Crystal Structure Of 304 Stainless Steel: The Ultimate B2B Sourcing Guide for Global Buyer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, understanding the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel is crucial for businesses seeking reliable and high-quality materials. As a widely used austenitic stainless steel, 304 offers superior corrosion resistance and versatility, making it a preferred choice across various industries. However, sourcing the right grade and type can be challenging, particularly for international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel and its applications, providing actionable insights for informed purchasing decisions.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will explore the unique properties of 304 stainless steel, including its chemical composition, mechanical characteristics, and processing methods. Additionally, we will cover essential topics such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and the implications of different finishes and forms. By empowering B2B buyers with in-depth knowledge, this guide aims to facilitate effective sourcing strategies and enhance overall procurement processes. Whether you are looking for stainless steel sheets, tubes, or custom solutions, understanding the nuances of 304 stainless steel is key to achieving operational excellence and maintaining a competitive edge in your market.
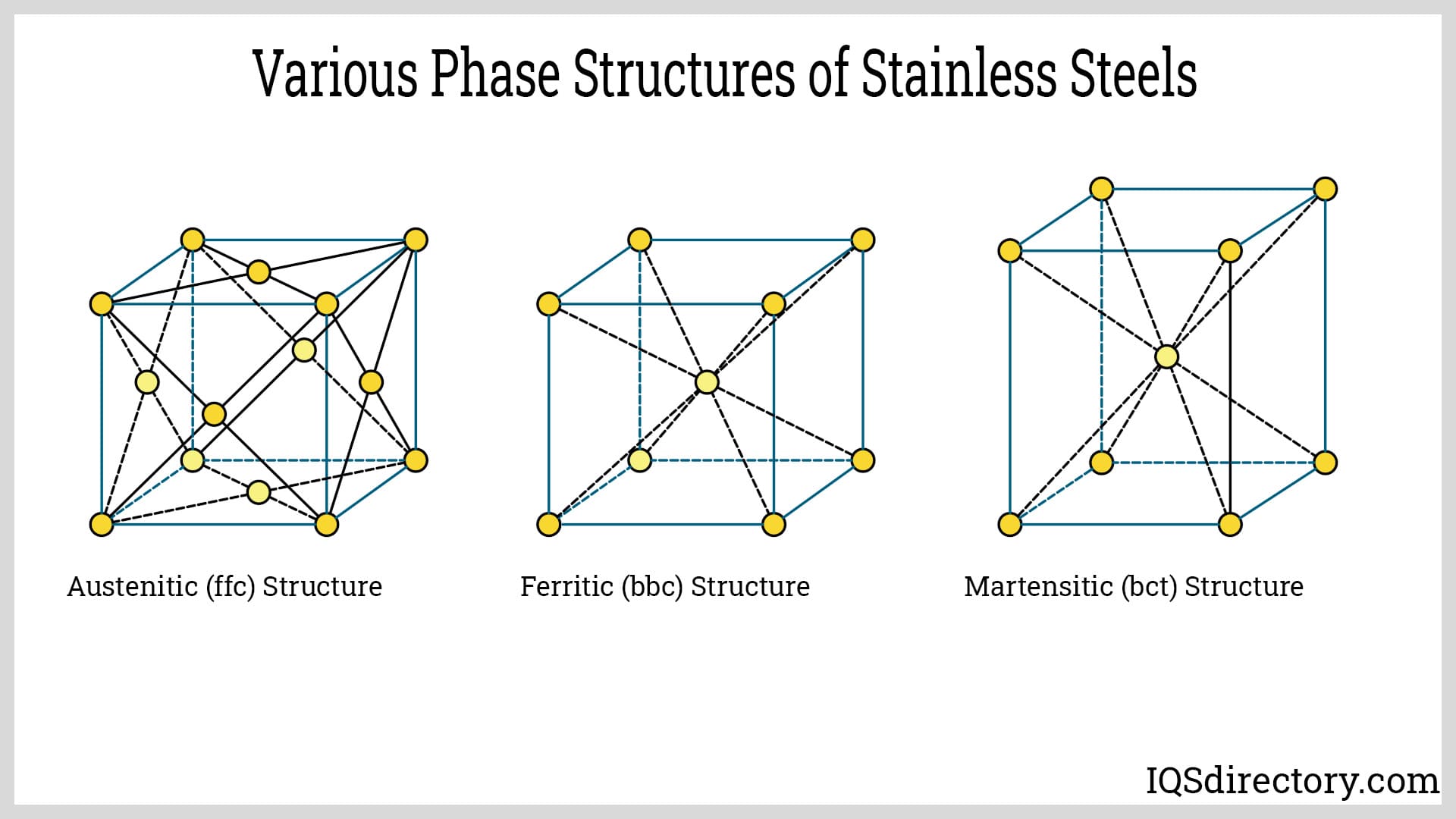
Understanding crystal structure of 304 stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | Austenitic structure with 18% chromium and 8% nickel | Kitchen equipment, chemical containers | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance; Cons: Susceptible to pitting in chloride environments. |
| 304L Stainless Steel | Lower carbon content (≤0.03%) for improved weldability | Food processing, medical applications | Pros: Better corrosion resistance; Cons: Lower strength compared to standard 304. |
| 304H Stainless Steel | Higher carbon content (0.040-0.10%) for high-temperature applications | Power generation, pressure vessels | Pros: Maintains strength at elevated temperatures; Cons: More brittle, requiring careful handling. |
| 304LN Stainless Steel | Nitrogen alloyed for enhanced strength at low temperatures | Cryogenic applications, aerospace | Pros: Better toughness in extreme conditions; Cons: Higher cost due to specialized processing. |
| Dual Certified 304/304L | Meets both 304 and 304L specifications | Versatile applications across industries | Pros: Flexibility in meeting varying requirements; Cons: May not be optimal for specific applications. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of 304 Stainless Steel?
304 stainless steel is a versatile austenitic alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance and formability. Composed primarily of 18% chromium and 8% nickel, it is widely used in applications ranging from kitchen equipment to chemical containers. However, it can be prone to pitting corrosion in chloride-rich environments, which is a key consideration for buyers in coastal or chemical-heavy industries.
How Does 304L Stainless Steel Differ from Standard 304?
304L stainless steel features a lower carbon content, which enhances its weldability and makes it suitable for applications involving heavy welding. This variant is particularly favored in food processing and medical applications where corrosion resistance is paramount. Buyers should note that while it offers improved weldability, it may not possess the same strength as standard 304, making it less suitable for high-stress applications.
In What Situations Is 304H Stainless Steel Preferred?
304H stainless steel is characterized by a higher carbon content, allowing it to maintain strength and durability at elevated temperatures. This makes it ideal for applications in power generation and pressure vessels where heat resistance is critical. However, its increased brittleness necessitates careful handling, and buyers should ensure compatibility with their specific operational conditions.
Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
What Advantages Does 304LN Stainless Steel Offer?
304LN stainless steel is alloyed with nitrogen, enhancing its strength and toughness, particularly at low temperatures. This variant is ideal for cryogenic applications and aerospace components where performance under extreme conditions is crucial. While it offers significant benefits, the cost may be higher due to the specialized processing required, which is an important consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Why Consider Dual Certified 304/304L Stainless Steel?
Dual certified 304/304L stainless steel combines the properties of both grades, offering flexibility for a range of applications across various industries. This variant allows buyers to meet diverse requirements without needing multiple materials. However, while it provides versatility, it may not be the best option for applications requiring the specific advantages of either 304 or 304L alone, necessitating careful assessment of project needs.
Key Industrial Applications of crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of crystal structure of 304 stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Manufacturing of food processing equipment, such as mixers and storage tanks | Ensures hygiene and corrosion resistance, critical for food safety | Ensure compliance with food safety standards and certifications |
| Chemical Processing | Construction of reactors and storage tanks for corrosive chemicals | Provides durability and resistance to chemical attacks, enhancing longevity | Assess the suitability for specific chemicals and temperatures |
| Architecture and Construction | Use in structural components and architectural facades | Offers aesthetic appeal along with strength and corrosion resistance | Consider local climate conditions and design specifications |
| Pharmaceutical Industry | Production of cleanroom equipment and storage for active ingredients | Maintains sterile conditions, ensuring product integrity and safety | Verify compatibility with cleaning protocols and regulatory compliance |
| Oil and Gas | Use in pipelines and storage tanks for oil and gas products | High corrosion resistance in harsh environments, reducing maintenance costs | Evaluate specifications for pressure and temperature ratings |
How is the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel used in the food and beverage industry?
In the food and beverage sector, the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel is leveraged in the manufacturing of food processing equipment such as mixers, storage tanks, and conveyor systems. Its austenitic structure provides excellent corrosion resistance and hygienic properties, which are essential for food safety. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, must ensure that suppliers comply with food safety standards such as FDA or EU regulations to avoid contamination risks.
What are the benefits of 304 stainless steel in chemical processing?
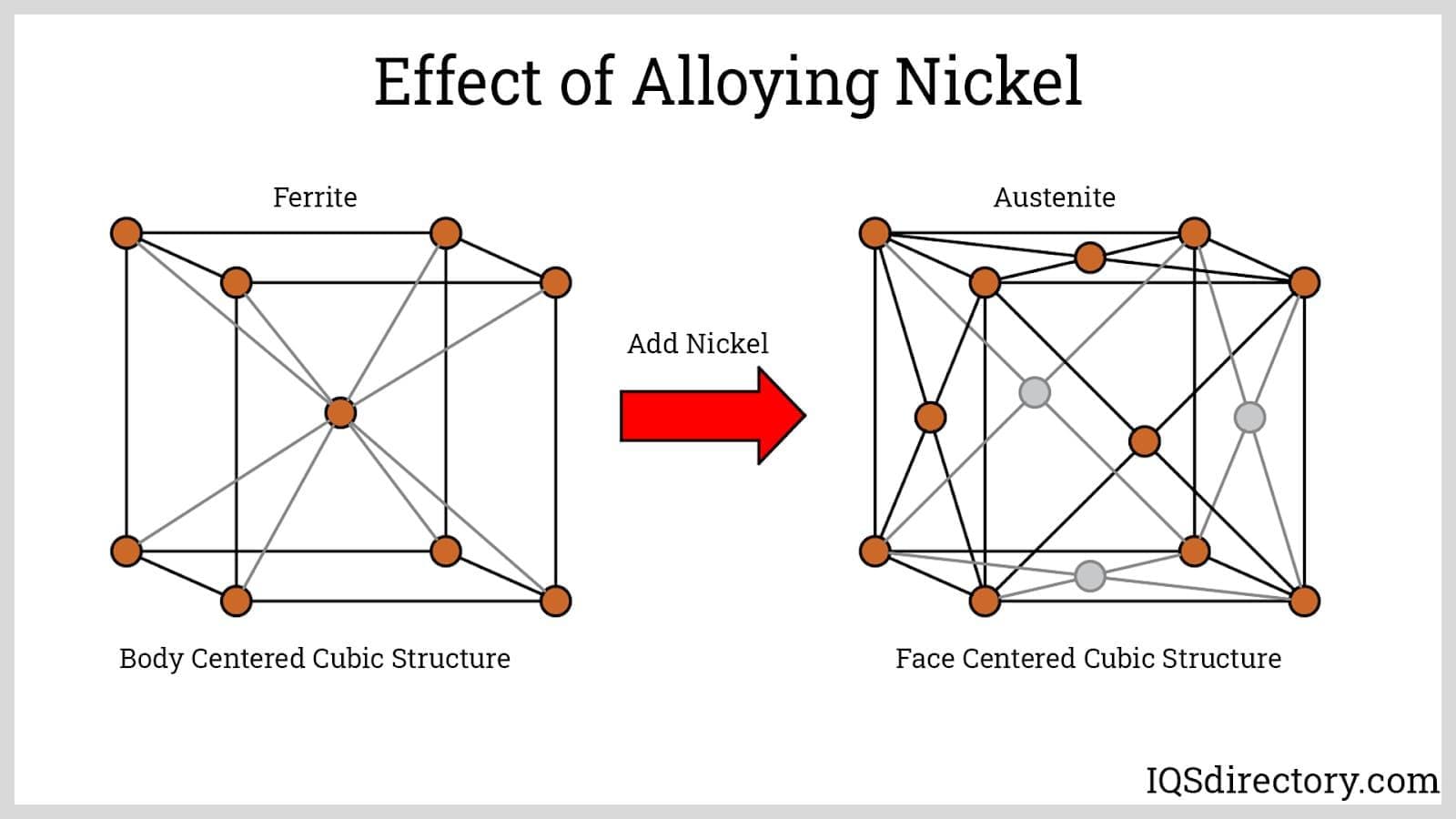
In chemical processing, 304 stainless steel is utilized for constructing reactors, storage tanks, and piping systems due to its resistance to various corrosive substances. The face-centered cubic structure contributes to its durability and ability to withstand harsh chemical environments. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe need to ensure that the material specifications align with the chemicals being processed, including temperature and pressure ratings, to prevent failures and enhance operational efficiency.
Why is 304 stainless steel preferred in architecture and construction?
The crystal structure of 304 stainless steel is frequently employed in architectural applications, including structural components and facades, due to its strength, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to environmental factors. This versatility allows it to meet both functional and design requirements. B2B buyers from Europe and Africa should consider local climate impacts on corrosion resistance and ensure that the sourced materials meet specific design and load-bearing criteria.
Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
How does 304 stainless steel contribute to the pharmaceutical industry?
In the pharmaceutical industry, 304 stainless steel is essential for manufacturing cleanroom equipment and storage solutions for active ingredients. Its crystal structure ensures a sterile environment, crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of pharmaceutical products. Buyers in this sector should confirm that their suppliers adhere to stringent cleaning protocols and regulatory compliance, particularly in regions with strict health standards like Europe and South America.
What role does 304 stainless steel play in the oil and gas sector?
The oil and gas industry utilizes 304 stainless steel in pipelines and storage tanks, where its resistance to corrosion in harsh environments is vital. The austenitic structure allows it to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions, which is critical for operational safety and efficiency. Sourcing considerations for international buyers, especially in Africa and the Middle East, should include evaluating the material’s specifications against the operational demands to mitigate risks associated with corrosion and leaks.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘crystal structure of 304 stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Corrosion Resistance in Varied Environments
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when selecting 304 stainless steel for applications in environments that may expose it to corrosive agents. For instance, industries operating in coastal areas or near chemical plants must contend with high chloride concentrations that can lead to pitting and crevice corrosion in 304 stainless steel. This creates uncertainty about the material’s longevity and performance, leading to potential project delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To effectively use 304 stainless steel in such environments, buyers should first conduct a thorough assessment of the operational conditions. This includes evaluating the presence of chlorides and the potential for stress corrosion cracking. If the project demands high corrosion resistance, consider specifying 304L or 316 stainless steel, which contains molybdenum for enhanced durability in saline conditions. Additionally, implementing protective coatings or regular maintenance schedules can mitigate corrosion risks. Collaborating closely with suppliers to ensure proper material certification and adherence to ASTM A240 standards will further help in sourcing the right grade for specific applications.
Scenario 2: Challenges in Machining 304 Stainless Steel
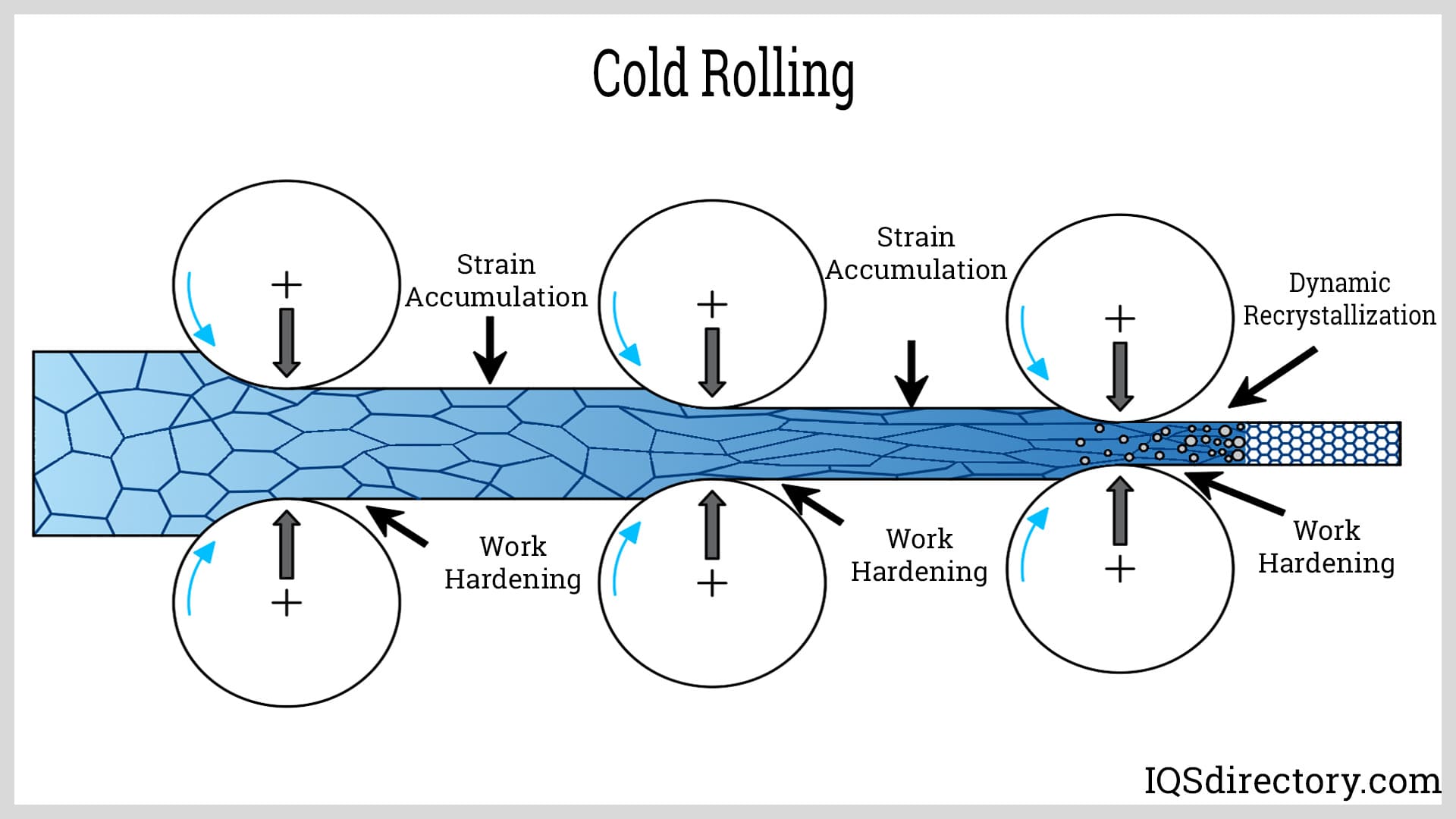
The Problem: Many manufacturers struggle with the machinability of 304 stainless steel, which can lead to production inefficiencies and increased operational costs. The tendency of 304 to work-harden means that as it is machined, it becomes harder, making cutting more difficult and resulting in rapid tool wear. This is particularly frustrating for businesses that require precise components and have limited downtime for machinery maintenance.
Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
The Solution: To overcome these machining challenges, B2B buyers should focus on optimizing their machining processes. This includes using sharp, high-quality cutting tools specifically designed for stainless steel and employing appropriate cutting speeds to minimize work-hardening. Additionally, utilizing coolant during machining operations can help manage heat build-up, reducing the risk of hardening and improving tool life. Buyers should also consider investing in training for their machining teams to ensure they understand the unique properties of 304 stainless steel, which can lead to better techniques and reduced production times.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Variability of Crystal Structure
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter variability in the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel, which can affect its mechanical properties and performance in various applications. This inconsistency can arise from differences in manufacturing processes, such as hot or cold working, and can lead to unexpected results in strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. As a result, companies may face challenges in meeting specifications or quality standards, leading to product failures and loss of client trust.
The Solution: To navigate the complexities of crystal structure variability, it is crucial for buyers to establish clear specifications and quality control measures with their suppliers. Requesting detailed material test reports, including grain structure and mechanical properties, can help ensure consistency across batches. Additionally, engaging in a collaborative relationship with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding the expected crystal structure outcomes based on specific processing methods. Implementing rigorous testing protocols, such as tensile strength and corrosion resistance tests, before using the material in final products will provide an additional layer of assurance, enabling businesses to meet quality standards consistently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
What Are the Key Properties of 304 Stainless Steel Relevant to B2B Buyers?
304 stainless steel, recognized for its austenitic crystal structure, offers several key properties that are critical for various industrial applications. It features excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against rust and staining, making it suitable for environments that may expose it to moisture and mild chemicals. With a temperature rating of up to 925°C for continuous service, it can withstand a range of thermal conditions. However, it is susceptible to pitting in chloride-rich environments, which is a significant consideration for applications in coastal or chemical processing areas.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using 304 Stainless Steel?
The advantages of 304 stainless steel include its strong resistance to corrosion, ease of fabrication, and affordability. It is widely available and can be easily welded, making it a go-to choice for manufacturers. However, its limitations include susceptibility to pitting corrosion in harsh environments and challenges in machining due to work hardening. These factors can influence the overall manufacturing complexity and costs, especially for projects requiring precision components.
How Does 304 Stainless Steel Impact Specific Applications?
The impact of 304 stainless steel on applications is significant. It is commonly used in kitchen equipment, chemical containers, and architectural structures due to its non-reactive nature and durability. However, in applications involving high chloride exposure, such as marine environments, alternative materials like 316 stainless steel may be more appropriate. B2B buyers must assess the specific media compatibility and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting 304 Stainless Steel?
For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS is paramount. Understanding the regional preferences and availability of 304 stainless steel variants, such as 304L or 304H, can also influence the selection process. Buyers should consider logistical aspects, including sourcing and transportation costs, as well as the potential need for certifications or quality assurances.
| Material | Typical Use Case for crystal structure of 304 stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | Kitchen equipment, chemical containers, architectural structures | Excellent corrosion resistance in mild environments | Susceptible to pitting in chloride-rich conditions | Medium |
| 304L Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment, medical devices | Lower carbon content reduces risk of carbide precipitation | Limited high-temperature performance compared to 304H | Medium |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Marine applications, chemical processing | Superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments | Higher cost compared to 304 and 304L | High |
| 304H Stainless Steel | High-temperature applications, pressure vessels | Enhanced strength at elevated temperatures | More brittle in certain forming processes | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection considerations for 304 stainless steel, emphasizing its properties, advantages, disadvantages, and the specific needs of international B2B buyers.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of 304 Stainless Steel?
The manufacturing process of 304 stainless steel involves several critical stages that ensure the material meets the necessary specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess the capabilities of suppliers and make informed purchasing decisions.
Material Preparation: How Is 304 Stainless Steel Initially Processed?
The first step in manufacturing 304 stainless steel is material preparation, which involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, typically iron ore, chromium, and nickel. These materials are melted together in an electric arc furnace (EAF) at high temperatures, usually exceeding 1600°C. This melting process ensures a homogeneous mixture, which is essential for achieving the desired crystal structure.
Once the alloy is melted, it undergoes refining to remove impurities. This is typically achieved through techniques like Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD), which helps in controlling the carbon content and achieving the precise composition required for 304 stainless steel.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape 304 Stainless Steel?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming. This process includes both hot and cold working techniques. Hot working involves shaping the metal at high temperatures (900°C to 1180°C) to facilitate significant deformation without fracturing. Techniques such as forging, rolling, and extrusion are commonly used during this phase.
Cold working, on the other hand, is performed at room temperature and is primarily used to enhance the strength and hardness of the material without altering its crystal structure. Cold rolling or drawing can be employed to produce sheets, plates, and bars with precise dimensions.
Assembly: How Are Components Fabricated from 304 Stainless Steel?
In the assembly stage, various components made from 304 stainless steel are fabricated to meet specific applications. This may include cutting, machining, and welding. Due to its austenitic structure, 304 stainless steel is relatively easy to weld using techniques like TIG and MIG welding, which are commonly adopted in manufacturing settings.
When assembling components, it is crucial to ensure that proper welding techniques are employed to maintain the integrity of the material. The use of compatible filler materials, such as 308L stainless steel, is recommended to ensure that the welded joints exhibit similar properties to the base material.
Finishing: What Are the Final Steps in Preparing 304 Stainless Steel Products?
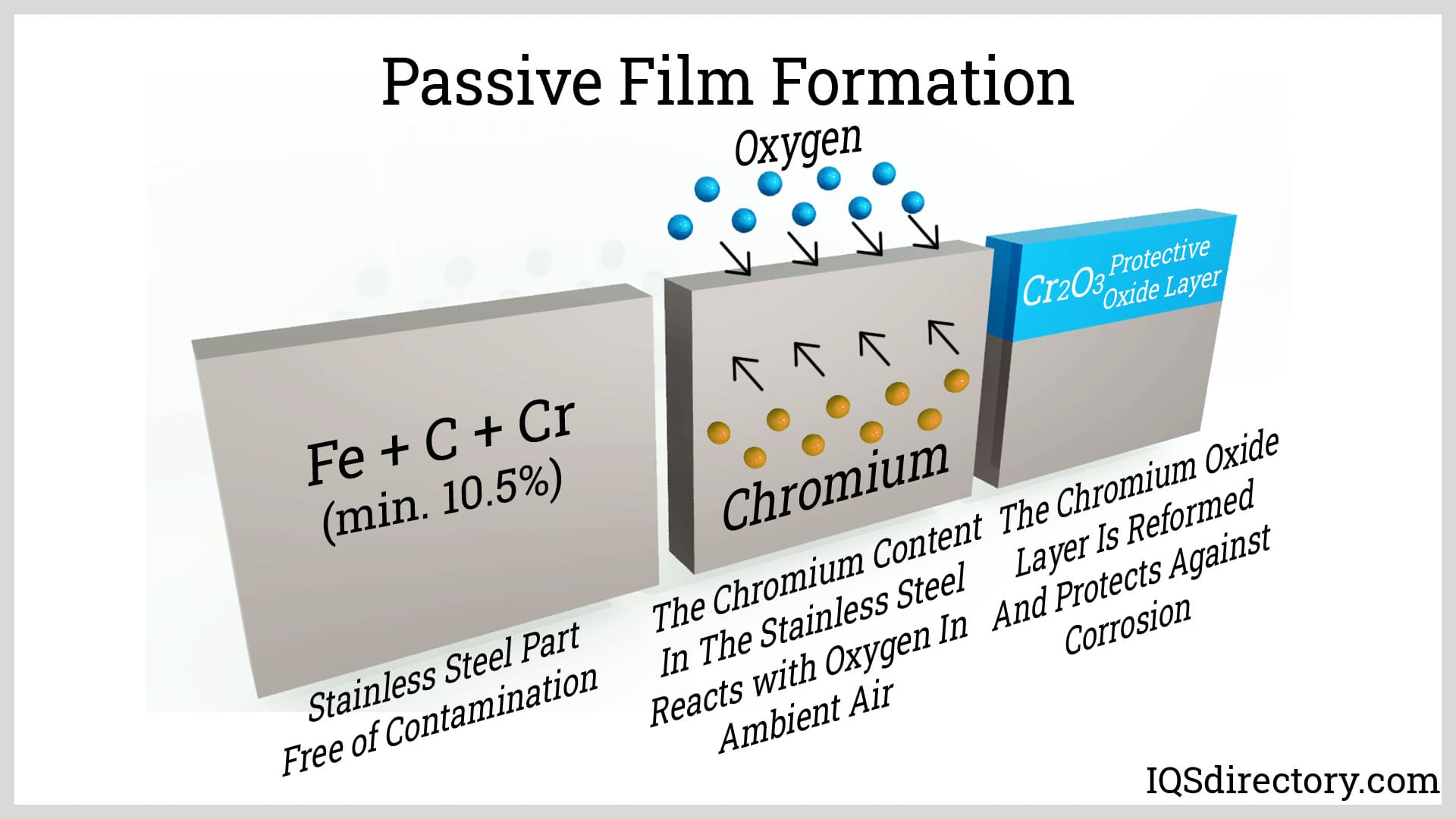
The finishing stage involves various processes to enhance the surface quality and appearance of the 304 stainless steel products. Techniques such as pickling and passivation are used to remove oxides and contaminants, thus improving corrosion resistance.
Additionally, surface treatments like polishing can be applied to achieve desired finishes, such as No.4 or No.8, which are often required for aesthetic applications. This stage is critical, especially for products intended for food processing or medical applications, where cleanliness and surface integrity are paramount.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented During 304 Stainless Steel Production?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for 304 stainless steel. Implementing robust QA measures ensures that the final products meet international standards and customer specifications.
Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
What International Standards Govern the Quality of 304 Stainless Steel?
Manufacturers of 304 stainless steel typically adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE marking and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may be applicable, depending on the intended application of the stainless steel products. These certifications indicate that the products meet specific regulatory requirements and safety standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the final products meet established specifications. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production process. It ensures that only high-quality materials are used, minimizing defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor critical parameters, such as temperature, composition, and dimensional accuracy. This proactive approach allows manufacturers to identify and rectify issues before they escalate.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, comprehensive testing is performed on the finished products. This may include mechanical testing, corrosion resistance tests, and dimensional inspections to ensure compliance with specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality in 304 Stainless Steel?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to verify the quality of 304 stainless steel. Common methods include:
Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
-
Chemical Composition Analysis: Techniques like Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) are used to analyze the elemental composition of the alloy, ensuring it meets the specified standards.
-
Mechanical Testing: Tensile tests, hardness tests, and impact tests are conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of the material, such as strength and ductility.
-
Corrosion Testing: Tests like salt spray tests or immersion tests are performed to assess the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in different environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential to ensure that they receive reliable products. Here are some actionable strategies:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting regular supplier audits is an effective way to assess the quality management systems in place. Buyers should develop a checklist based on relevant standards and their specific requirements. During the audit, buyers can review documentation, observe manufacturing processes, and assess the effectiveness of quality control measures.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Control Reports?
B2B buyers should request quality control reports from suppliers, including certificates of compliance and test results. These documents provide transparency regarding the manufacturing process and the quality assurance measures implemented.
Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play in Verifying Quality?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be scheduled at various stages of production and serve as an additional layer of assurance that the products meet the required standards.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing and Quality Assurance Crucial for B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for 304 stainless steel is crucial. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality materials that meet their specific needs, ultimately contributing to the success of their projects and operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘crystal structure of 304 stainless steel’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring materials related to the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel. Understanding the properties and specifications of this widely used alloy is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with your project’s requirements.
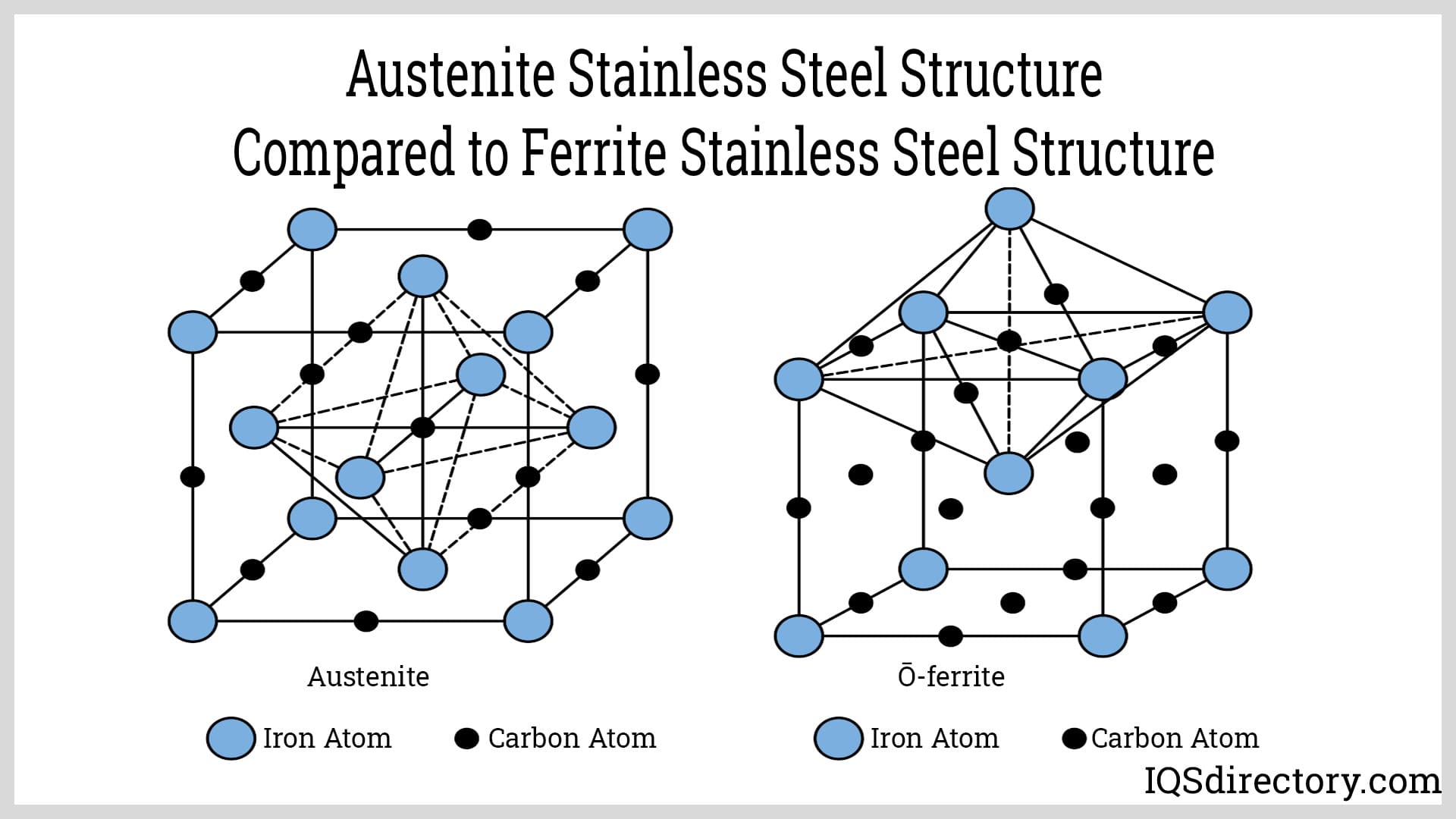
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
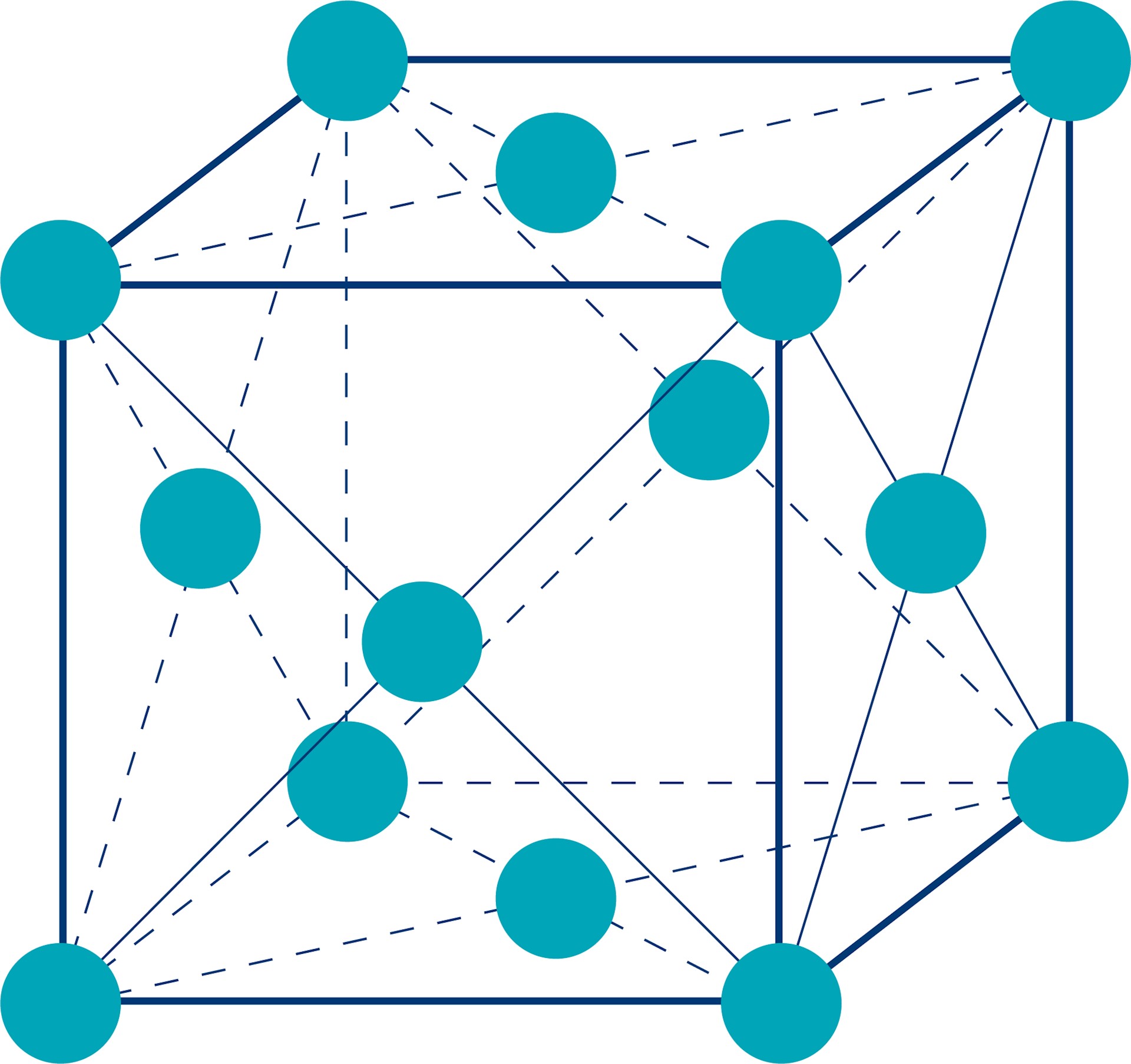
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical specifications for 304 stainless steel. This includes understanding its crystal structure, which is face-centered cubic (FCC), and its composition of 18% chromium and 8% nickel. Precise specifications will guide you in selecting the right product and ensure it meets your project’s performance criteria.
Step 2: Research Supplier Expertise
Identify suppliers with a proven track record in providing 304 stainless steel products. Look for companies that specialize in austenitic stainless steels and have extensive experience in your industry. Supplier expertise not only influences product quality but also impacts delivery times and customer support.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar sectors or regions. This step is critical to ensure the supplier can meet your quality and delivery expectations, thus minimizing risks in your supply chain.
Step 4: Verify Material Certifications
Ensure that the stainless steel you are sourcing is certified to relevant standards, such as ASTM A240. Certifications guarantee that the material meets specific quality and performance criteria, which is essential for applications where safety and durability are paramount. Ask for documentation that verifies compliance with international standards.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Investigate the production capabilities of potential suppliers, including their ability to customize sizes, shapes, and finishes. Understanding their manufacturing processes, such as cold working and welding methods, will help you determine if they can meet your specific project requirements. Additionally, assess their capacity for large orders if necessary.
Step 6: Request Samples and Test for Quality
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the 304 stainless steel to conduct quality tests. This step allows you to evaluate the material’s properties, including corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, directly. Testing samples can help prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the material aligns with your technical specifications.

Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate terms that include pricing, delivery timelines, and payment conditions. Clear agreements help establish expectations and accountability on both sides. Ensure that all terms are documented in a formal contract to protect your interests throughout the procurement process.
By following these steps, you can streamline your sourcing process and ensure that you procure high-quality 304 stainless steel that meets your project’s needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for crystal structure of 304 stainless steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 304 Stainless Steel?
When sourcing 304 stainless steel, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, which includes the price of nickel, chromium, and other alloys that constitute 304 stainless steel, plays a significant role in the overall pricing. Fluctuations in the prices of these metals can directly impact sourcing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs are incurred during the manufacturing process, including skilled workers involved in shaping, welding, and finishing the steel. Regions with higher labor rates can significantly elevate production costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can help minimize these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The expense for tools and dies used in the manufacturing process is another critical factor. Custom tooling for specific shapes or sizes can lead to higher initial costs, but may offer long-term savings through efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the stainless steel meets specified standards (like ASTM A240) incurs additional costs. Investing in stringent QC processes can prevent costly returns or failures in applications.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs depend on the distance from the supplier, the mode of transport, and shipping conditions. International buyers should consider additional fees related to customs and duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the pricing, which can vary significantly based on their business model and market positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing 304 Stainless Steel?
Several factors can influence the pricing of 304 stainless steel, including:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger order volumes or minimum order quantities (MOQ). Bulk purchases can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications or unique finishes can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of raw materials and certifications (like ISO, ASTM) can affect the price. Higher quality often commands a premium but can reduce long-term operational risks.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and delivery capabilities can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived reliability.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) will determine how costs are allocated between the buyer and seller. Understanding these terms is vital for accurate cost forecasting.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for 304 Stainless Steel?
B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing of 304 stainless steel should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing structures. Requesting volume discounts can yield significant savings.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. TCO includes maintenance, lifespan, and operational efficiencies. Investing in higher-quality materials may reduce overall costs over time.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding fluctuations in raw material prices and global market conditions can help buyers time their purchases effectively.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations. It also allows buyers to compare quality and service levels.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. This is particularly relevant for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
What Should International Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, it is important to be aware of specific pricing nuances:

Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can significantly impact costs, so it’s wise to monitor currency trends when negotiating prices.
-
Import Duties and Tariffs: Understanding the import regulations and potential tariffs in your country can help in calculating the total landed cost.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding negotiation and pricing strategies. Adapting to these cultural nuances can facilitate smoother transactions.
-
Quality Assurance: Ensure that suppliers can provide the necessary documentation and certifications to meet local compliance and quality standards.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for 304 stainless steel can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing crystal structure of 304 stainless steel With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to 304 Stainless Steel Crystal Structure
When evaluating the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel, it is essential to consider alternative materials or technologies that may offer similar benefits or improved performance for specific applications. The choice of material can significantly affect the overall efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness of a project. This analysis will compare 304 stainless steel with other viable alternatives, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their unique requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Crystal Structure Of 304 Stainless Steel | Alternative 1 Name (316 Stainless Steel) | Alternative 2 Name (Aluminum Alloy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance; non-magnetic | Superior corrosion resistance, especially in chloride environments | Lightweight; good strength-to-weight ratio |
| Cost | Moderate; widely available | Higher cost due to molybdenum content | Generally lower than stainless steel |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to fabricate and weld | Similar ease of fabrication; requires careful welding | Easy to machine; less challenging than stainless |
| Maintenance | Requires regular cleaning; susceptible to pitting | Low maintenance; resistant to pitting | Requires protective coatings for longevity |
| Best Use Case | Kitchen equipment, chemical containers | Marine applications, chemical processing | Aerospace, automotive components |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
316 Stainless Steel: A Superior Alternative for Corrosive Environments
316 stainless steel is an upgraded version of 304, incorporating molybdenum, which enhances its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in chloride-rich environments. This makes it an excellent choice for marine applications and chemical processing facilities. However, the cost of 316 is generally higher than that of 304, which can impact budget considerations for large-scale projects. While it offers superior performance in harsh conditions, the increased material cost may not be justified for less demanding applications.
Aluminum Alloy: A Lightweight Solution
Aluminum alloys present a lightweight alternative to stainless steel, making them attractive for industries where weight reduction is crucial, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. These alloys can deliver a good strength-to-weight ratio and are easier to machine than stainless steel. However, aluminum generally has lower corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel, requiring protective coatings to ensure durability in certain environments. Additionally, while aluminum is cost-effective, it may not provide the same level of structural integrity as stainless steel in heavy-duty applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate material for your project, it is vital to assess the specific requirements of your application, including environmental conditions, budget constraints, and performance expectations. While 304 stainless steel offers a balanced combination of corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication, and affordability, alternatives like 316 stainless steel or aluminum alloys may be more suitable for specialized applications. B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their unique needs and consider both the advantages and limitations of each option to make the most informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of 304 Stainless Steel?
When considering 304 stainless steel, understanding its key technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
304 stainless steel is classified under ASTM A240 and equivalent grades such as 1.4301 (EN) and SUS304 (JIS). This grade indicates austenitic stainless steel with 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which provides excellent corrosion resistance and formability. For B2B buyers, selecting the correct material grade ensures compatibility with their specific applications, particularly in environments prone to corrosion. -
Tensile Strength
The tensile strength of 304 stainless steel typically ranges between 505 MPa to 720 MPa (73,000 to 104,000 psi). This property measures the material’s ability to withstand pulling forces without failing. In industries where structural integrity is critical—like construction and manufacturing—understanding tensile strength aids buyers in selecting materials that meet safety and durability standards. -
Yield Strength
Yield strength for 304 stainless steel is approximately 215 MPa (31,200 psi). This property defines the stress at which the material begins to deform plastically. For B2B buyers, knowing the yield strength is vital for designing components that can endure operational loads without permanent deformation, ensuring longevity and reliability. -
Corrosion Resistance
304 stainless steel exhibits excellent resistance to rust and corrosion in various environments, including fresh water and mild chemicals. However, it is susceptible to pitting in chloride-rich environments. Buyers in industries such as food processing or chemical manufacturing should assess the corrosion resistance based on their operational conditions to avoid premature material failure. -
Thermal Expansion Coefficient
The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) for 304 stainless steel is approximately 16.0 x 10^-6 /°C. This property measures how much the material expands when heated. Understanding CTE is essential for B2B buyers involved in applications where temperature fluctuations are common, as it informs decisions regarding assembly and design to prevent structural issues. -
Work Hardening Rate
304 stainless steel has a moderate work hardening rate, meaning it becomes harder and stronger when deformed. This property is significant for manufacturers who utilize processes like cold working, as it affects tooling, machining processes, and overall material performance in finished products.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to 304 Stainless Steel?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology enhances communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For B2B buyers, working with OEMs ensures quality and compatibility with existing systems, particularly in sectors like automotive and industrial machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory levels effectively and negotiate better pricing terms, especially for bulk purchases of materials like stainless steel. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific quantities of goods. B2B buyers should issue RFQs to multiple suppliers to compare costs, delivery times, and terms, ensuring they secure the best deal for 304 stainless steel products. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. For B2B buyers, understanding Incoterms helps in managing logistics, shipping costs, and risk during the purchase of 304 stainless steel. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Knowing the lead time is essential for B2B buyers to plan their production schedules and maintain supply chain efficiency, especially when sourcing materials like stainless steel that might have variable availability. -
Certification
Certification indicates that a product meets specific industry standards. For 304 stainless steel, certifications might include compliance with ASTM standards or equivalent international standards. Buyers should prioritize sourcing certified materials to ensure quality, safety, and regulatory compliance in their applications.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate procurement processes effectively, ensuring optimal material selection and successful project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for 304 Stainless Steel?
The global market for 304 stainless steel is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including construction, automotive, and food processing. The austenitic structure of 304 stainless steel, characterized by its face-centered cubic (FCC) arrangement, provides excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, making it a preferred choice for manufacturers. Notably, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly sourcing this material due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness.

Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
Emerging trends in the B2B landscape include the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and AI, which enhance production efficiency and reduce lead times. Digital sourcing platforms are also gaining traction, enabling buyers to compare suppliers and negotiate better terms. Furthermore, sustainability concerns are influencing sourcing decisions, with an increasing emphasis on materials that minimize environmental impact.
The competitive landscape is evolving, with suppliers diversifying their offerings to include various finishes and custom sizes. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about market fluctuations, particularly regarding raw material prices and geopolitical factors that may affect supply chains. By understanding these dynamics, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of 304 Stainless Steel?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of 304 stainless steel, as businesses seek to reduce their environmental footprint. The production of stainless steel typically involves significant energy consumption and carbon emissions. Therefore, buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes.

Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as stakeholders demand transparency in the supply chain. Companies that can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and ethical labor practices gain a competitive edge. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract conscientious buyers.
Moreover, the market is seeing a rise in the availability of ‘green’ materials, including those that are certified as having reduced environmental impacts. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who can provide documentation of their sustainability claims, ensuring that the materials they source align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
What Is the Historical Context of 304 Stainless Steel in the B2B Market?
304 stainless steel, developed by W.H. Hatfield in 1924, was a significant advancement in metallurgical engineering. This alloy, containing 18% chromium and 8% nickel, was designed to offer superior corrosion resistance compared to its predecessors. Initially marketed under the name “Staybrite 18/8,” 304 stainless steel quickly gained popularity in various industries, thanks to its durability and versatility.
Over the decades, the understanding of its crystal structure and mechanical properties has led to widespread applications in kitchen equipment, chemical containers, and architectural structures. Today, 304 stainless steel remains a cornerstone material in numerous sectors, continually evolving to meet modern demands for sustainability and performance.
Illustrative image related to crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
In summary, the sourcing trends for 304 stainless steel reflect a complex interplay of market dynamics, sustainability considerations, and historical advancements. International B2B buyers must navigate this landscape with an informed perspective to leverage opportunities effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
-
How do I determine the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel?
The crystal structure of 304 stainless steel is a face-centered cubic (FCC) lattice, which contributes to its excellent ductility and corrosion resistance. To confirm the crystal structure, you can utilize X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques, which provide insights into the arrangement of atoms within the material. Additionally, consulting with suppliers who provide detailed material specifications and certifications can help verify the structural characteristics of the stainless steel you are sourcing. -
What are the key properties of 304 stainless steel relevant to its crystal structure?
The face-centered cubic structure of 304 stainless steel allows for high toughness and workability, making it suitable for various applications. Its austenitic nature provides excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, particularly in environments with moisture or mild chemicals. The FCC arrangement also ensures that the material is non-magnetic, an important consideration in industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals where contamination is a concern. -
What is the best application for 304 stainless steel based on its crystal structure?
304 stainless steel is ideal for applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance and formability, such as kitchen equipment, chemical containers, and architectural components. Its face-centered cubic structure allows for extensive deformation without fracturing, making it suitable for complex shapes and designs. Additionally, its non-reactive nature makes it a preferred choice for food and medical applications, ensuring safety and compliance with health regulations. -
How can I verify the quality of 304 stainless steel before purchase?
To ensure the quality of 304 stainless steel, request material test reports (MTRs) from your supplier, which should include details such as chemical composition, mechanical properties, and crystal structure confirmation. It is also advisable to conduct third-party inspections and audits, especially if sourcing from international suppliers. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality management processes. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for 304 stainless steel products?
Minimum order quantities for 304 stainless steel products can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the product type, size, and finish. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons. When negotiating with suppliers, clarify the MOQ to ensure it aligns with your project needs, and inquire about potential flexibility in orders, especially for new customers or smaller businesses. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing 304 stainless steel internationally?
Payment terms for international orders of 304 stainless steel typically range from upfront payment to net 30 or net 60 days after shipment. Some suppliers may offer letter of credit (LC) options for larger orders, providing additional security for both parties. It’s crucial to discuss and negotiate payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
How does the logistics process work for importing 304 stainless steel?
Importing 304 stainless steel involves several logistical steps, including selecting a reliable freight forwarder who understands customs regulations in your country. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as commercial invoices and certificates of origin, to facilitate customs clearance. It’s also beneficial to discuss shipping methods and costs upfront, as well as delivery timelines, to effectively plan your inventory and production schedules. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for 304 stainless steel?
When vetting suppliers for 304 stainless steel, consider their experience and reputation in the industry, especially in your target market. Request references and check for certifications such as ISO and ASTM compliance. It’s also wise to assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and lead times. Establishing clear communication channels and understanding their customer service approach can further ensure a successful long-term partnership.
Top 5 Crystal Structure Of 304 Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SteelPro Group – Grade 304 Stainless Steel
Domain: steelprogroup.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Grade 304 stainless steel is a versatile and widely used alloy known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and good formability. It contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including food processing, chemical equipment, and architectural structures. Grade 304 is non-magnetic and can be easily welded and fabricated. It is also resistant…
2. IQS Directory – Stainless Steel 304 and 304L Overview
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel 304 (UNS S30400) and 304L (UNS S30403) are widely used austenitic stainless steels known for their adaptability and extensive applications. Key specifications include:
– Composition: 18% chromium and 8% nickel (18/8 stainless steel)
– Grades:
– Stainless Steel 304:
– ASTM A240 and ASTM A666
– AISI/SAE 304
– JIS SUS 304
– German Grade 1.4301
– ISO X5CrN…
3. Reddit – Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steels
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Precipitation hardened stainless steels can have a crystal structure that is predominantly martensitic, typically containing Mo-Cu precipitates. Some austenitic grades exist that use Ti-Al, but they are less common. The structure in PH stainless steels is usually martensitic after heat treatment. Common examples include AISI 630 (17-4PH) which consists of mostly ductile lath martensite with some r…
4. ArchToolbox – Stainless Steel Grades
Domain: archtoolbox.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Stainless Steel Grades: 300 Series, 400 Series, 904L Stainless Steel. 300 Series: Austenitic, high corrosion resistance, includes 301 (decorative applications), 304 (most common, 18% chromium, 8% nickel), 316 (higher corrosion resistance, used in medical/food industry), 317 (higher corrosion resistance than 316). 400 Series: Ferritic and martensitic, includes 430 (decorative applications, magnetic…
5. Greenwood Magnetics – Stainless Steel Solutions
Domain: greenwoodmagnetics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 304 stainless steel: Contains chromium (min. 18%), nickel (min. 8%), slightly responsive to magnetic fields, austenitic structure. 316 stainless steel: Molybdenum-alloyed, negligibly responsive to magnetic fields, used in non-magnetic applications, contains varying concentrations of other elements. Both have paramagnetic characteristics, with 304SS being more likely to be held in the flow than 316…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for crystal structure of 304 stainless steel
In conclusion, understanding the crystal structure of 304 stainless steel is essential for B2B buyers aiming to optimize material selection for diverse applications. The face-centered cubic (FCC) structure of 304 stainless steel not only enhances its mechanical properties but also contributes to its excellent corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice in various industries, including food processing, architecture, and chemical storage.
Strategic sourcing of 304 stainless steel allows businesses to leverage its strengths while mitigating potential drawbacks, such as susceptibility to pitting in chloride-rich environments. By partnering with reliable suppliers that offer customized sizes and finishes, companies can ensure they meet specific project requirements effectively.
As international markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for high-quality materials like 304 stainless steel is set to rise. Now is the time to engage with trusted suppliers, invest in quality materials, and secure your competitive advantage. Embrace the future of manufacturing and construction by prioritizing strategic sourcing—your projects deserve nothing less.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.