Choosing Your Stone Etching Acid: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stone etching acid
Navigating the global market for stone etching acid presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Sourcing the right stone etching acid can significantly impact the quality and durability of stone products, which are increasingly sought after in construction, architecture, and art. With a plethora of options available, buyers must consider various factors such as types of acids, their applications, supplier credibility, and cost implications.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of stone etching acid, detailing the different types available, their specific applications in various industries, and essential criteria for vetting suppliers. It also provides insights into pricing structures and market trends, enabling buyers to make informed decisions that align with their project needs and budget constraints.
By understanding the nuances of stone etching acid, B2B buyers will be empowered to select the most suitable products that enhance their offerings while ensuring compliance with local regulations and environmental considerations. Ultimately, this guide serves as a valuable resource for those looking to navigate the complexities of sourcing stone etching acid effectively, ensuring quality and sustainability in their procurement processes.
Understanding stone etching acid Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid | Strong, fast-acting acid; effective on various stones. | Industrial cleaning, stone finishing | Pros: Quick results, effective on tough stains. Cons: Requires safety precautions, can damage sensitive surfaces. |
| Phosphoric Acid | Less aggressive; ideal for polishing and etching. | Food industry, stone restoration | Pros: Safer on delicate surfaces, versatile. Cons: Slower action, may require multiple applications. |
| Citric Acid | Natural, weak acid; eco-friendly option. | Residential cleaning, DIY projects | Pros: Non-toxic, biodegradable. Cons: Less effective on heavy etching, longer application time. |
| Acetic Acid (Vinegar) | Easily accessible; effective on light etching. | Home cleaning, maintenance | Pros: Readily available, safe for most surfaces. Cons: Limited effectiveness on severe etching. |
| Sulfuric Acid | Highly corrosive; used for heavy-duty applications. | Industrial manufacturing, etching | Pros: Extremely effective for deep etching. Cons: Very hazardous, requires careful handling. |
What Are the Characteristics of Hydrochloric Acid for Stone Etching?
Hydrochloric acid is a powerful etching agent known for its rapid action on various types of stone, including granite and marble. This acid is commonly used in industrial settings for cleaning and finishing stone surfaces. B2B buyers should consider its effectiveness in removing tough stains and etching marks; however, the strong nature of hydrochloric acid necessitates strict safety precautions to prevent damage to sensitive stones and harm to users.
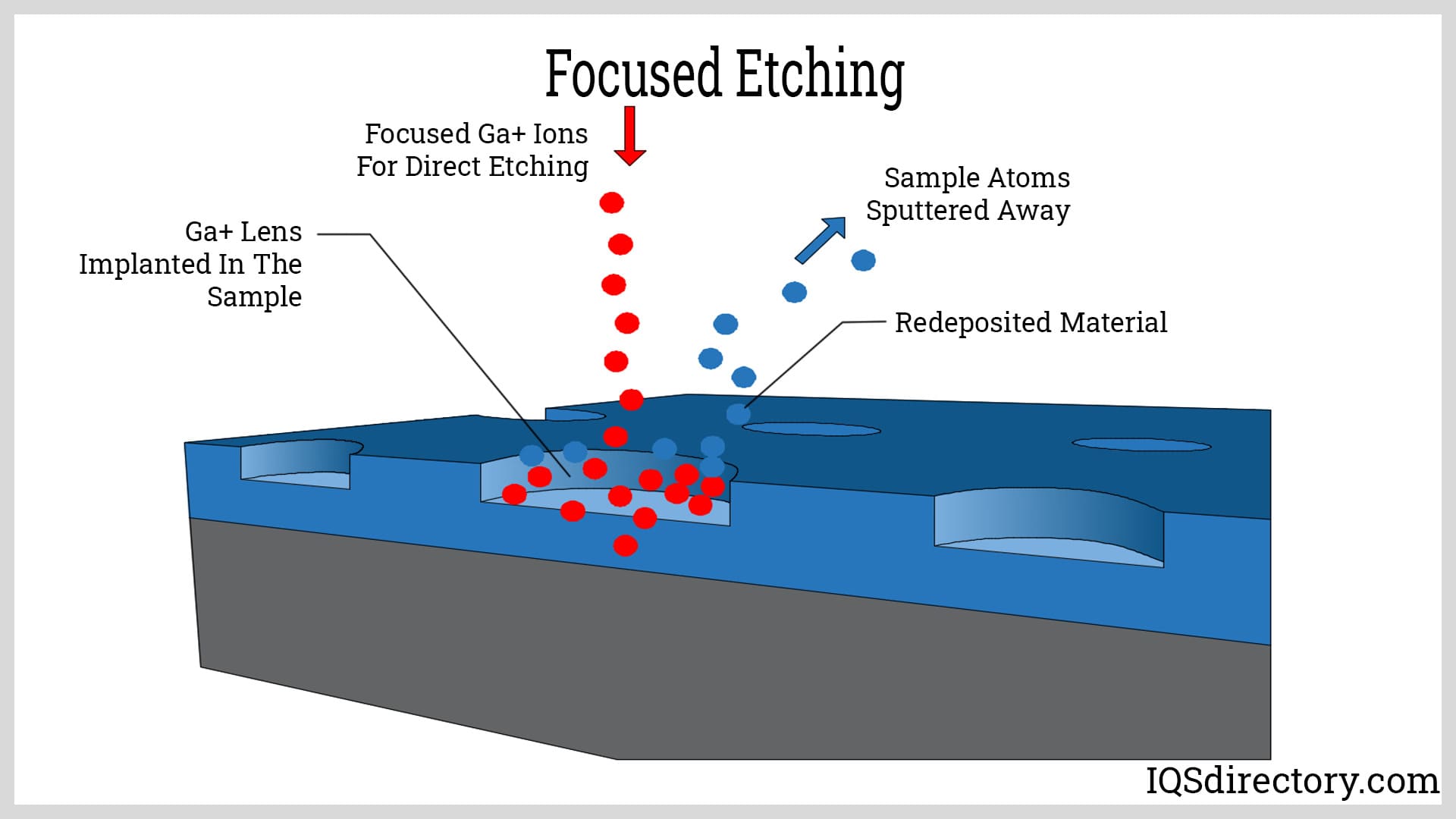
Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
How Does Phosphoric Acid Differ in Application and Suitability?
Phosphoric acid is a more moderate acid, making it suitable for polishing and etching without the aggressive effects seen with stronger acids. It is often utilized in the food industry and stone restoration projects. For B2B buyers, the key consideration is its balance between effectiveness and safety; it is less likely to damage delicate stone surfaces, but may require multiple applications for optimal results, which can extend project timelines.
Why Choose Citric Acid as an Eco-Friendly Option?
Citric acid is a natural, weak acid derived from citrus fruits, making it an eco-friendly choice for etching and cleaning. Its applications are primarily in residential cleaning and DIY projects, appealing to buyers seeking sustainable options. While citric acid is non-toxic and biodegradable, it may not be as effective on severe etching compared to stronger acids. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of safety and environmental impact against the potential need for longer application times.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Acetic Acid (Vinegar)?
Acetic acid, commonly found in vinegar, is readily accessible and effective for light etching and cleaning. It is often used in home maintenance, making it a popular choice for small-scale B2B applications. The advantages include its availability and safety for most surfaces; however, buyers should note its limited effectiveness on more severe etching, which might necessitate stronger alternatives for comprehensive stone restoration.
When Is Sulfuric Acid the Right Choice for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Sulfuric acid is one of the most potent etching agents available, often utilized in industrial manufacturing and heavy-duty etching processes. Its extreme effectiveness makes it suitable for deep etching and significant restoration tasks. However, the highly corrosive nature of sulfuric acid poses substantial risks, requiring careful handling and extensive safety measures. B2B buyers must assess whether the benefits of rapid and thorough etching outweigh the associated hazards and handling complexities.
Key Industrial Applications of stone etching acid
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of stone etching acid | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction & Architecture | Surface finishing of natural stone facades | Enhances aesthetics and durability of stone surfaces | Quality of acid, safety data sheets, and eco-friendliness |
| Stone Restoration | Restoration of damaged marble and granite surfaces | Restores value and appearance of stone installations | Expertise in application methods and compatibility with stone types |
| Art & Design | Creating textured finishes on sculptures and decor | Adds unique visual appeal and tactile quality | Sourcing from reliable suppliers with artistic experience |
| Landscaping | Etching stone pavers and garden features | Provides decorative elements that enhance outdoor spaces | Availability of various acid types and environmental safety measures |
| Manufacturing | Producing acid-etched decorative tiles | Differentiates product offerings in a competitive market | Consistency in acid quality and regulatory compliance |
How is Stone Etching Acid Used in Construction and Architecture?
In the construction and architecture sector, stone etching acid is employed to finish natural stone facades, providing a textured and aesthetically pleasing surface. This application not only enhances the visual appeal of buildings but also increases the durability of the stone against environmental wear. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing high-quality acids that comply with local regulations is crucial. Additionally, suppliers should provide safety data sheets to ensure safe handling during application.
What Role Does Stone Etching Acid Play in Stone Restoration?
Stone etching acid is essential in the restoration of damaged marble and granite surfaces, effectively removing etch marks and stains that standard cleaning cannot address. By restoring the original beauty of stone installations, businesses can significantly increase the value of their properties. Buyers in the stone restoration industry must consider the acid’s compatibility with different stone types and the expertise required for effective application. This is particularly important in regions with rich stone heritage, like Europe and the Middle East.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
How is Stone Etching Acid Utilized in Art and Design?
In the art and design industry, stone etching acid is used to create textured finishes on sculptures and decorative pieces, enhancing their aesthetic appeal. This technique allows artists to reveal the natural beauty of the stone while adding a unique tactile quality. For B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers that understand artistic applications and provide various acid options is essential. Buyers should also prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to safety and environmental responsibility.
What Benefits Does Stone Etching Acid Provide in Landscaping?
In landscaping, stone etching acid is applied to etch patterns into stone pavers and garden features, adding decorative elements that elevate outdoor spaces. This application not only enhances the visual appeal of landscapes but also helps in creating non-slip surfaces. Buyers in this sector should ensure the availability of various acid types suitable for different stone materials and confirm that suppliers adhere to environmental safety standards, especially in regions where eco-friendly practices are increasingly prioritized.
How is Stone Etching Acid Used in Manufacturing Decorative Tiles?
Manufacturers use stone etching acid to produce decorative tiles with unique, acid-etched designs, differentiating their products in a competitive market. This process allows for customization and creativity in tile design, appealing to a broader customer base. For B2B buyers in the manufacturing sector, consistency in acid quality and adherence to regulatory compliance are critical factors. Buyers should seek suppliers who can provide reliable sourcing and technical support to ensure successful product development.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stone etching acid’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Identifying the Right Acid for Stone Etching Applications
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate acid for etching different types of stone. With various stone materials like marble, granite, and limestone having unique properties, the wrong choice can lead to inadequate etching results or, worse, damage the stone surface. This uncertainty can be particularly challenging for buyers looking to maintain quality while adhering to cost constraints. Missteps in acid selection not only impact the quality of the final product but can also lead to increased costs due to rework or the need for professional restoration services.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the stone types they are working with and consult technical data sheets provided by acid manufacturers. A standardized approach involves categorizing stones by their pH sensitivity and etching characteristics. For instance, while diluted hydrochloric acid can effectively etch limestone, it may dull the finish of polished marble. It’s advisable to procure a sample of the acid solution and perform small-scale tests on inconspicuous areas before full application. Additionally, engaging suppliers who offer detailed product guidance and technical support can facilitate informed decision-making, ensuring that the right acid is sourced for specific stone types.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns During Acid Etching Processes
The Problem: The use of stone etching acids presents significant safety risks, including chemical burns and inhalation of harmful fumes. B2B buyers, particularly those in regions with stringent safety regulations, must navigate the complexities of ensuring worker safety while managing the etching process. This concern is heightened when working with concentrated acids that require specialized handling and protective equipment, creating additional layers of complexity in training and compliance.
The Solution: To mitigate safety risks, businesses should implement a comprehensive safety protocol that includes employee training on the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and respirators. Buyers should also invest in high-quality, eco-friendly acid solutions where possible, as these typically have less harmful exposure levels. Furthermore, establishing a well-ventilated workspace or utilizing fume extraction systems can significantly reduce inhalation risks. Regular safety audits and refresher training sessions will reinforce safe practices, ensuring a culture of safety throughout the organization.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Etching Results Leading to Product Variability
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the issue of inconsistent etching results across different projects, leading to variability in product quality. Factors such as uneven application, varying stone compositions, and environmental conditions can all contribute to unpredictable outcomes. This inconsistency can damage reputations, particularly in industries where aesthetic appeal is crucial, such as in high-end architecture or interior design.
The Solution: To achieve consistent etching results, buyers should adopt standardized procedures and protocols for the application of stone etching acids. This includes precise measurements for dilution, consistent application techniques, and environmental controls (such as humidity and temperature). Utilizing high-quality application tools, such as brushes or sprayers designed for acid application, can also lead to more uniform results. Additionally, implementing a quality control system that includes visual inspections and performance evaluations will help in identifying and correcting any deviations early in the process, ensuring that all finished products meet established quality standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stone etching acid
When selecting materials for stone etching acids, it is vital for B2B buyers to consider the properties, advantages, and limitations of various acid solutions. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in stone etching applications: Hydrochloric Acid, Phosphoric Acid, Citric Acid, and Acetic Acid. Each of these acids has unique characteristics that influence their effectiveness and suitability for different stone types.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
What are the Key Properties of Hydrochloric Acid for Stone Etching?
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) is a strong mineral acid known for its high reactivity and ability to dissolve a wide range of materials, including certain types of stone. It has a boiling point of 110°C and can effectively etch surfaces by removing mineral deposits and stains. However, its corrosive nature requires careful handling and appropriate protective measures.
Pros & Cons: Hydrochloric Acid is highly effective for cleaning and etching due to its strength, making it suitable for tough stains on stones like limestone and marble. However, it can cause significant damage to more delicate stones and requires neutralization after use, adding complexity to the application process.
Impact on Application: This acid is particularly effective on calcareous stones but may not be suitable for silicate-based stones, such as granite. International buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of strong acids and ensure compliance with safety standards.
How Does Phosphoric Acid Compare for Etching Stone?
Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4) is a less aggressive acid often used in stone etching and cleaning applications. It has a lower corrosive potential than hydrochloric acid, making it safer for various stone types. Phosphoric Acid is effective at removing rust and mineral deposits without significantly damaging the stone surface.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Pros & Cons: Its moderate strength allows for effective etching while being less likely to harm delicate stone surfaces. However, it may require longer application times and multiple treatments for severe stains, which can increase labor costs.
Impact on Application: Phosphoric Acid is compatible with a wide range of stones, including marble and granite. B2B buyers should consider its effectiveness in different climates, as humidity and temperature can affect performance.
What are the Benefits of Using Citric Acid for Stone Etching?
Citric Acid, a weak organic acid found in citrus fruits, is an eco-friendly alternative for stone etching. Its mild nature makes it suitable for delicate stones, and it can effectively remove light stains and etch surfaces without the harsh effects of stronger acids.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of Citric Acid is its safety and environmental friendliness, making it an appealing choice for companies focused on sustainability. However, its effectiveness is limited to minor etching and cleaning, which may not meet the needs of all applications.
Impact on Application: Citric Acid is an excellent option for softer stones and can be used in residential settings where safety is a priority. International buyers should verify the availability of this acid in their region, as sourcing may vary.
Why Consider Acetic Acid for Stone Etching?
Acetic Acid, commonly known as vinegar, is another mild acid that can be used for etching stone surfaces. It is particularly effective for cleaning and removing mineral deposits. Its low pH (around 2.4) allows it to interact with stone surfaces without causing significant damage.
Pros & Cons: Acetic Acid is inexpensive and readily available, making it an attractive option for smaller businesses. However, its effectiveness is limited compared to stronger acids, and it may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Impact on Application: This acid is suitable for softer stones and can be used in various settings, including residential and commercial. Buyers should ensure compliance with local health and safety regulations when using any acid-based products.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Stone Etching Acid
| Material | Typical Use Case for stone etching acid | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric Acid | Heavy-duty etching and cleaning | Highly effective for tough stains | Corrosive, requires neutralization | High |
| Phosphoric Acid | General stone etching and cleaning | Safer for delicate stones | Longer application time | Medium |
| Citric Acid | Light etching and eco-friendly cleaning | Environmentally friendly | Limited effectiveness | Low |
| Acetic Acid | Mild cleaning and etching | Inexpensive and readily available | Not suitable for heavy-duty use | Low |
This guide provides a strategic overview of materials used in stone etching acid applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and local regulations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stone etching acid
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Stone Etching Acid?
The manufacturing process of stone etching acid involves several key stages that ensure the product meets industry standards and customer expectations. Here’s a breakdown of these stages:
1. Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The initial phase involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, typically acids like hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, or citric acid. Suppliers must ensure that these chemicals meet international quality standards. Depending on the intended application, additives may also be included to enhance the etching properties or reduce environmental impact.
2. Forming: How Is the Acid Mixture Prepared?
Once the raw materials are gathered, they are mixed in controlled environments to create the etching solution. This stage includes precise measurements to ensure the correct chemical balance. Advanced mixing techniques, such as vacuum mixing or high-shear mixing, may be employed to achieve uniformity in the solution.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
3. Assembly: How Are Packaging and Labeling Handled?
After the etching solution is prepared, it is transferred into appropriate containers that are resistant to corrosion. This may include high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or glass bottles. Proper labeling is crucial, as it provides safety information and instructions for use. This stage may also involve the assembly of additional safety kits or application tools, depending on the supplier’s offerings.
4. Finishing: What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented?
The final stage of manufacturing involves quality assurance checks and packaging. Each batch of stone etching acid must undergo rigorous testing to ensure it meets the specified pH levels and etching capabilities. This phase also includes compliance with regulatory requirements, particularly for hazardous materials.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Stone Etching Acid Production?
Quality assurance in the production of stone etching acid is governed by several international standards that ensure product safety and efficacy. Here are the most relevant standards:
ISO 9001: How Does This Standard Affect Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Companies involved in the manufacturing of stone etching acid must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. This involves documenting processes, conducting regular audits, and implementing continuous improvement strategies.
CE Marking: What Does It Indicate for Buyers?
For products sold in the European Union, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Buyers from Europe should ensure that their suppliers provide products with the CE mark, which signifies that the stone etching acid has undergone necessary evaluations and complies with EU directives.
API Standards: Are They Applicable?
For companies involved in the oil and gas sector, American Petroleum Institute (API) standards might be relevant, particularly if the etching acid is used in maintenance or restoration of stone structures in these industries. Suppliers should be able to provide documentation on compliance with API standards to reassure buyers of product safety and effectiveness.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control is integral at various stages of the manufacturing process. Here are the primary checkpoints:
Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): How Is Raw Material Quality Assured?
IQC involves testing raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This includes verifying the chemical composition and purity of acids and additives to ensure they meet predefined specifications. Non-conforming materials must be flagged and rejected to maintain overall product quality.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): What Monitoring Is Conducted During Production?
During the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring critical parameters such as mixing time, temperature, and pH levels. Regular sampling is conducted to ensure the product remains consistent throughout the production cycle. Any deviations from established parameters necessitate immediate corrective actions.
Final Quality Control (FQC): What Tests Are Performed Before Shipping?
FQC is the last checkpoint before the product is packaged and shipped. This stage includes comprehensive testing of the final product for its etching effectiveness, pH levels, and safety compliance. Batch records and test results are documented to provide traceability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, verifying supplier quality control practices is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are several methods to consider:
Audits: What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to assess quality control processes. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s QMS, compliance with international standards, and their track record in product testing and safety protocols. A well-documented audit report can provide insights into the supplier’s operational integrity.
Quality Reports: How Important Are They?
Quality reports that detail testing results, compliance certifications, and production processes are essential for buyers. Suppliers should provide documentation that outlines their QC measures and the results of recent tests. This transparency helps in building trust and ensures that the product meets the buyer’s expectations.
Third-Party Inspections: Are They Necessary?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. This is particularly important for buyers in regions where regulations are stringent, as third-party verification can help ensure compliance with local and international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Regulatory Compliance: What Local Regulations Must Be Considered?
Different countries may have varying regulations concerning the import and use of chemical products like stone etching acid. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local laws and ensure that their suppliers comply with these regulations to avoid legal issues.
Language and Communication Barriers: How Can They Be Overcome?
Language barriers can complicate communication regarding quality control practices. Buyers should seek suppliers who offer multilingual support or use translation services to ensure that specifications and quality requirements are clearly understood.
Cultural Considerations: How Do They Impact Business Relationships?
Cultural differences can influence business practices and expectations regarding quality assurance. Understanding these cultural nuances can help buyers foster better relationships with suppliers, ensuring smoother negotiations and improved collaboration.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in the Stone Etching Acid Supply Chain
For B2B buyers in the stone etching acid market, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is critical. By knowing the stages of production, relevant standards, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and establish partnerships with reliable suppliers. Quality assurance not only safeguards investments but also ensures the effectiveness and safety of the products in various applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stone etching acid’
In the competitive landscape of sourcing stone etching acid, having a clear and actionable checklist can streamline your procurement process. This guide is designed to equip B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with essential steps to effectively source quality stone etching acid.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific types of stone etching acid you require based on your intended applications. Consider the acid concentration, compatibility with various stone types (like marble, granite, and limestone), and whether you need a product for industrial-scale use or smaller projects. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough market research to identify suppliers with a solid reputation in the stone etching acid industry. Look for companies with positive reviews, a proven track record, and experience in international trade. Utilize platforms such as industry-specific directories and trade shows to discover potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s vital to perform a comprehensive evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, product samples, and references from past clients, particularly those in similar industries or regions. This due diligence ensures that the supplier meets your quality and reliability standards.
- Check for Certifications: Verify that the suppliers hold necessary certifications such as ISO standards, which indicate quality management practices.
- Assess Product Quality: Request certifications for the acid’s efficacy and safety, ensuring it meets regulatory requirements in your market.
Step 4: Understand Regulatory Compliance
Familiarize yourself with the regulations governing the import and use of acidic materials in your region. Each country may have specific safety, handling, and disposal requirements for hazardous substances. Ensuring compliance not only prevents legal issues but also protects your business’s reputation.
Step 5: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes. Ensure the quotes include costs for shipping, handling, and any potential tariffs. Compare the pricing structures but also consider the value offered—higher quality may justify a higher price.
- Consider Bulk Discounts: Inquire about bulk purchasing options that could lower your overall costs.
- Evaluate Payment Terms: Review the payment options and terms offered, as favorable conditions can improve cash flow.
Step 6: Conduct a Trial Order
Before placing a large order, conduct a trial purchase with your chosen supplier. This allows you to assess the quality of the stone etching acid and the supplier’s reliability in terms of shipping and customer service. Gather feedback from your team on the product’s performance in real-world applications.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
After a successful trial order, consider establishing a long-term partnership with your supplier. Consistent procurement can lead to better pricing, priority service, and more favorable terms. Regular communication helps to foster trust and ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations and quality standards.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing stone etching acid more effectively, ensuring they find reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stone etching acid Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Stone Etching Acid?
When considering the procurement of stone etching acid, it is essential to understand the various cost components involved. These typically include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the acid itself, which can vary based on its concentration and purity. Common acids used for etching, such as hydrochloric acid or citric acid, have different pricing structures depending on their source and quality.
-
Labor: The cost of labor involves not only the workforce required to produce the acid but also the skilled labor necessary for quality control and compliance with safety regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to the production environment, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and depreciation.
-
Tooling: Specific tools and machinery may be required to handle and process the acids safely. The initial investment in these tools can impact overall costs.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that the acid meets industry standards necessitates rigorous testing and quality assurance protocols, adding to the overall expense.
-
Logistics: Transporting chemicals requires specialized handling and compliance with international shipping regulations, particularly for hazardous materials. This can significantly affect logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a markup to cover their operational costs and desired profit margin. This can vary widely based on market conditions and competitive pressures.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Stone Etching Acid Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of stone etching acid, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Understanding the MOQ can help negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions may incur higher costs. If specific concentrations or formulations are required, be prepared for a premium price.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher purity acids or those with environmental certifications may come at a higher cost but can offer better performance and compliance with regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: Relationships with suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a good track record may offer better terms than newer or less reputable ones.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (Incoterms) can significantly affect the total landed cost. Understanding whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties is crucial for accurate budgeting.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Stone Etching Acid?
B2B buyers looking to source stone etching acid should consider several strategic approaches:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating better terms, especially when placing large orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts or favorable payment terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors like quality, shelf life, and the potential for waste or rework.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Trade: Different regions may have distinct pricing structures and regulations. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of these variations and factor them into their sourcing decisions.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keep an eye on market conditions that might impact pricing, such as changes in raw material availability or geopolitical factors affecting shipping routes.
-
Consider Environmental Impact: As regulations around chemical usage tighten globally, sourcing environmentally friendly options may not only be a compliance issue but also a selling point in your own market.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
The costs associated with stone etching acid can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. Prices should be considered indicative and may fluctuate based on market dynamics, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations before finalizing any procurement decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stone etching acid With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Stone Etching Acid: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of stone surface treatment, various solutions exist alongside stone etching acid, each offering unique benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers who aim to select the most effective solution for their specific applications. Below, we compare stone etching acid with two viable alternatives: mechanical polishing and laser etching.
| Comparison Aspect | Stone Etching Acid | Mechanical Polishing | Laser Etching |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Effective for dulling and creating a textured finish | Restores shine and smoothness | Precise designs with high detail |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing material costs | Higher labor costs; equipment investment | High initial investment; low ongoing costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires protective gear and careful application | Requires skilled labor and equipment | Requires specialized equipment and training |
| Maintenance | Minimal; occasional reapplication needed | Regular maintenance for optimal results | Minimal; permanent results |
| Best Use Case | Enhancing natural stone appearance | Restoring worn stone surfaces | Creating intricate designs on stone |
Understanding Mechanical Polishing: Advantages and Disadvantages
Mechanical polishing utilizes abrasives to smooth out the surface of natural stone, effectively restoring its original shine. This method is ideal for surfaces that have become scratched or dull over time. While it delivers excellent results, the process can be labor-intensive and requires skilled professionals to operate the equipment safely and effectively. Additionally, it may not achieve the same textural effects as acid etching, making it less suitable for those seeking a matte or distressed finish.
Evaluating Laser Etching: Pros and Cons
Laser etching represents a cutting-edge approach that employs focused laser beams to engrave designs or textures onto stone surfaces. This method allows for high precision and can create intricate patterns that are difficult to achieve with other techniques. While laser etching is highly effective and offers permanent results, the initial investment in specialized machinery can be substantial. Moreover, the need for trained operators can increase labor costs, making it less accessible for smaller businesses.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Stone Surface Treatment Solution
When selecting a solution for stone surface treatment, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including the specific application, desired finish, and budget constraints. Stone etching acid is ideal for those looking to enhance the natural beauty of stone with a textured finish, while mechanical polishing is better suited for restoring shine to worn surfaces. Laser etching, on the other hand, offers unparalleled precision for decorative purposes. By evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases of each option, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stone etching acid
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Stone Etching Acid?
When considering the procurement of stone etching acid, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring effective application and compliance with industry standards. Here are the key specifications that B2B buyers should focus on:
-
Acid Concentration
The concentration of the acid is a critical property that determines its effectiveness in etching stone surfaces. Common concentrations range from 10% to 30% for commercial applications. Higher concentrations yield faster etching but may require more stringent safety measures. Understanding the appropriate concentration needed for specific stone types helps buyers choose the right product for their application. -
pH Level
The pH level indicates the acidity of the etching solution. A lower pH (below 7) signifies stronger acidity, which is essential for effective etching. For instance, hydrochloric acid typically has a pH of around 1, making it highly effective for etching but also more hazardous. Buyers must assess the pH to ensure compatibility with the stone type and the desired finish. -
Material Compatibility
Different types of stone, such as marble, granite, and limestone, react differently to various acids. Buyers should ensure that the etching acid is compatible with the specific material being processed to avoid unwanted damage. This property is particularly significant for restoration projects where preserving the stone’s integrity is paramount. -
Safety Data and Handling Instructions
Given the corrosive nature of etching acids, comprehensive safety data sheets (SDS) are vital. These documents provide information on handling, storage, and emergency measures in case of exposure. Buyers must prioritize suppliers that provide clear safety guidelines to ensure the health and safety of their workforce. -
Shelf Life and Storage Conditions
The shelf life of stone etching acids varies based on formulation and storage conditions. Generally, acids should be stored in a cool, dry place and away from incompatible substances. Knowing the shelf life helps buyers manage inventory effectively and reduce waste.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Used in the Stone Etching Acid Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for smooth transactions and effective communication among buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms relevant to stone etching acid:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or products that are sold under another company’s brand name. In the context of stone etching acids, an OEM might manufacture specialized formulations for specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers looking to manage their budgets and inventory levels effectively. Lower MOQs can be beneficial for smaller operations or those testing new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate quotes that meet their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smoother international transactions. -
Batch Number
The batch number is a unique identifier assigned to a specific production run of a product. It is essential for tracking quality control and ensuring that the correct formulation is used in applications. Buyers should always request batch numbers for traceability. -
Neutralization
This term refers to the process of counteracting the effects of an acid with a base, commonly through the use of baking soda or similar substances. Understanding neutralization is critical for safe handling and disposal of etching acids, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing stone etching acid, ultimately leading to successful projects and satisfied customers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stone etching acid Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Stone Etching Acid Sector?
The global stone etching acid market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand in construction and home improvement sectors. Natural stone materials, such as marble and granite, are favored for their aesthetic appeal and durability, leading to a surge in the use of etching acids for both decorative and maintenance purposes. In regions like Africa and South America, the burgeoning construction industry, coupled with rising urbanization, is propelling demand. Additionally, buyers in the Middle East and Europe are increasingly seeking specialized etching solutions that can enhance the visual appeal of stone surfaces.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards digitalization in sourcing practices. B2B buyers are utilizing online platforms for procurement, enabling them to compare suppliers, read reviews, and access a wider range of products. Furthermore, innovative technologies, such as eco-friendly acid formulations and automated application systems, are gaining traction. These advancements not only improve efficiency but also align with the growing preference for sustainable practices in the industry.
In terms of market dynamics, the supply chain is becoming more globalized, with suppliers from various regions competing for market share. For international buyers, understanding local regulations and sourcing trends is crucial. Countries like Vietnam and Brazil are becoming key players, with their unique stone types and processing capabilities influencing global supply patterns. Buyers should focus on establishing relationships with reliable suppliers who can provide consistent quality and innovation.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing for Stone Etching Acid?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the stone etching acid sector. Environmental impact considerations are driving buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. Traditional etching acids, often derived from harsh chemicals, can pose risks to both human health and the environment. As a result, there is a growing demand for ‘green’ alternatives that utilize natural acids or biodegradable formulations.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. B2B buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains for transparency and sustainability. This includes evaluating suppliers based on their waste management practices, carbon footprint, and adherence to ethical labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Green Seal for eco-friendly products are gaining prominence, providing buyers with assurance regarding their suppliers’ commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, the emphasis on sustainability is not just a regulatory compliance issue; it’s also a market differentiator. Companies that adopt sustainable sourcing practices often find themselves favored by environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing their brand reputation and customer loyalty. International buyers should leverage these trends by prioritizing partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing.
What Is the Historical Context of Stone Etching Acid in B2B Markets?
The use of etching acids in the stone industry has evolved significantly over the decades. Initially, etching was a rudimentary process primarily focused on cleaning and maintaining stone surfaces. As the construction and design sectors grew, so did the techniques and applications of stone etching acids. The introduction of more sophisticated and less harmful acids in the 20th century marked a turning point, allowing for creative applications in decorative stonework.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Today, the market has transitioned from basic maintenance solutions to advanced etching techniques that enhance the aesthetic appeal of stone materials. This evolution reflects broader trends in consumer preferences for unique and customized design solutions. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential as it shapes current market offerings and informs sourcing strategies that prioritize innovation and quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stone etching acid
-
How do I solve etching problems on stone surfaces?
To address etching issues on stone surfaces, it’s essential to first identify the cause—typically acidic substances like vinegar or lemon juice. For minor etching, you can use a mild acid solution combined with physical abrasion, such as a soft cloth or sponge, to gently buff the affected area. Always test on a small, inconspicuous spot first. If the etching is severe or widespread, consider hiring a professional stone restoration service that has the expertise and equipment to restore the stone effectively without causing further damage. -
What is the best stone etching acid for commercial use?
The best stone etching acids for commercial use typically include phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid, or specialized stone etching products. The choice depends on the type of stone and the desired finish. For example, phosphoric acid is effective for etching limestone and marble, while hydrochloric acid is used for heavier-duty tasks. Always ensure the acid is suitable for the specific stone type to prevent damage. It’s also wise to consult with suppliers about product recommendations tailored to your specific needs. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing stone etching acid internationally?
When sourcing stone etching acid internationally, consider factors such as supplier credibility, product quality, compliance with local regulations, and shipping logistics. Verify the supplier’s certifications and quality assurance processes. Evaluate the cost of shipping and import duties, and ensure that the product meets safety standards in your country. Additionally, establish clear communication regarding lead times and delivery schedules to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
How can I vet potential suppliers of stone etching acid?
To vet potential suppliers, start by reviewing their reputation in the industry through references and customer testimonials. Assess their production capabilities, quality control measures, and compliance with international safety standards. Request samples to evaluate product quality and consistency. Engaging in direct communication can also reveal their responsiveness and willingness to address your specific needs. Lastly, consider their experience in exporting to your region, especially if you are based in Africa, South America, or the Middle East. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) for stone etching acid?
Minimum order quantities for stone etching acid can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific product. Typically, MOQs range from 100 liters to 1,000 liters for bulk purchases. However, some suppliers may offer flexibility for smaller orders, especially for new customers. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your business needs while ensuring cost-effectiveness. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing stone etching acid?
Payment terms for purchasing stone etching acid can vary, but common practices include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. Letters of credit are also frequently used in international transactions to ensure security for both parties. Always clarify the payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, PayPal) and any associated fees. Establishing clear payment terms in the contract can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) when buying stone etching acid?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing stone etching acid, request documentation that outlines the product specifications, safety data sheets (SDS), and compliance certificates. Conduct regular quality audits and inspections of shipments upon arrival. Establish a clear communication channel with your supplier for feedback and resolution of any quality issues. Additionally, consider implementing a testing protocol for new batches to ensure they meet your performance and safety standards. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing stone etching acid?
When importing stone etching acid, consider logistics such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and storage requirements. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling hazardous materials, as acid can be classified as such. Be aware of the import regulations specific to your region, including labeling and safety requirements. Ensure that your storage facilities are equipped to handle chemicals safely, with proper ventilation and containment measures in place to comply with local laws.
Top 3 Stone Etching Acid Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Orchid – Acid Etching Techniques
Domain: orchid.ganoksin.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the use of acids for etching, dyeing, or staining stones in jewelry making. Various acids mentioned include Nitric acid, Hydrofluoric acid, HCL (Hydrochloric acid), and Sulphuric acid, with a focus on their effectiveness on different types of stones. The conversation suggests that results can vary significantly based on the type of rock and its mineral composition. S…
2. ArmorPoxy – ArmorEtch Concentrated Acid Safe Etching Kit
Domain: armorpoxy.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: ArmorEtch Concentrated Acid Safe Etching Kit is designed for safe and effective etching on various surfaces. It is acid-safe, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. The kit includes concentrated etching solution, which allows for precise application and control. Ideal for glass, ceramics, and other materials, it provides a durable finish that enhances the appearance of the etched surf…
3. Stone Doctor – Stone Care Products
Domain: stonedoctor.com.au
Introduction: Enjoy up to 20% OFF + FREE SHIPPING when you purchase larger quantities. Brands include Lithofin Stone Sealers, Tenax Stone Mastics, MB Stone Care, Aqua Mix Protection, and more. Popular products include SDA Bundles & Kits, Diamond Tools, and various cleaning supplies. Services offered include marble cleaning, sealing, re-honing, and polishing. The company caters to residential, commercial, and in…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stone etching acid
In the evolving landscape of stone etching acids, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for B2B buyers aiming to enhance their competitive edge. Understanding the nuances of etching processes and the impacts of various acidic solutions allows businesses to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and environmental standards. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who not only provide high-quality products but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and safety practices.
As the demand for aesthetic stone finishes continues to rise in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is a significant opportunity for businesses to innovate and differentiate themselves. By leveraging partnerships with reliable suppliers and investing in advanced etching techniques, companies can enhance their product offerings while meeting the diverse needs of their clientele.

Illustrative image related to stone etching acid
Looking ahead, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to stay abreast of industry trends and regulatory changes impacting stone etching acids. Engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive training and support to maximize the effectiveness of your stone etching projects. By taking proactive steps today, businesses can secure a prosperous future in the competitive stone industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.