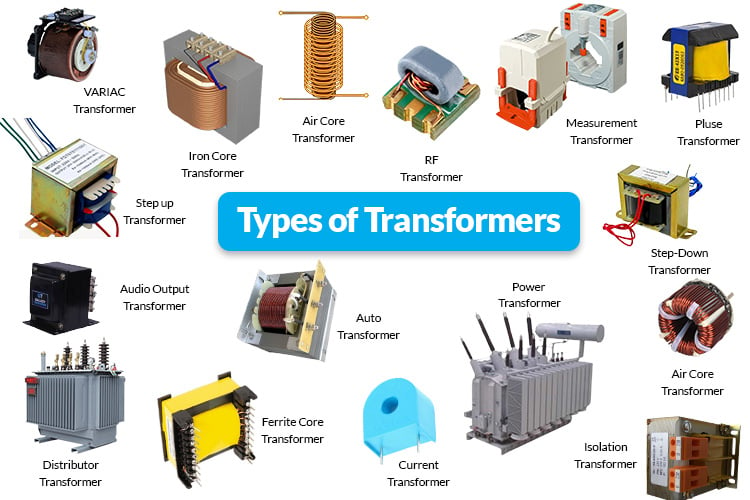
Choosing Your Transformers And Their Types: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for transformers and their types
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing the right transformers and their types is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their electrical systems. With the variety of options available, from liquid-filled to dry-type transformers, international B2B buyers often face the challenge of identifying which solution best fits their operational needs. This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify the complexities of the global transformer market, providing insights into the various types of transformers and their specific applications.
Throughout this guide, we will explore key categories, including substation, padmount, and pole mount transformers, alongside their unique benefits and ideal use cases. Moreover, we will address essential considerations such as supplier vetting processes, cost analysis, and installation requirements, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your strategic goals.
For B2B buyers from diverse regions—whether in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, including Germany and Brazil—this guide serves as an invaluable resource. By equipping you with actionable insights and expert recommendations, we empower you to navigate the complexities of transformer procurement, facilitating a smoother purchasing process and ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency. Let’s embark on this journey to unlock the potential of transformers in your business.
Understanding transformers and their types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid-Filled Transformers | Use dielectric fluid for cooling and insulation; rugged design | Outdoor installations, substations | Pros: Better heat dissipation; can handle overloads. Cons: Requires containment and maintenance. |
| Dry-Type Transformers | Air-cooled; no liquid; designed for indoor use | Commercial buildings, industrial facilities | Pros: No fluid, lower maintenance; safer for indoor use. Cons: Less effective in overload situations. |
| Padmount Transformers | Tamper-proof design; compact and low-profile | Urban areas, public facilities | Pros: Economic; easy installation; blends into surroundings. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Substation Transformers | Rugged tank design; equipped for high capacity | Heavy industrial zones, utility substations | Pros: High reliability; suitable for harsh environments. Cons: Requires more space; higher initial costs. |
| Autotransformers | Single coil design; cost-effective for small voltage adjustments | General industrial applications | Pros: Smaller footprint; economical for specific uses. Cons: Limited isolation; not suitable for all applications. |
What Are Liquid-Filled Transformers and Where Are They Used?
Liquid-filled transformers utilize a dielectric fluid for cooling and insulation, making them ideal for outdoor applications and substations. Their rugged design allows them to handle overload conditions effectively, which is crucial for businesses that require a reliable power supply. However, they do require containment systems and regular maintenance to prevent leaks, making them a significant consideration for businesses operating in environmentally sensitive areas.
How Do Dry-Type Transformers Function and What Are Their Applications?
Dry-type transformers are primarily air-cooled and designed for indoor environments. They are commonly used in commercial buildings and industrial facilities where safety and maintenance are paramount. With no liquid involved, they pose a lower risk of environmental contamination. However, their ability to manage overload situations is limited compared to liquid-filled transformers, so businesses should assess their specific power demands before choosing this option.

Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
What Makes Padmount Transformers Suitable for Urban Installations?
Padmount transformers are designed with a tamper-proof, compact design that makes them ideal for installation in urban areas and public facilities. Their low-profile appearance helps them blend into the environment, which is often a requirement for aesthetic reasons. Economically advantageous, they are easier to install than traditional transformers. However, their application is limited to specific scenarios, so businesses must ensure they meet their operational needs before purchasing.
Why Choose Substation Transformers for Heavy Industrial Use?
Substation transformers are built for high-capacity applications and are typically found in heavy industrial zones. Their rugged tank design and external monitoring capabilities make them suitable for harsh environments. While they offer high reliability, they require more space and come with higher initial costs. Businesses in sectors like manufacturing or energy should consider these transformers for their robust performance and ability to manage heavy loads.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Autotransformers?
Autotransformers feature a single coil design that provides a cost-effective solution for stepping voltages up or down within a small range. They are particularly useful in general industrial applications where isolation between primary and secondary circuits is not critical. While they are more economical and space-efficient, the lack of isolation can pose risks in certain applications. Companies should evaluate their specific voltage requirements and safety needs before opting for this transformer type.
Key Industrial Applications of transformers and their types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of transformers and their types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Distribution | Substation Transformers for power grid management | Enhances reliability and efficiency in electricity distribution. | Consider voltage ratings, cooling requirements, and installation space. |
| Manufacturing | Dry-Type Transformers for machinery and equipment power supply | Ensures stable voltage supply, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. | Evaluate load capacity, environmental conditions, and safety standards. |
| Telecommunications | Pole Mount Transformers for remote communication infrastructure | Supports uninterrupted service and network reliability. | Assess environmental resilience and maintenance access. |
| Construction | Liquid-Filled Transformers for site power supply | Provides robust power solutions for temporary construction needs. | Consider portability, cooling methods, and compatibility with local grids. |
| Renewable Energy | Autotransformers for wind and solar power systems | Optimizes energy conversion and enhances system efficiency. | Focus on power handling capacity, voltage regulation, and environmental suitability. |
How Are Transformers Used in Energy Distribution?
Substation transformers play a crucial role in managing the power grid, stepping down high voltages for distribution. This is essential for ensuring that electricity reaches homes and businesses safely and efficiently. For international buyers, especially in regions with developing infrastructure, the selection of transformers must consider local voltage standards and the capability to handle peak loads to avoid outages.
What Role Do Transformers Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, dry-type transformers are commonly used to provide stable power to machinery and equipment. This stability is vital for minimizing operational disruptions and enhancing productivity. Buyers should prioritize transformers with high thermal ratings and those designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of their facilities, especially in industrial sectors prevalent in South America and Africa.
Why Are Transformers Important for Telecommunications?
Pole mount transformers are integral to telecommunications infrastructure, particularly in remote areas. They ensure a reliable power supply for communication networks, which is critical for maintaining service continuity. B2B buyers in this sector should consider the transformers’ durability against weather conditions and ease of access for maintenance, as these factors can significantly affect operational reliability.
How Do Transformers Support Construction Projects?
Liquid-filled transformers are often deployed at construction sites to provide temporary power solutions. Their robust design makes them suitable for outdoor use, ensuring that construction activities can proceed without electrical interruptions. When sourcing these transformers, buyers should evaluate their portability, cooling systems, and compatibility with local power grids to ensure seamless integration.
What Are the Benefits of Autotransformers in Renewable Energy?
Autotransformers are increasingly utilized in renewable energy applications, such as wind and solar farms, to optimize energy conversion. They facilitate efficient voltage regulation, which is essential for integrating renewable sources into the grid. Buyers in this sector should focus on the transformer’s power handling capabilities and its adaptability to various environmental conditions, ensuring reliable performance in diverse geographical locations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘transformers and their types’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Choosing the Right Transformer Type for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when selecting the appropriate transformer type for their specific needs. This can stem from the wide variety of transformers available, such as liquid-filled, dry-type, padmount, or substation transformers. Buyers may be unsure of the operational environments, voltage requirements, and cooling needs of their applications, which can lead to costly mistakes or equipment failures. For instance, a buyer might mistakenly choose a dry-type transformer for an outdoor application where a liquid-filled transformer would be more appropriate, resulting in inadequate cooling and potential overheating.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment, considering factors such as application environment, load requirements, and safety regulations. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier is crucial. Suppliers can provide guidance on the specific advantages and limitations of each transformer type. Additionally, buyers should utilize resources like technical datasheets and installation guidelines, which often detail the performance characteristics and ideal use cases for different transformers. Collaborating with electrical engineers or consultants who specialize in power distribution can further ensure that the right transformer is selected, ultimately leading to optimized performance and reliability.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Transformer Efficiency and Energy Loss Concerns
The Problem: Another significant pain point for B2B buyers is the efficiency of transformers and the associated energy losses. In regions with unstable power supplies, such as certain parts of Africa and South America, inefficient transformers can lead to higher operational costs and energy waste. Buyers often find it challenging to understand the efficiency ratings of various transformer types and how these ratings impact their overall energy consumption and operational budgets.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize the selection of transformers with high efficiency ratings, typically above 98%, to minimize energy losses. To make informed decisions, it is essential to ask suppliers for detailed efficiency data, including loss calculations at different load levels. Implementing regular maintenance schedules can also enhance transformer performance and efficiency. Investing in smart monitoring solutions can help track energy consumption and identify inefficiencies over time. Furthermore, buyers can consider participating in energy efficiency programs that may offer incentives or rebates for upgrading to more efficient transformer technologies.
Scenario 3: Managing Installation and Space Constraints for Transformers
The Problem: Installation logistics and space limitations can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in urban areas where real estate is at a premium. Buyers may struggle to find suitable locations for larger transformers, such as substation transformers or pole-mounted units, which require specific installation conditions. This often leads to delays in project timelines and increased costs if modifications or additional infrastructure are needed.
The Solution: To effectively manage installation constraints, buyers should engage in detailed site assessments during the planning phase. This includes evaluating space availability, accessibility, and local regulations related to transformer installations. Buyers should consider compact transformer designs, such as encapsulated or padmount transformers, which are specifically engineered for limited spaces. Collaborating with installation experts who can provide tailored solutions and recommendations based on the site conditions can also streamline the installation process. Additionally, utilizing modular transformer systems can offer flexibility in design and installation, allowing for future scalability without significant alterations to existing infrastructure.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for transformers and their types
What Are the Key Materials Used in Transformers and Their Types?
When selecting materials for transformers, it is crucial to consider the properties that directly impact performance, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in transformer construction, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Transformer Windings?
Copper is widely regarded as the standard material for transformer windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 200°C, making it suitable for high-performance applications. Copper’s resistance to corrosion ensures longevity, especially in humid environments.
Pros: The primary advantage of copper is its superior electrical conductivity, which allows for smaller wire sizes and reduced energy losses. Its durability and resistance to fatigue make it ideal for transformers that experience frequent load changes.
Cons: The main drawback is cost; copper is generally more expensive than alternatives like aluminum. Additionally, copper is heavier, which can complicate manufacturing and installation.
Impact on Application: Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for applications requiring efficient power transmission, such as high-voltage transformers in industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN or IEC, which often specify copper for high-performance applications.
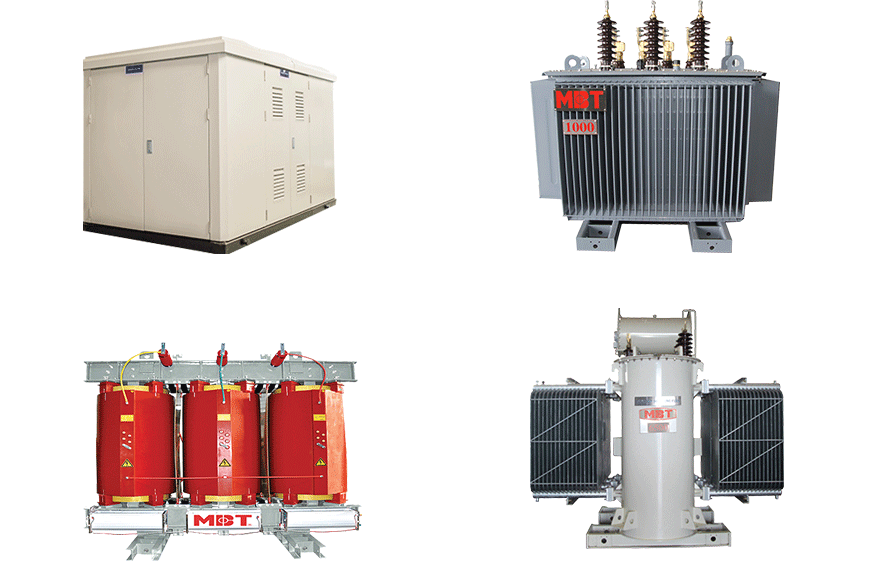
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Transformer Material?
Aluminum is another popular choice for transformer windings, known for its lightweight and cost-effectiveness. It has a lower conductivity than copper but is still suitable for many transformer applications, particularly in lower voltage scenarios.
Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
Pros: The key advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and lighter weight, which can lead to savings in transportation and installation. It is also resistant to corrosion when properly treated.
Cons: Aluminum’s electrical conductivity is about 60% that of copper, which may necessitate larger wire sizes to achieve the same performance. Its lower tensile strength also makes it less durable in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in distribution transformers and applications where weight is a critical factor, such as pole-mounted transformers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards that may favor copper over aluminum for certain applications. Compliance with ASTM standards is also essential for ensuring quality.
What Role Does Silicon Steel Play in Transformer Cores?
Silicon steel is commonly used for transformer cores due to its magnetic properties, which enhance efficiency by minimizing energy losses through hysteresis and eddy currents. The typical temperature rating for silicon steel in transformers is around 150°C.

Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
Pros: The primary advantage of silicon steel is its high magnetic permeability, which improves the efficiency of transformers. It also has good mechanical properties, allowing for robust core designs.
Cons: Silicon steel can be more expensive than non-silicon alternatives, and its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring careful handling to avoid damage.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel is essential in power transformers and distribution transformers where efficiency is critical, particularly in high-load scenarios.
Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the silicon steel used complies with international standards like JIS or ASTM, especially when sourcing from different regions.
Why Is Resin Used in Dry-Type Transformers?
Resin is often used in dry-type transformers as an insulating material, particularly in encapsulated transformers. It provides excellent electrical insulation and mechanical protection, withstanding temperatures up to 220°C.
Pros: The key advantage of resin is its ability to offer superior insulation and protection against environmental factors, making it ideal for harsh conditions. It is also non-toxic and environmentally friendly.

Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
Cons: The main disadvantage is the higher manufacturing complexity and cost associated with resin-encapsulated transformers compared to traditional designs.
Impact on Application: Resin is particularly beneficial in urban environments where space is limited and environmental conditions can be challenging, making it suitable for submersible and network transformers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that resin materials meet local environmental regulations and standards, particularly in regions with stringent safety requirements.
Summary Table of Transformer Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for transformers and their types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-voltage transformers | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Distribution transformers | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower conductivity and tensile strength | Medium |
| Silicon Steel | Power and distribution transformers | High magnetic permeability | More expensive and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Resin | Dry-type transformers (encapsulated) | Excellent insulation and environmental protection | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials used in transformers, enabling informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for transformers and their types
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Transformers?
The manufacturing of transformers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the specific requirements for performance and reliability. The primary stages of transformer manufacturing include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Are Materials Prepared for Transformer Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the foundational step in transformer manufacturing. It begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, which typically include electrical steel for the core, copper or aluminum for windings, and dielectric fluids for liquid-filled transformers. Suppliers must adhere to strict quality standards to ensure that these materials have the necessary electrical and thermal properties.
Electrical steel sheets are cut and treated to reduce losses due to eddy currents. For copper and aluminum, careful attention is paid to the purity and conductivity of the materials. Insulation materials, such as Kraft paper or epoxy resin, are also prepared to ensure they can withstand the operational temperatures and electrical stresses within the transformer.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Transformer Manufacturing?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves shaping the core and windings. The core is typically constructed from laminated sheets of electrical steel, which are stacked to minimize magnetic losses. Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and precision punching are employed to ensure accurate dimensions and reduce material waste.
For windings, either copper or aluminum wire is wound around the core. The winding process must be performed with precision to ensure proper electrical characteristics. Techniques such as automatic winding machines are often utilized to maintain consistent tension and alignment, which are crucial for the performance of the transformer.
How Is the Assembly Process Carried Out in Transformer Manufacturing?
After forming, the next step is assembly. This process involves integrating the core and windings into a complete transformer unit. For liquid-filled transformers, the core and windings are placed into a sealed tank, which is then filled with dielectric fluid. This fluid serves both as an insulator and a coolant.
During assembly, various components such as terminals, bushings, and tap changers are added. Quality control measures are critical at this stage, as any misalignment or improper installation can lead to performance issues or failures in the field.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Transformer Manufacturing?
The finishing stage focuses on ensuring the transformer is ready for deployment. This includes applying protective coatings, conducting electrical tests, and implementing safety measures. Transformers may undergo a vacuum drying process to remove moisture from the windings, which is essential for long-term reliability.
Final assembly involves attaching all necessary labels, certifications, and documentation. This stage is crucial for ensuring compliance with international standards and industry regulations, making it easier for B2B buyers to validate the quality and safety of the product.
What International Standards and Quality Control Measures Are Important in Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in transformer manufacturing. International standards such as ISO 9001 set the framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers adhere to best practices throughout the production process. For transformers, industry-specific certifications like CE and API are also essential, particularly in regions such as Europe and the Middle East.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Transformer Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints during the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, regular inspections are conducted to monitor adherence to specifications. This includes dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, transformers undergo rigorous testing, including dielectric strength tests, temperature rise tests, and short-circuit tests. These tests verify that the transformer operates within its designed parameters.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. There are several effective methods to verify QC practices:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. This firsthand evaluation can identify potential risks and ensure compliance.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports from suppliers can provide insights into their testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and product quality. This is particularly valuable for international transactions, where buyers may be unfamiliar with local practices.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in verifying the quality and compliance of transformers. Differences in regulations, standards, and certifications can complicate procurement processes.
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Buyers must familiarize themselves with the relevant standards in their region, such as IEC standards in Europe or ANSI standards in the U.S. Understanding these differences can help in selecting suppliers that meet local compliance requirements.
-
Documentation and Certification: Ensure that all transformers come with appropriate certification documents. This includes test reports, compliance certificates, and warranty information, which are crucial for legal and operational purposes.
-
Cultural and Language Considerations: Effective communication is vital. Buyers should ensure that suppliers can provide documentation and support in a language they understand, which can help prevent miscommunications regarding specifications and requirements.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing transformers, ultimately ensuring that they select reliable suppliers capable of meeting their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘transformers and their types’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of transformers can be a complex process, particularly for international B2B buyers. This step-by-step checklist is designed to streamline your sourcing journey, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and compliance requirements. Whether you’re looking for liquid-filled or dry-type transformers, following these steps will help you select the right equipment and supplier for your project.
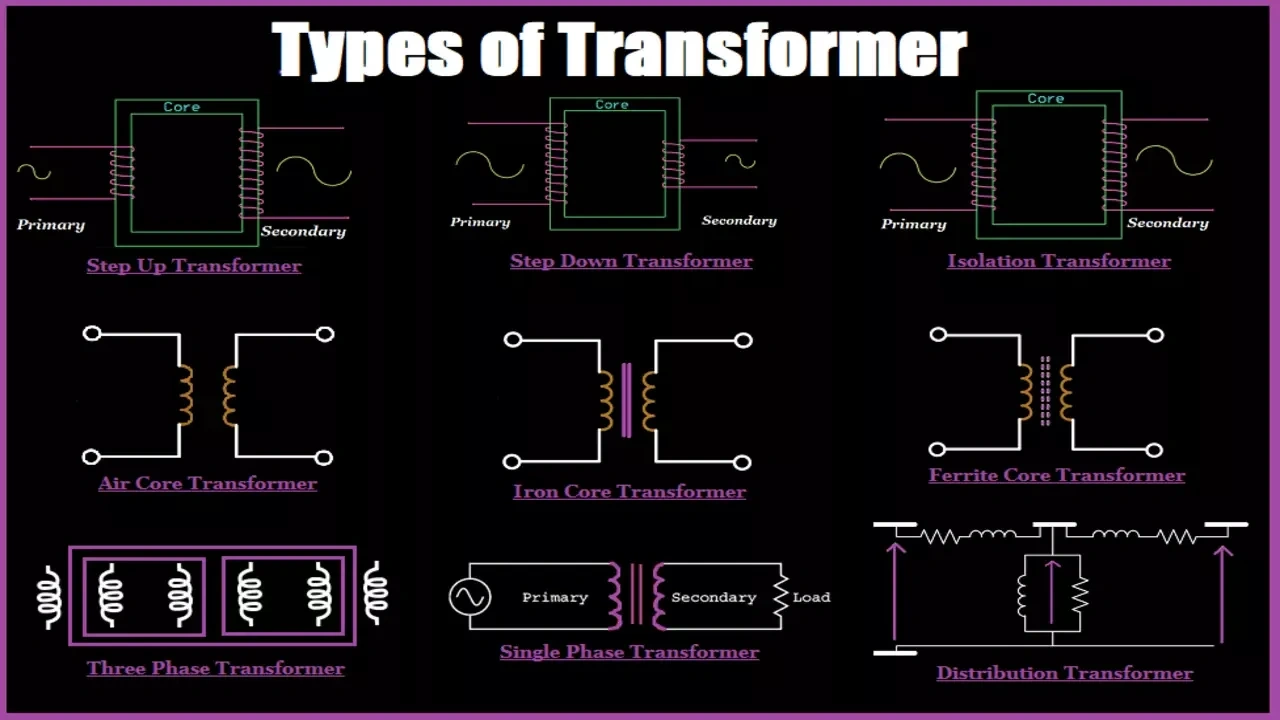
Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes voltage levels, phase configurations, and specific applications for the transformers, such as whether you need substation, padmount, or pole mount transformers. Precise specifications will help eliminate options that do not meet your needs and facilitate better communication with suppliers.
Step 2: Research Different Transformer Types
Understanding the various types of transformers is crucial for making an informed choice. Familiarize yourself with the differences between liquid-filled and dry-type transformers, as well as specific models like cast coil or autotransformers. Each type serves different environments and applications, so knowing their advantages will aid in selecting the most suitable option for your project.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and references from clients in similar industries. Pay attention to their experience with international buyers and their ability to meet specific regional regulations, especially if you are sourcing from Africa, South America, or the Middle East.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure the supplier holds necessary certifications for quality and safety, such as ISO or IEC compliance.
- Review Product Availability: Confirm that the supplier has a reliable inventory and can provide timely delivery.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that break down pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty options. A comprehensive quote allows for better comparison and understanding of what is included in the price. Be wary of unusually low quotes, as they may indicate compromises on quality or service.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Inquire about the after-sales support that suppliers offer. This includes installation guidance, maintenance services, and access to technical support. Reliable after-sales service can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the longevity of your transformers.

Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
- Training Options: Check if the supplier provides training for your staff on the operation and maintenance of the transformers.
- Spare Parts Availability: Ensure that the supplier can provide spare parts in case of future repairs.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Reputation and Reliability
Investigate the reputation of your selected suppliers through reviews, case studies, and industry feedback. Engage with other businesses that have previously worked with them to gauge their reliability and responsiveness. A supplier with a strong track record is more likely to deliver quality products and service.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Agreement
Finally, negotiate the terms of your agreement, focusing on payment conditions, delivery schedules, and any warranties. Make sure to clarify all aspects of the transaction to avoid misunderstandings. A well-structured agreement will protect your interests and ensure a smooth procurement process.
By following these steps, you can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing transformers and ensure that your procurement aligns with your operational needs and business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for transformers and their types Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Transformer Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of transformers is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. Copper and aluminum are common for winding, with copper being more expensive but offering better conductivity. The dielectric fluids used in liquid-filled transformers also add to the material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the manufacturing of transformers. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographical location, with higher costs typically in Europe compared to regions like South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, maintenance, and factory management. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific transformer designs can be a significant upfront investment. However, this cost is often amortized over large production runs, making it less impactful per unit in high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are vital to ensure reliability and compliance with international standards. This process can add to the overall cost but is crucial for minimizing failures and ensuring long-term operational efficiency.
-
Logistics: Shipping transformers involves considerable logistics costs, especially for international buyers. These include freight charges, insurance, and potential tariffs, which can vary based on the destination.
-
Margin: Suppliers add a profit margin that varies by company, market conditions, and competition. Understanding this margin is essential for buyers to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Transformer Procurement?
Several factors influence transformer pricing, making it essential for buyers to consider these elements during procurement:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom transformers designed for specific applications may incur higher costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected expenses later.
-
Material Choices: The selection of materials impacts both performance and price. Buyers must balance cost with the desired quality and durability.
-
Quality Certifications: Transformers that meet international standards (like ISO or IEC certifications) may carry a premium price. However, investing in certified products can reduce long-term risks and maintenance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect overall costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Transformer Prices?
For B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets, negotiating transformer prices can lead to significant savings. Here are some strategic tips:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing prices and competitor offerings. This knowledge empowers buyers during negotiations.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price, but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, operation, and potential downtime. A higher initial cost may be justified by lower operational costs.
-
Leverage Relationships: Build long-term relationships with suppliers to secure better pricing and terms. Loyalty can often lead to discounts or priority service.
-
Flexibility in Specifications: If possible, be open to alternative specifications that can lower costs without compromising essential performance metrics.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce logistics costs and lead to faster delivery times.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for transformers can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and changes in labor costs. It is advisable for buyers to seek multiple quotes and conduct due diligence to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing transformers and their types With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Transformers
In the realm of electrical distribution and power management, transformers play a pivotal role in stepping voltage up or down to meet specific operational needs. However, as technology evolves, several alternative solutions have emerged that can also address voltage regulation and power management. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking for cost-effective, efficient, and suitable solutions for their unique applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Transformers And Their Types | Voltage Regulators | Power Converters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Highly efficient in voltage transformation; suitable for various applications | Effective for maintaining voltage levels; less efficient at large scales | Versatile; can convert AC to DC and vice versa; high efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment; long-term cost-effective due to durability | Generally lower upfront costs; ongoing operational costs for regulation | Can be expensive, especially for high-capacity systems; ROI can vary |
| Ease of Implementation | Installation can be complex and requires specific site preparation | Easier to install; often requires minimal infrastructure changes | Installation can be technical, especially for large systems; may require specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance checks; robust and durable | Minimal maintenance; may require occasional calibration | Regular maintenance needed; can be complex depending on the system |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial applications requiring voltage transformation | Best for applications needing consistent voltage levels, such as sensitive electronics | Suitable for renewable energy systems, data centers, and applications needing different voltage types |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are Voltage Regulators and How Do They Compare?
Voltage regulators serve the essential function of maintaining a constant voltage level within a power system. They are particularly effective in environments where voltage fluctuations can adversely affect sensitive equipment. The main advantage of voltage regulators is their lower initial investment and ease of installation compared to transformers. However, they may not be suitable for large-scale applications where significant voltage step-up or step-down is required. In such cases, their performance could diminish, leading to inefficiencies.
How Do Power Converters Function as an Alternative?
Power converters, which include devices like inverters and rectifiers, are designed to change the form of electrical power from AC to DC or vice versa. They are highly versatile and can be used in various applications, including renewable energy systems and electric vehicle charging stations. While power converters can provide high efficiency, their cost can be significant, especially for high-capacity systems. Furthermore, installation can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate electrical solution for your business, it’s essential to evaluate your specific requirements against the characteristics of transformers and their alternatives. Transformers remain a robust choice for applications requiring reliable voltage transformation, while voltage regulators may serve well for systems needing consistent voltage levels. Power converters offer versatility for modern energy solutions but come with their own set of complexities. By carefully analyzing performance, cost, implementation ease, maintenance needs, and best use cases, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for transformers and their types
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Transformers?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of transformers is crucial for B2B buyers, as these properties can significantly affect performance, reliability, and overall cost-effectiveness. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the transformer can handle without breaking down. This specification is vital for ensuring compatibility with the electrical systems in which the transformer will operate. An incorrect voltage rating can lead to equipment failure and safety hazards, making it imperative for buyers to verify that the transformer meets their operational requirements. -
Power Rating (kVA)
Measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA), the power rating specifies the maximum load the transformer can supply. This rating is crucial for determining the capacity needed for specific applications, whether in industrial settings or commercial buildings. Selecting a transformer with an inadequate power rating can result in overheating and reduced lifespan, while an oversized unit may lead to unnecessary costs. -
Efficiency (%)
Transformer efficiency reflects the ratio of output power to input power, usually expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency means lower energy losses during operation, which is particularly important for long-term operational costs. B2B buyers should prioritize transformers with high efficiency ratings to enhance energy savings and reduce environmental impact. -
Temperature Rise (°C)
This specification indicates the maximum temperature increase above ambient conditions that the transformer can tolerate during operation. Understanding temperature rise is vital for ensuring the transformer operates within safe limits, preventing premature failures. Buyers should assess the cooling mechanisms in place, especially in regions with extreme climates. -
Insulation Class
The insulation class defines the thermal endurance of the transformer’s insulating materials. Each class (e.g., A, B, F, H) corresponds to a different maximum temperature rating. Choosing the appropriate insulation class is essential for ensuring reliability and longevity, particularly in environments with fluctuating temperatures. -
Dielectric Strength (kV)
Dielectric strength measures the electrical insulation’s ability to withstand high voltage without breakdown. This property is critical for safety and performance, particularly in high-voltage applications. A transformer with high dielectric strength ensures minimal risk of insulation failure, which can lead to catastrophic failures and safety hazards.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Transformer Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry-specific terminology can facilitate smoother negotiations and purchasing processes. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of transformers, especially when considering custom solutions. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their procurement strategies and budget accordingly. For international buyers, understanding MOQ can also impact shipping and inventory management. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific goods or services. This term is crucial in the B2B context as it initiates the procurement process and allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers efficiently. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and tariffs, ensuring a clear understanding of obligations and reducing the risk of misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning, especially in industries where timely delivery is critical for operational success. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the performance and reliability of the transformer. Awareness of warranty terms can significantly influence purchasing decisions, providing buyers with peace of mind regarding product durability and support.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimizing their procurement strategies and enhancing operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the transformers and their types Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Transformers Market for International Buyers?
The global transformers market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing energy demands and infrastructure development in emerging economies. In Africa and South America, urbanization and industrialization are prompting substantial investments in electrical infrastructure, leading to a surge in demand for various types of transformers, including distribution and substation transformers. Additionally, the Middle East’s focus on diversifying its energy sources, alongside Europe’s stringent regulations on energy efficiency, is shaping market dynamics.
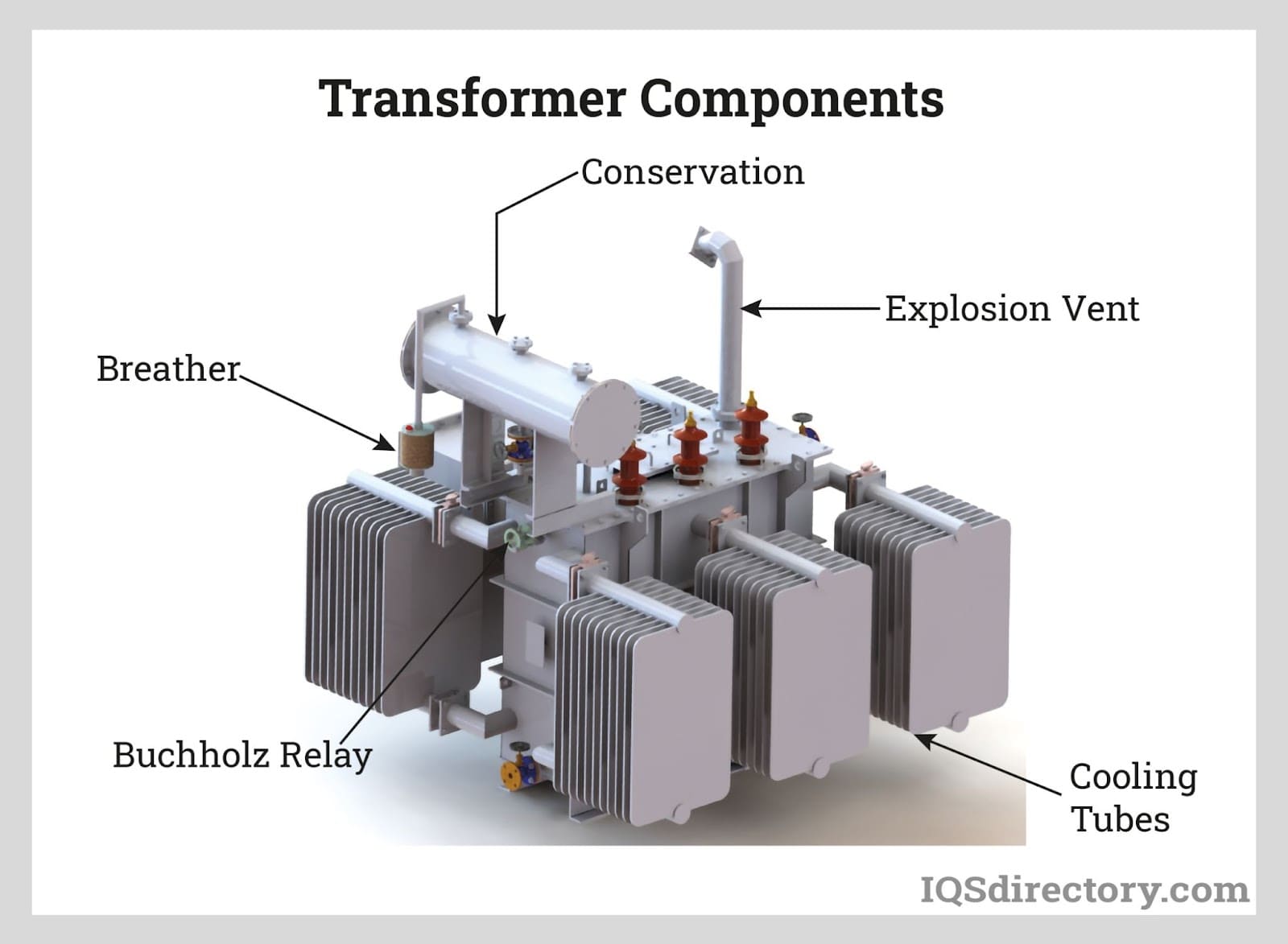
Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
Emerging technologies are also influencing sourcing trends. The integration of smart grid technology is enhancing transformer efficiency and reliability, making it essential for B2B buyers to source transformers that are compatible with these advancements. Digital platforms for procurement are becoming increasingly popular, allowing international buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and compare products effectively. Moreover, the growing trend towards modular transformers offers flexibility in installations, catering to diverse industrial needs.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Transformers Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the transformers sector, as both manufacturers and buyers recognize the environmental impact of production and operation. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of environmentally friendly materials and processes in transformer production. The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated; buyers are now more vigilant about sourcing from companies that prioritize labor rights and environmental stewardship.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish credibility in the global market. Additionally, the adoption of green materials, such as recyclable or bio-based insulation, is on the rise. This shift not only helps reduce the carbon footprint of transformers but also meets the growing demand from consumers and regulators for greener products.
What Is the Historical Context Behind Modern Transformers?
The evolution of transformers dates back to the late 19th century, with the invention of the first practical transformer by Hungarian engineer Ottó Bláthy. Initially, transformers were used primarily in telegraph systems, but their application expanded rapidly with the advent of electrical power distribution. The development of alternating current (AC) systems allowed transformers to become integral to electricity distribution networks, facilitating the long-distance transmission of power.

Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
Over the decades, advancements in materials and technology have led to more efficient and compact transformer designs, catering to diverse applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Today, the market is characterized by a variety of transformer types, including liquid-filled and dry-type transformers, each tailored to specific operational needs and environments. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that shape current offerings and future innovations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of transformers and their types
-
How do I choose the right transformer for my application?
Choosing the right transformer involves understanding your specific voltage requirements, load conditions, and environmental factors. Start by identifying whether you need a liquid-filled or dry-type transformer based on your installation setting—outdoor or indoor. Consider the voltage levels you need, the power capacity (kVA), and any specific features like weather resistance or space constraints. Consulting with a transformer manufacturer can provide tailored recommendations based on your unique operational needs. -
What is the best type of transformer for outdoor installations?
For outdoor installations, liquid-filled transformers, such as padmount transformers, are typically the best choice due to their durability and tamper-proof design. They effectively dissipate heat and are better equipped to handle overload situations. If space is a constraint, substation transformers can also be used in outdoor settings, especially in industrial areas. Always ensure that the selected transformer complies with local regulations and environmental standards. -
How do I vet a transformer supplier for international purchases?
Vetting a transformer supplier involves multiple steps. First, check their industry reputation and customer reviews to gauge reliability. Request certifications, such as ISO or IEC standards, to ensure compliance with international quality standards. It’s beneficial to ask for references from other businesses in your region. Finally, consider visiting their facilities or arranging a virtual meeting to discuss their manufacturing processes, quality assurance measures, and customer support capabilities. -
What customization options are available for transformers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for transformers to meet specific project requirements. Common customizations include altering voltage ratings, adjusting physical dimensions, and adding specialized insulation materials for harsh environments. Some suppliers may also provide options for integrated monitoring systems or enhanced cooling solutions. Discuss your specific needs with the supplier early in the design process to ensure optimal performance and compliance with local regulations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for transformers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for transformers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the type of transformer being ordered. Generally, MOQs range from one unit for standard products to larger quantities for custom designs. It’s advisable to inquire directly with suppliers about their MOQs, as some may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or specific project needs, especially in international transactions. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing transformers internationally?
Payment terms for international transformer purchases can vary widely depending on the supplier and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and the balance upon delivery. Some suppliers may also accept letters of credit or escrow services for added security. Always clarify payment terms in your contract to avoid any misunderstandings and ensure compliance with international trade regulations. -
How can I ensure quality assurance during transformer procurement?
To ensure quality assurance during transformer procurement, request detailed documentation from the supplier, including test reports and certifications. Establish clear quality standards and specifications in your purchase agreement. It may also be beneficial to arrange for third-party inspections or audits of the manufacturing process. Regular communication with the supplier throughout production can help address any potential quality issues before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for transformer shipments?
Logistics for transformer shipments involve several key considerations. First, evaluate the shipping methods available, including ocean freight for large units or air freight for expedited delivery. Understand the customs regulations in your country to ensure compliance and avoid delays. Additionally, consider the packaging requirements to protect the transformers during transit, and ensure you have a clear plan for installation upon arrival, including any necessary equipment or personnel.
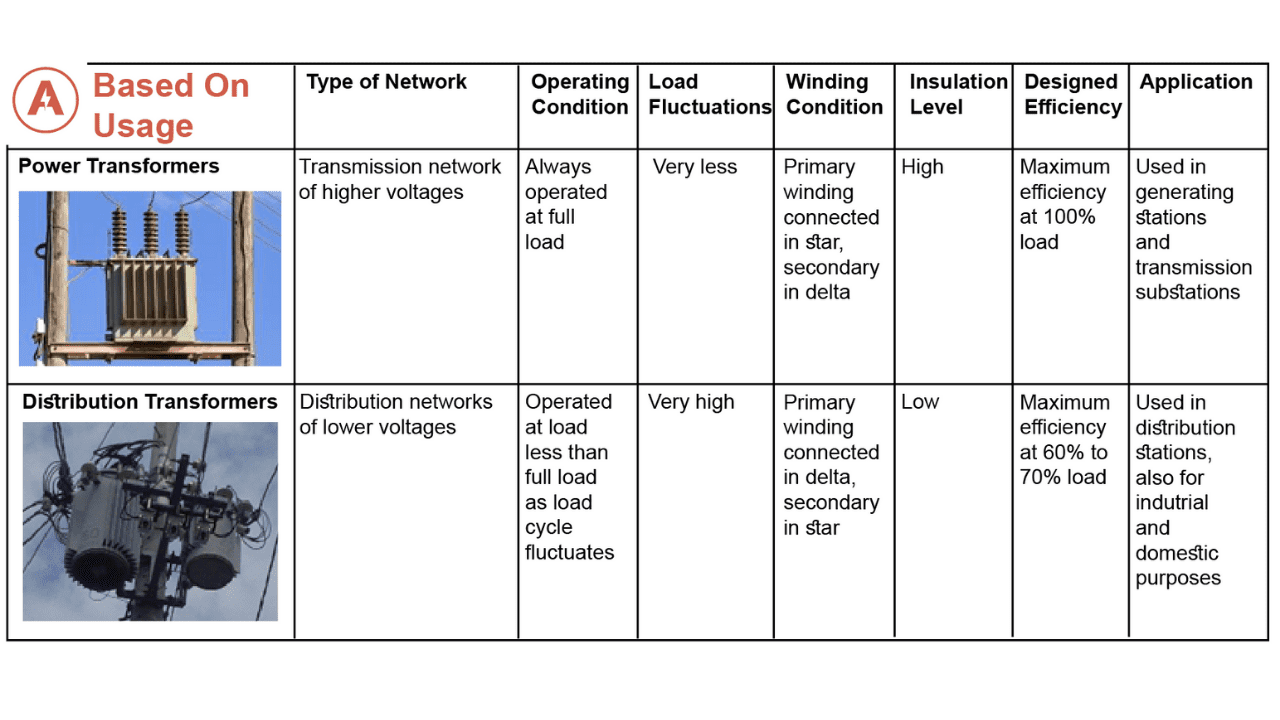
Top 8 Transformers And Their Types Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Maddox – Types of Transformers
Domain: maddox.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers: 1. Padmount Transformers: a. 3-Ph Padmount Transformer b. 1-Ph Padmount Transformer c. Polemount Transformers 2. Substation Transformers 3. Dry-Type Transformers: a. Low Voltage Dry-Type Transformers b. Medium Voltage Dry-Type Transformers c. Cast Coil Transformers 4. Mini Power Centers 5. Switchgear: a. Metal-Enclosed Switchgear b. Pad-Mounted Switchgear
2. Electronics Tutorials – Transformers
Domain: electronics-tutorials.ws
Introduction: Transformers are electrical devices consisting of two or more coils of wire used to transfer electrical energy by means of a changing magnetic field. They have no internal moving parts and are typically used to change voltage levels for energy transfer through electromagnetic induction. Transformers operate on the principle of Mutual Induction, linking two or more electrical circuits through a com…
3. Vietnam Transformer – Key Types of Transformers
Domain: vietnamtransformer.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Types of transformers based on core design: Core Type Transformer, Shell Type Transformer, Berry Type Transformer. Types based on voltage conversion: Step Up Transformer, Step Down Transformer. Types based on purpose: Power Transformer, Distribution Transformer, Isolation Transformer, Instrument Transformers (Current Transformer, Potential Transformer). Types based on windings: Two Winding Transfo…
4. Monolithic Power – Distribution Transformers
Domain: monolithicpower.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Distribution transformers play a crucial role in electrical power distribution, carrying out the final voltage transformation stage before delivering electrical energy to the end user. They reduce high voltage electrical power transferred over long distances to lower voltage levels suitable for commercial, industrial, and residential settings. Characteristics include operation at lower voltage lev…
5. Byju’s – Transformers Explained
Domain: byjus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The transformer is a device that steps up or steps down voltage, widely used in the distribution and transmission of alternating current power. It operates on the principles of electromagnetic induction and mutual induction. Key types include: 1. Step-up Transformer: Increases output voltage. 2. Step-down Transformer: Decreases output voltage. Transformers can also be classified based on core medi…
6. UTB Transformers – Power Transformers
Domain: utbtransformers.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Power transformers are essential components of electric infrastructure, converting electrical energy from one circuit to another without moving parts. They can modify voltage and current levels, with key types including: 1. Step Up Transformers: Convert low-voltage, high-current power to high-voltage, low-current power, commonly used at power generation sources. 2. Step Down Transformers: Convert …
7. Elprocus – Types of Transformers
Domain: elprocus.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Types of Transformers: Step-Up Transformer, Step-Down Transformer, Air-Core Transformer, Iron Core Transformer, Two Winding Transformer, AutoTransformer, Power Transformer, Distribution Transformer, Potential Transformer, Power Transformer, 1-ϕ Transformer, 3-ϕ Transformer, Autotransformer. Applications: Power generation, distribution, transmission, and utilization of electrical power.
8. Electrical4U – Power Transformers
Domain: electrical4u.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Power Transformer Definition: A static device that transfers electrical energy between circuits without changing frequency, using electromagnetic induction. Voltage Adjustment: Modifies voltage levels for energy efficiency and safety in power transmission and distribution. Types: Step-up, step-down, single-phase, and three-phase transformers. Applications: Essential in power generation, transmissi…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for transformers and their types
In the dynamic landscape of electrical infrastructure, understanding the diverse types of transformers is crucial for international B2B buyers. From liquid-filled to dry-type transformers, each variant serves specific applications, optimizing efficiency and reliability. Businesses must prioritize strategic sourcing to ensure they select the right transformer type that aligns with their operational needs, local regulations, and environmental conditions.
Investing in high-quality transformers not only enhances energy distribution but also minimizes downtime and maintenance costs. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this means leveraging local suppliers who understand regional challenges and can provide tailored solutions. Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers can also lead to better pricing and access to the latest technologies.
As the demand for sustainable and efficient energy solutions continues to grow, forward-thinking organizations should stay informed about advancements in transformer technology. Embracing innovative solutions today will position businesses for success in tomorrow’s competitive market. Take the next step in your sourcing strategy—connect with experts in the field to ensure your operations are powered by the most effective transformer solutions available.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
Illustrative image related to transformers and their types
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.