Choosing Your Toroidal Transformer Winding: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for toroidal transformer winding
Navigating the complexities of sourcing toroidal transformer winding can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With the increasing demand for efficient and compact transformer solutions, understanding the nuances of various transformer types, their applications, and the best practices for supplier vetting is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide aims to demystify the global market for toroidal transformers by providing a comprehensive overview of their operating principles, advantages, and a variety of applications across industries.
In this resource, we will explore the distinct types of toroidal transformers, including power, isolation, and three-phase transformers, highlighting their unique benefits such as reduced electromagnetic interference and improved energy efficiency. Additionally, we will delve into key factors influencing cost, including material quality and manufacturing processes, to help you identify the most cost-effective solutions tailored to your business needs.
Moreover, we will offer actionable insights on how to evaluate suppliers effectively, ensuring you partner with reputable manufacturers who meet your quality and compliance standards. By equipping you with this knowledge, our guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the toroidal transformer winding market confidently, ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency and supporting your business growth in a competitive landscape.
Understanding toroidal transformer winding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Primary Winding | One winding for primary input; simple design | Power supplies, audio equipment | Pros: Cost-effective, compact; Cons: Limited voltage flexibility. |
| Dual Primary Winding | Two primary windings allowing for multiple input voltages | Industrial machinery, telecommunications | Pros: Versatile voltage options; Cons: More complex design, higher cost. |
| Single Secondary Winding | One secondary winding; common for straightforward applications | Consumer electronics, small appliances | Pros: Simplified design; Cons: Limited output configurations. |
| Dual Secondary Winding | Two secondary windings for varied output voltages | Medical devices, specialized equipment | Pros: Increased functionality; Cons: More space required, potential for higher losses. |
| Split Winding | Windings divided into sections for better magnetic coupling | High-performance audio, precision instruments | Pros: Enhanced performance, reduced electromagnetic interference; Cons: Higher manufacturing complexity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Single Primary Winding Toroidal Transformers?
Single primary winding toroidal transformers feature a straightforward design with one winding dedicated to the primary input. This type is particularly suited for applications requiring a compact and cost-effective solution, such as power supplies and audio equipment. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the transformer’s voltage ratings and efficiency, as this type may have limited flexibility in output voltages, making it less ideal for applications with varying power requirements.
How Do Dual Primary Winding Toroidal Transformers Enhance Voltage Flexibility?
Dual primary winding transformers are designed with two separate windings, allowing them to accommodate multiple input voltages. This versatility makes them suitable for industrial machinery and telecommunications, where different voltage levels may be necessary for various components. Buyers should consider the additional complexity and cost associated with this design, but the ability to adapt to different voltage requirements can justify the investment in many scenarios.
What Are the Benefits of Using Single Secondary Winding Toroidal Transformers?
Single secondary winding toroidal transformers are characterized by having one winding for the secondary output, making them ideal for straightforward applications such as consumer electronics and small appliances. Their simplified design allows for efficient manufacturing and reduced costs. However, buyers should be aware of their limited output configurations, which may not meet the needs of more complex systems requiring multiple voltage outputs.
Why Choose Dual Secondary Winding Toroidal Transformers for Specialized Applications?
Dual secondary winding transformers provide two separate outputs, enabling varied voltage levels for specialized applications like medical devices and precision instruments. This increased functionality allows for the simultaneous powering of multiple devices or circuits, enhancing operational efficiency. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages of flexibility against the potential for higher losses and the need for more physical space in installations.
What Advantages Do Split Winding Toroidal Transformers Offer for High-Performance Needs?
Split winding toroidal transformers utilize a design that divides the windings into sections, improving magnetic coupling and overall performance. This configuration is particularly beneficial in high-performance audio systems and precision instruments, where reduced electromagnetic interference is crucial. While the enhanced performance comes at the cost of increased manufacturing complexity, B2B buyers in industries requiring high-quality power delivery may find this investment worthwhile for achieving superior operational results.
Key Industrial Applications of toroidal transformer winding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of toroidal transformer winding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Power conditioning in solar inverters | Improved efficiency and reduced size of power electronics | Certifications for safety and efficiency; local regulations |
| Audio Equipment | High-fidelity amplifiers | Enhanced sound quality and reduced electromagnetic interference | Custom specifications for voltage and current ratings |
| Medical Devices | Isolation in diagnostic imaging systems | Increased safety and reliability in critical applications | Compliance with medical standards and certifications |
| Industrial Automation | Control systems in robotic applications | Higher power density and better thermal management | Availability of custom windings and quick delivery options |
| Telecommunications | Power supplies for communication equipment | Reliable performance in demanding environments | Ruggedness and environmental ratings for outdoor applications |
How Are Toroidal Transformer Windings Used in Renewable Energy Applications?
In the renewable energy sector, toroidal transformer windings are crucial for power conditioning in solar inverters. These transformers help convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) suitable for the grid. The compact design of toroidal transformers allows for higher efficiency and reduced size of power electronics, making them ideal for space-constrained installations. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should consider sourcing transformers that meet local regulatory standards and certifications for safety and efficiency.
What Role Do Toroidal Transformers Play in Audio Equipment?
In the audio equipment industry, toroidal transformer windings are extensively used in high-fidelity amplifiers. Their design minimizes electromagnetic interference, which is crucial for maintaining sound clarity and quality. By delivering clean power with lower noise levels, these transformers enhance the overall audio experience. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should look for manufacturers that offer custom specifications to meet specific voltage and current ratings, ensuring compatibility with their audio systems.
Why Are Toroidal Transformers Essential in Medical Devices?
In medical devices, toroidal transformer windings are employed for isolation in diagnostic imaging systems, such as MRI and CT scanners. The isolation provided by these transformers is vital for patient safety and device reliability. They help mitigate risks associated with electrical noise and provide stable power supply, crucial in critical medical applications. Buyers in the healthcare sector should prioritize sourcing transformers that comply with stringent medical standards and certifications to ensure safety and performance.
How Do Toroidal Transformers Benefit Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, toroidal transformer windings are utilized in control systems for robotic applications. Their high power density and efficient thermal management capabilities enable the operation of complex machinery while minimizing space requirements. These transformers contribute to the reliability and longevity of automation systems. Buyers from regions with burgeoning industrial sectors, such as Africa and South America, should seek suppliers that offer customizable winding options and quick delivery times to maintain their production schedules.
What Advantages Do Toroidal Transformers Offer in Telecommunications?
In telecommunications, toroidal transformer windings are critical for powering communication equipment. They provide a reliable performance under demanding environmental conditions, essential for maintaining uninterrupted service. The compact design also supports space-efficient installations in telecom infrastructure. Buyers in this sector must consider sourcing transformers with ruggedness and environmental ratings suitable for outdoor applications, ensuring durability and reliability in various climates.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘toroidal transformer winding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Overheating Issues in Toroidal Transformers
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges B2B buyers face with toroidal transformer winding is overheating during operation. This can lead to efficiency losses, potential equipment failure, and increased maintenance costs. Users in regions with fluctuating voltage, such as parts of Africa and South America, often find that their transformers run hotter than expected, risking damage to the insulation and core materials.
The Solution: To mitigate overheating, it’s crucial to select a toroidal transformer that fits the application’s voltage and current requirements precisely. Buyers should look for transformers with higher thermal ratings and effective heat dissipation features. Additionally, installing temperature monitoring systems can help track operating conditions. Ensuring adequate ventilation and considering the ambient temperature during installation will also aid in maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Furthermore, consulting with manufacturers about custom winding options that optimize thermal performance can provide a tailored solution to specific applications.
Scenario 2: Inaccurate Voltage Outputs
The Problem: Another common issue is the inconsistency in voltage output from toroidal transformers, which can vary significantly depending on load conditions. This problem is particularly concerning for B2B buyers in industries that require precise voltage levels for sensitive equipment, such as medical or audio applications. Fluctuations can lead to equipment malfunction or even damage, resulting in costly downtime.
The Solution: To address voltage accuracy, buyers should prioritize transformers designed with regulated output capabilities. It’s advisable to work with manufacturers who offer detailed specifications on voltage tolerance and load variations. Implementing a feedback control system can also ensure that voltage remains stable across varying loads. Additionally, using transformers with multiple secondary windings allows for more flexible voltage options, accommodating diverse operational needs. Regular maintenance checks and adjustments can further ensure that the transformers continue to operate within their specified voltage ranges.
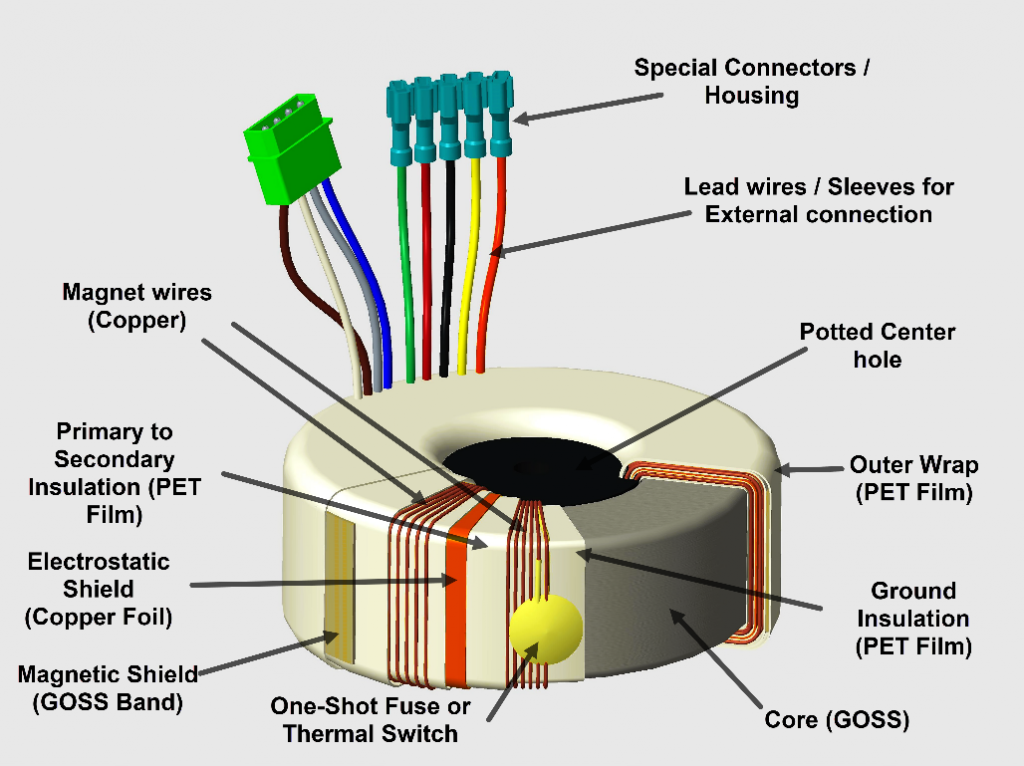
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
Scenario 3: Difficulties in Winding Modifications
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when attempting to modify the secondary windings of toroidal transformers to meet specific voltage requirements. This task can be daunting, especially for those without extensive technical expertise, and mistakes can lead to significant electrical issues or even equipment damage. Buyers may feel frustrated by the complexity of access to the windings and the risks associated with improper modifications.
The Solution: To simplify winding modifications, it’s advisable to collaborate with manufacturers who provide detailed documentation on their winding layouts. Buyers should inquire about transformers that feature accessible winding designs or consider custom solutions that allow for easy modification. Alternatively, employing a skilled technician with experience in transformer winding can facilitate the process and ensure modifications are done safely and effectively. Buyers might also explore variable transformer solutions that can adjust output voltage without physical modifications to the windings. This approach not only saves time but also minimizes the risk associated with manual winding alterations, ensuring reliable performance tailored to specific needs.
By addressing these common pain points with targeted solutions, B2B buyers can optimize their use of toroidal transformers, enhancing performance and reducing operational risks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for toroidal transformer winding
When selecting materials for toroidal transformer windings, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and compliance with international standards. The choice of materials can significantly impact the performance, durability, and overall suitability of the transformer in various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in toroidal transformer winding.
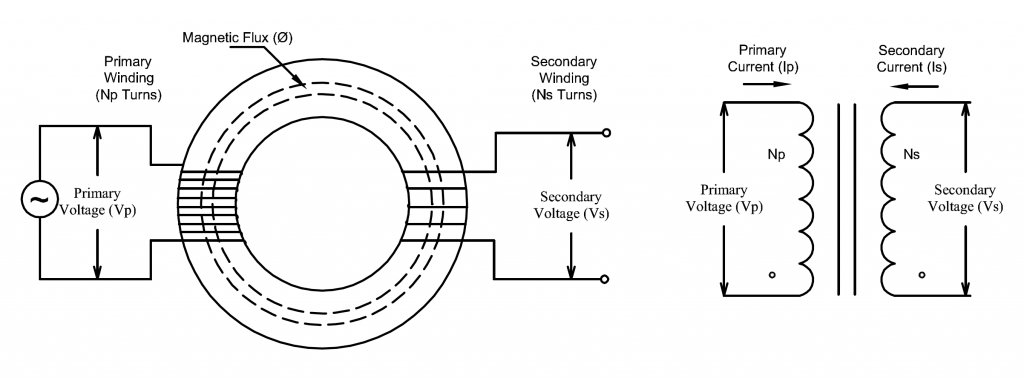
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
What are the Key Properties of Copper for Toroidal Transformer Windings?
Copper is the most widely used material for transformer windings due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It boasts a conductivity rating of approximately 59.6 x 10^6 S/m, making it highly efficient for energy transfer. Additionally, copper has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and good thermal conductivity, which helps in heat dissipation.
Pros: Copper windings provide high efficiency and low resistance, which translates to minimal energy losses. They are also relatively easy to work with during manufacturing processes.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in humid or harsh environments. This necessitates protective coatings, which can add to manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with a wide range of media, making it suitable for various applications, including audio equipment and industrial machinery.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for electrical materials, as these can vary by region.
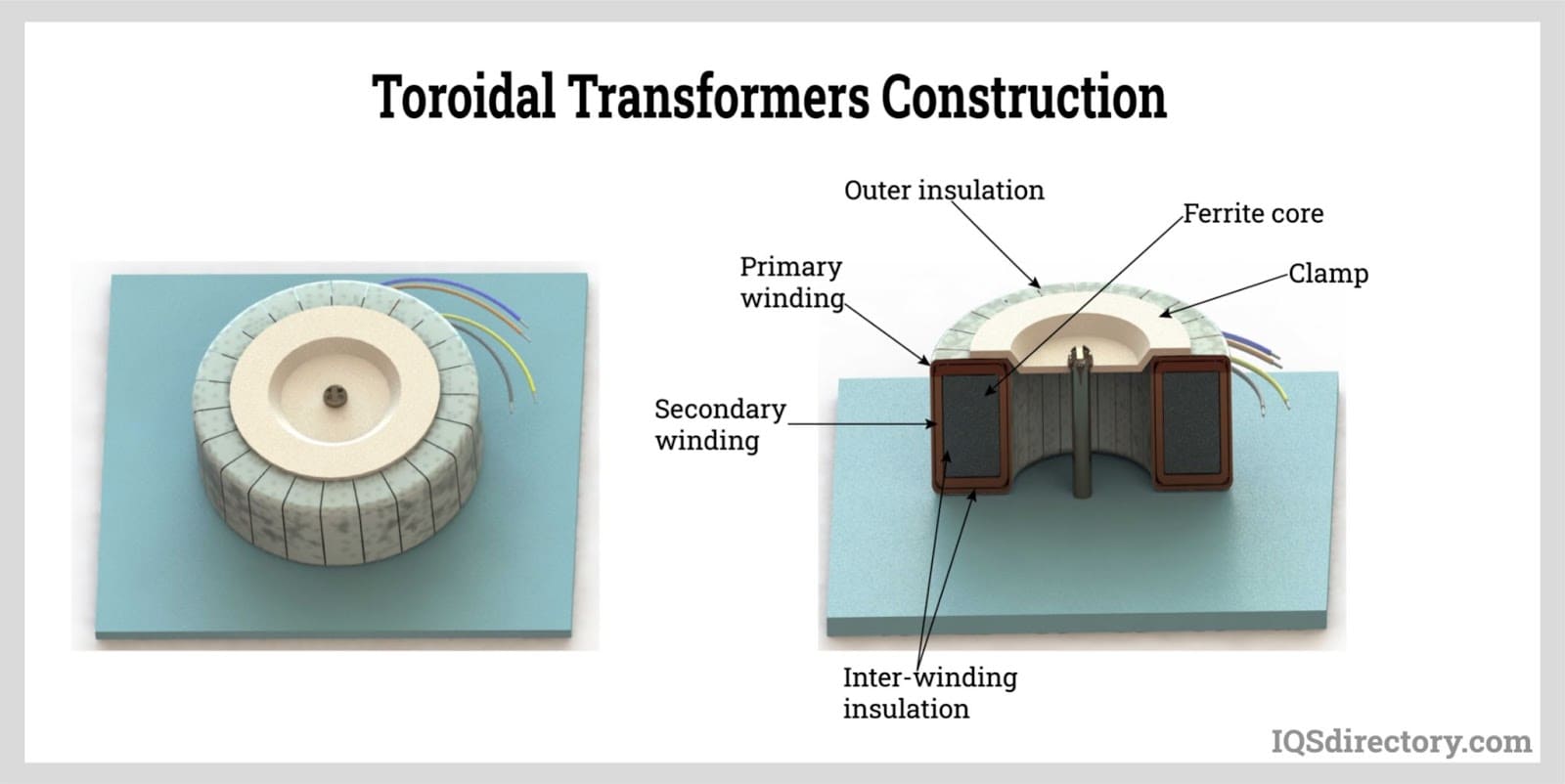
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
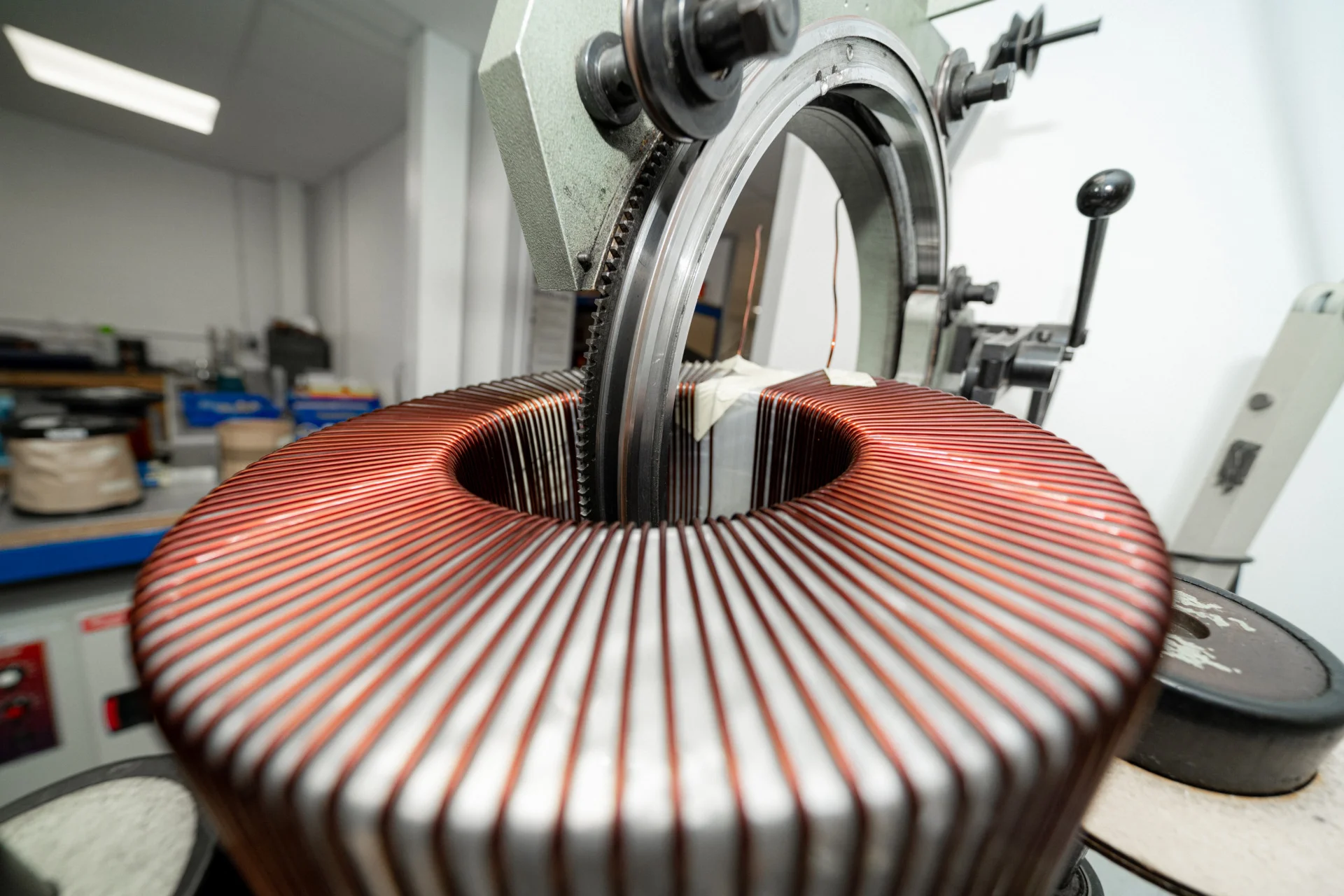
How Does Aluminum Compare to Copper for Toroidal Transformer Windings?
Aluminum is another popular choice for transformer windings, known for its lower cost and lighter weight compared to copper. While its conductivity (approximately 37.7 x 10^6 S/m) is lower than that of copper, it can still be effective in many applications when designed correctly.
Pros: Aluminum is less expensive and lighter, which can reduce shipping costs and make installation easier. It also has a good resistance to corrosion when properly treated.
Cons: The lower conductivity means that aluminum windings may require more turns to achieve the same performance as copper, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity.
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight and cost are critical factors, such as in portable equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards is essential, as aluminum may not be as widely accepted in high-performance applications compared to copper.
What Role Does Enamel Insulation Play in Toroidal Transformer Windings?
Enamel insulation is often used to coat copper or aluminum wire in transformer windings. This insulation is crucial for preventing short circuits and ensuring electrical safety.
Pros: Enamel insulation provides excellent dielectric strength, allowing for compact winding designs. It is also resistant to heat and moisture, enhancing the durability of the winding.
Cons: The manufacturing process for enamel-coated wire can be more complex and costly compared to bare wire. Additionally, if the insulation is damaged, it can lead to significant failures.
Impact on Application: Enamel insulation is compatible with various electrical media, making it versatile for different types of transformers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the enamel insulation meets international safety standards, which can vary by region.

Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
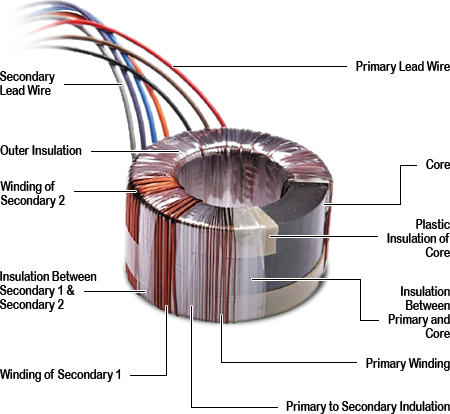
Why is Ferrite Material Important for Toroidal Transformer Cores?
Ferrite materials are often used in the cores of toroidal transformers, providing a high magnetic permeability that enhances efficiency.
Pros: Ferrite cores are lightweight and have high electrical resistivity, which minimizes eddy current losses. They are also effective in high-frequency applications.
Cons: Ferrite materials can be more brittle than metal cores, making them susceptible to cracking during manufacturing or installation.
Impact on Application: Ferrite cores are ideal for applications requiring high-frequency operation, such as in RF transformers.
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards for magnetic materials is crucial, particularly for buyers in Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Toroidal Transformer Windings
| Material | Typical Use Case for toroidal transformer winding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | High-performance transformers | Excellent conductivity and efficiency | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Aluminum | Cost-sensitive applications | Lightweight and lower cost | Lower conductivity, requires more turns | Medium |
| Enamel Insulation | Insulation for copper/aluminum windings | High dielectric strength | Manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Ferrite | High-frequency transformers | Lightweight with minimal eddy current loss | Brittle, can crack easily | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in toroidal transformer windings, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for toroidal transformer winding
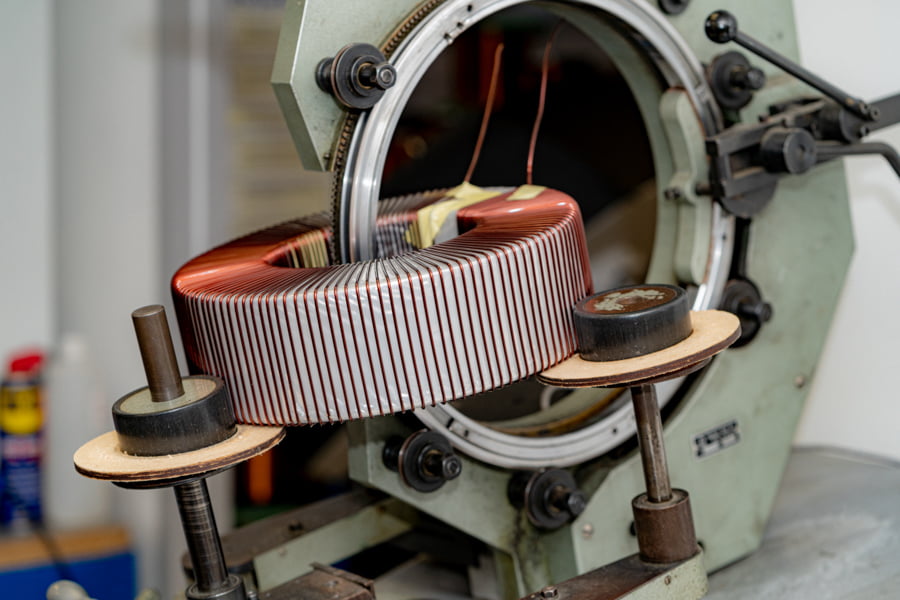
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Toroidal Transformer Windings?
The manufacturing process of toroidal transformer windings is a meticulous endeavor that requires precision and quality control at each stage. The process typically unfolds in four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Core and Wire Selected for Toroidal Transformers?
The first step in manufacturing involves selecting high-quality core materials, often made from silicon steel or ferrite, which are crucial for efficient magnetic properties. The wire used for winding is usually copper, chosen for its excellent electrical conductivity. Suppliers must ensure that these materials meet specific standards to guarantee performance. This preparation phase also includes cutting the core material into the appropriate dimensions and preparing the copper wire by stripping and insulating it as necessary.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Create Toroidal Shapes?
Forming the core into a toroidal shape is a critical step. This is typically achieved through a process known as toroidal winding, where the wire is wound around the core in a continuous loop. Advanced techniques such as automated winding machines are used to enhance precision and reduce human error. The use of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines can also ensure that the winding is uniform and tightly packed, which is essential for minimizing losses and ensuring the transformer operates efficiently.
3. Assembly: How Are Toroidal Transformers Assembled for Maximum Efficiency?
Once the winding is complete, the next stage is assembly. This involves securely attaching the winding to the core and incorporating any necessary components, such as insulation materials and terminals. The assembly process may also include the application of varnish or resin to protect the windings and enhance durability. Attention to detail during this phase is critical to ensure that electrical connections are stable and that the transformer can withstand environmental stresses.
4. Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied Before Quality Checks?
In the finishing stage, the transformer undergoes final inspection and packaging. This may involve additional varnishing to improve insulation, as well as testing the transformer to ensure it meets specified electrical characteristics. Proper labeling and documentation are crucial at this stage, especially for international shipments, where compliance with various regulations and standards is required.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Toroidal Transformers?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of toroidal transformers is essential for ensuring product reliability and performance. Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles that improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
1. What International and Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with relevant international standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for maintaining consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking demonstrates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: If transformers are intended for use in the oil and gas industry, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards is crucial.
Understanding these standards can help buyers assess the credibility and quality of potential suppliers.
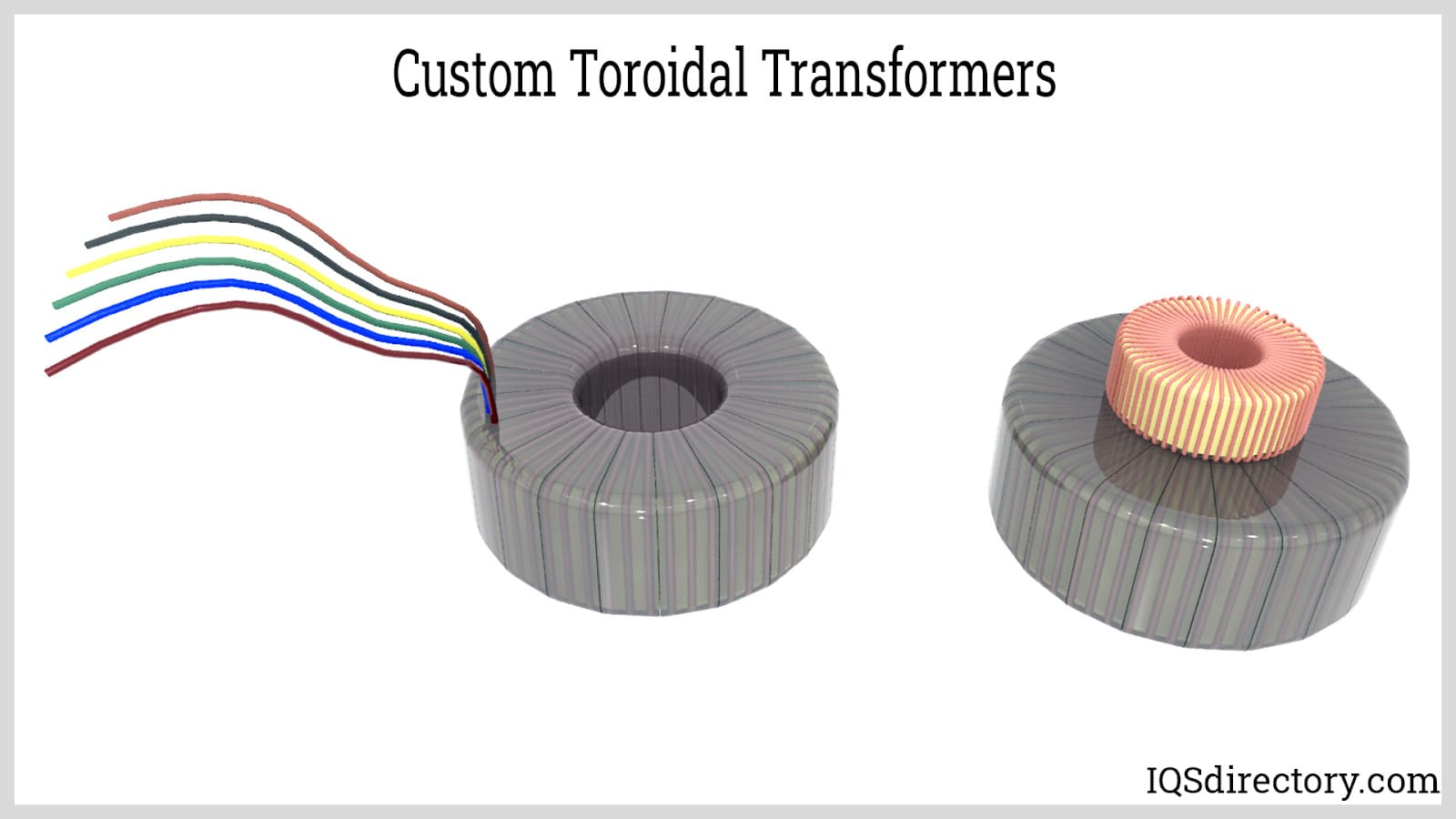
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process and can be categorized as follows:
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various checkpoints are established to monitor and document compliance with quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the transformer is assembled, it undergoes final testing to verify that it meets electrical specifications and performance criteria.
Each of these checkpoints is critical for identifying defects early and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
3. What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for toroidal transformers vary but typically include:
- Electrical Testing: This involves checking voltage, current, and resistance to ensure the transformer operates within specified limits.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluating the thermal performance of the transformer helps identify potential overheating issues during operation.
- Insulation Resistance Testing: This test ensures that the insulation materials can withstand operational voltages without failure.
Implementing a combination of these testing methods helps ensure that the final product is reliable and safe for end-users.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can help assess the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. Buyers should consider scheduling periodic visits to the manufacturing facility.
-
Request Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports should be transparent and easy to understand.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. This is particularly important for buyers in regions with specific regulatory requirements.
-
Understand Certification Nuances: B2B buyers should be aware of the nuances of certifications in their respective markets, as certain regions may have specific requirements that differ from others.
By following these steps, buyers can ensure they are partnering with reliable suppliers who prioritize quality and compliance.
Conclusion: Why Is Quality Assurance Vital in the Toroidal Transformer Market?
In the competitive landscape of toroidal transformer manufacturing, maintaining high quality through rigorous processes and standards is crucial. For B2B buyers, understanding the intricacies of manufacturing and quality assurance can lead to better purchasing decisions and ultimately improve their product offerings. By focusing on quality, reliability, and compliance, buyers can secure partnerships that foster long-term success in their respective markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘toroidal transformer winding’
When sourcing toroidal transformer winding, it is essential to follow a structured approach to ensure you select the right components and suppliers that meet your technical needs and business requirements. This checklist will guide you through the critical steps to make informed procurement decisions, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline the technical specifications of the toroidal transformer winding you require. Consider factors such as voltage, current ratings, core material, and winding configurations. Providing precise specifications helps suppliers understand your needs and reduces the risk of errors in the final product.
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Identify the operational requirements of your application.
- Core Material: Decide between options like ferrite or laminated steel based on performance and cost.
- Winding Configuration: Determine whether you need single-phase, three-phase, or custom designs.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in toroidal transformer windings. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of potential manufacturers.
- Industry Reputation: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in quality and reliability.
- Geographical Considerations: Consider local suppliers for faster shipping and easier communication, especially if you are operating in regions like Africa or South America.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and compliance of potential suppliers to ensure they meet international quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can be an indicator of their commitment to quality management.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure that the supplier follows stringent quality control processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Check if they comply with relevant electrical standards in your market.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk order, request samples of the toroidal transformer windings to evaluate their quality and suitability for your application. Testing samples can help you identify any potential issues early in the process.
- Performance Testing: Assess the efficiency, thermal performance, and noise levels of the sample.
- Material Quality: Inspect the materials used in the winding for durability and adherence to specifications.
Step 5: Inquire About Lead Times and Pricing
Discuss lead times and pricing with your shortlisted suppliers. Understanding these factors will help you plan your project timelines and budget effectively.
- Negotiation Flexibility: Some suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts.
- Shipping Options: Inquire about shipping methods and costs, especially if you are importing from overseas.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support
Evaluate the after-sales support offered by the suppliers. Reliable support can be invaluable in addressing any issues that arise post-purchase.
- Technical Assistance: Ensure that the supplier provides technical support for installation and troubleshooting.
- Warranty and Returns Policy: Understand the warranty terms and what to expect in case of defects or performance issues.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order
Once you have gathered all necessary information and are satisfied with your supplier’s capabilities, finalize your order. Ensure that all agreed-upon specifications, pricing, and delivery terms are clearly documented to avoid misunderstandings.
- Purchase Agreement: Draft a clear purchase agreement outlining all terms and conditions.
- Payment Terms: Confirm payment methods and schedules to ensure smooth transactions.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can systematically approach the procurement of toroidal transformer windings, ensuring they select the right suppliers and products that align with their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for toroidal transformer winding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Toroidal Transformer Winding Sourcing?
When sourcing toroidal transformer windings, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The core materials, such as high-quality silicon steel or ferrite for the toroidal core, significantly influence costs. Additionally, the wire used for winding—often copper or aluminum—varies in price based on purity and gauge.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the precise winding of toroidal transformers. Labor costs can vary by region; for example, labor may be more affordable in some South American or African countries compared to Europe. The complexity of the winding process also affects labor costs, with more intricate designs requiring specialized skills.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead and thus lower overall costs.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for manufacturing toroidal transformers involves tooling costs for winding machines and molds. These are often amortized over large production runs, making it essential to consider volume when assessing tooling costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of the transformers involves testing and inspection processes. Higher QC standards, especially for certifications (such as ISO or UL), can increase costs but are crucial for reliability and customer trust.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the supplier’s location, the shipping method, and the destination country. International shipping fees, tariffs, and potential delays should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, market conditions, and the supplier’s pricing strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Toroidal Transformer Winding Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating MOQs can be beneficial, especially for B2B buyers looking to optimize their spending.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific voltage ratings can lead to higher costs due to the need for specialized materials or processes. Clear communication of specifications can help avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can increase costs but may be necessary for specific applications, particularly in regulated industries. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of quality against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer suppliers might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the delivery terms specified in the Incoterms is essential. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost.
What Tips Can Help International B2B Buyers Optimize Costs for Toroidal Transformers?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
-
Negotiate: Leverage volume purchases and long-term contracts to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders or repeat business.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the total cost over the product’s lifecycle rather than just the initial purchase price. High-quality transformers may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to savings through lower failure rates and maintenance costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and the impact of currency fluctuations. Building relationships with local suppliers can also provide insights into market trends and pricing strategies.
-
Stay Informed: Monitor industry trends and supplier performance. Knowledge of market conditions can empower buyers during negotiations and help in making informed sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for toroidal transformer windings can fluctuate based on market conditions, material availability, and supplier policies. The information provided is indicative and should be validated with suppliers for accurate and current pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing toroidal transformer winding With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Toroidal Transformer Windings in Electrical Applications
In the realm of electrical power management, toroidal transformers have gained popularity due to their efficiency and compact design. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications or budgets. This analysis evaluates toroidal transformer windings against other solutions, providing B2B buyers with insights to guide their decision-making process.
| Comparison Aspect | Toroidal Transformer Winding | Conventional Laminated Transformer | Switching Power Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, low magnetic leakage, excellent thermal management | Good efficiency but higher losses due to heat | Very high efficiency at variable loads |
| Cost | Generally higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost, but can lead to higher operational costs | Moderate cost with potential savings on power consumption |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized handling during installation | Easier to integrate into existing systems | Generally straightforward installation with standardized components |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to solid construction | Moderate maintenance; susceptible to wear and overheating | Low maintenance; relies on solid-state components |
| Best Use Case | Audio equipment, medical devices, and precision electronics | General industrial applications and power distribution | Consumer electronics, LED lighting, and battery chargers |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Conventional Laminated Transformers?
Conventional laminated transformers are widely used in various applications, particularly in industrial settings. They are typically less expensive than toroidal transformers, making them an attractive option for projects with budget constraints. However, they can suffer from higher energy losses due to heat generation, leading to increased operational costs over time. Their bulkier design also requires more space, which could be a consideration for compact installations.
How Do Switching Power Supplies Compare in Efficiency and Cost?
Switching power supplies represent a modern alternative that offers high efficiency, especially under varying loads. They convert electricity using high-frequency switching, which reduces energy loss. While the initial cost can be moderate, the long-term savings on electricity bills can be significant. However, switching supplies may introduce electrical noise, which can be a drawback in sensitive applications like audio equipment or precise measurement devices.
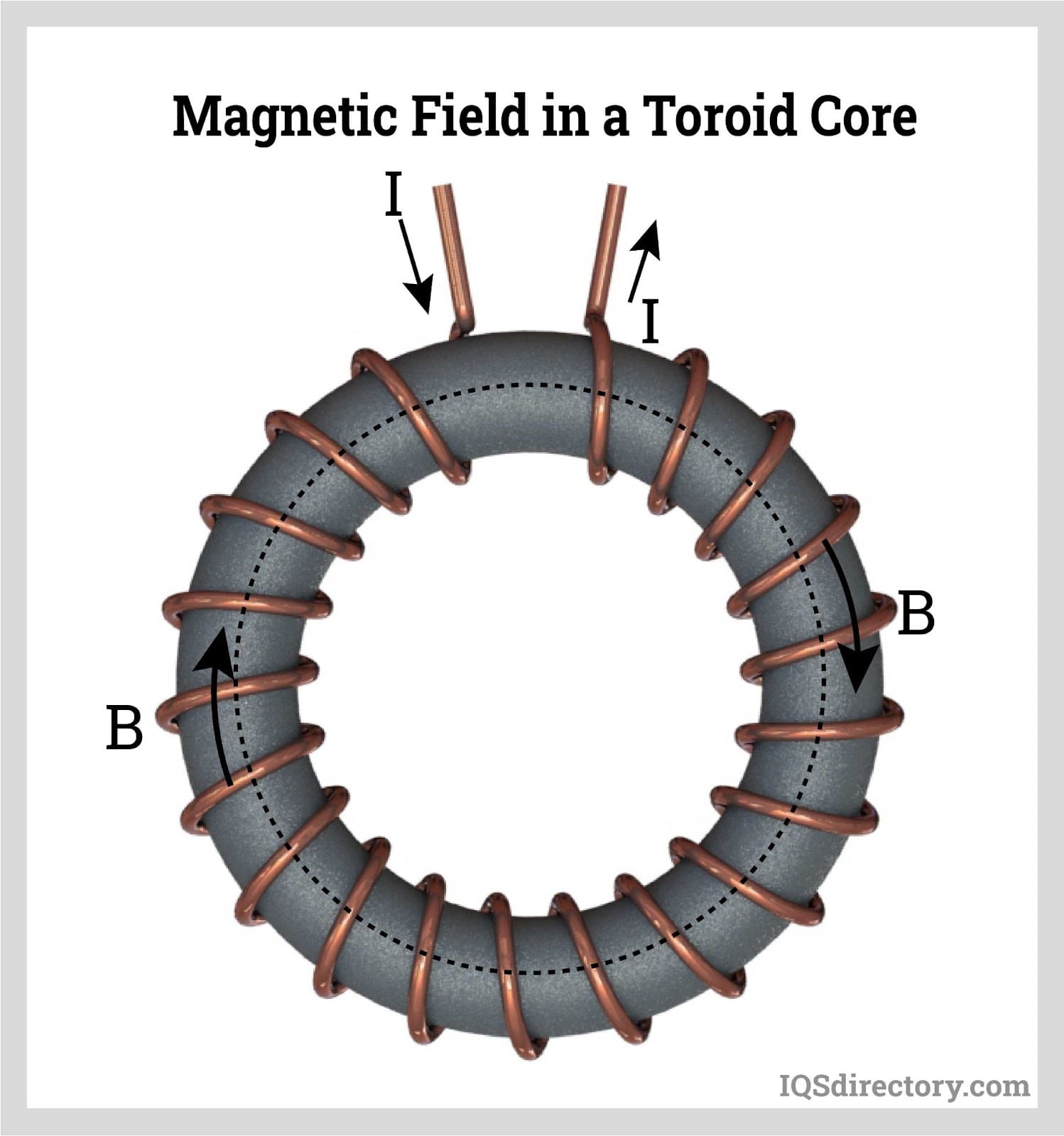
Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
Conclusion: Which Solution Is Right for Your Needs?
When choosing between toroidal transformer windings and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, installation complexity, and maintenance capabilities. For high-performance applications requiring minimal magnetic interference, toroidal transformers remain a top choice. Conversely, for those prioritizing cost and ease of integration, conventional laminated transformers or switching power supplies may provide a more suitable solution. Careful evaluation of the specific application and long-term goals will ultimately guide the selection of the most appropriate transformer technology.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for toroidal transformer winding
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Toroidal Transformer Windings?
Understanding the essential technical properties of toroidal transformer windings is crucial for B2B buyers in making informed decisions about sourcing and purchasing these components. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The core material used in toroidal transformers typically consists of high-grade silicon steel or ferrite. The choice of material affects the magnetic permeability and efficiency of the transformer. High-grade materials minimize energy losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents, ensuring better performance and longevity. For buyers, selecting the right material grade can lead to reduced operational costs and improved reliability in their applications.
2. Winding Tolerance
Winding tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in the number of turns in the winding process. A tighter tolerance results in better voltage regulation and lower losses. For manufacturers, maintaining precise winding tolerances is essential to ensure consistent performance. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate stringent quality control measures to guarantee the reliability of their toroidal transformers.
3. Inductance Value
Inductance is a measure of a transformer’s ability to store energy in its magnetic field. The inductance value, typically expressed in henries (H), impacts the transformer’s efficiency and voltage rating. Understanding the inductance requirements for specific applications helps buyers select transformers that meet their operational needs, particularly in high-frequency applications or where size constraints are critical.
4. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage that the transformer can handle safely. It is vital for ensuring that the transformer operates within its limits, preventing overheating and potential failure. B2B buyers must assess the voltage requirements of their applications to avoid costly downtimes and ensure compliance with industry standards.
5. Temperature Rise
Temperature rise refers to the increase in temperature of the transformer during operation compared to ambient conditions. A lower temperature rise indicates better thermal management and higher efficiency. Buyers should consider transformers with specifications that align with their operational environment to ensure longevity and reliability.
6. Core Shape and Size
The toroidal shape of the transformer core contributes to its efficiency by reducing magnetic leakage and improving space utilization. The size of the core, often specified in terms of its diameter and height, impacts the transformer’s power rating and application suitability. Buyers should evaluate the physical dimensions of the transformer to ensure compatibility with their equipment.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Toroidal Transformer Windings?
Navigating the procurement process involves understanding industry jargon. Here are several common terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of toroidal transformers, buyers often engage with OEMs to procure custom transformers that meet specific design and performance criteria.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units that a supplier requires a buyer to purchase in a single order. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for businesses looking to minimize excess stock or initial investment.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. When sourcing toroidal transformers, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, aiding in the decision-making process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms helps buyers navigate shipping costs, insurance, and risk management associated with the procurement of toroidal transformers from global suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from placing an order to receiving the product. For toroidal transformers, lead times can vary based on manufacturing capabilities and supply chain logistics. Buyers should account for lead times in their project timelines to avoid delays.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO or IEC, indicate that a product meets specific quality and safety benchmarks. Buyers should prioritize suppliers whose products comply with relevant certification standards to ensure reliability and regulatory compliance in their applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure the right toroidal transformers for their specific needs while optimizing costs and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the toroidal transformer winding Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for toroidal transformer windings is evolving rapidly, driven by increasing demand for efficient energy solutions across various sectors, including renewable energy, automotive, and consumer electronics. Key trends include the growing adoption of lightweight and compact designs, which enhance portability and energy efficiency. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on sourcing toroidal transformers that offer superior performance while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The rise in energy costs and the push for sustainability are compelling businesses to seek out high-quality transformers that can minimize energy losses during power conversion.
Emerging technologies, such as smart grid implementations and electric vehicle infrastructure, are also reshaping the landscape for toroidal transformers. These advancements necessitate transformers with advanced winding techniques that can handle varying loads and improve efficiency. Moreover, the demand for customization is on the rise; buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet specific operational requirements. As international trade continues to expand, understanding regional market dynamics and technological trends will be vital for B2B buyers looking to secure competitive advantages in their sourcing strategies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
In today’s business environment, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for international B2B buyers in the toroidal transformer winding sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek suppliers that prioritize eco-friendly practices. Using recycled materials and low-impact manufacturing methods can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with transformer production. Buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing practices and who hold certifications such as ISO 14001, which indicates a commitment to environmental management.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, especially in regions where labor practices may vary. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor standards and provide safe working conditions is essential for maintaining a reputable brand image. The growing consumer awareness around corporate responsibility is influencing B2B purchasing decisions, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to social and environmental stewardship. By prioritizing ‘green’ certifications and sustainable materials in their sourcing strategies, companies can not only enhance their market positioning but also contribute positively to global sustainability efforts.
Brief Evolution/History
The concept of toroidal transformers dates back to the early 20th century, when advancements in electromagnetic theory and materials science made it feasible to create more efficient transformer designs. Initially, toroidal transformers were primarily used in specialized applications due to their complex winding process. However, as the demand for compact and efficient electrical devices grew, the popularity of toroidal transformers surged. Their unique design, which minimizes electromagnetic interference and improves energy efficiency, has made them increasingly favored in various industries.
In recent years, the advent of digital technology and renewable energy sources has further accelerated the development of toroidal transformers. Innovations in winding techniques and materials have enabled manufacturers to produce transformers that meet the stringent requirements of modern applications, thereby expanding their market reach. As the industry continues to evolve, international B2B buyers can expect ongoing advancements that enhance the performance and sustainability of toroidal transformer windings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of toroidal transformer winding
-
How do I select the right toroidal transformer winding for my application?
Choosing the appropriate toroidal transformer winding depends on several factors, including voltage requirements, power rating, and load type. Start by determining the input and output voltage specifications for your application. Assess the current requirements and ensure the transformer can handle the load without overheating. Additionally, consider the physical space available for installation, as toroidal transformers are often more compact than traditional ones. Consulting with manufacturers or suppliers can provide insights into optimal configurations and customizations. -
What are the advantages of toroidal transformers over traditional transformers?
Toroidal transformers offer several advantages, including higher efficiency and lower electromagnetic interference. Their circular design minimizes stray magnetic fields, which can improve performance in sensitive applications. Additionally, toroidal transformers tend to be lighter and smaller than traditional transformers, making them easier to integrate into various systems. They also have lower losses due to reduced winding resistance, which can result in lower operating costs over time. -
What customization options are available for toroidal transformer windings?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for toroidal transformer windings, including adjustments to voltage ratings, power levels, and winding configurations. You can specify the type of insulation, core material, and even the number of secondary windings based on your application needs. Discussing your specific requirements with potential suppliers will help you understand what custom solutions they can provide and any associated costs. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQs) should I expect when sourcing toroidal transformers?
Minimum order quantities for toroidal transformers can vary significantly between suppliers. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as 10-50 units, while others may require larger orders depending on their production capabilities and the complexity of the customization. It’s advisable to communicate your anticipated needs upfront to negotiate favorable terms and ensure that the supplier can meet your volume requirements. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of toroidal transformers?
Payment terms can differ widely among suppliers, but common practices include upfront payment, partial deposits, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, options such as letters of credit or payment through escrow services may also be available to protect both parties. Discussing payment terms early in the negotiation process is essential to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. -
How can I assess the quality assurance (QA) processes of toroidal transformer manufacturers?
To evaluate a manufacturer’s QA processes, request documentation of their quality control measures and certifications (such as ISO 9001). Inquire about testing protocols for transformers, including performance testing under load, thermal cycling, and insulation resistance tests. Visiting the factory, if feasible, or reviewing third-party audits can also provide valuable insights into their commitment to quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing toroidal transformers?
When importing toroidal transformers, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Ensure that the supplier can provide the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Be aware of import duties and taxes in your country, as these can significantly affect overall costs. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can help streamline the import process and mitigate potential delays. -
How do I handle after-sales support and warranty claims for toroidal transformers?
Before finalizing your purchase, clarify the after-sales support and warranty policies with the supplier. Understand the duration of the warranty and what it covers, including repairs or replacements for defective products. It’s also beneficial to know the process for filing warranty claims and any associated costs. Establishing a good communication channel with the supplier can facilitate quicker resolutions to any issues that may arise post-purchase.
Top 4 Toroidal Transformer Winding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. IQS Directory – Toroidal Transformers
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Toroidal transformers possess a core in the form of a torus or donut, with primary and secondary windings encircling the core, separated by insulating material. They offer high energy efficiency, silent operation, low heat emission, and a compact form. Common applications include power supply systems, audio equipment, control systems, and power inverters. They operate based on electromagnetic indu…
2. Yoofab – Bifilar Transformer
Domain: yoofab.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: A bifilar transformer is an electromagnetic coil featuring two parallel, twisted windings. The term ‘bifilar’ means ‘two threads’, referring to the two strands of wire. The winding process involves using solderable enamelled wire, typically 0.58 mm thick (approximately 24 SWG or 23 AWG). The guide includes detailed steps for winding a ten-turn bifilar transformer, emphasizing the importance of mai…
3. DIY Audio – Voltage Considerations
Domain: diyaudio.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: This company, DIY Audio – Voltage Considerations, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Talema – Toroidal Transformers
Domain: talema.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Toroidal transformers are electrical transformers with a doughnut-like shape, offering increased design flexibility, efficiency, and compactness compared to traditional transformers. They are suitable for low-KVA applications (up to 15 KVA) in medical, industrial, renewable energy, and audio sectors. Key features include:
– Lightweight and smaller size due to short wire length and high flux densit…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for toroidal transformer winding
As the global demand for efficient power management solutions continues to rise, the strategic sourcing of toroidal transformer windings presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of quality and reliability in sourcing, as toroidal transformers are known for their compact design, reduced electromagnetic interference, and enhanced efficiency. By prioritizing suppliers who adhere to stringent manufacturing standards, businesses can ensure the longevity and performance of their electrical systems.
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also fosters strong partnerships that can enhance innovation and responsiveness to market changes. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage local market insights while engaging with global suppliers to maximize their procurement strategies.
Looking ahead, the landscape of toroidal transformer technology is poised for evolution with advancements in materials and manufacturing processes. Now is the time for B2B buyers to engage proactively with suppliers, ensuring they are well-positioned to meet future electrical demands. Embrace the potential of strategic sourcing to drive your business forward, enhancing both efficiency and sustainability in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.

Illustrative image related to toroidal transformer winding
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.