Choosing Your Pea Seeder: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pea seeder
Navigating the complexities of the global market for pea seeders can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With diverse agricultural practices and varying climatic conditions, sourcing the right pea seeder that meets specific operational needs is crucial. This guide aims to simplify the process by providing a comprehensive overview of the types of pea seeders available, their applications, and key considerations for supplier vetting and cost analysis.
Understanding the different functionalities of pea seeders—ranging from manual options for small-scale farms to advanced mechanized models for larger operations—will empower buyers to make informed decisions. The guide delves into essential factors such as seed spacing, depth adjustment, and hopper capacity, which directly impact planting efficiency and crop yield. Furthermore, we will address regional preferences and challenges, offering insights tailored to specific markets, such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia.
By leveraging this resource, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing pea seeders, ensuring they select equipment that enhances productivity and sustainability in their agricultural endeavors. This guide not only streamlines the decision-making process but also connects buyers with reputable suppliers, ultimately facilitating successful procurement in a competitive global landscape.
Understanding pea seeder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Garden Seeder | Interchangeable seed plates, adjustable furrow opener | Small to medium-scale farms, community gardens | Pros: Versatile, user-friendly, precise planting. Cons: Limited capacity for large-scale operations. |
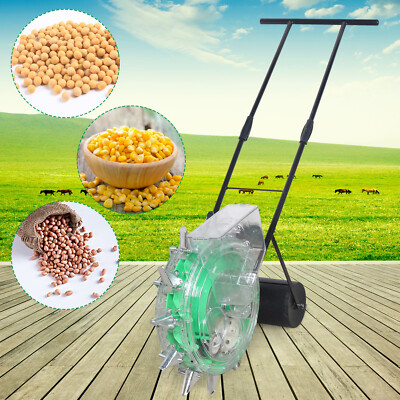
| Large Grain Seeder | High capacity, mechanical seed distribution, adjustable row spacing | Large agricultural operations, commercial farming | Pros: Efficient for bulk planting, customizable. Cons: Requires tractor for operation, higher initial investment. |
| Hand-Push Roller Seeder | Manual operation, roller design for uniform seed placement | Small farms, urban gardening, educational purposes | Pros: Affordable, no power needed, easy to use. Cons: Labor-intensive, slower compared to mechanized options. |
| Air Seeder | Pneumatic seed delivery, suitable for various seed types | Large-scale grain production, precision agriculture | Pros: High accuracy, effective for irregular seeds. Cons: Complex setup, requires maintenance. |
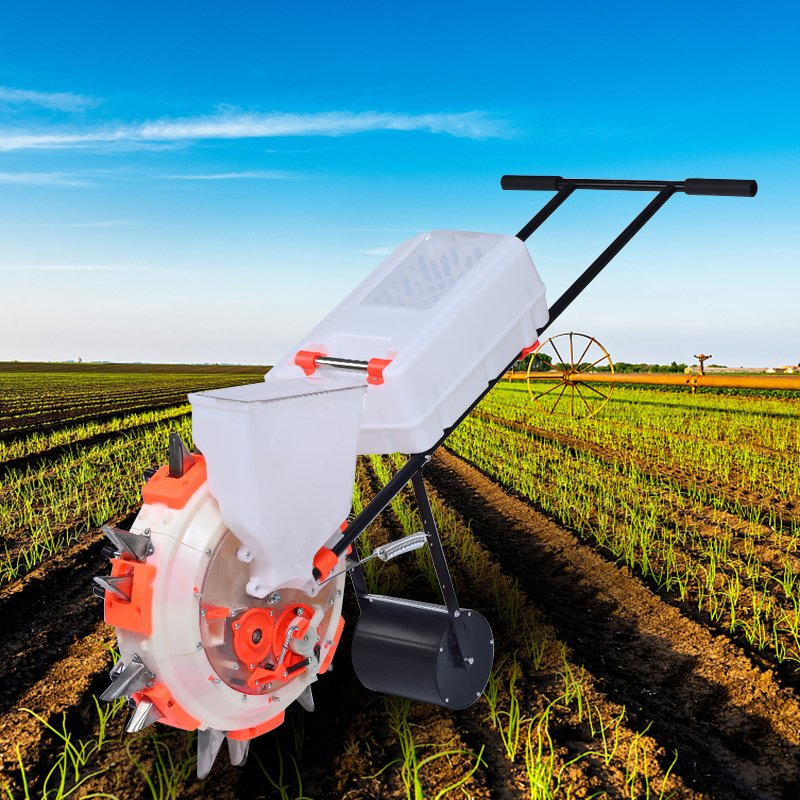
| Pea Seeder Aggregate | Multi-row capability, adjustable seeding depth and rate | Commercial pea production, mechanized farming | Pros: High efficiency for large areas, adjustable settings. Cons: Requires specific tractor compatibility, higher cost. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Precision Garden Seeders?
Precision garden seeders are designed for accuracy and ease of use, featuring interchangeable seed plates that cater to various seed sizes and types. These seeders are ideal for small to medium-scale operations, such as community gardens and urban farming projects. Buyers should consider soil preparation and the seeder’s compatibility with different crops, as its performance is optimal in well-tilled conditions.
How Do Large Grain Seeders Benefit Commercial Farming?
Large grain seeders are characterized by their high capacity and mechanical seed distribution systems, which allow for efficient planting over extensive areas. These seeders are best suited for large agricultural operations that require bulk planting of grains. When purchasing, businesses should assess the required tractor power and ensure compatibility with their existing equipment to maximize operational efficiency.
What Advantages Does a Hand-Push Roller Seeder Offer?
Hand-push roller seeders are manual devices that facilitate uniform seed placement without the need for power sources. They are particularly beneficial for small farms and educational projects, offering an affordable option for those looking to manage smaller plots. However, potential buyers should be aware that while they are easy to operate, they may require more labor and time compared to mechanized alternatives.
In What Scenarios Are Air Seeders Most Effective?
Air seeders utilize pneumatic technology to deliver seeds accurately, making them suitable for various seed types, including irregularly shaped ones. They are particularly effective in large-scale grain production and precision agriculture, where accuracy is crucial. Businesses considering air seeders should evaluate their operational complexity and maintenance needs, as these systems can be more intricate than traditional seeders.
What Makes Pea Seeder Aggregates Ideal for Commercial Production?
Pea seeder aggregates are designed with multiple rows and adjustable settings for seeding depth and rate, making them highly efficient for commercial pea production. These seeders are particularly beneficial for mechanized farming operations looking to optimize planting efficiency across large areas. When selecting a pea seeder aggregate, it is vital for buyers to confirm tractor compatibility and assess the initial investment against potential yield improvements.
Key Industrial Applications of pea seeder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pea seeder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Large-scale pea cultivation for food production | Increases planting efficiency and crop yield | Durability, capacity, and adaptability to local soil types |
| Horticulture | Small-scale gardening and community gardens | Facilitates precision planting and reduces labor costs | Ease of use, weight, and compatibility with various seeds |
| Agro-forestry | Cover cropping and soil improvement practices | Enhances soil health and reduces erosion | Seed depth adjustment, row spacing options, and reliability |
| Organic Farming | Planting organic pea varieties in diverse ecosystems | Supports sustainable farming practices and biodiversity | Compliance with organic standards and seed variability |
| Export and Import | Pea seed distribution and processing | Streamlines seed preparation and ensures quality control | Quality certifications, seed variety specifications, and logistics |
How is a pea seeder utilized in large-scale agriculture?
In large-scale agriculture, pea seeders are essential for efficient planting of peas, a staple crop in many regions. These machines allow farmers to plant seeds at precise depths and spacing, which is crucial for maximizing yield. By automating the process, they significantly reduce labor costs and time, enabling farmers to cover larger areas in shorter periods. Buyers in this sector should consider the seeder’s durability, capacity for various seed types, and adaptability to local soil conditions to ensure optimal performance.
What benefits do pea seeders offer to horticulture and community gardening?
In horticulture, particularly within community gardens, pea seeders simplify the planting process. They enable gardeners to achieve uniform seed placement, which is vital for consistent crop growth. This precision reduces seed wastage and improves overall productivity. When sourcing pea seeders for these applications, ease of use, lightweight design, and compatibility with different seed varieties are critical factors to consider, especially for novice gardeners.
How do pea seeders contribute to agro-forestry practices?
Pea seeders play a significant role in agro-forestry by facilitating the planting of cover crops that improve soil quality and prevent erosion. These practices are increasingly important as farmers seek to enhance biodiversity and soil health. The ability to adjust seeding depth and row spacing is particularly beneficial for integrating peas into existing forestry systems. Buyers in this field should prioritize seeders that offer flexibility in settings and reliability under various environmental conditions.
Why are pea seeders important for organic farming?
For organic farmers, pea seeders are vital for planting organic varieties, which require careful management to maintain compliance with organic standards. These machines help in achieving precise planting while minimizing soil disturbance, which is essential for maintaining soil health. Buyers should look for seeders that ensure seed quality and variability, as well as those that meet organic farming regulations, to support sustainable practices.
How do pea seeders streamline the export and import of pea seeds?
In the export and import sector, pea seeders are utilized to prepare seeds efficiently for distribution. By ensuring uniform planting and high germination rates, these machines help maintain the quality of seeds being processed. For businesses involved in this sector, sourcing seeders with quality certifications and specifications for different seed varieties is crucial. This ensures that they meet international standards and can effectively manage logistics in various markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pea seeder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Even Seed Spacing
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges when it comes to achieving uniform seed spacing with traditional planting methods. Inconsistent seed spacing can lead to uneven crop growth, affecting yield and quality. This issue is particularly pronounced in larger agricultural operations where precision is crucial for maximizing land use and ensuring optimal harvests. Buyers may find that manual sowing or using outdated equipment results in varied distances between seeds, leading to competition for nutrients and water among plants.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should invest in precision seeders specifically designed for peas. Models like the EarthWay Precision Garden Seeder allow users to select from various seed plates tailored to different seed sizes, ensuring optimal spacing. When sourcing a seeder, buyers should look for features such as adjustable furrow openers and row markers that facilitate consistent planting depth and spacing. Additionally, proper training for operators on how to adjust and use the equipment effectively can significantly enhance planting accuracy. Utilizing a precision seeder not only improves crop uniformity but also boosts overall productivity by reducing seed wastage.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Seed Compatibility and Size Variability
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is dealing with the variability in seed sizes and shapes, particularly when planting different pea varieties. Seeds may vary from smooth and round to wrinkled and irregular, affecting how they flow through traditional seeders. This inconsistency can lead to issues such as double seeding or skipped spots, which ultimately impacts yield and increases operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should opt for seeders that offer interchangeable seed plates, like those available with the JD1 single-row large grain seeder. This feature allows users to customize their seeder based on the specific seed type being planted. Buyers should also consider investing in seed grading equipment to separate seeds by size before planting, ensuring compatibility with their chosen seeder. When sourcing equipment, it’s crucial to consult with manufacturers to ensure that the seeder can accommodate the specific seed varieties the buyer plans to use. Additionally, conducting test runs with different seed types can help identify the best combinations for optimal planting efficiency.
Scenario 3: Inefficiencies in Labor and Time Management
The Problem: Many agricultural businesses struggle with labor-intensive planting processes that consume significant time and resources. Manual sowing methods can be physically demanding and slow, particularly for larger fields, leading to delays in planting schedules and increased labor costs. This inefficiency not only affects productivity but can also impact the timing of the harvest, further complicating operations.
The Solution: To enhance efficiency, B2B buyers should consider investing in mechanized pea seeders that allow for faster planting with less labor. Equipment such as the Aqronaft Pea Seeder Aggregate, with options for 13 or 15 rows, can dramatically reduce planting time while maintaining accuracy. When selecting a seeder, buyers should evaluate its capacity, working width, and seeding rate to ensure it meets the demands of their operations. Additionally, integrating technology such as GPS tracking for field mapping can optimize planting strategies and labor allocation. By transitioning to mechanized solutions, businesses can not only streamline their planting processes but also allocate labor more effectively, focusing on other critical aspects of farm management.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pea seeder
When selecting materials for pea seeders, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of the agricultural environment and the operational demands of the equipment. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of pea seeders, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Pea Seeders?
Steel is a widely used material in agricultural machinery, including pea seeders. Its key properties include high tensile strength, excellent durability, and resistance to deformation under load. Steel can withstand significant pressure and is often treated for corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor agricultural applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and longevity, which translates to reduced maintenance costs over time. However, it can be heavier than other materials, potentially affecting the ease of use and maneuverability of the seeder. Additionally, the cost of high-quality steel can be relatively high, impacting the overall production cost of the seeder.
Impact on Application: Steel seeders can handle a variety of soil types and conditions, making them versatile for different agricultural practices. However, they may require additional coatings or treatments to prevent rust in humid or wet environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local agricultural machinery standards. In Europe, adherence to standards such as EN 1090 for structural steel may be necessary.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Pea Seeder Design?
Aluminum is another popular material due to its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. It is often used in components where weight reduction is essential without sacrificing strength.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight property of aluminum allows for easier handling and operation, which is beneficial for smaller farms or community gardens. However, aluminum may not be as strong as steel, making it less suitable for high-stress applications. The cost of aluminum can also be higher than that of steel, depending on market conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum seeders are particularly effective in regions with high humidity or saline conditions, as they resist corrosion effectively. However, they may not perform as well in rocky or hard soil conditions compared to steel counterparts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum in their local markets and the potential need for specialized manufacturing techniques. Compliance with environmental regulations regarding lightweight materials may also be a factor in regions like Europe.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Pea Seeder Construction?
Plastic, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is increasingly used in agricultural machinery due to its resistance to chemicals and moisture. It is often utilized in seed hoppers and other components that require flexibility and impact resistance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic is its lightweight and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for seeders that are exposed to various environmental conditions. However, plastic may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as metal materials, which could limit its application in more demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Plastic components can help reduce the overall weight of the seeder, facilitating easier transport and operation. However, they may need to be replaced more frequently than metal components, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastic materials used meet international safety and quality standards, such as ASTM D638 for tensile strength. Additionally, understanding the recycling and disposal regulations for plastic in their regions is vital.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Pea Seeder Performance?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass-reinforced plastics, offer a unique combination of strength and lightweight properties. These materials are increasingly being utilized in agricultural equipment for their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Pros & Cons: Composites can provide excellent resistance to corrosion and UV degradation, making them suitable for long-term outdoor use. However, they can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which could complicate supply chains.
Impact on Application: Composite seeders can perform well in diverse conditions, offering flexibility and durability. However, they may not be as widely accepted or understood in all markets, which could pose a challenge for international buyers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of composite materials in their regions and the potential need for specialized maintenance. Compliance with international standards for composite materials, such as ISO 9001, may also be necessary.
| Material | Typical Use Case for pea seeder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, frames | High strength and durability | Heavier, potential rust issues | High |
| Aluminum | Seed hoppers, lightweight parts | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Less strong than steel | Medium |
| Plastic | Seed hoppers, flexible parts | Lightweight, moisture-resistant | May not withstand high temperatures | Low |
| Composite | Specialized components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher production costs | High |
This material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their pea seeder investments, ensuring they choose materials that align with their operational needs and local agricultural conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pea seeder
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Pea Seeder?
The manufacturing process of a pea seeder involves several key stages, each critical to producing a reliable and effective planting tool. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, typically aluminum or steel, known for their durability and resistance to corrosion. Materials are inspected for defects before being cut to size according to the specifications required for different components of the seeder.
-
Forming: In this phase, materials are shaped into parts using techniques like stamping, bending, or machining. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed to ensure precision in creating parts such as seed plates, furrow openers, and hoppers. This precision is essential for the accurate planting of seeds.
-
Assembly: The assembly stage brings together all formed components into a complete seeder. This is typically done in a controlled environment to minimize contamination and ensure quality. Workers or automated systems will install components like seed hoppers, furrow openers, and row markers, ensuring that each part functions seamlessly with others.
-
Finishing: The final stage includes processes such as powder coating or painting, which enhance the seeder’s durability and aesthetic appeal. This stage also involves the installation of any optional accessories, like fert-a-ply attachments. Quality checks are conducted to ensure that the finishing processes meet the required standards.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Pea Seeder Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a pivotal aspect of manufacturing pea seeders, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations. The QA process typically includes adherence to relevant international and industry-specific standards.
-
International Standards Compliance: Many manufacturers adhere to ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. This certification ensures that companies have established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, compliance with CE marking may be required for products sold in the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, several quality control checkpoints are established:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to ensure that processes are being followed correctly and components are within tolerance limits.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the finished product undergoes thorough testing to verify its functionality, durability, and adherence to specifications. -
Common Testing Methods: Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure quality. These may include:
– Functional Testing: Assessing the seeder’s performance under real-world conditions to ensure it plants seeds accurately.
– Durability Testing: Simulating extended use to evaluate the seeder’s longevity and resistance to wear.
– Material Testing: Analyzing the mechanical properties of materials used to ensure they can withstand operational stresses.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers looking to purchase pea seeders should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control practices. Buyers should review the supplier’s quality management systems, production capabilities, and adherence to international standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports from suppliers can help buyers understand the effectiveness of their quality control measures. These reports should detail inspection results, testing methods, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspectors can evaluate the manufacturing process, verify compliance with industry standards, and conduct random sampling of finished products.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control when sourcing pea seeders.
-
Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding the regulatory environment in different regions is crucial. For instance, certain countries may have stricter import regulations or additional certifications required for agricultural machinery. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to avoid compliance issues.
-
Local Market Preferences: Different regions may have distinct preferences regarding the design and functionality of pea seeders. For example, buyers in Africa may prioritize durability and ease of use in rugged conditions, while European buyers may focus on precision and efficiency. Understanding these preferences can influence purchasing decisions.
-
Language and Communication Barriers: Effective communication with suppliers can be challenging, particularly when dealing with international partners. B2B buyers should ensure that they have clear communication channels and possibly consider hiring local representatives who understand both the market and the suppliers.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with pea seeders is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the details of production, the significance of quality control, and the nuances of international trade, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pea seeder’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring a pea seeder, this guide offers a structured approach to ensure informed decisions that meet operational needs. Understanding the intricacies of sourcing the right equipment can significantly enhance agricultural productivity and efficiency.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your pea seeder. Consider factors such as the type of peas being planted (e.g., yellow peas vs. processing peas), desired row spacing, and planting depth. This clarity will streamline your search and help identify products that align with your agricultural goals.
Step 2: Research Supplier Credentials
Verify the credentials of potential suppliers to ensure they have a proven track record in the agricultural equipment industry. Look for certifications, quality standards (such as ISO), and testimonials from previous clients. This step is crucial as it helps mitigate risks associated with equipment failure or subpar performance.
Step 3: Evaluate Product Features
Analyze the specific features of the pea seeders you are considering. Key features to assess include:
– Seed Plate Variability: Ensure the seeder can accommodate various seed sizes and types.
– Durability and Material Quality: Select seeders made from rust-resistant materials like aluminum, which can withstand various environmental conditions.
Understanding these features will help you select a product that offers longevity and efficiency.
Step 4: Check for Customization Options
Explore whether suppliers offer customization options for their pea seeders. Custom features can include adjustable row spacing, seed hopper capacities, and specific seeding mechanisms. Customization can significantly enhance operational efficiency, especially if your farming practices require unique specifications.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Samples
If possible, request a demonstration or samples of the pea seeders you are considering. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the equipment’s functionality and ease of use in real-world conditions. Observing the seeder in action can provide insights into its efficiency and suitability for your farming practices.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Investigate the after-sales support provided by the supplier, including warranty terms and availability of spare parts. A strong support system can save time and costs in the long run, especially in regions where access to replacement parts may be limited. A comprehensive warranty indicates the supplier’s confidence in their product’s quality.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Payment Terms
Finally, compare the pricing structures and payment terms of different suppliers. Look for transparency in pricing, including any additional costs for shipping or customs duties. Negotiate terms that align with your budget while ensuring you do not compromise on quality. Consider bulk purchase discounts if applicable.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for a pea seeder, ensuring they select the right equipment to meet their agricultural needs while maximizing productivity.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pea seeder Sourcing
When sourcing pea seeders, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis breaks down the various components that contribute to the overall cost and highlights factors that can influence pricing in the global market.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Pea Seeder Manufacturing?
The cost structure for pea seeders typically includes several core components:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing pea seeders include high-quality aluminum, steel, and durable plastics. The choice of materials significantly impacts the durability and performance of the seeder, which can affect pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, while those with higher labor standards may see increased costs passed onto buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can add to initial costs. However, investing in quality tooling can lead to better production efficiency and lower costs over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that products meet international standards, which may incur additional costs. However, this is vital for maintaining product reliability and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the destination, shipping methods, and the Incoterms agreed upon. This is particularly relevant for international buyers, as these costs can significantly influence the total purchase price.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely. Understanding the typical margin for your supplier can help in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Pea Seeder Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of pea seeders:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts, as suppliers are willing to lower prices for larger orders. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better deals.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized seeders designed for specific crops or soil types may come at a premium. Buyers should assess whether the additional features justify the higher price.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can increase costs but may also provide assurance of reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, experience, and production capabilities of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and the quality of their products.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can significantly affect the final pricing. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) will dictate who bears the shipping and insurance costs, impacting the total expense for the buyer.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Pea Seeder Procurement?
Buyers can adopt several strategies to optimize their procurement process:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage information about competitors and market trends to negotiate better terms. Don’t hesitate to ask for volume discounts or explore different suppliers.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, durability, and operational efficiency. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions, which can affect pricing.
-
Evaluate Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and priority access to new products.
Conclusion
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers is essential for B2B buyers of pea seeders. By leveraging negotiation strategies, focusing on total cost of ownership, and considering the nuances of international procurement, buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their investment in agricultural equipment. Remember, prices can fluctuate based on various market conditions, so it is advisable to gather multiple quotes and conduct thorough market research before finalizing any purchase.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pea seeder With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Pea Seeders
In the agricultural sector, selecting the right seeding technology is crucial for maximizing efficiency and crop yield. While pea seeders are designed specifically for planting peas, various alternative solutions can also achieve similar planting objectives. This section explores these alternatives, comparing them based on several critical aspects to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Pea Seeder | JD1 Single Row Seeder | Precision Garden Seeder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy for row planting | Good for single-row planting | Versatile for multiple crops |
| Cost | Moderate ($148.83) | Low to moderate ($80-$150) | Moderate ($148.83) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple setup and operation | Requires some manual effort | User-friendly with clear instructions |
| Maintenance | Low (occasional cleaning) | Low (basic maintenance) | Low (durable materials) |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for larger pea fields | Suitable for small gardens | Best for varied crop types |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
JD1 Single Row Seeder
The JD1 Single Row Seeder is a manual device designed for planting seeds in single rows. It is an economical option for small-scale farmers or those with limited budgets. The primary advantage of this seeder is its simplicity and ease of use, making it accessible for farmers with less experience. However, its limitations include lower efficiency in larger fields and the need for manual effort to operate effectively, which may not be ideal for larger operations looking for speed and precision.
Precision Garden Seeder
This seeder is a versatile tool capable of planting a variety of crops, including peas. It features interchangeable seed plates, allowing users to adapt to different seed sizes and types, which enhances its usability across diverse planting scenarios. The lightweight design and straightforward assembly make it user-friendly. However, it may not provide the same level of specialized performance for peas as dedicated pea seeders, particularly in terms of planting depth and spacing accuracy.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Seeding Solution
When selecting the right seeding solution, B2B buyers should consider the specific needs of their operation, including field size, crop types, and budget constraints. A dedicated pea seeder is ideal for operations focused solely on pea production, offering precision and efficiency. In contrast, alternatives like the JD1 Single Row Seeder and Precision Garden Seeder provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness for diverse planting needs. Ultimately, understanding the operational requirements and performance metrics of each option will empower buyers to choose the best solution that aligns with their agricultural goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pea seeder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pea Seeders?
When sourcing pea seeders for agricultural operations, understanding the essential technical properties can significantly impact purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The construction material of a pea seeder, often aluminum or high-grade steel, is crucial for durability and resistance to rust. A high-quality material ensures longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements, which is especially important for buyers in harsh climates. -
Seed Hopper Capacity
– This specification refers to the volume of seeds the hopper can hold, typically measured in liters. A larger capacity allows for extended planting sessions without the need for frequent refills, making it an efficient option for large-scale operations. Buyers should assess their planting needs to select the appropriate size. -
Seeding Depth Adjustment
– The ability to adjust the seeding depth, usually within a range of 3 to 8 cm, is vital for optimizing seed germination and crop yield. Different crops may require varying depths, and an adjustable mechanism allows for flexibility, catering to diverse agricultural practices. -
Seeding Rate
– Expressed in kilograms per hectare (kg/ha), this specification indicates how many seeds can be planted in a given area. An adjustable seeding rate is beneficial for adapting to different crop types and soil conditions, ensuring optimal planting density. -
Row Spacing
– This refers to the distance between each row of seeds, which can usually be adjusted based on the crop’s growth requirements. Proper row spacing is essential for maximizing light exposure and nutrient uptake, influencing overall crop health. -
Hitch Type
– The hitch type determines how the seeder is connected to a tractor. Common types include 3-point linkage or drawbar hitches. The right hitch type ensures compatibility with existing machinery, facilitating ease of use and operational efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Pea Seeder Industry?
Understanding trade terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms used in the pea seeder industry:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Knowing if a seeder is an OEM product can assure buyers of its quality and compatibility with existing equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is particularly important for buyers planning large-scale agricultural projects, as it impacts budgeting and inventory management. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific quantities of goods or services. This is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare costs and make informed decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. -
Lead Time
– This refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is critical for planning planting schedules, particularly for time-sensitive crops. -
Warranty
– A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer that the product will meet certain performance standards for a specified period. A robust warranty can provide peace of mind to buyers, ensuring support in case of defects or malfunctions.
These technical properties and trade terms are essential for B2B buyers to navigate the purchasing landscape effectively, ensuring they select the right equipment for their agricultural needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pea seeder Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Pea Seeder Sector?
The pea seeder sector is experiencing dynamic changes driven by several global factors. Increasing agricultural productivity demands, especially in regions like Africa and South America, are pushing farmers to adopt more efficient planting methods. This demand has fostered a rise in technologically advanced seeders that incorporate precision planting capabilities. In Europe and the Middle East, the focus is shifting towards equipment that not only improves yield but also minimizes labor costs, with automated and semi-automated seeders becoming increasingly popular.
Emerging technologies, such as smart farming and IoT-enabled machinery, are also shaping the market. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring and adjustment of planting parameters, enhancing the efficiency of seed placement and depth. Additionally, international B2B buyers are now prioritizing multi-functional seeders that can handle various crops, which enhances the return on investment. The growing trend of sustainable agriculture practices is influencing sourcing decisions, with buyers showing a preference for equipment that aligns with eco-friendly farming practices.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Pea Seeder Sector?
Sustainability is a critical consideration in the pea seeder market, as environmental impacts become more pronounced. Buyers are increasingly aware of the ecological footprint associated with agricultural machinery, leading to a demand for seeders made from sustainable materials and designed for energy efficiency. Manufacturers are responding by sourcing components from ethical suppliers and utilizing recyclable materials in their products.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, particularly in a global market where transparency is paramount. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish trust with international buyers. This shift towards ethical sourcing not only helps mitigate environmental risks but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. As such, B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, thereby contributing to a more responsible agricultural sector.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Pea Seeders in the Agricultural Landscape?
The evolution of pea seeders reflects significant advancements in agricultural technology. Historically, planting was a labor-intensive process relying heavily on manual methods. Over time, the introduction of mechanical seeders revolutionized planting efficiency. In the mid-20th century, seeders began to incorporate features like adjustable seed plates and furrow openers, allowing for greater precision in seed placement.
Today, modern seeders are equipped with advanced technology that facilitates automated planting, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing overall efficiency. This evolution has not only improved yield outcomes but has also made it easier for farmers in developing regions to adopt mechanized farming practices. As the agricultural landscape continues to evolve, the pea seeder sector is poised for further innovations that will meet the needs of a growing global population while addressing sustainability concerns.
In summary, international B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies in the pea seeder market, prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing, and recognize the historical advancements that have shaped the current landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pea seeder
-
How do I solve common issues when using a pea seeder?
To address common issues such as uneven seed spacing or clogging, ensure that the seeder is properly calibrated for the specific seed type. Regular maintenance, including cleaning seed plates and adjusting the seed depth and spacing, is essential. Additionally, using high-quality, uniform seeds can help mitigate problems. If issues persist, consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or reach out to customer support for tailored solutions. -
What is the best pea seeder for small-scale farming?
For small-scale farming, a precision garden seeder with interchangeable seed plates is ideal. These seeders allow for adjustable furrow depth and spacing, ensuring optimal seed placement. Models like the EarthWay Precision Garden Seeder are praised for their user-friendly design and versatility, making them suitable for various crops, including peas. Evaluate your specific needs, such as row width and seed capacity, to find the best fit for your operation. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for pea seeders?
When vetting suppliers, assess their reputation through customer reviews and industry feedback. Verify their production capabilities, quality control processes, and compliance with international standards. Request product samples to evaluate quality firsthand and ensure they can meet your specifications. Additionally, inquire about their experience in exporting to your region and their ability to provide after-sales support and warranty services. -
Can I customize a pea seeder to suit my specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for pea seeders, allowing you to tailor features such as row spacing, seed hopper size, and planting depth. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and any unique requirements your operation may have. This ensures that the final product meets your needs while potentially enhancing efficiency and productivity in your farming practices. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for pea seeders?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may allow single-unit purchases, especially for smaller or specialized models, while others may require larger orders for bulk pricing. It’s essential to clarify MOQs during initial discussions with suppliers to determine if their terms align with your purchasing needs and budget constraints. -
What payment terms are typically offered by manufacturers of pea seeders?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, or installment payments based on production milestones. Establishing clear payment terms upfront is crucial for managing cash flow and ensuring that both parties are aligned on expectations. Always request written confirmation of agreed terms to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure the quality of the pea seeders I purchase?
To ensure quality, request detailed product specifications and certification documents from the supplier. Conduct a pre-shipment inspection to verify that the products meet your standards. Additionally, inquire about the warranty and return policy, as these can provide insights into the manufacturer’s confidence in their product quality. Building a long-term relationship with a reliable supplier can also enhance the assurance of consistent quality. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing pea seeders?
When importing pea seeders, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with logistics providers who have experience in agricultural equipment to navigate these complexities. Ensure all documentation is complete and accurate to avoid delays at customs. It’s also advisable to account for lead times in production and shipping to align with your planting schedules.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Pea Seeder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. EarthWay – Precision Garden Seeder
Domain: earthway.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Precision Garden Seeder
Part Number: 10001
Price: $148.83
Stock: 916 in stock
Key Features:
– Interchangeable seed plates for various crops
– Adjustable furrow opener for seed depth
– Made with high-quality aluminum for durability
– Lightweight construction for user-friendliness
– Optional accessories: fert-a-ply attachment and additional seed plate set (sold separately)
Warranty: On…
2. Terradonis – JD1 1-Row Large Grain Seeder
Domain: terradonis.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Product Name: JD1 1-Row Large Grain Seeder
Type: Manual Seeder
Designed For: Planting large seeds (corn, peas, cotton, etc.)
Price: 740,00 € (without disks)
Weight: 11 kg
Features:
– Lightweight and robust design
– Soft, flexible fiber brush for seed dosing
– Transparent, rust-proof hopper for easy cleaning and visibility of seed quantity
– Hopper design allows for easy removal and pouring of sur…
3. Manual Roller Corn Pea Peanut Seeder – New Vegetable Planter
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Manual Roller Corn Pea Peanut Seeder Seed Fertilizer Vegetable Planter”, “Condition”: “New”, “Price”: “US $159.73”, “Shipping”: “Free Standard Shipping”, “Location”: “La Puente, California, United States”, “Delivery Estimate”: “Between Mon, Sep 8 and Thu, Sep 11”, “Returns”: “30 days returns, Seller pays for return shipping”, “Payment Options”: [“PayPal Credit”, “Klarna”], “Featu…
4. Jang – Seeder & Snap Peas
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: jang seeder, snap peas, rollers, jang model (jp vs td)
5. New Ag Talk – Yellow Peas vs Processing Peas
Domain: talk.newagtalk.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The text discusses the differences between yellow peas and processing peas, highlighting that peas for grain are smooth and round, while processing peas are wrinkled and not round. It mentions the use of a box drill for planting yellow peas, noting that they flow more easily compared to garden peas.
6. Sutton Ag – Seed Plate for EarthWay Garden Seeder
Domain: suttonag.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
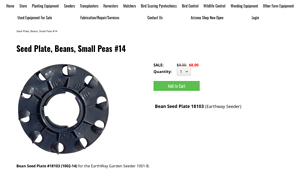
Introduction: Seed Plate, Beans, Small Peas #14; Bean Seed Plate #18103 (1002-14) for the EarthWay Garden Seeder 1001-B; 3.6″ spacing; will plant small peas size 0.450″/11.4mm; Earthway planter tips available on the Earthway Seed Plate Guide page; included with purchase of EarthWay unit and Standard Seed Plate Set; color may vary; made in USA.
7. Aqronaft – Pea Seeder Aggregate
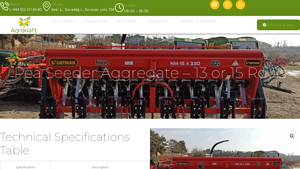
Domain: aqronaft.az
Introduction: {“Model”:”Pea Seeder Aggregate – 13/15 Row”,”Number of Rows”:”13 or 15″,”Row Spacing”:”12 – 16 cm (adjustable)”,”Working Width”:”1.6 – 2.4 meters (depending on model)”,”Seed Hopper Capacity”:”200 – 300 liters”,”Seeding Rate”:”60 – 200 kg/ha (adjustable)”,”Seeding Depth”:”3 – 8 cm (adjustable)”,”Seeding Mechanism”:”Mechanical seed distributor”,”Seeding Accuracy”:”±5%”,”Hitch Type”:”3-point linkage”…
8. Manitoba Pulse – AAC Carver Yellow Pea Seed
Domain: manitobapulse.ca
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
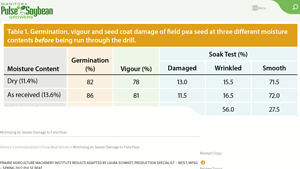
Introduction: The study focused on minimizing air seeder damage to field peas, specifically using AAC Carver yellow pea seed. The seeding rate was 222.7 lbs/ac (3.7 bu/ac), targeting approximately 7.4–8.4 live plants/ft2 (or 3.5–3.8 bu/ac). The fertilizer used was MES15 at a rate of 20 lbs P205/ac, resulting in 59.7 lbs/ac of product (or 19.8 lbs/ac of P205). The air drill used was a 65-ft, 2010 Bourgault Paral…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pea seeder
As international markets continue to evolve, the strategic sourcing of pea seeders emerges as a pivotal element for agricultural efficiency and productivity. By investing in high-quality, precision-engineered seeders, buyers can significantly enhance their planting accuracy and reduce labor costs. The variety of options available—from manual models suitable for small farms to larger aggregates designed for extensive operations—provides flexibility to meet diverse agricultural needs across different regions.
Key considerations for B2B buyers include evaluating the seeder’s durability, ease of use, and adaptability to local soil conditions and crop types. This ensures that operations can be optimized, leading to better yield outcomes. Moreover, fostering relationships with reputable suppliers can offer additional benefits such as warranty support and access to specialized accessories, enhancing the overall value proposition.
Looking ahead, the demand for efficient agricultural solutions will only grow, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing strategic sourcing of pea seeders today, businesses can position themselves for success in tomorrow’s competitive market. Engage with trusted suppliers to explore the best options for your agricultural needs, and invest in the tools that will drive your productivity forward.