Choosing Your Plug Without Holes: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plug without holes
As international B2B buyers seek to optimize their procurement processes, understanding the nuances of sourcing a plug without holes becomes paramount. This type of plug, often essential in various industrial and commercial applications, presents unique challenges, particularly when navigating diverse global markets. The absence of holes in these plugs can influence functionality, safety, and compatibility with existing systems, making informed sourcing critical.
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad aspects of plugs without holes, including their types, applications across different sectors, and essential criteria for supplier vetting. It will also explore cost considerations, ensuring that buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Vietnam—can make financially sound decisions. By providing actionable insights and detailed analysis, this guide empowers B2B buyers to confidently navigate the complexities of the global market.
Armed with knowledge about the specifications, regulatory standards, and potential suppliers, you will be better positioned to enhance operational efficiency and drive your business forward. Whether you are looking to streamline your supply chain or ensure product compliance, this guide serves as a valuable resource for making strategic purchasing decisions in the ever-evolving landscape of industrial components.
Understanding plug without holes Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Plug without Hole | Made from durable rubber, no holes for sealing | Flooring machinery, industrial tools | Pros: Excellent sealing, robust material. Cons: Limited ventilation. |
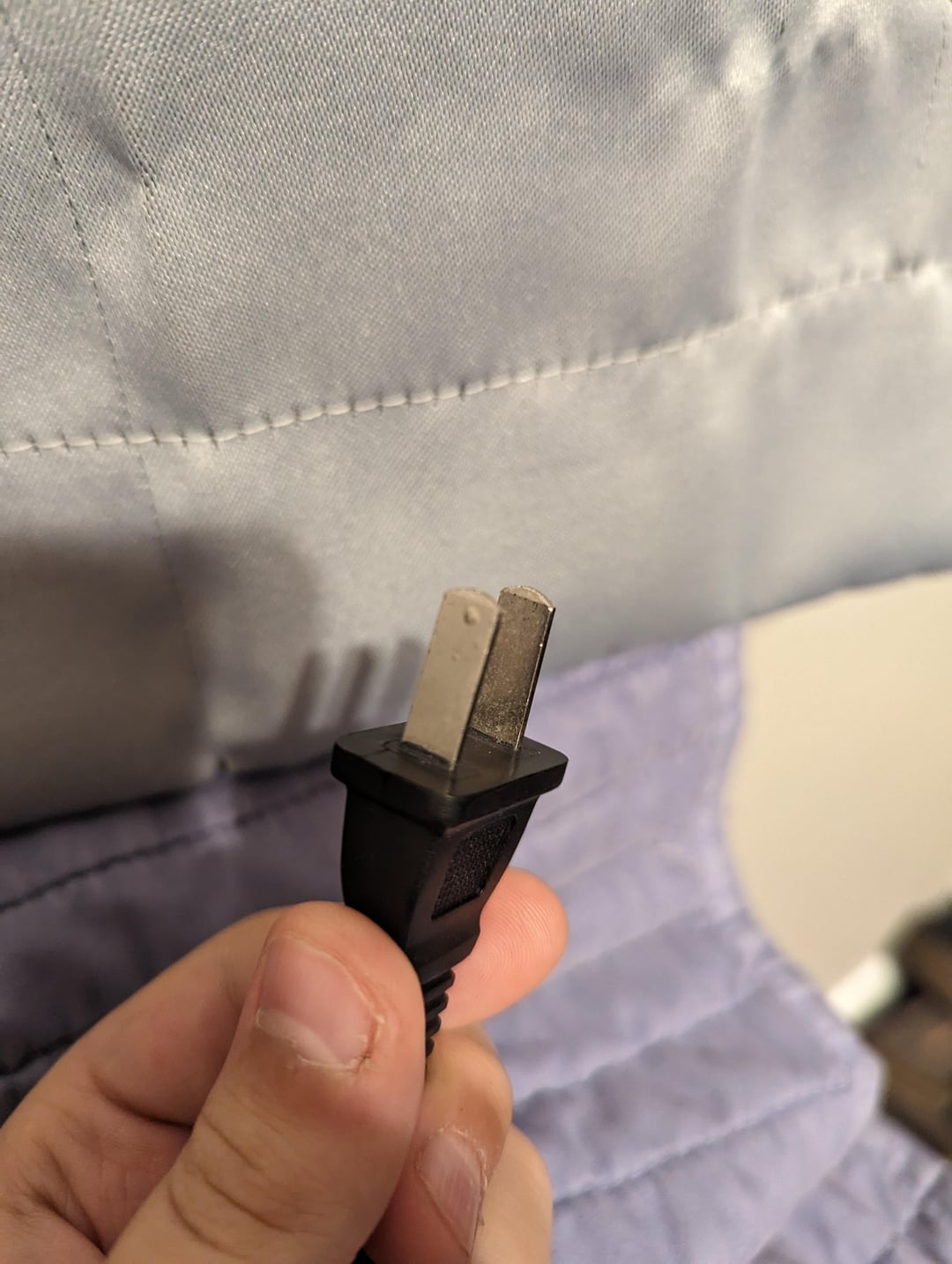
| Electrical Plug without Hole | Standardized prongs, typically ungrounded | Household appliances, electronics | Pros: Simplified design, cost-effective. Cons: Less safety due to lack of grounding. |
| Tint Plug without Hole | Compact, designed for specific feeding applications | Beekeeping, food industry | Pros: Easy to use, prevents spills. Cons: Limited to specific sizes. |
| Mechanical Plug without Hole | Often used in mechanical assemblies, no holes for locking | Automotive, machinery | Pros: Secure fit, minimizes wear. Cons: May require specialized tools for installation. |
| Grommet Plug without Hole | Soft, flexible material, used for cable management | Electronics, manufacturing | Pros: Protects cables, reduces friction. Cons: Not suitable for heavy-duty applications. |
What are the characteristics of Rubber Plugs without Holes?
Rubber plugs without holes are crafted from high-quality rubber, ensuring a tight seal that prevents the ingress of dirt and moisture. These plugs are typically used in flooring machinery and industrial tools, where a secure seal is essential for optimal performance. When purchasing, consider the specific size and compatibility with existing machinery, as well as the durability of the rubber material, which directly impacts longevity and effectiveness in demanding environments.
Why are Electrical Plugs without Holes commonly used in B2B?
Electrical plugs without holes are designed with standardized prongs, making them versatile for various household appliances and electronics. Their ungrounded nature simplifies the design and reduces manufacturing costs, making them an economical choice for many businesses. However, buyers should weigh the benefits of cost-effectiveness against the potential safety concerns of using ungrounded plugs, particularly in environments where electrical safety is paramount.
What makes Tint Plugs without Holes suitable for the food industry?
Tint plugs without holes are specifically designed for applications like beekeeping and food storage, where they serve as effective sealing solutions for feeding buckets. Their compact size and ease of use make them ideal for preventing spills and maintaining cleanliness. When considering bulk purchases, buyers should assess the compatibility with their specific feeding systems and the material quality to ensure food safety standards are met.
How do Mechanical Plugs without Holes function in industrial applications?
Mechanical plugs without holes are essential components in automotive and machinery applications, providing a secure fit without the need for locking mechanisms. These plugs enhance the longevity of mechanical assemblies by minimizing wear and tear. Buyers should focus on the specific application requirements, including size and material specifications, to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with their machinery.
In what scenarios are Grommet Plugs without Holes advantageous?
Grommet plugs without holes are designed to protect cables and wires from damage while minimizing friction in electronic and manufacturing environments. Their soft, flexible material allows for easy installation and adaptability to various cable sizes. When considering these plugs, B2B buyers should prioritize the flexibility and durability of the material to ensure it can withstand the specific conditions of their operational environment.
Key Industrial Applications of plug without holes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plug without holes | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Sealing equipment in flooring applications | Prevents dust and debris ingress, enhancing tool longevity | Material durability, compatibility with various flooring types |
| Food & Beverage | Sealing containers for honey and other liquids | Maintains product integrity and prevents contamination | Food-grade materials, compliance with safety regulations |
| Electrical & Electronics | Sealing electrical components to prevent moisture ingress | Increases product lifespan and reliability | Electrical insulation properties, temperature resistance |
| Automotive | Plugging holes in engine components during assembly | Reduces risk of leaks and enhances performance | Heat resistance, compatibility with various engine types |
| Manufacturing | Use in machinery to prevent fluid leakage | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces maintenance costs | Custom sizing, resistance to chemicals and wear |
How is ‘Plug Without Holes’ Used in the Construction Industry?
In the construction industry, plugs without holes are commonly used to seal gaps in flooring equipment. These plugs help prevent dust and debris from entering machinery, which can lead to malfunctions and increased maintenance costs. For international buyers, especially in regions with high dust levels, sourcing durable, high-quality rubber plugs is essential. Buyers should ensure that the plugs are compatible with various flooring types and can withstand heavy use on job sites.
What Role Do ‘Plug Without Holes’ Play in the Food & Beverage Sector?
In the food and beverage sector, plugs without holes are vital for sealing containers, particularly for liquids such as honey. These plugs help maintain product integrity by preventing contamination and ensuring that the contents remain fresh. Buyers in this sector must prioritize food-grade materials that comply with safety regulations, as well as consider the plugs’ sealing effectiveness to protect against leaks during transport and storage.
How Do ‘Plug Without Holes’ Enhance Electrical & Electronics Applications?
In electrical and electronics applications, plugs without holes are employed to seal components against moisture ingress, which can lead to failures. This sealing capability is crucial for maintaining product reliability and longevity. International buyers should focus on sourcing plugs that offer excellent electrical insulation properties and can withstand varying temperatures, particularly in regions with extreme climates.
Why Are ‘Plug Without Holes’ Important in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, plugs without holes are often used to seal engine components during assembly. This prevents leaks and contributes to the overall performance of the vehicle. Buyers need to consider the heat resistance of the materials used for these plugs, as well as their compatibility with various engine types. Ensuring that the plugs meet automotive standards is critical for maintaining vehicle safety and efficiency.
How Does ‘Plug Without Holes’ Improve Manufacturing Processes?
In manufacturing, plugs without holes are utilized to prevent fluid leakage from machinery, which can disrupt operations and lead to costly downtime. By enhancing operational efficiency and reducing maintenance requirements, these plugs provide significant value to manufacturers. Buyers should look for plugs that can be custom-sized to fit specific machinery needs and possess resistance to chemicals and wear to ensure longevity in demanding environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plug without holes’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Ensuring Proper Fit and Seal
The Problem: One common challenge B2B buyers encounter with plugs without holes is ensuring a proper fit and seal in various applications. Many industrial settings, especially in manufacturing and construction, require components that can withstand vibration, pressure, and environmental factors. A poorly fitting plug can lead to leaks, inefficiencies, or equipment failure. This not only results in increased operational costs but can also compromise safety standards. Buyers may feel overwhelmed when trying to identify the right specifications for a plug without holes that will meet their particular needs, especially when various plug sizes and materials are available.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of their application requirements. First, they should measure the diameter and depth of the hole or cavity where the plug will be used. It is crucial to consider the material compatibility as well; for example, rubber plugs work well in environments with exposure to moisture or chemicals. Buyers should source plugs from reputable manufacturers who provide detailed specifications and application guidance. Additionally, they can consult technical support teams for insights on the best product to ensure a tight seal. Implementing a testing phase before full-scale use can also help identify any potential issues with fit and seal early on, allowing for adjustments without significant downtime.

Illustrative image related to plug without holes
Scenario 2: Limited Availability of Compatible Products
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with the limited availability of compatible plugs without holes, particularly in regions with less access to diverse suppliers. This scarcity can hinder project timelines, as businesses may need to wait for shipments or may be forced to compromise on quality or specifications. Moreover, suppliers may not always stock the specific sizes or materials needed, leading to frustration and potential project delays.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers to ensure a steady flow of compatible products. Diversifying the supplier base not only enhances availability but also opens the door to negotiating better pricing and terms. Buyers should actively research suppliers that specialize in industrial components and keep an updated inventory list of the most frequently used plug sizes and materials. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can further optimize stock levels and reduce the risks of running out. Additionally, buyers may consider custom manufacturing options for specific needs, which can often be sourced from local manufacturers to reduce lead times.
Scenario 3: Misunderstanding of Applications and Uses
The Problem: Many B2B buyers may not fully understand the specific applications and uses for plugs without holes, leading to incorrect purchases and wasted resources. This misunderstanding can stem from a lack of training or knowledge about the product’s functionality, which can result in operational inefficiencies or safety hazards. For example, using a plug designed for a low-pressure application in a high-pressure environment could lead to catastrophic failures.
The Solution: To overcome this knowledge gap, companies should invest in training programs for their procurement and operations teams that focus on the various applications of plugs without holes. Collaborating with manufacturers to provide product demonstrations or workshops can also be beneficial. Buyers should take advantage of product documentation, such as technical data sheets and application guides, that outline the intended use cases for each product. Additionally, creating a centralized knowledge base within the organization can help ensure that all team members have access to vital information and best practices regarding plug selection and application. This proactive approach will not only enhance understanding but also lead to more informed purchasing decisions, ultimately improving efficiency and safety in operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plug without holes
What Are the Key Materials for Manufacturing Plugs Without Holes?
When selecting materials for plugs without holes, it is essential to consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and compatibility with specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the production of plugs without holes, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber is known for its excellent elasticity, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and wear. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically between -40°C to 100°C, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber plugs are durable and can effectively seal against liquids and gases. However, they may degrade over time due to exposure to UV light and certain chemicals. The manufacturing process is relatively simple, but sourcing high-quality rubber can be costly.
Impact on Application:
Rubber plugs are particularly effective in applications involving water or other non-corrosive fluids. They are not recommended for use with oils or solvents, which can cause swelling or degradation.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the rubber used meets local compliance standards, such as ASTM D2000. In Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is crucial.
2. Plastic (Polyethylene or Polypropylene)
Key Properties:
Plastics like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are lightweight, resistant to moisture, and have good chemical resistance. They can typically operate within a temperature range of -30°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons:
Plastic plugs are cost-effective and can be produced in various shapes and colors. They are less durable than rubber and may become brittle over time, especially when exposed to UV light. The manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized molds.
Impact on Application:
These materials are suitable for applications involving non-corrosive liquids and gases. However, they may not hold up well in high-pressure environments.
International Considerations:
Buyers should check for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 and ensure that the plastics used are free from harmful substances, especially in markets like Europe where strict regulations apply.
3. Metal (Aluminum or Stainless Steel)
Key Properties:
Metal plugs are incredibly durable and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Aluminum typically operates well up to 150°C, while stainless steel can handle even higher temperatures and is resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
Metal plugs offer excellent strength and longevity, making them suitable for demanding applications. However, they are heavier and more expensive than rubber or plastic options. The manufacturing process can be complex, involving machining and finishing processes.
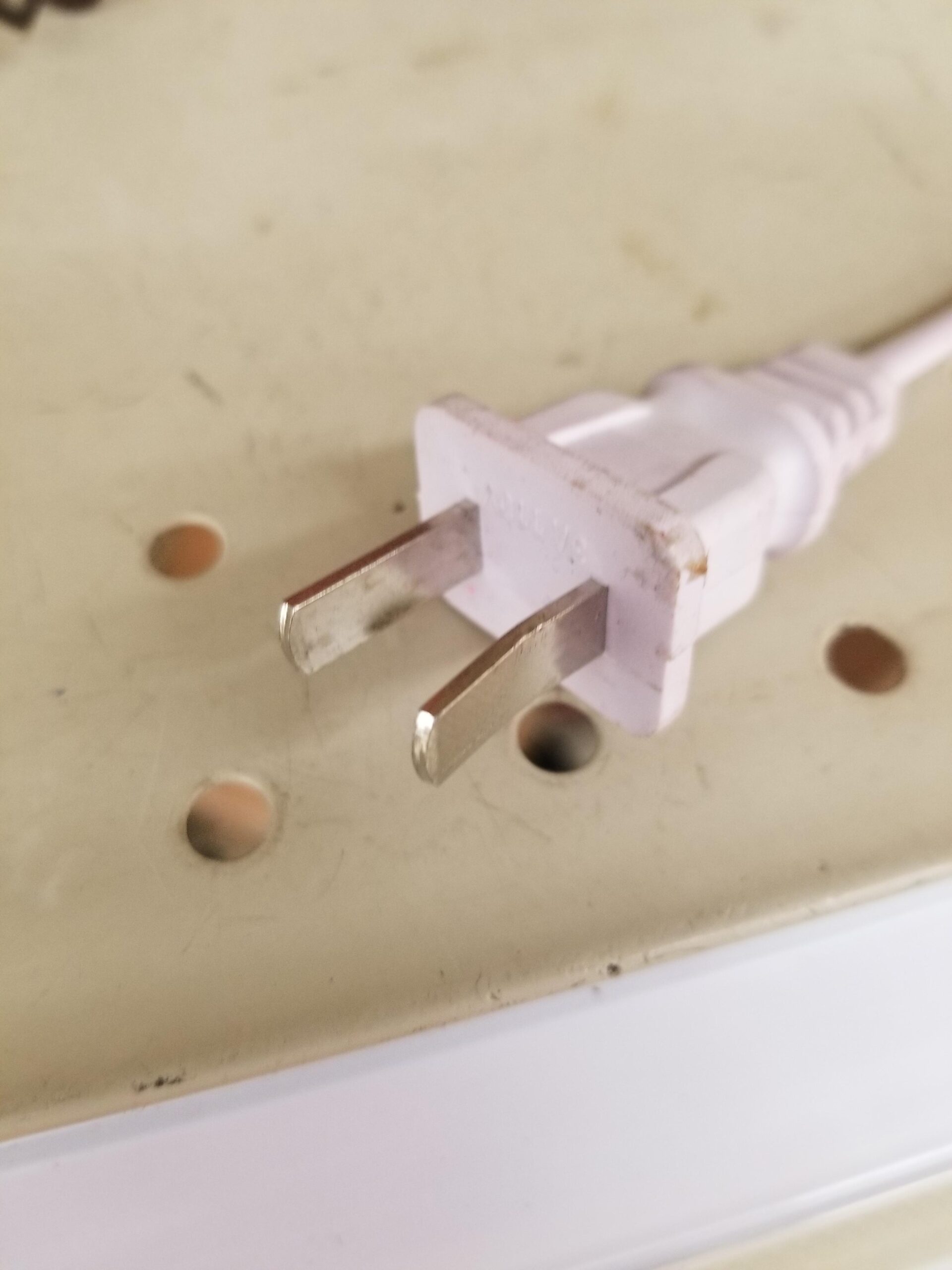
Illustrative image related to plug without holes
Impact on Application:
These plugs are ideal for high-pressure applications or environments where mechanical strength is critical. They are not suitable for applications involving corrosive environments unless stainless steel is used.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers should ensure that metal plugs comply with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. In regions like the Middle East, where corrosion can be a significant issue, selecting the right grade of stainless steel is essential.
4. Silicone
Key Properties:
Silicone is known for its high-temperature resistance (up to 200°C) and flexibility. It is also resistant to UV light, ozone, and various chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
Silicone plugs offer excellent sealing properties and can withstand extreme conditions without degrading. However, they are typically more expensive than rubber and plastics, and their manufacturing process can be more complex.
Impact on Application:
These plugs are suitable for high-temperature applications and environments where chemical exposure is a concern. They are often used in the food and pharmaceutical industries due to their non-toxic nature.
International Considerations:
B2B buyers should ensure that silicone materials meet food safety standards such as FDA compliance in the U.S. or EU regulations in Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Plugs Without Holes
| Material | Typical Use Case for plug without holes | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Sealing in plumbing applications | Excellent flexibility | Degrades with UV exposure | Medium |
| Plastic | General-purpose sealing | Cost-effective | Less durable under pressure | Low |
| Metal | High-pressure industrial applications | Exceptional strength | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Silicone | High-temperature or chemical exposure | Superior temperature resistance | Higher cost and complexity | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials available for plugs without holes, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plug without holes
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing ‘Plug Without Holes’?
The manufacturing process for plugs without holes involves several key stages, each critical for ensuring product quality and performance.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The primary material for plugs without holes is high-quality rubber or thermoplastic elastomer (TPE). These materials are selected for their durability, flexibility, and resistance to various environmental factors. During the material preparation stage, raw materials are sourced, inspected, and tested for compliance with international standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers use materials that meet relevant certifications, such as RoHS or REACH, to guarantee safety and environmental compliance.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
The forming stage typically involves processes such as injection molding or compression molding. In injection molding, molten rubber is injected into a mold that shapes the plug. This method is preferred for its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision. Compression molding, on the other hand, involves placing rubber in a heated mold and applying pressure to form the product. Both methods require careful temperature and pressure control to ensure uniformity and prevent defects.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
For plugs without holes, the assembly process is relatively straightforward since these plugs are typically single-component products. However, in cases where plugs are part of a larger assembly, such as machinery or equipment, integration with other components must be handled with precision. Ensuring proper alignment and fit during assembly is vital for the plug’s performance, especially in applications where sealing and pressure resistance are essential.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used?
Finishing techniques such as trimming, surface treatment, and quality testing are essential to ensure that the plugs meet the specified standards. Trimming removes any excess material from the molding process, while surface treatments may involve applying coatings or treatments to enhance durability and resistance to wear. Additionally, final inspections are conducted to check for defects, ensuring that only products meeting quality standards are packaged and shipped.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Plug Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of manufacturing plugs without holes, ensuring that products are safe, reliable, and meet customer expectations.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a significant role in quality assurance. ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. For plugs without holes, compliance with industry-specific standards like CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for those used in petroleum applications is also crucial. Buyers should request proof of compliance to these standards from suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical in the manufacturing process. These typically include:

Illustrative image related to plug without holes
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, random samples are tested to monitor the process and detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, final inspections are conducted to ensure that the finished products meet all specifications and quality requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the integrity and performance of plugs without holes. These may include:
- Dimensional Testing: Ensures that the plugs meet specified size and shape requirements.
- Material Testing: Assesses the physical and chemical properties of the rubber or elastomer used.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates how the plugs perform under stress, temperature variations, and exposure to chemicals or environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from regions with different manufacturing standards.
What Should Buyers Look For in Supplier Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports that outline the supplier’s QC processes and any certifications obtained. Regular audits, either conducted by the buyer or third-party organizations, can provide insight into the supplier’s compliance with international standards. These audits should focus on evaluating the effectiveness of the supplier’s QMS and adherence to industry-specific regulations.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Third-party inspections serve as an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and the quality of the final products. Engaging a recognized third-party inspection agency can help verify that the products meet the required specifications and standards. This step is particularly important for international buyers who may not be able to conduct on-site inspections.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When sourcing plugs without holes from international suppliers, buyers must navigate various certification and quality control nuances.
How Do Regional Standards Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific standards that impact the quality assurance process. For example, European buyers must ensure compliance with CE marking, while buyers from the Middle East may need to adhere to GSO standards. Understanding these regional requirements is critical to avoid compliance issues that could delay shipments or result in product recalls.
What Role Does Documentation Play in Ensuring Quality?
Proper documentation is vital for ensuring traceability and compliance. Buyers should request certificates of conformity, material safety data sheets (MSDS), and test reports to confirm that the products meet all necessary standards. This documentation not only aids in quality assurance but also serves as evidence of compliance during audits or inspections.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance for plugs without holes involve meticulous attention to detail at every stage. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to international standards and maintain robust quality control systems to ensure the reliability and performance of their products. By doing so, they can enhance their operational efficiency and strengthen their market position.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plug without holes’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure ‘plug without holes.’ These products are essential for various industrial applications, including flooring machinery and electrical equipment, where a secure, sealed connection is crucial. By following this step-by-step approach, you can ensure that you make informed decisions and find the best suppliers for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly define the technical specifications of the plugs you require. This includes dimensions, material type (e.g., rubber), and any specific compliance standards relevant to your industry. Understanding your needs will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and avoid purchasing items that do not meet your operational requirements.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Pricing
Conduct thorough market research to understand current trends and pricing for plugs without holes. Price fluctuations can occur based on material costs and demand. By analyzing market conditions, you can negotiate better terms and identify suppliers offering competitive pricing. Consider using industry reports or trade publications to gather insights.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Pay attention to the following:
– Quality Assurance: Inquire about quality control measures and certifications (e.g., ISO standards).
– Delivery Capabilities: Assess their ability to meet delivery timelines and volume requirements.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Always request samples of the plugs before finalizing your order. Testing samples allows you to verify the quality and compatibility of the products with your equipment. It also provides an opportunity to assess the supplier’s responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your needs.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your selected suppliers hold the necessary certifications and comply with industry standards. This is particularly important for international transactions, where regulations may vary. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific safety compliance certifications relevant to your region.

Illustrative image related to plug without holes
Step 6: Review Payment and Shipping Terms
Carefully review the payment and shipping terms offered by the supplier. Consider factors such as:
– Payment Options: Determine if they offer flexible payment methods that suit your financial processes.
– Shipping Policies: Understand their shipping options, costs, and estimated delivery times to avoid unexpected delays.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Once you’ve successfully sourced plugs without holes, aim to build a long-term relationship with your supplier. Regular communication can lead to better pricing, priority service, and collaboration on future projects. Consider signing a contract that outlines terms for future orders to ensure consistency and reliability in your supply chain.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can efficiently navigate the sourcing process for plugs without holes, ensuring they find the right products to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plug without holes Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Plug Without Holes?
When sourcing plugs without holes, B2B buyers must understand the various cost components that contribute to the final pricing. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.

Illustrative image related to plug without holes
-
Materials: The primary material for plugs without holes is typically rubber or a similar polymer. The cost can vary significantly based on the quality and sourcing of the raw materials. Buyers should evaluate suppliers who offer high-quality materials at competitive rates to ensure durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers involved in the production process. This can vary by region, with countries in Africa or South America often having lower labor costs compared to Europe. Understanding the labor market in the supplier’s location can help buyers gauge total production costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to running the production facility, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overheads, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: If custom molds or tooling are required for specific designs, these costs can significantly impact the initial investment. Buyers should discuss tooling costs upfront, especially for large orders or customized products.
-
Quality Control: Implementing strict QC measures ensures that the plugs meet safety and performance standards. While these processes add to the cost, they are crucial for minimizing returns and maintaining customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, mode of transportation, and current fuel prices. Buyers should consider these costs in their total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin that reflects their profit expectations. Understanding the margin structure can aid in negotiations and help buyers identify potential areas for cost savings.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Plug Without Holes Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of plugs without holes, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Suppliers may offer lower prices for larger minimum order quantities (MOQs), making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders when possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements may increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against their budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The type of material used and any quality certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can affect pricing. Higher-quality materials and certifications may justify a higher price due to their longer lifespan and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and manufacturing capabilities can impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade (Incoterms) is crucial for international transactions. These terms dictate who bears the cost and risk during shipping, influencing the overall price.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs?
Effective negotiation is essential for achieving cost-efficiency in sourcing plugs without holes. Here are some strategies:
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ask for itemized quotes that break down costs. This transparency can reveal areas for negotiation, such as labor or logistics.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Highlight potential future orders or bulk purchases to negotiate better rates. Suppliers are often willing to provide discounts for guaranteed volume.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Engaging with several suppliers allows for comparison and can create competitive pressure, leading to better pricing.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Focus not just on the initial purchase price but also on long-term costs, including maintenance, replacements, and shipping. This broader perspective can justify a higher upfront cost if it leads to lower overall expenses.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect the final cost. Understanding these factors can lead to more informed negotiation outcomes.
Conclusion: What Should B2B Buyers Keep in Mind?
In summary, sourcing plugs without holes requires a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers. Buyers should be proactive in negotiations and consider factors that contribute to the total cost of ownership. By leveraging insights into cost components and price influencers, B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategy and achieve better financial outcomes. Always remember that indicative prices may vary based on market conditions and supplier capabilities, so continuous market research is vital for successful sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plug without holes With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Plug Without Holes
In the realm of industrial and manufacturing applications, the choice of plugs can significantly affect operational efficiency and equipment longevity. ‘Plug without holes’ serves a specific purpose in various sectors, but there are alternative solutions that may offer comparable benefits. This analysis will compare ‘plug without holes’ against two viable alternatives: traditional plugs with holes and adhesive sealing methods.
| Comparison Aspect | Plug Without Holes | Traditional Plugs with Holes | Adhesive Sealing Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides a secure fit without the risk of debris entering. | Enhanced grip due to holes, but may accumulate dirt. | Creates a complete seal, preventing leaks or contamination. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable. | May be slightly higher due to additional materials. | Cost varies based on adhesive quality and application. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation with no special tools required. | Requires precise alignment for optimal performance. | Easy to apply but requires surface preparation. |
| Maintenance | Minimal; infrequent replacement needed. | Moderate; requires regular inspection for wear. | Low; can be replaced as needed but may require cleaning. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for environments where cleanliness is paramount. | Suitable for high-movement applications needing secure connections. | Effective in temporary setups or where a permanent seal is not feasible. |
What are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Traditional Plugs with Holes?
Traditional plugs with holes are designed for better grip and contact with sockets, making them a reliable choice for many applications. The holes allow for a more secure fit by accommodating bumps in the outlet, reducing the risk of accidental disconnection. However, these plugs can accumulate dust and debris in the holes, potentially leading to electrical issues over time. They also require careful alignment during installation, which can complicate the setup process in environments with tight spaces.
How Do Adhesive Sealing Methods Compare?
Adhesive sealing methods provide an alternative approach that can create a complete barrier against contaminants. They are particularly useful in scenarios where a temporary seal is needed or where traditional plugs may not fit. The application of adhesives is generally straightforward; however, it may require surface preparation to ensure proper bonding. The cost of adhesive solutions can vary widely based on the type of adhesive used, and while they offer low maintenance, they may need to be reapplied periodically, especially in high-use environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Plug Solution?
When selecting the appropriate plug solution for your specific needs, it’s crucial to consider factors such as operational efficiency, environmental conditions, and cost implications. ‘Plug without holes’ is ideal for applications demanding cleanliness and minimal maintenance, while traditional plugs with holes may suit scenarios requiring a more secure fit. On the other hand, adhesive sealing methods can be advantageous for temporary setups. By evaluating the operational demands and potential challenges of each option, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and budget constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plug without holes
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Plug Without Holes?
When evaluating plugs without holes, it’s crucial to understand their technical specifications. These properties directly impact performance, compatibility, and application across various industries.
1. Material Grade
The material composition is vital for durability and application suitability. Common materials for plugs without holes include rubber, silicone, and plastic. Rubber plugs are often favored for their elasticity and resistance to wear, making them ideal for environments that require flexibility and longevity. Understanding the material grade helps businesses select the right plug for specific operational conditions.
2. Dimensional Tolerances
Tolerances define the allowable variation in the size of the plug. For plugs without holes, precise dimensions are essential to ensure a snug fit within the intended receptacle. Tighter tolerances can enhance performance by minimizing gaps that could lead to leaks or disconnections. For B2B buyers, choosing plugs with appropriate tolerances ensures reliability and reduces the risk of operational failures.
3. Temperature Resistance
This property refers to the plug’s ability to withstand temperature fluctuations without degrading. Depending on the application, plugs may need to function effectively in extreme heat or cold. For instance, plugs used in industrial machinery may need to endure high temperatures, while those for refrigeration units require low-temperature resilience. Buyers should assess this specification to ensure optimal performance in their specific environments.
4. Hardness Rating
The hardness of a plug, typically measured on the Shore durometer scale, indicates its resistance to deformation. A higher hardness rating means the plug can withstand more pressure without losing shape, which is essential in applications where plugs experience significant mechanical stress. Understanding this rating helps businesses choose plugs that will maintain their integrity under operational loads.
5. Chemical Resistance
For applications involving exposure to various chemicals, the chemical resistance of the plug material is critical. Plugs that can withstand acids, bases, and solvents without degrading ensure long-term functionality and safety. Buyers should prioritize chemical resistance specifications to prevent premature failures in industrial or laboratory settings.
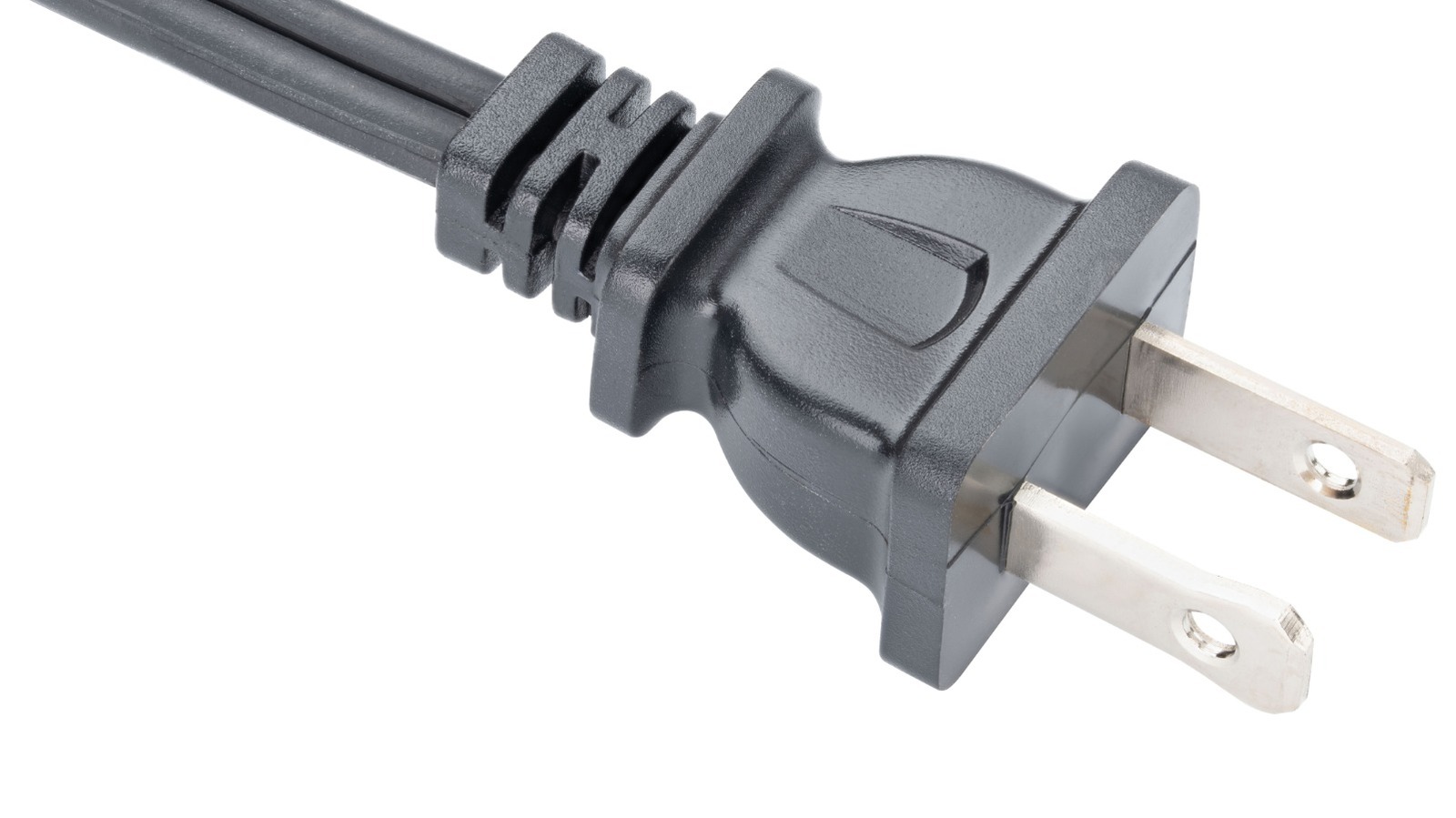
Illustrative image related to plug without holes
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Plugs Without Holes?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some key terms relevant to plugs without holes:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of plugs without holes, OEMs supply components that meet specific standards required by other manufacturers, ensuring compatibility and quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory management. It can also impact pricing, as larger orders often lead to better per-unit costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the case of plugs without holes, an RFQ helps businesses compare offers and negotiate better deals based on their requirements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping, insurance, and risk management, especially when sourcing plugs from international suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. For plugs without holes, knowing the lead time helps businesses plan their operations and manage inventory effectively, ensuring that they have the necessary components when needed.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the technical properties and trade terminology associated with plugs without holes is essential for B2B buyers. This knowledge aids in making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and strategic goals.
Illustrative image related to plug without holes
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plug without holes Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Plug Without Holes Sector?
The global market for plugs without holes is experiencing a notable shift driven by several factors. A growing demand for streamlined, efficient solutions in various industries—ranging from construction to manufacturing—has led to increased adoption of these specialized components. In particular, regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing rapid industrialization, necessitating reliable and durable plug solutions that minimize wear and tear. Countries like Germany and Vietnam are at the forefront of this trend, leveraging advanced manufacturing technologies to produce high-quality plugs that meet international standards.
Emerging B2B technologies are also reshaping sourcing strategies. The integration of digital procurement tools and platforms is facilitating more efficient supply chain management, enabling buyers to access a wider range of manufacturers and suppliers. This trend is particularly beneficial for international buyers who require consistent quality and timely delivery. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce in B2B sectors is making it easier for buyers to compare products, prices, and suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
Another significant trend is the increasing emphasis on customization. Businesses are seeking plugs that can be tailored to specific applications, enhancing operational efficiency. As a result, manufacturers are investing in research and development to innovate and diversify their product offerings, which further enhances competition in the market.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Plug Without Holes Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations in the plug without holes sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning raw materials and waste management, is drawing scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies alike. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recyclable materials and reducing carbon footprints during production.
Additionally, ethical supply chains are gaining importance as businesses recognize the value of transparency and social responsibility. Suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmentally friendly operations are becoming more attractive to buyers, especially in regions where ethical sourcing is mandated by law or consumer demand. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
The trend towards sustainability also extends to product design. Plugs without holes that utilize eco-friendly materials not only appeal to environmentally conscious buyers but can also provide a competitive edge in the marketplace. As awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, the demand for sustainable and ethically sourced products will likely increase, compelling suppliers to innovate and adapt to these new expectations.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Plugs Without Holes?
The evolution of plugs without holes is closely linked to advancements in electrical engineering and manufacturing processes. Historically, electrical plugs were designed with holes to enhance connection stability and prevent disconnection due to weight. However, as technology progressed, the demand for simpler and more efficient plug designs emerged, leading to the creation of plugs without holes.
These plugs have become particularly popular in specialized applications where ease of use and reliability are paramount. The development of rubber materials has further improved the durability and performance of plugs without holes, making them suitable for various industrial settings. Today, manufacturers continue to innovate, focusing on creating plugs that meet the diverse needs of global markets, particularly in emerging economies where infrastructure development is on the rise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plug without holes
-
How do I determine the right specifications for a plug without holes?
To select the appropriate plug without holes, consider the specific application requirements, including size, material compatibility, and environmental factors. For instance, rubber plugs are ideal for sealing and vibration dampening in machinery, while plastic options may be more suitable for lightweight applications. Conducting a thorough needs assessment and consulting with technical specifications from manufacturers can ensure that you choose the right product for your specific use case. -
What are the advantages of using plugs without holes over traditional plugs?
Plugs without holes provide a more secure seal, preventing dust and contaminants from entering machinery or systems. They are often used in applications where a watertight or airtight seal is crucial. Additionally, these plugs can reduce wear and tear on equipment by minimizing vibration and movement, leading to longer operational life and lower maintenance costs. -
What customization options are available for plugs without holes?
Many suppliers offer customization options, including size adjustments, color variations, and material choices to meet specific industry needs. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with manufacturers or distributors, as they may provide tailored solutions such as custom shapes or compounds that enhance durability or chemical resistance based on your application’s demands. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for plugs without holes?
The MOQ for plugs without holes can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Typically, it ranges from a few dozen to several hundred units. For larger purchases, negotiating with suppliers may yield better pricing or reduced minimums, especially if you are establishing a long-term partnership or are a repeat customer. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted by suppliers of plugs without holes?
Payment terms can vary, but many international suppliers accept various methods, including bank transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. Standard terms often range from upfront payment to net 30 or net 60 days upon receipt of goods. It is essential to clarify payment terms during negotiations to ensure they align with your cash flow and procurement practices. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for plugs without holes?
To ensure quality, request certifications and test reports from suppliers, such as ISO 9001 or relevant industry-specific standards. Conducting a quality audit or inspection before shipment can also be beneficial. Establishing clear specifications and performance criteria upfront will help in receiving products that meet your operational requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing plugs without holes internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping methods, lead times, customs regulations, and duties that may apply. Engage with logistics partners who have experience in handling similar products and can navigate import/export regulations. Effective communication with your supplier about shipping terms, such as Incoterms, is crucial to avoid unexpected costs or delays. -
What are the best practices for vetting suppliers of plugs without holes?
To effectively vet suppliers, evaluate their reputation through industry reviews and testimonials. Request references from other clients and assess their production capabilities and quality control processes. Additionally, visiting the supplier’s facility or using third-party inspection services can provide insights into their operational standards, helping you make an informed decision.
Top 2 Plug Without Holes Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Lagler – Rubber Plug without Hole
Domain: floormechanics.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Lagler Rubber Plug without Hole”, “SKU”: “P946”, “MSRP”: “$16.80”, “weight”: “1.00 LBS”, “current_stock”: “Available”, “shipping_info”: “Free Shipping on Orders over $75”, “category”: “Parts by Brand”, “brand”: “Lagler”}
2. Titan WNC – Electrical Cords
Domain: titanwnc.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Electrical cords come in two primary types: two-prong and three-prong. Two-prong cords have a hot prong and a neutral prong, while three-prong cords include an additional ground prong for safety. The holes in the prongs were historically designed to prevent slipping from wall outlets, but modern outlets do not require these holes for a secure connection. The presence of holes may also be attribute…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plug without holes
In the dynamic landscape of international sourcing, understanding the strategic value of plug without holes is crucial for B2B buyers. These plugs offer significant advantages, such as enhanced durability and reliability in various applications, particularly in machinery and industrial settings. By opting for plugs without holes, businesses can mitigate risks associated with equipment failure, reduce maintenance costs, and improve operational efficiency.
Strategic sourcing of these components not only ensures quality but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who understand the specific needs of diverse markets, including those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As you consider your procurement strategies, prioritize suppliers who can provide comprehensive product support and competitive pricing, while also being responsive to the unique challenges of your region.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality, reliable plugs without holes is set to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increasing industrialization across emerging markets. Now is the time to assess your sourcing strategies and align with trusted partners who can help you navigate this evolving landscape. Embrace innovation and quality in your supply chain to ensure a competitive edge in your market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
Illustrative image related to plug without holes
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.