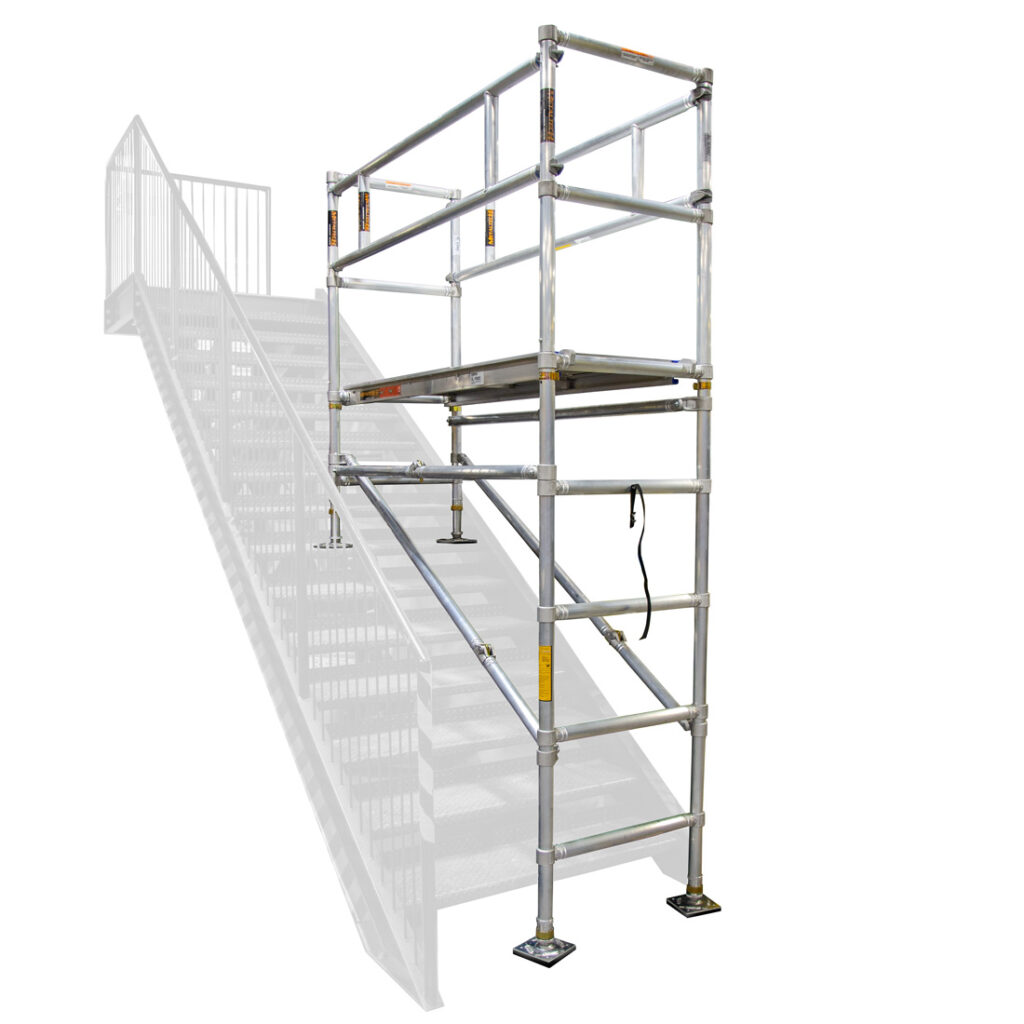
Choosing Your Scaffolding Ladder: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for scaffolding ladder
In the ever-evolving landscape of global construction, sourcing high-quality scaffolding ladders presents a significant challenge for B2B buyers. Whether you are an importer in Africa, a contractor in South America, or a supplier in the Middle East, navigating the complexities of this market requires not only an understanding of product specifications but also insight into regional regulations and standards. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for international buyers, addressing various types of scaffolding ladders, their applications, and critical factors to consider when sourcing them.
As you delve into the intricacies of scaffolding ladders, you will find detailed information on materials, load capacities, and safety features that cater to diverse project needs. Additionally, the guide offers valuable insights into supplier vetting processes, pricing strategies, and logistical considerations, ensuring that your purchasing decisions are both informed and strategic.
Empowering B2B buyers with actionable knowledge, this guide aims to streamline your sourcing process, enabling you to make confident choices that enhance productivity and safety on your job sites. By understanding the global market dynamics and aligning your procurement strategies with best practices, you can effectively meet the demands of your projects while fostering sustainable business relationships across continents.
Understanding scaffolding ladder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaffold Access Ladder | Typically made of steel or aluminum, designed to attach directly to scaffold frames. | Construction sites, maintenance work. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to install. Cons: Limited height options, may require additional safety measures. |
| Extension Ladder | Adjustable height, lightweight, often made of aluminum. | General construction, roofing, painting. | Pros: Versatile, portable. Cons: Less stable than scaffold ladders, requires proper handling. |
| Multi-Function Ladder | Combines features of step ladders and scaffold ladders, often adjustable. | Versatile applications in construction and maintenance. | Pros: Highly adaptable, saves space. Cons: Complexity can lead to misuse if not properly trained. |
| Rolling Scaffold Ladder | Equipped with wheels for mobility, often features guard rails. | Large scale construction, warehouse applications. | Pros: High stability, easy to move. Cons: Heavier and may require more storage space. |
| Fixed Scaffold Ladder | Permanently installed, offers a stable climbing option, often integrated into scaffold systems. | Long-term construction projects, industrial settings. | Pros: Extremely stable and safe. Cons: Not portable, higher upfront cost. |
What Are Scaffold Access Ladders and Their Applications?
Scaffold access ladders are essential for providing safe access to scaffolding systems. Constructed from durable materials like steel or aluminum, these ladders attach directly to scaffold frames, ensuring stability during use. Ideal for construction sites and maintenance work, they offer a cost-effective solution for accessing elevated work areas. Buyers should consider compatibility with existing scaffolding systems and the ladder’s load capacity when making purchasing decisions.
How Do Extension Ladders Differ from Other Types?
Extension ladders are characterized by their adjustable height, typically made from lightweight aluminum, making them easy to transport. These ladders are versatile and can be used for various applications, including general construction, roofing, and painting. While they offer portability and adaptability, buyers must be mindful of their stability, especially when working at greater heights. Proper handling and safety measures are crucial to mitigate risks associated with their use.
What Makes Multi-Function Ladders Ideal for Various Applications?
Multi-function ladders combine the features of both step and scaffold ladders, often with adjustable components. This versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications in construction and maintenance. They can serve multiple purposes, saving space and reducing the need for multiple ladder types. However, their complexity may lead to misuse if users are not adequately trained. Buyers should prioritize training and safety instructions when implementing these ladders in their operations.
Why Choose Rolling Scaffold Ladders for Large Scale Projects?
Rolling scaffold ladders are designed for mobility, featuring wheels and often including guard rails for added safety. They are particularly useful in large-scale construction and warehouse applications, where frequent movement between work areas is necessary. While they provide high stability and ease of movement, they tend to be heavier and require more storage space than other ladder types. Buyers should assess their workspace dimensions and mobility requirements before investing in rolling scaffold ladders.
What Are the Benefits of Fixed Scaffold Ladders?
Fixed scaffold ladders are permanently installed and offer a highly stable climbing option, typically integrated into scaffold systems. These ladders are ideal for long-term construction projects or industrial settings where consistent access is required. Their stability and safety features make them a preferred choice for many businesses. However, they are not portable and come with a higher upfront cost. Buyers must evaluate the long-term benefits against their initial investment when considering fixed scaffold ladders.
Key Industrial Applications of scaffolding ladder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of scaffolding ladder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Accessing elevated work areas during building projects | Enhances worker safety and efficiency on-site | Compliance with local safety regulations; load capacity specifications |
| Maintenance & Repair | Facilitating maintenance on high-rise buildings | Reduces downtime and improves service delivery | Durability against weather elements; portability and ease of use |
| Oil & Gas | Supporting inspections and repairs on rigs | Ensures safe access to critical infrastructure | Resistance to corrosion; compliance with industry standards |
| Telecommunications | Installing and maintaining communication towers | Increases operational uptime and reliability | Weight capacity; compatibility with existing scaffolding systems |
| Event Management | Constructing temporary structures for events | Provides flexible and safe access solutions | Ease of assembly/disassembly; rental options for short-term use |
How is Scaffolding Ladder Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction sector, scaffolding ladders are essential for accessing elevated work areas, such as building facades and roofs. These ladders provide a safe platform for workers to perform tasks like bricklaying, painting, and electrical installations. By improving access, scaffolding ladders reduce the risk of accidents and enhance overall productivity. International buyers must consider local safety regulations and ensure that the ladders meet specific load capacity requirements to protect their workforce.
What is the Role of Scaffolding Ladders in Maintenance & Repair?
In the maintenance and repair industry, scaffolding ladders facilitate access to high-rise buildings for tasks such as window cleaning, facade repairs, and HVAC servicing. They help minimize downtime by allowing technicians to reach elevated areas safely and efficiently. Buyers in this sector should prioritize ladders that are durable and weather-resistant, ensuring they can withstand various environmental conditions while remaining portable for easy transport.
How Do Scaffolding Ladders Support Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, scaffolding ladders are crucial for inspections and maintenance on offshore rigs and drilling platforms. These ladders provide safe access to critical infrastructure, allowing workers to perform necessary repairs and inspections without compromising safety. Buyers should focus on sourcing ladders that resist corrosion and meet industry-specific standards to ensure long-lasting performance in challenging environments.
What Applications Exist for Scaffolding Ladders in Telecommunications?
Telecommunications companies utilize scaffolding ladders for the installation and maintenance of communication towers. These ladders enable technicians to safely reach significant heights for equipment installation, repairs, and upgrades. Buyers in this field must consider the ladders’ weight capacity and compatibility with existing scaffolding systems to ensure seamless integration into their operational workflow.
How are Scaffolding Ladders Utilized in Event Management?
In event management, scaffolding ladders are often employed to construct temporary structures, such as stages and viewing platforms. They provide flexible access solutions that can be quickly assembled and disassembled as needed. For international buyers, sourcing ladders that are easy to transport and set up is crucial, as well as considering rental options for short-term projects to optimize cost-effectiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘scaffolding ladder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Safety Compliance Challenges with Scaffolding Ladders
The Problem: In many regions, especially in Africa and South America, regulatory requirements for construction safety are stringent. B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring that the scaffolding ladders they purchase meet local safety standards. This concern is heightened in environments with varying regulations, leading to confusion over which products are compliant. Non-compliance can result in costly fines, project delays, and increased liability risks.
The Solution: To address these compliance challenges, buyers should conduct thorough research on local regulations and safety standards regarding scaffolding equipment. It’s crucial to partner with reputable suppliers who provide detailed documentation on the safety certifications of their ladders. When sourcing, look for products that are tested and certified by recognized safety organizations, ensuring they meet or exceed local and international standards. Buyers should also consider investing in training for their workforce on the proper use and maintenance of these ladders, reinforcing a culture of safety on-site. Additionally, keeping abreast of any changes in regulations will ensure ongoing compliance, minimizing risks associated with safety violations.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Scenario 2: Managing the Logistics of Scaffolding Ladder Supply
The Problem: For construction companies operating in remote areas or regions with limited access to suppliers, managing the logistics of scaffolding ladder procurement can be a daunting task. Delays in delivery can halt projects, leading to increased labor costs and project overruns. Moreover, poor-quality ladders sourced from unreliable suppliers can lead to safety incidents, further complicating logistics and project timelines.
The Solution: To streamline the supply chain for scaffolding ladders, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate risks associated with delays. A diversified supplier base can provide alternative options if one source encounters issues. Additionally, buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer reliable delivery timelines and track their shipments to anticipate any potential delays. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can also help manage stock levels effectively, ensuring that ladders are available as needed without overstocking. Furthermore, conducting periodic evaluations of suppliers based on quality, reliability, and service can lead to better long-term partnerships.
Scenario 3: Selecting the Right Type of Scaffolding Ladder for Diverse Projects
The Problem: Different construction projects require various types of scaffolding ladders, and B2B buyers often struggle to determine the best options for their specific needs. This decision-making process can be complicated by factors such as project scale, height requirements, and the types of materials being handled. Poor choices can lead to inefficiencies and safety risks, affecting the overall success of the project.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
The Solution: To effectively select the right type of scaffolding ladder, buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their project requirements. This includes evaluating the maximum height needed, the load capacity required, and the specific tasks that will be performed using the ladder. Buyers should engage with manufacturers or suppliers who can provide expert advice based on their project specifications. Additionally, investing in versatile ladder systems that can be adjusted or modified for different tasks can enhance operational flexibility. It’s also beneficial to conduct hands-on trials or demonstrations of ladders to assess their functionality and suitability before making bulk purchases. Finally, maintaining an open line of communication with suppliers about emerging needs or project changes will allow for quicker adjustments to ladder specifications, ensuring optimal performance on-site.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for scaffolding ladder
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Scaffolding Ladders?
When selecting materials for scaffolding ladders, it’s crucial to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for various applications. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, steel, fiberglass, and wood.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum is one of the most popular materials for scaffolding ladders due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically withstands temperatures up to 300°F (149°C) and is resistant to rust, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros: The primary advantages of aluminum include its ease of handling, which reduces labor costs, and its resistance to corrosion, which extends the ladder’s lifespan.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than other materials and may not support as much weight as steel options. Its lower tensile strength can also be a limitation in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum ladders are ideal for environments where moisture is prevalent, such as coastal regions or areas with high humidity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like the Middle East and Africa should ensure compliance with local safety standards, such as ASTM or EN, to guarantee product reliability.
Steel: Strength and Durability
Steel is another common choice for scaffolding ladders, known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand extreme temperatures and is often treated for corrosion resistance.
Pros: Steel ladders can support heavier loads compared to aluminum, making them suitable for industrial applications. Their robust nature ensures longevity even in harsh conditions.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Cons: The main drawbacks include susceptibility to rust if not properly coated, and their heavier weight can increase transportation costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is particularly effective in construction sites where heavy materials are moved frequently.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the necessary coatings to prevent rust in humid climates, and ensure compliance with local standards like JIS in Japan or DIN in Europe.
Fiberglass: Non-Conductive and Weather-Resistant
Fiberglass ladders are increasingly popular for their non-conductive properties, making them ideal for electrical work. They are also resistant to chemicals and moisture.
Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Pros: The primary advantage of fiberglass is its safety in electrical applications, as it does not conduct electricity. Additionally, it is resistant to weathering, making it suitable for outdoor use.
Cons: However, fiberglass ladders are generally heavier than aluminum and can be more expensive to manufacture.
Impact on Application: Fiberglass is particularly beneficial in environments where electrical hazards are present, such as maintenance work on electrical installations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that fiberglass ladders meet international safety standards, especially in regions with strict electrical safety regulations.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Wood: Traditional and Cost-Effective
Wood has been a traditional material for scaffolding ladders, valued for its aesthetic appeal and cost-effectiveness.
Pros: Wood is generally less expensive and can be easily sourced in many regions. It also offers good load-bearing capabilities.
Cons: However, wood is prone to rot and insect damage, which can significantly reduce its lifespan. It also requires regular maintenance to remain safe and effective.
Impact on Application: Wood ladders are best suited for light-duty applications or temporary setups where aesthetics are a consideration.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that wood ladders are treated for pest resistance and comply with local safety standards to prevent accidents.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Scaffolding Ladders
| Material | Typical Use Case for scaffolding ladder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Outdoor construction and maintenance | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower weight capacity compared to steel | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy industrial applications | High strength and durability | Susceptible to rust if uncoated | Medium |
| Fiberglass | Electrical work and chemical exposure | Non-conductive and weather-resistant | Heavier and more costly | High |
| Wood | Light-duty and aesthetic applications | Cost-effective and easy to source | Prone to rot and requires maintenance | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for scaffolding ladders, highlighting critical factors that international B2B buyers should consider to make informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for scaffolding ladder
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Scaffolding Ladders?
The manufacturing of scaffolding ladders involves several key stages that ensure durability, safety, and compliance with industry standards. The process typically includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The initial stage involves sourcing high-quality raw materials, primarily aluminum and steel, which are essential for creating robust scaffolding ladders. Materials are selected based on their tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and overall weight. This stage may also involve cutting the materials into required sizes and conducting preliminary inspections to check for defects.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is forming them into the desired shapes. Techniques such as extrusion (for aluminum) and stamping (for steel) are commonly used. These methods allow manufacturers to create specific ladder designs that meet safety requirements. Advanced technology such as CNC machining may also be employed to ensure precision in dimensions and shapes.
Assembly
After forming, the components are assembled into a complete ladder. This process may involve welding, bolting, or using rivets to secure parts together. Quality control checkpoints are crucial here, as the structural integrity of the ladder depends heavily on the quality of the assembly. Manufacturers often employ automated assembly lines to improve efficiency while maintaining high standards.
Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which includes applying protective coatings to prevent rust and enhance durability. Options such as powder coating or galvanization are popular choices. This stage also involves a thorough inspection to ensure that the finish is even and free from defects.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Scaffolding Ladder Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of scaffolding ladder manufacturing, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. The QA process typically incorporates various international standards, checkpoints, and testing methods.
International Standards and Certifications
Manufacturers often adhere to internationally recognized standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management principles. Specific certifications like CE marking (for European markets) and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications are also crucial for compliance in various regions. These standards ensure that the products are safe for use and meet performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is implemented at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint ensures that all raw materials meet specified requirements before they are used in production. Any defective materials are rejected to prevent future issues.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, IPQC involves continuous monitoring of processes to catch any deviations from quality standards. This may include dimensional checks and visual inspections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): At the end of the manufacturing process, FQC ensures that the finished product meets all specifications and standards. This includes load testing, stability assessments, and final inspections.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Scaffolding Ladder Quality?
Testing methods play a vital role in verifying the quality and safety of scaffolding ladders. Common testing techniques include:
Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
-
Load Testing: This is perhaps the most critical test, where ladders are subjected to weights exceeding their specified load capacity to ensure they can withstand real-world conditions.
-
Material Testing: Various tests, such as tensile and yield strength tests, are conducted on the raw materials to ensure they meet the required specifications.
-
Corrosion Resistance Testing: This assesses the effectiveness of the protective coatings applied during the finishing stage, ensuring the ladder can withstand exposure to elements.
-
Dimensional Accuracy Testing: All dimensions are checked against design specifications to confirm compliance with safety standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some strategies to ensure that suppliers maintain high standards:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to safety standards. This firsthand evaluation can provide insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality assurance processes, including inspection reports and certifications. Regularly updated quality assurance documentation can reflect ongoing compliance with standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can add an extra layer of verification. These organizations can conduct independent assessments and provide unbiased reports on the supplier’s quality control practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances that differ from region to region. In regions like Africa and South America, local regulations may not align perfectly with international standards, leading to potential compliance issues. Buyers should be aware of these discrepancies and ensure that their suppliers not only meet international standards but also comply with local regulations.
In the Middle East, particularly in countries like Saudi Arabia, buyers should pay attention to local certifications that may be required for scaffolding products. Understanding these regional requirements can help buyers avoid legal complications and ensure that the products they procure are safe and compliant.
Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for scaffolding ladders are critical factors that B2B buyers must consider. By understanding these processes and employing effective verification methods, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers who deliver safe and high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘scaffolding ladder’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of scaffolding ladders requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with local regulations. This step-by-step checklist is designed for B2B buyers in diverse international markets, helping them make informed decisions when sourcing scaffolding ladders.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your project requirements is the first step in sourcing scaffolding ladders. Specify the load capacity, height, and material preferences—whether aluminum or steel—based on the project’s nature. Consider factors such as environmental conditions and intended use to ensure you select the right type of ladder.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Step 2: Research Relevant Standards and Regulations
Different regions may have specific safety and construction standards governing scaffolding equipment. Familiarize yourself with local regulations to ensure compliance, as this can prevent legal issues and enhance worker safety. Look for certifications from recognized bodies that validate the quality and safety of the ladders.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s vital to assess their credibility and reliability. Request comprehensive company profiles, including their history, customer testimonials, and case studies relevant to your industry. A well-established supplier with a track record in your region can provide assurance of product quality and service reliability.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers possess the necessary certifications and compliance documents. Look for ISO certifications or specific safety standards applicable to scaffolding equipment. This step is crucial to guarantee that the products meet safety requirements and are manufactured to high standards.
Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Step 5: Request Samples or Product Demonstrations
Before finalizing your order, request samples or arrange for product demonstrations. This allows you to evaluate the quality, functionality, and suitability of the ladders for your specific applications. Pay attention to the ease of setup and stability, as these factors significantly impact operational efficiency and safety.
Step 6: Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures, including bulk discounts and payment terms. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including shipping and potential duties, will help you budget effectively. Negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring favorable conditions for both parties.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Delivery Timeline
Effective project management hinges on timely delivery. Confirm the supplier’s ability to meet your delivery requirements, considering potential delays in shipping or customs. A clear timeline will help coordinate your project schedule and ensure that your scaffolding ladders arrive when needed, minimizing downtime.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing scaffolding ladders, ultimately leading to successful project execution and enhanced safety on-site.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for scaffolding ladder Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Scaffolding Ladder Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of scaffolding ladders is vital for B2B buyers looking to make informed sourcing decisions. The primary cost components include:
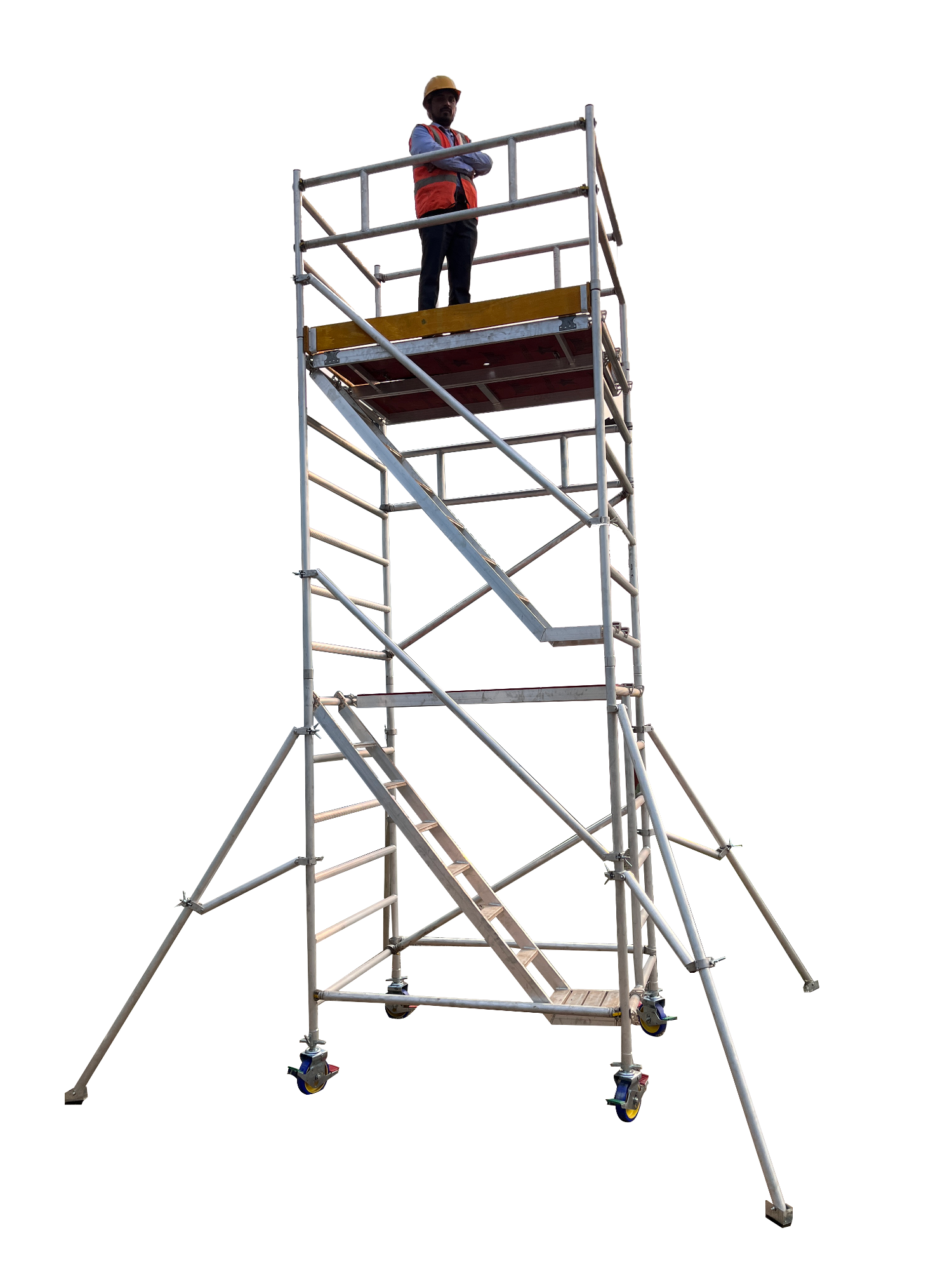

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost. Common options like aluminum and galvanized steel vary in price, with aluminum generally being more expensive due to its lightweight and rust-resistant properties. The quality of the raw materials affects not only the initial cost but also the longevity and safety of the product.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the manufacturing location. Regions with higher labor costs may yield higher overall prices. Additionally, skilled labor is often required for quality assurance and assembly, contributing to increased labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and operational management. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, but they remain a crucial part of the overall pricing structure.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is significant, especially for custom or specialized ladders. This cost can be amortized over larger production runs, making it essential to consider volume when negotiating prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that scaffolding ladders meet safety standards incurs costs for testing and certification. High-quality products often come with rigorous QC processes, which can increase the price but are necessary for compliance with international safety standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling play a critical role in the final cost. Factors such as distance, transport mode, and packaging impact logistics costs. International shipments may require additional customs clearance fees and tariffs, adding to the overall expense.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically set a profit margin that can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product. Understanding this aspect can help buyers gauge the potential for negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Scaffolding Ladder Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of scaffolding ladders:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for discounts. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchasing to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific features (like adjustable heights or added safety features) can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or OSHA compliance) typically come at a premium but are essential for safety and reliability, particularly in demanding environments.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived quality and service levels, while new entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost Insurance and Freight) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Scaffolding Ladder Sourcing?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Being informed about market prices and competitor offers can strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with the ladders, including maintenance, repair, and replacement. A slightly higher initial investment in quality products can lead to lower TCO over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: When sourcing from different regions, be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions. Building relationships with local suppliers can also lead to better pricing and service.
-
Documentation and Compliance: Ensure all necessary documentation is in place to avoid delays and additional costs during shipping. Compliance with local regulations can also prevent costly fines and rework.
By understanding these components, influences, and strategies, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they source scaffolding ladders that meet their quality standards and budgetary constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing scaffolding ladder With Other Solutions
When evaluating scaffolding solutions, it’s essential to consider various alternatives that may fulfill similar roles in construction and maintenance projects. This analysis aims to provide a comparative overview of scaffolding ladders against other viable solutions, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Scaffolding Ladder | Mobile Scaffolding Tower | Extension Ladder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High stability for vertical access | Versatile for various heights | Limited height access |
| Cost | Moderate cost (e.g., $100-$300) | Higher initial investment (e.g., $500-$2,000) | Lower cost (e.g., $50-$200) |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick setup and takedown | Requires assembly and disassembly | Simple to deploy |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance needs | Moderate; periodic checks needed | Low; inspect for wear |
| Best Use Case | Small to medium heights, tight spaces | Larger projects, multiple heights | General access for roofs, ladders |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile Scaffolding Towers?
Mobile scaffolding towers offer a versatile solution for reaching different heights. They can be adjusted and moved easily, making them suitable for larger projects that require mobility across job sites. However, their initial investment is significantly higher than scaffolding ladders, which may not be justifiable for smaller operations. Moreover, while they provide more stability than extension ladders, they require some assembly and periodic maintenance checks to ensure safety.
How Do Extension Ladders Compare to Scaffolding Ladders?
Extension ladders are often favored for their lower cost and ease of use, particularly in situations where quick access to height is needed. They are lightweight and portable, making them ideal for tasks such as roof repairs or painting. However, extension ladders lack the stability and safety features of scaffolding ladders, especially when working at greater heights. Their limited height access can also be a drawback for larger structures or projects requiring extensive work above ground level.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
Selecting the right scaffolding solution hinges on understanding the specific requirements of your project. If your work involves frequent movement and varying heights, a mobile scaffolding tower may be the best fit despite its higher cost. For smaller tasks or projects where budget constraints are critical, scaffolding ladders provide a reliable balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. Conversely, if you need a lightweight, easily deployable option for minimal height access, extension ladders may suffice, although they come with increased safety risks. By carefully considering these factors, B2B buyers can align their scaffolding solutions with their operational needs, ensuring both safety and efficiency on the job site.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for scaffolding ladder
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Scaffolding Ladders?
Understanding the technical specifications of scaffolding ladders is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure safety, durability, and efficiency in construction projects. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Scaffolding ladders are typically made from materials such as aluminum, steel, or a combination of both. Aluminum ladders are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for environments with high moisture levels. Steel ladders, while heavier, offer superior strength and load-bearing capacity. Buyers should assess the material grade to ensure it meets the specific demands of their projects.
2. Load Capacity
The load capacity of a scaffolding ladder indicates the maximum weight it can safely support. This specification is critical for ensuring worker safety and compliance with local regulations. For instance, a ladder rated for 375 lbs may be suitable for general tasks, while heavier-duty models can support up to 1,167 lbs for more demanding applications. Buyers should match the load capacity with the expected usage to avoid accidents.
3. Dimensions and Reach Height
The dimensions of the ladder, including its height and width, determine its suitability for different tasks. Standard widths range from 17 to 28 inches, which affects stability and maneuverability. Additionally, the reach height is essential for accessing elevated areas safely. Buyers must consider the work environment and the specific height requirements when selecting a ladder.
4. Weight and Portability
The weight of the ladder plays a significant role in its portability. Lighter ladders are easier to transport and set up, while heavier models may offer increased stability but can be cumbersome. For projects requiring frequent relocation, prioritizing weight and portability can enhance efficiency.
5. Safety Features
Safety features such as guardrails, locking mechanisms, and non-slip surfaces are vital for preventing accidents. Buyers should look for ladders that comply with safety standards and offer additional protective features to ensure the safety of workers at heights.
6. Durability and Weather Resistance
The durability of scaffolding ladders is often influenced by their construction materials and protective coatings. Weather-resistant finishes are essential for outdoor projects, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures or humidity. Selecting durable ladders can lead to long-term cost savings and reduced maintenance.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Scaffolding Ladder Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some essential terms for B2B buyers:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality manufacturers and assess the origin of their scaffolding ladders.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it affects inventory management and overall project budgeting. Knowing the MOQ helps in planning purchases effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. B2B buyers use RFQs to compare offers and negotiate better deals, ensuring they get the best value for their investments.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping logistics, risk transfer, and cost distribution.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. This is a critical factor in project planning, as it affects timelines and resource allocation. Buyers should consider lead times when ordering scaffolding ladders to ensure timely project completion.
6. Certification Standards
Certification standards, such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) or ANSI (American National Standards Institute), indicate that a product meets specific safety and performance criteria. Buyers should prioritize ladders that comply with these standards to ensure worker safety and regulatory compliance.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing scaffolding ladders, ultimately enhancing project efficiency and safety.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the scaffolding ladder Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Scaffolding Ladder Sector?
The scaffolding ladder market is experiencing significant growth globally, driven by a surge in construction activities, infrastructure development, and a shift towards safety-oriented practices. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are increasingly investing in high-quality scaffolding solutions to meet both regulatory requirements and safety standards. The rise of urbanization and industrialization in these regions has further amplified demand, with key markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam leading the charge.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends in the scaffolding ladder sector. Digital platforms and e-commerce solutions are becoming vital for international buyers seeking competitive pricing and comprehensive product specifications. Innovations such as modular scaffolding systems and lightweight materials are gaining traction, offering enhanced portability and ease of assembly. Additionally, data analytics tools are being utilized to assess market trends, enabling buyers to make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
Sustainability is another critical factor influencing market dynamics. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing products that adhere to environmental regulations and sustainability standards. This trend is leading manufacturers to innovate with eco-friendly materials and practices, positioning themselves favorably in a competitive landscape.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Scaffolding Ladder Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are paramount in the scaffolding ladder sector, particularly as global awareness of environmental impact grows. The construction industry is known for its significant carbon footprint, and scaffolding products, including ladders, contribute to this environmental challenge. As a result, B2B buyers are actively seeking suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing waste and emissions throughout their supply chains.
Ethical sourcing entails ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly, considering both environmental and social factors. Buyers should look for suppliers who provide transparency in their supply chain practices, adhering to fair labor standards and promoting safe working conditions. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Moreover, the demand for ‘green’ materials is on the rise. Buyers are increasingly interested in scaffolding ladders made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials, which not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance brand reputation. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international buyers can align with global trends and meet the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Scaffolding Ladders?
The evolution of scaffolding ladders can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where rudimentary structures were used to support construction efforts. Over the centuries, advancements in materials and engineering have transformed scaffolding into a critical component of modern construction. The introduction of lightweight materials such as aluminum and innovative designs has significantly improved safety and efficiency on job sites.
In the late 20th century, the development of modular scaffolding systems revolutionized the industry. These systems allowed for quicker assembly and disassembly, catering to the fast-paced demands of construction projects. Today, scaffolding ladders are not only designed for functionality but also for compliance with stringent safety regulations. The ongoing evolution of scaffolding technology continues to enhance worker safety and operational efficiency, making it a vital aspect of contemporary construction practices.
Through understanding these dynamics and trends, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with market demands and sustainability goals, ultimately fostering successful procurement strategies in the scaffolding ladder sector.

Illustrative image related to scaffolding ladder
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of scaffolding ladder
-
How do I choose the right scaffolding ladder for my project?
Selecting the appropriate scaffolding ladder requires assessing several factors, including the height and weight requirements of your project, the material (steel or aluminum), and the specific design features needed (like adjustable heights or portability). Consider the load capacity as well; it should exceed the maximum weight of the workers and materials. Additionally, check for compliance with local safety regulations to ensure the ladder meets industry standards. -
What are the key features to look for in a scaffolding ladder?
When sourcing a scaffolding ladder, look for features such as stability, weight capacity, and ease of assembly. Key aspects include non-slip surfaces, locking mechanisms, and weather-resistant materials for outdoor use. Portability can also be crucial if the ladder needs to be frequently relocated. Ensure the ladder’s design allows for secure attachment to scaffolding frames, enhancing safety during use. -
What is the typical lead time for scaffolding ladder orders?
Lead times for scaffolding ladder orders can vary significantly based on the supplier, order volume, and customization requirements. Generally, expect a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks for standard orders. Custom orders may take longer due to design and manufacturing processes. Always confirm lead times with your supplier to ensure they align with your project schedules. -
How can I verify the quality and safety of scaffolding ladders?
To ensure quality and safety, request certifications that comply with local and international standards, such as OSHA in the U.S. or EN standards in Europe. Inspect samples if possible, focusing on materials, craftsmanship, and load ratings. Additionally, seek testimonials or reviews from other B2B buyers. A reputable supplier should provide detailed specifications and quality assurance documentation. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for scaffolding ladders?
Minimum order quantities for scaffolding ladders can differ by supplier and region. Typically, MOQs can range from as low as 10 units to several hundred, depending on the ladder type and customization options. Clarifying MOQs upfront is essential to align your purchasing strategy with your project needs and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing scaffolding ladders internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established buyers. Always negotiate terms that suit your cash flow and ensure you understand any implications for international transactions. -
How do I handle shipping and logistics for international scaffolding ladder orders?
When managing shipping and logistics for international orders, consider factors like shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties. Choose a reliable freight forwarder who understands your destination country’s requirements. Ensure that your supplier provides accurate shipping documentation and tracking information. It’s also wise to account for potential delays and plan your project timelines accordingly. -
Can I customize scaffolding ladders to meet specific project requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for scaffolding ladders, including adjustments in size, material, and design features. Customization can enhance functionality for specific applications, such as unique height requirements or additional safety features. Engage with your supplier early in the process to discuss your needs, as custom orders may require additional lead time and cost considerations.
Top 4 Scaffolding Ladder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Scaffold Express – 10′ Galvanized Ladder (Wide)
Domain: scaffoldexpress.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: [{‘name’: “10′ Galvanized Ladder (Wide)”, ‘product_code’: ‘PSV-RL-961017’, ‘price’: ‘$41.09’, ‘weight’: ‘35.9 lbs’, ‘material’: ‘hot dipped Galvanized Steel’, ‘dimensions’: ’17” C/C of Leg’}, {‘name’: ’10\’x28″ Aluminum Hatch Deck w/ Ladder’, ‘product_code’: ‘PSV-1110’, ‘price’: ‘$358.80’, ‘load_rating’: ’50 lbs per square ft.’, ‘maximum_load’: “1,167 lbs at 10′ length”}, {‘name’: “3′ Galvanized L…
2. American Ladders – Cross Brace and Standard Frames
Domain: americanladders.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Cross Brace 7′ – From $48.99; Cross Brace 10′ – Regular price $71.99; Standard Frame 2×5 – Regular price $115.99; Standard Frame 3×5 – Regular price $140.99; Standard Frame 5×5 – Regular price $169.99; Standard Frame 4×5 – Regular price $159.99; Standard Frame 6’4″x5 – Regular price $186.99; Light Duty Frame 2’x 4′ – Regular price $136.00; 6′ X 4′ Light Duty Scaffold Frame – Regular price $280.99;…
3. Sunbelt Rentals – Scaffolding and Ladders
Domain: sunbeltrentals.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Scaffolding and Ladders Rentals include: Extension Ladders, Scaffolding – Interior, Adjustable Step Ladders, Trestle Ladders/A Frame, Straddle Adapter.
4. Louisville Ladder – Fiberglass Twin Front Step Ladder
Domain: panthereast.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Shop Ladders and Scaffolding for Roofers, Painters & Professional Contractors | Brands: Louisville Ladder, WERNER, Green Bull, Nu-Wave Scaffold | Products include: Fiberglass Twin Front Step Ladder – Type 1AA, Nu-Wave Scaffold Lean Flat Carts (6 FT or 4 FT), Ladder Derrick Long-Handle Ladder Hoisting Wheel, Fiberglass Straight Ladder – 8″ Type 1A, Fiberglass Extension Ladder – Type 1A, Ladder Jack…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for scaffolding ladder
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Scaffolding Ladders?
In today’s dynamic construction environment, strategic sourcing of scaffolding ladders is pivotal for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse product offerings, such as aluminum and galvanized steel options, enables businesses to make informed decisions that align with safety standards and project requirements. Prioritizing features like portability, load capacity, and weather resistance can significantly enhance operational efficiency and safety on job sites.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Competitive Edge?
Effective strategic sourcing not only streamlines procurement processes but also fosters relationships with reliable suppliers, ensuring consistent quality and supply chain resilience. Buyers should leverage market insights to negotiate favorable terms and explore bulk purchasing options to maximize cost efficiency.
What Does the Future Hold for Scaffolding Ladder Procurement?
As global construction demands evolve, the need for innovative and adaptable scaffolding solutions will continue to grow. International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should remain proactive in sourcing high-quality scaffolding ladders that meet both current and future needs. By investing in strategic sourcing initiatives today, businesses can secure a competitive advantage and contribute to safer, more efficient construction practices tomorrow. Engage with trusted suppliers and explore the latest offerings to stay ahead in this essential market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.