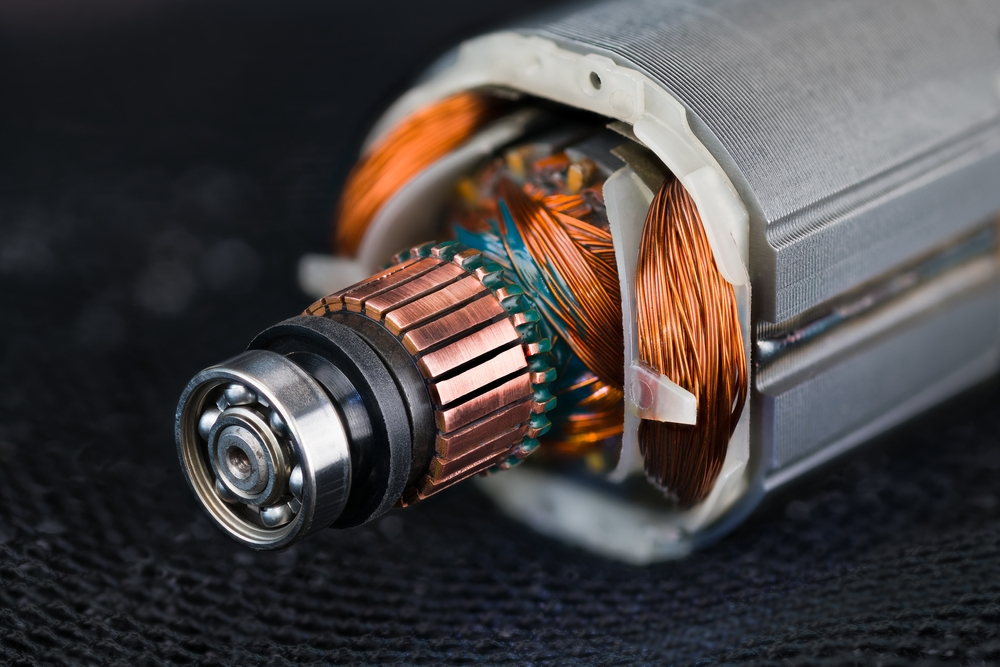
Choosing Your Stator Of Dc Motor: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for stator of dc motor
In today’s fast-paced global economy, sourcing the right stator for DC motors can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially when considering the diverse applications and performance requirements across industries. The stator, being a critical component of DC motors, plays a vital role in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion. This guide aims to demystify the complexities associated with procuring stators, offering insights into various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
As international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the market, they face unique challenges, including fluctuating costs, varying quality standards, and the need for reliable suppliers. This comprehensive resource addresses these challenges head-on, providing a detailed analysis of the different types of stators, their specific applications, and the key factors to consider when evaluating suppliers.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers will be equipped with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the most suitable stator for their operational needs. From understanding the advantages of brushed versus brushless DC motors to evaluating long-term cost implications, this guide serves as an essential tool for maximizing efficiency and driving success in today’s competitive landscape.
Understanding stator of dc motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Permanent Magnet Stator | Utilizes permanent magnets to create a constant magnetic field | Robotics, Electric Vehicles | Pros: High efficiency, compact design. Cons: Limited torque at high speeds. |
| Series Stator | Winding connected in series with the rotor, high torque at low speeds | Cranes, Hoists | Pros: High starting torque. Cons: Speed varies with load, less control. |
| Shunt Stator | Winding connected parallel to the rotor, allows for speed control | Conveyor Systems, Machine Tools | Pros: Stable speed, good control. Cons: Lower starting torque. |
| Compound Stator | Combination of series and shunt windings, versatile performance | Industrial Drives, Elevators | Pros: Good starting torque and speed regulation. Cons: More complex design. |
| Brushless Stator | Uses electronic commutation, no brushes required | High-performance applications, HVAC | Pros: Low maintenance, high efficiency. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
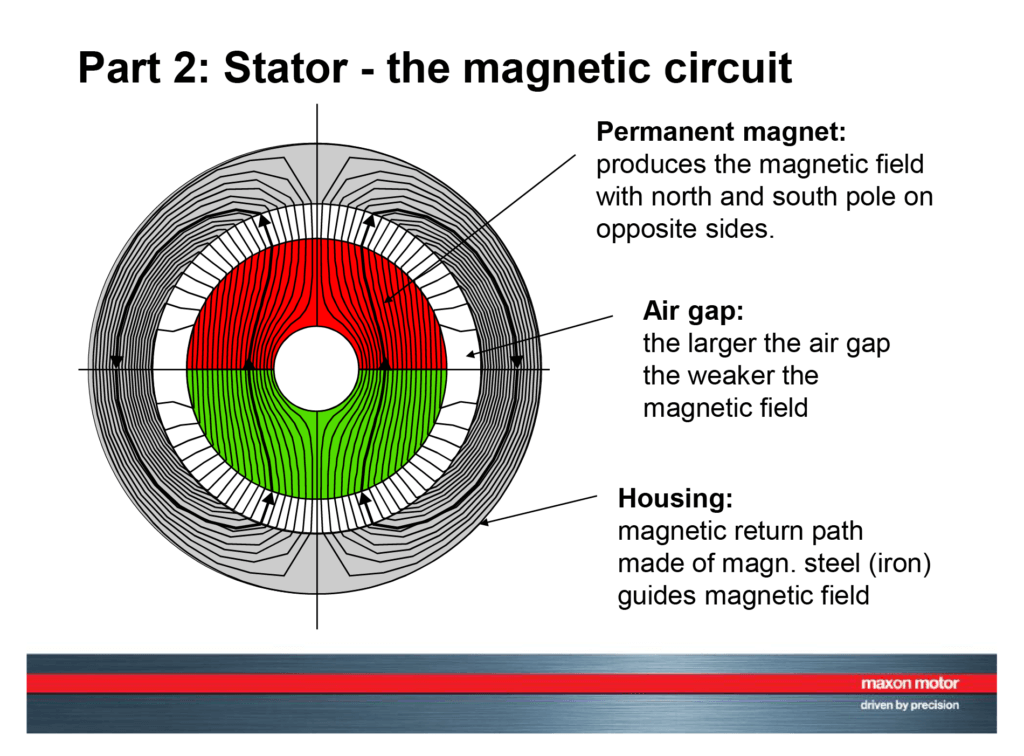
What are the Characteristics of Permanent Magnet Stators?
Permanent Magnet Stators are characterized by the use of permanent magnets to generate a constant magnetic field, which enhances efficiency and reduces the overall size of the motor. These types are particularly suitable for applications requiring compact designs and high performance, such as in robotics and electric vehicles. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate the operational environment to ensure that the permanent magnets can maintain performance without demagnetization.
How Do Series Stators Provide High Torque?
Series Stators are designed with windings connected in series with the rotor, which allows for high torque generation, especially at low speeds. This feature makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications like cranes and hoists, where starting torque is crucial. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high torque against the limitations of speed control, as series motors can experience significant speed variation depending on the load.
What Benefits Do Shunt Stators Offer?
Shunt Stators feature windings that are connected in parallel with the rotor, enabling better speed regulation compared to series types. They are commonly used in conveyor systems and machine tools where stable operational speeds are necessary. Buyers should consider the trade-off between starting torque and operational stability when selecting shunt motors, as they typically offer lower starting torque than series motors.
Why Choose Compound Stators for Versatility?
Compound Stators combine features of both series and shunt configurations, providing a balance of high starting torque and good speed regulation. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including drives and elevators. When purchasing, businesses should assess the complexity of the motor’s design and maintenance needs, as compound motors can be more intricate than simpler designs.
What Advantages Do Brushless Stators Present?
Brushless Stators utilize electronic commutation instead of mechanical brushes, resulting in reduced maintenance and increased efficiency. They are ideal for high-performance applications, including HVAC systems and precision machinery. Buyers should consider the higher initial costs associated with brushless motors, but they often benefit from long-term savings due to lower maintenance and higher efficiency over time.
Key Industrial Applications of stator of dc motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of stator of dc motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Enhanced efficiency in material handling processes | Durability under heavy loads, compatibility with existing systems |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbines | Reliable power generation and energy conversion | High-performance specifications, resistance to environmental factors |
| Automotive | Electric Vehicle Drive Systems | Improved torque and speed control for electric motors | Compliance with international standards, weight-to-power ratio |
| Robotics | Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) | Precision movement and operational efficiency | Size constraints, integration with sensors and controllers |
| HVAC | Fans and Blowers | Energy-efficient climate control solutions | Noise levels, energy consumption, and maintenance requirements |
How is the stator of a DC motor utilized in manufacturing conveyor systems?
In manufacturing, the stator of a DC motor is integral to conveyor systems, which facilitate the efficient movement of materials and products across production lines. The stator generates a magnetic field that drives the rotor, enabling precise speed control and torque necessary for heavy loads. This application helps businesses streamline operations, reduce manual labor, and enhance overall productivity. Buyers should consider the motor’s durability under heavy loads and its compatibility with existing conveyor systems to ensure seamless integration.
What role does the stator of a DC motor play in renewable energy applications like wind turbines?
In renewable energy, particularly wind turbines, the stator of a DC motor is crucial for converting kinetic energy into electrical energy. The stator’s design allows it to withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining high efficiency in power generation. This application addresses the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions. Buyers in this sector must prioritize high-performance specifications and resistance to environmental factors to ensure long-term reliability and efficiency.
How is the stator of a DC motor essential for electric vehicle drive systems?
The stator of a DC motor is vital in electric vehicle (EV) drive systems, where it provides the necessary torque and speed control for efficient vehicle operation. This technology enables rapid acceleration and smooth driving experiences, critical for customer satisfaction. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, sourcing motors that comply with international standards while offering an optimal weight-to-power ratio is essential for vehicle performance and regulatory compliance.
Why is the stator of a DC motor important in robotics, specifically for Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)?
In robotics, particularly with Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), the stator of a DC motor is key to achieving precise movement and operational efficiency. The motor’s ability to provide quick response times and controlled motion allows AGVs to navigate complex environments effectively. Buyers should focus on size constraints and the motor’s ability to integrate with sensors and controllers, ensuring that AGVs operate smoothly in industrial settings.
How does the stator of a DC motor enhance HVAC systems, particularly in fans and blowers?
The stator of a DC motor plays a significant role in HVAC systems, specifically in fans and blowers, by driving airflow efficiently while minimizing energy consumption. This application is crucial for maintaining optimal indoor climates in commercial and industrial settings. Buyers should consider factors such as noise levels, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements when sourcing motors for HVAC applications to ensure they meet both performance and regulatory standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘stator of dc motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Reliable Stators for DC Motors
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to find reliable suppliers for stators of DC motors, especially in regions like Africa and South America where access to quality components can be limited. Inconsistent quality and long lead times can disrupt production schedules, leading to increased costs and diminished trust from end customers. Furthermore, buyers may face challenges in verifying the authenticity of the parts and ensuring they meet specific industry standards.
The Solution: To effectively source reliable stators, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers and manufacturers known for their quality and reliability. Conducting thorough market research is crucial—utilize online platforms, trade shows, and industry networks to identify reputable vendors. Request samples and certifications that demonstrate compliance with international quality standards. Additionally, consider forming strategic partnerships with suppliers who can provide ongoing support and quick delivery options. This proactive approach will help mitigate risks associated with sourcing and ensure that production runs smoothly.
Scenario 2: High Maintenance Costs Due to Stator Wear and Tear
The Problem: Maintenance costs can be a significant pain point for companies relying on DC motors, particularly those with stators that are prone to wear and tear. The friction between the stator and rotor, along with environmental factors, can lead to accelerated degradation, resulting in costly repairs and downtime. This is especially problematic for industries such as manufacturing and logistics, where operational efficiency is paramount.
The Solution: To address high maintenance costs, buyers should focus on selecting stators with high-quality materials and advanced designs that minimize wear. Opt for stators equipped with better insulation and cooling mechanisms to enhance longevity. Implementing a regular maintenance schedule that includes inspections and cleaning can also help identify issues early before they escalate. Additionally, investing in predictive maintenance technologies can provide real-time data on motor performance, allowing for timely interventions and reducing overall maintenance expenses.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Integrating Stators with Existing Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when integrating new stators into existing DC motor systems. Compatibility issues, such as mismatched dimensions or electrical specifications, can lead to operational failures and require additional modifications. This is particularly common in sectors such as automotive and industrial automation, where precision and reliability are crucial.
The Solution: To ensure smooth integration of stators, buyers should conduct comprehensive compatibility assessments before making a purchase. This involves closely reviewing the specifications of both the new stator and the existing motor system. Working with engineers during the selection process can provide insights into potential challenges and solutions. Additionally, consider investing in customizable stators that can be tailored to fit specific operational requirements. By prioritizing compatibility from the outset, buyers can minimize integration issues, ensuring a seamless transition that enhances productivity and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for stator of dc motor
What Are the Key Materials Used for the Stator of a DC Motor?
Selecting the appropriate materials for the stator of a DC motor is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in stator construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Silicon Steel
Key Properties: Silicon steel is characterized by its excellent magnetic properties, high electrical resistivity, and good thermal conductivity. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silicon steel is its high magnetic permeability, which enhances efficiency by reducing energy losses due to hysteresis. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, including lamination to minimize eddy current losses.
Impact on Application: Silicon steel is particularly suitable for applications requiring high efficiency and low noise, such as in electric vehicles and industrial machinery. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile across different environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A677. The availability of silicon steel may vary, necessitating reliable suppliers who can meet demand.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a moderate thermal conductivity. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce the overall mass of the motor, enhancing efficiency. However, its lower magnetic permeability compared to silicon steel can lead to higher losses, making it less suitable for high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in portable tools and consumer electronics. Its corrosion resistance also makes it suitable for humid or coastal environments.
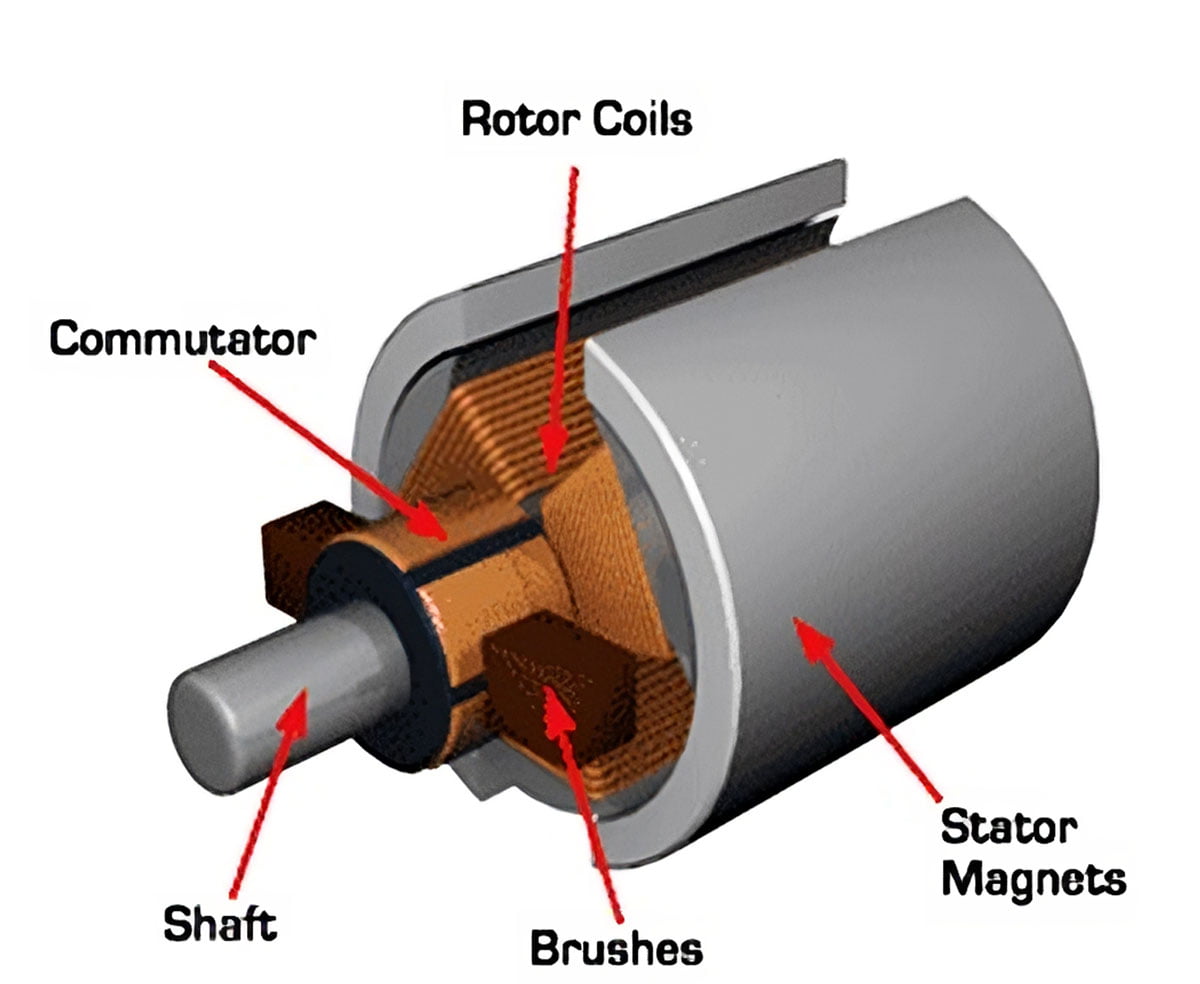
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding aluminum sourcing and recycling, particularly in Europe, where sustainability is a priority. Compliance with standards like DIN 17615 may be necessary.
3. Copper
Key Properties: Copper boasts excellent electrical conductivity and thermal performance, with a melting point around 1,085°C. It is resistant to corrosion and can handle high current loads.
Pros & Cons: The high conductivity of copper allows for efficient energy transfer, making it ideal for high-performance motors. However, copper is more expensive than aluminum and can add significant weight to the motor.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in motors that require high torque and quick response times, such as in robotics and industrial automation. Its compatibility with various operating conditions enhances its application range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the fluctuating prices of copper and the potential impact on overall project budgets. Compliance with international standards such as JIS H 3100 is also essential for quality assurance.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite materials can be engineered for specific applications, offering tailored properties such as lightweight, high strength, and resistance to environmental factors. Their thermal stability can vary widely based on the composition.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their versatility; they can be designed to meet specific performance criteria. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, and not all composites are suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in specialized applications where traditional materials may not suffice, such as in aerospace or high-performance automotive sectors. Their adaptability makes them valuable for innovative designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in emerging markets, the availability of composite materials may be limited. It is crucial to work with suppliers who understand local regulations and can provide materials that meet international standards.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for stator of dc motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | Electric vehicles, industrial machinery | High magnetic permeability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Portable tools, consumer electronics | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower magnetic permeability | Medium |
| Copper | Robotics, industrial automation | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost and added weight | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, high-performance automotive | Tailored properties for applications | Complex and costly manufacturing | Medium to High |
This guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions on material selection for the stator of DC motors, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with relevant standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for stator of dc motor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a Stator for a DC Motor?
The manufacturing process of a stator for a DC motor involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the production of a high-quality component that meets industry standards. Understanding these stages will enable B2B buyers to better evaluate suppliers and ensure product reliability.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The first step in manufacturing a stator is selecting the appropriate materials. Typically, high-grade electrical steel is chosen for its magnetic properties, which enhance efficiency. The steel sheets are cut into specific shapes and sizes, often using laser cutting or shearing techniques.
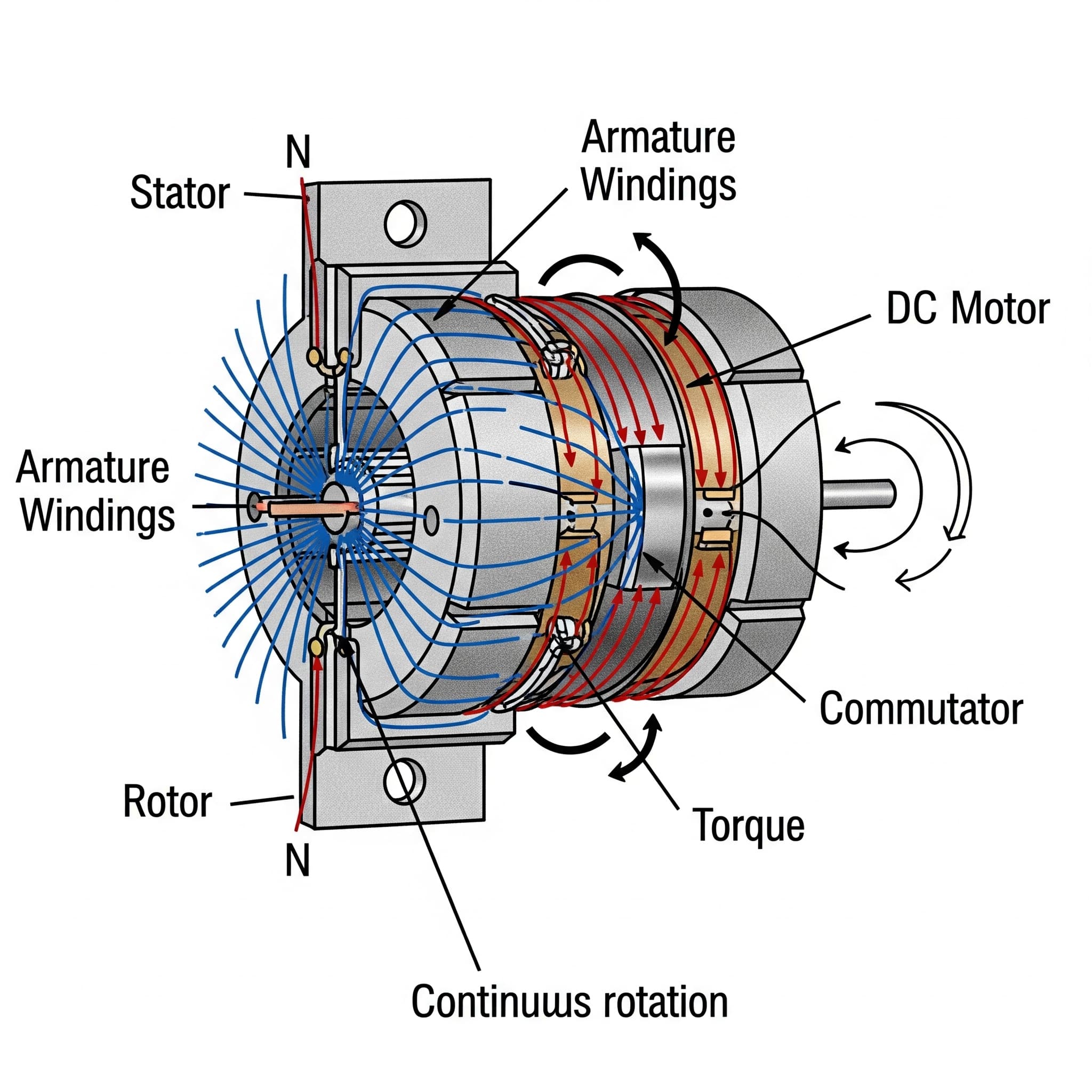
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
After cutting, the sheets undergo a process called stacking, where they are assembled in layers to reduce eddy current losses. This step is crucial for improving the overall efficiency of the DC motor. Depending on the design requirements, materials such as insulation coatings may also be applied to enhance electrical performance and reduce losses.
2. What Techniques Are Used for Forming the Stator Components?
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming the stator components. This typically involves stamping or die-casting, where the stacked sheets are shaped into the final form of the stator. Stamping is a common technique that ensures precision and consistency, while die-casting can be used for creating intricate geometries.
For stators that require windings, the forming process also includes the preparation of slots where the winding coils will be placed. These slots must be accurately positioned and sized to ensure optimal performance when the motor is assembled. The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software is prevalent in this stage to ensure precision.
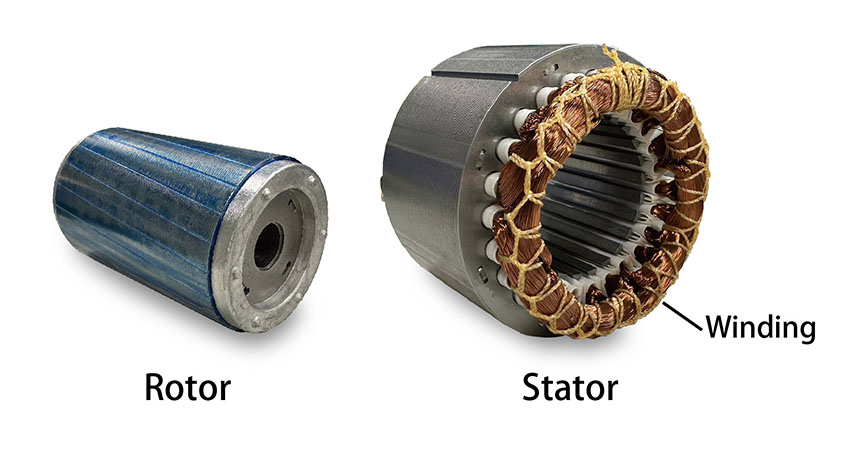
3. How Is the Assembly of the Stator Conducted?
The assembly stage involves placing the windings into the slots of the stator. This is typically done using automated winding machines, which enhance speed and accuracy. The winding process can vary based on whether the motor is a brushed or brushless type, as the winding patterns differ.
Once the windings are inserted, the stator undergoes a process known as impregnation. This involves applying resin or varnish to the windings to secure them in place and enhance insulation. The stator is then cured in an oven to harden the resin, ensuring durability and longevity.
4. What Finishing Techniques Are Implemented?
The final stage of the manufacturing process is finishing, which includes several steps aimed at enhancing the stator’s performance and aesthetics. This often involves machining to remove any burrs or sharp edges, ensuring a smooth surface for assembly with other motor components.
Additionally, surface treatments such as painting or coating may be applied to protect against corrosion and environmental factors. Quality checks during this phase are critical to ensure that the stator meets all specifications and standards before it is shipped.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Stators of DC Motors?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of the manufacturing process for stators, ensuring that each product meets international standards and customer expectations. Buyers must understand the QA measures in place at their chosen suppliers.
1. Which International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
To ensure high-quality manufacturing, B2B buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001. This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that processes are in place to consistently deliver products that meet customer requirements.
Additionally, compliance with industry-specific standards like CE marking or API can indicate that the products meet safety and environmental regulations. Such certifications are especially important for buyers operating in regions with stringent regulatory frameworks.
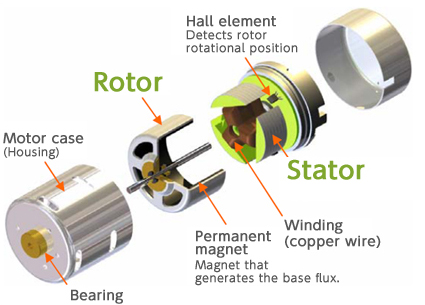
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
2. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Typically, these checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various inspections are conducted to monitor quality at each stage, from material preparation to assembly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the stators are completed, a thorough inspection is performed to check for defects, ensuring that all components are functioning correctly.
3. How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers have several avenues for verifying a supplier’s quality control practices. Conducting audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their processes and adherence to standards.
Requesting documentation such as quality control reports, test results, and certifications is another effective method. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality management practices.
4. What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional regulations and standards is crucial. Different regions may have specific compliance requirements that need to be addressed.
Buyers should also consider logistical factors, such as shipping and handling, which can affect product quality. Establishing clear communication with suppliers about quality expectations and potential challenges is essential for maintaining quality across borders.
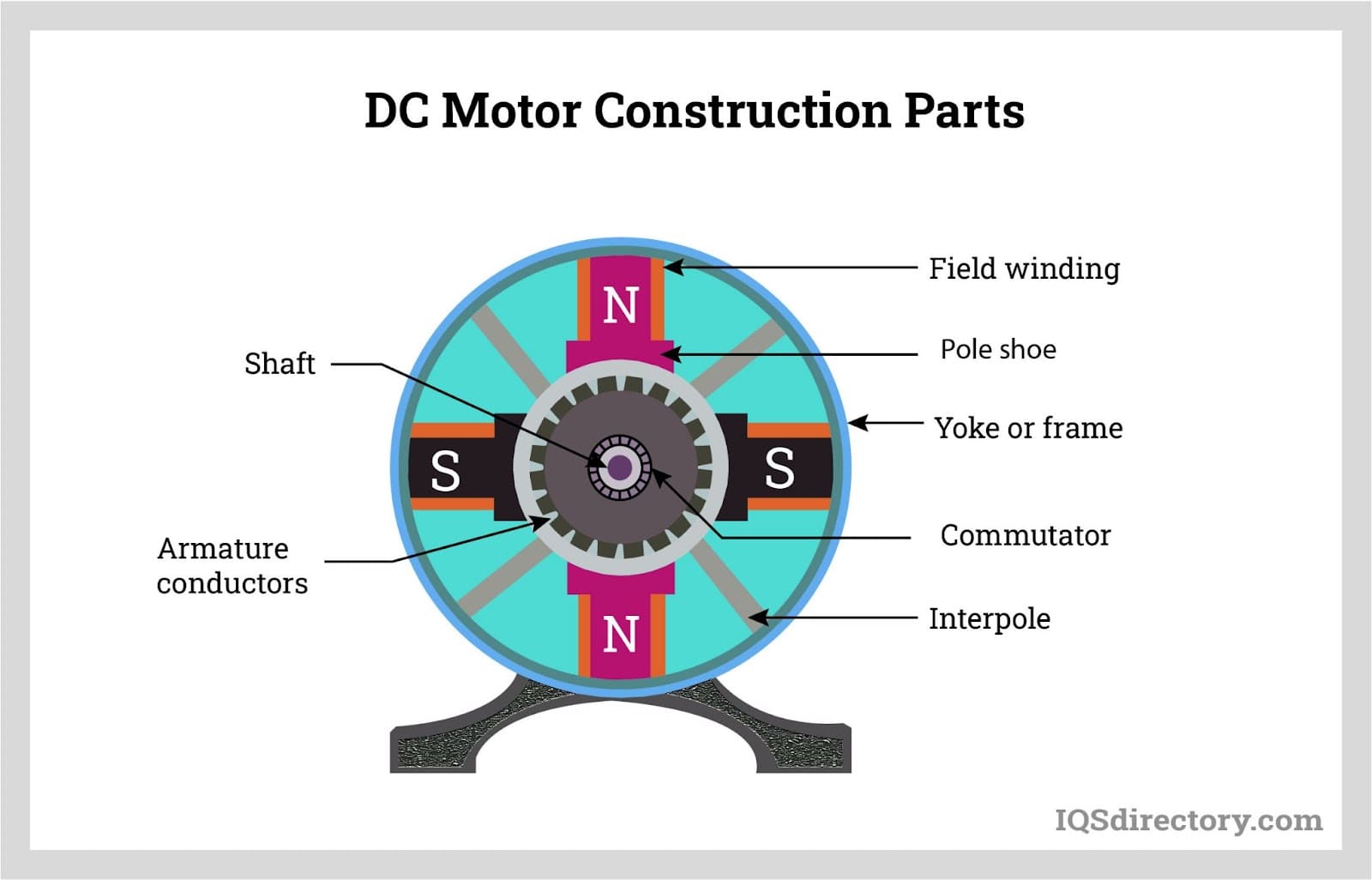
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for the stator of a DC motor are complex and critical for ensuring reliability and performance. By understanding these processes and the associated quality control practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. This knowledge not only enhances product quality but also fosters long-term partnerships within the global supply chain.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘stator of dc motor’
Introduction
Sourcing a stator for a DC motor involves several critical steps to ensure the final product meets your specifications and operational requirements. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, you can make informed decisions that enhance your procurement process and ensure a successful partnership with suppliers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications for the stator is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider the dimensions, material types, and electrical characteristics necessary for your application. This information will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure that the stators you receive meet your operational needs.
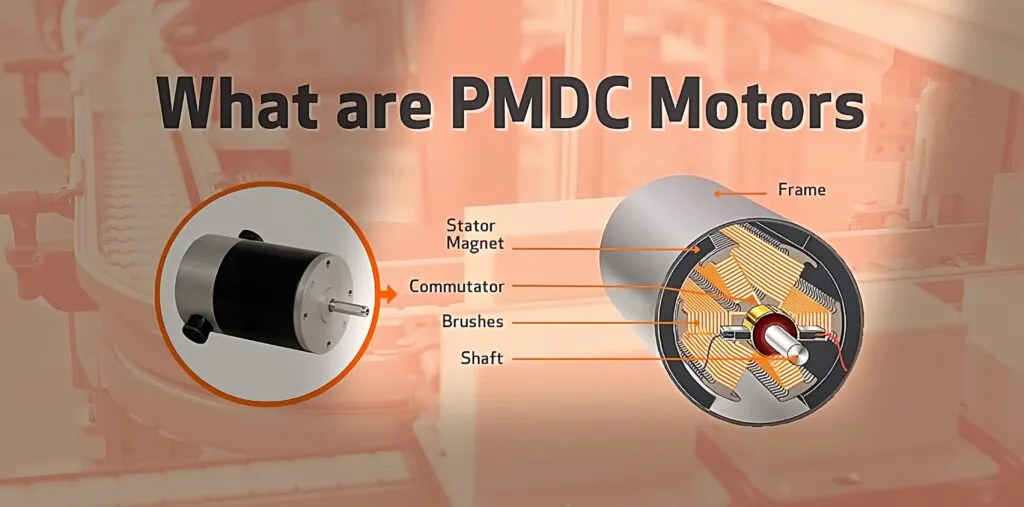
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
- Key Considerations:
- Voltage and current ratings
- Required torque and speed characteristics
- Environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity)
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reliable suppliers of DC motor stators. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to gather a list of candidates. A well-researched supplier can significantly impact your product quality and delivery timelines.
- Focus Areas:
- Company reputation and history
- Product range and specialization
- Market presence in your region
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding with a supplier, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management, while industry-specific certifications can assure you of their expertise.
- What to Look For:
- ISO or other relevant quality certifications
- Compliance with local and international safety standards
- Evidence of previous successful projects
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Once you’ve shortlisted suppliers, request samples of their stators to evaluate quality and compatibility with your specifications. Analyzing samples allows you to assess the workmanship, materials, and overall design.
- Evaluation Criteria:
- Visual inspection for defects
- Performance testing under controlled conditions
- Compatibility with your existing motor systems
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Pricing is a crucial factor in your sourcing decision. Obtain detailed quotations from multiple suppliers and analyze the cost structure, including shipping and customs duties. Be sure to consider the total cost of ownership, not just the initial price.
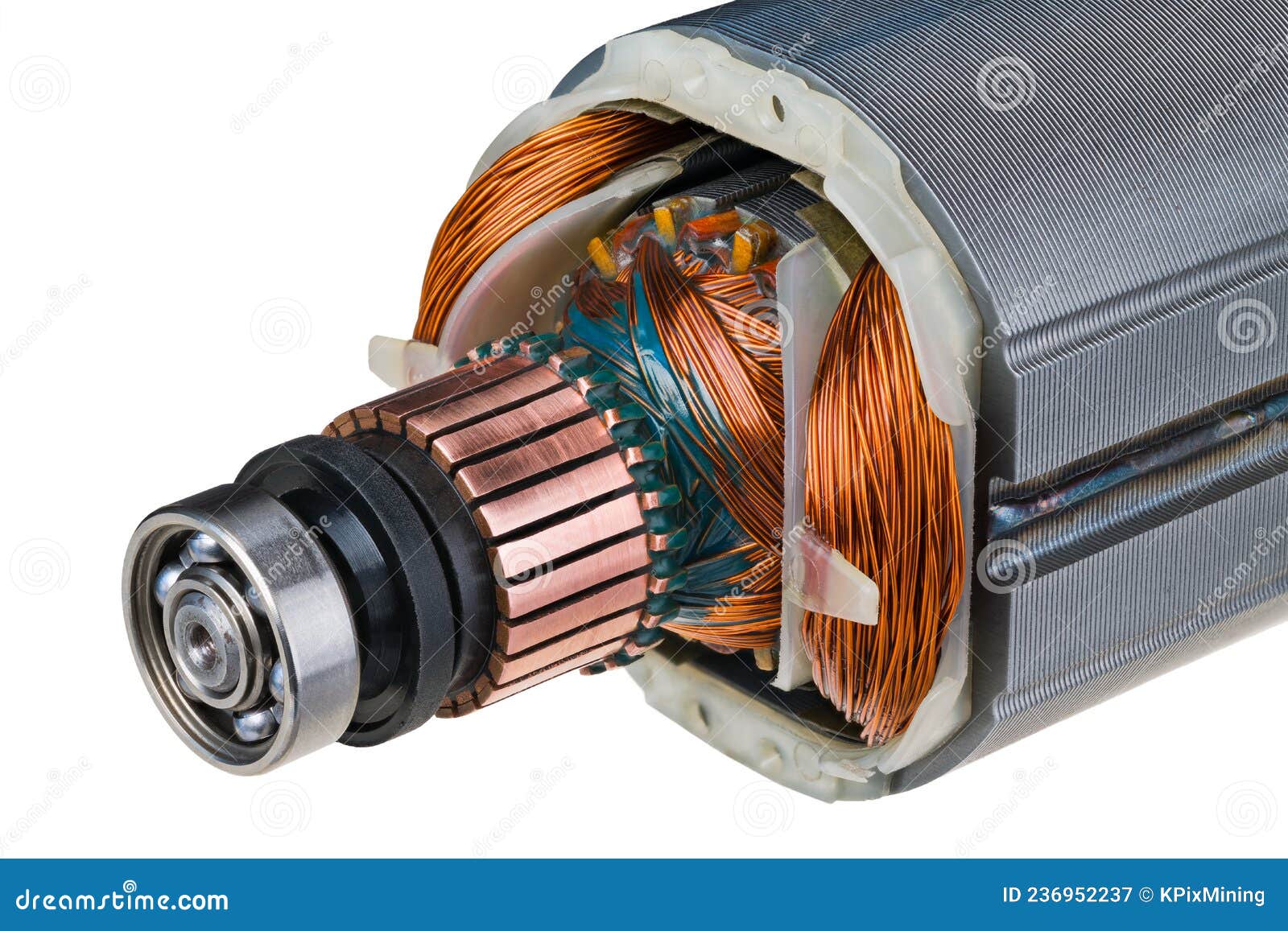
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
- Considerations:
- Payment terms (e.g., upfront, net 30)
- Volume discounts for bulk orders
- Warranty and return policies
Step 6: Negotiate Contract Terms
Once you’ve selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of the contract. Clear agreements on delivery timelines, quality expectations, and after-sales support can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Key Elements to Discuss:
- Lead times and shipping arrangements
- Quality assurance processes
- Support for installation and maintenance
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is essential throughout the sourcing process. Establish regular check-ins with your supplier to discuss progress, address concerns, and adjust specifications as needed. A strong partnership often hinges on transparent and open communication.
- Best Practices:
- Schedule regular updates via email or calls
- Use project management tools for tracking milestones
- Foster a collaborative relationship for future projects
By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process for stators in DC motors and build lasting relationships with suppliers that contribute to your business success.
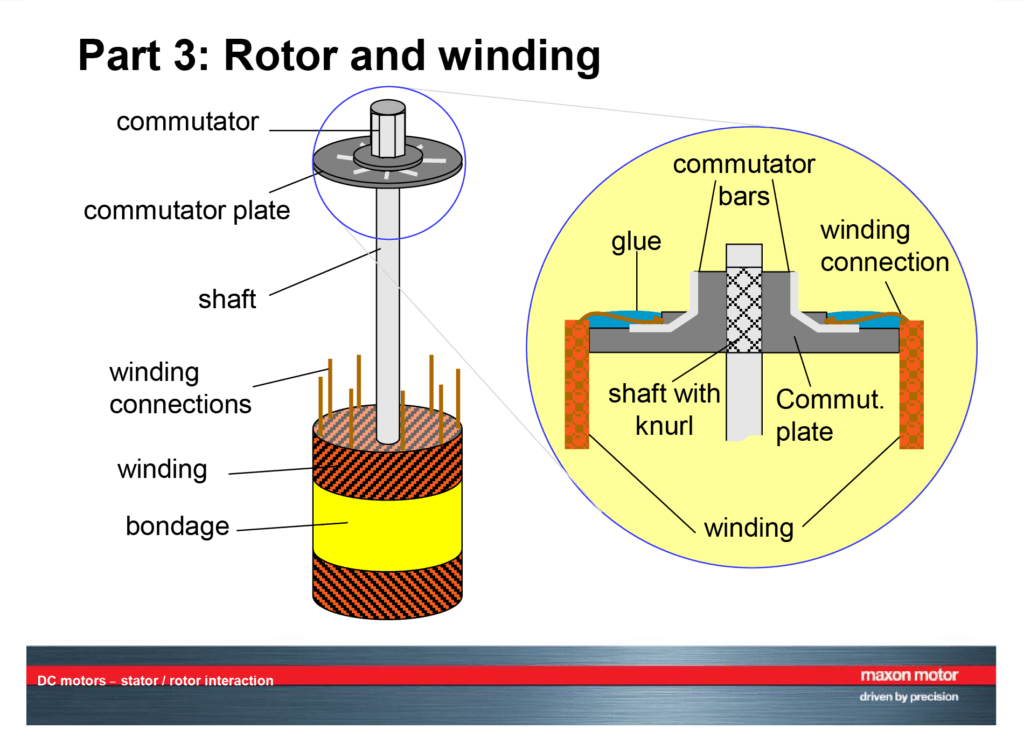
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for stator of dc motor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing a Stator of a DC Motor?
When sourcing a stator for a DC motor, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiations. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The stator is typically made from high-quality electrical steel, copper windings, and insulation materials. Prices for these materials can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier availability, and quality specifications. High-grade materials often result in better performance and longevity, justifying a higher cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process and the skill level required. In regions with higher labor costs, manufacturers may pass these expenses onto buyers. Conversely, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs may reduce the overall price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Effective manufacturing processes can optimize these costs, making it essential for buyers to assess potential suppliers based on their operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: If customization or specific design features are required, tooling costs can significantly impact the overall price. Investing in specialized tools may increase upfront costs but can lead to better quality and efficiency in production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the stators meet industry standards requires investment in quality control processes. This might include testing for electrical performance, durability, and adherence to certifications. Higher QC standards can lead to increased costs, but they also reduce the risk of failures and associated costs in the long term.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including transportation and warehousing, can add to the overall expense, especially for international buyers. Factors like distance, Incoterms, and shipping methods will influence these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary widely based on market competition and the perceived value of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of a DC Motor Stator?
Several factors can influence the pricing of a stator for a DC motor:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often result in bulk discounts, making it more economical per unit. Buyers should assess their needs and consider potential future demands when negotiating.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized stators designed for specific applications often incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements and explore options for standard products that may offer cost savings.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts cost. While premium materials enhance performance, they also raise prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of durability and efficiency against their budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Stators that meet international quality standards or specific certifications may command higher prices. However, investing in quality can lead to long-term savings by reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Engaging with established suppliers may provide peace of mind but can also mean higher costs. Evaluating multiple suppliers for quality, price, and service is essential.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can affect the total cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing DC Motor Stators?
To ensure cost-effective sourcing of DC motor stators, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Leverage potential long-term partnerships to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. This includes maintenance, energy efficiency, and potential downtime costs.
-
International Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to labor costs, material availability, and economic conditions. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these nuances can lead to significant savings.
-
Supplier Assessment: Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Consider their production capabilities, quality control processes, and customer service reputation.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends affecting material prices and availability. This knowledge can enhance negotiation leverage and purchasing strategies.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for stators can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is recommended to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough research before making purchasing decisions to ensure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing stator of dc motor With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Stator of DC Motors
In the realm of industrial applications, selecting the appropriate motor technology is crucial for optimizing performance and efficiency. While the stator of a DC motor has been a traditional choice for various applications, there are alternative solutions that can provide similar or enhanced functionalities. This analysis will compare the stator of DC motors against two viable alternatives: Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) and Stepper Motors, focusing on their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
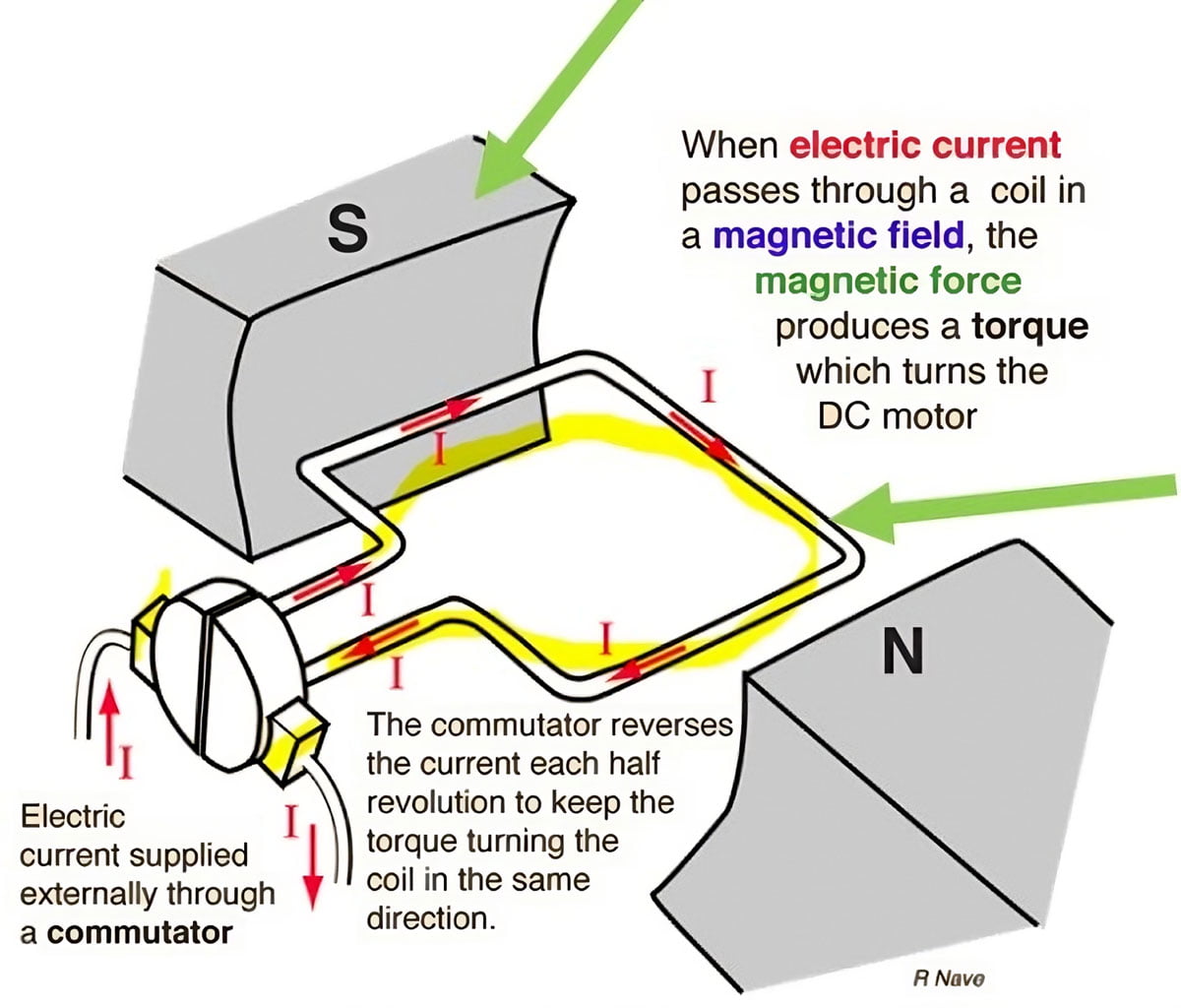
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Stator of DC Motor | Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) | Stepper Motor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque and good speed regulation | High efficiency and smooth operation | Precise positioning and control |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment | Moderate cost, depending on complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple design, easy to integrate | Requires electronic control | Straightforward setup, often needs a controller |
| Maintenance | Higher due to brush wear | Low, minimal wear parts | Moderate, depends on usage |
| Best Use Case | Applications needing robust torque (e.g., cranes, conveyors) | Applications requiring efficiency and speed (e.g., electric vehicles) | Applications needing precise control (e.g., 3D printers, robotics) |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
Brushless DC motors are known for their electronic commutation, which eliminates the need for brushes and commutators. This design significantly enhances their efficiency and lifespan, making them suitable for high-performance applications. While they typically require a higher initial investment due to their complexity and need for electronic controllers, they offer lower maintenance costs and higher reliability over time. BLDC motors are ideal for applications where energy efficiency and smooth operation are critical, such as in electric vehicles and HVAC systems.
Stepper Motor
Stepper motors operate by dividing a full rotation into a series of discrete steps, allowing for precise control over position and speed. Their straightforward design makes them easy to implement in various applications, particularly in robotics and CNC machinery. However, they may require a specialized controller to manage their operation effectively. While stepper motors are generally more affordable than BLDC motors, their maintenance can vary based on the application and load. They excel in scenarios where precision is paramount, such as in 3D printing and automated manufacturing processes.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When evaluating the appropriate motor technology, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs and constraints. The stator of DC motors is an excellent choice for applications requiring high torque and simple integration, especially in environments where cost is a critical factor. On the other hand, if energy efficiency and longevity are priorities, investing in BLDC motors may prove beneficial in the long run. For tasks demanding precise control and positioning, stepper motors offer a compelling alternative. Ultimately, understanding the unique requirements of each application will guide buyers in selecting the most suitable motor technology to enhance their operational efficiency and performance.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for stator of dc motor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Stator in a DC Motor?
Understanding the essential technical properties of the stator in a DC motor is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking reliability and efficiency in their applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The stator is typically constructed from high-grade electrical steel or laminations that minimize energy losses. The choice of material affects the stator’s magnetic properties, thermal conductivity, and overall efficiency. For buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures optimal performance, especially in demanding industrial environments. -
Magnetic Flux Density
This parameter indicates the strength of the magnetic field within the stator. Higher magnetic flux density leads to better torque generation and efficiency. Buyers should consider the magnetic flux density when evaluating motor performance for specific applications, such as robotics or electric vehicles, where precision is critical. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in the stator’s dimensions. Tight tolerances are essential for ensuring proper alignment and minimizing wear and tear on the motor components. B2B buyers must ensure that the manufacturers can meet these tolerances to maintain operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. -
Cooling Requirements
The stator must effectively dissipate heat generated during operation to prevent overheating and extend its lifespan. Cooling methods can include air cooling, liquid cooling, or the use of heat sinks. Understanding cooling requirements is vital for buyers to ensure that the motor operates within safe temperature limits, particularly in high-load applications. -
Insulation Class
This classification indicates the maximum temperature the stator can withstand without degrading its insulation properties. Common insulation classes include Class A, B, F, and H, with Class H being the most heat-resistant. Buyers should select the appropriate insulation class based on their operational environment to ensure longevity and reliability. -
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of the stator must align with the power supply available in the intended application. Ensuring compatibility with local voltage standards is essential for maximizing performance and avoiding potential damage. Buyers should verify that the voltage rating meets the requirements of their specific operational context.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Stators in DC Motors?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers as it often impacts pricing, quality assurance, and the availability of replacement parts. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers must consider MOQs when planning purchases to ensure they can meet production needs without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing RFQs is an effective way to compare costs and terms from different manufacturers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including who pays for shipping and insurance. Understanding these terms is vital for buyers to clarify shipping costs and delivery timelines. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This is a critical consideration for buyers, as longer lead times can impact production schedules and project timelines. -
Warranty Period
The warranty period is the duration during which a manufacturer guarantees that the product will perform as specified. Buyers should carefully review warranty terms to understand the level of protection they have against defects or failures.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing stators for DC motors, ensuring they choose reliable and efficient components for their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the stator of dc motor Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Impacting the Stator of DC Motor Sector?
The stator of the DC motor sector is witnessing significant evolution driven by several global factors. The growing demand for energy-efficient solutions in industrial applications is a primary market driver. Industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly focusing on automation and modernization, which enhances the need for reliable and efficient DC motors, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, transportation, and renewable energy. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as the rise of brushless DC motors (BLDC), are reshaping the competitive landscape, offering higher efficiency and reduced maintenance costs compared to traditional brushed DC motors.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards digitalization and the Internet of Things (IoT). Smart motors equipped with sensors are becoming more prevalent, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, thus reducing operational downtime. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to enhance productivity and minimize costs. Furthermore, regional disparities in sourcing practices are evident; for instance, buyers in Europe may prioritize sourcing from suppliers with robust quality certifications, while those in Africa might focus on cost-effectiveness and local availability.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Stator of DC Motor Supply Chains?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the stator of DC motor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of products is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. This shift is not only about compliance but also about enhancing brand reputation and meeting consumer expectations for corporate responsibility.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Companies are now more aware of the implications of their supply chains, including labor practices and material sourcing. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers that hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety. Additionally, the use of recycled materials in the production of stators can be a selling point, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses alike. Emphasizing sustainability and ethical sourcing can provide a competitive advantage in an increasingly conscientious market.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of the Stator in DC Motors?
The development of DC motors has roots dating back to the early 19th century, with the first DC motors appearing in the 1830s. Initially, the stator design was rudimentary, relying on simple magnetic configurations. However, as technology advanced, the stator evolved to incorporate more sophisticated designs, including the use of permanent magnets and electromagnetic windings, enhancing efficiency and performance.
Throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the introduction of the electrical grid and improvements in battery technology catalyzed the commercial viability of DC motors. The transition from brushed to brushless designs marked a significant turning point, leading to the modern DC motors we see today, which are characterized by enhanced efficiency, reduced maintenance needs, and greater application versatility. This evolution reflects the ongoing demands of various industries for more reliable and efficient solutions, setting the stage for the current trends in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of stator of dc motor
-
How do I choose the right stator for my DC motor application?
Choosing the right stator involves understanding the specific requirements of your application, including voltage, current ratings, and operational environment. Consider the motor’s intended use—whether it’s for industrial machinery, automotive, or consumer products. Evaluate performance factors like torque, speed, and efficiency, as well as the type of DC motor (brushed or brushless). Additionally, ensure compatibility with other components in your system, such as the rotor and controller, to achieve optimal performance. -
What are the key specifications to look for in a stator?
Key specifications to consider include the stator’s electrical characteristics (voltage, current, and resistance), physical dimensions (diameter and height), material composition (copper windings, insulation type), and thermal performance. Additionally, look for efficiency ratings, torque capabilities, and any certifications relevant to your industry. These specifications will help ensure that the stator meets your operational demands and regulatory requirements. -
How can I ensure quality when sourcing stators for DC motors internationally?
To ensure quality, vet suppliers by checking their certifications, production processes, and quality assurance protocols. Request samples to evaluate the stator’s performance and durability. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or using third-party inspection services to assess manufacturing standards. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and who can provide references from other international clients. -
What customization options are available for stators?
Customization options for stators can include variations in winding configurations, insulation types, and materials used. Suppliers may also offer bespoke dimensions to fit specific applications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to see if they can accommodate modifications in design, performance characteristics, or even branding. Ensure that they can provide prototypes for testing before finalizing your order. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for stators?
MOQs for stators can vary widely among manufacturers and depend on factors like production capabilities and material costs. Generally, you might encounter MOQs ranging from 50 to several hundred units. When sourcing, clarify the MOQ with your supplier, and discuss potential options for lower quantities, especially if you are testing a new design or are a smaller business. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing stators internationally?
Payment terms can differ by supplier, but common practices include a deposit (usually 30-50%) upfront with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net terms, allowing payment within 30, 60, or 90 days after delivery. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letter of credit) and ensure that the terms are documented in your purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping when sourcing stators?
When sourcing stators internationally, coordinate logistics with your supplier to determine shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Consider factors such as customs duties, import regulations, and delivery times to your location. Use reliable freight forwarders who can assist with documentation and ensure compliance with international trade regulations. Discuss Incoterms with your supplier to clarify responsibilities for shipping costs and risk management. -
What are the common challenges in sourcing stators from international suppliers?
Common challenges include language barriers, differing quality standards, and varying production capabilities. Cultural differences may also affect communication and negotiation. To mitigate these issues, establish clear expectations and maintain open communication with your supplier throughout the process. Consider working with local intermediaries or agents who understand both markets to facilitate smoother transactions and reduce risks.
Top 10 Stator Of Dc Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Magnetic Innovations – Brushless Torque Motors & Actuators
Domain: magneticinnovations.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Brushless Inrunner Torque Motors: IR-F 52 mm, IR-F 85 mm, IR-F 170 mm; Torque Motors (Outrunner): MI-F 40, MI-F 40 Combined, MI-F 110, MI-F 110 Combined, MI-F 250, MI-F 250 Combined, MI-F 485; High Speed Linear Actuator; Moving Magnet Actuators: 1525, 1555, 3070, 5536, 9054, 240-380; Electric Linear Actuators: MMB 1525, MMB 1555, MMB 3070, MMB 4090, MMB 5536, MMB 9054; Motor Controller; Vacuum Act…
2. Jkongmotor – Brushless and Stepper Motors
Domain: jkongmotor.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Jkongmotor specializes in producing brushless motors, stepper motors, and their corresponding drivers. They have 15 years of experience in motor manufacturing and offer a range of brushless motors in sizes such as 42mm, 57mm, 60mm, 80mm, 86mm, 90mm, 110mm, and 130mm. The key components of a DC motor stator include: 1. Main Magnetic Poles: Made of silicon steel plates (0.5mm to 1.5mm thickness) wit…
3. GRWinding – DC Motors
Domain: grwinding.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: DC motors include a stator as a core component that generates the magnetic field necessary for rotor movement. The stator consists of a core (often laminated steel), windings or coils of wire, and an outer housing. Key components of a DC motor stator include main magnetic poles, commutating poles, motor housing, and a brush device. Different types of DC motors (brushed, brushless, series, shunt, a…
4. ISL Products – Key Components of DC Motors
Domain: shop.islproducts.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Key components of DC motors include: 1. Armature: Converts electrical energy into mechanical motion; constructed from insulated metal sheets and copper wire windings, affecting torque, speed, and efficiency. 2. Commutator: Ensures continuous electrical flow in armature windings; made of insulated copper segments; requires maintenance to prevent wear and ensure performance. 3. Brushes: Maintain con…
5. UBC – DC Motors
Domain: phas.ubc.ca
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: DC Motors are familiar to many, often associated with electric toys. Key components include the stator (stationary part) and rotor (rotating part). In permanent magnet DC motors, the stator consists of permanent magnets, while the rotor has windings connected to a mechanical commutator. The rotor has three pole pairs, and opposite polarities attract, causing rotation. Reversing connections changes…
6. Monolithic Power – Magnetic Field Solutions
Domain: monolithicpower.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, Monolithic Power – Magnetic Field Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Electronics Tutorials – DC Motors Overview
Domain: electronics-tutorials.ws
Introduction: DC Motors are electromechanical devices that convert electrical energy into rotary mechanical energy. They are continuous actuators ideal for applications requiring speed control and positioning. There are three main types of DC motors: Brushed Motors, Brushless Motors, and Servo Motors. Brushed Motors are cost-effective and simple, using a commutator and brushes for operation. Brushless Motors us…
8. Byju’s – DC Motor
Domain: byjus.com
Introduction: A DC motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy using direct current (DC). It consists of several main parts: Armature or Rotor (a rotating part insulated from magnetic laminations), Field Coil or Stator (a non-moving part that produces a magnetic field), Commutator (cylindrical structure made of copper segments supplying current to the armature), and Bru…
9. Nidec – Motor Components
Domain: nidec.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Motor components are classified into five main portions: (1) Rotor – the rotating part; (2) Bearing – supports the rotating shaft of the rotor; (3) Stator – generates force to rotate the rotor; (4) Bracket or end plate – supports the bearing integral for the stator; (5) Lead wire – connects to the drive circuit supplying power to the motor. Typical stator structures include: A) Stator of distribut…
10. HowStuffWorks – Electric Motors
Domain: electronics.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Electric motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy using magnets. There are two main types of electric motors: AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). A simple DC motor consists of six parts: stator (permanent magnet), rotor (moving part), commutator, brushes, axle, and DC power supply. The rotor acts as an electromagnet, while the stator provides a permane…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for stator of dc motor
In navigating the complexities of sourcing stators for DC motors, B2B buyers must prioritize strategic partnerships that enhance both quality and reliability. Understanding the critical role that stators play in the efficiency and longevity of DC motors is essential for optimizing performance in various applications, from industrial machinery to renewable energy systems.
Strategic sourcing not only mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions but also opens avenues for innovation and cost-effectiveness. By leveraging relationships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers, buyers can ensure they are accessing high-quality components that meet rigorous industry standards. Additionally, recognizing the shift towards brushless DC motors highlights the importance of adapting sourcing strategies to include the latest technologies, enhancing competitive advantage.
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor
As the global market continues to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers are encouraged to adopt a proactive approach in their procurement strategies. Embrace the opportunity to collaborate with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and technological advancements. The future of motor applications is bright, and with strategic sourcing, your business can thrive in this dynamic landscape.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Illustrative image related to stator of dc motor