply with industry standards and possess the necessary pressure capabilities to operate effectively in harsh environments, particularly in regions with stringent regulatory frameworks.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘2 classifications of hydraulic pumps’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overcoming Contamination Issues in Hydraulic Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant challenges related to hydraulic pump contamination, particularly when using piston pumps in demanding environments. Contaminants such as dirt, water, and air can compromise the performance and lifespan of these pumps. Buyers often report increased maintenance costs and unexpected downtime as they struggle to manage these issues effectively. The intricate designs of piston pumps, with their tighter tolerances and additional moving parts, make them particularly vulnerable to contamination, leading to inefficient operation and potential system failures.
The Solution: To combat contamination, it is essential to implement a robust filtration system tailored to the specific requirements of piston pumps. Investing in high-quality filters that can effectively capture particulates and moisture is crucial. Additionally, regular maintenance schedules should be established to inspect and replace filters as needed. Furthermore, using closed-loop hydraulic systems can minimize exposure to contaminants by ensuring that fluid is kept within a controlled environment. Training personnel on proper maintenance procedures and contamination control can also significantly reduce the risk of damage, ensuring that hydraulic pumps operate at peak efficiency and extend their service life.
Scenario 2: Navigating the Complexity of Variable Displacement Pumps
The Problem: Buyers often encounter difficulties when selecting and operating variable displacement piston pumps. The complexity of these pumps, which require precise adjustments to the swash plate angle to control flow, can lead to confusion and mismanagement. This can result in suboptimal performance, increased wear on components, and ultimately, higher operational costs. For businesses that rely on variable flow applications, such as construction or waste management, understanding how to optimize these pumps is critical.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the complexities of variable displacement pumps, buyers should prioritize comprehensive training for their technicians and operators. This training should cover the operational principles of variable displacement systems, including how to interpret pressure signals and adjust the swash plate correctly. Additionally, investing in advanced diagnostic tools can help monitor pump performance in real time, allowing for timely adjustments and reducing the likelihood of costly errors. Buyers should also consider collaborating with pump manufacturers or suppliers who can provide tailored advice and support, ensuring that their variable displacement pumps are configured correctly for their specific applications.
Scenario 3: Addressing High Initial Costs of Piston Pumps
The Problem: One of the most common pain points for B2B buyers is the high initial cost associated with piston pumps compared to gear pumps. This can be particularly daunting for businesses operating on tight budgets or those looking to scale operations quickly. Buyers often hesitate to invest in piston pumps, fearing that the upfront expenses will not translate into proportional returns, especially if they are uncertain about their long-term hydraulic needs.
The Solution: To alleviate concerns about the high upfront costs of piston pumps, buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis. This analysis should factor in not only the initial purchase price but also the long-term savings associated with efficiency and reduced maintenance. By considering the total cost of ownership, including energy savings and increased productivity, businesses can make a more informed decision. Additionally, buyers should explore financing options, such as leasing or installment plans, which can spread the cost over time. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier who can provide insights into the specific applications and operational advantages of piston pumps will also help buyers justify their investment, ensuring they choose the right pump for their needs while managing costs effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
What Are the Key Materials Used in Hydraulic Pumps?
When selecting materials for hydraulic pumps, particularly gear and piston types, it’s crucial to consider their performance characteristics, durability, and compatibility with various operating conditions. Here, we analyze three common materials: Cast Iron, Aluminum, and Stainless Steel, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
How Does Cast Iron Perform in Hydraulic Pump Applications?
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. It typically has a tensile strength of around 250 MPa and can handle operating temperatures up to 400°F (204°C).
Pros & Cons: The durability of cast iron makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications; however, its weight can be a drawback, especially in mobile equipment. Additionally, while cast iron is relatively inexpensive, its manufacturing complexity can lead to higher production costs compared to lighter materials.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is compatible with a wide range of hydraulic fluids, making it versatile for various applications. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if exposed to certain chemicals, necessitating careful fluid selection.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. Cast iron’s weight may also affect shipping costs and logistics, which is crucial for budget-conscious buyers.
Why Choose Aluminum for Hydraulic Pump Components?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and exhibits good corrosion resistance, with a tensile strength of approximately 200 MPa. It can handle temperatures up to 300°F (149°C) and is often anodized to enhance its protective qualities.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can improve the overall efficiency of mobile hydraulic systems. However, it has a lower pressure rating compared to cast iron, making it less suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for environments where moisture or corrosive fluids are present. However, it may not be suitable for applications requiring high durability under extreme conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should be aware of the varying grades of aluminum and their respective standards. Compliance with local regulations regarding aluminum use in hydraulic systems is also essential.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Hydraulic Pumps?
Key Properties: Stainless steel boasts exceptional corrosion resistance and can operate effectively at temperatures up to 800°F (427°C) with a tensile strength of around 500 MPa. Its ability to withstand harsh environments makes it a preferred choice for many hydraulic applications.
Illustrative image related to 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
Pros & Cons: The durability and longevity of stainless steel are significant advantages, especially in corrosive environments. However, it is more expensive than both cast iron and aluminum, which can impact overall project budgets.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various hydraulic fluids, including those that are corrosive or high-temperature. Its robustness ensures reliable performance in demanding applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should consider the specific grades of stainless steel and their compliance with international standards. The higher cost may be justified in applications requiring longevity and reliability.
Illustrative image related to 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
Summary Table of Material Selection for Hydraulic Pumps
| Material | Typical Use Case for 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Gear pumps in heavy-duty applications | Excellent wear resistance | Heavy and less corrosion-resistant | Medium |
| Aluminum | Piston pumps in mobile hydraulic systems | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower pressure rating | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure hydraulic systems in corrosive environments | Exceptional durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for hydraulic pumps, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
Hydraulic pumps are crucial components in various industrial applications, and understanding their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is vital for B2B buyers. This section delves into the typical manufacturing stages and quality control practices for two classifications of hydraulic pumps: gear pumps and piston pumps.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Hydraulic Pumps?
The manufacturing of hydraulic pumps involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the performance and reliability of the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Hydraulic Pumps?
Material preparation is the foundational step in hydraulic pump manufacturing. High-quality materials such as cast iron, aluminum alloys, and various steels are selected based on their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
- Material Selection: Suppliers should provide certifications for materials, ensuring they meet industry specifications and standards.
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut and shaped using techniques like CNC machining, which allows for precision in producing complex components such as pump housings and gears.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Hydraulic Pump Production?
The forming process involves transforming raw materials into functional components. Techniques vary depending on the pump type.
- Casting: For gear pumps, components such as the housing and covers are often produced through sand or die casting, allowing for intricate designs and reducing machining time.
- Machining: Piston pumps require high precision; therefore, components like pistons and swash plates are typically machined to tight tolerances to ensure optimal performance.
- Stamping and Forging: Some parts may be stamped or forged for added strength and durability, especially those subjected to high pressures.
How Are Hydraulic Pumps Assembled?
Assembly is where individual components come together to form a complete hydraulic pump.
- Sub-Assembly: Components like gears, pistons, and seals are first assembled into sub-units. This step often involves the use of automated machinery to ensure consistency.
- Final Assembly: The sub-units are assembled into the main housing. Precision alignment is crucial to prevent leaks and ensure efficient operation.
- Integration of Electronics: For pumps with electronic control features, integration of sensors and control systems occurs during this stage.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Hydraulic Pumps?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic of hydraulic pumps.
- Surface Treatment: Components may undergo surface treatments such as anodizing or powder coating to improve corrosion resistance and wear properties.
- Quality Inspection: Before packaging, each pump undergoes thorough inspection to ensure it meets design specifications and quality standards.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are in Place for Hydraulic Pumps?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of hydraulic pumps, ensuring reliability and safety. Several international and industry-specific standards guide these practices.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Hydraulic Pump Manufacturing?
Adhering to international standards is essential for manufacturers aiming to compete globally.
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system, emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards for equipment used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that hydraulic pumps meet specific operational requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Hydraulic Pump Production?
Quality control checkpoints are crucial at various stages of the manufacturing process.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for quality and conformity to specifications before being used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections are performed during the manufacturing process to identify defects early. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) are often employed.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed pumps undergo rigorous testing, including pressure tests, flow tests, and performance evaluations, to ensure they meet design specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Hydraulic Pumps?
Testing methods validate the performance and reliability of hydraulic pumps.
- Hydraulic Testing: Pumps are subjected to high-pressure conditions to ensure they can handle operational stresses.
- Performance Testing: Flow rates, pressure outputs, and efficiency metrics are measured against specified benchmarks.
- Durability Testing: Components may undergo fatigue testing to assess their lifespan under continuous operation.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should ensure that their suppliers maintain stringent quality control measures.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help buyers assess compliance with international standards and internal quality processes.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including test results and inspection documentation, provides insight into the supplier’s quality management practices.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control processes.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances based on their geographical and regulatory context.
- Regional Compliance: Different regions may have specific compliance requirements, such as UL certification in North America or EN standards in Europe. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can help buyers negotiate quality expectations and foster better relationships.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication regarding quality standards and expectations is critical. Buyers may need to consider language differences when discussing quality assurance processes.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for hydraulic pumps is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on key manufacturing stages, relevant quality standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they partner with reliable suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘2 classifications of hydraulic pumps’
In this guide, we provide a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure hydraulic pumps, specifically focusing on gear and piston pumps. Understanding the nuances of each type is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements for the hydraulic pumps. This includes understanding the application, maximum pressure, flow rate, and system compatibility. Defining these specifications helps narrow down options and ensures you select pumps that can effectively meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Different Pump Classifications
Familiarize yourself with the two primary classifications of hydraulic pumps: gear and piston pumps. Gear pumps are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for applications with lower pressure requirements. In contrast, piston pumps are designed for high-pressure applications and offer variable displacement options, providing flexibility in flow rates. Understanding these distinctions will guide you in choosing the appropriate pump type.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Credentials
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers with a solid reputation and industry experience. Verify their certifications, such as ISO or equivalent standards, which indicate quality assurance and adherence to safety regulations. Engaging with reliable suppliers ensures that you receive products that meet global quality standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Documentation
Before finalizing your order, request samples or technical documentation from shortlisted suppliers. This can include product specifications, performance data, and maintenance guidelines. Analyzing this information allows you to assess the pump’s compatibility with your existing systems and provides insight into long-term reliability.
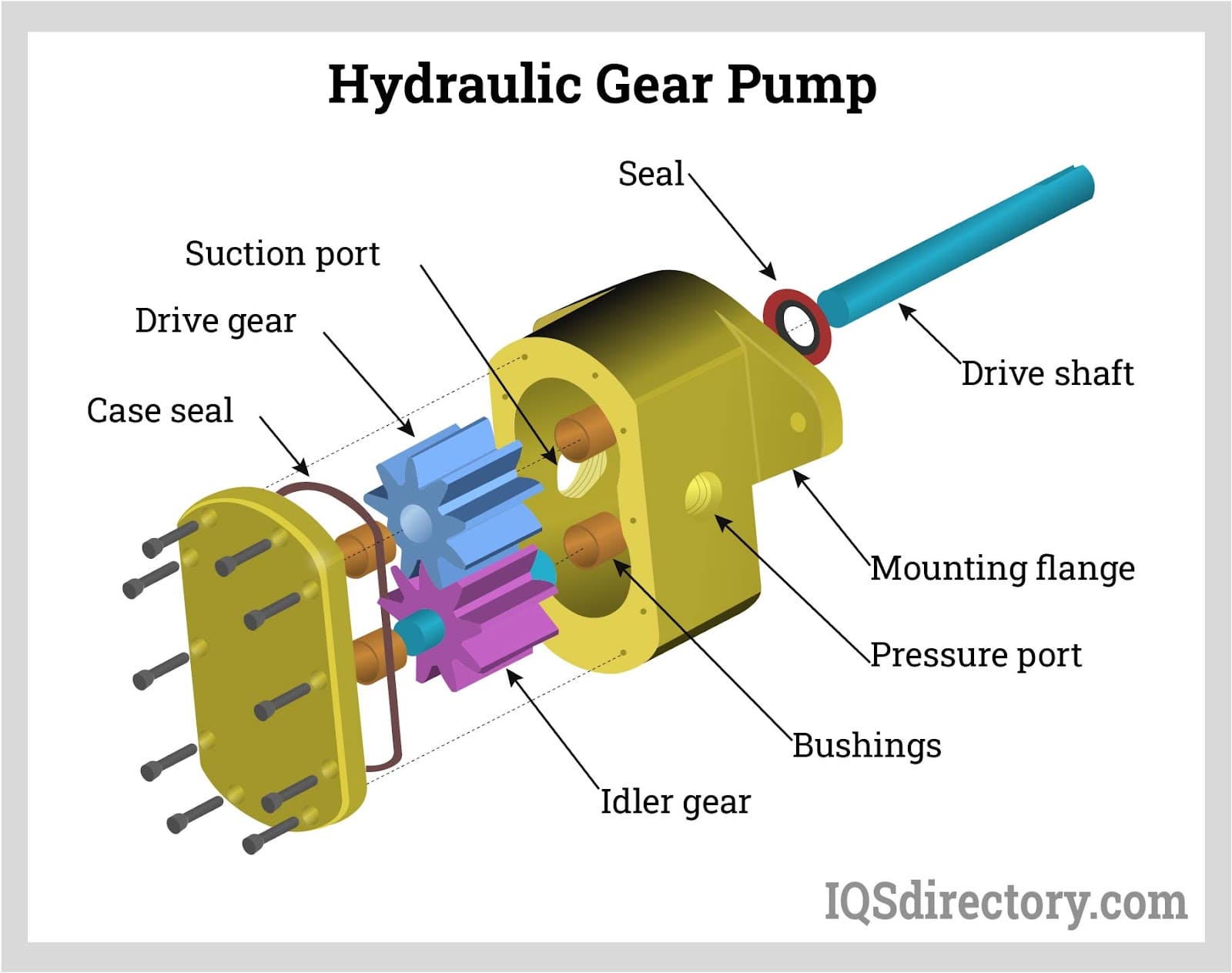
Illustrative image related to 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
Step 5: Consider After-Sales Support and Warranty
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by suppliers, including warranty terms and availability of replacement parts. A robust support system can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs. Ensure that the supplier offers comprehensive service options, such as technical support and training, to facilitate smooth operations.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Payment Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and payment terms. Consider factors like bulk order discounts, payment flexibility, and delivery timelines. Establishing clear financial terms can lead to better cost management and strengthen your business relationship with the supplier.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Monitor Delivery
After agreeing on terms, finalize the order and closely monitor the delivery process. Confirm that the products match your specifications upon arrival and inspect them for any signs of damage. Timely delivery and product quality are essential to maintain operational efficiency and avoid project delays.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing hydraulic pumps, ensuring they select the right products that align with their operational needs and industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Hydraulic Pumps?
When sourcing hydraulic pumps, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials directly impacts the durability and performance of hydraulic pumps. For example, high-grade steel or aluminum may increase initial costs but reduce long-term maintenance needs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as some in Africa and South America, production costs may be lower, but this could impact quality and consistency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, depreciation of equipment, and facility maintenance. These costs are often fixed and can be spread over larger production volumes.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling for producing hydraulic pumps can be a significant upfront investment. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs, especially if customized designs are required.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes are essential to ensure reliability. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can add to the cost but are often necessary for international trade.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including tariffs and insurance, can vary based on the origin and destination of the pumps. Buyers should consider Incoterms to understand their responsibilities and potential additional costs.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can differ widely based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the typical margins in the region can help in negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Hydraulic Pump Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of hydraulic pumps, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases typically lead to lower unit prices. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their projected volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized pumps or those with specific performance criteria will generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications ensure better performance but can raise costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced performance against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Different shipping terms can significantly affect total costs. Buyers should understand terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to manage expenses effectively.
What Tips Can Buyers Use to Negotiate Better Prices?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to enhance their sourcing experience and achieve cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can facilitate better pricing. Open discussions about volume and long-term partnerships can lead to favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Buyers should consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, operation, and disposal. A lower initial price may lead to higher lifetime costs if the pump is less reliable.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International transactions can introduce complexities such as fluctuating exchange rates and tariffs. Buyers should factor these into their budget and negotiate pricing that considers these variables.
-
Market Research: Conducting thorough market research can provide insights into competitive pricing. Understanding local market conditions in regions like Africa, South America, and Europe can help buyers gauge fair pricing and leverage it during negotiations.
Disclaimer
The prices and costs discussed herein are indicative and can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough due diligence and obtain multiple quotations to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Hydraulic Pumps: What Are Your Options?
In the realm of hydraulic systems, hydraulic pumps, particularly the classifications of gear and piston pumps, are essential for converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. However, various alternatives exist that can serve similar functions in different contexts. This analysis will compare these two classifications of hydraulic pumps against alternative technologies such as electric actuators and pneumatic systems, providing B2B buyers with critical insights to inform their purchasing decisions.
Illustrative image related to 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | 2 Classifications Of Hydraulic Pumps | Electric Actuators | Pneumatic Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, variable pressure | High torque at low speed, limited pressure | Fast actuation, limited by air pressure |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, ongoing maintenance costs | Higher upfront costs, low maintenance | Lower initial costs, potential ongoing costs for air supply |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires hydraulic infrastructure | Simple installation, minimal space | Requires air compressor and piping |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed, susceptible to contamination | Minimal maintenance, high reliability | Regular checks on air supply and leaks |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications, variable flow requirements | Precision control, compact applications | Quick actuation, lightweight applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Actuators
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, providing precise control over movement. They offer high torque at low speeds and can be easily integrated into existing electrical systems. However, their initial costs can be higher than hydraulic systems, and they may require more space for installation. Maintenance is minimal, and they are generally more reliable due to fewer moving parts. Electric actuators are ideal for applications requiring precision and compact design, such as in robotics or automated machinery.
Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems utilize compressed air to generate motion and are known for their speed and simplicity. They are often less expensive upfront compared to hydraulic pumps and are widely used in lighter applications where rapid actuation is needed. However, their performance can be limited by the availability and pressure of the compressed air supply. Additionally, pneumatic systems may require regular checks for leaks, which can lead to increased operational costs over time. These systems are best suited for applications such as assembly lines, where speed is crucial, but the force requirements are lower.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating the right solution for hydraulic applications, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Gear and piston pumps excel in heavy-duty applications where variable flow and high pressure are necessary, but alternatives like electric actuators and pneumatic systems may provide cost-effective solutions for less demanding tasks. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary limitations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Pumps?
Understanding the essential technical properties of hydraulic pumps is critical for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that you should consider:
-
Displacement Type (Fixed vs. Variable)
Displacement refers to the volume of fluid that a pump can move with each rotation. Fixed displacement pumps deliver a constant flow rate, making them suitable for applications with consistent hydraulic demands. Variable displacement pumps adjust their output based on system requirements, allowing for efficiency in varying operational conditions. For international buyers, selecting the right displacement type can directly impact operational efficiency and energy consumption. -
Maximum Pressure Rating
This specification indicates the highest pressure the pump can handle without risk of failure. Hydraulic systems often operate under high pressure, making this rating essential for ensuring the reliability and longevity of equipment. Buyers in industries such as construction and agriculture must consider this property to avoid costly downtime due to pump failure. -
Material Grade
The materials used in pump construction can significantly affect performance, corrosion resistance, and durability. Common materials include cast iron, aluminum, and various alloys. Buyers should prioritize pumps made from high-grade materials to ensure longevity, especially in harsh environments or applications involving abrasive fluids. -
Contamination Tolerance
This property refers to a pump’s ability to operate effectively in environments with dirt, debris, or other contaminants. Gear pumps, for instance, typically offer better contamination tolerance than piston pumps. For B2B buyers operating in regions with less-than-ideal conditions, selecting a pump with higher contamination tolerance can minimize maintenance costs and extend service life. -
Efficiency Rating
Efficiency refers to the amount of input energy converted into hydraulic energy. Higher efficiency means lower operational costs and reduced wear on components. Buyers should evaluate the efficiency ratings of pumps to ensure they are making a cost-effective investment that aligns with their operational goals. -
Speed Limitations
This specification indicates the maximum rotational speed at which a pump can operate safely. Exceeding this limit can lead to mechanical failures. For buyers, understanding speed limitations is vital for ensuring compatibility with existing systems and avoiding potential damage.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Hydraulic Pumps?
Navigating the hydraulic pump market requires familiarity with specific jargon that can impact purchasing decisions. Here are several important trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components that are sold under another brand’s name. In the hydraulic pump industry, purchasing from an OEM ensures that the components meet specific quality standards and are compatible with your existing systems. For buyers, understanding the distinction between OEM and aftermarket parts is crucial for ensuring reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. When dealing with hydraulic pumps, understanding MOQ can help in negotiating bulk purchases to reduce overall costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the hydraulic pump industry, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare different suppliers and make informed purchasing decisions. It’s an essential step for ensuring competitive pricing and favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms is vital for international B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the risk and cost at each stage of the shipping process. Buyers should be well-versed in Incoterms to avoid unexpected costs and delays. -
Hydraulic Horsepower (HHP)
This term measures the power transmitted through hydraulic systems. It is essential for determining pump capacity and compatibility with machinery. Buyers should understand HHP to ensure that the hydraulic pumps they select meet the power requirements of their applications. -
Closed vs. Open Center Systems
These terms describe the type of hydraulic circuit in which a pump operates. Open center systems allow fluid to flow continuously through the pump, while closed center systems only allow flow when needed. Understanding these systems is crucial for selecting the right hydraulic pump for your applications and ensuring optimal performance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Hydraulic Pumps Sector?
The hydraulic pumps market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing industrial automation and the demand for efficient hydraulic systems across various sectors, including construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. Key trends include the adoption of advanced technologies such as IoT and AI for predictive maintenance and system optimization, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly looking for suppliers that offer not only high-performance products but also smart technologies that can integrate seamlessly into existing systems.
Moreover, the shift towards electric and hybrid hydraulic systems is gaining traction, fueled by the need for energy-efficient solutions in regions facing stringent environmental regulations. The push for sustainability is prompting manufacturers to innovate and produce hydraulic pumps that are lighter, more efficient, and made from recyclable materials. As buyers in emerging markets like Brazil and Nigeria seek reliable and cost-effective solutions, understanding local market dynamics, including regulatory frameworks and regional supply chain capabilities, becomes crucial for successful sourcing.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Hydraulic Pumps Market?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the hydraulic pumps sector, with increasing emphasis on minimizing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. International buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing practices, ensuring that materials are responsibly sourced and that production processes are environmentally friendly. This shift is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where regulatory compliance regarding emissions and waste management is stringent.
The use of “green” certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for recyclable materials, is becoming a crucial factor in supplier selection. Buyers are also encouraged to seek hydraulic pumps made from sustainable materials that reduce the carbon footprint of their operations. By aligning with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability, businesses not only enhance their corporate social responsibility profile but also gain a competitive edge in the market as consumers increasingly favor environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Hydraulic Pumps Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of hydraulic pumps dates back to the 19th century, with the introduction of basic gear pumps for various industrial applications. Over the decades, advancements in engineering and materials science have led to the development of more sophisticated designs, including piston and vane pumps, which offer enhanced efficiency and performance under varying operational conditions.
The introduction of variable displacement pumps in the mid-20th century marked a significant milestone, allowing for more precise control of hydraulic flow and pressure, which is particularly beneficial in complex machinery applications. As industries continue to evolve and adopt new technologies, the hydraulic pumps sector remains at the forefront of innovation, providing B2B buyers with increasingly efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly solutions. Understanding this evolution helps buyers appreciate the technological advancements that inform current product offerings and sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
-
1. How do I choose the right hydraulic pump for my application?
Selecting the appropriate hydraulic pump hinges on understanding your specific application requirements. Consider factors such as required pressure, flow rate, and the type of hydraulic system (open or closed center). Gear pumps are typically ideal for lower pressure applications due to their durability and cost-effectiveness, while piston pumps are better suited for high-pressure demands. Evaluate the environment in which the pump will operate, including contamination levels and space constraints, as these can influence your choice significantly. -
2. What are the key differences between gear pumps and piston pumps?
Gear pumps are known for their simplicity, fewer moving parts, and tolerance to contamination, making them cost-effective for low-pressure applications. They provide fixed displacement, meaning they deliver a constant flow rate. Conversely, piston pumps can handle higher pressures and offer variable displacement options, allowing for flow adjustments based on operational needs. However, piston pumps are more complex and typically come with higher initial costs and maintenance requirements. -
3. What is the typical lead time for ordering hydraulic pumps internationally?
Lead times for international orders of hydraulic pumps can vary widely based on the supplier, the complexity of the pump, and shipping logistics. Generally, expect a timeframe of 4 to 12 weeks, including manufacturing and shipping. It’s advisable to confirm lead times with your supplier and factor in any potential delays related to customs clearance, especially when sourcing from regions with varying import regulations. -
4. How do I vet suppliers for hydraulic pumps effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Check for certifications, client testimonials, and case studies that demonstrate their experience with hydraulic pumps. Inquire about their manufacturing capabilities, quality control processes, and after-sales support. It can also be beneficial to request samples or arrange factory visits to assess their operations firsthand. Engaging in discussions with current clients can provide valuable insights into their reliability. -
5. Are there customization options available for hydraulic pumps?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific application needs. This can include modifications to pump size, materials, and performance specifications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to determine what customization options they provide, such as special coatings for corrosion resistance or adaptations for unique mounting configurations. Ensure that any customizations comply with industry standards to maintain quality and performance. -
6. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for hydraulic pumps?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as pump type and customization level. Typically, MOQs can range from 1 to 50 units. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for standard products, while custom orders might require higher quantities. Always clarify MOQ policies upfront to avoid unexpected costs and ensure your purchasing plan aligns with your operational needs. -
7. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing hydraulic pumps internationally?
Payment terms for international transactions often include options such as upfront deposits, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Suppliers might require a deposit of 30% to 50% before production begins, with the balance due upon completion or delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk management strategies. Ensure to discuss currency exchange rates and transaction fees, which can impact overall costs. -
8. How can I ensure the quality of hydraulic pumps during procurement?
To ensure quality, start by selecting suppliers with robust quality assurance processes, including ISO certifications. Request documentation such as test reports and certifications for materials used. Implement a thorough inspection process upon receipt of the pumps, checking for compliance with specifications and functionality. Establish clear communication with your supplier regarding quality expectations and consider periodic audits of their manufacturing processes to maintain standards.
Top 3 2 Classifications Of Hydraulic Pumps Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Muncie Power – Hydraulic Pumps
Domain: munciepower.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Types of Hydraulic Pumps: 1. Gear Pumps – Most common design for truck-mounted hydraulic systems. Characteristics: fewer moving parts, easy to service, tolerant of contamination, relatively inexpensive, fixed displacement, used in open center hydraulic systems. Rated by maximum pressure, cubic inch displacement, and maximum input speed. 2. Piston Pumps – Used for high operating pressures, withstan…
2. Worlifts – Hydraulic Pumps
Domain: worlifts.co.uk
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic pumps are critical equipment used in various industries including mining, vehicle, oil and gas, forestry, marine, agriculture, and construction. The global hydraulic pump market is estimated to increase by $3.53 billion (£2.82 billion) from 2021 to 2026. There are three primary types of hydraulic pumps: gear, piston, and vane pumps, which can be further classified into fixed displacement…
3. Panagon Systems – Hydraulic Pumps Overview
Domain: panagonsystems.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Types of Hydraulic Pumps: 1. Piston Pumps: Positive displacement device with high-pressure seals and driving pistons. Versatile, effective with solid particles and viscous media. Types: Axial and Radial. 2. Axial Piston Pumps: Cylinders around a central axis, can have fixed or variable displacement. 3. Radial Piston Pumps: Pistons arranged along the radius, used for high-operating pressures. 4. Va…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 2 classifications of hydraulic pumps
In summary, understanding the distinctions between gear and piston hydraulic pumps is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their hydraulic systems. Gear pumps, with their cost-effectiveness and robustness, are ideal for applications requiring moderate pressure and flow rates. Conversely, piston pumps excel in high-pressure environments, offering versatility through fixed and variable displacement options, albeit with increased complexity and cost.
Strategic sourcing of hydraulic pumps enables businesses to enhance operational efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure reliability in demanding applications. By establishing strong partnerships with reputable suppliers, organizations can gain access to innovative technologies and tailored solutions that meet their specific needs.
As global markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential for buyers to stay informed about the latest advancements in hydraulic pump technology. Embrace these insights and leverage them to make informed purchasing decisions. Engage with trusted suppliers and industry experts to future-proof your operations and drive sustained growth in your hydraulic applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.