Collared Bolt Explained: From A to Z for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for collared bolt
In today’s global marketplace, sourcing collared bolts can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As industries increasingly demand high-quality fastening solutions to ensure structural integrity and operational efficiency, understanding the nuances of collared bolt specifications, applications, and sourcing is essential. This guide addresses the complexities of navigating the collared bolt market, offering a detailed exploration of various types, their applications across different sectors, and insights into the vetting process for suppliers.
By providing comprehensive knowledge on the cost factors associated with collared bolts, this resource empowers international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re looking to procure for construction, manufacturing, or specialized machinery, the information contained within this guide will help you identify reliable suppliers and negotiate favorable terms.
With a focus on practical strategies tailored to the unique challenges faced by buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, this guide serves as a vital tool in your sourcing journey. Equip yourself with the insights needed to enhance your procurement strategy, ensuring that you not only meet but exceed your operational requirements for quality and reliability in collared bolts.
Understanding collared bolt Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Collared Bolt | Circular collar that prevents loosening | Heavy machinery, construction, automotive | Pros: Reliable fastening; Cons: Limited size options. |
| Flanged Collared Bolt | Integrated flange for added load distribution | Structural applications, bridges, buildings | Pros: Enhanced strength; Cons: Higher cost. |
| Tapered Collared Bolt | Tapered design for easier installation | Oil and gas, mining, aerospace | Pros: Improved alignment; Cons: Requires precise tooling. |
| Locking Collared Bolt | Special locking mechanism to prevent rotation | Aerospace, military applications | Pros: High security; Cons: More complex installation. |
| Custom Collared Bolt | Tailored design for specific applications | Specialized machinery, custom projects | Pros: Optimized performance; Cons: Longer lead times. |
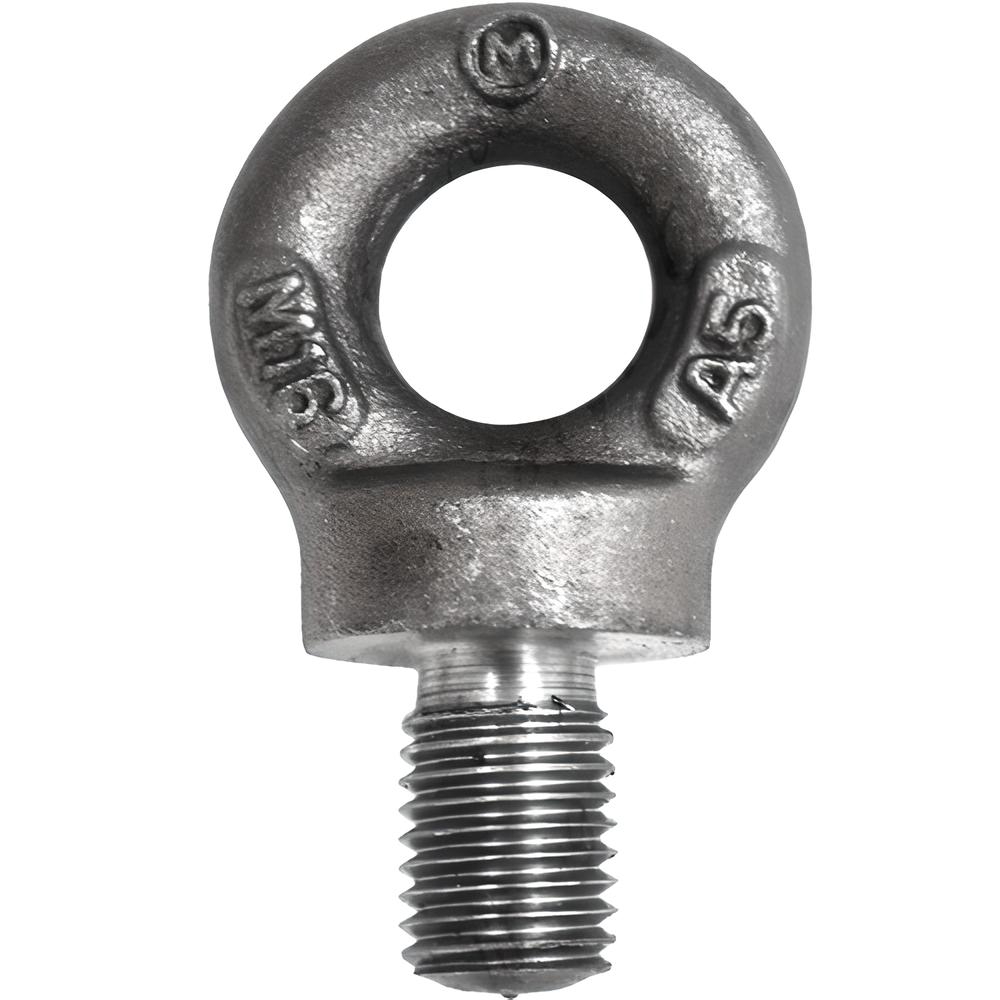
What are the Characteristics of Standard Collared Bolts?
Standard collared bolts feature a simple circular collar that effectively prevents loosening under vibration. This makes them suitable for heavy machinery and automotive applications where reliability is paramount. When purchasing, buyers should consider the bolt’s material and corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments. The main advantage of standard collared bolts is their dependable fastening capability, but they may have limited size options, which could restrict their use in specific applications.
How Do Flanged Collared Bolts Enhance Structural Integrity?
Flanged collared bolts come with an integrated flange that helps distribute loads more evenly across the material they are fastening. This feature is particularly beneficial in structural applications, such as bridges and buildings, where load-bearing capacity is critical. Buyers should assess the flange size and material compatibility when selecting these bolts. While they offer enhanced strength and stability, flanged collared bolts typically come at a higher cost compared to standard options.
Why Choose Tapered Collared Bolts for Precision Applications?
Tapered collared bolts are designed with a tapered end, facilitating easier installation and improved alignment. This type is commonly used in industries like oil and gas, mining, and aerospace, where precision is crucial. Buyers should consider the specific tooling required for installation, as it may demand more specialized equipment. The primary advantage of tapered collared bolts is their alignment efficiency, though they may require precise tooling that could increase installation time.
What Security Benefits Do Locking Collared Bolts Provide?
Locking collared bolts incorporate a unique locking mechanism that prevents rotation, making them ideal for high-security applications such as aerospace and military. When selecting locking collared bolts, buyers should evaluate the locking mechanism’s reliability and the bolt’s overall strength. While these bolts provide superior security against loosening, their installation can be more complex, which may necessitate additional training or expertise.
How Can Custom Collared Bolts Meet Unique Project Needs?
Custom collared bolts are tailored to meet the specific requirements of specialized machinery or unique projects. This adaptability allows for optimized performance in niche applications. Buyers should be prepared for longer lead times and potential increases in cost due to the custom design process. The main benefit of custom collared bolts is their ability to enhance operational efficiency, but the trade-off includes the need for careful planning and potentially higher expenses.
Key Industrial Applications of collared bolt
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of collared bolt | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Used in heavy machinery and equipment assembly | Enhances durability and safety in construction sites | Ensure compliance with local regulations and standards |
| Mining | Securing components in drilling and excavation equipment | Improves operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Source from reputable suppliers with quality guarantees |
| Oil & Gas | Connecting pipeline components and drilling rigs | Ensures leak prevention and structural integrity | Verify material specifications for harsh environments |
| Agriculture | Implementing in agricultural machinery for soil cultivation | Increases equipment reliability and crop yields | Consider local agricultural practices and machinery compatibility |
| Telecommunications | Fixing components in underground cable installation | Supports infrastructure development in remote areas | Assess compatibility with existing systems and local regulations |
How Are Collared Bolts Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, collared bolts are primarily utilized for securing heavy machinery and equipment. Their design allows for superior grip and stability, crucial for maintaining safety on construction sites. By providing enhanced durability, these bolts help prevent equipment failure and extend the lifespan of machinery, which is vital for project timelines and budgets. International buyers should ensure that the collared bolts meet regional construction standards and certifications, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa and the Middle East.

Illustrative image related to collared bolt
What Role Do Collared Bolts Play in Mining Operations?
In mining, collared bolts are essential for securing components of drilling and excavation equipment. These bolts withstand extreme stress and environmental conditions, thus improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime due to equipment failure. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing bolts that meet specific strength and corrosion resistance requirements, particularly in regions with challenging mining conditions such as South America and Africa.
Why Are Collared Bolts Critical in the Oil & Gas Sector?
Collared bolts are vital in the oil and gas industry for connecting pipeline components and securing drilling rigs. Their robust design helps prevent leaks, which is crucial for safety and environmental protection. Businesses should focus on sourcing high-quality materials that are resistant to corrosion and wear, especially in harsh environments found in regions like the Middle East. Compliance with international safety and quality standards is also a critical consideration for sourcing.
How Do Collared Bolts Benefit Agricultural Machinery?
In agriculture, collared bolts are implemented in machinery used for soil cultivation and harvesting. They provide increased reliability and help improve crop yields by ensuring that equipment operates efficiently. Buyers in this sector should consider local agricultural practices and compatibility with existing machinery when sourcing collared bolts. Understanding the specific requirements of agricultural applications can lead to better performance and productivity.
What Importance Do Collared Bolts Have in Telecommunications?
In the telecommunications industry, collared bolts are used to fix components during underground cable installations. Their ability to ensure structural integrity is essential for supporting infrastructure development, especially in remote areas. Buyers should assess the compatibility of collared bolts with existing systems and take into account local regulations governing telecommunications infrastructure. This attention to detail can enhance project success and operational reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘collared bolt’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing High-Quality Collared Bolts
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers for collared bolts that meet specific quality standards. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions like Africa and South America, where local suppliers may not have the infrastructure or quality assurance processes in place. Buyers frequently encounter issues with inconsistent product quality, leading to operational disruptions and potential safety hazards in their projects. Additionally, language barriers and lack of technical support can make it hard for buyers to assess the specifications and performance characteristics of the bolts they are considering.
The Solution: To ensure the procurement of high-quality collared bolts, buyers should establish relationships with reputable manufacturers and distributors who have a proven track record in the industry. Conducting thorough research and due diligence, including reviewing customer testimonials and seeking references, can help identify reliable sources. It’s advisable to request sample products and perform quality checks, such as tensile strength tests, before placing larger orders. Furthermore, leveraging online platforms that specialize in industrial fasteners can provide access to a broader range of suppliers with transparent reviews and ratings. Engaging with suppliers who offer comprehensive product literature and technical support can also help clarify specifications and ensure the bolts meet required standards.
Scenario 2: Incompatibility with Equipment Specifications
The Problem: Another common pain point is the incompatibility of collared bolts with existing equipment or machinery. B2B buyers often find that the bolts they purchase do not fit the specific models of their machinery, leading to delays in projects and additional costs for replacements or modifications. This issue is particularly concerning for businesses in the construction and manufacturing sectors, where precise specifications are crucial for operational efficiency.
The Solution: To mitigate this problem, buyers should invest time in understanding the exact specifications required for their applications. This includes consulting equipment manuals or liaising with equipment manufacturers to confirm the necessary bolt dimensions, thread types, and material requirements. Utilizing CAD software can help visualize how the collared bolts will fit into the existing systems, reducing the risk of ordering incorrect sizes. When sourcing bolts, buyers should also inquire about the manufacturer’s compatibility charts or databases that list which bolts work with specific machinery models. Establishing a consistent communication channel with suppliers can facilitate quick resolution of any compatibility issues and streamline the ordering process.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Installation and Maintenance
The Problem: Installation and maintenance of collared bolts can be complex, especially for teams that lack experience with this type of fastener. Improper installation can lead to premature failure of the bolts, which not only affects the integrity of the assembly but also poses safety risks. This is particularly relevant in industries like construction and mining, where structural integrity is paramount. Buyers often face difficulties in finding clear installation guidelines or support during the assembly process, leading to further complications.
The Solution: To address these installation challenges, buyers should seek out comprehensive installation guides and training from suppliers. Many manufacturers provide detailed documentation and videos that demonstrate proper installation techniques, which can be invaluable for teams unfamiliar with collared bolts. Additionally, investing in training sessions or workshops can enhance the skill set of the workforce, ensuring that they are well-equipped to handle installations correctly. Implementing a maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections of collared bolts can also help identify wear and tear early, preventing failures. Suppliers that offer ongoing technical support and maintenance recommendations can be particularly beneficial in ensuring the longevity and reliability of the fasteners.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for collared bolt
What Are the Most Common Materials Used for Collared Bolts?
When selecting materials for collared bolts, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each option is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of collared bolts: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and aluminum.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform as a Material for Collared Bolts?
Carbon steel is one of the most widely used materials for collared bolts due to its excellent strength and affordability. It typically has a high tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance, which can be a drawback in humid or corrosive environments.
Pros:
– High strength and durability.
– Cost-effective compared to other materials.
– Easy to machine and manufacture.
Cons:
– Prone to rust and corrosion without proper coatings.
– Limited temperature resistance compared to alloys.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is ideal for applications in construction and heavy machinery where high strength is required, but it may require protective coatings in environments with moisture or chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A307 or DIN 933. In regions like Africa and South America, where humidity can be high, additional protective measures may be necessary.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Collared Bolts?
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It is commonly used in applications requiring hygiene and cleanliness, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. The material can withstand a wide range of temperatures and is less likely to rust compared to carbon steel.
Pros:
– Superior corrosion resistance.
– High-temperature resistance.
– Minimal maintenance required.
Cons:
– Higher cost than carbon steel.
– More challenging to machine, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel collared bolts are suitable for marine applications, chemical processing, and environments where sanitation is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards like ASTM A193 or JIS G4303 is essential. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe may prefer stainless steel for its durability in harsh environments.
How Does Alloy Steel Compare for Collared Bolt Applications?
Alloy steel combines carbon steel with other elements to enhance specific properties, such as strength and toughness. This material can be tailored to meet the demands of high-stress applications, making it a versatile choice for collared bolts.
Pros:
– High strength and toughness.
– Can be engineered for specific applications.
– Good wear resistance.
Cons:
– Generally more expensive than carbon and stainless steel.
– Requires precise manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Alloy steel is ideal for high-performance applications such as automotive and aerospace, where reliability and strength are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM A574 or DIN 931. In regions with stringent quality requirements, such as Europe, alloy steel may be preferred despite the higher cost.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Collared Bolt Manufacturing?
Aluminum is a lightweight alternative to traditional steel materials. It offers good corrosion resistance and is often used in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Pros:
– Lightweight, reducing overall project weight.
– Excellent corrosion resistance.
– Good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Cons:
– Lower tensile strength compared to steel.
– More expensive than carbon steel.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum collared bolts are suitable for applications in transportation and electronics, where weight savings are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B211. In regions like South America and Africa, where weight considerations are crucial, aluminum may be favored despite its higher cost.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Collared Bolts
| Material | Typical Use Case for collared bolt | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Heavy machinery, construction | High strength, cost-effective | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, machining complexity | High |
| Alloy Steel | Automotive, aerospace | High strength and toughness | More expensive, precise mfg | Med |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, electronics | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | High |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for collared bolts, ensuring they can make informed decisions tailored to their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for collared bolt
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Collared Bolts?
The manufacturing process for collared bolts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and performance standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with selecting high-quality raw materials, typically carbon steel or stainless steel, known for their strength and durability. These materials are often sourced from reputable suppliers who comply with international standards. The initial step includes cutting the steel into appropriate lengths, followed by heating treatments to improve ductility and strength. This ensures that the materials can withstand the stress they will encounter during application.
Forming Techniques
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming the bolt. This can be achieved through various techniques, such as:

Illustrative image related to collared bolt
- Cold Heading: A cost-effective method where the material is shaped into the desired bolt form at room temperature. This technique preserves the material’s structural integrity and enhances its strength.
- Hot Forging: Used for larger or thicker bolts, this method involves heating the metal to a malleable state before shaping it. This process can yield stronger bolts but may increase production costs.
After forming, threads are typically rolled onto the bolts to ensure compatibility with corresponding nuts and other fasteners.
Assembly Process
For collared bolts, assembly may involve integrating additional components such as collars or washers. This step is crucial as it affects the bolt’s performance in applications, especially in environments where vibration or movement is expected. Manufacturers may utilize automated assembly lines to enhance efficiency and consistency.
Finishing Processes
The final stage in manufacturing collared bolts is finishing, which includes surface treatments to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Common methods include:
- Galvanization: A process where a zinc coating is applied to protect against rust.
- Powder Coating: A technique that provides a durable finish while allowing for a variety of colors.
These finishing processes not only enhance the durability of the bolts but also contribute to their overall performance in various applications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance is vital for ensuring that collared bolts meet both safety and performance requirements. B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international and industry-specific standards, which can serve as benchmarks for evaluating suppliers.
International Standards (ISO 9001)
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems. Manufacturers adhering to this standard demonstrate their commitment to producing high-quality products consistently. Buyers should inquire about a supplier’s ISO certification, as this indicates a structured approach to quality assurance.
Industry-Specific Certifications (CE, API)
In addition to ISO standards, certain industries may require specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in the European Economic Area or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications. Understanding these requirements can help buyers ensure that they are sourcing products suitable for their particular industry.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential for maintaining product quality throughout the manufacturing process. Typically, these checkpoints include:

Illustrative image related to collared bolt
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing helps identify defects early, reducing waste and rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed products undergo rigorous testing to verify they meet all specifications and standards before shipment.
Implementing these QC checkpoints ensures that any issues are detected and addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of defective products reaching the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods can be employed to assess the quality of collared bolts, including:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength of the bolt to ensure it can withstand the required loads.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s resistance to deformation, which is critical for durability.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Evaluates how well the bolt can withstand environmental factors that may lead to rust and degradation.
By utilizing these testing methods, manufacturers can verify that their products meet both customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers adhere to quality control standards is crucial. Here are several strategies to verify supplier QC processes:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and compliance with standards firsthand. This can provide valuable insights into a supplier’s capabilities.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes and results from testing. These reports can help buyers understand the reliability of the products.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices, providing peace of mind before making large orders.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification. Variations in regional standards and regulations can impact product acceptability in different markets.
Buyers should conduct thorough research to understand the specific certifications required in their target markets. Additionally, establishing strong communication with suppliers can facilitate a better understanding of their compliance with both local and international standards.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for collared bolts is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘collared bolt’
When sourcing collared bolts, a systematic approach can significantly streamline the procurement process. This checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers through essential steps to ensure they acquire high-quality products from reliable suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s vital to clearly outline your technical requirements. Collared bolts come in various sizes, materials, and strengths, depending on their application. Specify dimensions such as diameter, length, and the type of collar required, as well as any relevant industry standards that need to be met.
- Material Specifications: Determine if you need stainless steel, carbon steel, or another material based on environmental conditions.
- Load Requirements: Assess the load-bearing capacity needed for your specific application.
Step 2: Identify Your Sourcing Regions
Understanding where to source your collared bolts can impact both cost and delivery timelines. Different regions may offer varying levels of quality and pricing.
- Local vs. International Suppliers: Consider sourcing from local suppliers for faster delivery times and reduced shipping costs, but do not overlook international suppliers that may offer better pricing or superior products.
- Market Research: Investigate which regions are known for high-quality bolt manufacturing, such as Europe or Asia.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. This step is crucial to ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers.
- Company Profiles and Certifications: Request documentation on quality certifications (like ISO) and relevant industry experience.
- Customer References: Ask for references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Quality Checks
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of the collared bolts for testing. This hands-on approach helps verify that the products meet your specifications.
Illustrative image related to collared bolt
- Quality Assurance Testing: Check for adherence to size, material properties, and overall build quality.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensure that the samples work with your existing equipment or machinery.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Effective negotiation can lead to more favorable terms and pricing. Be prepared to discuss not just the cost per unit but also payment terms, delivery schedules, and potential bulk discounts.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing breaks for larger orders.
- Payment Terms: Clarify payment methods and conditions to avoid misunderstandings later.
Step 6: Finalize the Contract
Once you are satisfied with the supplier’s offerings, finalize a contract that outlines all terms agreed upon during negotiations. A well-structured contract protects both parties and sets clear expectations.
- Inclusion of Specifications: Ensure that technical specifications, delivery timelines, and penalties for non-compliance are included.
- Review Clauses: Pay attention to clauses regarding returns, warranties, and liability.
Step 7: Monitor Delivery and Quality Assurance
After placing your order, maintain communication with the supplier to track the delivery process. Upon receipt, conduct a final quality check to ensure compliance with your specifications.
- Delivery Tracking: Use tracking tools to stay updated on shipment status.
- Post-Delivery Inspection: Inspect the received bolts against the order to ensure that they meet quality standards and specifications.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can ensure a successful procurement process for collared bolts, optimizing both quality and cost-effectiveness in their sourcing strategy.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for collared bolt Sourcing
When sourcing collared bolts, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. A thorough analysis of the various cost components and price influencers can lead to better procurement decisions and enhanced negotiation strategies.
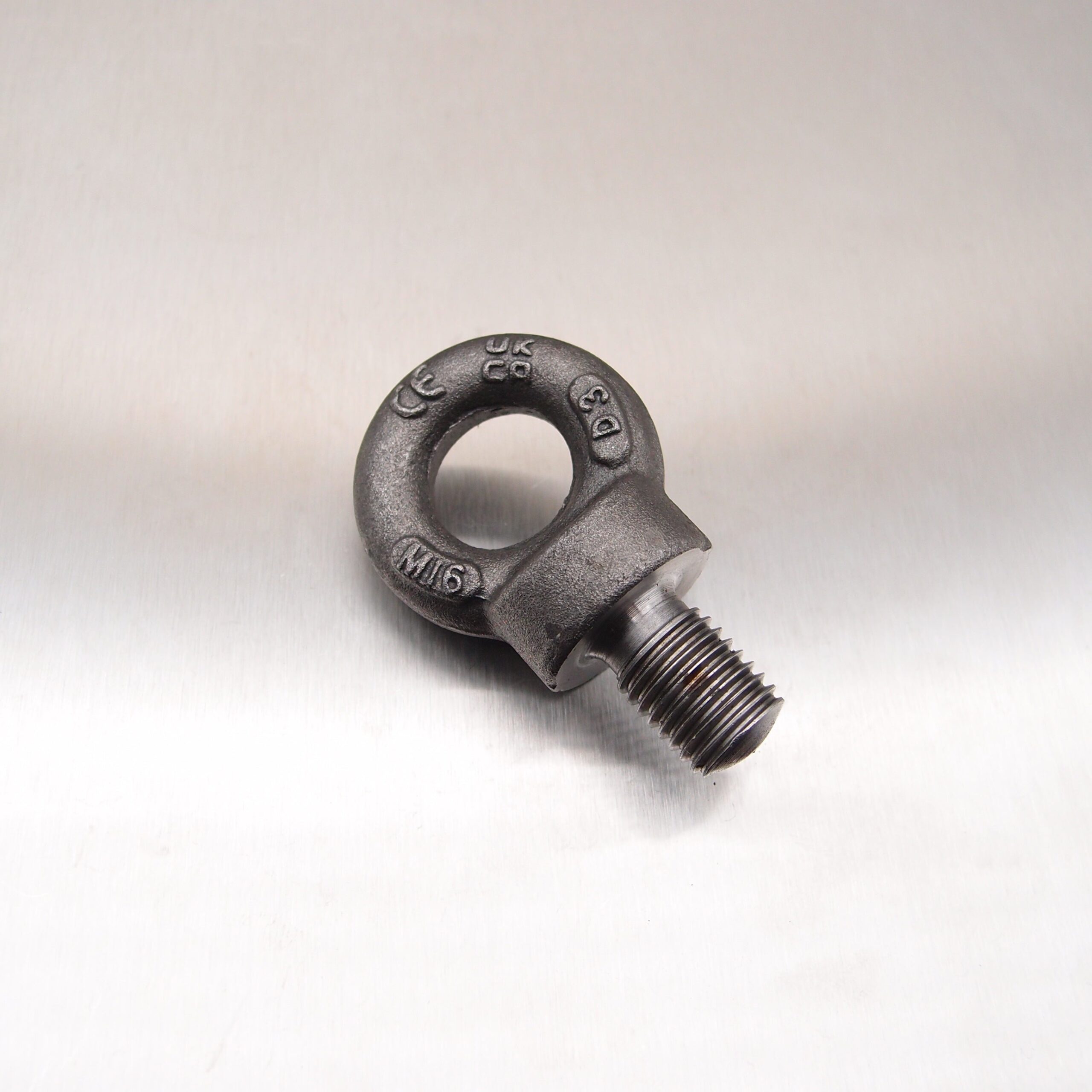

Illustrative image related to collared bolt
What Are the Key Cost Components in Collared Bolt Sourcing?
The total cost of collared bolts encompasses several critical components:
-
Materials: The primary cost driver for collared bolts is the raw materials used, including steel grades and coatings. Higher-grade materials or specialized coatings for corrosion resistance can significantly increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region of production. In countries with lower labor costs, buyers might find competitive pricing. However, skilled labor for precision manufacturing can be more expensive, impacting the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs, which are often passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are essential, particularly for custom or specialized bolts. If a supplier needs to create new tooling for a specific order, this will add to the initial costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the bolts meet specifications requires investment in quality assurance processes. Buyers should consider suppliers with robust QC systems as they can reduce the risk of defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight, customs duties, and handling fees, must be factored in. Incoterms can also influence logistics costs, impacting the final price delivered to the buyer.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their operational risks and profits. Understanding the typical margin in the industry can help buyers gauge fair pricing.
What Influences the Pricing of Collared Bolts?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of collared bolts:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized bolts tailored to specific applications will generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) may command higher prices due to the additional compliance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms can shift costs and responsibilities between the buyer and seller, affecting the total landed cost of the bolts.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Strategy?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your position as a buyer by negotiating not just on price, but also on payment terms, delivery schedules, and volume discounts. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also yield better terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the purchase price but also maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime costs. A slightly higher initial cost may lead to savings in the long run if the bolts are more durable or reliable.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Factors such as currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local market conditions can impact pricing. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of these dynamics when sourcing from Europe or Asia.
-
Request Quotes from Multiple Suppliers: Diversifying your supplier base can provide a better understanding of market pricing and help identify the best value options.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly monitor material prices and industry trends to anticipate changes in pricing. This proactive approach can help buyers make informed decisions and budget effectively.
Conclusion
When sourcing collared bolts, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial. By considering the various cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic tips, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing efforts, ensuring they get the best value for their investment. Always remember to factor in the total cost of ownership to make well-rounded purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing collared bolt With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Collared Bolts in Industrial Applications
In the fast-evolving landscape of industrial fastening solutions, buyers must consider various alternatives to collared bolts. Each solution offers unique advantages and limitations, making it essential to evaluate them based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and suitability for specific applications. Below is a comparative analysis of collared bolts against two viable alternatives: Hex Bolts and Tension Bolts.
| Comparison Aspect | Collared Bolt | Hex Bolt | Tension Bolt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High tensile strength; prevents loosening due to vibration | Good tensile strength; versatile use | Excellent for high-load applications; minimizes slip |
| Cost | Moderate cost; may vary with specifications | Generally lower cost; widely available | Higher cost due to specialized design |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific tools for installation | Easy to install with standard tools | Requires specialized tools; more complex |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable materials | Low maintenance; easily replaceable | Moderate maintenance; requires periodic checks |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for heavy machinery and construction | Suitable for general fastening needs | Best for structural applications requiring high tension |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hex Bolts Compared to Collared Bolts?
Hex Bolts are one of the most common fastening solutions used in various industries. They are characterized by their hexagonal head, which allows for easy tightening with a wrench. The primary advantage of hex bolts is their lower cost and availability, making them a go-to option for many applications. However, they may not perform as well as collared bolts under conditions with high vibrations, as they can loosen over time without the use of additional locking mechanisms.
How Do Tension Bolts Stand Against Collared Bolts in Industrial Applications?
Tension Bolts are specifically designed for applications that require high load-bearing capabilities. They are engineered to maintain a constant tension, minimizing the risk of loosening. Their primary advantage lies in their ability to handle heavy loads and resist slippage. However, they come with a higher price tag and may require specialized installation tools, making them less accessible for standard applications compared to collared bolts.

Illustrative image related to collared bolt
Conclusion: Which Fastening Solution Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When selecting the right fastening solution, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific needs and application requirements. Collared bolts offer a robust solution for high-stress environments, particularly in heavy machinery and construction settings. In contrast, hex bolts provide a cost-effective and versatile option for general use, while tension bolts excel in applications demanding superior load management. By evaluating performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for collared bolt
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Collared Bolt?
Understanding the technical specifications of a collared bolt is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance in various applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of a collared bolt is a critical specification that indicates its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each offering unique benefits. For instance, stainless steel bolts are preferred in corrosive environments, while carbon steel bolts are commonly used for their strength and cost-effectiveness. Selecting the right material grade ensures the bolt can withstand the operational conditions of your project.
2. Diameter and Length
The diameter and length of a collared bolt are fundamental dimensions that determine its fit and application. Standard sizes range from 3/8 inch to 1 inch in diameter and can vary in length based on the specific use case. Accurate measurements are essential for ensuring proper installation and load-bearing capacity, particularly in heavy machinery or construction settings.
3. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is a measure of how much pulling force a bolt can withstand before failing. This property is often measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or megapascals (MPa). For B2B buyers, understanding the tensile strength helps in choosing bolts that can handle the specific loads of their applications, thus preventing premature failure and enhancing safety.
4. Finish Type
The finish of a collared bolt can significantly affect its performance and longevity. Common finishes include zinc plating, black oxide, and hot-dip galvanizing. Each finish offers varying levels of corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. For international buyers, selecting the appropriate finish is essential for ensuring compliance with local regulations and environmental standards.
5. Thread Type
The thread type (e.g., coarse or fine) influences the bolt’s grip and load distribution. Coarse threads are typically easier to install and provide greater resistance to stripping, while fine threads offer better tensile strength and load capacity. Understanding thread specifications is vital for achieving the desired fastening performance in different applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Collared Bolts?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication and transactions. Here are some common terms related to collared bolts:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components that are used in the manufacturing of other products. In the context of collared bolts, OEM specifications ensure that the bolts meet the original design and performance criteria set by the equipment manufacturer. B2B buyers should prioritize OEM parts to maintain equipment integrity and warranty compliance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. For international buyers, negotiating MOQs can lead to better pricing and supply chain efficiencies.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. Using RFQs helps B2B buyers obtain competitive pricing and evaluate different suppliers effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is critical for inventory management and project scheduling, especially in industries where timely delivery is essential for operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.

Illustrative image related to collared bolt
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the collared bolt Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Collared Bolt Sector?
The global collared bolt market is experiencing a dynamic shift driven by several factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for robust fastening solutions in infrastructure projects, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. These regions are investing heavily in construction and infrastructure, which propels the need for high-quality, durable fasteners. Additionally, technological advancements in manufacturing and sourcing processes are enhancing the efficiency and customization of collared bolts, allowing manufacturers to meet specific project requirements more effectively.
Emerging B2B technologies such as digital procurement platforms and supply chain management software are transforming how businesses source collared bolts. These innovations facilitate real-time inventory tracking, supplier performance analysis, and streamlined order processing, making it easier for international buyers to access the products they need. Sustainability is also becoming a focal point, with many companies prioritizing eco-friendly materials and processes. As a result, buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with sustainability standards and certifications.
Market dynamics are further influenced by geopolitical factors and trade policies, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East. Tariffs, import regulations, and trade agreements can significantly impact sourcing strategies for collared bolts. International buyers must stay informed about these changes to navigate the complexities of global supply chains effectively.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Collared Bolt Supply Chain?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for businesses in the collared bolt sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials used in collared bolts is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt greener practices. This includes utilizing recycled materials, reducing waste, and minimizing carbon footprints throughout the production process.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, as buyers increasingly demand transparency in sourcing practices. Suppliers that can demonstrate responsible sourcing and adherence to labor and environmental standards are more likely to gain a competitive advantage. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as benchmarks for buyers looking to partner with responsible manufacturers.
Moreover, the shift towards sustainable practices is not merely a trend but a necessity in today’s market. Buyers who prioritize sustainability in their sourcing decisions can not only enhance their corporate image but also mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance and supply chain disruptions. As the global focus on sustainability intensifies, aligning with suppliers committed to ethical practices will be crucial for long-term success in the collared bolt market.
What Is the Historical Context of Collared Bolts in B2B Sourcing?
The evolution of collared bolts dates back several decades, with their design primarily aimed at enhancing the durability and effectiveness of fastening solutions in various applications. Initially used in heavy machinery and construction, collared bolts have expanded their reach into diverse industries, including transportation and energy.
Over time, advancements in material science and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of high-strength collared bolts capable of withstanding extreme conditions. This evolution has been crucial for international B2B buyers who require reliable and efficient fastening solutions for increasingly complex projects. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for innovative and sustainable collared bolt solutions will likely shape the future of sourcing strategies in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of collared bolt
-
1. How do I select the right collared bolt for my application?
Choosing the right collared bolt depends on several factors, including the specific machinery or equipment it will be used with, the load requirements, and environmental conditions. Start by identifying the OEM specifications for your machinery, as many collared bolts are designed to fit specific models. Consider the material of the bolt; stainless steel offers corrosion resistance while carbon steel provides strength. Additionally, consult with suppliers about the performance characteristics of their products to ensure compatibility with your operational needs. -
2. What are the common applications for collared bolts?
Collared bolts are commonly used in various industries, including construction, mining, and equipment manufacturing. They are particularly effective in applications requiring secure fastening in high-stress environments, such as trenchers and horizontal directional drilling (HDD) machines. Their design allows for enhanced stability and load distribution, making them ideal for heavy machinery. Always verify with your supplier for specific applications to ensure optimal performance in your intended use. -
3. How can I ensure the quality of collared bolts from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, it’s essential to conduct thorough supplier vetting. Request certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Ask for product samples and specifications to verify compliance with industry standards. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facility or using third-party inspection services to assess quality control processes. Establishing a good communication channel with the supplier can also help address any quality concerns promptly. -
4. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for collared bolts?
Minimum order quantities for collared bolts can vary significantly between suppliers, ranging from as few as 100 pieces to several thousand. Factors influencing MOQ include the supplier’s production capabilities, material availability, and customization requirements. When negotiating, clarify your needs and explore the possibility of lower MOQs for initial orders, especially if you are a new customer. This can help you test the product quality without committing to a large inventory upfront. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing collared bolts internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiating power. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. For larger orders, you may negotiate partial payments, where a percentage is paid upfront, and the balance is settled upon receipt of goods. Be sure to clarify all terms in your purchase agreement, including currency, payment methods, and any applicable fees, to avoid misunderstandings later. -
6. What shipping options are available for collared bolts, and how can I choose the best one?
Shipping options for collared bolts typically include air freight for expedited delivery and sea freight for cost-effective bulk shipments. Your choice will depend on urgency, budget, and the destination’s logistics infrastructure. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping, customs duties, and handling fees. Working with a freight forwarder can help navigate international shipping regulations and provide insights into the best shipping methods for your specific needs. -
7. Can collared bolts be customized to fit specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for collared bolts, including varying lengths, diameters, and materials. If you have specific performance criteria or environmental conditions, discuss these with your supplier. Customization may involve additional costs and longer lead times, so it’s essential to plan ahead. Providing detailed specifications will help the supplier understand your needs and deliver the most suitable product for your application. -
8. How do I handle logistics and customs for importing collared bolts?
Navigating logistics and customs involves understanding the regulations and documentation required for importing collared bolts into your country. Ensure you have all necessary paperwork, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Engaging a customs broker can simplify the process, as they are familiar with local regulations and can expedite clearance. Additionally, monitor shipment tracking to address any issues proactively, ensuring timely delivery to your location.
Top 5 Collared Bolt Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. McMaster – T-Bolts and Fasteners
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – T-Bolts and Fasteners, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Ballantine – 3/8 Bolt for Collar
Domain: ballantineinc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“Part No”: “V4478003”, “Specifications”: “3/8\” Bolt (For Collar) (OEM reference # 4478003)”, “Compatible Brands and Models”: [“Vermeer® D7X11”, “Vermeer® D7X11A”, “Vermeer® D7X11 Series II”, “Vermeer® D9X13 Series II”, “Vermeer® D10X15”, “Ditch Witch® JT920”, “Ditch Witch® JT920L”, “Ditch Witch® JT921”, “Ditch Witch® JT922”, “Ditch Witch® JT1210”]}
3. SefuAE – Collar Bolts
Domain: sefuae.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Collar bolts are special fasteners used to grip bundles in detachable bundle heat exchangers, preventing channel elimination without breaking the cover between the shell and tube sheet. They are threaded hardware fasteners with external male threads, closely related to screws. Collar bolts prevent turning when nuts are tightened and are used in pressure vessel and heat exchanger products. They als…
4. Rapala – Collar Bolt
Domain: rapala.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Collar Bolt”, “description”: “Replacement bolt to attach the power ice drill to your power head assembly.”, “item_number”: “COLLARBOLT”, “price”: “$6.49”, “availability”: “Available”, “shipping_info”: “FREE GROUND SHIPPING ON ORDERS $99+”}
5. Miller Motor Cars – Flexible Payment Options
Domain: store.millermotorcars.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, Miller Motor Cars – Flexible Payment Options, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for collared bolt
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of collared bolts is vital for international buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reliability in their projects. By focusing on high-quality materials and reputable suppliers, businesses can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs associated with machinery failures. The global demand for robust fastening solutions, particularly in industries like construction and manufacturing, underscores the necessity of a thorough sourcing strategy that considers not just cost but also durability and compatibility with existing equipment.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, buyers are encouraged to leverage digital platforms and trade networks to identify trustworthy suppliers. Engaging in direct relationships with manufacturers can also facilitate better pricing and customized solutions, ensuring that the right products meet specific project needs.
Looking ahead, the future of sourcing collared bolts will likely be shaped by advancements in technology and sustainability. Buyers should stay informed about innovations that improve product performance and environmental impact. By adopting a proactive approach to sourcing, businesses can not only secure their supply chains but also position themselves competitively in an increasingly interconnected market. Explore your options today and partner with suppliers who align with your strategic goals.

Illustrative image related to collared bolt
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.