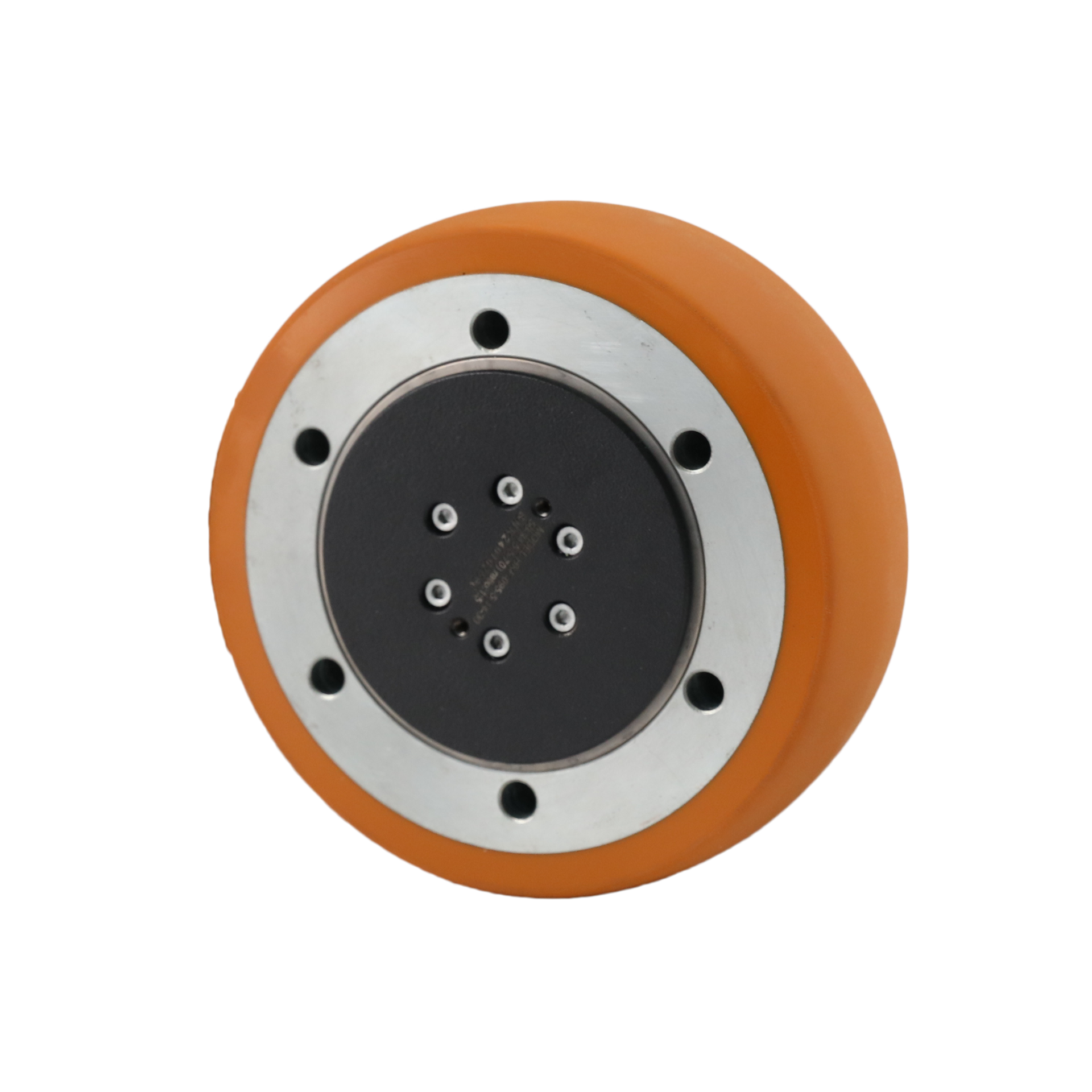
Choosing Your Planetary Wheel: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for planetary wheel
In today’s dynamic global market, sourcing reliable planetary wheel systems can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These complex gear systems, essential for maximizing torque and speed within compact designs, are utilized across various industries, from construction machinery to automotive applications. This comprehensive guide aims to equip international buyers with the insights necessary to navigate the intricacies of planetary wheels, covering critical aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
Throughout this guide, you will discover the diverse configurations of planetary wheels, including their unique advantages and potential applications tailored to specific operational needs. The importance of selecting the right supplier cannot be overstated; we will provide actionable strategies for assessing manufacturer credibility and product quality, ensuring that your procurement decisions are both informed and strategic. Additionally, we will delve into cost factors and potential ROI, empowering you to make budget-conscious choices that align with your business objectives.
By leveraging the knowledge and insights presented in this guide, B2B buyers can confidently approach the purchasing process for planetary wheels, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitiveness in the global marketplace.
Understanding planetary wheel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheel Drives | Compact design with high torque output | Mobile machinery, construction equipment | Pros: High efficiency, space-saving. Cons: Limited customization options. |
| Shaft Output Drives | Direct output from the shaft, often with high RPM | Automotive, robotics | Pros: Simple design, easy integration. Cons: May require additional support systems. |
| Flanged Output Drives | Features flanges for easy mounting | Industrial automation, conveyor systems | Pros: Versatile installation options. Cons: May increase overall system weight. |
| Compact Drives | Smaller footprint while maintaining power density | Agricultural machinery, compact equipment | Pros: Space-efficient, lightweight. Cons: Potentially lower torque capacity. |
| Swing Drives | Rotational movement for applications needing pivoting | Construction, forestry equipment | Pros: Enhanced maneuverability. Cons: More complex design may lead to higher maintenance. |
What are the Characteristics of Wheel Drives and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Wheel drives are characterized by their compact design and ability to deliver high torque output. This makes them ideal for mobile machinery and construction equipment, where space is at a premium and power needs are high. For B2B buyers, selecting wheel drives can result in enhanced operational efficiency, but they may face limitations in customization, which could affect specific application needs.
How Do Shaft Output Drives Function and What Should Buyers Consider?
Shaft output drives provide direct output from the shaft, often achieving high RPMs. They are commonly used in automotive and robotics applications where precision and speed are critical. Buyers should consider the simplicity of design and ease of integration; however, they may need to account for additional support systems to ensure optimal performance.
What Are the Benefits of Flanged Output Drives in Industrial Applications?
Flanged output drives are designed with flanges that facilitate easy mounting, making them suitable for industrial automation and conveyor systems. Their versatility in installation can be a major advantage for B2B buyers looking to streamline their operations. However, the added flanges can increase the overall system weight, which should be factored into the design and application.
Why Choose Compact Drives for Agricultural Machinery?
Compact drives offer a smaller footprint while maintaining high power density, making them particularly suitable for agricultural machinery and compact equipment. This space efficiency can be a significant advantage in environments where size constraints are critical. Buyers should note that while compact drives are lightweight, they may have a lower torque capacity compared to larger systems.
What Makes Swing Drives Unique for Construction and Forestry Equipment?
Swing drives are designed to provide rotational movement, making them ideal for applications requiring pivoting, such as in construction and forestry equipment. Their enhanced maneuverability is a key selling point for B2B buyers; however, the complexity of their design may lead to higher maintenance requirements, which should be considered when evaluating long-term costs.
Key Industrial Applications of planetary wheel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of planetary wheel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Feed Mixers | Enhanced efficiency in mixing, leading to better feed quality and animal health. | Customizable gear ratios to match specific mixer designs. |
| Construction | Excavators and Cranes | High torque output in a compact design, enabling heavy lifting and precise control. | Durability under extreme conditions and compatibility with existing machinery. |
| Automotive | Differential Gears | Improved vehicle handling and performance through efficient torque distribution. | Compliance with automotive standards and performance testing. |
| Mining and Quarrying | Conveyor Systems | Reliable operation in transporting materials with reduced maintenance needs. | High load capacity and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind Turbines | Enhanced energy conversion efficiency, maximizing power generation from wind. | Ability to withstand high rotational speeds and environmental stress. |
How is the planetary wheel used in agriculture, and what problems does it solve?
In the agriculture sector, planetary wheels are integral to feed mixers, where they optimize the mixing process. By providing high torque in a compact design, these gear drives enhance the efficiency of feed preparation, resulting in better quality feed that supports animal health and productivity. Buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing options that allow for customizable gear ratios, ensuring compatibility with specific mixer designs and operational requirements. Considerations such as durability and ease of maintenance are also crucial to minimize downtime.
What role do planetary wheels play in construction equipment?
In the construction industry, planetary wheels are commonly used in excavators and cranes. Their design allows for high torque output while maintaining a compact profile, which is essential for heavy lifting and precise movement in confined spaces. This application addresses the challenge of managing heavy loads with accuracy. When sourcing planetary wheels for construction machinery, buyers should prioritize durability to withstand harsh working conditions and ensure compatibility with existing equipment, which can significantly impact operational efficiency.
How do planetary wheels enhance automotive performance?
Planetary wheels are vital components in automotive differential gears, improving vehicle handling and performance through efficient torque distribution. They help manage the varying wheel speeds during turns, contributing to smoother driving experiences. For B2B buyers in the automotive sector, it is essential to source planetary wheels that comply with industry standards and undergo rigorous performance testing. This ensures reliability and safety, which are paramount in automotive applications.
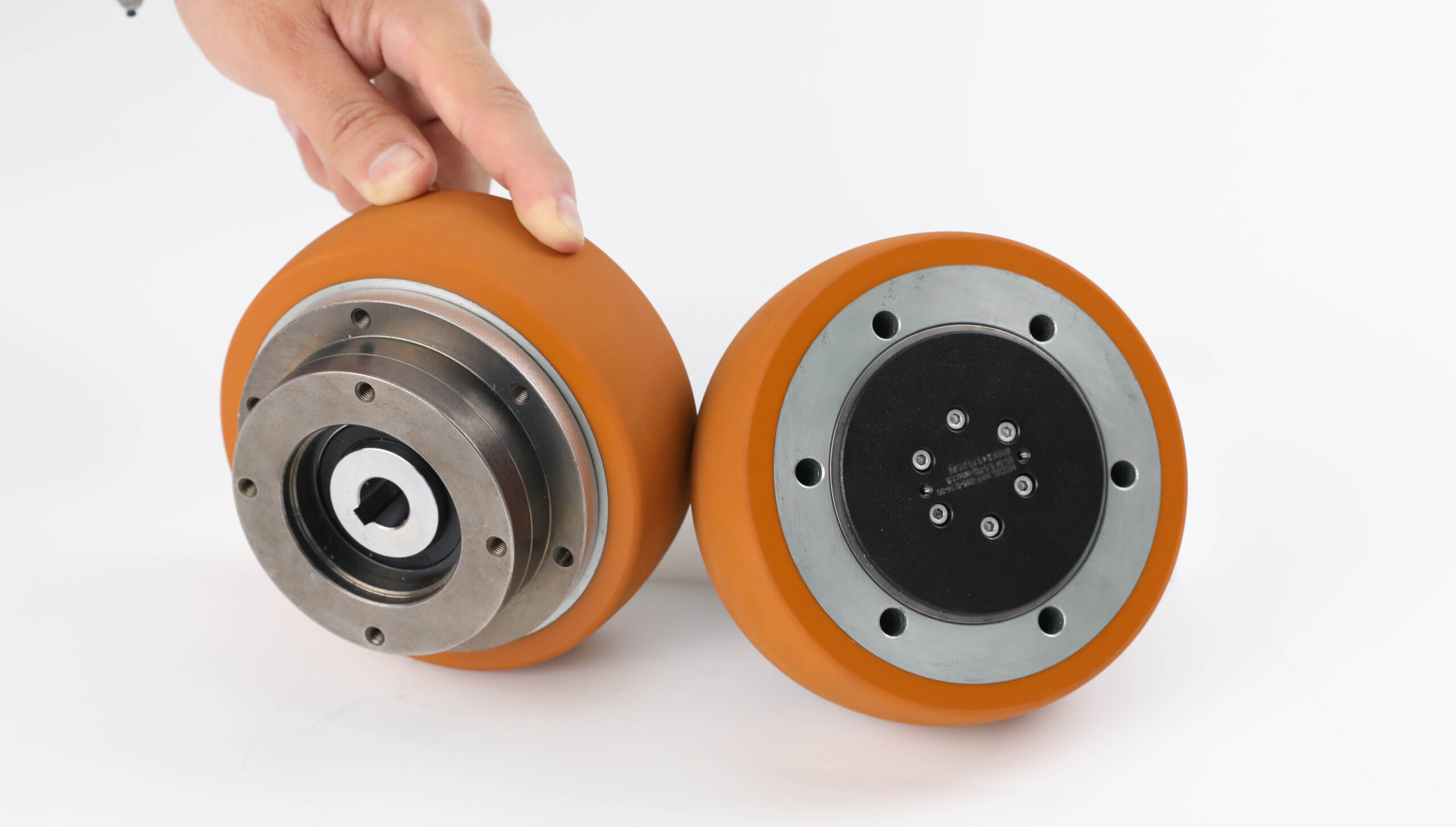

Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
In what ways are planetary wheels utilized in mining and quarrying?
In mining and quarrying, planetary wheels are utilized in conveyor systems, where they enhance the reliability of material transportation. The design allows for high load capacities while minimizing maintenance needs, addressing the challenges of operating in harsh environments. For international buyers, especially in regions with extreme conditions, sourcing planetary wheels that offer resistance to wear and tear, as well as high durability, is critical to maintaining operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
How do planetary wheels contribute to renewable energy solutions?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbines, planetary wheels play a crucial role in enhancing energy conversion efficiency. They enable the effective transfer of energy from the turbine blades to the generator, maximizing power generation from wind. Buyers in this field should seek planetary wheels that can withstand high rotational speeds and environmental stress, ensuring long-term reliability and performance. This focus on durability and efficiency is essential for optimizing energy output in renewable applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘planetary wheel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Planetary Gear Ratio for Your Application
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with determining the appropriate gear ratio for their specific applications. The challenge lies in balancing the need for high torque output while maintaining operational efficiency. For instance, in heavy machinery or automotive applications, an incorrect gear ratio can lead to inadequate performance, increased wear and tear, and even catastrophic failures, resulting in costly downtime and repairs. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America may also face additional hurdles, such as limited access to technical resources or expertise, further complicating their decision-making process.
The Solution: To effectively choose the right planetary gear ratio, begin by conducting a thorough analysis of your application’s requirements. Understand the torque and speed needs, as well as the load characteristics and operating conditions. Collaborate with manufacturers that offer in-house engineering support, as they can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific use case. For example, companies like Auburn Gear provide custom design options and prototype support, allowing you to test different configurations before making a commitment. Additionally, utilize simulation tools to model the performance of various gear ratios under expected load conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
Scenario 2: Overcoming Concerns About Durability and Maintenance of Planetary Gears
The Problem: Buyers are often apprehensive about the durability and maintenance requirements of planetary gears. In sectors such as agriculture or construction, where equipment is subjected to harsh conditions, the risk of failure can be significant. Many users report issues with premature wear and the need for frequent maintenance, leading to increased operational costs and reduced equipment reliability. This concern is particularly pronounced in emerging markets where supply chains for spare parts and service support may be less robust.
The Solution: To mitigate concerns about durability, select planetary gear systems that are designed with enhanced materials and engineering features to withstand extreme conditions. Look for manufacturers that provide detailed information about the materials used and their testing protocols to ensure reliability. Implement a preventive maintenance program that includes regular inspections and lubrication, which can significantly extend the lifespan of the gears. Additionally, consider investing in gear systems that offer improved load distribution, such as those with multiple planet gears, as these designs can reduce wear and increase overall resilience. Engaging with suppliers who have a strong reputation for customer service can also ensure that you receive timely support and replacement parts when needed.
Scenario 3: Navigating the Complexity of Customization and Sizing
The Problem: Many buyers encounter challenges when attempting to customize planetary wheel systems to meet their unique specifications. Whether it’s for a specialized industrial application or a bespoke piece of machinery, understanding the options for customization can be daunting. This complexity can lead to frustration, as buyers may feel overwhelmed by technical jargon or unsure of how to communicate their needs effectively to manufacturers. This is particularly relevant in diverse markets where local expertise may be limited.
The Solution: Start by clearly defining your application requirements, including dimensions, load capacities, and performance parameters. Utilize available resources, such as technical documentation and online calculators, to get a basic understanding of the customization options. When approaching manufacturers, clearly articulate your needs and ask for their input on feasible solutions. A reputable supplier will offer engineering consultation services to help refine your specifications and ensure that the end product meets your expectations. Additionally, consider suppliers that provide prototype support; this allows you to test the customized planetary wheel in real-world scenarios before full-scale production, ensuring that it meets performance standards and reduces the risk of costly modifications later on.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for planetary wheel
What Are the Key Materials for Planetary Wheels and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for planetary wheels, it’s essential to consider their mechanical properties, compatibility with operational environments, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of planetary wheels: steel, aluminum, plastic, and composite materials.
How Does Steel Perform as a Material for Planetary Wheels?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials for planetary wheels due to its excellent mechanical properties. It exhibits high strength and rigidity, making it suitable for high-load applications. Steel also has good wear resistance, especially when treated or alloyed with other elements, such as chromium or molybdenum, to enhance its properties.
Pros: Steel offers superior durability and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other high-performance materials.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion unless adequately treated. Additionally, manufacturing processes for steel components can be complex, requiring advanced machining and heat treatment.
Impact on Application: Steel planetary wheels are compatible with various media, including oils and greases, making them ideal for heavy machinery in industries such as construction and mining.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN. Corrosion resistance is particularly crucial in humid or coastal environments.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum for Planetary Wheels?
Aluminum is another popular choice for planetary wheels, especially in applications where weight reduction is critical. It has a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for lighter designs without sacrificing performance.
Pros: Aluminum is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor applications. It also offers ease of manufacturing due to its malleability.
Cons: The main limitation of aluminum is its lower strength compared to steel, which may not be suitable for high-load applications. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than steel.

Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
Impact on Application: Aluminum planetary wheels are often used in aerospace and automotive applications, where weight savings are essential without compromising strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like JIS for aluminum alloys is necessary. Buyers should also consider the availability of aluminum in their local markets.
How Do Plastics Compare for Planetary Wheel Applications?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like nylon and polycarbonate, are increasingly used in planetary wheels for specific applications. They offer excellent wear resistance and can operate in a wide range of temperatures.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They also have the advantage of being quieter in operation compared to metal components.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is their lower load-bearing capacity compared to metals. Plastics can also be sensitive to UV light and may degrade over time if exposed.
Impact on Application: Plastic planetary wheels are suitable for applications in food processing and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and resistance to chemicals are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with food safety standards, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
What Are the Benefits of Composite Materials in Planetary Wheels?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, are gaining traction in high-performance planetary wheel applications. They combine the best properties of both plastics and metals.
Pros: Composites are lightweight yet strong, offering excellent fatigue resistance. They can also be tailored to specific performance requirements.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be expensive and complex, which may increase overall costs. They also require careful handling to avoid damage during assembly.
Impact on Application: Composite planetary wheels are ideal for aerospace and high-speed applications where weight and performance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards for composites in their region and ensure that suppliers can provide the necessary certifications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Planetary Wheels
| Material | Typical Use Case for planetary wheel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy machinery, mining | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength than steel | High |
| Plastic | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Lightweight and chemical-resistant | Lower load-bearing capacity | Medium |
| Composite | Aerospace, high-performance vehicles | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions when sourcing planetary wheels, considering both performance requirements and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for planetary wheel
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Planetary Wheels?
Manufacturing planetary wheels involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure high performance and durability. The typical process includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Planetary Wheel Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality materials, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, or even specialized composites, are selected based on the application’s requirements. These materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specific mechanical properties and chemical compositions.
Once the materials are sourced, they are cut and shaped into rough forms using techniques like laser cutting or waterjet cutting. This stage often includes heat treatment processes, such as annealing or hardening, to enhance the material’s strength and wear resistance.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Planetary Wheel Production?
After preparation, the forming stage begins. Techniques such as forging, casting, and machining are employed to create the various components of the planetary wheel.
-
Forging: This technique is commonly used for producing high-strength components. The material is heated and shaped under pressure, ensuring uniform grain structure and improved mechanical properties.
-
Casting: For more complex shapes, casting can be an effective method. Molten metal is poured into molds to create parts like gears and carriers.
-
Machining: Precision machining processes, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, are used to achieve exact dimensions and tolerances. This is crucial for ensuring the components fit together seamlessly and function efficiently.
How Are Planetary Wheels Assembled?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the complete planetary wheel system. This process typically involves several steps:
-
Component Inspection: Before assembly, each component undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets quality standards.
-
Assembly: Components such as the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear are assembled in a specific order. This often requires specialized fixtures to maintain alignment and positioning.
-
Lubrication: Proper lubrication is critical for the longevity of planetary wheels. Lubricants reduce friction and wear, enhancing performance.
-
Final Assembly: The assembled components are then integrated into the final planetary wheel structure. This may also include the installation of seals and bearings.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Applied to Planetary Wheels?
Finishing processes enhance the performance and longevity of planetary wheels. Common techniques include:
-
Surface Treatment: Processes like shot peening or surface hardening improve fatigue resistance and wear properties.
-
Coating: Applying protective coatings, such as phosphating or anodizing, can prevent corrosion and enhance surface durability.
-
Final Inspection: The finished product undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all specifications before shipping.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Planetary Wheel Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in planetary wheel manufacturing, and adherence to international standards is crucial for maintaining product integrity. Key standards include:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: Particularly relevant for the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that products meet specified standards. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify any deviations from quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product is subjected to comprehensive testing to verify its performance and durability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Planetary Wheels?
Testing methods are vital for verifying the functionality and reliability of planetary wheels. Common methods include:
-
Torque Testing: Measures the torque output under various loads to ensure the gear set performs as expected.
-
Vibration Testing: Identifies potential issues with balance or misalignment that could lead to premature wear.
-
Fatigue Testing: Simulates long-term use to assess the durability of the components under cyclic loading.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC practices is essential. Here are some strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes and QC systems firsthand. This transparency fosters trust and assurance.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can provide insights into the supplier’s quality management practices and any certifications they hold.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and compliance with relevant standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of specific certification nuances when sourcing planetary wheels:
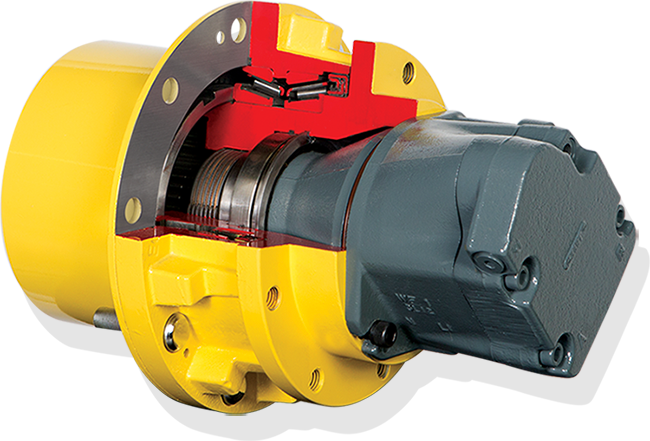

Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
-
Regional Compliance: Understanding local regulations and standards is crucial. For example, CE marking is necessary for products sold in Europe, while different standards may apply in Africa or South America.
-
Documentation: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation, including test results and compliance certificates, which may be necessary for customs clearance or local regulations.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building relationships with suppliers in different regions can enhance communication and facilitate smoother transactions. Understanding cultural nuances can also improve negotiation outcomes.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in planetary wheel production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality components tailored to their specific application needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘planetary wheel’
To assist international B2B buyers in successfully procuring planetary wheels, this practical sourcing guide outlines essential steps to ensure quality, compatibility, and supplier reliability. By following this checklist, buyers can make informed decisions that meet their technical and operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider factors such as size, load capacity, gear ratio, and the specific application for which the planetary wheel will be used. Detailed specifications will guide your search and help suppliers understand your requirements, ensuring compatibility with your equipment.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Applications
Stay informed about the latest trends in planetary wheel applications across various industries. Understanding how these components are utilized in sectors such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing can provide insights into the best options for your needs. This knowledge allows you to identify innovative solutions and potential suppliers who specialize in those applications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions to gauge their reputation. Look for established manufacturers with a proven track record, as well as those that offer customization options to meet your unique specifications.
- Check for certifications: Ensure suppliers have relevant industry certifications, which indicate adherence to quality standards.
- Assess production capabilities: Evaluate whether the supplier has the necessary technology and facilities to meet your production volume and quality requirements.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Once you’ve narrowed down your supplier list, request samples or prototypes of the planetary wheels. This step is crucial for assessing the quality and performance of the products before making a bulk order. Testing samples can reveal potential issues related to compatibility, durability, or performance under specific conditions.
Step 5: Review Warranty and Support Policies
Understanding the warranty and post-sale support policies of your chosen supplier is essential. A robust warranty can provide peace of mind and protect your investment against defects or failures. Additionally, inquire about the level of technical support available, as ongoing assistance can be vital for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
When you are satisfied with your chosen supplier, it’s time to negotiate terms and conditions. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and penalties for late delivery. Clear agreements will help prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Finally, consider establishing a long-term relationship with your supplier. Building rapport can lead to better pricing, priority service, and insights into new technologies or trends. Regular communication and feedback will foster a partnership that benefits both parties and enhances your supply chain resilience.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring planetary wheels effectively, ensuring they choose the right components for their operational needs while fostering strong supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for planetary wheel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Planetary Wheels?
When sourcing planetary wheels, it is essential to understand the various cost components that contribute to the final price. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials significantly influences the durability and performance of planetary wheels. Common materials used are high-strength steel, aluminum, and specialized alloys, which can vary in price based on availability and sourcing location.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ based on the manufacturing location. Regions with a skilled workforce may have higher labor costs, but they might also offer superior craftsmanship, which can justify the price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, thereby lowering the overall cost of the planetary wheels.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs or large-scale production can be a significant upfront investment. However, once established, tooling costs can be amortized over larger production runs, making it cost-effective for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is crucial for ensuring product reliability. The costs associated with QC, including testing and certifications, can add to the overall price but are essential for maintaining product standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the distance and mode of transport. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is vital as they dictate who bears the cost and risk during transport.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the unique value proposition of the supplier.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Planetary Wheel Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of planetary wheels:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications can significantly affect costs. While standard products may be cheaper, custom solutions may provide better long-term value through improved performance.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can increase costs but are often necessary for compliance in certain industries. Buyers should weigh the costs against the benefits of enhanced durability and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can help buyers manage costs effectively. Different terms can shift costs and risks, affecting the total landed cost of the products.
What Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency for Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
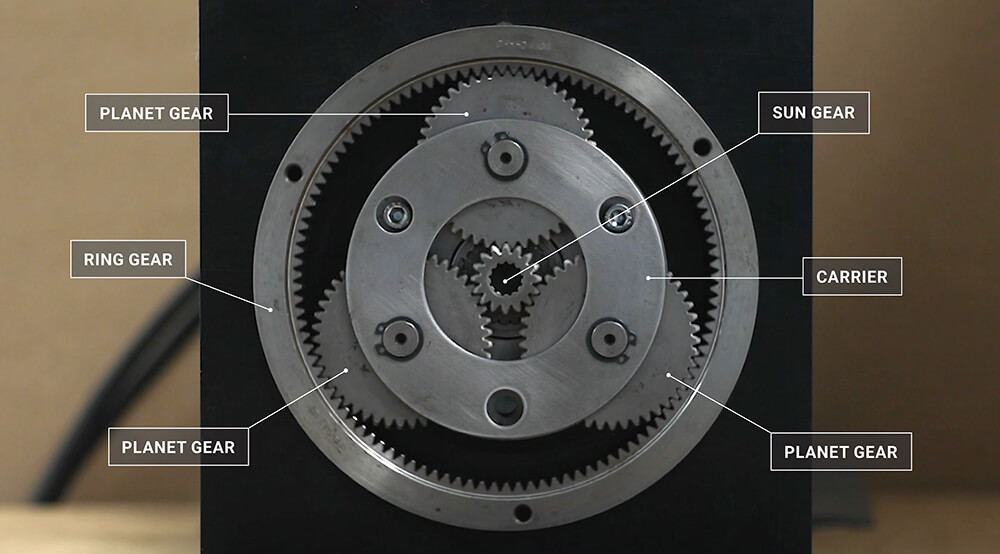
Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
-
Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the upfront costs but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. A higher initial investment in quality may lead to lower TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. Currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local economic conditions can all impact the final price. Buyers should factor in these elements when making purchasing decisions.
-
Supplier Diversity: Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for planetary wheels can vary widely based on the factors discussed. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage with suppliers directly to obtain accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing planetary wheel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Planetary Wheel Solutions
In the realm of mechanical systems, the choice of gear drives can significantly impact performance, efficiency, and operational costs. While planetary wheels are a popular option due to their compact design and high torque capabilities, it is prudent for B2B buyers to explore alternative solutions that might better suit their specific applications. This analysis compares planetary wheels against two viable alternatives: cycloidal drives and worm gear drives.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Planetary Wheel | Cycloidal Drive | Worm Gear Drive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque density; compact size | Very high torque with reduced backlash | Good torque but larger size and lower efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on customization | Generally high due to precision engineering | Lower initial cost but less efficient |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires precise alignment | Complex setup and alignment needed | Simple installation, often requires minimal space |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to balanced load distribution | Moderate; can require regular lubrication | Higher maintenance due to wear on gears |
| Best Use Case | Robotics, automotive, and aerospace | Heavy machinery, robotics, and automation | General machinery, conveyor systems |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Cycloidal Drive
Cycloidal drives utilize an eccentric cam mechanism, providing exceptional torque output with minimal backlash. They are particularly advantageous in applications requiring high load capacities and precise motion control, such as robotic arms and heavy machinery. However, the complexity of their design can make installation and alignment challenging, potentially increasing the time and cost of implementation. While cycloidal drives excel in performance, they often come with a higher price tag due to the precision engineering involved.
Worm Gear Drive
Worm gear drives consist of a worm (screw) and a worm wheel (gear), offering a unique solution for applications requiring significant speed reduction and torque multiplication. They are simpler to install and can fit into compact spaces, making them ideal for general machinery and conveyor systems. However, they tend to have lower efficiency compared to planetary wheels, as they can generate more heat and wear over time, leading to higher maintenance needs. Furthermore, their performance diminishes under heavy loads, making them less suitable for demanding applications.
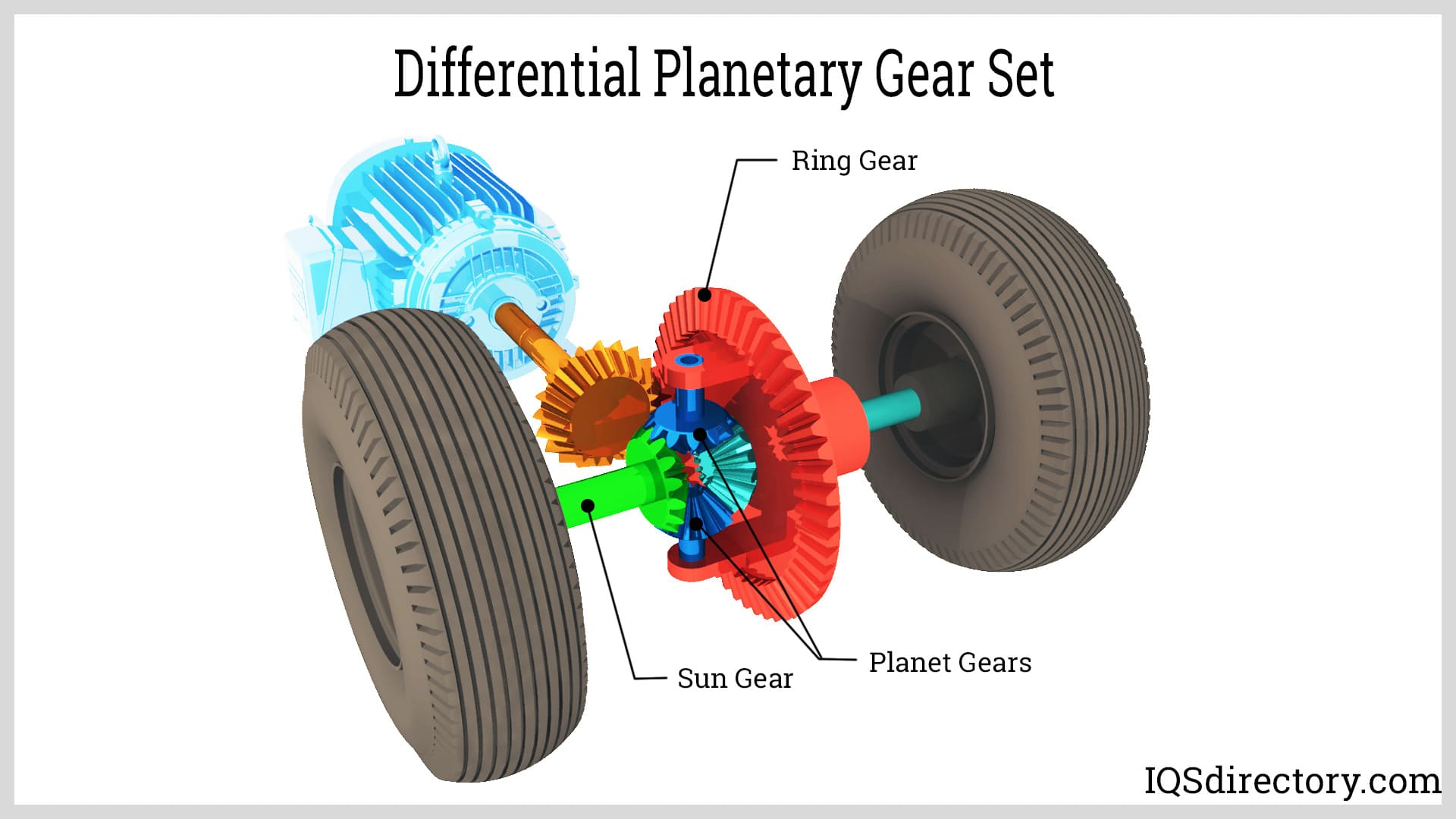
Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate gear drive solution requires a nuanced understanding of specific operational requirements, including load capacity, space constraints, and budget. Planetary wheels offer a robust, high-performance option for applications needing compact design and high torque. However, if cost is a significant factor or if the application involves less demanding torque requirements, exploring cycloidal or worm gear drives may provide viable alternatives. Ultimately, B2B buyers should evaluate the pros and cons of each solution in the context of their unique applications to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for planetary wheel
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Planetary Wheels?
Understanding the technical properties of planetary wheels is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure the right fit for their applications. Here are some key specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material used in the construction of planetary wheels significantly affects their durability and performance. Common materials include high-strength steel, aluminum alloys, and composite materials. Selecting the appropriate material is vital for ensuring that the planetary wheel can withstand operational stresses and environmental conditions, which is essential for industries like construction, agriculture, and mining.
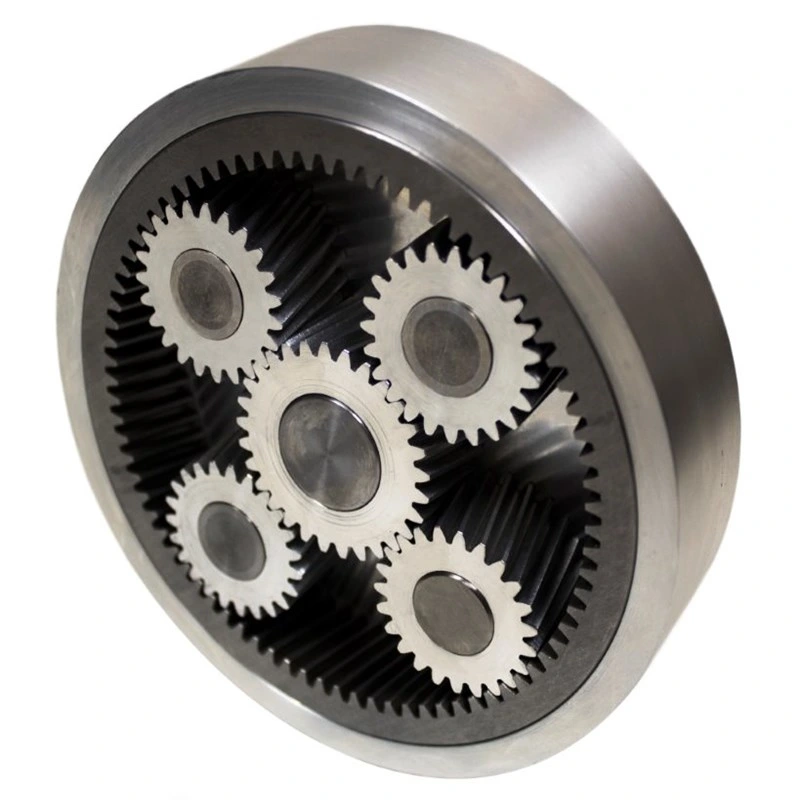

Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
2. Gear Ratio
The gear ratio indicates the relationship between the input speed and the output speed of the planetary wheel system. This property is critical for applications requiring specific torque and speed characteristics. A higher gear ratio allows for greater torque multiplication, making it suitable for heavy machinery. Buyers should consider the required gear ratio to optimize the performance of their equipment.
3. Tolerances
Tolerances refer to the permissible limits of variation in the dimensions of the planetary wheel components. Tight tolerances ensure precise meshing of gears, which enhances the overall efficiency and lifespan of the drive system. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers who can meet specific tolerance requirements to avoid premature wear and operational failures.
4. Load Capacity
This specification defines the maximum load that a planetary wheel can support without failure. Load capacity is a critical consideration for buyers, especially in heavy-duty applications where the wheel must handle significant forces. Understanding the load capacity helps buyers select a planetary wheel that can operate safely and effectively within their application’s requirements.
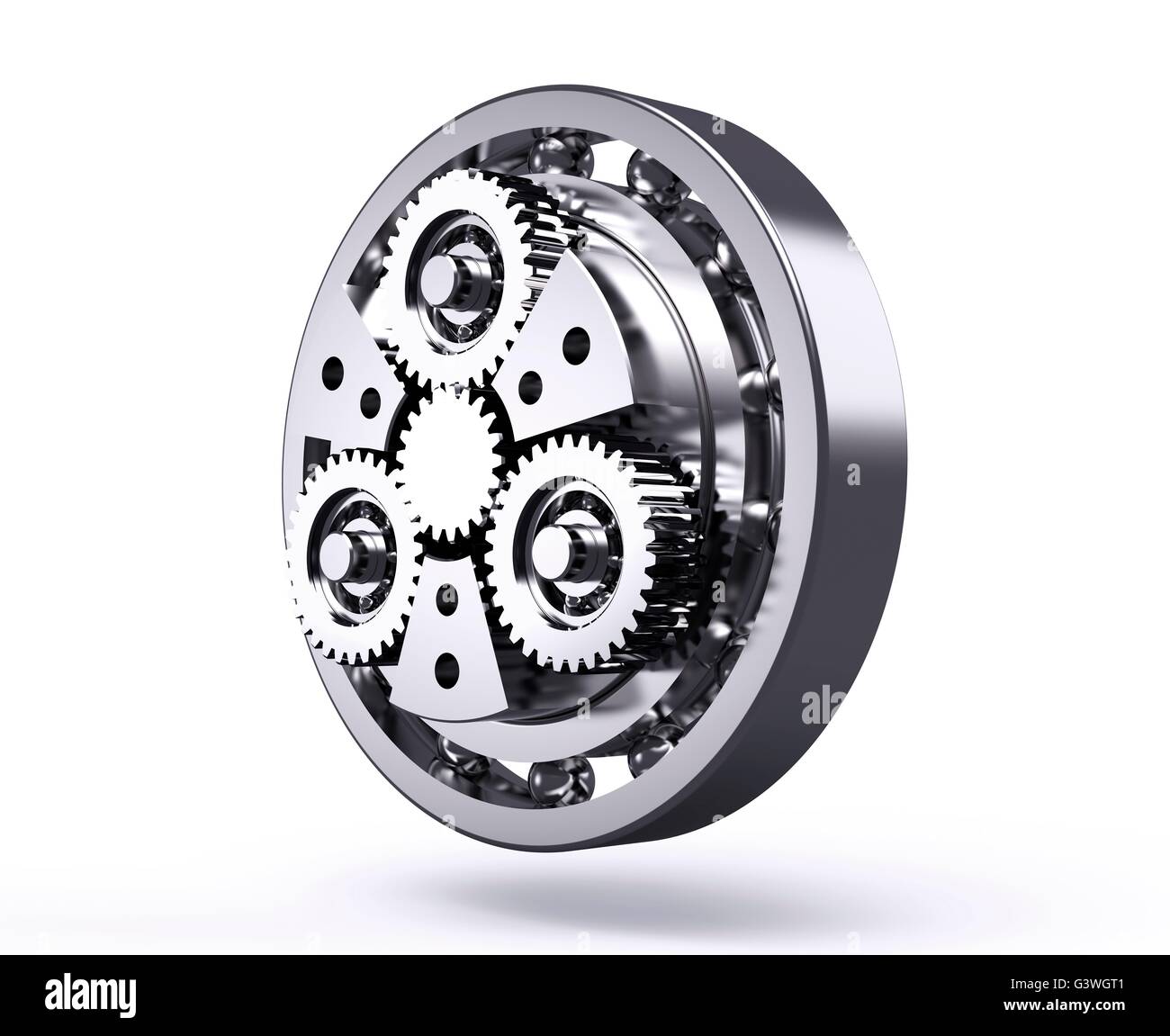

Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
5. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings indicate how effectively a planetary wheel converts input power to output power, accounting for losses due to friction and heat. High-efficiency planetary wheels are essential for applications requiring energy savings and enhanced performance. Buyers should assess efficiency ratings to ensure optimal energy usage and reduced operational costs.
6. Thermal Management
Planetary wheels generate heat during operation, which can affect performance and longevity. Effective thermal management properties, such as heat dissipation design and materials that withstand high temperatures, are crucial. Buyers should look for planetary wheels designed with thermal management features to prevent overheating and ensure consistent operation.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Planetary Wheels?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline the purchasing process and facilitate better communication with suppliers. Here are some common terms used in the planetary wheel market:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components that are used in another company’s products. In the context of planetary wheels, OEMs are critical for buyers seeking high-quality, reliable components that meet their specific application standards. Engaging with OEMs often ensures better support and customization options.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is essential for buyers to plan their budgets and inventory. A higher MOQ might lead to cost savings per unit but can pose a challenge for smaller businesses that cannot justify large orders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This process helps buyers compare offers from different manufacturers and select the best option based on price, quality, and delivery terms. A well-prepared RFQ can expedite the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify obligations and costs involved in international transactions, ensuring smooth logistics and compliance.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. It is an essential factor for B2B buyers to consider when planning their projects. Shorter lead times can enhance project efficiency, while longer lead times might necessitate adjustments in scheduling and inventory management.
6. Customization
Customization refers to the ability to modify standard planetary wheel designs to meet specific requirements. This can include changes in size, material, or performance characteristics. Buyers seeking tailored solutions should inquire about a manufacturer’s customization capabilities to ensure their unique needs are met effectively.
By understanding these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing planetary wheels, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the planetary wheel Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Planetary Wheel Sector?
The planetary wheel sector is experiencing robust growth driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for high-efficiency power transmission systems across various industries. Key drivers include the rising need for compact and lightweight machinery, particularly in the automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors. Additionally, the expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) is propelling demand for efficient planetary gear systems that enhance performance while reducing energy consumption. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is critical for making informed sourcing decisions.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards automation and smart technologies within the planetary gear market. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating IoT capabilities into their gear systems, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This technological evolution not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces downtime, which is crucial for businesses operating in competitive markets. Furthermore, customization has become a focal point, with suppliers offering tailored solutions to meet specific application needs, enhancing the value proposition for international buyers.

Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
Another notable trend is the growing emphasis on local sourcing. As supply chains become more complex, buyers are prioritizing suppliers that can provide shorter lead times and greater flexibility. This shift is particularly relevant for businesses in developing markets, where logistical challenges can impede timely project execution. By fostering strong relationships with local manufacturers, buyers can enhance their supply chain resilience and responsiveness.
How is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the Planetary Wheel Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a pivotal factor in the sourcing decisions of B2B buyers within the planetary wheel sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, along with the increasing regulatory focus on sustainable practices, is prompting businesses to seek suppliers committed to ethical sourcing and minimal environmental footprints. For example, manufacturers that prioritize the use of recycled materials or implement energy-efficient production methods are becoming increasingly attractive to discerning buyers.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers’ practices to ensure compliance with environmental standards and labor laws. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish credibility and trust within the international market. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also provide assurance to buyers that the products they source meet rigorous quality and environmental standards.
In addition to compliance, the use of ‘green’ materials in manufacturing planetary wheels is gaining traction. Suppliers that utilize bioplastics or environmentally friendly lubricants are more likely to resonate with buyers focused on reducing their overall carbon footprint. As global awareness of environmental issues continues to rise, the demand for sustainable products will likely influence sourcing strategies and supplier selection processes.
What is the Historical Context of the Planetary Wheel Sector?
The planetary wheel sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially designed for simple mechanical applications, advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies have transformed planetary gears into sophisticated systems capable of handling complex tasks. The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools in the late 20th century revolutionized the development process, allowing engineers to create highly efficient designs tailored for specific applications.
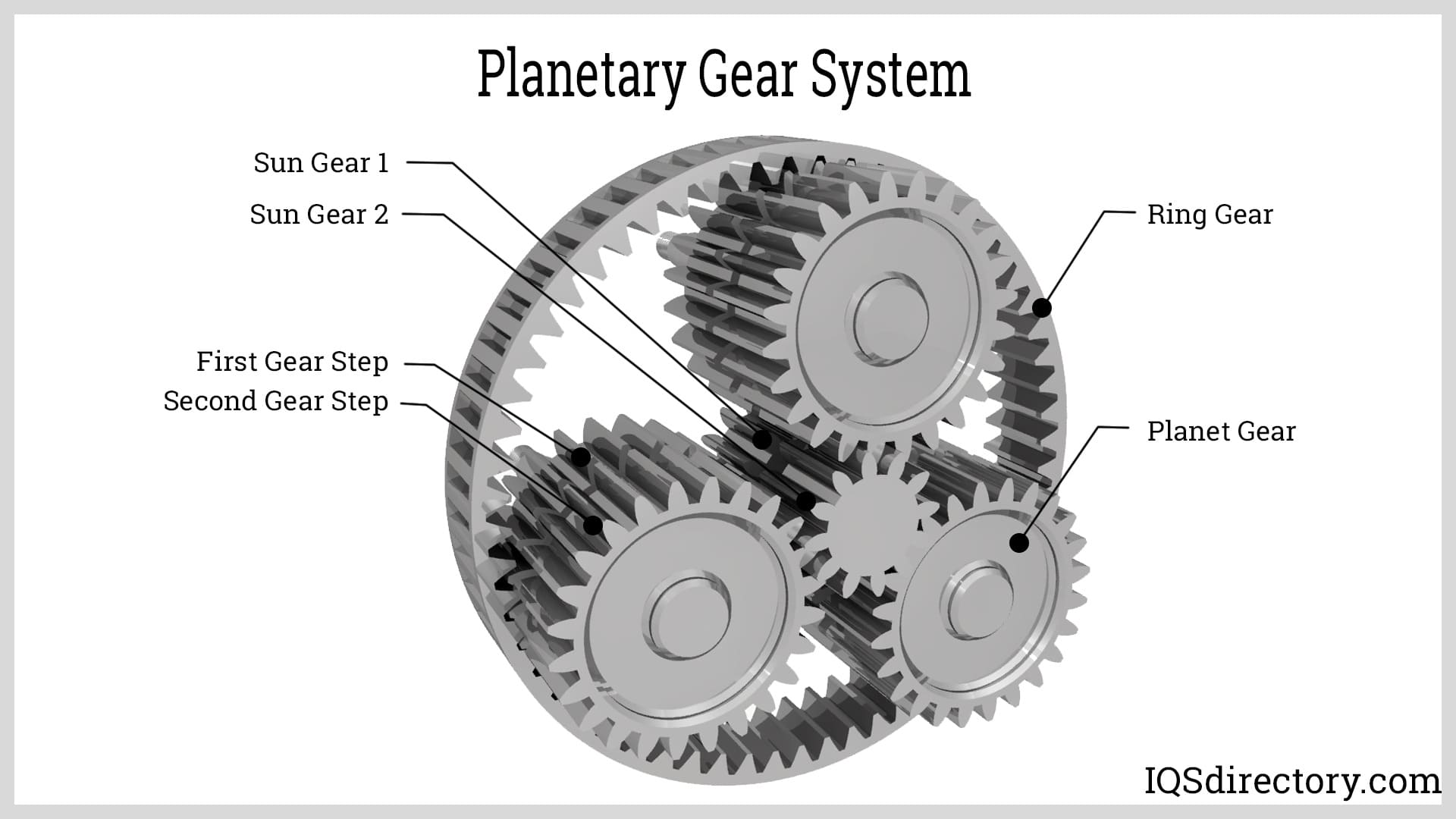
Illustrative image related to planetary wheel
Over the decades, the shift towards automation and precision engineering has further propelled the evolution of planetary wheels. As industries demand more compact and efficient solutions, manufacturers have responded by innovating designs that maximize torque output while minimizing size. Today, planetary gears are integral components in a wide array of applications, from industrial machinery to consumer electronics, showcasing their versatility and adaptability in a rapidly changing market landscape. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers to appreciate the technological advancements that have shaped the current offerings in the planetary wheel sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of planetary wheel
-
How do I choose the right planetary wheel for my application?
Choosing the right planetary wheel involves understanding your specific application requirements, such as load capacity, speed, and torque needs. Consider factors like the operational environment, including temperature and potential exposure to contaminants. Collaborating with manufacturers who offer in-house engineering support can help you tailor a solution that meets your unique needs. Additionally, prototype support allows you to test different configurations before finalizing your selection, ensuring optimal performance. -
What customization options are available for planetary wheels?
Many manufacturers provide customization options to meet specific application needs. This can include variations in gear ratio, output configurations (like shaft or flange outputs), and even the material used for durability. Inquire about the manufacturer’s ability to create prototypes or modified designs, which can be essential for applications requiring unique specifications. Ensuring you have a clear understanding of your requirements will help in discussing potential custom solutions effectively. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for planetary wheels?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers, often depending on the complexity of the product and the customization required. Some manufacturers may have flexible MOQs for standard products, while custom solutions typically require larger orders to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the sourcing process to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your purchasing strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing planetary wheels internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can differ based on supplier policies and the buyer’s creditworthiness. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments at order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. Letters of credit or escrow services may also be used for larger transactions to mitigate risks. Clarifying payment terms upfront and understanding any potential currency exchange implications is crucial to avoid surprises later in the transaction. -
How can I assess the quality assurance practices of a planetary wheel supplier?
Evaluating a supplier’s quality assurance practices involves reviewing their certifications, such as ISO standards, and inquiring about their testing protocols. Request information about their manufacturing processes, including quality checks at various production stages. Engaging with other customers for testimonials or case studies can provide insights into the supplier’s reliability. Additionally, visiting the production facility, if feasible, can give you a firsthand understanding of their commitment to quality. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing planetary wheels?
Logistics is a critical aspect of sourcing planetary wheels, particularly for international transactions. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs clearance processes specific to your region. Work closely with suppliers to understand their shipping capabilities and any potential delays. Additionally, factor in local regulations and tariffs that may impact the total cost and delivery time. A well-planned logistics strategy will help ensure timely and efficient procurement. -
Are there specific industries that commonly use planetary wheels?
Planetary wheels are utilized across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing. Their ability to provide high torque in compact designs makes them suitable for applications in heavy machinery, robotics, and renewable energy systems. Understanding the common applications within your industry can guide you in selecting the right planetary wheel and help you connect with suppliers who have expertise in your sector. -
What are the advantages of using planetary wheels over other gear types?
Planetary wheels offer several advantages, including high torque density, compact design, and efficient power transmission. They distribute loads evenly, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of the gearbox compared to traditional gear systems. Their versatility allows for significant speed reduction and increased mechanical efficiency, making them ideal for applications requiring precise control and durability. Understanding these benefits can help you justify the investment in planetary wheel technology for your operations.
Top 1 Planetary Wheel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. eBay – Planetary Gear Hub for E-Bikes
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Planetary Gear Hub products available on eBay include various types and brands, primarily for electric bikes (E-bikes). Key details include: Compatible bike types such as E-City and E-Mountain bikes, with a large selection of universal options. The number of items ranges from single units to sets of three or more. Common part types include motors and hubs, with brands like BAFANG and unbranded opt…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for planetary wheel
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial applications, the strategic sourcing of planetary wheels and gear drives presents a critical opportunity for international B2B buyers. By leveraging the unique advantages of planetary gear systems—such as compact design, high torque density, and versatile customization options—businesses can significantly enhance their operational efficiency. Companies like Auburn Gear exemplify the importance of quality manufacturing and dedicated support, ensuring that clients receive tailored solutions that meet their specific needs.
Understanding the complexities and advantages of planetary gear technology allows buyers to make informed decisions that drive productivity and reduce costs. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to embrace innovation, the demand for reliable and efficient power transmission solutions will only grow.
To capitalize on these opportunities, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with established manufacturers who offer robust post-sale support and engineering expertise. As you navigate the sourcing process, consider how strategic partnerships can not only fulfill immediate needs but also position your business for future advancements. Engage with trusted suppliers today to ensure your operations are equipped for tomorrow’s challenges in the dynamic global marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.