Choosing Your Water Filtration System Diagram: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for water filtration system diagram
In today’s global economy, sourcing effective water filtration system diagrams presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse regional needs and varying regulations across markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of water filtration systems becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide will delve into various types of water filtration systems, their applications across different industries, and the nuances of supplier vetting to ensure quality and compliance.
Additionally, it will provide insights into cost considerations and installation requirements, enabling buyers to make informed decisions. This guide aims to empower B2B purchasers by equipping them with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the water filtration market. With a focus on practical solutions and actionable insights, buyers will learn how to identify the most suitable products for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and sustainability.
In an era where clean water access is paramount, this resource serves as a vital tool for making strategic purchasing decisions that align with both operational goals and regulatory frameworks. Whether you are in Germany looking to enhance your industrial water quality or in Brazil seeking sustainable solutions, this guide will facilitate your journey toward effective water filtration.
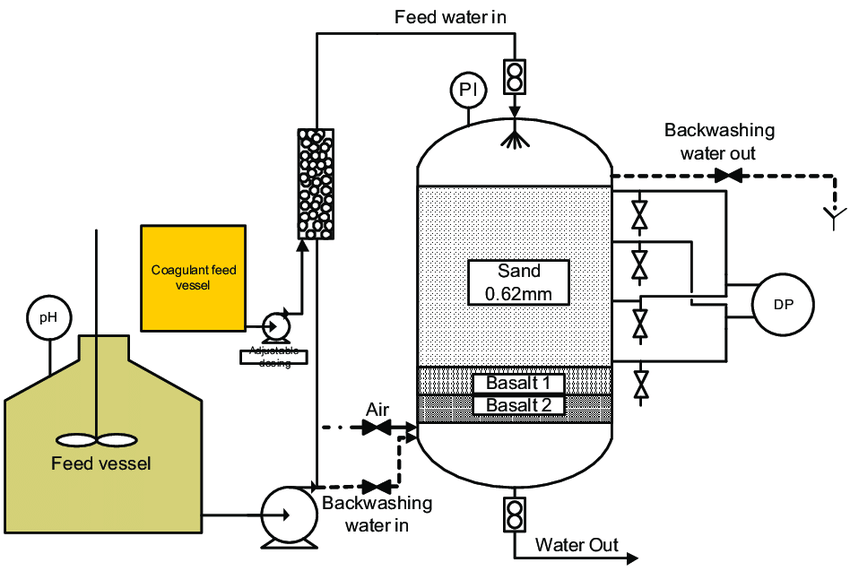
Understanding water filtration system diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse Osmosis (RO) System | Multi-stage filtration, removes up to 99% contaminants | Beverage production, pharmaceuticals | Pros: High purity, effective against various contaminants. Cons: Higher cost, requires maintenance. |
| Whole House Filtration System | Filters water for entire property, multi-stage options | Residential and commercial buildings | Pros: Provides clean water throughout the property. Cons: Installation complexity, space requirements. |
| Activated Carbon Filters | Uses carbon to absorb contaminants, easy to install | Restaurants, hotels, and cafes | Pros: Improves taste and odor, cost-effective. Cons: Limited lifespan, not effective against all contaminants. |
| Ultraviolet (UV) Purification | Uses UV light to disinfect water, chemical-free | Hospitals, laboratories, food processing | Pros: Effective against bacteria and viruses. Cons: Does not remove chemicals, requires electricity. |
| Sediment Filtration System | Removes larger particles, typically first stage | Industrial applications, municipal water systems | Pros: Protects downstream equipment, low maintenance. Cons: Does not remove dissolved contaminants. |
What are the Characteristics of Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are known for their multi-stage filtration process, which effectively removes up to 99% of contaminants, including heavy metals, salts, and other impurities. This makes RO systems ideal for industries like beverage production and pharmaceuticals, where water purity is critical. When considering an RO system, B2B buyers should evaluate the initial investment and ongoing maintenance needs, as these systems can be more costly than other filtration options.
How Do Whole House Filtration Systems Work?
Whole house filtration systems are designed to treat all water entering a property, providing comprehensive protection against contaminants. These systems typically utilize multiple filtration stages, allowing for the removal of sediment, chlorine, and other impurities. They are suitable for both residential and commercial applications, enhancing water quality throughout the entire building. Buyers should consider installation complexity and space requirements, as these systems often need a dedicated area for housing the equipment.
What Are the Benefits of Activated Carbon Filters?
Activated carbon filters are popular for their ability to absorb chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other contaminants, significantly improving water taste and odor. They are particularly beneficial in the hospitality industry, such as restaurants and hotels, where water quality can directly impact customer satisfaction. While these filters are cost-effective and easy to install, buyers should be aware of their limited lifespan and the fact that they do not effectively remove all types of contaminants.
How Effective is Ultraviolet (UV) Purification?
Ultraviolet (UV) purification systems utilize UV light to disinfect water, effectively killing bacteria and viruses without the use of chemicals. This makes them ideal for sensitive environments like hospitals, laboratories, and food processing facilities, where water quality is paramount. While UV systems provide a high level of disinfection, buyers should note that they do not remove chemical contaminants and require a constant electricity supply for operation.
What Role Do Sediment Filtration Systems Play?
Sediment filtration systems are designed to remove larger particles such as sand, silt, and rust from water, acting as the first line of defense in the filtration process. These systems are commonly used in industrial applications and municipal water systems to protect downstream equipment from damage caused by larger debris. While sediment filters are low maintenance and cost-effective, they do not address dissolved contaminants, making it essential for buyers to consider complementary filtration solutions for comprehensive water treatment.
Key Industrial Applications of water filtration system diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of water filtration system diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation water filtration | Ensures clean water for crop irrigation, enhancing yield and quality | Local water quality standards, filtration capacity |
| Food and Beverage | Process water purification | Guarantees safety and compliance with health regulations, improving product quality | Certification for food safety, maintenance support |
| Pharmaceuticals | Water for injection (WFI) systems | Meets strict purity standards, essential for drug manufacturing | Compliance with regulations, reliability of supplier |
| Hospitality | Whole-house filtration systems for hotels | Enhances guest experience with clean, safe water, reducing operational costs | Energy efficiency, ease of maintenance |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Cooling water filtration systems | Protects equipment from corrosion and scaling, ensuring operational efficiency | Material compatibility, flow rate requirements |
How is Water Filtration Used in Agriculture and What Problems Does It Solve?
In agriculture, water filtration systems are crucial for ensuring that irrigation water is free from contaminants such as sediments, pathogens, and chemicals. By utilizing a water filtration system diagram, farmers can identify the best filtration methods for their specific water source, ensuring optimal crop health and yield. This is particularly important in regions with variable water quality, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers should consider local water quality standards and the filtration capacity needed to meet their irrigation demands.
What Role Does Water Filtration Play in the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage sector, water filtration is essential for maintaining high safety and quality standards. The water filtration system diagram helps manufacturers visualize the filtration process necessary for compliance with health regulations. This is critical in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where stringent food safety laws are enforced. Buyers must prioritize suppliers who can provide systems that meet food safety certifications and offer ongoing maintenance support to ensure continuous compliance.
How is Water Filtration Critical in Pharmaceutical Production?
Pharmaceutical companies rely on water for injection (WFI) systems that must adhere to rigorous purity standards. The water filtration system diagram illustrates the complex processes involved in producing WFI, which is vital for drug manufacturing. In regions with varying regulatory frameworks, such as Brazil and Germany, understanding these diagrams helps companies ensure compliance with local laws. Buyers should focus on suppliers with a proven track record of meeting pharmaceutical regulations and providing reliable system performance.
How Does Water Filtration Enhance Guest Experience in Hospitality?
In the hospitality industry, whole-house water filtration systems are increasingly being adopted by hotels to provide guests with clean and safe drinking water. A water filtration system diagram can help hotel managers understand the installation and maintenance of these systems, enhancing guest satisfaction and reducing operational costs associated with bottled water. International buyers should consider energy efficiency and ease of maintenance when sourcing these systems, as they directly impact the hotel’s bottom line.
What are the Benefits of Water Filtration in Industrial Manufacturing?
Industrial manufacturing processes often require large volumes of cooling water, which must be free from impurities to prevent equipment damage. Water filtration system diagrams can guide manufacturers in selecting the appropriate filtration methods, thereby protecting machinery from corrosion and scaling. Buyers in this sector, especially in developing regions, should evaluate material compatibility and flow rate requirements to ensure optimal system performance and longevity.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘water filtration system diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Understanding Complex Filtration Diagrams
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter intricate water filtration system diagrams that are challenging to interpret. This can lead to confusion when making purchasing decisions or during system installations. Buyers may struggle to understand how different components interact within the system, which can result in miscommunication among team members or with suppliers. This misunderstanding can delay projects, increase costs, and reduce overall confidence in the chosen filtration solution.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should seek diagrams that are not only clear but also include annotations explaining each component’s function and importance. When sourcing diagrams, prioritize those that are designed specifically for commercial applications, as they often provide additional context and real-world applications. Furthermore, consider engaging with suppliers who offer educational resources or training sessions on interpreting these diagrams. Utilizing visual aids alongside hands-on demonstrations can enhance understanding, ensuring that all stakeholders are on the same page. Additionally, leveraging software tools that allow for interactive exploration of filtration systems can help demystify complex diagrams, leading to better-informed decisions.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality Across Different Filtration Systems
The Problem: B2B buyers may face inconsistencies in water quality due to varying filtration systems, especially when dealing with multiple suppliers. This inconsistency can result in unreliable product performance and can lead to compliance issues in regions with stringent water quality regulations. Buyers may find it difficult to assess which systems will deliver the expected level of filtration and performance, creating significant risk for their operations.
The Solution: To address this pain point, buyers should develop a standardized evaluation process for assessing the quality of water filtration systems. This process should include a detailed review of the system diagrams alongside performance metrics, such as flow rates, contaminant reduction percentages, and maintenance requirements. Collaborating with trusted suppliers who provide robust documentation and case studies can also help ensure that the systems meet regional compliance standards. Additionally, conducting pilot tests using small-scale installations can provide first-hand insights into system performance and reliability before committing to larger orders. This proactive approach allows buyers to mitigate risks associated with inconsistent water quality.
Scenario 3: Challenges with System Installation and Maintenance
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the complexity of installing and maintaining water filtration systems. Many diagrams do not include comprehensive installation instructions or maintenance guidelines, leading to potential installation errors or inefficient upkeep. These issues can create operational downtime, increase maintenance costs, and necessitate the hiring of external contractors, which can strain budgets and resources.
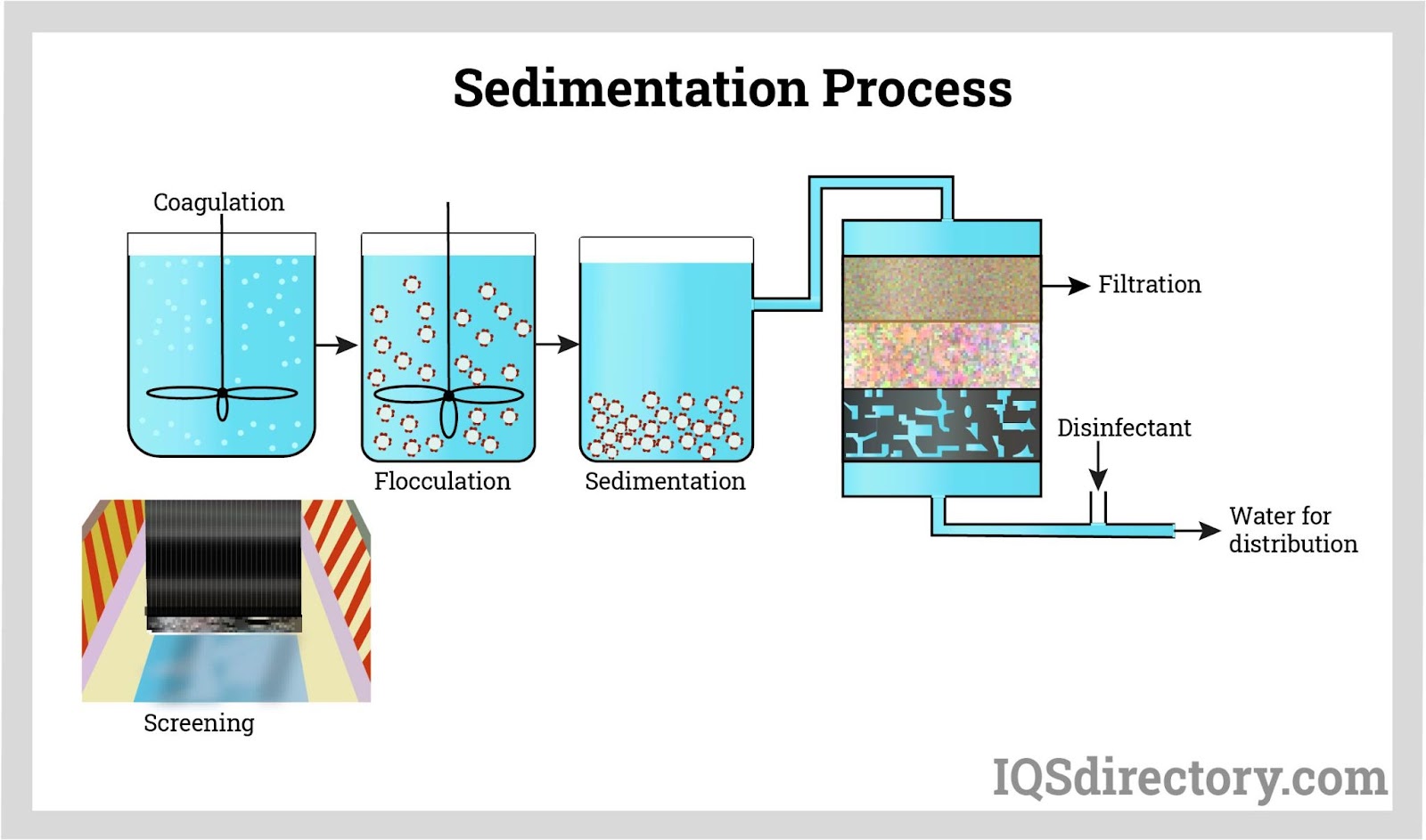
Illustrative image related to water filtration system diagram
The Solution: To streamline installation and maintenance, buyers should prioritize sourcing filtration systems that come with detailed, user-friendly diagrams accompanied by step-by-step installation and maintenance guides. It’s beneficial to select systems from manufacturers that provide ongoing support, including access to customer service for troubleshooting. Buyers can also consider investing in training for their team on the specific systems they are implementing, which can enhance their ability to perform installations and routine maintenance effectively. Additionally, leveraging digital tools that offer virtual installation support or maintenance reminders can significantly reduce the burden on staff and improve operational efficiency. By fostering a culture of knowledge-sharing and continuous improvement, organizations can ensure that their water filtration systems are installed correctly and maintained effectively over time.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for water filtration system diagram
What Are the Key Materials Used in Water Filtration Systems?
Selecting the right materials for water filtration systems is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze several common materials used in these systems, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Polypropylene Perform in Water Filtration Systems?
Key Properties: Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, low density, and high melting point (around 160°C). It can withstand moderate pressure and is resistant to corrosion from various chemicals, making it suitable for water filtration applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of polypropylene is a significant advantage, as it resists degradation from UV exposure and moisture. It is also cost-effective, making it a popular choice for manufacturers. However, its manufacturing complexity can be higher than some alternatives, and it may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: PP is commonly used in filter housings and membranes, compatible with various filtration media such as activated carbon and sediment filters. Its compatibility with different media enhances the overall effectiveness of the filtration system.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure that the polypropylene used meets local compliance standards, such as ASTM or DIN. Additionally, understanding the local availability of PP can impact procurement strategies.
What Role Does Stainless Steel Play in Filtration Systems?
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grades 304 and 316, offers excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C) and pressures, making it ideal for robust filtration applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to corrosion, which reduces maintenance costs over time. However, it is more expensive than other materials, and its heavier weight can complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in high-capacity filtration systems, including reverse osmosis units and industrial applications. Its compatibility with various filtration media ensures effective contaminant removal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as JIS and ASTM is crucial for stainless steel components. Buyers in Europe, particularly Germany, may prioritize materials that meet stringent environmental and safety regulations.
Why Is PVC a Popular Choice for Water Filtration Systems?
Key Properties: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile plastic known for its rigidity and resistance to chemicals and moisture. It has a temperature rating of up to 60°C and is lightweight, making it easy to handle and install.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and widely available, making it an attractive option for many applications. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and can be susceptible to UV degradation if not properly protected.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in piping and fittings within filtration systems, compatible with various filtration media. Its lightweight nature facilitates easier installation in both residential and commercial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that PVC products comply with local regulations, especially in regions with stringent environmental standards. Understanding the quality of PVC available in different markets can influence material selection.
How Does Activated Carbon Enhance Filtration Systems?
Key Properties: Activated carbon is a porous material with a high surface area, enabling it to effectively adsorb contaminants and impurities from water. It operates efficiently at ambient temperatures and is compatible with various filtration setups.
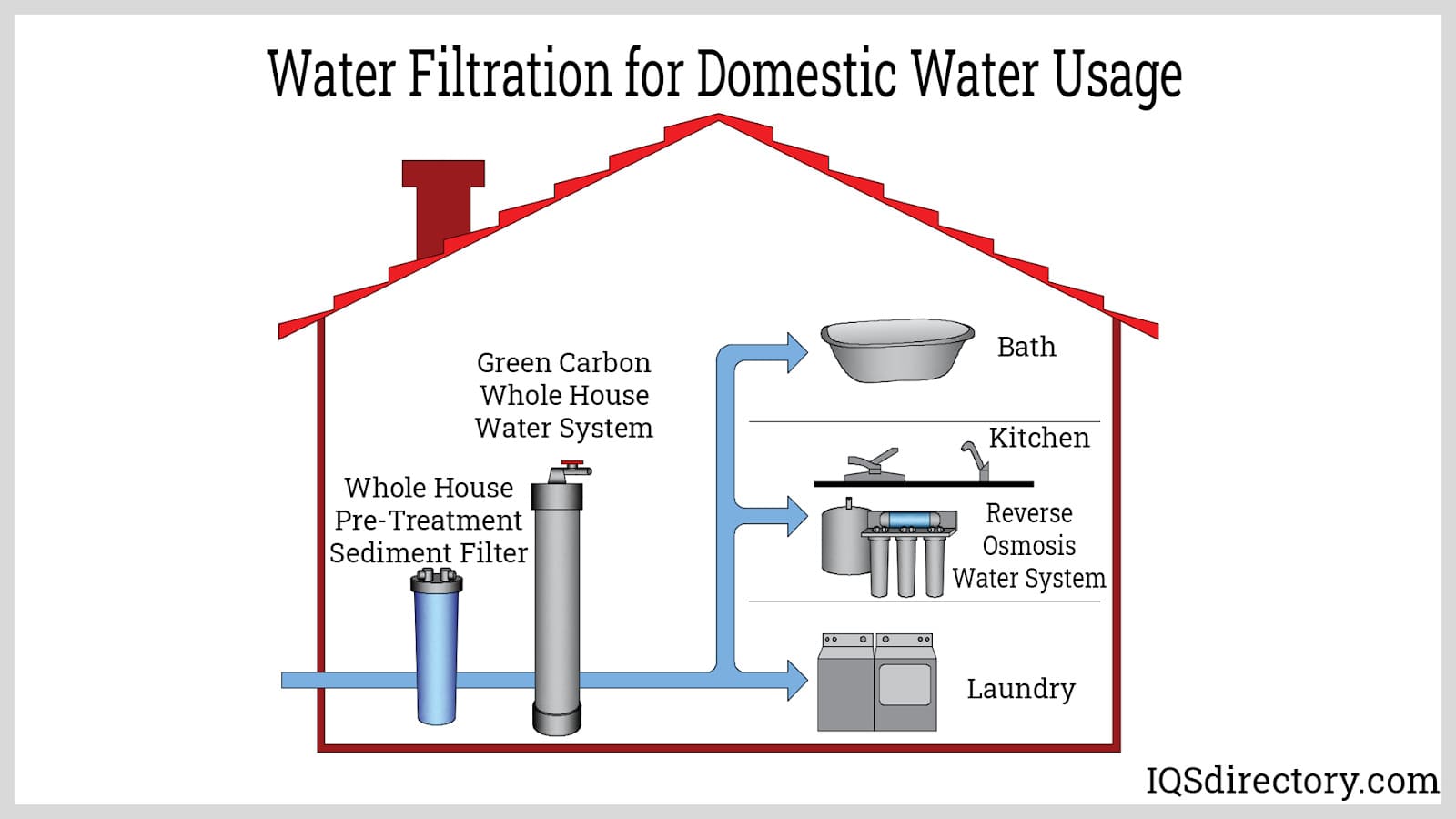
Illustrative image related to water filtration system diagram
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of activated carbon is its effectiveness in removing chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other contaminants, significantly improving water taste and quality. However, it has a limited lifespan and requires regular replacement, which can add to maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Activated carbon is widely used in both residential and industrial filtration systems, often in combination with other media to enhance overall performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that activated carbon meets local health and safety standards, particularly in regions where water quality regulations are stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Water Filtration Systems
| Material | Typical Use Case for water filtration system diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | Filter housings and membranes | Excellent chemical resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High-capacity filtration systems | Long-lasting and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and weight | High |
| PVC | Piping and fittings | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable and UV susceptible | Low |
| Activated Carbon | Adsorption media in filtration systems | Highly effective in contaminant removal | Limited lifespan requiring regular replacement | Medium |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific filtration needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for water filtration system diagram
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Water Filtration Systems?
The manufacturing of water filtration systems involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the end product meets the required quality and efficiency standards. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating potential suppliers.
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Water Filtration Systems?
-
Material Preparation
– The first stage involves selecting and preparing the materials that will be used in the filtration systems. Common materials include various plastics, metals, and filtration media such as activated carbon or ceramic.
– Suppliers often prioritize sourcing high-quality materials that comply with international standards to ensure durability and effectiveness. For instance, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is frequently chosen for its resistance to chemicals and UV radiation. -
Forming
– The forming process may involve techniques such as injection molding, blow molding, or extrusion. These methods are employed to create the essential components of the filtration systems, including housing units, filter cartridges, and connectors.
– Advanced technologies like 3D printing are also becoming popular for prototyping and producing complex shapes that traditional methods may not easily achieve. -
Assembly
– After forming, the components are assembled into complete filtration systems. This stage often requires precision to ensure that all parts fit together correctly, which is crucial for the system’s functionality.
– Automated assembly lines are increasingly common, as they enhance consistency and reduce human error. Manual assembly may still be utilized for intricate components or final quality checks. -
Finishing
– The finishing process may include surface treatments, coating, or additional filtration media application. This stage is essential for enhancing the aesthetics and performance of the water filtration systems.
– Quality checks during this stage ensure that components are free from defects and that the system is ready for the market.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in the Manufacturing of Water Filtration Systems?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each water filtration system meets or exceeds industry standards. B2B buyers must be aware of the QA protocols to assess supplier reliability effectively.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Water Filtration Systems?
-
ISO 9001
– ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer has effective processes in place for managing quality.
– For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s ISO 9001 certification can provide assurance that the manufacturing processes are consistently evaluated and improved. -
CE Marking
– In Europe, CE marking is required for many products, including water filtration systems. It signifies that the product conforms to European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– B2B buyers from Europe should ensure that their suppliers can provide evidence of CE compliance, as this can affect marketability and legal compliance. -
API Standards
– The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards relevant to products used in oil and gas industries, including certain filtration systems. API certification can be crucial for buyers in these sectors, ensuring that products meet stringent performance criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Water Filtration Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues before products reach the market.
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– This initial QC stage involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified quality standards. This could include verifying certifications, conducting physical inspections, and testing material properties.
– Effective IQC helps prevent defective materials from entering the production line, which can save time and costs associated with rework. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During production, IPQC involves continuous monitoring of the manufacturing process. This may include regular inspections and tests to ensure that components are produced within the specified tolerances.
– Key metrics monitored during this stage can include dimensions, weight, and material properties, which contribute to the overall quality of the final product. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– FQC occurs after assembly and finishing, where the complete water filtration systems undergo rigorous testing. This may include functional testing, performance evaluations, and stress tests to ensure the systems operate as intended.
– Documentation of FQC results is vital for traceability and can serve as proof of compliance for B2B buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
When sourcing water filtration systems, B2B buyers should actively verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers. This process can include several key strategies:
-
Supplier Audits
– Conducting on-site audits of suppliers allows buyers to assess manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and overall operational efficiency. This firsthand insight can be invaluable in determining supplier reliability.
– Audits should focus on the effectiveness of the QMS, adherence to international standards, and the presence of any corrective action plans for non-conformities. -
Quality Reports
– Requesting quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes and outcomes. These reports should detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC, as well as any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues.
– Consistent reporting demonstrates a commitment to quality and transparency, which can enhance trust in the supplier. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be particularly beneficial for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct audits themselves.
– Third-party inspectors can evaluate compliance with relevant standards and provide certification that may be required for market entry.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider several nuances when assessing quality control practices:
-
Regional Standards and Regulations
– Different regions may have varying regulations and standards for water filtration systems. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
– For instance, regulations in the European Union may differ significantly from those in South America, impacting the certification and testing processes required for market entry. -
Cultural Considerations
– Understanding cultural differences can facilitate better communication with suppliers and enhance collaboration. Buyers should be aware of how cultural factors may influence quality perceptions and expectations.
– Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to improved transparency and trust, which are crucial for successful B2B partnerships. -
Logistical Challenges
– International buyers may encounter logistical challenges that can affect quality assurance, such as shipping delays or customs regulations. It’s essential to have contingency plans in place to address these potential issues and maintain product quality.
– Developing a robust supply chain strategy that includes multiple suppliers can help mitigate risks associated with international sourcing.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for water filtration systems is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier quality control, compliance with international standards, and regional nuances, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and ensure the reliability of their water filtration solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘water filtration system diagram’
In the quest to procure an effective water filtration system diagram, B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of technical specifications, supplier credibility, and regulatory compliance. This guide serves as a practical checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that meet your organization’s needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by outlining the specific requirements for your water filtration system diagram. Consider factors such as the type of filtration technology (e.g., reverse osmosis, activated carbon), the scale of operation (residential vs. industrial), and the contaminants to be addressed. A clear specification will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure they can meet your needs.
Step 2: Research Supplier Expertise
Investigate potential suppliers to assess their expertise in water filtration systems. Look for companies with a proven track record in your region, especially those that have experience with the unique water quality challenges in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. Supplier expertise can significantly influence the reliability and efficiency of the filtration systems they offer.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that your shortlisted suppliers hold the necessary certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO or NSF/ANSI certifications. These certifications not only ensure product quality but also demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to safety and environmental regulations. Request documentation to confirm their standing.
Step 4: Request Detailed Diagrams and Documentation
Ask suppliers for detailed diagrams and technical documentation of their water filtration systems. This includes installation guides, maintenance procedures, and operational schematics. Having comprehensive documentation is crucial for understanding system performance and ensuring proper installation and maintenance, which can reduce long-term operational costs.
Step 5: Assess Customization Options
Inquire whether suppliers offer customization for their water filtration systems. Depending on your specific needs, you may require unique configurations or additional components. Understanding a supplier’s flexibility in tailoring solutions can enhance system performance and ensure that it aligns with your operational requirements.
Step 6: Check References and Case Studies
Request references and case studies from suppliers to gauge their reliability and customer satisfaction levels. Reach out to previous clients, especially those in similar industries or geographical areas, to understand their experiences with the supplier’s products and services. This step provides insights into the supplier’s ability to deliver on their promises.
Step 7: Evaluate After-Sales Support and Warranty
Lastly, assess the after-sales support and warranty options offered by potential suppliers. Reliable technical support can be invaluable for troubleshooting and maintenance, while a robust warranty can protect your investment. Ensure that the supplier is committed to providing ongoing assistance and has a clear process for handling warranty claims.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing water filtration system diagrams, leading to successful implementations that enhance water quality and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for water filtration system diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Water Filtration System Diagrams?
When sourcing water filtration system diagrams, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and procurement. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
Illustrative image related to water filtration system diagram
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials used in diagram creation, such as paper, ink, and digital resources. High-quality materials may lead to increased costs but can enhance the durability and clarity of the diagrams.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for the design and creation of accurate filtration diagrams. The cost may vary based on the complexity of the diagrams and the expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. These costs are often distributed across all products, impacting the final pricing of diagrams.
-
Tooling: Specialized software and equipment used in the design process can be significant cost factors. Investing in advanced design tools may incur higher initial costs but can improve efficiency and output quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that diagrams meet industry standards and customer specifications is essential. QC processes may require additional labor and resources, influencing overall costs.
-
Logistics: The costs associated with distributing the diagrams, whether digital or printed, are critical. This includes shipping, handling, and any customs duties applicable in international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary widely based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Water Filtration System Diagram Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of water filtration system diagrams, making it essential for B2B buyers to understand these elements.
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities typically reduces the per-unit cost. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to benefit from bulk pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized diagrams tailored to specific filtration systems can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate the need for customization against their budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly impact pricing. Higher-quality materials may lead to better diagrams but will also increase costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Diagrams that meet specific industry certifications may carry a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget and project requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms and conditions is vital for cost management. Incoterms can affect the total landed cost, including shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Water Filtration System Diagrams?
Navigating the procurement landscape for water filtration system diagrams requires strategic approaches to ensure cost-effectiveness.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Use market research to inform negotiations and identify competitive pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes installation, maintenance, and potential training costs for using the diagrams effectively.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and tariffs that may affect pricing. Building relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some international cost challenges.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Always remember that prices can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors and market dynamics. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and perform due diligence before finalizing any procurement decisions.
By understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and practical tips for negotiation, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their sourcing strategies for water filtration system diagrams.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing water filtration system diagram With Other Solutions
Introduction to Water Filtration Alternatives
In the quest for clean and safe drinking water, businesses and organizations often evaluate various water filtration solutions. The “water filtration system diagram” serves as a critical tool for understanding the mechanics of filtration systems. However, it is essential to consider alternative methods and technologies that can achieve similar goals. This comparison will explore the pros and cons of a traditional water filtration system diagram against other viable solutions, including reverse osmosis systems and UV water purification.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Water Filtration System Diagram | Reverse Osmosis System | UV Water Purification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good for sediment and larger contaminants | Excellent for dissolved solids and contaminants | Effective against bacteria and viruses |
| Cost | Low initial investment; costs vary by design | Moderate to high initial cost; ongoing filter replacements | Low to moderate; bulb replacement needed |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires some plumbing knowledge | Moderate; often requires professional installation | Easy; typically requires minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Regular filter changes; depends on water quality | Regular filter and membrane replacements; more intensive | Bulb replacement every 12 months; low maintenance otherwise |
| Best Use Case | Residential and small-scale applications | Industrial and residential applications needing high purity | Treatment of microbiologically unsafe water in homes and businesses |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Reverse Osmosis System
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems utilize a semi-permeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. This technology is highly effective in eliminating dissolved solids, making it suitable for regions where water quality is poor. However, RO systems can be costly to install and maintain, as they require regular replacement of filters and membranes. Additionally, they waste a significant amount of water in the filtration process, which can be a concern in areas with limited water resources.
Illustrative image related to water filtration system diagram
UV Water Purification
UV water purification systems use ultraviolet light to kill or inactivate bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens in water. This method is particularly effective for treating microbiologically unsafe water, making it a popular choice in both residential and commercial settings. The installation process is relatively straightforward, and the maintenance primarily involves replacing the UV bulb annually. However, UV systems do not remove chemical contaminants or sediment, which means they should be used in conjunction with other filtration methods for comprehensive water treatment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Water Filtration Solution
When selecting a water filtration solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including water quality, budget, and application. The water filtration system diagram provides a foundational understanding of traditional filtration methods, suitable for basic applications. In contrast, reverse osmosis systems are ideal for those requiring high purity, while UV purification offers a reliable solution for microbial concerns. Assessing these factors will enable businesses to choose the most effective and cost-efficient solution for their water filtration requirements, ensuring safety and compliance with local regulations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for water filtration system diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Water Filtration Systems?
Understanding the essential technical properties of water filtration systems is critical for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating different systems for specific applications. Here are some key specifications that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
The material used in the construction of filtration systems is crucial for durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel, PVC, and polypropylene. Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for industrial applications. In contrast, PVC is lightweight and cost-effective but may not withstand high-pressure environments. Choosing the right material can significantly impact the longevity and maintenance costs of the system. -
Flow Rate
The flow rate indicates how much water can be filtered within a specific time frame, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM). This specification is vital for ensuring that the system meets the operational demands of the facility. A higher flow rate may be necessary for commercial or industrial applications, while residential systems may require lower rates. Understanding flow rates helps buyers match filtration systems to their specific water usage requirements. -
Filtration Efficiency
This property defines the system’s ability to remove contaminants from water, often represented as a percentage. Higher filtration efficiency means that a greater proportion of impurities are eliminated. B2B buyers should consider the types of contaminants they need to filter out, such as sediment, chlorine, or heavy metals, and choose systems with appropriate efficiency ratings. -
Operating Pressure
The operating pressure indicates the pressure range within which the filtration system functions optimally. This specification is critical for ensuring that the system can handle the existing water pressure in the facility’s plumbing without causing leaks or failures. Systems designed for higher pressures are often used in commercial settings, while residential systems may operate at lower pressures. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the acceptable deviations in measurements and dimensions within the filtration system components. This property is important to ensure proper fit and function, especially when integrating the system into existing infrastructure. Buyers should be aware of the tolerances specified by manufacturers to avoid compatibility issues.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Water Filtration Systems?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and streamline purchasing processes. Here are some essential trade terms relevant to water filtration systems:
Illustrative image related to water filtration system diagram
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of water filtration systems, OEMs often provide components like membranes and filters, ensuring quality and compatibility with various systems. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and quality products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell at one time. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as it can affect inventory management and cost. Buyers should evaluate their needs against the MOQ to ensure they are not overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. In the water filtration industry, an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive quotes from various manufacturers, facilitating informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, as they can impact the total cost and logistical considerations of purchasing filtration systems. -
WQA (Water Quality Association)
The WQA is a trade association representing the water treatment industry. They provide certifications, standards, and educational resources. Membership or certification from WQA can indicate a company’s commitment to quality, which can be a valuable consideration for buyers. -
Lifetime Cost
This term refers to the total cost of owning a filtration system over its entire operational life, including initial purchase price, installation, maintenance, and replacement parts. B2B buyers should evaluate lifetime costs to make economically sound decisions that align with their budget and operational needs.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers in the water filtration industry to make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the water filtration system diagram Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Water Filtration System Diagram Market?
The global water filtration system market is experiencing significant growth, driven by several factors, including increasing awareness of water quality, regulatory pressures, and technological advancements. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly keen on sourcing effective filtration solutions. The rise in urbanization and industrialization in these areas is leading to heightened demand for reliable water treatment systems. Additionally, the growing prevalence of waterborne diseases is pushing businesses to prioritize the installation of filtration systems.
Emerging technologies, including IoT-enabled filtration systems and advanced filtration materials, are reshaping the market. These innovations not only enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of water purification processes but also facilitate real-time monitoring and maintenance, making it easier for businesses to ensure compliance with local water quality standards. Furthermore, B2B buyers are increasingly looking for modular and scalable solutions, which allow for customization according to specific operational needs. The trend towards smart water management systems is also gaining traction, as companies seek to integrate filtration solutions into broader environmental management strategies.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends for Water Filtration Systems?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the sourcing of water filtration systems. B2B buyers are increasingly focused on the environmental impact of their procurement choices, emphasizing the importance of ethical supply chains. Companies are recognizing that sourcing materials from responsible suppliers not only enhances their brand reputation but also contributes to the overall sustainability of their operations.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and NSF/ANSI standards for drinking water treatment systems are becoming essential in the decision-making process. Buyers are more inclined to choose products that are certified ‘green’ or made from recyclable materials, ensuring that their water filtration systems meet environmental and safety standards. Moreover, the push for sustainability is leading to innovations in filtration technologies, such as the development of biodegradable filters and energy-efficient systems. These advancements are critical for companies looking to reduce their carbon footprint while meeting regulatory demands.
How Has the Water Filtration System Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the water filtration system market has been marked by significant technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Initially, water filtration systems were basic, focusing primarily on mechanical filtration. However, as concerns about water quality grew, especially in industrial and urban environments, the market saw the introduction of more sophisticated technologies, such as reverse osmosis and UV purification.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards smart filtration solutions that integrate IoT technology for enhanced monitoring and maintenance capabilities. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the B2B sector, where businesses are increasingly prioritizing efficiency and sustainability. The growing demand for customized solutions tailored to specific needs further illustrates how the market continues to adapt to the complexities of modern water quality challenges. As the market progresses, B2B buyers can expect to see an even greater emphasis on innovation and sustainability in water filtration systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of water filtration system diagram
-
How do I choose the right water filtration system diagram for my needs?
Selecting the appropriate water filtration system diagram begins with understanding your specific requirements. Consider factors such as the source of water (municipal or well), the contaminants you need to remove, and the expected flow rate. Research the common filtration methods like reverse osmosis, activated carbon, or UV treatment to determine which is most effective for your situation. Additionally, consult with suppliers to see if they provide tailored diagrams that align with your specifications, ensuring that your system is efficient and compliant with local regulations. -
What is the best type of water filtration system for industrial applications?
For industrial applications, multi-stage filtration systems, including reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration, are often recommended. These systems can handle large volumes of water and effectively remove a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved solids and microorganisms. When sourcing diagrams, look for those that illustrate high-capacity systems designed for specific industry needs, such as food and beverage processing or pharmaceuticals, to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. -
How can I verify the quality of a water filtration system diagram provided by a supplier?
To verify the quality of a water filtration system diagram, request documentation that includes certifications, testing results, and case studies from the supplier. Ensure that the diagram aligns with industry standards, such as NSF or ANSI certifications, which confirm the safety and efficiency of the system. Additionally, seek testimonials from other B2B buyers in your region who have used the supplier’s products, as this can provide insight into their reliability and performance. -
What customization options are available for water filtration system diagrams?
Many suppliers offer customization options for water filtration system diagrams to meet specific operational needs. This can include adjustments in component sizes, materials, or configurations based on your water quality and usage requirements. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their ability to modify designs and whether they can provide CAD drawings or 3D models for better visualization. Custom solutions can enhance system efficiency and longevity, tailored to your unique challenges. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for water filtration systems?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for water filtration systems can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may require a MOQ of 10 units for standard systems, while others may offer flexibility for custom designs. When sourcing, communicate your needs clearly and negotiate MOQs that align with your purchasing capabilities. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can sometimes lead to more favorable terms, especially if you anticipate larger orders in the future. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing water filtration systems?
Payment terms for water filtration systems often vary by supplier and can include options such as 30% upfront payment with the balance due upon delivery, or net 30/60 terms after receipt of goods. When negotiating, consider discussing flexible payment options that may include financing or letter of credit arrangements, particularly for larger orders. It’s also advisable to confirm the currency of the transaction and any potential tariffs or import taxes that could affect the overall cost. -
How can I ensure the reliability of my water filtration system during logistics?
To ensure reliability during logistics, choose suppliers that have robust shipping and handling procedures in place. Request information about their packaging methods, shipping times, and the types of carriers used to mitigate damage during transit. Additionally, consider arranging for insurance on shipments and tracking options to monitor the status of your order. Engaging with logistics experts can also help streamline the process and ensure compliance with international shipping regulations. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in water filtration system suppliers?
When evaluating suppliers for water filtration systems, inquire about their quality assurance (QA) processes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management. Request details on their testing protocols, including performance evaluations of their filtration systems under various conditions. Suppliers should also provide documentation of regular audits and compliance with relevant industry standards, ensuring that the products you receive are reliable and effective for your needs.
Top 7 Water Filtration System Diagram Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Clean Water Store – Water Treatment Systems
Domain: cleanwaterstore.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Clean Water Store offers a variety of water treatment systems and products, including: Drinking Water Systems, City Water Systems, Well Water Systems, Carbon Backwash Filters, Carbon Upflow Filters, Fluoride Filters, Reverse Osmosis Systems, Water Softeners, Salt-Free Water Conditioners, Arsenic Filters, Acid Neutralizer Filters, Chlorination Systems, Iron & Manganese Filters, Nitrate Filters, Ult…
2. Shutterstock – Filtration System Infographic
Domain: shutterstock.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: This company, Shutterstock – Filtration System Infographic, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Pinterest – Water Purification System Diagram
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Water purification system with labeled filtration stages outline diagram. Educational clean and fresh drinking liquid technology with coagulant, fluoride and disinfectant addition vector illustration. Editable Vector for Commercial Use.
4. Boshart – Spin Out Sediment Filters
Domain: blog.boshart.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Traditional water filtration systems use filter cartridges installed at the point-of-entry (POE) into a home, filtering water through a media with a micron rating that determines the size of particulates stopped. Spin out sediment filters operate differently, using centrifugal force to separate heavy sediment from water, allowing for better flow and reduced clogging of traditional filters. A 1000 …
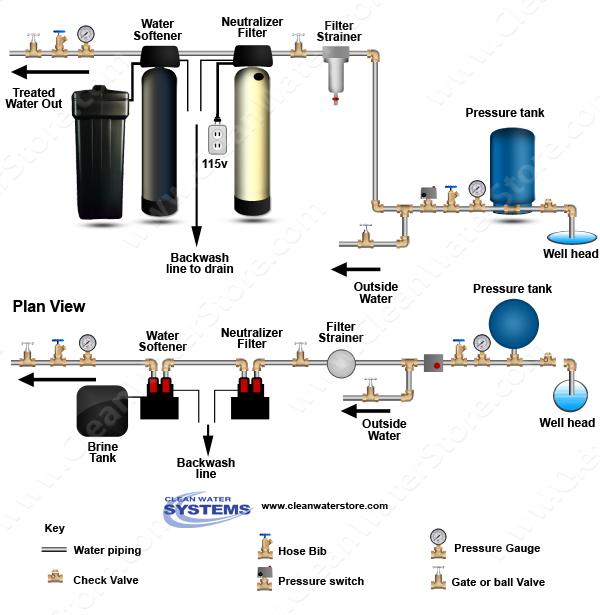
5. Well Water Filtration – Key Components
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This diagram illustrates a well water filtration and treatment system, detailing the flow of water from the well head to the final treated output. Key components include: 1. Pressure tank – regulates water pressure and stores supply. 2. Sediment filter – removes larger particles. 3. Optional filter strainer – provides additional purification. 4. 25/1 Micron filter – removes finer contaminants. 5. …
6. H2O Distributors – Reverse Osmosis Systems
Domain: h2odistributors.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Reverse Osmosis Diagram – H2O Distributors. Most Orders Ship Today. Free Shipping On All Orders $150 And Over! Contact: 1-800-955-8561. Product Categories: Residential Reverse Osmosis Systems, Under Sink Systems, Countertop Water Filter Systems, Whole House Systems, Commercial Systems, Inline Shower Filter Systems, Replacement Filter Cartridges, Reverse Osmosis Filter Kits, Ultraviolet Sterilizati…
7. Water Filter Guru – Whole House Installation Guide
Domain: waterfilterguru.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Whole house water filter system installation guide includes: tools needed (pipe cutter, drill, screwdriver, adjustable wrench, bucket), parts (filtration system, mounting bracket, push fittings, tubing, shut-off valve, optional bypass valve, plumber’s tape), installation steps (choose location, shut off water, cut into main water line, sand pipe, install shutoff valves, consider bypass and pressur…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for water filtration system diagram
In the rapidly evolving market for water filtration systems, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in optimizing procurement processes and ensuring long-term sustainability. By leveraging detailed diagrams and schematics, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific regional needs and regulatory requirements. Understanding the complexities of various filtration technologies—such as reverse osmosis and whole house systems—enables buyers to select solutions that maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
Illustrative image related to water filtration system diagram
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond cost savings; it fosters partnerships with reliable suppliers, enhances supply chain resilience, and drives innovation. As buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate their unique challenges, the emphasis on quality filtration systems cannot be overstated. Clean water is essential for health, industry, and agriculture, making it a critical investment.
Looking ahead, it is imperative for international buyers to engage in continuous learning and adaptation. By staying informed about emerging technologies and market trends, businesses can better position themselves for success. Embrace strategic sourcing today, and secure a sustainable, clean water future for your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Illustrative image related to water filtration system diagram