Choosing Your Shank Thread: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shank thread
In an increasingly interconnected global market, sourcing the right shank thread for various industrial applications poses significant challenges for B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances between shank and full-threaded fasteners is crucial, especially when it comes to ensuring structural integrity and performance in demanding environments. This guide delves into the diverse types of shank threads available, their specific applications across different industries, and essential factors for evaluating suppliers.
We will explore critical considerations such as material specifications, compliance with international standards, and the impact of manufacturing processes on the quality and performance of shank threads. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost structures, helping you navigate pricing strategies that align with your budgetary constraints while ensuring quality.
For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—this guide serves as a comprehensive resource. It empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions by equipping you with the knowledge to vet suppliers effectively, understand market trends, and identify the right products that meet your unique operational needs. By leveraging this information, you can enhance your procurement strategy and ensure that your projects are supported by the highest quality fastening solutions available on the market.
Understanding shank thread Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Thread | Entire length threaded; provides consistent tension | Aerospace, pressure vessels, machinery | Pros: Allows for precise tensioning; Cons: May weaken under shear loads. |
| Reduced Shank | Shank diameter smaller than major thread diameter | Custom applications, high-strength needs | Pros: Reduces weight; Cons: May not be suitable for all applications. |
| Undersized Shank | Approximately equal to pitch diameter | Light-duty applications, machine screws | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited strength and durability. |
| Cut Thread | Threads are cut or chased; equal to major diameter | High-precision fastening, automotive | Pros: High dimensional accuracy; Cons: More expensive to produce. |
| Rolled Thread | Cold-formed threads increase strength | Heavy machinery, construction | Pros: Higher tensile strength; Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Full Thread Shank?
Full thread shank bolts feature a threaded length that extends the entire length of the bolt. This design is particularly advantageous in applications requiring precise tensioning, such as in aerospace and pressure vessels. The ability to measure elongation during installation makes full thread bolts essential in high-stakes environments. However, buyers should consider that while they offer excellent tensioning capabilities, they may not be ideal for applications where shear loads are prevalent, as this can compromise the integrity of the threaded section.
How Does a Reduced Shank Differ from Other Shank Types?
Reduced shank bolts have a diameter smaller than the major thread diameter, allowing for a lighter fastener that can still provide adequate strength. They are often custom-made for specific applications where weight savings are critical, such as in automotive and aerospace sectors. When considering reduced shank options, buyers should ensure that the application can accommodate the lower strength characteristics, as these fasteners may not perform well under heavy loads compared to their full-thread counterparts.
In What Situations is an Undersized Shank Preferred?
Undersized shank bolts have a diameter that approximates the pitch diameter of the thread, making them suitable for light-duty applications. Commonly used in machine screws, they are cost-effective and easy to manufacture. However, buyers should be aware that while these bolts can serve well in non-critical applications, their limited strength and durability may not be suitable for heavy-duty tasks. Understanding the specific requirements of the application will help in deciding if undersized shank bolts are the right choice.
What Advantages Do Cut Thread and Rolled Thread Offer?
Cut thread bolts are produced by cutting or chasing the threads, resulting in high dimensional accuracy that is essential in applications requiring precision. They are commonly used in automotive and high-performance settings where quality is paramount. On the other hand, rolled thread bolts are cold-formed, which increases their tensile strength, making them ideal for heavy machinery and construction applications. While cut threads may be more expensive due to their manufacturing process, rolled threads offer a balance of strength and cost-effectiveness, making them appealing for various B2B buyers.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of shank threads and their applications can significantly impact purchasing decisions in B2B environments. Buyers should evaluate their specific needs, considering factors such as strength, cost, and application suitability to select the most appropriate shank thread type.
Key Industrial Applications of shank thread
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of shank thread | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine assembly and structural components | Enhanced strength and alignment for critical assemblies | High precision requirements; compliance with aviation standards |
| Automotive | Chassis and suspension systems | Improved load distribution and resistance to shear forces | Material certifications; compatibility with existing designs |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling and extraction equipment | Robustness in harsh environments and high-stress applications | Corrosion resistance; ability to withstand extreme temperatures |
| Construction | Heavy machinery and structural frameworks | Stability and safety in load-bearing applications | Compliance with local regulations; availability of custom sizes |
| Marine | Shipbuilding and offshore structures | Durability against marine conditions and structural integrity | Resistance to saltwater corrosion; adherence to marine standards |
How is Shank Thread Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, shank threads are primarily used in engine assembly and structural components where precision and strength are paramount. Shank threads facilitate better load distribution and alignment, which is crucial when assembling components that must withstand significant stress and vibration during flight. For international buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing shank thread must involve strict adherence to aviation standards and certifications, ensuring that parts meet the required tolerances and performance metrics.
What Role Does Shank Thread Play in Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, shank threads are integral to chassis and suspension systems. They provide enhanced strength and resistance to shear forces, which are critical when vehicles are subjected to dynamic loads. Buyers in South America and Africa should consider sourcing shank threads that not only comply with international automotive standards but also offer durability and reliability, especially in varying environmental conditions. Customization may be necessary to fit specific vehicle models or designs.
Why is Shank Thread Important in Oil & Gas Industry?
The oil and gas industry utilizes shank threads in drilling and extraction equipment due to their robustness and ability to perform under high-stress conditions. These threads are designed to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures, making them essential for ensuring operational safety and efficiency. For B2B buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia, sourcing shank threads requires an emphasis on corrosion resistance and material integrity, given the harsh environments often encountered in extraction processes.
How Does Shank Thread Contribute to Construction Projects?
In construction, shank threads are vital for heavy machinery and structural frameworks, ensuring stability and safety in load-bearing applications. The use of shank threads allows for better load distribution, reducing the risk of structural failure. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that comply with local building codes and regulations, particularly in regions with stringent safety standards. Availability of custom sizes and specifications is also a crucial consideration for effective integration into existing structures.
What is the Significance of Shank Thread in Marine Applications?
In the marine sector, shank threads are extensively used in shipbuilding and offshore structures due to their durability against harsh marine conditions. These threads help maintain structural integrity and stability in vessels that are constantly exposed to saltwater and extreme weather. For international buyers, particularly in regions with significant maritime activities, sourcing shank threads that meet marine industry standards is essential. Attention should also be given to corrosion resistance properties to ensure longevity and safety in marine environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘shank thread’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Thread Type for Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate type of shank thread for specific applications. With various options available, including fully threaded and partially threaded studs, the decision can become overwhelming. Misalignment in specifications can lead to improper load distribution, risking structural integrity and safety in critical applications such as aerospace or heavy machinery. Buyers may find themselves caught between meeting regulatory standards and ensuring optimal performance, resulting in costly delays and potential safety hazards.
The Solution:
To navigate this complexity, buyers should begin by conducting a thorough analysis of their application requirements. This includes understanding the load conditions—whether tensile, shear, or bending forces will be present—and selecting a shank thread configuration that can handle those stresses. For instance, if the application involves shear loads, opting for a plain shank may provide better performance and alignment compared to a fully threaded option. Furthermore, consulting with manufacturers about the material properties and specific engineering standards can yield tailored solutions. Utilizing tools like CAD software for simulation can help visualize how different thread configurations behave under load, allowing for informed decisions that prioritize safety and efficiency.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality and Consistency in Thread Manufacturing
The Problem:
Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the inconsistency in thread quality across different suppliers. Variations in manufacturing processes, such as rolling vs. cutting threads, can lead to discrepancies in tolerances and fit, resulting in assembly challenges. For industries that require precision, such as automotive or aerospace, these inconsistencies can lead to failures, rework, and increased production costs, which are unacceptable in competitive markets.
The Solution:
To mitigate quality concerns, buyers should establish stringent supplier qualification processes. This includes requesting certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards like ISO or ASME. Additionally, implementing a robust quality assurance program that involves regular audits and inspections can ensure that suppliers maintain consistency in their manufacturing processes. Collaborating closely with suppliers to develop a shared understanding of quality expectations can also lead to better outcomes. Buyers can consider investing in advanced quality control technologies, such as automated inspection systems, to verify thread dimensions and tolerances before products are shipped, thereby safeguarding their operations from unexpected failures.
Scenario 3: Complications in Global Sourcing and Supply Chain Management
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges in global sourcing, particularly when it comes to shank threads. Variability in material availability, shipping delays, and fluctuating tariffs can create disruptions in supply chains, leading to project delays and increased costs. Buyers operating in regions such as Africa or South America may encounter additional hurdles due to infrastructural limitations or regulatory complexities that complicate the importation of specialized components.
The Solution:
To address these issues, buyers should develop a diversified sourcing strategy that includes multiple suppliers across different regions. This can help mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and ensure a more stable supply of shank threads. Establishing strong relationships with local suppliers can also provide quicker access to materials and reduce shipping times. Moreover, leveraging technology such as supply chain management software can enhance visibility into inventory levels and order statuses, allowing buyers to proactively manage potential disruptions. Engaging in strategic planning that includes contingency measures, such as safety stock levels for critical components, can further protect against supply chain uncertainties, ensuring smooth operations and project continuity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shank thread
When selecting materials for shank threads, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in shank threads: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and plastic composites. Each material has its unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and suitability for different environments and applications.
What are the Key Properties of Carbon Steel for Shank Threads?
Carbon steel is a widely used material for manufacturing shank threads due to its excellent mechanical properties. It typically offers high tensile strength and good wear resistance, making it suitable for applications that require durability. Carbon steel shank threads can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures, but they are susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated.
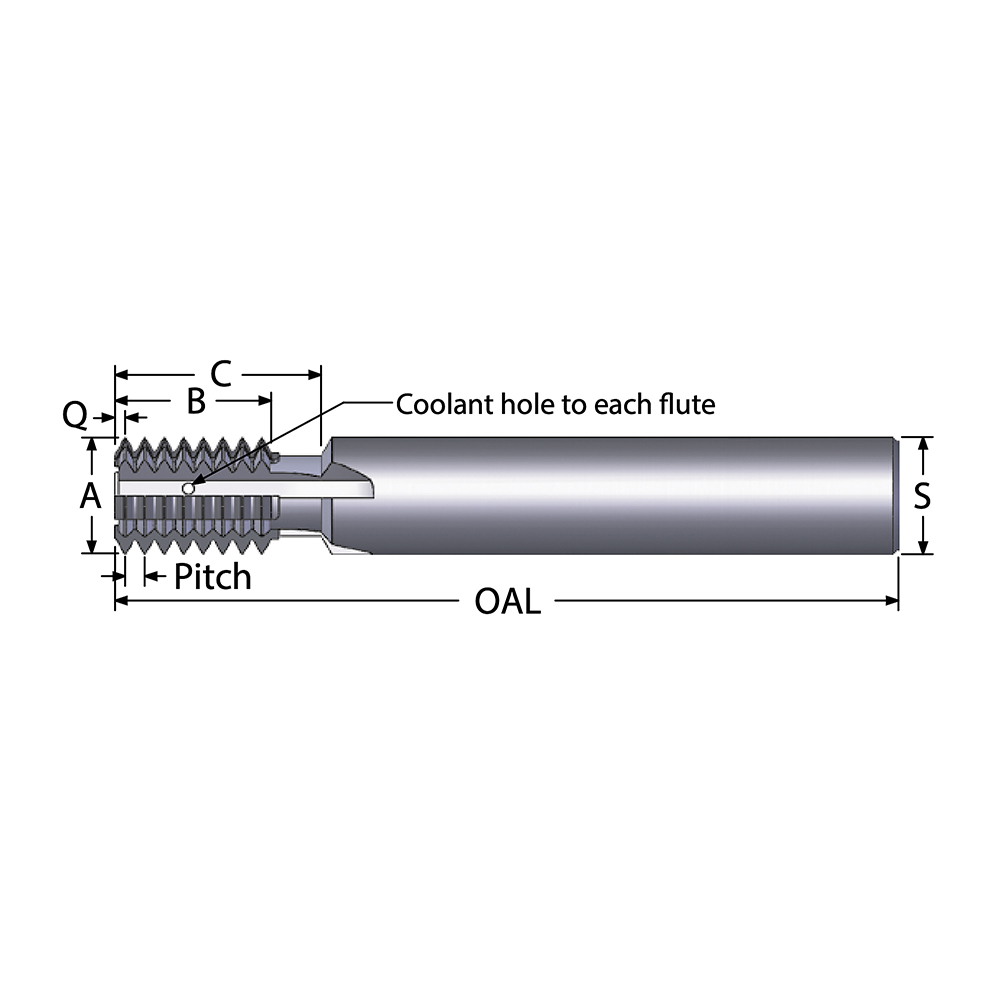
Illustrative image related to shank thread
Pros: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. Its high strength-to-weight ratio is advantageous in structural applications.
Cons: The primary limitation of carbon steel is its susceptibility to rust and corrosion, particularly in humid or corrosive environments. This necessitates protective coatings or treatments, which can add to the overall cost.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel shank threads are commonly used in construction and automotive applications, where strength is critical. However, they may not be suitable for environments with high corrosion risks.

Illustrative image related to shank thread
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Shank Thread Applications?
Stainless steel is known for its superior corrosion resistance, making it an excellent choice for shank threads used in harsh environments. It maintains its strength at elevated temperatures and is less likely to suffer from fatigue over time.
Pros: The corrosion resistance of stainless steel extends the lifespan of shank threads, making them ideal for marine, chemical, and food processing applications. They also have a polished finish that enhances aesthetic appeal.
Cons: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than carbon steel and can be more challenging to machine, which may increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel shank threads are often used in industries where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing. Compliance with standards like ASTM A193 is essential for international buyers.
What Advantages Do Alloy Steel Shank Threads Offer?
Alloy steel combines carbon steel with other elements to enhance specific properties, such as strength and toughness. This material is often used in high-stress applications where performance is critical.
Pros: Alloy steel shank threads exhibit excellent strength and toughness, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They can also be heat-treated to improve performance characteristics.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to standard carbon steel, along with increased manufacturing complexity due to the need for specialized processes.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel shank threads are often employed in the aerospace and automotive industries, where high strength and reliability are essential. Buyers must ensure compliance with specific standards such as JIS B 1186.
When Should Plastic Composites Be Considered for Shank Threads?
Plastic composites are becoming increasingly popular for shank threads, particularly in applications where weight reduction and corrosion resistance are critical. These materials can be engineered to provide specific mechanical properties.
Pros: Plastic composites are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for applications in chemical processing and marine environments. They can also be molded into complex shapes, offering design flexibility.
Cons: The primary limitation is their lower mechanical strength compared to metals, which may restrict their use in high-load applications. Additionally, they can be more expensive than traditional materials.
Impact on Application: Plastic composite shank threads are ideal for applications in industries such as electronics and automotive, where weight and corrosion resistance are priorities. International buyers should consider compliance with relevant standards like ISO 9001.
Summary of Material Selection for Shank Threads
| Material | Typical Use Case for shank thread | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Construction, automotive applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, chemical, food processing | Superior corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Alloy Steel | Aerospace, automotive heavy-duty | Excellent strength and toughness | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Med |
| Plastic Composites | Electronics, chemical processing | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower mechanical strength | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties and applications of different materials for shank threads, enabling informed decision-making based on specific operational needs and environmental conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shank thread
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Shank Threads?
The manufacturing process for shank threads involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Shank Thread Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality raw materials, typically carbon steel or alloy steel, are selected based on the required mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The material is then cut to the desired lengths using precision cutting tools. This stage may also involve heat treatment processes, such as annealing or quenching, to enhance the material’s strength and ductility.
What Forming Techniques Are Used for Shank Threads?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming, where the threads are created. Two primary techniques are employed:
-
Rolling: This is a cold-forming method where the material is passed through a series of dies to form the threads. Rolling not only shapes the threads but also enhances their strength due to the work hardening effect.
-
Cutting: In some cases, especially for smaller production runs or custom sizes, threads are cut using CNC machines. This method provides high precision and allows for tighter tolerances.
These techniques are chosen based on factors such as the production volume, required tolerances, and specific application needs.
How Are Shank Threads Assembled and Finished?
Following the forming process, the shank threads undergo assembly, where they may be combined with other components, such as nuts or washers, depending on the application. This stage may involve additional machining to ensure proper fit and alignment.

Illustrative image related to shank thread
Finishing is the final stage of the manufacturing process, which includes surface treatments such as galvanization, plating, or coating to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetics. These treatments are crucial for ensuring longevity, especially in harsh environments.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance for Shank Threads?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of shank threads is governed by various international standards, most notably ISO 9001. This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system, ensuring that manufacturers consistently produce products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications may also apply. For example, products used in the oil and gas sector may need to comply with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards, while those used in construction may require adherence to CE marking in Europe.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Shank Thread Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, with several checkpoints established to ensure product integrity. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications. This may involve checking for material certifications and conducting initial tests for mechanical properties.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, random samples are taken to ensure that the production techniques are yielding the desired results. This includes monitoring dimensions, thread quality, and surface finishes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the products are packaged and shipped, a final inspection is conducted to verify that all specifications have been met. This may include dimensional checks, mechanical testing, and visual inspections.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Shank Threads?
Testing methods play a crucial role in verifying the quality and performance of shank threads. Common methods include:
- Tensile Testing: This test measures the strength of the material and its ability to withstand pulling forces.
- Hardness Testing: This ensures that the material has the required hardness levels, which are critical for performance.
- Thread Profile Inspection: Using specialized gauges, manufacturers check the thread profile to ensure it meets specified standards.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: This is particularly important for threads that will be exposed to harsh environments, ensuring that coatings and treatments are effective.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards. This can provide insights into the supplier’s capabilities and commitment to quality.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation that outlines their quality control processes, including test results and compliance certifications. Regular reports can help buyers monitor ongoing quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly useful for buyers who may not have the resources for in-house inspections.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers face unique challenges when it comes to quality control. Understanding regional standards and regulations is crucial. For example, while ISO 9001 is recognized globally, local standards may vary significantly. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with both international and local regulations.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear communication channels and understanding the supplier’s quality culture can help mitigate these challenges.

Illustrative image related to shank thread
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for shank threads is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on the manufacturing stages, quality control checkpoints, testing methods, and verification strategies, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘shank thread’
To successfully procure shank thread for your business, it’s essential to follow a systematic approach that ensures quality and compliance with your specific needs. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the shank thread you need. This includes understanding the diameter, length, material type, and thread specifications.
– Considerations: Identify whether you require a full diameter shank or a reduced shank, as this can affect strength and application suitability.
– Application Needs: Different applications may demand specific thread types (e.g., rolled vs. cut threads) to meet operational standards.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Standards
Stay informed about the latest industry standards and market trends related to shank thread.
– Regulatory Compliance: Understand the regional regulations that may affect the quality and specifications of shank threads, such as ISO or ASTM standards.
– Industry Norms: Research common practices in your industry to ensure your procurement aligns with what is typically accepted.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to any supplier, conduct thorough evaluations to ensure they meet your requirements.
– Request Documentation: Ask for certifications, quality control processes, and product samples to assess their capabilities.
– Check References: Reach out to existing clients in your industry to gauge their satisfaction and the reliability of the supplier.
Step 4: Verify Quality Control Processes
A robust quality control process is essential for ensuring that the shank thread meets your specifications.
– Inspection Protocols: Inquire about the supplier’s inspection protocols and testing methods to ensure product integrity.
– Traceability: Ensure that the supplier can provide traceability for their products, which is crucial for quality assurance.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Terms of Sale
Evaluate the pricing structure and terms of sale offered by potential suppliers to find the best value for your business.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the upfront cost, but also shipping, handling, and potential tariffs if importing.
– Payment Terms: Negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow needs, while also considering the supplier’s policies.
Step 6: Conduct a Trial Order
Before making a large commitment, place a trial order to assess the supplier’s performance and product quality.
– Evaluate Delivery Times: Monitor the supplier’s ability to meet agreed-upon delivery timelines.
– Assess Product Quality: Test the received shank thread in your applications to ensure it meets your specifications and performance expectations.
Step 7: Establish Long-Term Relationships
Once you find a reliable supplier, focus on building a long-term relationship to enhance collaboration and supply chain efficiency.
– Regular Communication: Maintain open lines of communication regarding any changes in your requirements or market conditions.
– Feedback Loop: Provide feedback on product performance and service to foster a mutually beneficial partnership.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for shank thread, ensuring they select the best suppliers and products for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shank thread Sourcing
When sourcing shank thread products, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers. This analysis highlights the key cost components, price influencers, and buyer strategies to optimize sourcing and ensure value.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Shank Thread Sourcing?
-
Materials: The primary cost driver for shank thread is the raw materials used, typically high-strength steel or specialized alloys. The cost fluctuates based on global market conditions, material quality, and whether the supplier can offer bulk discounts.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce needed for manufacturing, assembly, and finishing processes. Skilled labor is often required for precision threading and quality checks, influencing the overall cost structure.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, which may be passed on to buyers in the form of competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be significant, particularly for custom shank threads. This includes the cost of molds, dies, and other equipment necessary for production. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs, especially when considering custom specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount, particularly for applications in aerospace or automotive sectors. QC processes add to the cost but are essential for compliance with industry standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly based on the destination, size of the order, and chosen Incoterms. International buyers must account for customs duties and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the supplier’s pricing model can help buyers negotiate better terms.
What Influences Pricing for Shank Threads?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes usually lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs to leverage volume discounts effectively.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs due to additional tooling and labor requirements. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against potential cost increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certified products (e.g., ISO, ASME) often come at a premium. Buyers should determine the acceptable quality level based on application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Engaging with established suppliers may yield better quality assurance but could come at a higher cost.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Buyers should understand the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to manage their total expenses effectively.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pricing on Shank Threads?
-
Establish Clear Specifications: Providing detailed specifications can help suppliers give accurate quotes, reducing the likelihood of unexpected costs later.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidating orders can improve negotiation power. Suppliers often provide better pricing for larger orders.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. This holistic view can lead to better long-term investment decisions.
-
Research Market Trends: Understanding current market conditions and material costs can provide leverage in negotiations. Buyers should stay informed about global supply chain trends that may affect pricing.
-
Build Relationships with Suppliers: Establishing long-term partnerships can lead to better pricing and service. Suppliers may be more willing to negotiate terms with trusted clients.
Conclusion
Sourcing shank thread products requires a nuanced understanding of various cost components and pricing influencers. By employing strategic negotiation techniques and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can optimize their sourcing strategies and achieve significant value. Always remember that prices can vary widely based on specifications and market conditions, so engaging with multiple suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the pricing landscape.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing shank thread With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Fastening Solutions
When selecting fastening solutions in industrial applications, it’s essential to consider various options that can meet specific requirements. Shank threads are widely utilized for their structural integrity and alignment capabilities. However, alternative methods may also offer distinct advantages depending on the application context, budget constraints, and operational efficiency. This analysis compares shank thread fasteners with two viable alternatives: full thread fasteners and engineered reduced shank fasteners.

Illustrative image related to shank thread
| Comparison Aspect | Shank Thread | Full Thread Fasteners | Engineered Reduced Shank Fasteners |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent shear strength; effective load distribution | Better for tensioning; can lead to reduced strength under shear loads | Customizable for specific load requirements; improved fatigue resistance |
| Cost | Generally moderate; cost-effective for bulk production | Typically lower cost due to widespread availability | Higher initial cost due to customization and engineering |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise alignment; installation can be complex | Easier to install in standard applications; can be tensioned directly | Installation requires additional design considerations; may need specialized tools |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; durable under stress | Moderate maintenance; can wear faster under load | Designed for longevity; may require specific maintenance protocols |
| Best Use Case | High-load applications where alignment is critical | General-purpose fastening, especially for tensioning | Specialized applications requiring tailored strength and fatigue resistance |
Exploring Full Thread Fasteners as an Alternative
Full thread fasteners are characterized by their complete threading from end to end. They are advantageous in applications requiring tensioning, as they allow for direct measurement of elongation during installation. However, their design can lead to stress concentrations that may compromise strength under shear loads, making them less suitable for high-load applications compared to shank threads. Moreover, full thread fasteners are generally more cost-effective and easier to source, making them a popular choice for general-purpose fastening needs.
Evaluating Engineered Reduced Shank Fasteners
Engineered reduced shank fasteners present a tailored alternative for specific applications where load characteristics are critical. These fasteners are designed to minimize weight while enhancing strength and fatigue resistance. While they may incur higher initial costs due to customization, their performance in specialized applications can justify the investment. However, the complexity of installation and potential need for specialized tools may deter some buyers. Their best use cases include high-stress environments, such as aerospace or heavy machinery, where precise engineering can yield significant operational benefits.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Fastening Needs
In selecting the appropriate fastening solution, B2B buyers should assess their specific application requirements, including load types, budget constraints, and installation capabilities. Shank threads offer robust performance in high-load situations, while full thread fasteners provide ease of use and lower costs for general applications. Engineered reduced shank fasteners are ideal for specialized needs, despite their higher costs. By carefully evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and enhance productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shank thread
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Shank Threads That B2B Buyers Should Know?
Understanding the essential technical properties of shank threads is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing fasteners for industrial applications. Here are several key specifications that impact performance and compatibility:
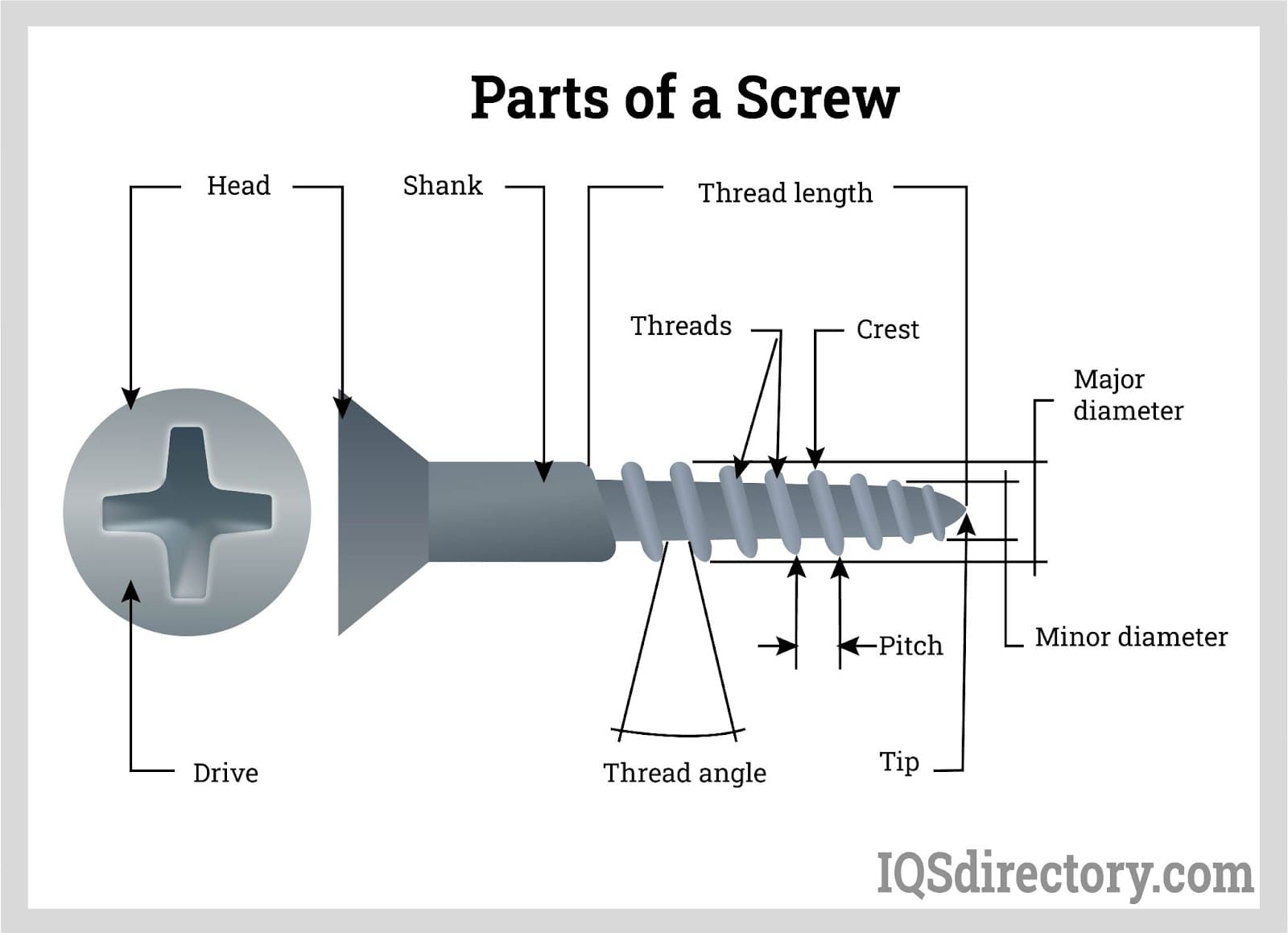
1. Material Grade
Material grade determines the mechanical properties of shank threads, such as strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each with specific grades (e.g., ASTM A193, A320) that indicate their suitability for different environments and loads. For buyers, selecting the correct material grade ensures the longevity and reliability of fastened assemblies.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in dimensions and physical properties of the shank thread. It is vital for ensuring proper fit and function between mating components. Common classes of tolerance include 1A, 2A, and 3A for external threads, with tighter tolerances providing better fit and performance. Understanding tolerance is essential for buyers to prevent misalignments that can lead to premature failure.
3. Thread Pitch
Thread pitch is the distance between adjacent threads, measured parallel to the axis. It significantly influences the load distribution and tightening characteristics of the fastener. For applications requiring precise adjustments, such as in machinery, selecting the appropriate thread pitch is critical for ensuring optimal performance and avoiding thread stripping.
4. Finish
The finish of a shank thread affects its resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals. Common finishes include zinc plating, black oxide, and passivation, each serving different protective purposes. Buyers must consider the operational environment when selecting a finish to enhance durability and performance.
Illustrative image related to shank thread
5. Shank Diameter
The shank diameter is critical as it dictates the load-bearing capacity of the fastener. A larger diameter generally provides greater strength and stability, which is particularly important in high-stress applications. B2B buyers should assess the shank diameter against the requirements of their projects to ensure the chosen fastener can withstand the intended loads.
6. Yield Strength
Yield strength indicates the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation. It is a crucial property for ensuring that fasteners can handle operational loads without failing. B2B buyers must evaluate yield strength to ensure that the fasteners meet the mechanical demands of their specific applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Shank Threads?
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are several common terms related to shank threads:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding OEM specifications ensures that the fasteners sourced will meet the required standards for integration into larger assemblies.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory effectively and to balance procurement costs with production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications for the desired products. Crafting a comprehensive RFQ helps buyers obtain competitive pricing and ensures clarity in terms of product expectations.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth logistics.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead time helps buyers plan their inventory and production schedules effectively, minimizing downtime and ensuring operational efficiency.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as ISO or ASTM, indicate that the products meet specific quality and safety criteria. Familiarity with these standards helps buyers ensure compliance with industry regulations and promotes trust in supplier capabilities.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing shank threads, ensuring optimal performance and alignment with their operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the shank thread Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Shank Thread Sector?
The global shank thread market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for high-strength fasteners across various industries, including construction, automotive, and aerospace. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable and durable fastening solutions, the focus is shifting towards products that offer enhanced performance and safety. In particular, applications requiring resistance to shear forces favor shank threads due to their structural integrity, making them a preferred choice over fully threaded alternatives in critical environments.
Emerging B2B technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies in the shank thread sector. Digital platforms facilitating direct connections between manufacturers and buyers are gaining traction, enabling streamlined procurement processes. Additionally, advancements in materials science have led to the development of high-strength alloys and corrosion-resistant coatings, increasing the longevity and reliability of shank thread products. As buyers become more sophisticated, they are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate technical expertise and an understanding of specific application requirements.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global sourcing, prompting buyers to diversify their supplier base and consider local manufacturing options. In regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, local production capabilities are expanding, driven by government initiatives to bolster domestic industries. This trend not only mitigates risks associated with long-distance shipping but also aligns with the growing emphasis on supporting local economies.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Shank Thread Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the shank thread sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in metalworking and fastener production, has come under scrutiny. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprints, buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient production methods, and responsible waste management strategies.

Illustrative image related to shank thread
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with buyers looking for supply chains that adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming benchmarks for assessing supplier reliability and commitment to sustainability. Moreover, the adoption of “green” materials, including recycled metals and non-toxic coatings, is gaining momentum. Suppliers that can provide transparency regarding their sourcing and manufacturing processes will have a competitive advantage in attracting discerning buyers focused on sustainability.
As the global market moves towards more responsible consumption, integrating sustainability and ethical considerations into procurement strategies is not just a trend but a necessity for long-term business viability. B2B buyers are encouraged to evaluate potential suppliers based on their environmental policies and ethical standards, ensuring that their sourcing decisions reflect their corporate values.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Shank Threads in B2B Context?
The evolution of shank threads can be traced back to the early developments of fastening technology. Initially, simple designs were used for basic applications, but as engineering requirements grew more complex, so did the designs. The introduction of standardized thread systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries laid the foundation for the modern shank thread, which emphasizes uniformity and interchangeability.

Illustrative image related to shank thread
By the mid-20th century, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes led to the creation of high-strength steel and other alloys, enhancing the performance characteristics of shank threads. Over the decades, the growing emphasis on safety and reliability in critical applications has further solidified the role of shank threads in various industries, making them a staple in the toolkit of engineers and procurement specialists alike. Today, the continuous innovation in materials and manufacturing techniques ensures that shank threads remain at the forefront of fastening solutions, catering to the evolving needs of global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shank thread
-
How do I select the right shank thread for my application?
Choosing the correct shank thread involves understanding the mechanical properties required for your application. Consider factors like tensile strength, shear load, and alignment capabilities. For applications requiring high strength and minimal bending under load, a full diameter shank is recommended. Conversely, if you’re operating in environments with less stress, a reduced shank might suffice. Always consult with your engineering team and suppliers to ensure compatibility with existing components and operational conditions. -
What are the key differences between shank and full-threaded studs?
Shank studs feature a smooth section that enhances alignment and load distribution, making them suitable for high-stress applications. Full-threaded studs, while versatile, may not handle shear loads effectively as the threads can weaken the bore. If your application requires precise tensioning, full-threaded options may be necessary, particularly in regulated industries. Evaluate the specific load requirements and installation conditions to make an informed choice. -
What customization options are available for shank threads?
Many manufacturers offer customization for shank threads, including variations in length, diameter, thread pitch, and material type. Customization can help meet specific industry standards or unique application requirements. When discussing options with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and any compliance standards your products must meet. This ensures you receive a product tailored to your operational needs. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for shank threads?
Minimum order quantities for shank threads can vary significantly by supplier and region. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on factors such as manufacturing capabilities and material costs. For international buyers, it’s advisable to negotiate MOQs, especially if you’re looking to test a new supplier or product. Always inquire about bulk pricing options as larger orders may lead to cost savings. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing shank threads internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Common arrangements include net 30, net 60, or upfront payment for first-time orders. International buyers should also consider currency fluctuations and transaction fees. It’s essential to establish clear payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I ensure the quality of shank threads from suppliers?
To guarantee the quality of shank threads, request certifications such as ISO 9001 or relevant industry standards. Conducting supplier audits or requesting samples for testing can also help assess quality. Additionally, consider implementing a quality assurance (QA) process that includes inspection of incoming materials and final products. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also facilitate better quality control measures. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing shank threads?
Logistics for importing shank threads include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Evaluate whether air freight or sea freight is more suitable for your timeline and budget. Familiarize yourself with the import duties and taxes applicable in your region. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the process and help navigate potential challenges in international shipping. -
How do I vet suppliers for shank threads in international markets?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, experience, and client reviews. Request references and verify them to assess reliability. Additionally, check for certifications and compliance with international standards. Engaging with suppliers through trade shows or industry events can provide insights into their operational capabilities. It’s also prudent to start with smaller orders to evaluate quality and service before committing to larger contracts.
Top 5 Shank Thread Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Eng-Tips – Shank vs Full Thread Stud Bolts
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Shank vs Full Thread stud bolts; differences in strength and applications; shank preferred for shear loads and alignment; full thread required in ASME Sec VIII, Div 1 for tensioning; custom made options available; considerations for strength and fatigue.
2. Rifle Barrels – Thread Sizes and Compatibility
Domain: forum.accurateshooter.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around barrel shank sizes and thread differences for various rifle models. Key models mentioned include:
– Savage (standard and large shank barrel system)
– Remington 700
– Weatherby Mark V
– Ruger M77
The thread starter, ‘crustyrusty’, inquires about the sizes and compatibility of these barrel shanks. Other contributors mention that while there are differences among acti…
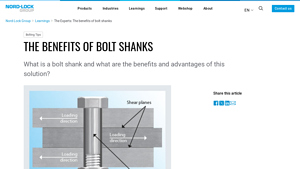
3. Nord-Lock – Bolt Shank Benefits
Domain: nord-lock.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
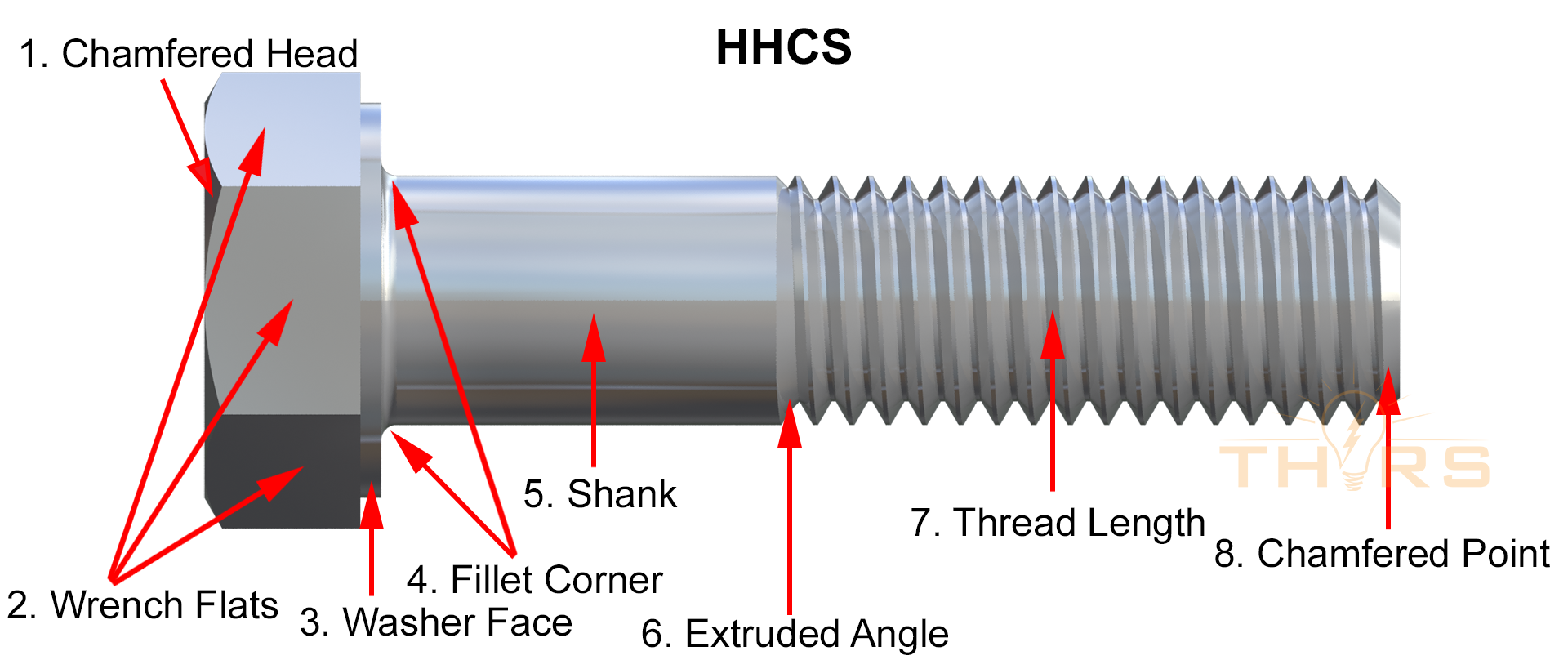
Introduction: The shank is the threadless part of the bolt between the head and thread. Benefits of bolt shanks include: 1. Increased shearing capacity by ensuring the shear plane is across the shank, not the threads. 2. Enhanced elastic resilience of the joint by reducing the shank in tension bolts. 3. Improved performance in shear loading due to larger areas and absence of stress concentration points. 4. Wais…
4. Makera – Thread Milling Bit
5. Lukr Faucets – U.S. Standard Thread Shank Stainless Steel
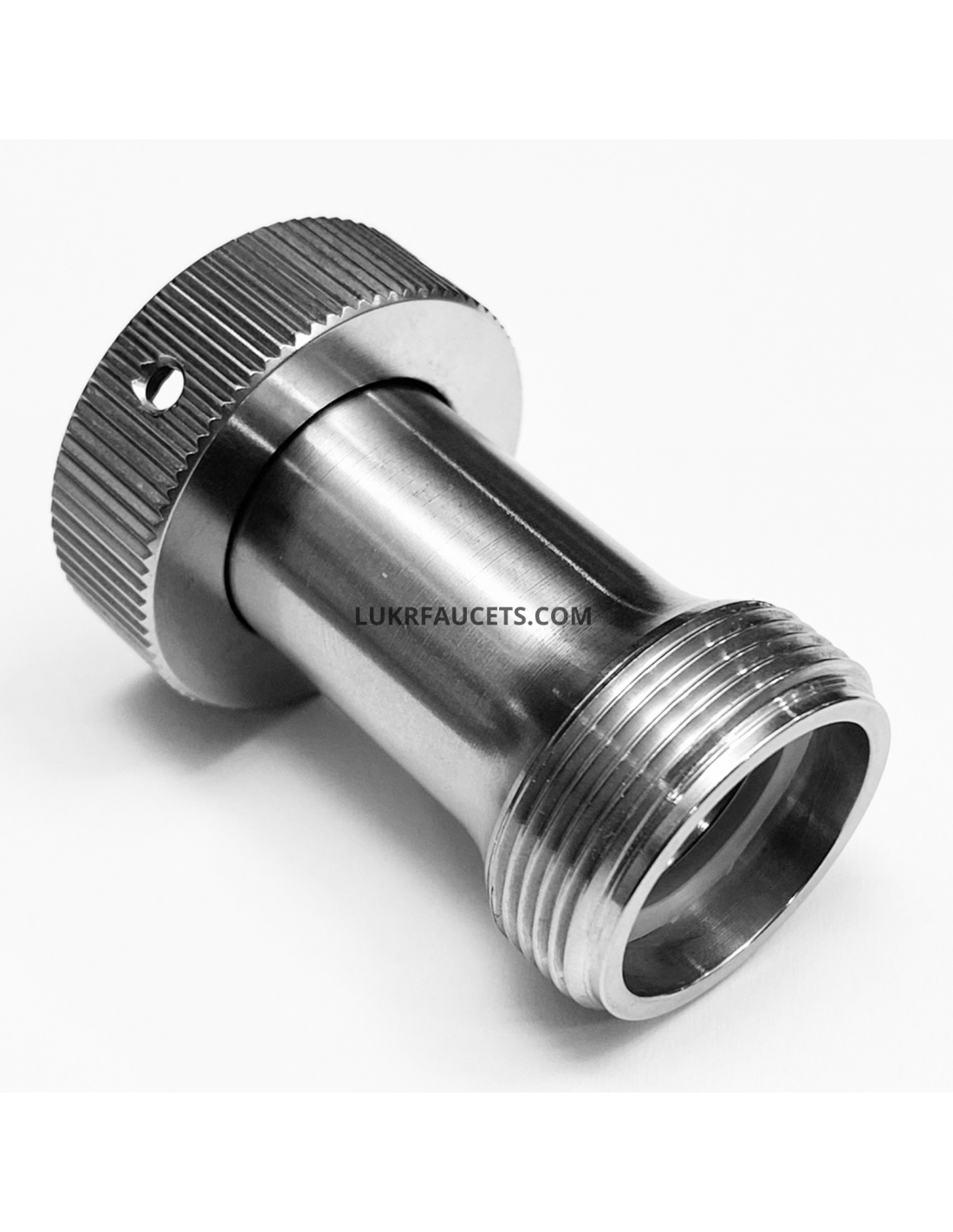
Domain: lukrfaucets.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“name”:”U.S. standard thread shank 1-1/8′-18, stainless steel”,”reference”:”11207″,”price_tax_included”:”€48.40″,”price_tax_excluded”:”€40.00″,”weight”:”0.1 kg”,”availability”:”In stock 11 Items”,”availability_date”:”2023-05-28″}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shank thread
In navigating the complexities of sourcing shank thread products, international B2B buyers can harness significant advantages by understanding the differences between shank and fully threaded options. Shank threads are preferred in applications requiring enhanced strength and alignment, particularly in high-stress environments. Their design minimizes risks associated with shear loads, making them a reliable choice for various sectors including aerospace and marine applications.
Strategic sourcing of shank thread components not only ensures quality and compliance with industry standards but also fosters long-term supplier relationships that can lead to cost savings and innovation. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who offer customizable solutions to meet specific project requirements, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Illustrative image related to shank thread
As the global market continues to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there is an increasing need for robust and resilient fastening solutions. By embracing strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves to leverage emerging opportunities. Take action today—evaluate your sourcing strategies, engage with reputable suppliers, and ensure your projects are equipped with the best shank thread solutions available.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.