Choosing Your Junior Channel: Key Specs to Compare in 2025
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for junior channel
In today’s competitive landscape, successfully navigating the global market for junior channels presents a formidable challenge for international B2B buyers. Sourcing engaging content and innovative products that resonate with young audiences while meeting diverse cultural preferences requires a strategic approach. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of junior channels, from animated series to interactive educational content, and explores their applications across different markets.
Buyers will gain insights into supplier vetting processes, ensuring that they partner with reputable companies that align with their brand values and target demographics. Additionally, the guide addresses cost considerations, helping businesses budget effectively while maximizing their return on investment.
As international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including Brazil and Nigeria) seek to expand their offerings, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions. By understanding market trends and consumer preferences, businesses can curate content that captivates young audiences and fosters brand loyalty. The actionable insights provided here will serve as a roadmap for navigating the complexities of the junior channel landscape, ultimately driving growth and success in an increasingly globalized market.
Understanding junior channel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Educational Channels | Focus on learning through interactive content and storytelling. | Schools, educational institutions, ed-tech companies. | Pros: Engaging content promotes learning; Cons: May require specialized content licensing. |
| Entertainment Channels | Emphasis on fun and entertainment with characters and stories. | Toy manufacturers, children’s apparel brands, entertainment agencies. | Pros: High engagement levels; Cons: Saturated market with intense competition. |
| Streaming Platforms | On-demand access to a variety of junior content. | Subscription services, digital content distributors. | Pros: Flexible viewing options; Cons: Subscription fatigue among consumers. |
| Interactive Platforms | Incorporates games and activities alongside video content. | Game developers, educational tech firms, interactive media companies. | Pros: Encourages active participation; Cons: Development costs can be high. |
| Themed Content Channels | Focused on specific themes (e.g., superheroes, animals). | Licensing opportunities, merchandise production, cross-promotion. | Pros: Strong brand identity; Cons: Limited audience appeal if niche is too narrow. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Educational Channels for Junior Content?
Educational channels are designed to provide engaging content that promotes learning and development for young audiences. These channels often utilize animated storytelling, interactive lessons, and educational games to enhance the learning experience. B2B buyers, such as schools and educational institutions, may find these channels particularly useful for supplementing their curriculum. When considering purchasing, it is essential to evaluate the alignment of content with educational standards and the potential for long-term licensing agreements.
How Do Entertainment Channels Differ in the Junior Market?
Entertainment channels prioritize fun and engaging content featuring beloved characters and stories. These channels are often linked to popular franchises, making them appealing to children and their parents alike. B2B applications include partnerships with toy manufacturers and children’s apparel brands that seek to leverage popular characters for merchandising. Buyers should assess the channel’s audience reach and engagement metrics, as well as the potential for collaboration on promotional events or product launches.
Why Are Streaming Platforms Gaining Popularity Among B2B Buyers?
Streaming platforms provide on-demand access to a diverse library of junior content, allowing families to choose what to watch at their convenience. This flexibility is attractive to B2B buyers like subscription services and digital content distributors, who can offer curated content tailored to specific demographics. However, buyers must consider the challenge of subscription fatigue, where consumers may become overwhelmed by the number of services available. Analyzing user retention rates and content diversity will be crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
What Are the Benefits of Interactive Platforms for Junior Content?
Interactive platforms blend video content with games and activities, fostering active participation among young viewers. These platforms are particularly appealing to B2B buyers in the educational tech space, as they promote skill development in areas like problem-solving and critical thinking. However, the costs associated with developing high-quality interactive content can be significant. Buyers should weigh the potential educational benefits against the investment required for content creation and platform maintenance.
How Do Themed Content Channels Create Unique Market Opportunities?
Themed content channels focus on specific motifs or genres, such as superheroes or animals, to engage their audience. This specialization can create strong brand identities and open up various B2B opportunities, including licensing deals and merchandise production. However, buyers must be cautious of the potential limitations in audience appeal if the theme is too niche. Conducting market research to gauge interest and exploring cross-promotional partnerships can help mitigate these risks while maximizing the channel’s commercial potential.
Key Industrial Applications of junior channel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of junior channel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education & E-Learning | Interactive Learning Platforms | Enhances student engagement and retention rates | Quality of content, localization, and curriculum alignment |
| Entertainment & Media | Children’s Programming Distribution | Expands audience reach and brand loyalty | Licensing agreements, viewership metrics, and content variety |
| Retail & E-commerce | Kids’ Product Marketing Campaigns | Drives sales through targeted promotions | Market trends, consumer insights, and competitive analysis |
| Health & Wellness | Children’s Health Education Initiatives | Promotes healthy habits and knowledge among families | Compliance with health standards and cultural relevance |
| Technology & Software | Development of Educational Apps for Kids | Fosters innovation and enhances learning experiences | User interface design, platform compatibility, and security features |
How is ‘junior channel’ Used in Education & E-Learning?
In the education sector, the junior channel is leveraged to create interactive learning platforms that engage young learners through gamification and multimedia content. This application addresses the challenge of maintaining student interest in educational material, particularly in regions where traditional teaching methods may fall short. International buyers must consider the quality of content, ensuring it aligns with local curricula and cultural nuances. Localized versions of educational resources can significantly enhance their effectiveness in diverse markets like Nigeria and Brazil.

Illustrative image related to junior channel
What Role Does the Junior Channel Play in Entertainment & Media?
The junior channel is pivotal in distributing children’s programming, which helps media companies expand their audience reach and build brand loyalty among young viewers. By offering diverse content tailored to various cultural contexts, businesses can effectively engage families. Buyers should focus on licensing agreements and analyze viewership metrics to ensure they are investing in shows with proven popularity. This is particularly relevant in regions such as the Middle East and Africa, where cultural relevance can drive viewership.
How Can Retail & E-commerce Benefit from the Junior Channel?
In retail, the junior channel is essential for marketing campaigns aimed at children’s products, enabling brands to connect with parents and young consumers effectively. This targeted approach can significantly boost sales and brand visibility. B2B buyers must analyze market trends and consumer insights to tailor their campaigns accordingly. Understanding regional preferences and competition will be crucial for success in diverse markets like South America and Africa, where purchasing behaviors can vary widely.
What is the Importance of the Junior Channel in Health & Wellness?
The junior channel plays a crucial role in health education initiatives aimed at children, promoting healthy habits and knowledge through engaging content. This application addresses the growing concern of childhood obesity and health-related issues by providing informative resources in an entertaining format. Buyers should ensure compliance with health standards and consider cultural relevance to maximize impact. This is particularly important in regions with varying health challenges, such as Nigeria, where educational outreach can lead to significant community benefits.
How Does the Junior Channel Enhance Technology & Software Development?
In the technology sector, the junior channel is utilized in developing educational apps designed for children, fostering innovation and enhancing learning experiences through interactive features. This application addresses the need for effective digital learning tools that can adapt to various learning styles. For international buyers, key considerations include user interface design, platform compatibility, and security features to protect young users. Ensuring that the software meets local regulations and educational standards is essential for successful implementation in global markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘junior channel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Content Localization for Diverse Markets
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with delivering localized content through junior channels that resonates with diverse cultural audiences. For international markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the challenge lies not only in translation but also in cultural relevance. A junior channel that fails to address local customs, languages, and educational norms can lead to disengaged audiences and ultimately, wasted marketing resources. This can be particularly frustrating when working with animated content that needs to appeal to young viewers in varying regions.
The Solution: To effectively localize content, B2B buyers should collaborate with local experts who understand the target demographic’s cultural nuances. Engaging local animators, voice actors, and cultural consultants can provide insights that ensure the content is relatable and engaging. Additionally, leveraging data analytics can help identify which themes and characters resonate most with specific audiences. Finally, implementing an iterative feedback loop with local focus groups during the content development phase can refine the messaging and presentation, making it more appealing to the intended audience.
Illustrative image related to junior channel
Scenario 2: Challenges in Measuring Engagement and ROI
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face difficulties in quantifying engagement levels and return on investment (ROI) from their junior channel initiatives. Traditional metrics may not adequately reflect the effectiveness of animated content aimed at younger audiences. This lack of clear measurement can result in uncertainty about how to allocate resources effectively, which is critical for maximizing marketing budgets in competitive markets.
The Solution: Implementing advanced analytics tools that track engagement metrics specifically tailored for junior channels can provide clearer insights into performance. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as viewer retention rates, interaction levels with educational games, and conversion metrics from content to sales should be established. Additionally, conducting A/B testing on different content formats can reveal what resonates best with the audience, allowing for data-driven decisions. Lastly, integrating feedback mechanisms, such as surveys or interactive features, can offer qualitative insights into audience perceptions and preferences, enhancing overall content strategy.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Securing Strategic Partnerships
The Problem: Establishing effective partnerships with local distributors or content creators can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers looking to expand their reach through junior channels. Many buyers may find it challenging to identify reputable partners who understand the intricacies of the local market, or they might struggle with the negotiation process, leading to missed opportunities for collaboration and market penetration.
The Solution: To navigate this issue, B2B buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify potential partners who have a proven track record in the junior content space. Attending industry conferences, networking events, and leveraging professional associations can facilitate connections with key players in the local markets. Furthermore, creating a clear value proposition that outlines mutual benefits can strengthen partnership negotiations. Establishing pilot projects or co-branded initiatives can also demonstrate commitment and build trust. Finally, fostering ongoing communication and collaboration can ensure both parties remain aligned and focused on shared goals, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes in the junior channel landscape.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for junior channel
What Are the Key Materials for the Junior Channel?
When selecting materials for the junior channel, particularly in the context of children’s entertainment products, it’s essential to consider properties that align with safety, durability, and functionality. Below, we analyze four common materials used in this sector, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
How Do Plastics Perform in Junior Channel Applications?
Plastics, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP), are widely used in the junior channel for toys, educational tools, and packaging.

Illustrative image related to junior channel
- Key Properties: HDPE offers excellent resistance to impact, moisture, and chemicals, with a temperature rating of up to 120°C. PP is known for its good fatigue resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 100°C.
- Pros & Cons: Plastics are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for mass production. However, they may not be as durable as metals and can degrade under UV exposure. Additionally, manufacturing processes can vary in complexity depending on the design.
- Impact on Application: These materials are compatible with various media, including water and cleaning agents, making them ideal for products that require frequent cleaning.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards such as ASTM F963 (USA) and EN 71 (Europe) is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should also consider local regulations regarding plastic use and recycling.
What Role Does Metal Play in Junior Channel Products?
Metals, particularly aluminum and stainless steel, are often used for structural components and durable toys.
- Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, with a temperature tolerance of up to 600°C. Stainless steel offers superior strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for high-wear applications.
- Pros & Cons: Metals provide exceptional durability and a premium feel, enhancing product longevity. However, they are generally more expensive and can complicate manufacturing due to required machining processes.
- Impact on Application: Metals are suitable for products that may experience rough handling, such as outdoor toys or equipment. Their compatibility with various environments makes them versatile.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems is essential. Buyers should also be aware of regional preferences for materials, as some markets may favor eco-friendly options.
How Do Composites Enhance Junior Channel Offerings?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are increasingly utilized in high-end junior channel products.
- Key Properties: Composites are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and can withstand temperatures up to 200°C. They also offer excellent resistance to corrosion and environmental degradation.
- Pros & Cons: Composites provide innovative design possibilities and exceptional durability. However, they are typically more expensive and require specialized manufacturing techniques, which can limit production scalability.
- Impact on Application: These materials are ideal for products that need to combine lightweight characteristics with high strength, such as sports equipment or advanced educational tools.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of composite manufacturing facilities in their region, as well as compliance with standards like ASTM D3039 for tensile properties.
What Are the Benefits of Wood in Junior Channel Products?
Wood remains a popular choice for toys and educational materials due to its natural appeal.
- Key Properties: Wood is strong, durable, and can be treated for moisture resistance. It is also biodegradable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
- Pros & Cons: Wood offers a premium aesthetic and tactile experience, appealing to consumers. However, it can be more expensive and less durable than synthetic materials, especially in humid environments.
- Impact on Application: Wood is suitable for products that require a natural look and feel, such as puzzles and building blocks. However, it may not be compatible with all cleaning agents.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with regulations regarding sustainable sourcing and treatment of wood is vital. Buyers should also be aware of local preferences for natural materials, particularly in regions that prioritize eco-friendly products.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Junior Channel
| Material | Typical Use Case for junior channel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastics | Toys, educational tools, packaging | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable, can degrade under UV | Low |
| Metals | Structural components, durable toys | Exceptional durability | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Composites | High-end toys, sports equipment | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, specialized manufacturing | High |
| Wood | Toys, educational materials | Natural aesthetic and feel | More expensive, less durable in humidity | Med |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for junior channel
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for the Junior Channel?
The manufacturing processes for products in the junior channel—such as toys, educational materials, and children’s entertainment devices—can be broken down into several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring the quality and safety of the final product, which is especially important given the target demographic of young children.
Material Preparation
This initial stage involves selecting high-quality, safe materials suitable for children. Common materials include non-toxic plastics, fabrics, and metals. Suppliers often conduct material testing to ensure compliance with safety standards, such as ASTM F963 in the U.S. or EN71 in Europe, which specify safety requirements for toys.
Forming
In this stage, raw materials are shaped into components through techniques such as injection molding, blow molding, or die-cutting. For instance, toy figurines might be produced using injection molding, where heated plastic is injected into molds to create detailed shapes. Ensuring the precision of forming techniques is vital, as any defects can lead to safety hazards or product malfunctions.
Assembly
After forming, components are brought together in the assembly phase. This can be a manual or automated process, depending on the complexity and scale of production. For example, assembling electronic toys may require skilled labor to correctly integrate circuit boards and battery compartments. Quality control is crucial during assembly to verify that all components fit correctly and function as intended.
Finishing
The finishing stage includes painting, coating, and packaging. Products often undergo surface treatments to enhance durability and aesthetics, such as applying non-toxic paint or protective coatings. Packaging must also be designed thoughtfully to ensure that it is both attractive and safe, as well as compliant with international shipping standards.
Which Quality Assurance Standards Are Important for the Junior Channel?
Quality assurance is paramount in the junior channel, where products are intended for children. International standards like ISO 9001 are critical, as they outline the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality throughout their processes.
In addition to ISO standards, product-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) and ASTM certifications (for North America) are essential. These certifications confirm that products meet safety and performance standards, helping to build trust with B2B buyers.

Illustrative image related to junior channel
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet defined standards at various stages. The primary QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon delivery to ensure they meet specified quality standards. Suppliers may use certificates of compliance or conduct random sampling tests to verify quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the manufacturing process. This includes checking for dimensional accuracy, assembly correctness, and ensuring that any machinery used is functioning properly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once products are completed, a final inspection assesses overall quality before shipment. This may involve functional testing, safety assessments, and visual inspections to detect any defects.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
To ensure product safety and quality, various testing methods are employed in the junior channel:
-
Mechanical Testing: Assessing the durability and strength of materials, including stress tests and impact tests, helps ensure that products can withstand regular use.
-
Chemical Testing: This includes testing for harmful substances such as phthalates, lead, and other toxic elements. Testing laboratories conduct these assessments to verify compliance with safety regulations.
-
Functional Testing: For electronic toys or devices, functional testing ensures that all features operate correctly. This may include battery life tests, sound quality checks, and responsiveness of interactive elements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial in establishing a reliable partnership. Here are several strategies to ensure that suppliers adhere to quality standards:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers’ facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and QC measures. Buyers should look for adherence to ISO standards and other relevant certifications.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation detailing their quality control measures and testing results. This includes reports from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checkpoints.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Hiring third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and product quality. These inspectors can conduct random checks and provide detailed reports on compliance with safety standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate specific nuances when it comes to quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding local regulations and cultural attitudes toward product safety can impact supplier selection. For instance, African markets may have different expectations regarding product durability compared to European markets.
-
Logistics and Shipping: International shipping can complicate quality assurance, as products may be exposed to varying conditions during transit. Buyers should ensure that packaging is designed to protect products from damage and contamination.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have distinct safety standards and regulations. Buyers must familiarize themselves with these requirements and ensure that their suppliers are compliant to avoid legal issues and ensure market access.
In summary, a robust manufacturing process combined with stringent quality assurance practices is essential for products in the junior channel. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality, safety, and compliance with international standards to foster successful partnerships and ensure the safety of their products for children.
Illustrative image related to junior channel
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘junior channel’
To effectively procure products or services related to the ‘junior channel’ for your business, it’s essential to follow a systematic approach. This checklist will guide you through each critical step in the sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your organizational needs and regional market dynamics.
Step 1: Define Your Target Audience and Objectives
Understanding who your target audience is and what you aim to achieve with the junior channel is crucial. Consider the demographics, preferences, and cultural factors specific to regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This clarity will guide your content and product selection, ensuring relevance and engagement with your audience.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Competitors
Before sourcing, it’s important to analyze current trends within the junior channel, including popular shows, themes, and educational content. Investigate what competitors are doing well and identify gaps in the market that your offerings can fill. This research helps you position your products or services effectively and differentiate from competitors.
Step 3: Identify and Vet Potential Suppliers
Finding the right suppliers is critical to your success. Look for companies that specialize in junior content production or distribution and have a proven track record in your target regions. Request case studies, customer testimonials, and references to evaluate their reliability and experience.
- Key aspects to check:
- Supplier’s experience in producing or distributing junior content.
- Their understanding of regional regulations and audience preferences.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and regulations, especially those pertaining to children’s content. This not only protects your business but also safeguards your audience’s interests. Check for certifications that validate their commitment to quality and safety.
Step 5: Assess Content Quality and Relevance
Review samples of the content provided by suppliers to assess its quality and educational value. Ensure that the content aligns with your brand values and objectives, and is culturally appropriate for your target audience. Consider conducting focus groups with children or parents to gather feedback on the content.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve identified suitable suppliers, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms and pricing. Ensure that the contract covers all aspects of delivery, intellectual property rights, and payment terms. This step is vital to avoid any misunderstandings and to secure a mutually beneficial agreement.
Step 7: Plan for Distribution and Marketing
After finalizing your supplier relationships, outline a strategy for how you will distribute and market the junior content. Consider utilizing multiple channels such as social media, educational platforms, and partnerships with local schools. Tailoring your marketing efforts to suit regional preferences will maximize your reach and impact.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for the junior channel, ensuring they make informed decisions that resonate with their target audience and enhance their market presence.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for junior channel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Junior Channel Sourcing?
When engaging in junior channel sourcing, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for optimizing profitability and ensuring competitive pricing. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used can significantly affect costs. For example, sourcing high-quality fabrics or non-toxic materials for toys can increase the overall material cost but may enhance product appeal and safety.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing processes involved. For instance, countries with higher wage standards may incur greater labor costs, which can impact the final price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient overhead management can lead to substantial savings.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for molds and specialized equipment can be substantial, especially for custom products. These costs are typically amortized over the production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC process is vital to ensure that products meet safety and quality standards. While this adds to costs, it can prevent costly recalls and damage to brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs must be accounted for, including international freight charges and customs duties. Geographic factors can greatly influence these expenses.
-
Margin: The desired profit margin will affect pricing strategies. Understanding market dynamics and competitive pricing is crucial to set margins that are both profitable and attractive to buyers.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Junior Channel Sourcing Decisions?
Several price influencers can affect the final pricing of products in the junior channel:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes typically yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities that align with their sales forecasts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized products often come with increased costs. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unnecessary changes that can inflate prices.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly alter costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of premium materials against budget constraints and market expectations.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that require certifications (e.g., safety standards for toys) may incur additional costs. Buyers should consider these factors when evaluating supplier options.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, production capacity, and payment terms can all influence pricing. Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is crucial for cost management. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate responsibility for costs and risks, which can impact overall pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Junior Channel Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following strategies to optimize costs:
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Buyers should leverage their market knowledge and supplier competition to negotiate favorable deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assessing the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price can lead to better long-term savings. This includes considering maintenance, logistics, and disposal costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that can impact pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies and understanding local regulations can mitigate these risks.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting supplier audits can ensure that potential partners meet quality and compliance standards, ultimately affecting cost efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics in junior channel sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers. By considering various cost components, price influencers, and practical tips, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance profitability while meeting market demands. Always remember that the prices mentioned in discussions are indicative and should be validated with suppliers for accuracy.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing junior channel With Other Solutions
In the fast-evolving landscape of children’s entertainment, businesses need to evaluate various solutions that cater to their target audience effectively. When considering options like the ‘junior channel,’ it’s crucial to compare it with other viable alternatives that can deliver similar outcomes in engaging and educating young viewers. This analysis highlights key alternatives, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
| Comparison Aspect | Junior Channel | Streaming Platforms (e.g., Netflix Kids) | Educational Apps (e.g., ABCmouse) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High engagement through curated content and character familiarity. | Offers a wide variety of content, including popular franchises and original programming. | Focuses on educational content that tracks progress and adapts to learning levels. |
| Cost | Moderate subscription fees; potential for high licensing costs for content. | Subscription-based, typically more economical with extensive content libraries. | Monthly subscription fees, often lower than traditional media costs, but may require additional purchases for full access. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires partnerships with content creators and networks; potentially complex licensing agreements. | User-friendly interfaces and readily available content make it easy to implement. | Simple setup, often with immediate access to a wealth of resources and materials. |
| Maintenance | Regular content updates needed to keep engagement high; requires ongoing partnerships. | Minimal maintenance, as platforms manage content updates and user engagement. | Requires regular updates and educational material refresh to maintain relevance. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for entertainment-focused platforms targeting preschool and early school-age children. | Best for families seeking diverse content options that include entertainment and educational programming. | Perfect for educational institutions or parents wanting structured learning environments for children. |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Streaming Platforms Compared to Junior Channels?
Streaming platforms like Netflix Kids provide a broad array of content, including beloved characters and educational shows. Their subscription models often result in lower costs per user compared to traditional channels. However, while they excel in variety and user experience, they may lack the focused engagement that dedicated junior channels offer, potentially diluting the brand connection with young audiences.
How Do Educational Apps Stand Against Junior Channels in Engaging Young Learners?
Educational apps such as ABCmouse are specifically designed to enhance learning through interactive content and personalized learning paths. These platforms often track progress, allowing parents and educators to tailor the experience to individual needs. However, the primary drawback is that they may not engage children in the same entertainment-driven manner as junior channels, which can lead to lower overall engagement for purely entertainment purposes.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the right solution for engaging young audiences, B2B buyers must consider their specific objectives. If the goal is to create an entertaining, character-driven experience, junior channels may be more suitable. Conversely, for those focused on educational outcomes, streaming platforms or educational apps could provide better value. Evaluating factors such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and the intended use case will empower businesses to make decisions that align with their strategic goals while effectively reaching their target demographics.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for junior channel
What Are the Key Technical Properties for the Junior Channel?
Understanding the essential technical properties of the junior channel is vital for B2B buyers, especially when considering product quality and compliance. Here are some critical specifications to keep in mind:
-
Content Quality Standards
The content quality standards dictate the educational and entertainment value of programming targeted at younger audiences. This includes age-appropriate language, themes, and visual elements. For buyers, ensuring compliance with these standards is crucial to meet regulatory requirements and audience expectations, which can influence market penetration and brand loyalty. -
Format Compatibility
The junior channel content must be compatible with various formats, including HD, 4K, and mobile formats. This specification is essential for distributors and broadcasters to ensure that content can be played across different devices and platforms, enhancing accessibility and audience reach. -
Localization Capabilities
Localization refers to adapting content to meet the cultural and linguistic needs of specific markets. For B2B buyers, understanding localization capabilities is critical, especially when targeting diverse regions such as Africa, South America, and Europe. This ensures that the content resonates with local audiences and complies with regional broadcasting standards. -
Content Distribution Rights
Distribution rights specify where and how content can be shared or broadcast. Buyers need to understand these rights to avoid legal pitfalls and ensure that they can effectively monetize content across various platforms. This includes linear TV, streaming services, and international syndication. -
Audience Engagement Metrics
Metrics related to audience engagement, such as viewership ratings, retention rates, and interactive features, are crucial for evaluating content effectiveness. B2B buyers should focus on these metrics to assess the potential return on investment and optimize content strategies accordingly.
Which Terms Are Commonly Used in the Junior Channel Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and decision-making in the junior channel space. Here are some common trade terms:
Illustrative image related to junior channel
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of the junior channel, OEM refers to companies that produce the original content or products that are later branded and sold by other entities. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess quality and reliability in content sourcing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of content or product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is important for budgeting and inventory management, especially when entering new markets or launching new products. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific content or services. This term is important for B2B transactions, as it helps buyers compare pricing and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as they clarify shipping responsibilities and costs. -
IP (Intellectual Property)
IP refers to the legal rights associated with creative works, including content created for the junior channel. For buyers, understanding IP rights is crucial to ensure that they are not infringing on copyrights and can capitalize on potential licensing opportunities. -
SOW (Statement of Work)
A SOW outlines the specific tasks and deliverables expected from a service provider. In the junior channel context, this could pertain to production schedules, content requirements, and quality benchmarks. Familiarity with SOWs helps buyers ensure clarity in contracts and project expectations.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can navigate the junior channel landscape more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the junior channel Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Junior Channel Sector?
The junior channel sector, which encompasses content, toys, and educational materials for children, is experiencing notable shifts driven by technology and consumer preferences. A significant global driver is the increasing adoption of digital platforms among young audiences. Streaming services such as Disney+ and Nickelodeon are reshaping content consumption habits, creating demand for interactive and engaging experiences. This trend is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where mobile penetration and internet accessibility are on the rise.
Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming how educational content is delivered. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing products that incorporate these technologies to meet the evolving demands of parents and educators. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a key consideration, with consumers increasingly favoring brands that prioritize eco-friendly practices. This shift presents opportunities for suppliers who can offer sustainable products or demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing.

Illustrative image related to junior channel
How Is Sustainability Shaping Ethical Sourcing in the Junior Channel?
As sustainability concerns continue to gain traction, the importance of ethical supply chains in the junior channel cannot be overstated. Environmental impacts, such as plastic pollution and resource depletion, are pressing issues that influence purchasing decisions. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who are committed to sustainable practices, which may include using recycled materials, reducing carbon footprints, and ensuring fair labor practices.
‘Green’ certifications, such as Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for paper products or certifications for non-toxic materials in toys, are increasingly sought after by buyers. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also align with consumer expectations for responsible sourcing. By investing in ethically sourced and environmentally friendly products, businesses can not only appeal to conscious consumers but also mitigate risks associated with potential backlash over unsustainable practices.
What Is the Evolution of the Junior Channel Sector?
The junior channel sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional media, the sector has expanded to include a diverse array of digital platforms and products tailored to young audiences. The rise of educational apps and online streaming services reflects a shift in how children engage with content, moving from passive consumption to interactive learning experiences.
This evolution has necessitated a shift in sourcing strategies for B2B buyers. Companies must now consider not just the products they offer but also the platforms through which they reach their audiences. As the market continues to evolve, staying attuned to technological advancements and consumer preferences will be crucial for success in the junior channel sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of junior channel
-
How do I assess the quality of junior channel suppliers?
To evaluate the quality of junior channel suppliers, conduct thorough research on their reputation in the industry. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from other clients. Request samples to assess the product quality firsthand. Additionally, verify certifications and compliance with international standards, particularly in the regions you operate in, such as Africa, South America, or Europe. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers about their quality assurance processes can provide further insights into their reliability. -
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a junior channel supplier?
When selecting a junior channel supplier, consider their experience and expertise in the specific products you need. Evaluate their production capacity and ability to meet your demands, including minimum order quantities (MOQ). Additionally, assess their logistics capabilities, delivery times, and customer service responsiveness. Understanding their payment terms and any potential customization options is also crucial to ensure they align with your business needs. -
What customization options are typically available for junior channel products?
Many junior channel suppliers offer customization options, including branding, packaging, and product modifications tailored to local market preferences. You can often request specific colors, designs, or even educational content that aligns with your target audience. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to understand their capabilities and limitations in customization, as this can significantly influence your product’s appeal in your market. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQ) for junior channel products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary widely among junior channel suppliers, often ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. Factors influencing MOQ include product type, customization requests, and supplier production capacity. To find a supplier that meets your needs, be upfront about your expected order volume and negotiate MOQs that fit your business model. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face additional shipping costs for lower-volume orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when dealing with junior channel suppliers?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from full payment upfront to a percentage deposit with the balance due upon delivery. Many suppliers may accept letters of credit, especially for larger orders. It’s essential to clarify payment terms during initial discussions to avoid misunderstandings later. Additionally, consider discussing flexible payment options that can help manage cash flow, especially when entering new markets in regions like Africa or South America. -
How do I ensure compliance with international trade regulations when sourcing junior channel products?
To ensure compliance with international trade regulations, familiarize yourself with the import/export laws specific to your country and those of your suppliers. This includes understanding tariffs, customs duties, and necessary documentation like certificates of origin and product safety standards. Engaging a freight forwarder or customs broker can also be beneficial in navigating these complexities, ensuring your shipments comply with local and international regulations. -
What logistics considerations are important when sourcing from junior channel suppliers?
Logistics plays a crucial role in the efficiency of your supply chain. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and costs associated with transportation from the supplier’s location to your market. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to handle logistics, including their experience with international shipping and customs clearance. Additionally, assess their warehousing capabilities if you require storage before distribution in your region. -
How can I build a strong relationship with junior channel suppliers?
Building a strong relationship with junior channel suppliers involves clear communication, mutual respect, and regular engagement. Establish open lines of communication to discuss expectations, feedback, and any potential issues. Regular visits to the supplier’s facilities can foster trust and understanding. Additionally, recognizing their efforts and successes can go a long way in nurturing a collaborative partnership, ultimately benefiting your business in the long run.
Top 6 Junior Channel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Metal World Inc – Junior Channel Steel
2. Steel Supply – Junior Channels
Domain: steelsupplylp.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Steel Supply – Junior Channels, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Farwest Steel – Junior Channels
Domain: farweststeel.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
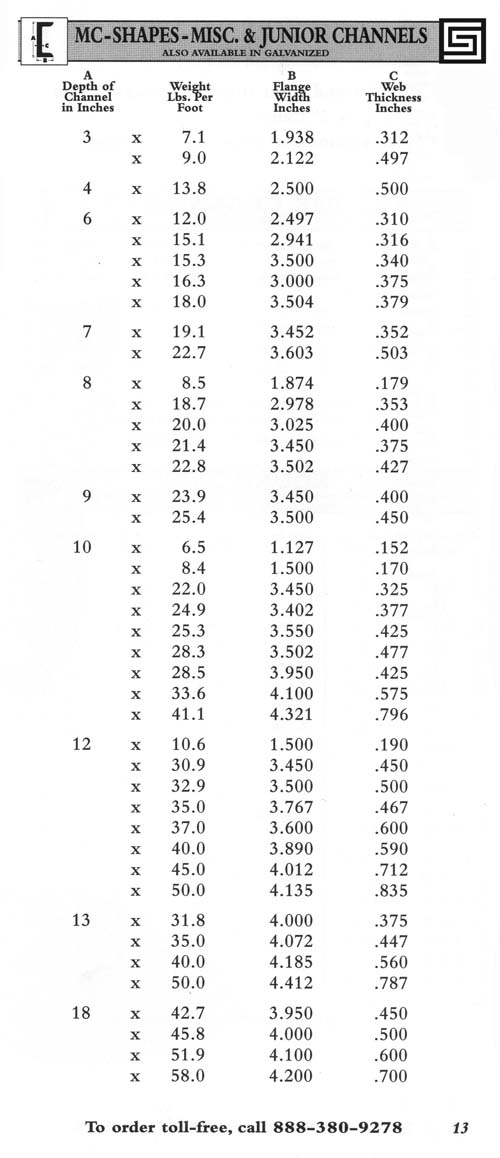
Introduction: Farwest Steel stocks a variety of Junior Channels ready for same or next day delivery. Junior Channels are lightweight rolled channels designed for stair stringers and other structural applications. They are suitable for most processing techniques, including saw cutting to exact specifications. Farwest offers inventory of Junior Channels in sizes ranging from 8″ x 8.5″ to 12″ x 10.6″, typically pr…
4. DisneyNOW – Disney Junior Shows
Domain: disneynow.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Disney Junior Shows – Full Episodes & Videos available on DisneyNOW. Includes a variety of shows such as Mickey Mouse, Princess, Star Wars, and Marvel. Features options for searching shows A-Z and includes parental guidelines and privacy policies.
5. BT Metals – Junior Channel Products
Domain: btmetals.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Junior Channel including Angles, Channels, Flat Bar, Hot Rolled Strip, Rounds, and Squares. A36 sizes between 8″ x 8.5 to 12″ x 10.6. Common lengths are 20′ and 40′. Typical physical properties: Yield KSI 36 Min, Tensile KSI 50 – 80 Min, Elongation % in 2″ 21 Min. Typical chemical properties: C – Carbon 0.26, P – Phosphorus 0.04, S – Sulphur 0.05, Si – Silicon 0.4.
6. Disney Channel – Kids’ Shows
Domain: disneychannel.ca
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Disney Channel offers a variety of shows including ‘The Villains of Valley View’, ‘Hamster & Gretel’, ‘Marvel’s Moon Girl & Devil Dinosaur’, ‘KIFF’, ‘Raven’s Home’, and ‘Bunk’D’. New episodes air on specific days and times, such as ‘The Villains of Valley View’ on Fridays at 8:00 PM E/P and ‘Raven’s Home’ on Tuesdays at 8:00 PM E/P. Additionally, Disney Channel content is available for streaming o…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for junior channel
In the evolving landscape of the junior channel, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal element for B2B buyers aiming to capture market share and foster sustainable growth. By leveraging data-driven insights and cultivating strong supplier relationships, businesses can enhance their product offerings, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of young audiences across various regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
The value of strategic sourcing lies not only in cost efficiency but also in the ability to innovate and respond swiftly to changing consumer preferences. Engaging with local suppliers can provide invaluable cultural insights and tailored solutions that resonate with target demographics, ultimately enhancing customer loyalty and brand recognition.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace a proactive approach in their sourcing strategies. By prioritizing partnerships and utilizing advanced sourcing technologies, businesses can navigate the complexities of the junior channel more effectively. As markets continue to evolve, those who invest in strategic sourcing today will be well-positioned to lead tomorrow. Now is the time to take action—evaluate your sourcing strategies and unlock new opportunities within the dynamic junior channel landscape.
Illustrative image related to junior channel
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.