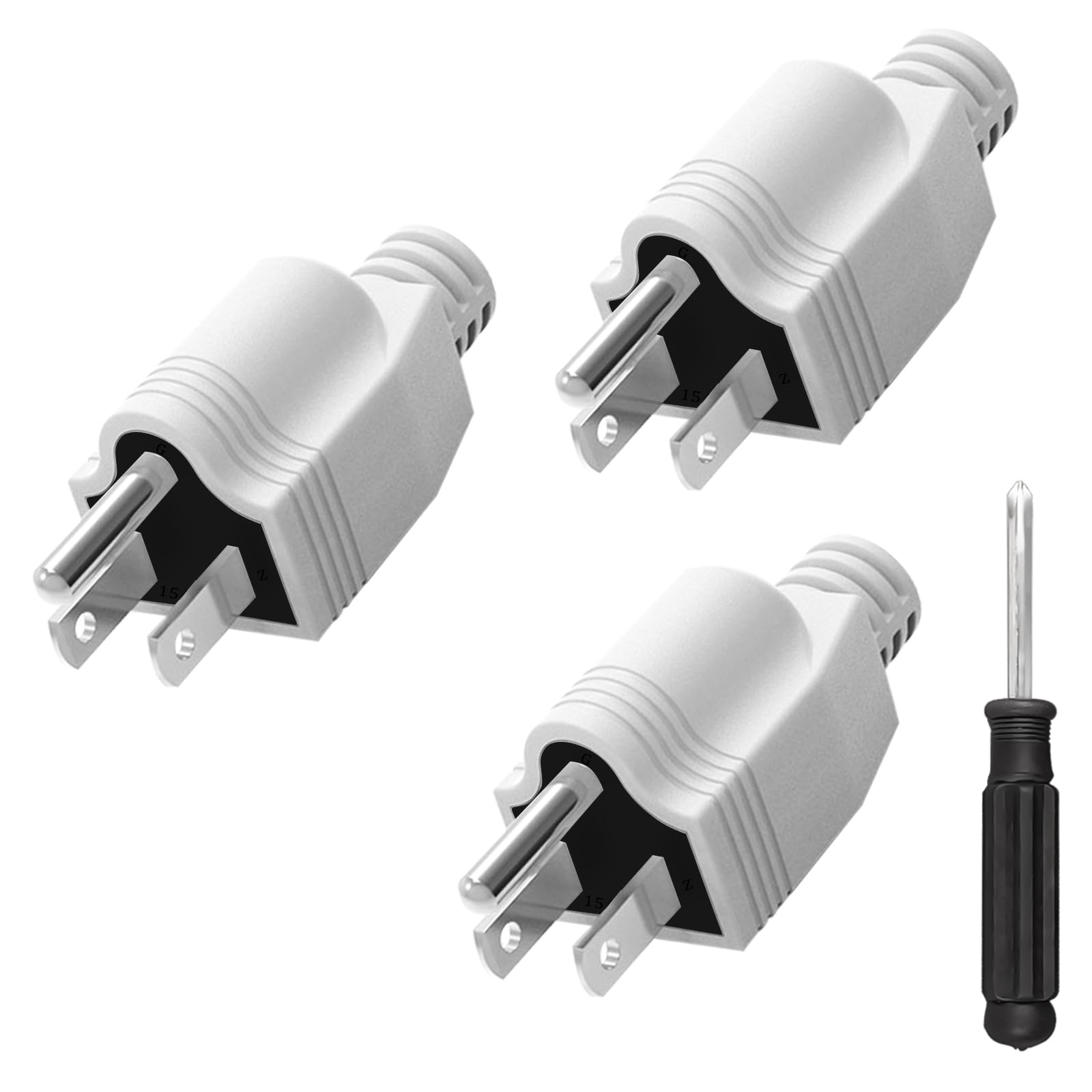
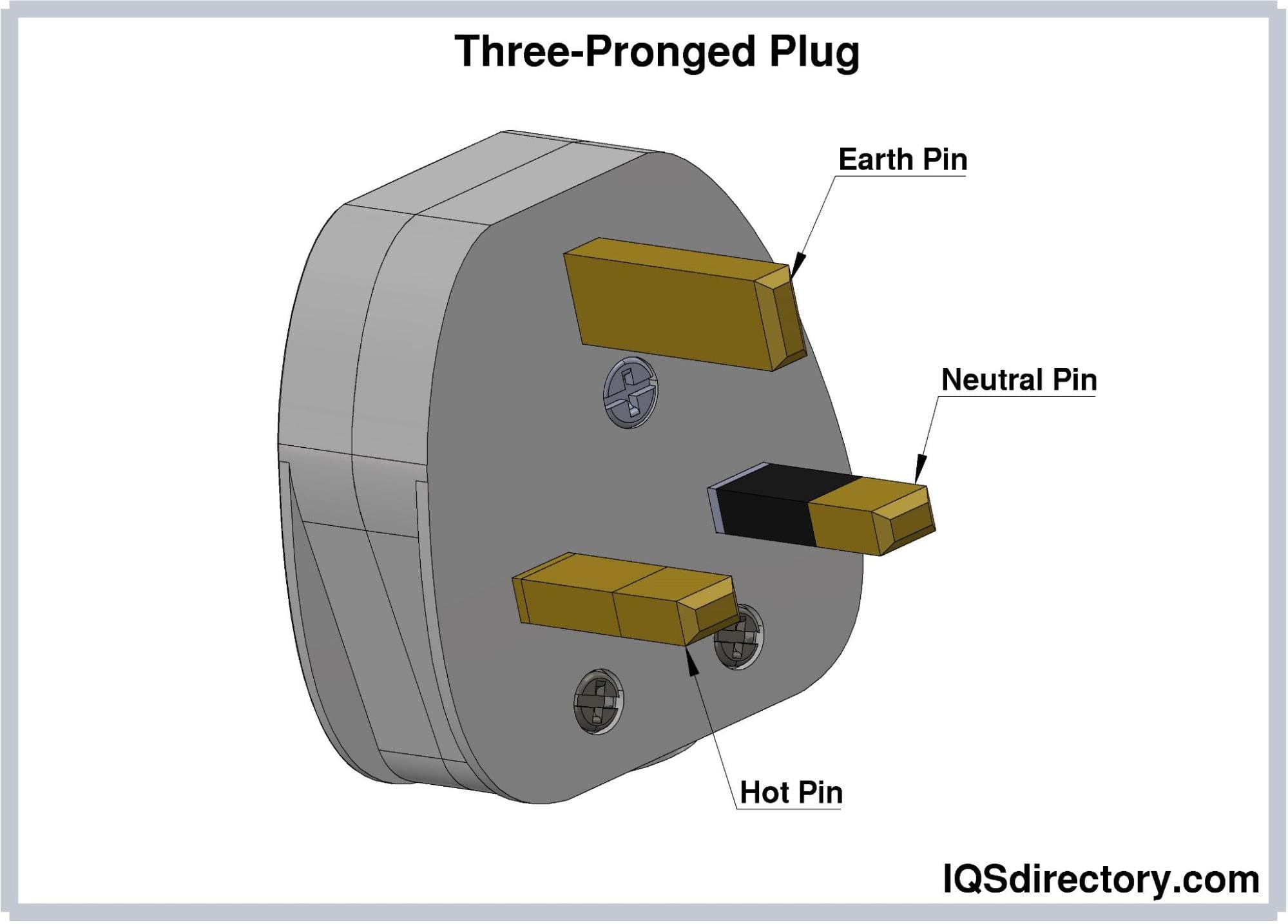
Choosing Your Three Prong Plug: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for three prong plug
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing reliable three prong plugs is a critical challenge for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their product offerings and ensure safety compliance. With diverse electrical standards across regions, navigating the global market for three prong plugs can be daunting. This comprehensive guide addresses key aspects such as types of plugs, their applications in various industries, best practices for supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Brazil and Vietnam, will find valuable insights tailored to their unique market dynamics. By understanding the nuances of different plug specifications and safety regulations, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
Moreover, this guide empowers B2B buyers to evaluate potential suppliers effectively, ensuring that they select partners who adhere to quality standards and provide competitive pricing. With actionable insights and a clear roadmap, readers will be equipped to navigate the complexities of sourcing three prong plugs, ultimately leading to enhanced product safety and customer satisfaction.
Understanding three prong plug Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 5-15P | Standard 120V plug with two flat parallel prongs and a round grounding prong | General electronics, appliances in North America | Pros: Widely compatible, easy to source. Cons: Limited to 120V applications. |
| NEMA 6-15P | Similar to NEMA 5-15P but rated for 250V; features angled prongs | Commercial equipment, heavy-duty appliances | Pros: Higher voltage capacity. Cons: Less common, may require special outlets. |
| Type I (Australia) | Flat angled prongs with a grounding pin, designed for 230V | Electrical appliances in Australia, New Zealand | Pros: Safe design, widely used in Oceania. Cons: Not compatible with other regions without adapters. |
| Type G (UK) | Three rectangular prongs in a triangular layout, with a fuse | Appliances in the UK, Middle East, Africa | Pros: Includes fuse for safety, robust design. Cons: Bulky and may not fit all sockets. |
| Type C (Europe) | Two round prongs, often used with a grounding adapter | Lightweight appliances, travel adapters | Pros: Versatile and compact. Cons: Not grounded by default, may lack safety features. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of NEMA 5-15P Plugs?
The NEMA 5-15P is the standard three-prong plug used in North America, designed for 120V applications. It features two flat parallel prongs and a round grounding prong, making it compatible with most household and light commercial devices. B2B buyers should consider the availability and compatibility of this plug with their existing equipment, as it is widely used across various sectors, including electronics and small appliances.
How Does the NEMA 6-15P Differ in Application?
The NEMA 6-15P is a three-prong plug designed for 250V applications, featuring angled prongs. It is commonly used in commercial settings and for heavy-duty appliances that require a higher voltage. B2B buyers should note the necessity of specialized outlets for this plug type, as well as its capacity to handle more demanding electrical loads, making it suitable for industrial applications.
What Makes Type I Plugs Suitable for Oceania?
Type I plugs, prevalent in Australia and New Zealand, are characterized by their flat angled prongs and grounding pin, designed for 230V systems. They are essential for appliances used in these regions. B2B buyers must ensure that their imported devices are compatible with Type I sockets, as this plug type is not widely used outside of Oceania, which could necessitate the use of adaptors for international equipment.
Why Choose Type G Plugs for the UK Market?
Type G plugs are known for their robust design, featuring three rectangular prongs in a triangular configuration and an integrated fuse for added safety. This plug type is standard in the UK and many countries in the Middle East and Africa. B2B buyers should appreciate the safety features of Type G plugs, but they should also consider the bulkiness and potential compatibility issues with non-standard sockets.
What Are the Advantages of Using Type C Plugs?
Type C plugs, with two round prongs, are often used for lightweight appliances and travel adapters, primarily in Europe. They are versatile and compact, making them ideal for various applications. However, B2B buyers should be aware that Type C plugs do not include a grounding feature by default, which could pose safety risks in certain environments. Therefore, buyers should assess the specific power requirements and safety standards of their devices before opting for this plug type.
Key Industrial Applications of three prong plug
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of three prong plug | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering machinery and equipment | Ensures operational efficiency and safety in industrial settings | Compliance with local electrical standards and safety regulations |
| Construction | Temporary power connections on job sites | Facilitates quick setup of electrical tools and equipment | Durability and weather resistance for outdoor applications |
| Hospitality | Connecting appliances in hotels and restaurants | Enhances guest experience through reliable power supply | Compatibility with various appliance types and energy efficiency |
| Retail | Powering displays and point-of-sale systems | Supports seamless customer transactions and enhances merchandising | Aesthetic design and cord length considerations for visibility |
| Healthcare | Connecting medical devices and equipment | Critical for patient safety and operational reliability | Compliance with medical safety standards and cord insulation |
How is the Three Prong Plug Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, three prong plugs are essential for powering various machinery and equipment. These plugs ensure a secure connection to the electrical supply, minimizing the risk of electrical shock and equipment failure. Businesses must consider local electrical standards, as regulations vary by region, especially in international markets like Africa and South America. Additionally, sourcing plugs that can withstand the demands of heavy machinery is crucial to maintain operational efficiency.
What Role Does the Three Prong Plug Play in Construction?
In construction, three prong plugs are frequently used for temporary power connections on job sites. This application allows workers to quickly set up electrical tools and equipment, which is vital for project timelines. Buyers in this sector should prioritize durability and weather resistance, as construction sites often face harsh environmental conditions. Ensuring that the plugs meet safety regulations can also prevent accidents and liabilities.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
Why is the Three Prong Plug Important in Hospitality?
The hospitality industry relies on three prong plugs to connect various appliances in hotels and restaurants, from kitchen equipment to guest room amenities. A reliable power supply enhances the guest experience by ensuring that appliances operate smoothly. Businesses should focus on the compatibility of plugs with different appliance types, as well as energy efficiency to reduce operational costs. Furthermore, sourcing aesthetically pleasing designs can improve the overall ambiance of guest areas.
How Do Retailers Utilize Three Prong Plugs?
In retail environments, three prong plugs are crucial for powering displays and point-of-sale systems. A consistent power supply supports seamless customer transactions and enhances merchandising efforts. Retail buyers should consider the aesthetic design of plugs and the length of cords to ensure they do not detract from product displays. Additionally, energy efficiency is a key consideration, as it can significantly impact operational costs.
What is the Significance of Three Prong Plugs in Healthcare?
In healthcare settings, three prong plugs are vital for connecting medical devices and equipment. These plugs are essential for ensuring patient safety, as they provide a reliable power source for critical equipment. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the plugs comply with stringent medical safety standards, including proper insulation and durability. The reliability of these connections directly impacts patient care and operational reliability in healthcare facilities.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘three prong plug’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Compatibility Issues with Equipment and Plugs
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges when trying to ensure that three prong plugs are compatible with a variety of equipment. Many businesses, especially those in manufacturing or construction, use a wide range of electrical devices. When sourcing three prong plugs, they may encounter devices that require specific plug configurations or voltages that are not universally supported. This can lead to operational delays, increased costs due to returns, or even safety hazards if incompatible plugs are used.
The Solution:
To mitigate compatibility issues, it is essential to conduct thorough research before purchasing three prong plugs. Buyers should create a detailed inventory of all equipment that will utilize these plugs, including specifications like voltage, amperage, and plug type. When sourcing plugs, prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive product details and compatibility information. Additionally, consider investing in adjustable or universal three prong plugs that can accommodate various devices. Establishing a relationship with a reputable supplier can also lead to better support and guidance in selecting the right plugs for specific applications.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns Related to Grounding
The Problem:
Safety is a paramount concern for B2B buyers, particularly when dealing with electrical components like three prong plugs. A common pain point arises when plugs are not properly grounded, which can lead to electric shock hazards or equipment damage. Businesses that use heavy machinery or electrical appliances with metal casings are especially vulnerable if grounding is not adequately addressed. This situation can result in costly accidents, injuries, and liability issues.
The Solution:
To ensure safety, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing three prong plugs that comply with international safety standards, such as IEC or UL certifications. It’s also vital to educate staff on the importance of proper installation and maintenance of grounding connections. Conduct regular audits of electrical systems to ensure that all three prong plugs are correctly installed and functioning. Additionally, consider integrating ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) into your electrical systems, as these devices provide an extra layer of protection by cutting off power when they detect grounding issues.
Scenario 3: Supply Chain Disruptions Affecting Availability
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with supply chain disruptions that can affect the availability of three prong plugs, particularly in regions like Africa and South America. Delays in shipments, unexpected price increases, or inadequate stock levels can lead to project hold-ups and financial losses. This issue is exacerbated when businesses have established timelines and depend on specific electrical components to meet project deadlines.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
The Solution:
To counter supply chain disruptions, businesses should develop a proactive procurement strategy that includes diversifying suppliers and maintaining a buffer stock of critical components like three prong plugs. Building relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions can provide alternative sourcing options in case of localized disruptions. Furthermore, consider utilizing demand forecasting tools to predict needs accurately and make timely orders. Engaging with suppliers who offer real-time inventory updates and reliable shipping options can significantly enhance supply chain resilience. Investing in local suppliers where feasible can also reduce lead times and improve reliability in supply.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for three prong plug
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Three Prong Plugs?
When selecting materials for three prong plugs, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The choice of material can significantly impact the performance, safety, and compliance of the product in various markets, particularly for international B2B buyers.
How Does PVC Impact the Performance of Three Prong Plugs?
Key Properties: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to moisture and chemicals. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 70°C and has a good dielectric strength.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for plug housings. However, it has a lower thermal resistance compared to other materials, which can limit its use in high-temperature applications.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
Impact on Application: PVC is suitable for indoor applications where exposure to high temperatures or harsh chemicals is minimal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the PVC used complies with local standards, such as ASTM or ISO, to avoid issues with product safety and performance.
What Are the Benefits of Using Nylon for Three Prong Plugs?
Key Properties: Nylon is a thermoplastic known for its high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and has good impact resistance.
Pros & Cons: The durability of nylon makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, but it is more expensive than PVC and can be more complex to manufacture.
Impact on Application: Nylon plugs are ideal for environments with mechanical stress or where plugs are frequently connected and disconnected.
Considerations for International Buyers: In Europe, compliance with RoHS and REACH regulations is crucial for nylon components, ensuring they are free from harmful substances.
How Does Metal Affect the Functionality of Three Prong Plugs?
Key Properties: Common metals used in prongs include brass and copper, which offer excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. They can typically handle high currents and temperatures.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
Pros & Cons: Metal prongs provide superior electrical performance and longevity. However, they can be more expensive and may require additional protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
Impact on Application: Metal components are essential for high-power applications, ensuring reliable connections and minimizing energy loss.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that metal components meet international standards for conductivity and corrosion resistance, particularly in humid environments like the Middle East.
What Role Does Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Play in Three Prong Plugs?
Key Properties: TPE combines the properties of rubber and plastic, offering flexibility, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures (up to 100°C).
Illustrative image related to three prong plug
Pros & Cons: TPE is highly resilient and can absorb shocks, making it suitable for outdoor or industrial applications. However, it can be more costly than traditional plastics.
Impact on Application: TPE is ideal for plugs used in environments where flexibility and durability are critical, such as construction sites.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with specific environmental regulations is essential, especially in Europe, where TPE must meet stringent safety standards.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
Summary Table of Material Selection for Three Prong Plugs
| Material | Typical Use Case for three prong plug | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Indoor residential plugs | Cost-effective and easy to mold | Lower thermal resistance | Low |
| Nylon | Heavy-duty industrial plugs | High strength and durability | More expensive and complex to manufacture | Medium |
| Metal (Brass/Copper) | High-power applications | Excellent conductivity and longevity | Higher cost, corrosion risk | High |
| Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | Outdoor and industrial plugs | Flexibility and shock absorption | Higher cost than traditional plastics | Medium |
This comprehensive analysis of materials used in three prong plugs provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regulatory requirements in various international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for three prong plug
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Three Prong Plug?
The manufacturing process for a three prong plug is intricate and involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring product quality and reliability.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Manufacturing Three Prong Plugs?
The first step in the manufacturing process involves sourcing high-quality raw materials. The primary materials used are:
- Thermoplastic or Thermosetting Plastics: These are used for the plug casing, providing durability and insulation. Common plastics include PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene).
- Metal Contacts: Copper is the standard material for the prongs due to its excellent conductivity. Some manufacturers may use nickel or other alloys to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Insulation Materials: These materials are essential for safety, ensuring that electrical components are adequately protected from accidental contact.
Suppliers need to verify that all materials comply with international safety and environmental standards, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals).
2. Forming: How Are Three Prong Plugs Shaped and Molded?
In the forming stage, the raw materials are shaped into the desired form. This typically involves:
- Injection Molding: For the plastic casing, injection molding is the preferred method. In this process, heated plastic is injected into a mold and cooled to form the plug body.
- Stamping and Machining: The metal contacts are stamped from copper sheets and then machined to achieve the necessary dimensions and surface finishes. This ensures a snug fit within the plug casing.
Quality assurance begins here as manufacturers monitor temperature, pressure, and cycle times closely to maintain consistency and avoid defects.
3. Assembly: What Techniques Are Used to Assemble Three Prong Plugs?
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins. This includes:
- Component Assembly: The metal prongs are inserted into the plastic casing. Precision is crucial here to ensure a secure fit and proper electrical connection.
- Soldering or Welding: In some designs, the metal contacts may be soldered or welded to the internal wiring, ensuring a robust electrical connection that can withstand wear and tear.
- Final Assembly and Inspection: Each plug is assembled, and an initial visual inspection is conducted to check for any obvious defects.
4. Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage involves several processes to ensure that the product is ready for sale:
- Surface Treatment: This may include plating the metal parts to prevent corrosion and enhance conductivity.
- Quality Testing: Each plug undergoes rigorous testing, including electrical continuity tests, dielectric strength tests, and mechanical stress tests.
- Packaging: Finally, the plugs are packaged in a manner that protects them during transportation and provides necessary labeling for compliance with international standards.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Commonly Used in Three Prong Plug Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of three prong plugs, as they are essential components in electrical safety. Manufacturers often adhere to international and industry-specific standards to ensure product safety and reliability.
Relevant International Standards: Which Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is applicable across industries, ensuring that manufacturers have consistent processes for quality control.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- UL Certification: In North America, UL certification signifies that the product meets safety standards established by Underwriters Laboratories.
- RoHS Compliance: This ensures that the product is free from hazardous substances, critical for environmental sustainability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process of three prong plugs. Commonly, these checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, ongoing checks are performed to monitor the quality of production, including machinery calibration and dimensional checks.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to ensure the final product meets all specifications and safety standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers utilize a variety of testing methods to ensure the safety and performance of three prong plugs, including:

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
- Electrical Testing: Continuity tests ensure that electrical connections are intact, while dielectric tests assess insulation integrity.
- Mechanical Testing: Stress tests evaluate the durability of the plugs under various conditions, simulating real-world usage.
- Temperature and Humidity Testing: These tests ensure that the plugs can function effectively in different environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control practices, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Audits: Conducting supplier audits allows buyers to assess manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand.
- Requesting Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality control reports, including results from testing and compliance with standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality assurance processes.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. It is vital for buyers to understand local compliance requirements.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers that offer transparency in their supply chains, including traceability of materials and components.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can aid in establishing effective communication and collaboration with suppliers.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing three prong plugs, ensuring that they meet both safety standards and operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘three prong plug’
In the fast-evolving landscape of electrical components, sourcing the right three-prong plug is crucial for ensuring safety and compatibility in various applications. This guide provides a practical checklist to assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions when procuring three-prong plugs, whether for industrial use, commercial projects, or large-scale distribution.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical requirements is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. Consider factors such as voltage ratings, current capacity, and environmental conditions (e.g., indoor vs. outdoor use). Define whether you need standard plugs or specialized types, such as those with weatherproof features or specific certifications for safety.
Step 2: Research Compliance and Safety Standards
Ensure that the three-prong plugs you are considering meet relevant international safety and compliance standards. This could include certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories), CE (Conformité Européenne), or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards. Compliance is vital not only for regulatory reasons but also for minimizing risks associated with electrical failures.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct thorough evaluations. Request detailed company profiles, including years in business, product ranges, and existing clientele. Ask for case studies or references from buyers in similar industries or regions to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 4: Check for Product Variety and Customization Options
Look for suppliers that offer a variety of three-prong plug options, including different sizes, colors, and configurations. Customization capabilities can be a significant advantage, allowing you to tailor products to your specific needs. This is especially useful for projects requiring unique specifications or branding.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Conduct a comparative analysis of pricing across different suppliers, considering not just the initial costs but also bulk pricing options and payment terms. Ensure that the pricing aligns with your budget while maintaining quality standards. Look for suppliers who offer flexible payment arrangements, which can help manage cash flow effectively.
Step 6: Request Samples for Quality Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the three-prong plugs for quality assessment. Testing samples can help you verify their durability, performance, and compatibility with your existing systems. This step is crucial to ensure that the products meet your technical specifications and safety standards.
Step 7: Finalize Logistics and Delivery Terms
Discuss logistics, including shipping options, lead times, and delivery terms. Ensure that the supplier can meet your timeline and that they have reliable shipping practices to avoid delays. Consider discussing return policies and warranty options to safeguard your investment in case of defects or issues.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement of three-prong plugs more effectively, ensuring they meet both technical and safety requirements while also managing costs and supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for three prong plug Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Three Prong Plugs?
When sourcing three prong plugs, understanding the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as PVC for insulation, copper for wiring, and metal for prongs significantly influences the overall price. Quality certifications (e.g., UL, CE) can increase material costs but ensure safety and compliance with international standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the production location. Countries with lower labor costs, such as Vietnam or some regions in Africa, may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to ensure that labor practices meet ethical standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs, leading to lower prices for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in molds and machinery for producing plugs can be substantial. This cost is typically amortized over the production run, affecting the price per unit. Custom designs will necessitate higher tooling costs, which should be factored into negotiations.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures is critical to ensure product reliability. This may involve additional costs, but it is a worthwhile investment for reducing defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly depending on the mode of transport, distance, and Incoterms agreed upon. Understanding these logistics can help buyers choose the most cost-effective shipping solutions.
-
Margin: Suppliers often have different pricing strategies based on their market positioning. Understanding a supplier’s margin expectations can facilitate better negotiation outcomes.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Three Prong Plugs?
Several factors influence the pricing of three prong plugs, which international B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs, but buyers must balance this against their inventory management capabilities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to specialized tooling and materials. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects durability and performance but also the price. Higher-quality materials often come with a premium, so buyers should assess their needs carefully.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products with recognized certifications typically command higher prices due to the assurance of safety and reliability. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certification against potential cost savings from uncertified products.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and service level can influence pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can affect total costs. Buyers must understand their responsibilities regarding shipping and customs to avoid hidden fees.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Three Prong Plug Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management are essential:
-
Negotiation: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your cost structure and market conditions. Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to strengthen your position.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, warranty, and maintenance costs.
-
International Pricing Nuances: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that may affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate some risks.
-
Supplier Diversification: Avoid dependency on a single supplier by diversifying your supplier base. This can enhance bargaining power and reduce risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
-
Local Partnerships: Consider partnering with local distributors or agents in target markets to navigate regulatory landscapes and optimize logistics.
Disclaimer
Prices for three prong plugs can vary widely based on the above factors and market conditions. It is advisable to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing three prong plug With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Three Prong Plug
In today’s diverse electrical landscape, the three prong plug is a standard solution for connecting devices to power sources safely. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific applications, particularly for B2B buyers in international markets. This section analyzes the three prong plug against two viable alternatives: the two prong plug and the power adapter with a built-in transformer.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Three Prong Plug | Two Prong Plug | Power Adapter with Built-in Transformer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for grounding and safety | Adequate but lacks grounding | High efficiency, adjustable voltage |
| Cost | Generally low-cost | Typically lower than three prong | Moderate to high, depending on specs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation | Very easy, plug and play | Requires careful selection of voltage |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Low maintenance | May require occasional checks |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty appliances, equipment | Lightweight devices, small appliances | Sensitive electronics needing voltage control |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Two Prong Plug
The two prong plug is a common alternative to the three prong plug, primarily used for devices that do not require grounding. While it is generally less expensive and easier to install, its lack of a grounding prong can pose safety risks, especially for devices with metal casings. For B2B buyers, this option is best suited for low-power appliances where grounding is not a critical concern, such as small household items or electronics that are double-insulated.
Power Adapter with Built-in Transformer
Power adapters with built-in transformers are another alternative that can offer enhanced versatility. These devices allow for different voltage outputs, making them suitable for various electronic applications. While they may come at a higher cost and require more careful selection to ensure compatibility with the equipment, they provide excellent performance and safety features, particularly for sensitive electronics. B2B buyers should consider this option for environments where equipment varies in voltage requirements or where devices are susceptible to damage from incorrect voltage.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right power connection solution depends on several factors, including the specific application, safety requirements, and budget constraints. The three prong plug excels in safety and is ideal for heavy-duty use, while the two prong plug offers a cost-effective and straightforward solution for low-power devices. In contrast, power adapters provide flexibility for varying voltage needs but may involve a higher initial investment. B2B buyers should evaluate their operational requirements and safety standards when choosing the most appropriate solution, ensuring that they align with the specific demands of their industry and market.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for three prong plug
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Three Prong Plug?
1. Material Composition
Three prong plugs are commonly made from thermoplastics such as PVC or nylon, which provide durability and insulation. The prongs are typically constructed from brass or copper for optimal conductivity. Understanding the material used is crucial for B2B buyers, as it directly influences the plug’s performance, safety, and longevity in various environmental conditions.
2. Voltage and Current Ratings
Each three prong plug has specified voltage and current ratings, often ranging from 120V to 250V and 10A to 16A, depending on the application. These ratings determine the plug’s suitability for different electrical devices. Buyers must ensure that the plug meets the electrical requirements of their equipment to prevent overheating or failure.
3. Grounding Mechanism
The grounding prong is a critical safety feature that prevents electrical shock by providing a path for fault current to ground. This is particularly important for devices with metal casings. In B2B transactions, it is essential to verify that the plugs comply with international safety standards, such as IEC 60320, to ensure safe operation in various markets.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
4. Length and Gauge of Wire
The wire length and gauge (thickness) used in a three prong plug can affect performance and usability. Typical wire gauges range from 16 to 12 AWG, with longer lengths requiring thicker wires to reduce voltage drop. Buyers should consider the application to choose the appropriate wire specifications, as this can impact efficiency and safety.
5. Tolerance and Certification Standards
Tolerance levels indicate the acceptable variations in dimensions and performance characteristics. Additionally, certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne) signify that the product meets specific safety and quality standards. For B2B buyers, ensuring that products are certified is vital for compliance with local regulations and market entry.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Three Prong Plugs?
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of three prong plugs, buyers often engage with OEMs to create customized solutions that meet specific requirements. Understanding OEM partnerships can lead to better pricing and tailored features.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs while ensuring they can meet demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers ask suppliers to provide pricing for specific products. For three prong plugs, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs, lead times, and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For B2B buyers sourcing three prong plugs from different countries, understanding Incoterms is essential to avoid unexpected costs and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. In the electrical components industry, lead times can vary significantly based on production capacity and shipping distance. For international buyers, managing lead times is critical to ensuring timely project execution and maintaining supply chain efficiency.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminology empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing three prong plugs, ensuring they meet safety standards and operational requirements while optimizing their procurement processes.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the three prong plug Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Three Prong Plug Sector?
The global market for three prong plugs is experiencing notable growth driven by increasing urbanization, rising demand for electrical appliances, and the expansion of infrastructure in developing regions. In Africa and South America, particularly in countries like Brazil and Vietnam, the growing middle class is leading to higher household electrification rates, which in turn drives the need for reliable and safe electrical components such as three prong plugs.
Emerging trends include the shift towards smart home technologies, which integrate three prong plugs into more advanced systems that require safety and connectivity. Additionally, the demand for customizable and modular plug solutions is on the rise, as businesses seek to meet specific regional electrical standards and consumer preferences. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can provide not only standard products but also innovative solutions tailored to local market needs.
Market dynamics also reflect a heightened emphasis on quality and safety certifications. International standards such as UL, CE, and IEC are critical for ensuring product reliability and compliance, particularly for buyers in Europe and the Middle East. As regulatory frameworks become more stringent globally, B2B buyers must ensure that their sourcing partners meet these compliance requirements to mitigate risks associated with electrical safety.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Three Prong Plug Sector?
Sustainability has become a key consideration for B2B buyers in the three prong plug sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and materials is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt eco-friendly practices. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who utilize sustainable materials, such as recyclable plastics and biodegradable components, in their products.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses recognize the necessity of transparent supply chains that respect labor rights and environmental regulations. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade practices are becoming essential in supplier selection. This trend is particularly relevant in regions such as Africa and South America, where ethical sourcing can significantly enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to socially conscious consumers.
Furthermore, the push for energy efficiency is influencing product design. Three prong plugs that incorporate energy-saving technologies, such as smart functionality that allows for power monitoring and control, are increasingly sought after. This not only reduces environmental impact but also appeals to cost-conscious buyers aiming to lower their energy bills.
What Is the Evolution of the Three Prong Plug and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of the three prong plug dates back to its introduction in the early 20th century, designed to provide enhanced safety through grounding. Initially, two prong plugs were standard; however, the inclusion of a third prong addressed electrical safety concerns by providing a path for fault current, significantly reducing the risk of electrical shock.
In the B2B context, this evolution signifies the growing emphasis on safety and regulatory compliance in electrical components. As markets expand globally, understanding the historical context of electrical standards can guide buyers in making informed sourcing decisions. Knowledge of the evolution of the three prong plug is crucial for international buyers, as it underpins current safety standards and technological advancements that are now foundational to electrical product design.
Overall, staying abreast of these market dynamics, sustainability trends, and historical contexts equips B2B buyers with the insights needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing three prong plugs effectively and responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of three prong plug
-
How do I choose the right three-prong plug for my electrical needs?
Selecting the appropriate three-prong plug involves understanding the specific requirements of your electrical devices. Consider the voltage and amperage ratings of your equipment, as well as the plug’s compatibility with local standards. For international buyers, ensure the plug conforms to the electrical codes in your region, including voltage (e.g., 120V or 240V) and frequency (e.g., 50Hz or 60Hz). It’s advisable to consult with your supplier to verify that the plugs meet safety certifications relevant to your market. -
What are the benefits of using three-prong plugs over two-prong plugs?
Three-prong plugs provide enhanced safety by incorporating a grounding prong that reduces the risk of electric shock. This is particularly important for appliances with metal casings, as the grounding feature directs excess electricity safely away from users. Additionally, three-prong plugs are commonly used for devices requiring higher power, ensuring reliable performance and compliance with modern electrical standards. For businesses, investing in three-prong plugs can lead to improved equipment longevity and reduced liability risks. -
What customization options are available for three-prong plugs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for three-prong plugs, including variations in length, color, and materials. Businesses can request specific features such as weather-resistant coatings for outdoor use or specialized connectors for unique applications. When sourcing, engage with your supplier to discuss your specific requirements, including branding options or compliance with regional standards. Customization can enhance product differentiation and meet the unique demands of your target market. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for three-prong plugs?
The MOQ for three-prong plugs varies by supplier and can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Smaller orders may be possible for established buyers or through specific arrangements. It’s essential to communicate your needs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure they can accommodate your order size while maintaining competitive pricing. Understanding MOQs can help businesses effectively manage inventory and cash flow. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing three-prong plugs internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases typically vary based on supplier policies and buyer relationships. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments, or net 30/60 days after delivery. Buyers should clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or online payment systems. Negotiating favorable payment terms can significantly impact cash flow management and financial planning, so it is advisable to establish clear agreements before finalizing orders. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for three-prong plugs sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, engage suppliers who adhere to international safety standards and certifications such as UL, CE, or RoHS. Request product samples to verify quality before placing larger orders. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or hiring third-party inspection services to evaluate manufacturing processes. Establishing a quality control plan and maintaining open communication with your supplier can help mitigate risks associated with product defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing three-prong plugs?
When importing three-prong plugs, consider shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations in your country. Determine whether air freight or sea freight is more economical based on your urgency and budget. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes to avoid unexpected costs. Additionally, partnering with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the shipping process and ensure compliance with local regulations, ultimately facilitating smoother transactions. -
What common mistakes should I avoid when sourcing three-prong plugs?
One common mistake is neglecting to research supplier credentials and product certifications, which can lead to compliance issues and safety risks. Additionally, failing to communicate specific requirements can result in receiving unsuitable products. Avoid underestimating lead times, as delays can disrupt operations. Finally, ensure you have a clear understanding of the total landed cost, including shipping and tariffs, to avoid budget overruns. Thorough diligence in these areas can lead to successful sourcing outcomes.
Top 6 Three Prong Plug Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Creative Cables – 3-Prong Plug
Domain: creative-cables.us
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: 3-Prong Plug, suitable for various electrical applications, designed for safety and reliability, compatible with standard outlets, available in multiple colors, made from durable materials, easy to install, ideal for DIY projects.
2. HowStuffWorks – Electrical Safety Plugs
Domain: electronics.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Two-pronged plugs have two vertical slots (neutral and hot) and do not provide grounding, while three-pronged plugs include a ground prong for safety against electric shock. The left slot in a three-prong plug is neutral (white wire), the right is hot (black wire), and the ground is connected to the green wire. Three-prong plugs are designed for appliances with metal casings to protect users from …
3. Sundial Wire – 3-Prong Plugs
Domain: sundialwire.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: 3-Prong Plugs: 1. Heavy Rubber Plug, Black – $4.00 2. Thermoplastic Plug – $3.00 3. Female Heavy-Duty Connector for 3-Prong Plug, Black – $7.50 4. Female Grounded Connector for 3-Prong Plug, Black – $7.50
4. Wadsworth City – Three-Prong Plug Safety
Domain: wadsworthcity.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The three-prong plug includes a third prong that provides a path to ground for stray or leaking electricity, enhancing safety by protecting equipment and preventing electric shock. It is advised not to remove or bend the third prong to fit a two-slot outlet; instead, use an adapter only if the grounding wire is connected to an electrical ground or install an appropriate three-slot outlet.
5. Reddit – Electrical Plugs Explained
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Plugs typically have two or three prongs. Two-prong plugs consist of a ‘hot’ prong that carries electrical current and a ‘neutral’ prong that returns it. Three-prong plugs include an additional ‘ground’ prong for safety, connecting external metal parts of appliances to ground to prevent electric shock in case of internal shorts. The use of three-prong plugs became mandated for major appliances in …
6. Target – Outlet Extenders & Surge Protectors
Domain: target.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Target – Outlet Extenders & Surge Protectors, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for three prong plug
In the competitive landscape of electrical components, particularly three prong plugs, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal approach for international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances of product specifications, compatibility, and safety standards is essential to ensure that your procurement processes align with regulatory requirements in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
By leveraging strategic sourcing, companies can not only reduce costs but also enhance supply chain resilience, ensuring a steady flow of high-quality products. Establishing partnerships with reliable manufacturers and suppliers who understand local market dynamics can significantly improve your product offerings and customer satisfaction.

Illustrative image related to three prong plug
As the demand for safe and efficient electrical solutions continues to rise, it is imperative for buyers to stay informed about innovations in design and technology associated with three prong plugs. Embrace the opportunity to diversify your sourcing strategies and invest in products that meet both safety standards and consumer expectations.
Looking ahead, consider how your sourcing decisions can shape your business’s future. Engage with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and quality to stay ahead of the competition. The time to act is now—optimize your sourcing strategy and position your business for success in the evolving global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.