Choosing Your Parts Of A Lock: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts of a lock
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right parts of a lock can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With varying security standards, compliance regulations, and technological advancements across regions, it is essential to understand the diverse components that make up a locking mechanism. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental parts of a lock, including cylinders, bolts, latches, and strike plates, and their specific applications in various markets.
By exploring the types of locks available, the intricacies of their functions, and the best practices for supplier vetting, this resource equips buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—understanding these components is crucial for ensuring the security of your operations and assets.
Moreover, this guide addresses critical factors such as cost considerations, quality assurance, and installation tips, providing a holistic view that empowers businesses to optimize their procurement strategies. With the right insights, you can confidently navigate the global market for lock parts, ensuring that your investments not only meet but exceed security expectations.
Understanding parts of a lock Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deadbolt | High security, requires a key for locking/unlocking | Commercial buildings, warehouses | Pros: Superior security; Cons: Requires drilling for installation. |
| Cylinder Lock | Key inserted into a cylinder; various key types available | Residential and commercial properties | Pros: Versatile; easy to rekey; Cons: Vulnerable to picking if not high-security. |
| Padlock | Portable, can be used with various hasps and chains | Temporary security, outdoor use | Pros: Flexible usage; Cons: Limited security for high-risk areas. |
| Smart Lock | Keyless entry, integrates with smart home systems | Modern offices, tech-savvy homes | Pros: Convenience and remote access; Cons: Dependent on power/internet. |
| Mortise Lock | Complex mechanism, installed inside the door | High-end residential and commercial | Pros: Robust security; Cons: More expensive and complex to install. |
What Are the Characteristics of Deadbolt Locks?
Deadbolt locks are renowned for their enhanced security features, making them a popular choice for B2B applications, especially in commercial buildings and warehouses. They typically require a key for locking and unlocking, providing a higher level of resistance against forced entry. When purchasing deadbolts, buyers should consider the grade of the lock, as higher grades offer better durability and security. Additionally, installation may require drilling, which could necessitate professional assistance, impacting overall costs.
How Do Cylinder Locks Differ in Functionality?
Cylinder locks are versatile locking mechanisms commonly used in both residential and commercial properties. They operate by inserting a key into a cylinder, which can be easily rekeyed when needed, making them a cost-effective choice for property managers. Buyers should evaluate the security features of the cylinder lock, including pin configurations and whether it meets industry standards for resistance against picking and bumping. While they offer flexibility, lower-quality cylinder locks may compromise security, so opting for high-security models is advisable.
Why Choose Padlocks for Temporary Security Solutions?
Padlocks are portable locking devices that can be used with various hasps and chains, making them ideal for temporary security applications, such as securing gates, lockers, or storage units. They are particularly useful in outdoor settings where flexibility is paramount. When selecting padlocks, B2B buyers should consider the material (steel, brass, or plastic) and the type of locking mechanism (keyed or combination) to ensure they meet specific security needs. However, it’s important to note that padlocks may not provide sufficient security in high-risk environments.
What Are the Advantages of Smart Locks in Modern Security?
Smart locks represent the cutting edge of locking technology, offering keyless entry and integration with smart home systems. They are increasingly being adopted in modern offices and tech-savvy homes for their convenience and ability to provide remote access. When considering smart locks, businesses should assess compatibility with existing systems, battery life, and the level of encryption used to protect against cyber threats. Although they enhance convenience, smart locks may pose risks if not properly secured, particularly in terms of power dependency and potential hacking.
What Makes Mortise Locks a Premium Choice?
Mortise locks are characterized by their complex internal mechanisms, which are installed within the door itself, providing a robust security solution. They are commonly used in high-end residential and commercial settings where aesthetics and security are paramount. Buyers should be aware that mortise locks typically require professional installation, which can increase initial costs. However, their durability and resistance to tampering make them a worthwhile investment for businesses looking for a long-term security solution.
Key Industrial Applications of parts of a lock
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of parts of a lock | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitality | Locking mechanisms in hotel room doors | Enhances guest security and privacy, improving customer satisfaction | Durability, ease of installation, compatibility with existing systems |
| Residential Security | Home lock systems including deadbolts and smart locks | Provides enhanced security for homeowners, reducing theft risks | Security ratings, certification standards, local regulations |
| Commercial Facilities | Access control systems for office buildings | Manages employee access, ensuring safety and security | Scalability, integration with existing security systems |
| Retail | Point-of-sale security locks and display case locks | Protects inventory and reduces loss from theft | Key management systems, tamper-resistant features, cost-effectiveness |
| Industrial | Locking systems for warehouses and storage facilities | Secures valuable assets and restricts unauthorized access | Heavy-duty materials, weather resistance, compliance with safety standards |
How are ‘parts of a lock’ utilized in the hospitality industry?
In the hospitality sector, parts of a lock, such as cylinders, deadbolts, and electronic access systems, play a crucial role in ensuring guest security. Hotels use advanced locking mechanisms to provide guests with privacy and peace of mind. The ability to upgrade to smart locks also allows for mobile access options, enhancing guest convenience. International buyers should consider durability and compatibility with existing systems, particularly in regions with varying climate conditions.
What is the significance of ‘parts of a lock’ in residential security?
For residential applications, parts of a lock are essential in providing security against break-ins. Deadbolts, latch mechanisms, and strike plates work together to secure entry points effectively. Homeowners are increasingly seeking locks that offer higher security ratings and certifications to deter theft. Buyers from diverse regions must ensure compliance with local regulations and consider the environmental factors that may affect the longevity of locking systems.
How do ‘parts of a lock’ enhance security in commercial facilities?
In commercial facilities, access control systems utilizing parts of a lock help manage employee access to sensitive areas. Components like electronic locks and key card systems ensure that only authorized personnel can enter restricted zones, significantly enhancing workplace safety. Businesses should focus on sourcing scalable solutions that can integrate seamlessly with existing security infrastructure, especially in regions where security concerns are paramount.
Why are ‘parts of a lock’ vital in the retail industry?
Retail environments rely on parts of a lock, such as point-of-sale locks and display case locks, to safeguard inventory from theft. The implementation of tamper-resistant features and robust locking systems not only protects assets but also fosters customer trust. Retailers must prioritize key management systems that are cost-effective while ensuring reliability, particularly in high-traffic areas where security risks are elevated.
How do ‘parts of a lock’ contribute to industrial security?
In industrial settings, parts of a lock are critical for securing warehouses and storage facilities. Heavy-duty locks and weather-resistant materials help protect valuable assets and limit unauthorized access. Buyers in this sector should consider compliance with safety standards and the durability of locking systems to withstand harsh environments, ensuring that their operations remain secure and efficient.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts of a lock’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Lock Performance in High-Traffic Areas
The Problem: B2B buyers managing facilities such as schools, hospitals, or commercial buildings often face the challenge of inconsistent lock performance in high-traffic areas. Frequent use can lead to wear and tear on components like latches, cylinders, and strike plates. This not only compromises security but can also cause inconvenience and frustration for staff and visitors when doors jam or fail to lock properly.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, buyers should invest in high-quality, heavy-duty lock components specifically designed for high-traffic environments. Selecting locks with reinforced strike plates and heavy-duty latches can significantly enhance durability. Regular maintenance schedules should be established, including lubrication of moving parts and periodic inspections to identify wear before it leads to failure. Additionally, sourcing parts from reputable manufacturers who provide warranties and support will ensure that replacement components meet the required standards for security and longevity.
Scenario 2: Complexity in Lock Specifications for International Projects
The Problem: When dealing with international projects, particularly in diverse regions like Africa and South America, B2B buyers often struggle with the complexities of lock specifications. Variations in lock standards, security regulations, and local installation practices can lead to confusion and errors in procurement. This can result in delays, increased costs, and compliance issues, especially when locks need to meet both local and international security standards.
The Solution: To streamline the procurement process, buyers should engage with experienced local distributors who understand both international and regional standards. Conducting thorough research on lock specifications and compliance requirements in the target market is crucial. Buyers can also develop a detailed checklist of required features, such as materials, security ratings, and installation methods, to ensure that all parts are compatible with local building codes. Collaborating with architects and security consultants familiar with the local market can provide invaluable insights and help prevent costly mistakes.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Finding Replacement Parts for Older Lock Systems
The Problem: Many businesses and institutions have older lock systems that use outdated or discontinued parts, creating significant challenges when replacements are needed. B2B buyers may encounter difficulties sourcing these parts, leading to prolonged downtimes and security vulnerabilities. The scarcity of compatible components can also result in the need for costly lock replacements rather than simple repairs.
The Solution: Buyers should proactively maintain an inventory of essential parts for older systems and establish relationships with manufacturers or specialty suppliers who can provide these components. Investing in universal or modular lock systems that allow for easy upgrades or replacements can also future-proof investments. Additionally, working with locksmiths who specialize in older systems can provide solutions for retrofitting or adapting new components to fit existing locks, thereby preserving functionality while enhancing security.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts of a lock
What Materials Are Commonly Used for Parts of a Lock?
When selecting materials for lock components, it is essential to consider their properties, performance, and suitability for specific applications. The following analysis covers four common materials used in the manufacturing of lock parts: brass, stainless steel, zinc alloy, and plastic. Each material presents unique advantages and challenges that can significantly impact product performance and market acceptance.
How Does Brass Perform in Lock Manufacturing?
Brass is a traditional material widely used in lock manufacturing, particularly for cylinders and internal mechanisms. Its key properties include excellent corrosion resistance and good machinability, making it suitable for intricate designs. Brass maintains strength and durability under various environmental conditions, which is crucial for locks exposed to outdoor elements.
Pros and Cons:
Brass is known for its durability and aesthetic appeal, often featuring a polished finish that enhances the lock’s appearance. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may not be as strong as stainless steel, particularly in high-security applications.
Impact on Application:
Brass is compatible with various media, including moisture and humidity, but it may tarnish over time if not properly maintained. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM B453 is vital to ensure quality.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Lock Parts?
Stainless steel is another popular choice for lock components, particularly for high-security applications. It offers superior strength and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for locks exposed to harsh environments, such as coastal areas.
Pros and Cons:
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to wear and tear. However, it can be more challenging to machine compared to brass, potentially increasing manufacturing complexity and costs. Additionally, the initial investment may be higher, but its longevity can justify the expense.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel locks are suitable for various applications, including commercial and industrial settings. International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM A240 for stainless steel to ensure product quality and reliability.
How Does Zinc Alloy Compare as a Material for Locks?
Zinc alloy is frequently used for less critical lock components, such as housings and decorative elements. It is lightweight and cost-effective, making it an attractive option for mass production.
Pros and Cons:
Zinc alloy provides good corrosion resistance and is easy to cast, allowing for intricate designs. However, it is less durable than brass or stainless steel, making it unsuitable for high-security applications. Its lower strength can lead to quicker wear and potential failure under stress.
Impact on Application:
Zinc alloy is often used in residential locks and is compatible with various environments. Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as JIS H 8601 for zinc alloys to maintain quality assurance.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Lock Component Manufacturing?
Plastic is increasingly being used in lock manufacturing, particularly for internal components and housings. It is lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be produced at a lower cost compared to metals.
Pros and Cons:
The main advantage of plastic is its affordability and versatility in design. However, plastic components may not offer the same level of security and durability as metal counterparts, making them less suitable for high-security applications.
Impact on Application:
Plastic locks are often used in low-security applications, such as interior doors. International buyers should consider the quality of plastic materials used, ensuring they meet standards like ISO 9001 for manufacturing processes.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Lock Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts of a lock | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Cylinders, internal mechanisms | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to others | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | High-security locks | Superior strength and durability | More challenging to machine | High |
| Zinc Alloy | Housings, decorative elements | Cost-effective and lightweight | Less durable than metals | Low |
| Plastic | Internal components, housings | Affordable and versatile | Lower security and durability | Low |
This strategic material selection guide aims to help international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on the unique properties and applications of various materials used in lock manufacturing.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts of a lock
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Lock Parts?
Manufacturing lock parts involves a systematic approach that ensures the quality and reliability of each component. The process can be broken down into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage incorporates specific techniques that contribute to the durability and functionality of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for Lock Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing lock parts is material preparation. Typically, manufacturers use high-quality metals such as brass, stainless steel, or zinc alloy, selected for their strength and resistance to corrosion. The raw materials undergo stringent quality checks to ensure they meet the required specifications.
Once the materials are approved, they are cut to size using techniques like laser cutting or shearing. This precision ensures that each part can be accurately formed during the next phase. Additionally, surface treatments such as cleaning and degreasing are performed to remove impurities that could affect subsequent processes.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
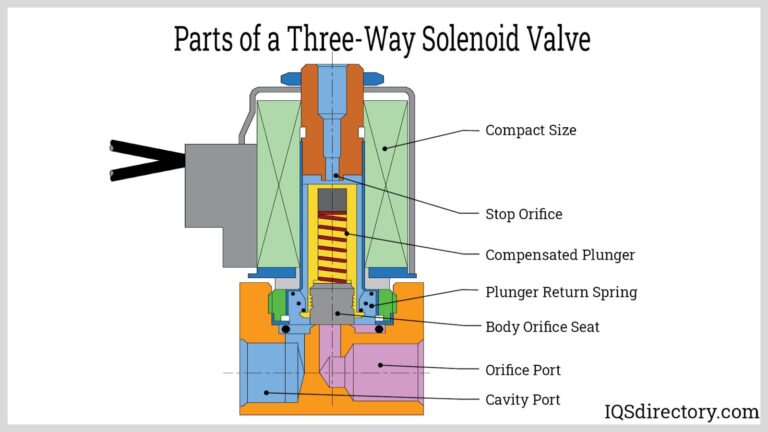
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into specific components, such as cylinders, bolts, and latches. Common techniques include:
-
Die Casting: This is particularly useful for creating complex shapes with high precision. Liquid metal is poured into a mold, and once cooled, it takes on the desired form.
-
Machining: For parts that require a high level of accuracy, machining techniques like milling and turning are employed. These processes remove material to create specific dimensions and tolerances.
-
Stamping: This technique involves pressing a die against the material to create flat parts. It is commonly used for producing components like strike plates and faceplates.
Each forming technique must adhere to strict tolerances to ensure that the parts fit together seamlessly during assembly.
How Are Lock Parts Assembled?
Assembly is a critical stage where various components are brought together to create a functional lock. This process can be manual or automated, depending on the complexity of the lock and production volume. Key steps in the assembly process include:
-
Component Alignment: Each part, such as the cylinder, pins, and springs, must be precisely aligned to ensure proper functionality.
-
Fastening: Components are secured using screws or other fastening methods. The choice of fastening technique can impact the lock’s overall strength and durability.
-
Testing for Functionality: Before moving to the finishing stage, assembled locks undergo initial functionality tests to confirm they operate smoothly and meet design specifications.
What Are the Finishing Processes in Lock Manufacturing?
The finishing stage adds the final touches to lock parts, enhancing their appearance and durability. Common finishing processes include:
-
Surface Treatment: Techniques such as plating, anodizing, or powder coating are applied to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
-
Quality Inspection: Each finished component undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure it meets all specifications. This inspection can include visual checks and dimensional measurements.
-
Packaging: Once approved, the parts are carefully packaged to prevent damage during transportation.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Standard in Lock Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that each lock part meets international standards and customer expectations. Key quality assurance measures include:
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE for European markets and API for oil and gas applications may be relevant. These certifications indicate compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
What Are Common Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process to ensure quality consistency. Typical checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing checks ensure that each stage adheres to quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection verifies that the finished products meet all specifications and performance criteria.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control measures:
-
Conduct Audits: Requesting a quality audit can provide insights into the supplier’s processes and adherence to standards.
-
Review Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control procedures and results from inspections.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Independent inspections can validate the supplier’s claims regarding their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Buyers should consider:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding product safety and quality. Familiarity with local laws can prevent compliance issues.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can enhance communication and expectations regarding quality.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Quality assurance does not end at the factory. Ensuring that products remain compliant during shipping and handling is vital.
By being informed about the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make educated decisions when sourcing lock parts, ensuring they receive reliable and high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts of a lock’
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring parts of a lock effectively, this practical sourcing guide provides a clear and actionable checklist. Understanding the components and the procurement process can significantly enhance security solutions and ensure that you receive high-quality products tailored to your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications is critical to ensure that the lock parts meet your security requirements. Consider the type of lock you need (e.g., deadbolts, latches, cylinders) and the intended application (residential, commercial, industrial). Include dimensions, materials, and any specific security features such as anti-picking or weather resistance.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Standards
Staying informed about market trends and industry standards can help you make educated decisions. Investigate the latest advancements in lock technology, such as smart locks or biometric systems, which may offer enhanced security features. Additionally, familiarize yourself with regional regulations and compliance standards that affect lock components in your target market.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations to ensure reliability and quality. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to gauge their expertise in the lock industry. It’s also beneficial to seek references from other businesses in your region to understand their experiences.
- Check for certifications: Ensure that suppliers comply with relevant quality standards, such as ISO certifications, which indicate a commitment to quality management.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Obtaining samples of the lock parts you intend to purchase is essential for assessing quality and compatibility. Evaluate the samples for durability, finish, and functionality to ensure they meet your expectations. Additionally, request detailed specifications and installation guides to prepare for potential integration challenges.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have selected potential suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms. Discuss pricing structures, bulk order discounts, payment terms, and shipping options. Ensure clarity on lead times and return policies, as these factors can impact your procurement process significantly.
Step 6: Verify Post-Purchase Support and Warranty
Assess the supplier’s commitment to post-purchase support and warranty terms before finalizing your order. A reliable supplier should offer robust customer service, including technical assistance and warranty coverage for their products. This support can be invaluable in case of installation issues or product defects.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Distribution
Finally, consider the logistics of transporting and distributing the lock parts. Evaluate the shipping options available, including freight forwarding and customs clearance, to ensure timely delivery to your location. Create a distribution plan that accounts for storage and inventory management to streamline your operations.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for lock parts with confidence, ensuring they secure quality products that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts of a lock Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Lock Parts?
When sourcing parts for locks, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used directly influences the cost. Common materials for lock components include steel, brass, and zinc alloys. Higher-quality materials may incur additional costs but can enhance durability and security.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly depending on the region and the complexity of manufacturing. Skilled labor for precision machining and assembly can raise overall expenses, particularly in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operation, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs, impacting the final price of the lock components.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom parts can be substantial. These costs cover the design and creation of molds and fixtures necessary for production. Understanding the tooling requirements early can help in budgeting accurately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures that components meet specifications and standards. This may increase costs, but it is vital for maintaining product integrity and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their operational costs and risks. Understanding the average margin in the industry can help buyers gauge the fairness of supplier pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Lock Part Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of lock parts, particularly for international B2B transactions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing capabilities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specific specifications may increase costs. Buyers must balance the need for customization with budget constraints, as bespoke components often entail higher tooling and production expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Components that meet international quality standards or certifications (e.g., ISO) may command higher prices but can provide assurance of reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The choice of supplier can significantly impact pricing. Local suppliers might offer lower logistics costs, while established international suppliers may provide better quality assurance and support.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affect cost responsibilities between buyer and seller, influencing overall pricing. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing logistics and customs duties effectively.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Lock Parts Procurement?
B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing lock parts:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure favorable terms. Discussing volume discounts, payment terms, and shipping costs can lead to significant savings.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and replacement costs over the product’s lifecycle. This approach can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local market conditions that may affect pricing. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some of these risks.
-
Conduct Market Research: Regularly assess market trends and competitor pricing to stay informed. This knowledge can empower buyers to make competitive offers and choose the right time to purchase.
-
Build Strong Supplier Relationships: Long-term partnerships with suppliers can yield benefits such as better pricing, priority service, and access to exclusive products.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers in the lock parts market is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on these elements, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategy while ensuring cost-efficiency. Always remember to verify pricing with suppliers, considering the unique needs of your market and business.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts of a lock With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Traditional Lock Parts
In the realm of security solutions, understanding the various components of traditional locks is essential. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can provide similar, if not enhanced, security benefits. This analysis will compare the classic ‘parts of a lock’ with two viable alternatives: smart locks and biometric systems. Each alternative offers unique features that cater to different security needs, particularly for B2B buyers looking to enhance their security infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parts Of A Lock | Smart Lock | Biometric Lock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Reliable mechanical security | High-tech, often integrates with smart home systems | Offers high security through unique identifiers |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Generally higher upfront cost with potential long-term savings | Higher initial cost, maintenance may vary |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation for most types | Requires Wi-Fi or Bluetooth setup, may need professional installation | Complex installation requiring calibration and programming |
| Maintenance | Low, but requires periodic checks | Moderate, relies on battery and software updates | Moderate to high, depends on system durability and usage |
| Best Use Case | Traditional security needs, residential and commercial | Modern, tech-savvy environments, integrated systems | High-security areas requiring strict access control |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Smart Locks
Smart locks are innovative devices that allow users to lock and unlock doors via smartphone apps, keypads, or voice commands. One of the significant advantages of smart locks is their integration with home automation systems, which can enhance overall security. However, they do come with a higher initial cost, and their reliance on batteries and Wi-Fi can present maintenance challenges. Smart locks are ideal for tech-savvy businesses or residential properties looking to modernize their security systems.
Biometric Locks
Biometric locks provide a cutting-edge security solution by using unique physical characteristics, such as fingerprints or retina patterns, to grant access. This technology offers superior security as it eliminates the risks associated with lost keys or forgotten codes. However, biometric systems tend to have a higher upfront cost and may require more maintenance due to potential wear and tear on scanning devices. These locks are best suited for high-security environments, such as data centers or sensitive areas within organizations where access control is critical.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Security Solution
When selecting a security solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific security needs, budget, and the operational environment. While traditional lock parts provide reliable security, alternatives like smart and biometric locks can offer enhanced features that may better suit modern business requirements. Evaluating the performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their unique security challenges. Ultimately, the right choice will align with the organization’s security goals while ensuring ease of use and effective protection.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts of a lock
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Lock Components?
When sourcing parts for locks, international B2B buyers must understand several critical technical properties that influence performance, durability, and security. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The material used in lock components significantly affects their strength and resistance to wear. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and zinc alloy. Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Brass, while less durable, offers aesthetic appeal and is often used in residential locks. Understanding material grades helps buyers select products that meet specific environmental conditions and security needs. -
Tolerance Levels
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In lock manufacturing, precise tolerances are crucial for ensuring that components fit together correctly, which directly impacts the lock’s functionality and security. A tolerance that is too loose can lead to vulnerabilities, while excessive tightness may cause operational issues. Buyers should look for suppliers who adhere to strict tolerance specifications to ensure product reliability. -
Finish Specifications
– The finish on lock components can enhance aesthetics and provide additional protection against corrosion and wear. Common finishes include polished, satin, and powder-coated options. A quality finish is particularly important for locks exposed to harsh environments, as it can prolong the lifespan of the product. Buyers should inquire about finish specifications to ensure they align with their application requirements. -
Strength Ratings
– Many lock components come with strength ratings, which indicate their ability to withstand force or manipulation. These ratings often follow industry standards such as ANSI/BHMA grading. For instance, Grade 1 locks are designed for high-security applications and can endure significant physical attacks. Understanding strength ratings helps buyers choose locks that provide the necessary security level for their intended use. -
Lifecycle Testing
– Lifecycle testing evaluates how long a lock can function effectively under repeated use. This includes testing for wear and tear on components like the cylinder, latch, and bolt. A lock with a high lifecycle rating indicates a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs, which is crucial for B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Lock Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for B2B buyers to navigate purchasing processes effectively. Here are several common terms used in the lock industry:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the lock industry, buyers often seek OEM parts to ensure compatibility and quality assurance. Knowing OEM specifications can help buyers maintain brand integrity and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage inventory and costs effectively. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production efficiencies, so negotiating favorable terms can lead to better pricing and reduced lead times. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and details about specific products. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers and make informed decisions. A well-structured RFQ can streamline negotiations and improve overall purchasing efficiency. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, minimizing misunderstandings. For B2B buyers, understanding Incoterms is vital for managing logistics and ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the lock industry, lead times can vary significantly based on manufacturing processes and supply chain logistics. Buyers should always inquire about lead times to effectively plan their projects and avoid disruptions.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right lock components that meet their specific security needs while navigating the procurement process efficiently.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts of a lock Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Influencing the Parts of a Lock Sector?
The global market for lock components is experiencing significant shifts driven by technological advancements, rising security concerns, and evolving consumer preferences. Key trends include the increasing demand for smart locking systems, which integrate IoT technology, allowing for remote access and enhanced security features. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers that can provide innovative solutions, including keyless entry systems and biometric locks.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on security in commercial and residential spaces is propelling the demand for robust locking mechanisms. Countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in infrastructure, leading to a surge in construction projects that require advanced lock components. This trend is also supported by the expansion of e-commerce platforms that facilitate the sourcing of lock parts, allowing international buyers to access a broader range of products. Additionally, customization is becoming a significant factor, as buyers look for tailored solutions that meet specific security needs and aesthetic preferences.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Trends for Lock Components?
Sustainability is increasingly at the forefront of B2B sourcing strategies in the lock parts industry. Buyers are becoming more conscientious about the environmental impact of their procurement choices, leading to a shift towards eco-friendly materials and processes. The demand for sustainable sourcing practices is particularly pronounced in markets across Europe, where regulations and consumer expectations are driving manufacturers to adopt ‘green’ certifications and materials.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, as businesses strive to ensure transparency and responsibility within their supply chains. This includes scrutinizing the origins of raw materials, such as metals used in lock components, to mitigate the environmental footprint. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled materials are becoming critical factors in the decision-making process for international buyers. By aligning with suppliers committed to sustainability, companies can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for responsible practices.
What Historical Developments Have Shaped the Lock Parts Industry?
The evolution of lock components can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where basic mechanisms were designed to secure valuable possessions. Over the centuries, advancements in metallurgy and engineering have led to more sophisticated locking systems. The 19th century marked a pivotal point with the invention of the pin tumbler lock, which remains a standard in modern locking mechanisms.
In recent decades, the industry has witnessed a rapid transformation driven by technological innovation. The introduction of electronic locks and smart technology has revolutionized the way locks function, providing enhanced security features and convenience. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as understanding these developments can inform their sourcing decisions and highlight the importance of choosing suppliers who are at the forefront of innovation.
Conclusion
Navigating the market dynamics of lock parts requires a keen awareness of current trends, sustainability practices, and historical developments. For international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets, aligning with suppliers who understand these factors is essential for securing reliable, innovative, and ethically sourced products. By prioritizing technology, sustainability, and historical context, businesses can make informed decisions that bolster their competitive edge in the evolving landscape of the lock parts industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts of a lock
-
How do I solve issues with faulty lock parts during installation?
To address issues with faulty lock parts during installation, first, double-check that all components are compatible and properly aligned. Inspect each part for damage or defects, as even minor issues can hinder functionality. If the problem persists, consult the manufacturer’s installation guide for troubleshooting tips. Additionally, consider reaching out to your supplier for replacement parts or technical assistance, especially if you are operating on a strict timeline. Ensuring quality control before installation can also prevent future issues. -
What is the best lock part for enhancing security in commercial settings?
For commercial settings, deadbolts are often regarded as the best choice for enhancing security due to their robust locking mechanism that provides superior resistance against forced entry. Additionally, consider high-security cylinders that offer advanced features like restricted keyways or pick-resistant pins. When selecting lock parts, evaluate the specific security needs of your facility, such as foot traffic and access control, to ensure you choose components that align with your overall security strategy. -
What customization options are available for lock parts in B2B orders?
Many suppliers offer customization options for lock parts, including tailored dimensions, finishes, and keying systems to meet specific client needs. Depending on your supplier, you can request features such as branding on lock bodies, unique key profiles, or specific color finishes that match your corporate identity. It’s essential to discuss your customization requirements upfront and confirm any additional costs or lead times associated with these modifications to ensure seamless integration into your projects. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lock parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for lock parts can vary significantly between suppliers. Typically, MOQs may range from 100 to 1,000 units depending on the type of lock part and the supplier’s production capacity. It’s advisable to communicate your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your business model, especially if you are a smaller enterprise or looking to test a new product line. Some suppliers may also offer flexibility for first-time orders or bulk purchases. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing lock parts internationally?
When sourcing lock parts internationally, payment terms can differ widely based on supplier policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include net 30, 50% upfront with the balance on delivery, or letter of credit arrangements for larger orders. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, credit cards, or trade financing options. Establishing favorable payment terms can enhance your cash flow and build trust with suppliers, so be prepared to negotiate. -
How can I effectively vet suppliers of lock parts?
To vet suppliers of lock parts effectively, begin by researching their industry reputation, customer reviews, and certifications. Request samples to evaluate product quality and ask for references from other B2B clients. Additionally, consider their production capabilities, lead times, and compliance with international standards, especially for regions like Africa and South America, where regulations may vary. Building relationships through site visits or meetings can also provide insight into their operations and reliability. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from lock part suppliers?
Quality assurance measures from lock part suppliers should include thorough inspections at various production stages, adherence to international quality standards (such as ISO certifications), and detailed documentation of testing procedures. Suppliers should be able to provide test reports for durability, security, and performance, ensuring their products meet your specifications. Establishing clear quality expectations upfront and discussing potential penalties for non-compliance can safeguard your interests and enhance product reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing lock parts internationally?
When sourcing lock parts internationally, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose a shipping method that balances cost with speed, such as air freight for urgent needs or sea freight for larger orders. Be aware of import duties and taxes in your country, as these can affect overall costs. Collaborating with a reliable logistics partner who understands the intricacies of international shipping can streamline the process and minimize delays.
Top 7 Parts Of A Lock Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Locksmiths.co.uk – Master Locksmith Services
Domain: locksmiths.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Master Locksmiths Association, Emergency Locksmith (24 Hour), Key Cutting, Lock Replacement, Change & Fitting, Locked Out Of House, Lost House Keys, Door & Window Lock Repair, Burglar Alarm Installation, Auto Car Locksmith, Car Key Cutting, Safe Opening & Repairs, Safe Removal & Disposal, Security Safe Installation, Commercial Locksmith Services, Locksmith Training Courses, MLA Qualification – Lev…
2. Mul-T-Lock – Deadbolt Parts
Domain: mul-t-lock-online.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: {“Deadbolt Parts”: [{“name”: “Bolt hub”, “part_number”: “1”}, {“name”: “Bolt actuator”, “part_number”: “2”}, {“name”: “Bolt extension”, “part_number”: “4”}, {“name”: “Bolt sleeve”, “part_number”: “5”}, {“name”: “Ball bearing anti-drill (6mm)”, “part_number”: “6”}, {“name”: “Protection shield”, “part_number”: “7”}, {“name”: “Tailpiece”, “part_number”: “8”}, {“name”: “Security ring (cylinder side)”,…
3. Hardware Hut – Door Lock Latches
Domain: hardwarehut.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Door Lock Latches and Latchbolts | Shop Door Lock Parts – 110 items available. Categories include: Door Hardware, Door Levers, Door Knobs, Door Entry Handlesets, Pocket & Sliding Door Handles & Locks, Door Accessories, Electronic & Pushbutton Locks, Deadbolts, Key In Locks, Knobs & Levers, Decorative Side Plates, Door Locks (Commercial), Door Hinges, Door Bottoms, Thresholds & Weatherstripping, Do…
4. Express Locksmiths – Traditional Door Locks
Domain: expresslocksmithshouston.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Traditional door locks, also known as mechanical locks, consist of keyholes and manual latches. Key components include: 1. Cylinder: Where the key is inserted, engaging spring-loaded pins to prevent turning when locked. 2. Bolt: Engages the door, holding it closed. 3. Box: Holds the bolt in place when locked. 4. Deadbolt components: Actual bolt, thumb latch, turnpiece, and keyhole. 5. Strike Plate…
5. Schlage – 40-104 Key Gauge
Domain: trudoor.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Key product details include a variety of lock parts and accessories from brands such as Schlage, Accentra, and Trudoor. The product types include deadlatch assemblies, springlatches, strike plates, rekeying kits, and key gauges, among others. Specific products listed are: Schlage – 40-104 Key Gauge ($13.87), Schlage – 40-119 Rekeying Pin Kit with Master Pins ($379.05), Trudoor – 2-3/8″ Backset Dea…
6. Reddit – Deadbolt Locks
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The bottom lock is called a deadbolt. The key-based lock is generally referred to as a door lock, and it is assumed that locks have a keyway unless specified otherwise, such as a combination lock.
7. Lock Component – Key Parts of a Lock Set
Domain: lockcomponent.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Key Components of a Lock Set: 1. Cylinder: The heart of the lock set, containing pins and springs that align with the correct key. 2. Deadbolt: Provides security by extending deep into the door frame; available in single-cylinder and double-cylinder varieties. 3. Latchbolt: Keeps the door closed and connects with the strike plate; retracts when the knob or lever is turned. 4. Strike Plate: Mounted…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts of a lock
In the evolving landscape of lock components, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. Understanding the intricate parts of a lock—such as cylinders, bolts, and strike plates—enables businesses to make informed procurement decisions that enhance security and operational efficiency. By prioritizing quality and compatibility in sourcing, companies can mitigate risks associated with faulty products and ensure the longevity of their security systems.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the focus should be on establishing reliable partnerships with manufacturers who offer innovative solutions tailored to diverse market needs. Investing in high-quality lock parts not only improves security but also builds trust with clients and stakeholders.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced locking mechanisms, including smart locks and enhanced deadbolts, is set to rise. As security concerns grow globally, now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies. Engage with reputable suppliers and explore new technologies to stay ahead in the competitive landscape. Embrace this opportunity to secure your operations and ensure peace of mind for your clients.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.