Common Uses Of Epoxy: The Ultimate 2025 B2B Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for common uses of epoxy
In today’s competitive global market, sourcing high-quality epoxy products can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets like Vietnam and established economies like Germany. The versatility of epoxy resin makes it a preferred choice across various industries, from construction to automotive and aerospace. However, understanding the complexities of its applications, types, and sourcing strategies is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the common uses of epoxy, providing insights into its various applications and the distinct types available in the market. Buyers will gain a clear understanding of how to effectively vet suppliers, assess costs, and navigate the regulatory landscape associated with epoxy products. By addressing critical factors such as environmental resistance, durability, and safety considerations, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to select the right epoxy solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Armed with this knowledge, businesses can streamline their procurement processes, ensuring they not only secure high-quality materials but also optimize operational efficiency. Whether you’re looking to enhance structural integrity in construction or improve product performance in automotive manufacturing, this guide will serve as a vital resource for making strategic decisions in the epoxy market.
Understanding common uses of epoxy Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol A | Most common type; strong adhesive properties | Coatings, adhesives, composite materials | Pros: Versatile, cost-effective; Cons: May have health concerns (BPA). |
| Novolac | Higher cross-link density; exceptional chemical resistance | Chemical processing, industrial coatings | Pros: Excellent durability; Cons: More expensive than Bisphenol A. |
| Aliphatic | UV stable; maintains clarity over time | Outdoor coatings, automotive finishes | Pros: Resistant to yellowing; Cons: Can be less durable than other types. |
| Flexible Epoxy | Enhanced flexibility; impact-resistant | Repairing delicate structures, bonding dissimilar materials | Pros: Reduces brittleness; Cons: May have lower chemical resistance. |
| High-Temperature | Maintains performance under extreme conditions | Aerospace, automotive components, electronics | Pros: Excellent thermal stability; Cons: Specialized applications can limit availability. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Bisphenol A Epoxy Resins?
Bisphenol A epoxy resins are the most widely used due to their strong adhesive properties and versatility. They are suitable for a broad range of applications, including coatings and adhesives in construction and automotive industries. When considering Bisphenol A for procurement, buyers should evaluate the health and environmental regulations in their region, as concerns about BPA have led to increased scrutiny and potential restrictions in various markets.
How Does Novolac Epoxy Stand Out in Industrial Applications?
Novolac epoxy resins are distinguished by their higher cross-link density, making them ideal for applications requiring exceptional chemical resistance. This type is particularly favored in chemical processing and industrial coatings where durability is paramount. B2B buyers should consider the specific chemical exposure their products will face, as Novolac offers a longer lifespan and better performance in harsh environments, albeit at a higher cost.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
Why Choose Aliphatic Epoxy for Outdoor Applications?
Aliphatic epoxy resins are specifically designed for UV stability, making them perfect for outdoor coatings and automotive finishes. They maintain clarity over time and resist yellowing, ensuring aesthetic appeal. Buyers should assess the environmental conditions their products will face, as Aliphatic epoxy is ideal for applications where long-term appearance and performance are critical, although it may not match the durability of other epoxy types under extreme conditions.
What Benefits Do Flexible Epoxy Resins Offer?
Flexible epoxy resins provide enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making them suitable for repairing delicate structures or bonding dissimilar materials. This type is advantageous in applications where traditional rigid epoxies may crack under stress. B2B buyers should evaluate the balance between flexibility and chemical resistance when selecting flexible epoxy, as this type may not perform as well in highly corrosive environments.
When Should High-Temperature Epoxy Be Used?
High-temperature epoxy resins are engineered to withstand extreme conditions, making them essential for aerospace, automotive components, and electronics. They maintain performance under elevated temperatures, which is critical in applications where thermal stability is necessary. Buyers must consider the specific temperature ranges and environmental factors their applications will encounter, as high-temperature epoxy can be more specialized and potentially harder to source than standard epoxy types.
Key Industrial Applications of common uses of epoxy
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of common uses of epoxy | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Epoxy coatings for floors and surfaces | Enhances durability and resistance to wear and chemicals | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards |
| Automotive | Bonding and reinforcing lightweight components | Reduces vehicle weight and improves fuel efficiency | Look for high-temperature resistance and adhesion strength |
| Aerospace | Structural components in aircraft manufacturing | Increases strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing performance | Verify certifications for aerospace-grade materials |
| Electronics | Potting and encapsulation of circuit boards | Protects against moisture and environmental damage | Source from suppliers with proven reliability and quality |
| Marine | Waterproofing and bonding in boat construction | Provides long-lasting protection against corrosion | Confirm compatibility with marine environments and conditions |
How is Epoxy Used in Construction, and What Problems Does It Solve?
In the construction sector, epoxy coatings are widely utilized for flooring and surface treatments. These coatings not only improve aesthetics but also enhance durability against heavy traffic, chemicals, and moisture. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality epoxy that meets local building codes is crucial. Additionally, businesses must consider the ease of application and curing times to minimize downtime during construction projects.
What Role Does Epoxy Play in the Automotive Industry?
Epoxy is instrumental in the automotive industry for bonding and reinforcing lightweight components, such as body panels and wheels. This application reduces overall vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and performance. B2B buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers that offer epoxy products with high-temperature resistance and superior adhesion strength, ensuring that they meet the rigorous demands of automotive manufacturing.
How is Epoxy Beneficial in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace manufacturing, epoxy is used to create structural components that require a high strength-to-weight ratio, such as wings and fuselages. The use of epoxy not only enhances the performance of aircraft but also contributes to fuel efficiency. Buyers in regions with stringent aerospace regulations, like Germany, must ensure that the epoxy products sourced meet specific certifications for aerospace-grade materials, thereby guaranteeing safety and compliance.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
Why is Epoxy Important for Electronics?
Epoxy’s role in the electronics industry is primarily in potting and encapsulation processes, protecting sensitive components from moisture, dust, and other environmental factors. This application is vital for ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic devices. International B2B buyers should seek suppliers with a proven track record in providing high-quality epoxy solutions that offer excellent insulation and stability, particularly in humid climates prevalent in regions like Southeast Asia.
How Does Epoxy Enhance Marine Applications?
In the marine industry, epoxy is commonly employed for waterproofing and bonding in boat construction. Its ability to withstand harsh marine environments makes it an ideal choice for protecting vessels from corrosion and wear. Buyers must ensure that the epoxy products sourced are compatible with marine conditions and can provide long-lasting protection, making it essential to work with reputable suppliers who understand the unique challenges of marine applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘common uses of epoxy’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Curing Time and Environmental Conditions
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face difficulties with epoxy curing times, particularly when environmental factors like humidity and temperature vary. For instance, construction firms in regions with high humidity may find that their epoxy coatings do not cure as expected, leading to delays and increased costs. Additionally, inconsistent curing can result in weak bonds and compromised structural integrity, which can jeopardize projects and lead to potential safety hazards.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, it is essential for buyers to select the right type of epoxy based on their environmental conditions. Manufacturers often provide specific guidelines for optimal curing conditions, including recommended temperature ranges and humidity levels. Buyers should invest in fast-curing epoxies or those formulated for high-humidity environments. Furthermore, sourcing from suppliers who offer technical support can provide insights into product performance under specific conditions. Implementing climate control measures, such as using dehumidifiers or heaters on-site, can also help maintain ideal conditions for curing.
Scenario 2: Adhesion Problems in Varied Substrates
The Problem: Adhesion failure is a common pain point for businesses using epoxy, especially when bonding different materials such as metal to concrete or plastic to wood. For example, a manufacturer might attempt to bond lightweight components to heavier structures but finds that the epoxy fails to create a strong bond, leading to product recalls and dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To overcome adhesion issues, it is crucial to conduct thorough surface preparation. Buyers should ensure that surfaces are clean, dry, and free of contaminants before applying epoxy. Additionally, utilizing primers or surface activators designed for specific materials can enhance adhesion. It’s advisable to consult with epoxy suppliers regarding the best practices for the specific substrates involved. Testing the bond strength with small-scale applications before full-scale implementation can help identify potential issues early, reducing risk and ensuring product reliability.
Scenario 3: Health and Safety Concerns During Application
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are increasingly concerned about the health and safety implications of using epoxy, especially in sectors like construction and manufacturing where workers are frequently exposed to chemicals. Issues such as skin irritation or respiratory problems can arise from improper handling and application, leading to workplace accidents and regulatory scrutiny.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
The Solution: To address these concerns, it is essential to implement comprehensive safety protocols. Buyers should prioritize sourcing epoxy products with lower volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and those labeled as safer for worker health. Providing adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respirators is also critical. Furthermore, conducting training sessions for employees on safe handling practices and ensuring proper ventilation in work areas can significantly reduce health risks. Regular audits of safety practices and compliance with local regulations will help maintain a safe working environment while enhancing the company’s reputation as a responsible employer.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for common uses of epoxy
What Are the Key Properties of Epoxy for Different Materials?
Epoxy resins are widely regarded for their versatility and strength, making them suitable for various applications across multiple industries. Below, we analyze several common materials used with epoxy, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Epoxy Perform with Concrete?
Key Properties:
Epoxy offers exceptional adhesion to concrete, with a tensile strength that can exceed 10,000 psi. It is highly resistant to moisture, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for flooring applications in industrial settings.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of epoxy coatings on concrete is a significant advantage, providing long-lasting protection against wear and tear. However, the initial cost can be higher than traditional flooring solutions, and the application process requires skilled labor to ensure proper curing and adhesion.
Impact on Application:
Epoxy’s compatibility with concrete allows it to seal surfaces effectively, preventing moisture ingress and enhancing structural integrity. This is particularly beneficial in environments such as warehouses and manufacturing plants where heavy machinery is used.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should be aware of local building codes and standards such as ASTM for the U.S. and DIN for Germany. Additionally, understanding the climatic conditions in regions such as Africa and the Middle East can influence the choice of epoxy formulations, particularly those that are UV resistant or designed for high temperatures.
What Are the Benefits of Using Epoxy in the Automotive Industry?
Key Properties:
Epoxy resins used in automotive applications provide excellent adhesion, impact resistance, and thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 150°C. They are also resistant to various automotive fluids, including oils and fuels.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of epoxy contributes to fuel efficiency and performance in vehicles. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and may require specialized equipment, which can increase production costs.
Impact on Application:
Epoxy is crucial for bonding and reinforcing components, such as body panels and structural parts, enhancing vehicle safety and longevity. The chemical resistance of epoxy ensures that automotive parts remain functional and visually appealing over time.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like South America and Europe should consider compliance with automotive industry standards, such as ISO/TS 16949. Additionally, local preferences for eco-friendly materials may influence the selection of epoxy formulations.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
How Is Epoxy Used in Aerospace Applications?
Key Properties:
In aerospace, epoxy resins exhibit high tensile strength and low weight, crucial for aircraft performance. They can endure extreme temperatures and pressures, withstanding conditions up to 200°C.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of using epoxy in aerospace is its ability to create lightweight, strong components that enhance fuel efficiency. However, the cost of high-performance epoxy can be significant, and the curing process often requires controlled environments.
Impact on Application:
Epoxy is essential for constructing composite materials used in wings and fuselages, contributing to overall aircraft safety and performance. Its resistance to fatigue and environmental factors is vital for long-term operation.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in the aerospace sector must adhere to stringent regulations and standards, such as AS9100. Understanding the specific requirements for different regions, including certifications and testing, is crucial for compliance.
What Role Does Epoxy Play in Electronics?
Key Properties:
Epoxy resins used in electronics provide excellent electrical insulation and moisture resistance, with dielectric strengths typically exceeding 20 kV/mm. They also offer thermal stability, making them suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons:
The protective qualities of epoxy ensure that electronic components are safeguarded against environmental damage. However, the curing process can be time-consuming, and improper mixing can lead to performance issues.
Impact on Application:
Epoxy is widely used for potting and encapsulating electronic components, protecting them from dust, moisture, and mechanical stress. This is particularly important in industries such as telecommunications and automotive electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of international standards such as IPC-610 for electronics manufacturing. Additionally, considerations for local environmental regulations regarding disposal and toxicity of epoxy components are essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Epoxy Applications
| Material | Typical Use Case for common uses of epoxy | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | Industrial flooring and repairs | Excellent adhesion and durability | Higher initial application cost | Medium |
| Automotive | Bonding and reinforcing vehicle parts | Lightweight and fuel-efficient | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Aerospace | Composite materials for aircraft | High strength-to-weight ratio | Significant material cost | High |
| Electronics | Potting and encapsulation of components | Superior electrical insulation | Time-consuming curing process | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the strategic selection of epoxy materials tailored to their specific industry needs. Understanding the unique properties and considerations for each material can facilitate informed purchasing decisions that align with regional standards and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for common uses of epoxy
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Epoxy Products?
The manufacturing process of epoxy products involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and client specifications. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Epoxy Production?
Material preparation is the first step in the epoxy manufacturing process. It typically involves the precise measurement and mixing of resin and hardener components. This stage is crucial because the ratio of these components directly affects the performance and curing time of the epoxy. Suppliers often utilize advanced mixing equipment to ensure thorough blending, reducing the risk of inconsistencies that could compromise product quality.
In addition to the primary components, additives may be introduced to enhance specific properties such as UV resistance, flexibility, or thermal stability. Understanding these additives can provide B2B buyers insights into the suitability of the epoxy for their particular applications.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Epoxy Products?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves techniques such as casting, molding, or extrusion, depending on the intended application of the epoxy.
-
Casting: This method is often used for creating complex shapes and is common in applications like art, jewelry, and decorative items. It requires careful control of temperature and humidity to ensure proper curing.
-
Molding: In industries such as automotive and aerospace, molding techniques are employed to create parts that require high strength and durability. This includes compression and injection molding processes, which allow for the mass production of identical components.
-
Extrusion: This technique is frequently used for creating continuous shapes, such as rods or sheets, which can be cut to size for various applications.
B2B buyers should assess the forming techniques used by suppliers to ensure they align with the desired specifications and performance characteristics of the epoxy products.
How Is the Assembly of Epoxy Components Handled?
The assembly stage often involves the bonding of various components using epoxy adhesives. This is particularly important in industries such as construction and automotive, where strength and reliability are paramount.
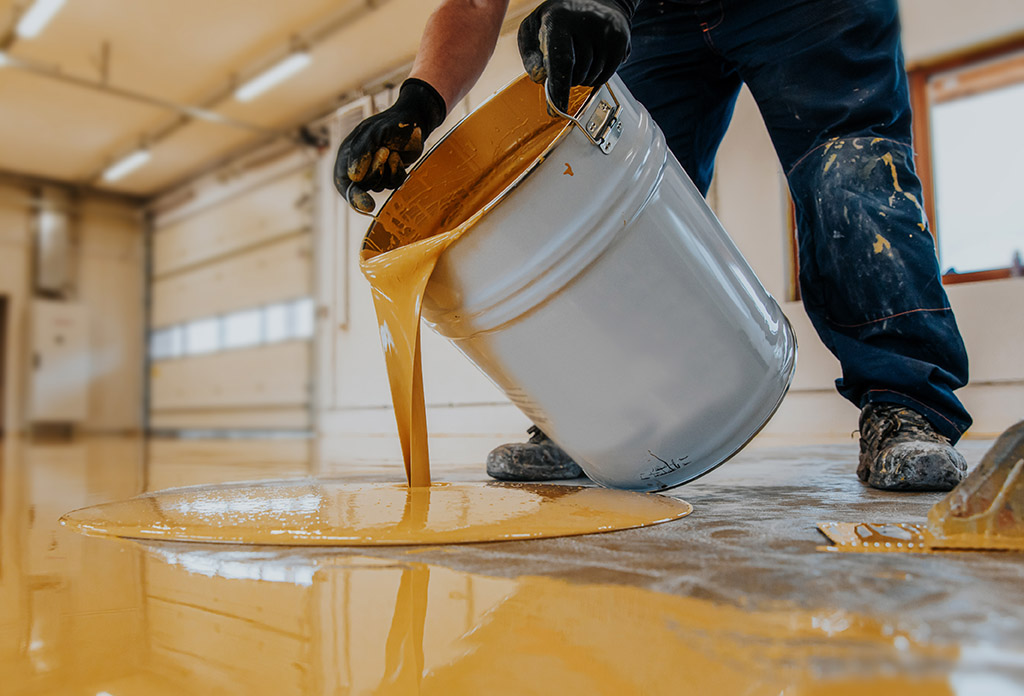

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
During this phase, proper surface preparation is essential to achieve optimal adhesion. Suppliers may employ techniques such as sanding, cleaning, or priming surfaces to enhance the bonding process. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly methods and surface preparation techniques used by suppliers to ensure they meet the standards required for their specific applications.
What Are the Finishing Techniques Applied to Epoxy Products?
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process, where products undergo treatments to enhance their aesthetic qualities and performance. Common finishing techniques include sanding, polishing, and applying additional coatings.
For instance, in the automotive industry, epoxy components may receive a UV-resistant topcoat to protect against sunlight exposure. In electronics, a protective layer may be added to prevent moisture infiltration. Buyers should evaluate the finishing processes used by suppliers to ensure they align with the durability and aesthetic standards necessary for their applications.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Epoxy Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a vital aspect of epoxy production, ensuring that products meet both international standards and specific industry requirements.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial for manufacturers aiming to ensure consistent quality management systems. This standard focuses on various aspects, including customer satisfaction and continual improvement processes.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific certifications like CE marking for construction materials and API standards for the oil and gas sector may be relevant. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers maintain these certifications to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Epoxy Production?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage assesses the raw materials for conformity to specifications, ensuring that only high-quality components are utilized in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, ongoing inspections monitor the quality of the product in real-time. This includes testing for viscosity, curing times, and adhesion properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection is conducted to ensure all specifications and standards are met. This may involve physical testing, such as tensile strength assessments or chemical resistance evaluations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure the quality of epoxy products, B2B buyers should actively engage in verifying supplier QC practices. This can be achieved through:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports to evaluate compliance.
-
Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed QC reports, documenting the results of inspections and tests conducted during production. This transparency is crucial for building trust and ensuring product reliability.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors to evaluate supplier facilities and processes can further validate quality claims. This is especially important for buyers operating in regions with strict regulatory requirements.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding QC?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality assurance across different regions is essential. Variances in regulatory standards and practices may exist between countries, particularly between regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
For instance, European standards may be more stringent than those in other regions, necessitating that suppliers meet specific requirements to export products. B2B buyers should be aware of these differences and ensure that their suppliers can comply with the necessary regulations in their target markets.
Furthermore, cultural differences in business practices can impact supplier relationships. Establishing clear communication channels and expectations regarding quality can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process.
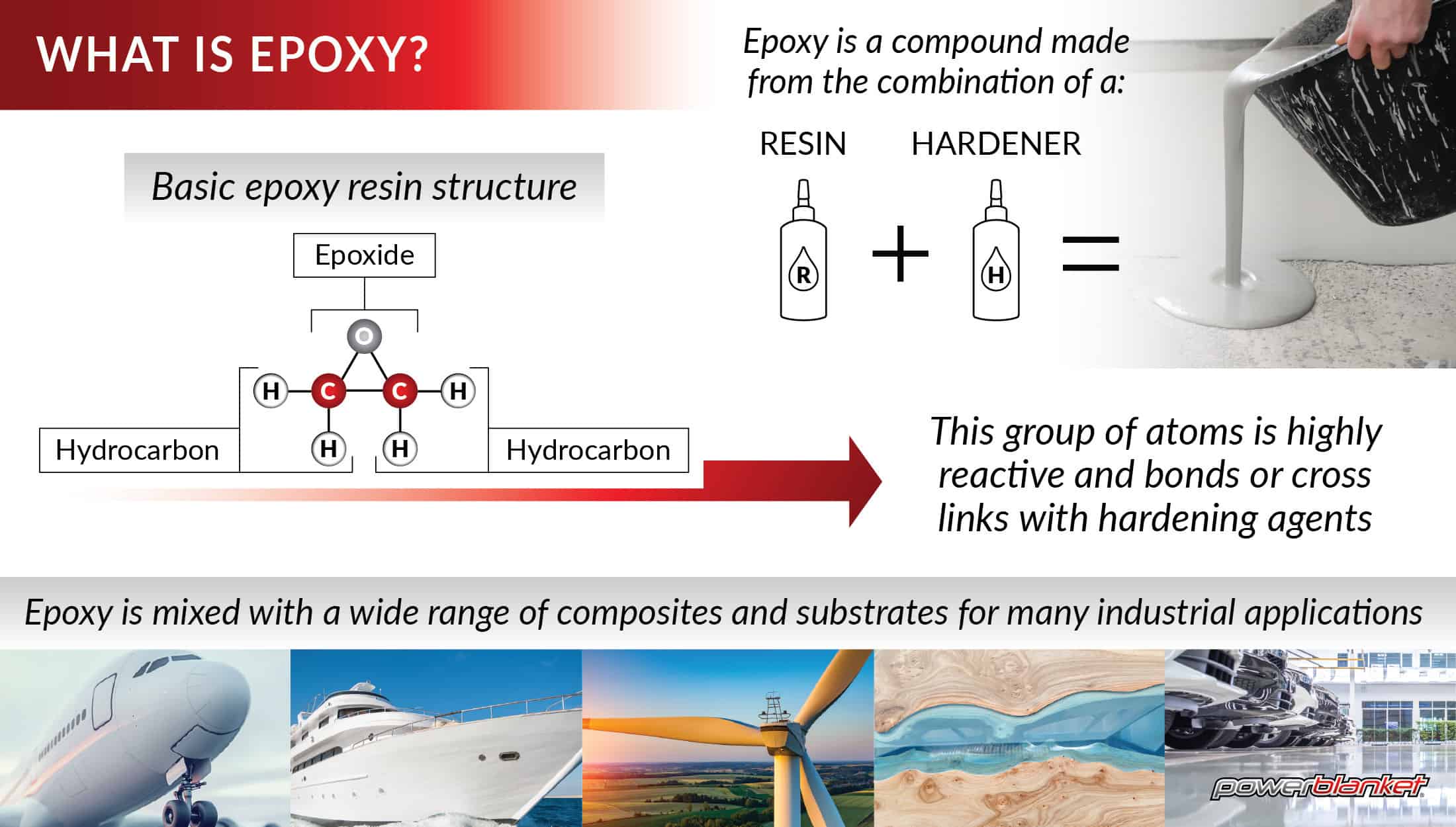
Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with epoxy products, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and quality standards. This knowledge empowers buyers to select reliable suppliers that meet their specific requirements, ultimately driving business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘common uses of epoxy’
The following guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring epoxy for various applications. This step-by-step approach will help ensure that you select the right epoxy products for your specific needs while considering quality, compliance, and supplier reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your project requirements is the first step in sourcing epoxy. Consider factors such as the desired application (e.g., construction, automotive, or electronics) and specific properties needed (e.g., chemical resistance, curing time, or adhesion strength). Clearly defined specifications will guide you in identifying the right epoxy products.
- Application Type: Different industries require different types of epoxy. Specify whether you need coatings, adhesives, or encapsulating resins.
- Performance Requirements: Identify any environmental conditions the epoxy must withstand, such as temperature extremes or exposure to chemicals.
Step 2: Research Available Epoxy Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of epoxy resins available in the market. Each type has unique characteristics that cater to specific applications, such as Bisphenol A for general use or Novolac for high chemical resistance.
- Common Types: Identify which type aligns best with your project needs.
- Curing Mechanisms: Understand the curing processes (e.g., heat-cured vs. room-temperature) to select the right product for your timeline.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers. This step is crucial to ensure that you partner with a reliable source that meets your quality and compliance standards.
- Request Documentation: Ask for company profiles, certifications, and references from existing clients in your industry.
- Assess Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about their quality control measures and any testing they perform on their products.
Step 4: Check Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the epoxy products you intend to purchase comply with local regulations, especially regarding safety and environmental impact. This is particularly important in regions with strict chemical regulations.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Always request SDS for the products to understand potential hazards and handling procedures.
- Regulatory Standards: Verify that the products meet any industry-specific standards, such as ISO or ASTM.
Step 5: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples to conduct your own testing. This step allows you to verify the product’s performance in real-world conditions.
- Application Testing: Evaluate how the epoxy performs in your specific application, including adhesion and curing time.
- Compatibility Checks: Test for compatibility with other materials you will be using in conjunction with the epoxy.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and confirmed product performance, negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
- Bulk Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for larger orders to maximize your budget.
- Delivery Timelines: Discuss lead times to ensure that the epoxy arrives when you need it for your project schedule.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Partnership
Consider establishing a long-term partnership with your chosen supplier. A reliable supplier can provide ongoing support, updated product lines, and timely delivery of materials.
- Feedback Loop: Maintain communication with your supplier to share feedback on product performance.
- Future Needs: Discuss potential future projects to explore bulk purchasing agreements or discounts.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they make informed decisions when sourcing epoxy, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for common uses of epoxy Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Epoxy Sourcing for B2B Buyers?
When evaluating the cost structure of epoxy sourcing, various components play a crucial role. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The base ingredients for epoxy production, typically resin and hardener, significantly influence pricing. The quality and type of epoxy (e.g., Bisphenol A, Novolac, or Aliphatic) can lead to variations in costs. Buyers should be aware that specialty resins might incur higher prices due to their unique properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the workforce involved in manufacturing and those in administrative roles. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, the overall epoxy price may be elevated compared to areas with lower labor costs, like parts of Africa and South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, maintenance, and facility operations. Efficient production processes can help lower overhead costs, which may be reflected in the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can add to the initial costs. However, investing in the right tools can lead to cost savings in the long term through increased production efficiency.
-
Quality Control: Rigorous QC processes ensure product consistency and compliance with industry standards. While these measures can increase upfront costs, they ultimately reduce the risk of failures and rework.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs vary by geographical region and can significantly impact the total cost of ownership. International buyers need to consider tariffs, customs duties, and local logistics when sourcing epoxy.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin that reflects their operational costs and profit expectations. Understanding market rates and supplier competition can aid buyers in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Epoxy Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence the pricing of epoxy products, which can vary significantly based on the specific needs and circumstances of the buyer.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk can lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers often offer discounts for larger orders, making it beneficial for businesses with high usage rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized epoxy formulations tailored to specific applications may come at a premium. Buyers should assess whether the added cost aligns with the performance benefits.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can greatly influence pricing. Epoxy formulations that require rare or high-performance materials will typically be more expensive.
-
Quality and Certifications: Epoxies that meet international quality standards or possess specific certifications may command higher prices. Buyers in regulated industries must weigh these costs against compliance benefits.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge more than lesser-known alternatives. However, the potential for better service and product quality often justifies the higher cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterm can clarify responsibilities for costs such as shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize risk and expense.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Epoxy Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider several strategies to optimize their epoxy sourcing process.
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with suppliers to explore flexible pricing options based on volume or long-term contracts. Building a relationship can lead to better terms and pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with installation, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if the product underperforms.
-
Local vs. International Sourcing: Consider sourcing locally to reduce logistics costs, especially if the quality meets your requirements. However, do not overlook international suppliers if they offer superior products at competitive prices.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations. This knowledge can empower buyers to make strategic purchasing decisions and time their orders effectively.
-
Trial Orders: Before committing to large purchases, consider placing smaller trial orders to assess product performance and supplier reliability. This can help mitigate risks associated with bulk purchasing.
In conclusion, understanding the cost components, price influencers, and effective sourcing strategies can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing epoxy. Always remember that pricing can vary widely based on multiple factors, and it’s advisable to conduct thorough market research before finalizing any sourcing agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing common uses of epoxy With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Epoxy Solutions
When evaluating materials for industrial applications, epoxy resin is often a go-to choice due to its versatility and strong adhesive properties. However, several alternative solutions may provide comparable benefits depending on the specific application and requirements. This analysis compares the common uses of epoxy with alternative materials, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Common Uses of Epoxy | Alternative 1 Name: Polyurethane | Alternative 2 Name: Silicone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent adhesion, chemical resistance | High flexibility, good abrasion resistance | Excellent temperature resistance, good adhesion |
| Cost | Moderate to high cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise mixing and curing | Easier to apply, quicker curing | Easy to use, requires minimal tools |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with durable finish | Moderate, may require regular inspections | Low maintenance, but can degrade over time |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications (construction, aerospace) | General-purpose bonding and coating | High-temperature applications, sealing |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Polyurethane?
Polyurethane is an effective alternative to epoxy, particularly for applications that require flexibility and impact resistance. It is often used in coatings and adhesives in various industries, including automotive and construction. The advantages of polyurethane include its lower cost and easier application process, making it accessible for a wider range of projects. However, it may not offer the same level of chemical resistance as epoxy, making it less suitable for harsh environments or applications involving solvents.
How Does Silicone Compare as an Alternative Solution?
Silicone is another versatile alternative, especially in applications requiring high temperature resistance and flexibility. It is commonly used in sealing and bonding applications across various industries, including electronics and automotive. Silicone has the advantage of being easy to apply and requiring minimal tools, making it user-friendly. Nevertheless, its adhesion strength may not match that of epoxy, and it can degrade over time when exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Industrial Needs
Choosing the right material for a specific application depends on several factors, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and ease of implementation. B2B buyers should carefully assess the unique needs of their projects and consider the operating conditions. For heavy-duty applications where durability and chemical resistance are paramount, epoxy remains a strong contender. Conversely, for applications requiring flexibility and lower costs, polyurethane or silicone may provide effective solutions. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each alternative, buyers can select the most suitable material for their specific use case, ensuring optimal performance and value.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for common uses of epoxy
What are the Key Technical Properties of Epoxy Relevant for B2B Buyers?
Epoxy resins are known for their superior performance across various industrial applications. Understanding their key technical properties is essential for businesses looking to select the right epoxy solutions for their needs.
1. Adhesive Strength
Epoxy resins exhibit exceptional adhesive properties, allowing them to bond effectively to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. This is crucial for industries such as automotive and construction, where strong, durable bonds are necessary for structural integrity and longevity.
2. Chemical Resistance
The ability of epoxy to withstand exposure to various chemicals, including acids, solvents, and oils, makes it a preferred choice in industries like manufacturing and chemical processing. This property helps maintain the structural integrity of components and reduces maintenance costs.
3. Cure Time
The cure time of epoxy can vary significantly depending on the formulation and environmental conditions. Understanding the cure time is vital for project planning and operational efficiency, as it affects how quickly a product can be put into service after application.
4. Thermal Stability
Epoxy resins typically exhibit good thermal stability, allowing them to maintain their properties under varying temperature conditions. This is particularly important in aerospace and automotive applications, where components may be subjected to extreme heat or cold.
5. Viscosity
The viscosity of epoxy affects its ease of application and flow characteristics. Low-viscosity epoxies are easier to work with and can penetrate fine cracks in substrates, making them ideal for repair applications. Higher-viscosity formulations may be used for structural applications where thickness is required.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
6. Flexural Strength
Flexural strength measures how much bending stress a material can withstand before failure. High flexural strength is critical in applications requiring load-bearing capabilities, such as flooring and structural components in construction.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know When Dealing with Epoxy?
Familiarity with industry jargon and trade terms can enhance communication and negotiation in the procurement of epoxy products.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial when sourcing epoxy products that need to fit specific machinery or equipment designs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, being aware of MOQs helps in budgeting and inventory management, ensuring that they do not over-commit resources.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of epoxy procurement, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive sourcing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery obligations when importing epoxy products.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its delivery. Knowing the lead time for epoxy products helps businesses plan their projects and manage timelines effectively, particularly in industries with tight schedules.
6. Batch Number
A batch number is a unique identifier assigned to a specific production run of a product. This term is vital for traceability in quality control processes, allowing buyers to track the performance and compliance of their epoxy products.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies equips B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding the procurement and application of epoxy products across various industries.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the common uses of epoxy Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Epoxy Sector?
The epoxy market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries including construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The global epoxy market was valued at approximately $9.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 6% over the next five years. This growth is fueled by the rising need for durable and high-performance materials, especially in emerging markets across Africa and South America, where infrastructure development is a priority.
One key trend is the adoption of advanced formulations that enhance the performance characteristics of epoxy resins, such as increased heat resistance and lower viscosity for easier application. Additionally, the shift towards digital solutions in sourcing, such as e-commerce platforms and online marketplaces, is making it easier for international B2B buyers to access a broader range of epoxy products. Suppliers are increasingly leveraging technology to provide real-time inventory updates and streamline the procurement process, catering specifically to the needs of buyers from regions like the Middle East and Europe.
Moreover, there is a notable increase in the use of epoxy in the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbine blade manufacturing, reflecting a shift towards sustainable applications. As international buyers become more aware of the benefits of epoxy in terms of performance and longevity, they are increasingly sourcing these materials from manufacturers who can meet stringent quality and compliance standards.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Epoxy Materials?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of epoxy materials, particularly as global awareness of environmental issues rises. The production of traditional epoxy resins can have a significant environmental impact due to the use of petrochemical-based raw materials. However, the industry is witnessing a shift towards bio-based epoxy resins, which are derived from renewable resources and offer a lower carbon footprint.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing practices. This includes transparency in the supply chain and adherence to environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Responsible Care program are becoming essential for suppliers looking to gain trust in the market. Buyers should look for manufacturers that provide eco-friendly options, such as low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) epoxy products, which are less harmful to human health and the environment.
Furthermore, the importance of ethical sourcing cannot be overstated. Many businesses are now aligning their procurement strategies with sustainability goals, which can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. As such, sourcing epoxy products from suppliers who prioritize sustainability will not only meet regulatory requirements but also contribute to long-term business viability.
What Is the Evolution of Epoxy Resins and Their Common Uses?
Epoxy resins have evolved significantly since their introduction in the mid-20th century. Initially used primarily as adhesives, their applications have expanded dramatically due to advancements in technology and manufacturing processes. Today, epoxy is widely recognized for its versatility and strength, finding applications in diverse sectors ranging from construction to electronics and art.

Illustrative image related to common uses of epoxy
In the construction industry, epoxy has become a preferred material for flooring and coatings, offering durability and resistance to wear and chemicals. In automotive and aerospace applications, its lightweight properties have made it indispensable for manufacturing components that require both strength and weight reduction. The marine industry also relies heavily on epoxy for boat building and maintenance, capitalizing on its waterproofing capabilities.
As the market continues to evolve, epoxy resins are increasingly tailored to meet specific industry needs, enhancing their performance characteristics. This evolution not only reflects the material’s adaptability but also underscores its importance as a strategic component in various manufacturing processes. B2B buyers must stay informed about these developments to make educated sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of common uses of epoxy
-
How do I choose the right epoxy for my specific industry application?
Choosing the right epoxy depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your application, such as temperature resistance, chemical exposure, and adhesion properties. For construction, consider high-strength epoxy for bonding and coating. In automotive applications, lightweight, heat-resistant epoxies are essential. In marine use, opt for water-resistant formulations. Always consult with suppliers who understand your industry’s needs and can recommend products based on their chemical composition and curing processes. -
What are the common applications of epoxy in construction?
In construction, epoxy is widely used for flooring, bonding concrete, and repairing structures. It serves as a durable coating that protects surfaces from wear, chemicals, and moisture. Epoxy adhesives bond materials like metal, wood, and glass effectively, ensuring long-lasting stability. Additionally, epoxy can be utilized for waterproofing applications and in the creation of structural components, making it an invaluable material in modern construction projects. -
What factors should I consider when vetting epoxy suppliers?
When vetting epoxy suppliers, consider their industry experience, product certifications, and customer testimonials. Verify their ability to meet your quality assurance standards and delivery timelines. Assess their responsiveness to inquiries and willingness to provide technical support. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing capabilities, minimum order quantities (MOQs), and whether they can accommodate custom formulations tailored to your specific needs. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ) for epoxy products?
Many suppliers set MOQs for epoxy products, which can vary significantly based on the type of epoxy, formulation, and supplier. Smaller businesses may find suppliers willing to accommodate lower MOQs for standard products, while custom formulations may require higher quantities. It’s advisable to communicate your needs directly with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your business scale and project requirements. -
What payment terms are typically offered by epoxy suppliers?
Payment terms for epoxy suppliers can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. Common terms include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and net 30 or net 60 terms after delivery. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or bulk purchases. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also open opportunities for more favorable terms, especially for repeat orders. -
How can I ensure the quality of epoxy products I receive?
To ensure the quality of epoxy products, request samples before placing a large order to evaluate their performance in your applications. Look for suppliers who provide certifications and detailed technical data sheets that outline the properties of their epoxy products. Regular communication and feedback can also help maintain quality standards. If possible, arrange for third-party testing to verify the epoxy’s compliance with industry standards and specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing epoxy internationally?
When sourcing epoxy internationally, consider shipping costs, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to handle logistics and whether they have experience with international shipping. Ensure that all documentation is complete to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, consider the potential impact of tariffs and duties on your overall costs, and factor in these expenses when calculating your budget. -
How can I customize epoxy formulations for specific applications?
Customizing epoxy formulations often involves adjusting the resin and hardener ratios or incorporating specific additives to enhance properties like flexibility, UV stability, or chemical resistance. Collaborate closely with your supplier to discuss your application requirements and desired performance characteristics. Many suppliers are equipped to develop tailored solutions, so providing detailed information about your needs can lead to the development of a product that perfectly suits your application.
Top 7 Common Uses Of Epoxy Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carved – Epoxy Resin Solutions
Domain: carved.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Carved – Epoxy Resin Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. MPI Matco – Epoxy Glue
Domain: mpi-matco.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Epoxy glue is a two-part adhesive composed of an epoxy polymer (resin) and a hardener. It creates a strong, rigid bond suitable for bonding similar or different materials, and is resistant to stress, moisture, heat, and environmental damage. It can also function as a gap-filler in its liquid state. Available as two separate components for manual mixing or as pre-mixed formulas. Key benefits includ…
3. ATC – Industrial Epoxy Solutions
Domain: atcepoxy.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: ATC offers a range of industrial epoxy products under widely recognized brands including ULTRABOND®, CRACKBOND®, and MIRACLE BOND®. Key applications include: 1. Anchoring & Doweling: Strong epoxy for anchoring railings, rebar, and bolts into concrete. 2. Bonding & Coating: Various strengths for bonding and coating applications in commercial and industrial settings, including airplane and machine p…
4. Epoxy Floor Experts – Durable Coatings and Adhesives
Domain: epoxyfloorexperts.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Epoxy is used for various applications including: 1. Adhesives – Known for durability and strength, bonding materials like metals, glass, wood, and some plastics. 2. Coatings – Primarily used for epoxy floor coatings in garages, basements, industrial settings, and hospitals, offering durability and easy maintenance. 3. Construction – Used to reinforce concrete, fill cracks, and repair damaged conc…
5. San Antonio Epoxy – Durable Adhesive Solutions
Domain: sanantonioepoxy.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Epoxy is a durable adhesive used in various residential applications. Key uses include securing furniture sections, creating protective varnish finishes, sealing exposed wires to protect pets, binding fiber wiring for telephony networks, repairing picture frame joints (especially antiques), reattaching golf club grips, and fixing loose shoe soles. Epoxy is a two-part resin consisting of resin and …
6. Idaho Epoxy – Durable Epoxy Coatings
Domain: idahoepoxy.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Epoxy paint is visually appealing and extremely durable, resistant to chipping, chemicals, stains, and abrasions. It helps conceal small spider cracks and flaws in concrete, increases friction when wet for safety, and prevents dust from cement floors. Common uses include:
1. Garage Floors: Durable, safe, and easy to clean.
2. Outdoor Patios: Tolerates sunlight, adds curb appeal, and has a coolin…
7. Xometry – Epoxy Solutions
Domain: xometry.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Epoxies are thermoset polymers known for their versatility in various applications, including coatings, adhesives, and 3D printing. They exhibit high tensile, compressive, and impact strength, making them suitable for structural uses. Epoxies are chemically resistant to acids, bases, solvents, and oils, and are heat resistant, serving aerospace and electronic needs. They also act as excellent elec…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for common uses of epoxy
As industries across the globe increasingly rely on epoxy for its unparalleled versatility and durability, strategic sourcing becomes paramount for B2B buyers. Epoxy’s applications span construction, automotive, aerospace, marine, and electronics, highlighting its crucial role in enhancing product performance and reliability. By investing in high-quality epoxy solutions, businesses can improve operational efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the selection of reliable suppliers is essential. Evaluate suppliers not just on price but on their ability to provide insights into product application, technical support, and adherence to safety regulations. Building partnerships with reputable manufacturers will enhance your supply chain resilience and ensure that you are equipped with the best materials for your projects.
Looking ahead, the demand for epoxy is expected to grow as industries evolve and seek sustainable solutions. Engage with suppliers who are innovating in epoxy formulations, particularly those that focus on environmentally friendly options. By prioritizing strategic sourcing now, you position your business to capitalize on future market trends and maintain a competitive edge.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.