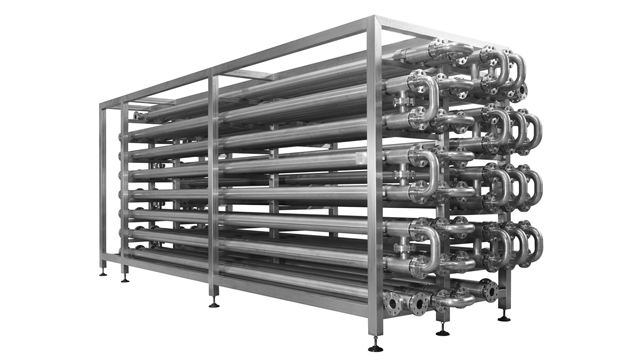
Choosing Your Tube Exchanger: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tube exchanger
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing the right tube exchanger can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With diverse applications ranging from petrochemical processes to power generation and HVAC systems, understanding the various types of tube exchangers—such as shell-and-tube, tube-in-tube, and custom solutions—is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip international buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the tube exchanger market. We delve into critical aspects such as identifying the right type for specific applications, evaluating supplier capabilities, and understanding cost factors that influence purchasing decisions. Additionally, we provide insights into the latest technological advancements and compliance standards that can impact operational efficiency and longevity of heat exchangers.
By addressing key considerations and challenges, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Whether you are in Brazil, Vietnam, or elsewhere, the information contained herein will help you streamline your procurement process, mitigate risks, and ultimately enhance your operational success in a global market.
Understanding tube exchanger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger | Comprises a series of tubes enclosed in a shell; can handle high pressures and temperatures. | Petrochemical, HVAC, power generation, food processing. | Pros: Versatile, high efficiency, customizable. Cons: Larger footprint, potential for fouling. |
| U-Tube Heat Exchanger | Features U-shaped tubes allowing for thermal expansion; often used in applications with temperature variations. | Chemical processing, oil refineries. | Pros: Compact design, easy maintenance. Cons: Limited to specific configurations. |
| Tube-in-Tube Heat Exchanger | Utilizes a smaller tube within a larger one for efficient heat transfer; ideal for low flow rates. | Sampling coolers, multi-phase fluids. | Pros: High efficiency, minimal dead zones. Cons: More complex design may increase costs. |
| Enhanced Surface Tube Exchanger | Employs specially designed tubes for improved heat transfer; often made from advanced materials. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, energy recovery. | Pros: Superior thermal performance, reduced size. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Double Wall Tube Exchanger | Features two walls for added safety; prevents fluid mixing in case of leaks. | Critical applications in nuclear and chemical industries. | Pros: Enhanced safety, leak prevention. Cons: Higher manufacturing costs, increased weight. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
Shell and tube heat exchangers are among the most widely used types due to their flexibility in handling various pressures and temperatures. They consist of a cylindrical shell housing multiple tubes through which one fluid flows while another flows around them. This design allows for efficient heat transfer and is suitable for applications across diverse industries such as petrochemical, HVAC, and food processing. Buyers should consider the specific thermal requirements and potential fouling issues when selecting this type.
How Do U-Tube Heat Exchangers Differ from Other Types?
U-tube heat exchangers feature tubes bent in a U-shape, allowing for thermal expansion without stressing the joints. This design is particularly advantageous in applications where temperature fluctuations are common, such as in chemical processing and oil refineries. While these exchangers are compact and easier to maintain, their configurations may limit adaptability for some industrial setups.
What Advantages Do Tube-in-Tube Heat Exchangers Offer?
The tube-in-tube design provides a highly efficient heat transfer mechanism by using a smaller inner tube within a larger outer tube. This configuration is particularly beneficial for applications involving low flow rates or multi-phase fluids, such as in sampling coolers. Buyers should note that while these exchangers minimize dead zones, their complexity can lead to higher costs and maintenance requirements.

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
Why Choose Enhanced Surface Tube Exchangers?
Enhanced surface tube exchangers feature specially designed tubes that significantly improve thermal performance. They are often used in industries requiring high efficiency, such as pharmaceuticals and energy recovery. While they may come with a higher initial investment, the long-term energy savings and reduced space requirements can make them an attractive option for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their operations.
What is the Importance of Double Wall Tube Exchangers?
Double wall tube exchangers are designed with two concentric walls, providing an additional layer of safety by preventing cross-contamination in case of leaks. This design is crucial for industries such as nuclear and chemical processing, where safety is paramount. However, buyers should be aware that the enhanced safety features come with increased manufacturing costs and weight considerations, making it essential to evaluate the specific needs of their applications before purchasing.
Key Industrial Applications of tube exchanger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tube exchanger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Heat recovery in refineries | Enhances energy efficiency, reduces operational costs | Material compatibility with corrosive fluids; compliance with TEMA standards |
| Power Generation | Condensing steam in power plants | Maximizes thermal efficiency, ensures reliable operation | Pressure ratings and materials suitable for high-temperature environments |
| Chemical Processing | Cooling and heating of process fluids | Improves product quality, maintains optimal process temperatures | Custom designs to fit specific plant layouts; corrosion resistance required |
| Food & Beverage | Pasteurization and cooling processes | Ensures product safety, extends shelf life | Sanitary design compliance; materials that meet food safety standards |
| HVAC Systems | Chilled water distribution | Enhances comfort, reduces energy consumption | Sizing and compatibility with existing systems; efficiency ratings |
How is Tube Exchanger Used in the Oil & Gas Sector?
In the oil and gas industry, tube exchangers are crucial for heat recovery processes within refineries. They facilitate the efficient transfer of heat between hot and cold fluids, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs. Buyers from this sector must prioritize sourcing materials that can withstand corrosive environments and adhere to TEMA standards for safety and reliability. Understanding the specific fluid properties and operating conditions is essential for optimal performance.
What Role Does Tube Exchanger Play in Power Generation?
Tube exchangers are integral to power generation, particularly in condensing steam applications. They maximize thermal efficiency by effectively transferring heat from steam to water, ensuring that power plants operate reliably. For international buyers, especially in regions with fluctuating energy demands, sourcing exchangers with appropriate pressure ratings and materials for high-temperature applications is vital to maintain safety and efficiency.
How is Tube Exchanger Applied in Chemical Processing?
In chemical processing, tube exchangers are employed to cool and heat various process fluids, which is essential for maintaining optimal temperatures and improving product quality. These systems can be customized to fit specific plant layouts, and buyers should consider the corrosion resistance of materials, given the aggressive nature of many chemicals. Compliance with industry regulations and standards is also a key factor when sourcing for this application.
Why is Tube Exchanger Important in Food & Beverage?
In the food and beverage sector, tube exchangers are used for pasteurization and cooling processes, ensuring product safety and extending shelf life. The design must comply with sanitary standards to prevent contamination. Buyers need to source materials that meet food safety regulations and ensure that the heat exchangers are easy to clean and maintain, which is crucial for operational efficiency.
How Does Tube Exchanger Enhance HVAC Systems?
In HVAC systems, tube exchangers are utilized for distributing chilled water, enhancing indoor comfort while reducing energy consumption. Efficient heat transfer is critical for maintaining desired temperature levels in commercial and residential settings. Buyers should focus on sizing the exchangers correctly and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Energy efficiency ratings are also important to consider for long-term cost savings.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tube exchanger’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Frequent Tube Bundle Failures Impacting Operations
The Problem: In industries reliant on tube exchangers, such as oil and gas or chemical processing, frequent failures of tube bundles can lead to significant downtime and financial losses. Corrosion, fouling, or mechanical failure of tubes may result in leaks, reduced efficiency, and ultimately, the need for costly replacements. Buyers often face the challenge of understanding the root causes of these failures to prevent reoccurrence, which can be exacerbated by varying fluid types and operational conditions across different regions.
The Solution: To mitigate tube bundle failures, buyers should focus on specifying the right materials and designs for their specific applications. Conduct a thorough assessment of the fluids being processed, including their temperature, pressure, and corrosive properties. When sourcing tube exchangers, opt for suppliers that offer a range of materials, including corrosion-resistant alloys and enhanced tube designs that improve heat transfer efficiency. Regular maintenance schedules should also be established to monitor and clean the tube bundles, reducing the risk of fouling and prolonging their lifespan. Engaging with manufacturers who provide detailed installation and operational guidelines can further enhance reliability.

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
Scenario 2: Difficulty Sourcing Replacement Tube Bundles
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when attempting to source replacement tube bundles, particularly for older or less common models. This issue can lead to delays in operations and increased costs, as manufacturers may not stock parts for every type or brand. Furthermore, the need for precise measurements and specifications adds complexity to the procurement process, potentially resulting in errors that could compromise system performance.
The Solution: To streamline the sourcing of replacement tube bundles, buyers should maintain comprehensive records of their existing equipment, including model numbers, specifications, and historical performance data. When seeking replacements, leverage manufacturers that specialize in custom solutions, as they can often replicate or modify existing designs based on provided specifications. Utilizing standardized measurement tools, such as blank drawings, can facilitate accurate reporting of dimensions and features. Additionally, establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can ensure access to a broader range of products and expedite the procurement process. Regularly reviewing supplier performance and exploring international options can also enhance sourcing efficiency.
Scenario 3: Inefficient Heat Transfer Leading to Increased Energy Costs
The Problem: Inefficient heat transfer in tube exchangers can significantly increase energy consumption, leading to higher operational costs. This issue may arise from improper sizing, fouling, or outdated technology. B2B buyers are often tasked with optimizing energy efficiency while balancing initial investment costs, which can be a complex challenge, especially in competitive markets.

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
The Solution: To address heat transfer inefficiencies, buyers should conduct a comprehensive energy audit of their current systems. This audit should assess the performance of existing tube exchangers and identify areas for improvement. Upgrading to modern, high-efficiency tube exchangers with enhanced surface designs or multi-stream capabilities can lead to substantial energy savings. Implementing predictive maintenance strategies can help in identifying fouling or performance drops before they escalate, allowing for timely interventions. Collaborating with engineering firms or consultants specializing in thermal systems can provide valuable insights and solutions tailored to specific operational needs, ultimately optimizing energy consumption and reducing costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tube exchanger
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Tube Exchangers?
When selecting materials for tube exchangers, it is crucial to understand the properties that directly influence performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: stainless steel, copper, titanium, and carbon steel.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Tube Exchangers?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength, making it suitable for a wide range of fluids. It typically withstands temperatures up to 1,200°F (650°C) and pressures exceeding 3,000 psi, depending on the grade.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to oxidation and corrosion, which translates to a longer service life. However, it is more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing can be complex due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including aggressive chemicals and high-temperature steam, making it ideal for petrochemical and food processing industries.

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with ASTM standards, as stainless steel grades vary globally. Understanding local regulations regarding material specifications is vital for successful procurement.
What Advantages Does Copper Offer for Tube Exchangers?
Key Properties: Copper is an excellent thermal conductor, with thermal conductivity significantly higher than that of stainless steel. It can handle temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and is often used in applications requiring efficient heat transfer.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its superior heat transfer capabilities, which can improve the efficiency of heat exchangers. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, especially in saline environments, and may require protective coatings. Additionally, copper is generally more expensive than carbon steel.

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for applications involving water or low-pressure steam but may not be suitable for corrosive fluids without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider local corrosion levels and the specific media used in their applications. Compliance with JIS and DIN standards may also be necessary.
Why Choose Titanium for Tube Exchangers?
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, especially in seawater and other aggressive environments. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,000°F (538°C) and high pressures.

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its durability and resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, titanium is significantly more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to fabricate, which may increase overall project costs.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly well-suited for marine applications and chemical processing where corrosion is a major concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Brazil and Vietnam should be aware of the high costs associated with titanium and ensure that their applications justify the investment. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B338 is essential.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Tube Exchangers?
Key Properties: Carbon steel is a cost-effective option with good strength and pressure resistance. It typically handles temperatures up to 800°F (427°C) and pressures around 2,000 psi.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of carbon steel is its low cost and ease of fabrication. However, it is prone to corrosion, especially in humid or saline environments, which can lead to a shorter lifespan.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications involving non-corrosive fluids, such as water or oil, but may require protective coatings or treatments in more aggressive environments.

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should consider local environmental conditions and ensure compliance with relevant standards like ASTM A106. Proper maintenance strategies should also be in place to mitigate corrosion risks.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Tube Exchangers
| Material | Typical Use Case for tube exchanger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Petrochemical and food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex fabrication | High |
| Copper | Water and low-pressure steam systems | Superior heat transfer capability | Susceptible to corrosion | Med |
| Titanium | Marine and chemical processing | Outstanding corrosion resistance | High cost and difficult to fabricate | High |
| Carbon Steel | Water and oil applications | Cost-effective and easy to fabricate | Prone to corrosion | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for tube exchangers, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tube exchanger
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Tube Exchangers?
The manufacturing process of tube exchangers is intricate and involves several critical stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is vital to ensure the final product meets the required performance specifications and industry standards.
-
Material Preparation:
The first step in manufacturing a tube exchanger involves selecting high-quality raw materials, such as stainless steel, copper, or specialized alloys. These materials are chosen based on their thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high pressures. Once selected, the materials undergo cutting and machining to create components like tubes, shells, and end caps. This preparation ensures precision in dimensions, which is crucial for the efficiency of heat transfer. -
Forming Techniques:
Forming techniques play a significant role in shaping the components of a tube exchanger. Common methods include bending, welding, and rolling. For instance, tube bundles may be formed using U-bending techniques or straight tube configurations, depending on the design requirements. Advanced welding methods, such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, are often employed to ensure strong joints that can withstand high pressures and temperatures. -
Assembly:
The assembly stage involves fitting together the prepared components to create the tube exchanger. This may include inserting tube bundles into the shell and securing them with proper fittings. The assembly process often utilizes jigs and fixtures to maintain alignment and prevent distortion. During this stage, manufacturers must ensure that all components are compatible and meet specified tolerances to avoid performance issues later on. -
Finishing:
After assembly, finishing processes are employed to enhance the performance and durability of the tube exchangers. This may involve surface treatments such as passivation or coating to improve corrosion resistance. Additionally, manufacturers often conduct a thorough inspection of the finished product to ensure it meets design specifications. This stage may also include cleaning the exchanger to remove any contaminants that could affect performance.
What International Standards and Quality Assurance Practices Are Relevant for Tube Exchangers?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of tube exchangers is paramount, especially for international B2B buyers who must ensure compliance with various standards. Here are some key international and industry-specific standards:
-
ISO 9001:
This is a widely recognized standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers of tube exchangers seeking ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to maintaining consistent quality in their products and processes. This certification is crucial for B2B buyers as it assures them of the supplier’s reliability and quality control processes. -
CE Marking:
In Europe, the CE marking indicates that a product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection legislation. For tube exchangers, this may involve adherence to specific directives related to pressure equipment and environmental sustainability. -
API Standards:
The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for equipment used in the oil and gas industry, including tube exchangers. Compliance with API standards is particularly important for manufacturers targeting markets in the Middle East and South America, where oil and gas applications are prevalent.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that tube exchangers meet specified standards and performance criteria. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. IQC checks for material specifications, dimensions, and any signs of damage. Ensuring that only high-quality materials enter the production process is critical for the overall integrity of the final product. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
IPQC occurs during the manufacturing stages, where operators monitor the processes and components at various intervals. This includes checking the accuracy of machining, the quality of welds, and the alignment of assembled components. Regular inspections help identify and address issues before they escalate. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
The FQC stage involves a comprehensive inspection of the finished tube exchangers. Testing methods may include pressure tests, thermal performance assessments, and visual inspections for defects. Documentation of these tests is crucial for verifying compliance with industry standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Tube Exchangers?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the performance and reliability of tube exchangers. These include:
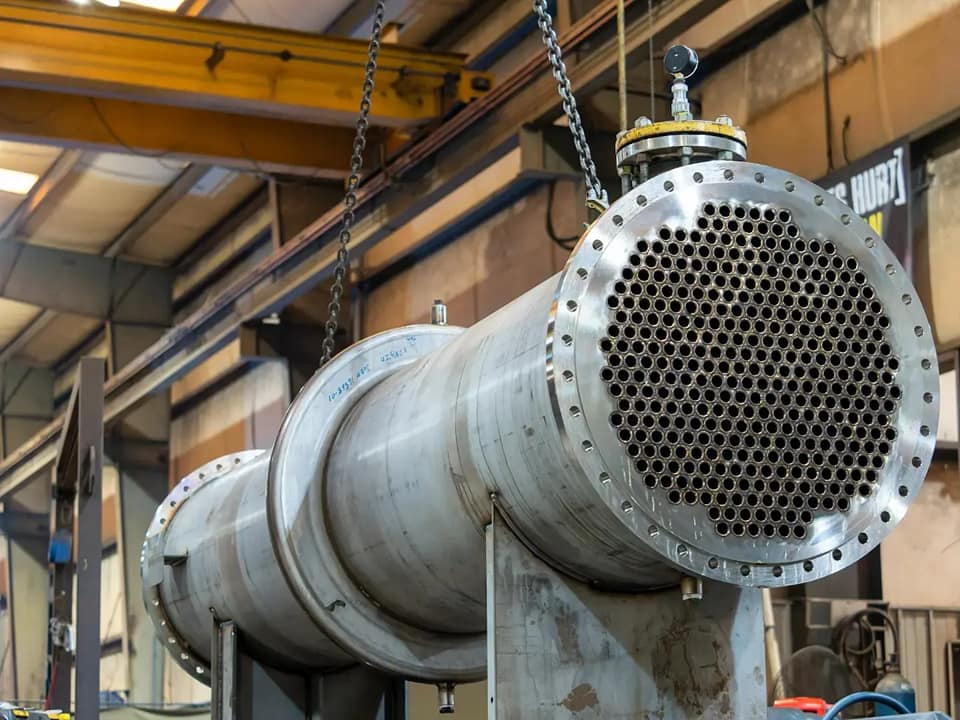
Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
-
Hydrostatic Testing:
This method involves filling the exchanger with water and pressurizing it to check for leaks. Hydrostatic testing is essential for confirming the structural integrity of the exchanger under operational pressures. -
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and radiographic testing are used to inspect welds and materials without causing damage. These methods help identify internal defects that could compromise the exchanger’s performance. -
Thermal Performance Testing:
This testing evaluates the exchanger’s efficiency in transferring heat under simulated operational conditions. It ensures that the product meets the thermal performance specifications outlined in its design.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits:
Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems. Buyers should evaluate the adherence to international standards and the implementation of QC checkpoints. -
Requesting Documentation:
Buyers should ask for quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports, test results, and certifications. This documentation provides transparency regarding the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly beneficial for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct thorough inspections themselves. -
Understanding Certification Nuances:
Buyers should be aware of the specific certification requirements in their regions. For instance, understanding the nuances of CE marking in Europe or API standards in the Middle East can help buyers make informed decisions about supplier selection.
By focusing on these aspects, B2B buyers can ensure they partner with manufacturers who prioritize quality in the production of tube exchangers, ultimately leading to better performance and reliability in their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tube exchanger’
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring tube exchangers effectively, this guide outlines a practical checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the right product and supplier for your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical as it directly impacts the efficiency and performance of the tube exchanger. Consider factors such as the type of fluids involved, the required temperature and pressure ratings, and the desired heat transfer efficiency. Be specific about the materials needed to combat corrosion or other environmental factors, ensuring they align with the intended application.
- Fluid Types: Identify whether the exchanger will handle liquids, gases, or slurries.
- Pressure and Temperature Requirements: Determine the maximum operational limits to prevent equipment failure.
Step 2: Research Industry Standards and Certifications
Understanding relevant industry standards is essential to ensure compliance and safety. Various standards, such as those from TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association) or ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers), dictate the design and manufacturing processes for tube exchangers.
- Certification Verification: Look for suppliers with certifications that validate their adherence to these standards, as this can significantly affect product reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. A robust evaluation process includes requesting company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This step is vital to ascertain the supplier’s reliability and experience in delivering high-quality products.
- Request Documentation: Ask for performance data and examples of past projects to gauge their expertise.
- Check Reviews: Look at online reviews and ratings to assess the supplier’s reputation in the market.
Step 4: Request Proposals and Quotes
After narrowing down your list of suppliers, request detailed proposals and quotations. This step will provide insight into pricing structures, lead times, and any additional services offered, such as installation or maintenance support.
- Compare Offers: Analyze the proposals not just on price but also on service terms and warranty conditions.
- Clarify Inclusions: Ensure all necessary components, such as gaskets and insulation, are included in the quote.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Services
After-sales support can significantly impact the long-term performance of your tube exchanger. Determine what services the supplier offers post-purchase, including maintenance, spare parts availability, and technical support.
- Warranty Conditions: Understand the warranty terms and conditions to protect your investment.
- Service Availability: Confirm whether the supplier can provide timely support, especially in emergencies.
Step 6: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Evaluate potential risks associated with the procurement process, such as supply chain disruptions or quality inconsistencies. Identifying these risks early can help mitigate issues later.
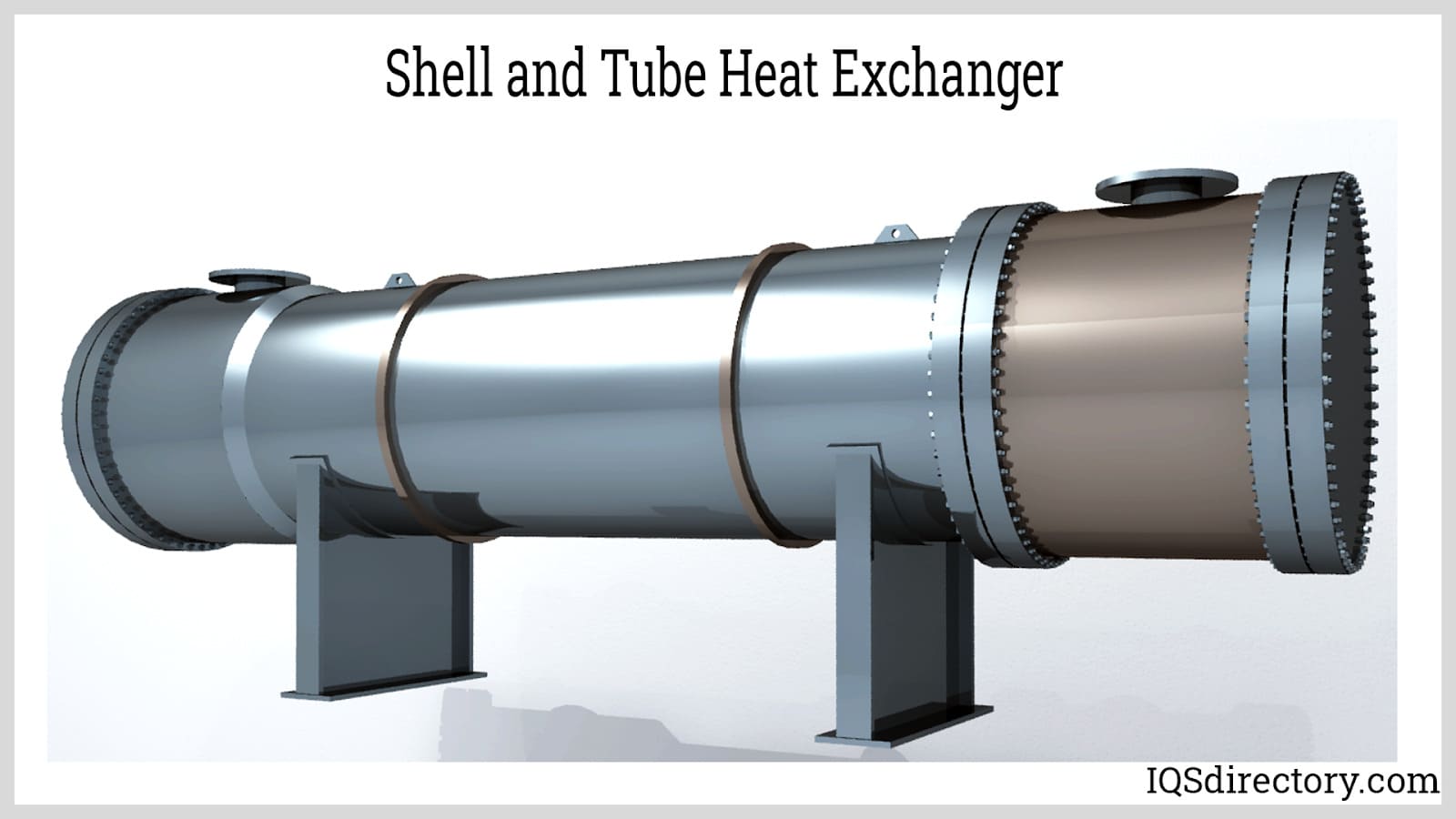
Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
- Contingency Plans: Discuss potential backup plans with suppliers to address possible delays or product failures.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Inquire about the supplier’s quality control measures to ensure product reliability.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once all evaluations are complete, finalize the purchase agreement with the chosen supplier. Ensure that all terms discussed are clearly documented, including delivery timelines, payment terms, and any conditions for returns or exchanges.
- Legal Review: Have legal counsel review the agreement to protect your interests.
- Clear Communication: Establish clear lines of communication for ongoing interactions post-purchase.
By meticulously following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing tube exchangers with confidence, ensuring they select a product that meets their operational needs while partnering with a reliable supplier.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tube exchanger Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Tube Exchanger Sourcing?
When sourcing tube exchangers, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and supplier margins.
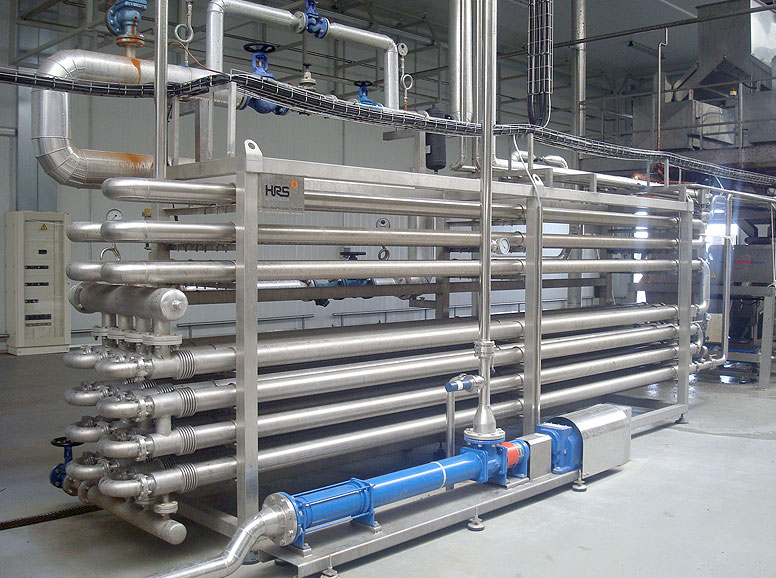

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and various alloys, each with different price points influenced by market availability and quality. Enhanced tubes or specialty alloys for high-performance applications typically incur higher costs.
-
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the manufacturing process and the region. Overhead expenses, including energy costs, maintenance, and facility operations, are also factored into the pricing. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, contributing to a more competitive price.
-
Tooling and Quality Control: Tooling refers to the equipment and tools used in the manufacturing process, which can be a significant upfront investment. Quality control is essential, especially for tube exchangers that must meet strict industry standards, adding to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely depending on the location of the supplier and the buyer. For international buyers, understanding the logistics costs—including shipping, customs duties, and insurance—is vital for calculating the total cost.
-
Supplier Margin: The margin that suppliers add to cover their risks and ensure profitability can differ based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s reputation.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Tube Exchanger Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of tube exchangers, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchasing can lead to significant cost savings, as suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ is essential for budgeting effectively.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized materials or manufacturing processes. It’s important to balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality and certifications (e.g., ASME, TEMA) can lead to increased pricing but are often necessary for compliance in certain industries. Buyers must weigh the cost against the potential risks of using lower-quality products.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and experience of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products and services but often provide better support and product quality.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can significantly impact logistics costs. Buyers should ensure they understand the terms related to shipping responsibilities, as this affects the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Tube Exchanger Prices?
Negotiation is a critical skill for B2B buyers looking to source tube exchangers efficiently. Here are some tips:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Before entering negotiations, conduct thorough research on market prices and benchmark against competitors to establish a fair price range.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and more favorable terms over time. Trust and communication can often lead to discounts and better service.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Factors like maintenance, energy efficiency, and lifespan can significantly affect overall costs.
-
Be Transparent: Sharing your needs and constraints with suppliers can lead to more tailored solutions and pricing. Transparency can foster collaboration and mutual benefits.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Tube Exchangers?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances can affect sourcing:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Be aware of how currency exchange rates can impact pricing. Consider locking in rates if a significant investment is required.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the products meet local regulations and standards, which can affect both price and availability.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances in negotiation styles and business practices can facilitate smoother transactions.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Remember About Pricing?
While the prices for tube exchangers can vary widely, understanding the cost components and pricing influencers is essential for making informed decisions. Buyers should approach negotiations strategically, keeping in mind total cost considerations and the unique challenges of international sourcing. Always seek clarity on pricing structures and remain adaptable to find the best solutions for your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tube exchanger With Other Solutions
In the realm of heat exchange solutions, selecting the right technology is crucial for optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness. Tube exchangers, renowned for their efficiency and versatility, face competition from various alternatives. Understanding these alternatives enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Tube Exchanger | Spiral Heat Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High thermal efficiency; versatile | Compact design; efficient for low flow | Excellent heat transfer at low pressure |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; long-term savings through efficiency | Higher upfront cost; lower operational costs | Lower initial cost; higher maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space; complex installation | Space-saving; easier to install | Simple installation; modular design |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection; accessible | Low maintenance; easy cleaning | Requires gaskets replacement; moderate upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Heavy industries; high-temperature applications | HVAC systems; food processing | Low to medium pressure applications; pharmaceutical |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Spiral Heat Exchangers?
Spiral heat exchangers are designed for applications where space is limited. Their compact nature allows for high thermal efficiency, especially in low flow scenarios, making them ideal for HVAC systems and food processing. However, the initial investment can be significantly higher than that of tube exchangers. While they require less maintenance due to fewer parts and a simpler cleaning process, their specialized design may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring high-pressure resistance.
How Do Plate Heat Exchangers Compare in Terms of Cost and Maintenance?
Plate heat exchangers offer a cost-effective solution for heat transfer, with a lower initial purchase price than tube exchangers. Their modular design simplifies installation and maintenance, but they do require regular gasket replacements, which can increase long-term operational costs. These exchangers excel in low to medium pressure applications, making them a popular choice in the pharmaceutical industry, though their efficiency can diminish in high-temperature scenarios.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Heat Exchange Solution?
When evaluating heat exchange technologies, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, including temperature and pressure conditions, space limitations, and budget constraints. Tube exchangers are ideal for heavy industries with high thermal demands, while spiral heat exchangers suit space-constrained environments. Plate heat exchangers are best for applications requiring moderate pressure and lower maintenance. By thoroughly assessing these factors, buyers can select the most appropriate solution that aligns with their operational goals and budgetary considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tube exchanger
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Tube Exchangers?
Understanding the technical specifications of tube exchangers is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure optimal performance and longevity in their applications. Here are several critical properties to consider:
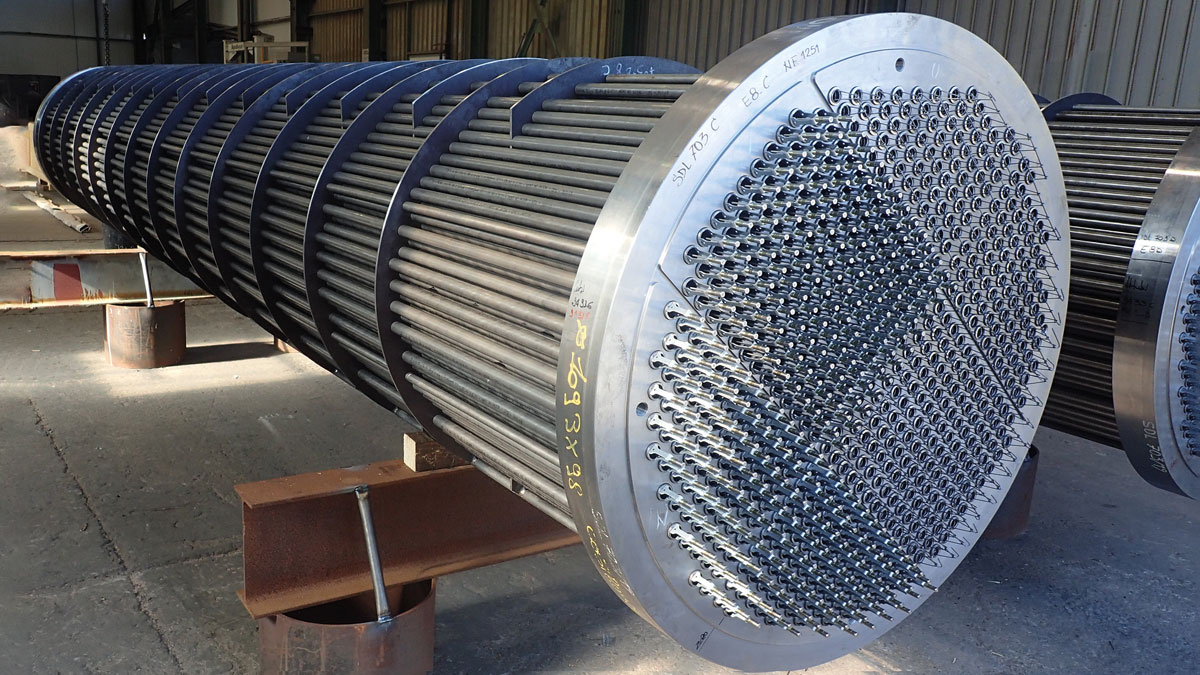

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
-
Material Grade
The material used in tube exchangers significantly affects their durability and performance. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and various alloys like nickel and titanium. Selecting the appropriate material depends on the working environment, including temperature, pressure, and the types of fluids being processed. For example, stainless steel is often preferred for its corrosion resistance, while copper is favored for its excellent thermal conductivity. -
Tolerances and Dimensions
Precision in dimensions and tolerances is essential for ensuring proper fit and function in applications. Tolerances dictate how much deviation from a specified dimension is acceptable. In tube exchangers, tight tolerances can minimize leakage and enhance heat transfer efficiency. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet specific dimensional requirements to avoid operational issues. -
Pressure Rating
Each tube exchanger comes with a designated pressure rating, indicating the maximum pressure it can withstand. This specification is vital for applications involving high-pressure fluids, as exceeding this limit can lead to catastrophic failure. Buyers must evaluate the expected operating conditions and choose a tube exchanger with an adequate pressure rating to ensure safety and reliability. -
Thermal Performance
The efficiency of heat transfer in tube exchangers is often influenced by the design of the tubes (e.g., plain, enhanced, or low-fin). Enhanced surface tubes can significantly improve thermal performance, making them suitable for applications where space and weight are constraints. Understanding the thermal performance metrics can help buyers select a tube exchanger that meets their specific heating or cooling needs. -
Flow Arrangement
Tube exchangers can feature various flow arrangements, such as counterflow, parallel flow, or crossflow. The choice of flow arrangement affects the heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop. Counterflow designs typically offer the highest efficiency, making them ideal for applications requiring maximum heat exchange. Buyers should consider the flow arrangement that best fits their operational requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Tube Exchanger Procurement?
Navigating the procurement process for tube exchangers requires familiarity with specific industry terminology. Here are several key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of tube exchangers, buyers may seek OEMs for replacement parts or custom designs that meet specific operational needs. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers who may need only a few units or require larger quantities for bulk pricing. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers negotiate better terms or identify suitable suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document requesting pricing and terms from suppliers. Buyers typically use RFQs to compare options and make informed purchasing decisions. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure that all necessary specifications are clearly communicated. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers ascertain who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby reducing the risk of unexpected costs. -
ASME Compliance
Compliance with American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of tube exchangers in various applications. Buyers should look for products that meet ASME requirements, particularly in industries like power generation and petrochemical processing.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing tube exchangers, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and safety.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tube exchanger Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Tube Exchanger Sector?
The global tube exchanger market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing energy efficiency demands and the rise of industrial applications across various sectors, including petrochemicals, power generation, and HVAC. Emerging economies in Africa and South America are particularly contributing to this growth, as industrialization accelerates and infrastructure investments expand. B2B buyers from regions such as Brazil and Vietnam are now prioritizing advanced heat exchanger designs that offer higher thermal efficiency and lower operational costs.
Recent technological advancements are reshaping sourcing strategies. Digital platforms and IoT-enabled devices are facilitating real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing the reliability of tube exchangers. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not only traditional shell and tube designs but also custom solutions that meet specific operational requirements. This shift towards customization is particularly prevalent in industries where process conditions are unique and demand tailored solutions.
Additionally, the trend toward modular designs is gaining traction, as these systems can be easily integrated into existing infrastructures, reducing installation costs and downtime. Sustainability is also influencing purchasing decisions, with buyers favoring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to energy-efficient products and sustainable practices. This is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks increasingly emphasize eco-friendly solutions.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Tube Exchanger Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount in the tube exchanger sector, as environmental impact assessments are becoming standard practice for B2B buyers. The manufacturing process for heat exchangers can be resource-intensive, and businesses are increasingly held accountable for their carbon footprints. To address this, many manufacturers are exploring sustainable materials and processes, such as utilizing recycled metals and eco-friendly coatings that enhance corrosion resistance while minimizing environmental harm.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining prominence. Buyers are more frequently requesting transparency regarding the sourcing of raw materials, especially in regions where mining and extraction practices may pose ethical concerns. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By opting for certified products, B2B buyers can ensure that their investments align with global sustainability goals and enhance their brand reputation.
Moreover, the focus on green technologies is influencing product development. Manufacturers are innovating to create energy-efficient heat exchangers that reduce waste and enhance thermal performance. This commitment to sustainability not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to a growing segment of environmentally conscious customers, making it a strategic differentiator in the competitive landscape.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Tube Exchangers in the B2B Context?
The evolution of tube exchangers can be traced back to the early 19th century when they were first utilized in steam engines. Over the decades, the technology has undergone significant transformations, adapting to the growing needs of various industries. Initially, these exchangers were primarily constructed from copper and iron, but advancements in metallurgy have introduced a wide range of materials, including stainless steel and specialized alloys, enhancing durability and performance.
By the mid-20th century, the demand for efficient heat transfer solutions surged, particularly in the petrochemical and energy sectors. The introduction of enhanced surface tube designs marked a pivotal shift, allowing for improved thermal performance in compact designs. Today, tube exchangers are integral to countless applications, from power generation to food processing, emphasizing their versatility and importance in modern industrial processes.
As B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the historical context of tube exchangers can provide valuable insights into current trends and future innovations, enabling them to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both operational goals and sustainability objectives.
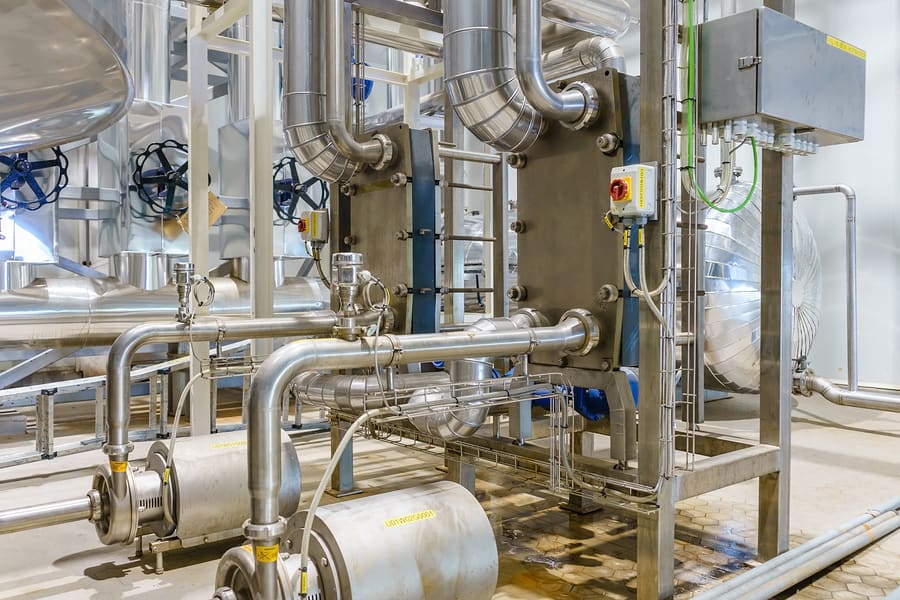

Illustrative image related to tube exchanger
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tube exchanger
-
How do I solve the issue of tube corrosion in heat exchangers?
Corrosion in tube exchangers can significantly impact performance and lifespan. To mitigate this, consider using materials resistant to corrosion, such as stainless steel or specialized alloys. Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to identify early signs of corrosion. Implementing proper fluid chemistry control can also minimize corrosive interactions. If corrosion has already occurred, replacing the tube bundle with a custom-designed solution may be necessary to ensure optimal performance and longevity. -
What is the best type of tube exchanger for high-temperature applications?
For high-temperature applications, shell-and-tube heat exchangers made from high-grade materials like titanium or nickel alloys are often the best choice. These materials can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures while maintaining structural integrity. Additionally, consider using enhanced surface tubes to improve heat transfer efficiency. Always consult with manufacturers to ensure the selected exchanger meets specific thermal and pressure requirements for your application. -
How can I ensure the quality of tube exchangers from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by vetting suppliers through industry certifications such as ASME or ISO standards. Request product samples and technical documentation to assess quality. It’s also beneficial to read customer reviews and case studies related to the supplier’s previous work. Establishing a clear communication channel for quality expectations and conducting factory audits can further enhance assurance regarding product quality. -
What customization options are available for tube exchangers?
Customization options for tube exchangers can include variations in materials, tube configuration (U-bend or straight), and specific dimensions to fit unique applications. Manufacturers may also offer enhanced tube designs for improved efficiency. Discussing your specific thermal requirements and operational conditions with the supplier can lead to tailored solutions that optimize performance for your particular use case. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing tube exchangers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the product. For standard models, MOQs may be low, allowing for smaller purchases. However, custom designs typically require higher MOQs due to tooling and setup costs. Always clarify MOQs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure they align with your purchasing capabilities. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with international suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms, consider options like letters of credit for added security, especially in international transactions. Standard practices may include a deposit upfront, followed by the balance upon delivery or after inspection. Ensure that terms are flexible enough to accommodate potential delays in shipping or production, and always read the fine print to understand any fees associated with payment methods. -
How can I manage logistics for importing tube exchangers?
Effective logistics management for importing tube exchangers involves selecting reliable freight forwarders who specialize in handling industrial equipment. Understand the shipping timelines and customs regulations for your country, particularly in regions like Africa or South America where procedures may vary. Consider using Incoterms to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties. Additionally, tracking shipments and maintaining open communication with your supplier can help avoid delays. -
What certifications should I look for in tube exchangers?
Certifications such as ASME, TEMA, and ISO are crucial indicators of quality and compliance in tube exchangers. ASME certification ensures that the equipment meets specific engineering standards, while TEMA standards are particularly relevant for heat exchangers in petrochemical applications. Additionally, check for compliance with local regulations that may apply in your region, as this can affect installation and operational safety.
Top 3 Tube Exchanger Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Emergent Coils – Custom & Replacement Tube Bundles
Domain: emergentcoils.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Emergent Coils offers custom and replacement tube bundles, including u-bend and straight tube designs. Key features include: average savings of 30-50% vs OEM, American-made with high-quality materials, quick shipping options (2-3 weeks standard, 1-2 days for expedited), and design capabilities for various types of tube bundles (U-tube, straight tube, enhanced tube, low-fin, lo-fin, integral tube b…
2. Thermopedia – Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Domain: thermopedia.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are popular for their flexibility in handling a wide range of pressures and temperatures. They are categorized into two main types: those used in the petrochemical industry (covered by TEMA standards) and those used in the power industry (such as feedwater heaters and condensers). A shell and tube exchanger consists of a cylindrical shell containing a bundle of tubes…
3. Armstrong – Tube Bundles & Heat Exchanger Supplies
Domain: boilersupplies.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Armstrong Tube Bundles for Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers, including:
– Armstrong “WS” Series Steam to Liquid Tube Bundle (In Stock)
– Armstrong “W” Series Liquid to Liquid Tube Bundle (In Stock)
– Armstrong Tube Bundle Replacement Gasket Set (In Stock)
– Heat Exchanger Tube Plugs (In Stock)
– Steel Boiler Tube Plugs (In Stock)
Features:
– Complete standard line of U-tube bundles ranging from 4″ di…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tube exchanger
The dynamic landscape of tube exchangers presents a wealth of opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways from this guide highlight the importance of selecting high-quality materials and designs tailored to specific operational needs. Understanding the nuances of tube configurations, such as U-bend versus straight tube bundles, can significantly enhance thermal efficiency and longevity.
Strategic sourcing is essential not only for reducing costs but also for ensuring compliance with international standards, which can enhance operational reliability. Buyers are encouraged to forge strong relationships with reputable suppliers who offer customization options, allowing for tailored solutions that meet unique application requirements.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative heat exchange solutions is expected to grow as industries prioritize sustainability and efficiency. As you explore procurement options, consider investing in advanced technologies and materials that can withstand challenging environments. By aligning your sourcing strategies with these trends, you can position your organization for success in the evolving global market. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operational efficiency and sustainability through strategic sourcing of tube exchangers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.